A Novel Provable Secured Signcryption Scheme
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Preliminaries
- 𝗁(α) ∈ [α] is a polynomial and the degree is 𝗁(α) ⩽ g
- 𝘧(α) ∈ 𝒻[α] is the monic polynomial, and the degree is 𝘧(α) ⩽ 2g + 1
- The points on the hyper-elliptic curve do not form a group unlike an elliptic curve
- The hyper-elliptic curve works on divisor which is branded as the formal and finite sum of points on a hyper-elliptic curve that can be further symbolized by Mumford as:
1.2. Hyper-Elliptic Curve Discrete Logarithm (HECDLP)
1.3. Basic Notations
| Represents a hyper-elliptic curve over the field | |
| : | Is a large prime number and the value of |
| : | Is the divisor of the generalized elliptic curve |
| 𝒽1, 𝒽2, 𝒽3: | Demonstrate the hash functions |
| 𝓒: | Epitomizes the ciphertext |
| m: | Epitomizes the plaintext or message |
| M = 𝓂.: | Represents the message concatenation with divisor |
| : | Represents the private key of the signcrypter |
| : | Represents the public key of the signcrypter |
| : | Represents the private key of the unsigncrypter |
| : | Represents the public key of the unsigncrypter |
| Is a fresh nonce | |
| : | Represent the secret key |
| , : | Representing the subdivided secret key |
| E/D: | Represents the encryption and decryption functions |
| Eyk (Exk(M)): | Represents double encryption |
| Dyk (Dxk(𝓒)): | Represents double decryption |
2. Formal Model of the Proposed Scheme
2.1. Proposed Scheme Construction
2.1.1. Key Generation
2.1.2. Signcryption
| Algorithm 1. Algorithm () |
| Randomly select a number γ from {1,…‥‥,q − 1}. |
| Select a nonce |
| Compute where is the divisor on a hyper-elliptic curve. |
| Divide into , |
| Compute |
| Compute |
| Divide into , |
| Compute |
| Compute 𝓒 = |
| Compute 𝓣 = (𝓒) |
| Compute 𝓢 = |
| Send ω = (𝓒, ) to Bob or Unsigncrypter |
2.1.3. Unsigncryption
| Algorithm 2. Algorithm () |
| Compute = () |
| Compute (.) |
| Divide into , |
| Divide into , |
| Use the double decryption method |
| Compute |
| Compare if equality holds then there is no change in |
| Verification of signature is done through 𝒵. + . |
3. Correctness
4. Security Analysis
4.1. Replay Attack
4.2. Confidentiality
4.3. Integrity
4.4. Authenticity
4.5. Unforgeability
4.6. Non-Repudiation
4.7. Forward Secrecy
4.8. Public Verifiability
- Compute ()
- Compute
- Compare if equality holds, then there is no change in
- Verification of signature is done through 𝒵. + ., if satisfy then the message from signcrypter otherwise not.
5. Computational Cost
- Intel Core i74510UCPU
- 2.0 GHz processor
- 8 GB of memory
- Windows 7 Home Basic
- Multi-precision Integer and Rational Arithmetic C Library (MIRACL)
6. Communication Cost
Generalized Formulas for the Reduction of Communication Cost
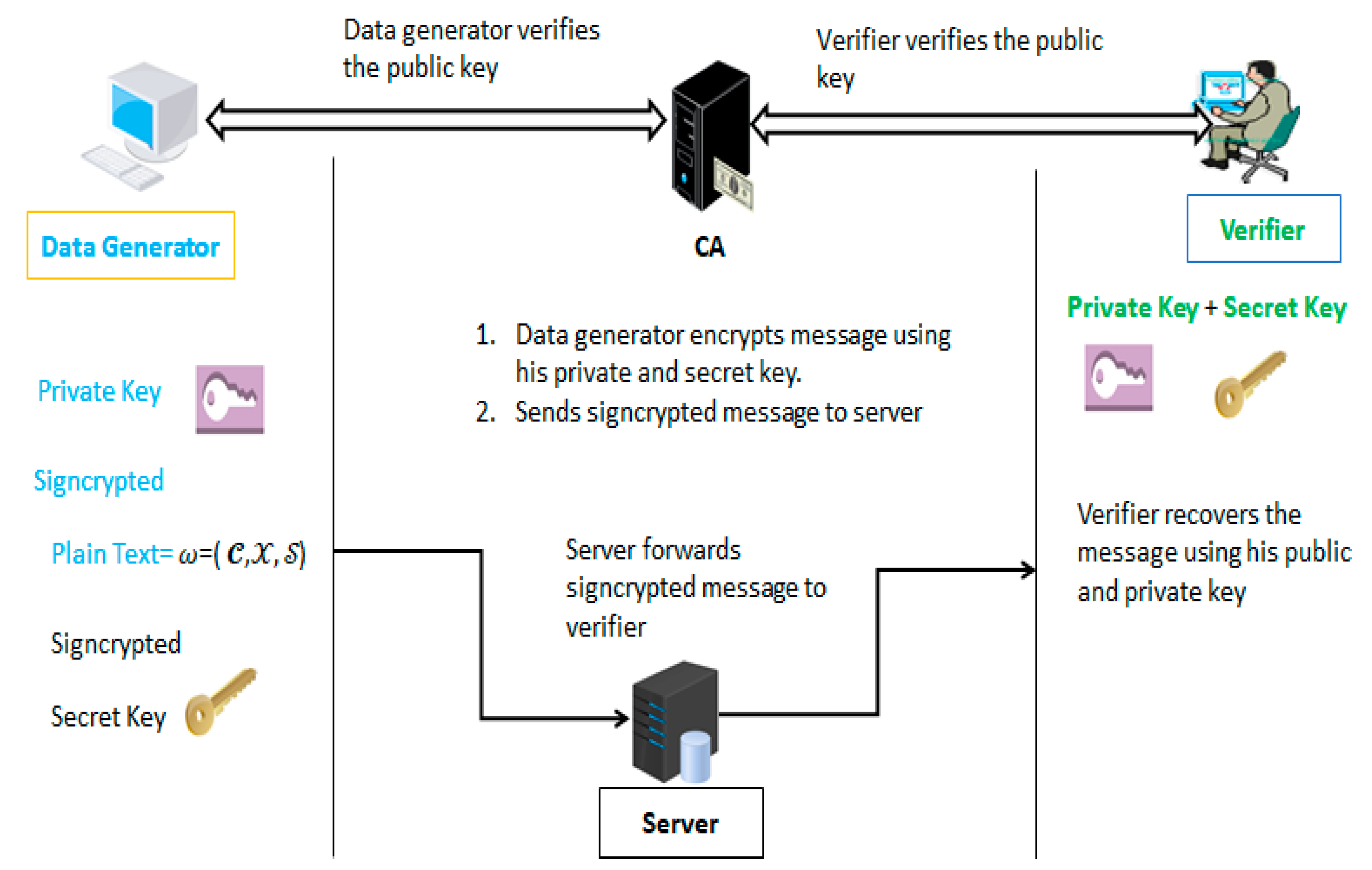
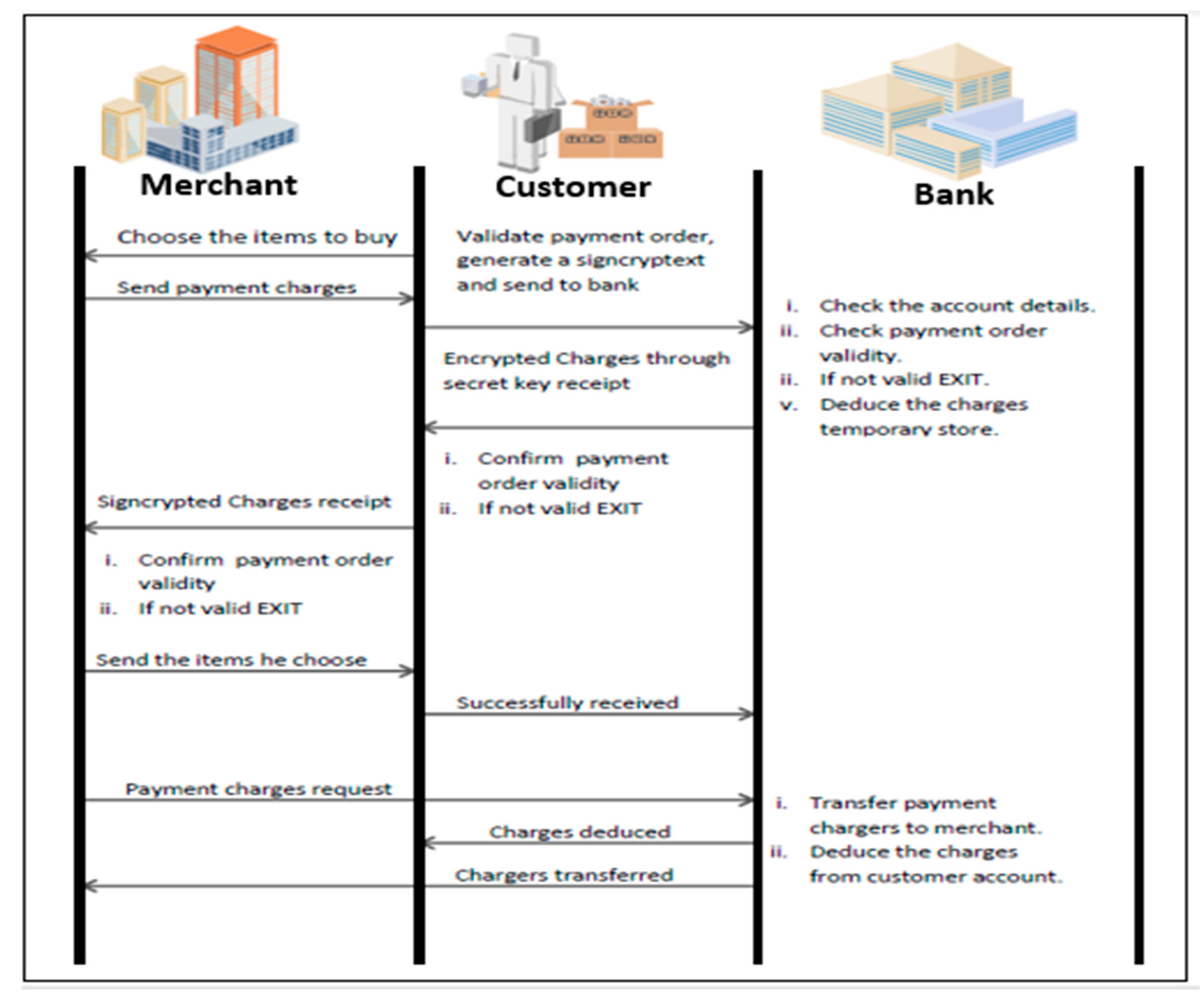
7. Applications
- Confirm payment order validity
- If not valid then EXIT
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- → H, HH, HHH: hash functions
- M: Is plain text or message
- → M’: Is the cipher text
- → Ju: public key of unsigncrypter
- → inv (Js): private key of signcrypter
- → inv (Ju): private key of unsigncrypter
- → Js: public key of signcrypter
- →(Signcrypter.{H1(M’.Xz’.Nr)}_inv(Js).{H2(Alpa’.H1(M’.Xz’.Nr).inv(Js)).Ju}_Eyk’.{M’.Nr.Exk’}_Eyk’): encryption
- → (Signcrypter.{H1(M’.Xz’.Nr)}_inv(Js).{H2(Alpa’.H1(M’.Xz’.Nr).inv(Js) ).Ju}_Eyk’.{M’.Nr.Exk’}_Eyk’): decryption.
- → Eyk, Exk: Symmetric key
- → Alpa’: random number
- , → Xz,Yz: Dividing
- Ki → intruder public key
- inv (ki) → intruder private key
- → {M’.Nr.Exk’}_Eyk’)
- → {H1(M’.Xz’.Nr)}_inv(Js)
- → {H2(Alpa’.H1(M’.Xz’.Nr).inv(Js) ).Ju}_Eyk’
| HLPSL Code () |
| role |
| %%start of the protocol by Signcrypter already knows the Unsigncrypter’s |
| role_Signcrypter(Signcrypter:agent,Unsigncrypter:agent,Ju:public_key,Js:public_key,Nr:text,Ns:text,SND,RCV:channel(dy)) |
| played_by Signcrypter |
| def= |
| local |
| %%start of the protocol by Signcrypter already knowing the %%Unsigncrypter’s public key |
| State:nat,Alpa:text,H1:hash_func,Xz:text,H2:hash_func,Eyk:symmetric_key,M:text,Exk:symmetric_key |
| init |
| State:= 0 |
| transition |
| %% signcrypter receives challenge from Unsigncrypter by using his public %%key and nonce, sends message to unsigncrypter in response |
| 1. State=0/\ RCV(Unsigncrypter.{Ns}_Js) =|> State’:=1/\ Eyk’:=new()/\ Exk’:=new()/\ M’:=new()/\ Xz’:=new()/\ Alpa’:=new()/\ SND(Signcrypter.{H1(M’.Xz’.Nr)}_inv(Js).{H2(Alpa’.H1(M’.Xz’.Nr).inv(Js)).Ju}_Eyk’.{M’.Nr.Exk’}_Eyk’)/\ SND(Signcrypter.{H2(Alpa’.H1(M’.Xz’.Nr).inv(Js)).Ju}_Eyk’)/\ SND(Signcrypter.{M’.Nr.Exk’}_Eyk’) |
| end role |
| role |
| %%defining the role played by signcrypter by using its keys… |
| role_Unsigncrypter(Signcrypter:agent,Unsigncrypter:agent,Ju:public_key,Js:public_key,Nr:text,Ns:text,SND,RCV:channel(dy)) |
| played_by Unsigncrypter |
| def= |
| local |
| State:nat,Alpa:text,H1:hash_func,Xz:text,H2:hash_func,Eyk:symmetric_key,M:text,Exk:symmetric_key |
| init |
| State:= 0 |
| transition |
| 1. State=0/\ RCV(start) =|> State’:=1/\ SND(Unsigncrypter.{Ns}_Js) |
| 2. State=1/\ RCV(Signcrypter.{H1(M’.Xz’.Nr)}_inv(Js).{H2(Alpa’.H1(M’.Xz’.Nr).inv(Js)).Ju}_Eyk’.{M’.Nr.Exk’}_Eyk’) =|> State’:=2 |
| 3. State=2/\ RCV(Signcrypter.{H2(Alpa.H1(M.Xz.Nr).inv(Js)).Ju}_Eyk) =|> State’:=3 |
| 4. State=3/\ RCV(Signcrypter.{M.Nr.Exk}_Eyk) =|> State’:=4 |
| end role |
| role |
| %%session1 between agents signcrypter and unsigncrypter |
| session1(Signcrypter:agent,Unsigncrypter:agent,Ju:public_key,Js:public_key,Nr:text,Ns:text) |
| def= |
| local |
| SND2,RCV2,SND1,RCV1:channel(dy) |
| composition |
| role_Unsigncrypter(Signcrypter,Unsigncrypter,Ju,Js,Nr,Ns,SND2,RCV2)/\ role_Signcrypter(Signcrypter,Unsigncrypter,Ju,Js,Nr,Ns,SND1,RCV1) |
| end role |
| role |
| %%session2 between agents signcrypter and unsigncrypter |
| session2(Signcrypter:agent,Unsigncrypter:agent,Ju:public_key,Js:public_key,Nr:text,Ns:text) |
| def= |
| local |
| SND1,RCV1:channel(dy) |
| composition |
| role_Signcrypter(Signcrypter,Unsigncrypter,Ju,Js,Nr,Ns,SND1,RCV1) |
| end role |
| role environment() |
| def= |
| const |
| hash_0:hash_func,nr:text,ju:public_key,alice:agent,bob:agent,js:public_key,ns:text,const_1: agent,const_2:public_key,const_3:public_key,const_4:text,const_5:text,auth_1:protocol_id, sec_2:protocol_id |
| intruder_knowledge = {alice,bob} |
| composition |
| session2(i,const_1,const_2,const_3,const_4,const_5)/\ session1(alice,bob,ju,js,nr,ns) |
| end role |
| goal |
| %% defining the goals as an aim of protocol |
| authentication_on auth_1 |
| secrecy_of sec_2 |
| end goal |
| environment() |
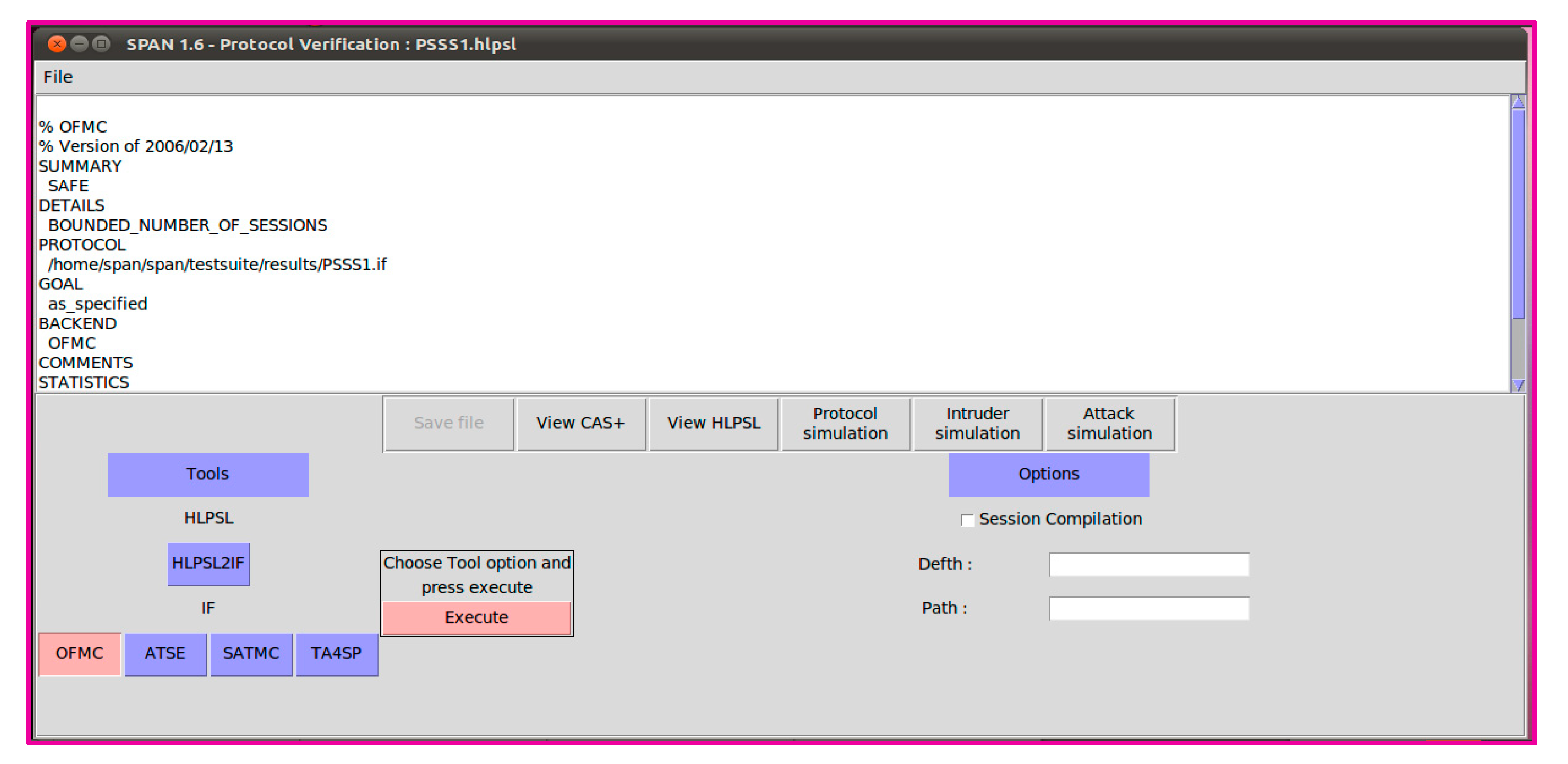

References
- Mehmood, A.; Ullah, I.; Noor-Ul-Amin; Umar, A.I. Public Verifiable Generalized Authenticated Encryption (ℙ℣₢Ǣ) based on Hyper Elliptic Curve. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci. 2017, 7, 194–200. [Google Scholar]
- Sadat, A.; Ahmad, R.; Ullah, I.; Khattak, H.; Ullah, S. Multi Receiver Signcryption Based On Hyper Elliptic Curve Cryptosystem. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci. 2017, 7, 194–200. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y. Digital signcryption or how to achieve cost (signature & encryption) ≪ cost (signature) + cost(encryption). Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 1997, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, F.; Deng, R.H. A signcryption scheme with signature directly verifiable by public key. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 1998, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y. Identification, signature and signcryption using high order residues modulo an RSA composite. In Public Key Cryptography; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 48–63. [Google Scholar]
- Malone-Lee, J.; Mao, W. Two Birds One Stone: Signcryption Using RSA. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2003, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.; Steinfeld, R.; Zheng, Y. Formal proofs for the security of signcryption. In Public Key Cryptography; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 80–98. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, G.; Bala, S.; Verma, A.K. An identity-based ring signcryption scheme. In IT Convergence and Security; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Imai, H. How to construct efficient signcryption schemes on elliptic curves. Inf. Process. Lett. 1998, 68, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, R.-J.; Lai, C.-H.; Su, F.-F. An efficient signcryption scheme with forward secrecy based on elliptic curve. Appl. Math. Comput. 2005, 167, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toorani, M.; Beheshti, A.A. An elliptic curve-based signcryption scheme with forward secrecy. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1005.1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizamuddin; Chudry, S.A.; Amin, N. Signcryption schemes withforward secrecybased on hyperelliptic curve cryptosystem. In Proceedings of the High Capacity Optical Networks and Enabling Technologies, (HONET), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 19–21 December 2011; pp. 244–247. [Google Scholar]
- Nizamuddin; Chudry, S.A.; Nasar, W.; Javaid, Q. Efficient signcryption schemes based on hyper elliptic curve cryptosystem. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Emerging Technologies (ICET), Islamabad, Pakistan, 5–6 September 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Malone-Lee, J. Identity Based Signcryption. Cryptology ePrint Archive, Report 2002/098. 2002. Available online: https://eprint.iacr.org/2002/098.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2019).
- Libert, B.; Quisquater, J.J. A new identity based signcryption scheme from pairings. In Proceedings of the IEEE Information Theory Workshop (Cat. No.03EX674), Paris, France, 31 March–4 April 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, S.S.M.; Yiu, S.M.; Hui, L.C.K.; Chow, K.P. Efficient Forward and Provably Secure ID-Based Signcryption Scheme with Public Verifiability and Public Ciphertext Authenticity. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2004, 352–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyen, X. Multipurpose Identity-Based Signcryption. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2003, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Malone-Lee, J. Improved identity-based signcryption. In Proceedings of the Public Key Cryptography-PKC’05, LNCS 3386, Les Diablerets, Switzerland, 23–26 January 2005; pp. 362–379. [Google Scholar]
- Barreto, P.S.L.M.; Libert, B.; McCullagh, N.; Quisquater, J.-J. Efficient and Provably-Secure Identity-Based Signatures and Signcryption from Bilinear Maps. In Advances in Cryptology—ASIACRYPT 2005; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 515–532. [Google Scholar]
- Selvi, S.S.D.; Vivek, S.S.; Rangan, C.P. Identity based public verifiable signcryption scheme. In Proceedings of the ProvSec’10, LNCS 6402, Malacca, Malaysia, 13–15 October 2010; pp. 244–260. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, S. Identity based signcryption scheme without random oracles. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 2009, 31, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Wen, Q.; Du, H. An improved semantically-secure identity-based signcryption scheme in the standard model. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2010, 36, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Muhaya, F.B.; Zhang, M.; Takagi, T. Efficient Identity-Based Signcryption in the Standard Model. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2011, 120–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H. Certificateless signcryption scheme in the standard model. Inf. Sci. 2010, 180, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Zhang, F.; Li, S.; Mu, Y. On security of a certificateless signcryption scheme. Inf. Sci. 2013, 232, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Yao, G.; Deng, R.; Chen, M.; Li, X. Cryptanalysis of a certificateless signcryption scheme in the standard model. Inf. Sci. 2011, 181, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. Certificateless signcryption scheme without pairing. J. Comput. Res. Dev. 2010, 47, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H. On the Security of a Certificateless Signcryption Scheme. In Proceedings of the IWECA 2014, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 8–9 May 2014; pp. 664–667. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Kumar, N.; Gong, P.; Zhang, Z. Cryptanalysis and improvement of a certificateless signcryption scheme without bilinear pairing. Front. Comput. Sci. 2014, 8, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wen, Q. An improved certificateless signcryption in the standard model. Int. J. Netw. Secur. 2015, 17, 597–606. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, S.; Li, F. Leakage-free and provably secure certificateless signcryption scheme using bilinear pairings. Comput. J. 2015, 58, 2636–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shirase, M.; Takagib, T. Certificateless hybrid signcryption. Math. Comput. Mod. 2013, 57, 324–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, R.K. Signcryption Schemes with forward Secrecy Based on Elliptic Curve Cryptography. Ph.D. Thesis, 2010. Available online: http://ethesis.nitrkl.ac.in/2009/ (accessed on 26 May 2019).
- Elkamchouchi, H.M.; El-Atiky, M.H.; Abouelkheir, E. A Public Verifiability Signcryption Scheme without Pairings. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2017, 157, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
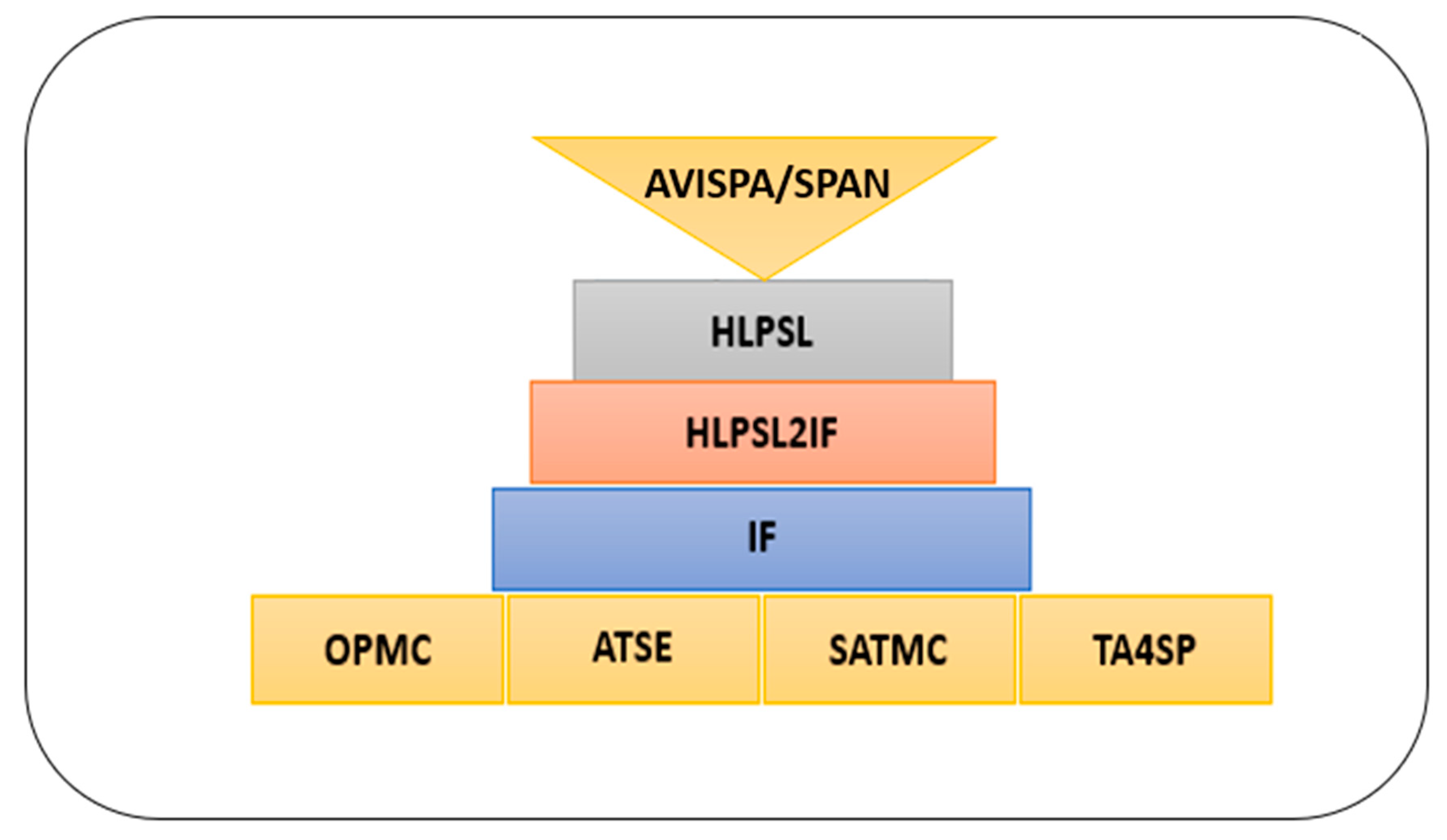
- Vigano, L. Automated security protocol analysis with the AVISPA tool. Electron. Notes Theor. Comput. Sci. 2006, 155, 61–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolev, D.; Yao, A. On the Security of Public-Key Protocols. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1983, 29, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basin, D.; Modersheim, S.; Vigan, L. An On-The-Fly Model-Checker for Security Protocol Analysis. In Proceedings of the ESORICS’03; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; LNCS 2808; pp. 253–270. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, J.; Jacob, J. A Survey of Authentication Protocol Literature: Version 1.0. 17 November 1997. Available online: www.cs.york.ac.uk/~jac/papers/drareview.ps.gz (accessed on 26 May 2019).
- Donovan, B.; Norris, P.; Lowe, G. Analyzing a Library of Security Protocols using Casper and FDR. In Proceedings of the FLOC’99 Workshop on Formal Methods and Security Protocols (FMSP’99); 1999. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.21.7256 (accessed on 26 May 2019).
- Chevalier, Y.; Vigneron, L. Automated Unbounded Verification of Security Protocols. In Proc. CAV’02, LNCS 2404; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/3-540-45657-0_24 (accessed on 26 May 2019).
- Armando, A.; Compagna, L. SATMC: A SAT-based Model Checker for Security Protocols. In Proc. JELIA’04, LNAI 3229; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-540-30227-8_68 (accessed on 26 May 2019 ).
- Boichut, Y.; Heam, P.-C.; Kouchnarenko, O.; Oehl, F. Improvements on the Genet And Klay Technique to Automatically Verify Security Protocols. In Proc. AVIS’04, ENTCS. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/246435265_Improvements_on_the_Genet_and_Klay_technique_to_automatically_verify_security_protocols (accessed on 26 May 2019).
- Ullah, S.; Junaid, M.; Habib, F.; Sana; Insafullah; Hizbullah. A novel proxy blind signcryption scheme based on hyper elliptic curve. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (ICNC-FSKD), Changsha, China, 13–15 August 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, W.; Mei, Y. Certificateless Key-Insulated Generalized Signcryption Scheme without Bilinear Pairings. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2017, 2017, 8405879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ch, S.A.; Nizamuddin; Sher, M. Public Verifiable Signcryption Schemes with Forward Secrecy Based on Hyperelliptic Curve Cryptosystem. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2012, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, S.A.; Farash, M.S.; Naqvi, H.; Sher, M. A secure and efficient authenticated encryption for electronic payment systems using elliptic curve cryptography. Electron. Commer. Res. 2015, 16, 113–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Chang, Y.F.; Chen, Y.H. An efficient authenticated encryption scheme based on ECC and its application for electronic payment. Inf. Technol. Control 2013, 42, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Schemes | 𝓒𝓞𝓝 | 𝓘𝓝𝓣 | 𝓐𝓤𝓣 | 𝓤𝓝𝓕 | 𝓝𝓡𝓟 | 𝓕𝓡𝓢 | 𝓟𝓥 | 𝓡𝓐𝓡 | 𝓢𝓔𝓒𝓥𝓝 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hwang [10] | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓝𝓞 | 𝓝𝓞 |
| Toorani [11] | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓝𝓞 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓝𝓞 | 𝓝𝓞 |
| Mohpathra [33] | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓝𝓞 | 𝓝𝓞 |
| Elkamchouchi [34] | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓝𝓞 | 𝓝𝓞 |
| Proposed | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 | 𝓨𝓢 |
| Schemes | Signcryption | Unsigncryption | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hwang [10] | 2 𝓔𝓒-𝓟𝓜 | 3 𝓔𝓒-𝓟𝓜 | 5𝓔𝓒-𝓟𝓜 |
| Toorani [11] | 2 𝓔𝓒-𝓟𝓜 | 3 𝓔𝓒-𝓟𝓜 | 5 𝓔𝓒-𝓟𝓜 |
| Mohpathra [33] | 3 𝓔𝓒-𝓟𝓜 | 2 𝓔𝓒-𝓟𝓜 | 5 𝓔𝓒-𝓟𝓜 |
| Elkamchouchi [34] | 2 𝓔𝓒-𝓟𝓜 | 4 𝓔𝓒-𝓟𝓜 | 6 𝓔𝓒-𝓟𝓜 |
| Proposed | 2 𝓗𝓒-𝓓𝓜 | 4 𝓗𝓒-𝓓𝓜 | 6 𝓗𝓒-𝓓𝓜 |
| Schemes | Signcryption | Unsigncryption | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hwang [10] | 1.94 | 2.91 | 4.85 |
| Toorani [11] | 1.94 | 2.91 | 4.85 |
| Mohpathra [33] | 2.91 | 1.91 | 4.85 |
| Elkamchouchi [34] | 2.91 | 3.88 | 5.86 |
| Proposed | 0.96 | 1.92 | 2.88 |
| Schemes | Communication Cost |
|---|---|
| Hwang [10] | |
| Toorani [11] | |
| Mohpathra [33] | |
| Elkamchouchi [34] | |
| Proposed |
| Schemes | Message Size | 128 bits | 256 bits | 1024 bits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hwang [10] | 128 + |160| + 2|160| = 608 | 256 + |160| + 2|160| = 736 | 1024 + |160| + 2|160| = 1504 | |
| Toorani [11] | 128 + |160| + 2|160| = 608 | 256 + |160| + 2|160| = 736 | 1024 + |160| + 2|160| = 1504 | |
| Mohpathra [33] | 128 + |160| + 2|160| = 608 | 256 + |160| + 2|160| = 736 | 1024 + |160| + 2|160| = 1504 | |
| Elkamchouchi [34] | 128 + |160| + |160| = 448 | 256 + |160| + |160| = 576 | 1024 + |160| + |160| = 1344 | |
| Proposed | 128 + |80| + |80| = 288 | 256 + |80| + |80| = 416 | 1024 + |80| + |80| = 1184 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah, I.; Amin, N.U.; Khan, J.; Rehan, M.; Naeem, M.; Khattak, H.; Khattak, S.J.; Ali, H.
A Novel Provable Secured Signcryption Scheme
Ullah I, Amin NU, Khan J, Rehan M, Naeem M, Khattak H, Khattak SJ, Ali H.
A Novel Provable Secured Signcryption Scheme
Ullah, Insaf, Noor Ul Amin, Junaid Khan, Muhammad Rehan, Muhammad Naeem, Hizbullah Khattak, Shah Jahan Khattak, and Haseen Ali.
2019. "A Novel Provable Secured Signcryption Scheme
Ullah, I., Amin, N. U., Khan, J., Rehan, M., Naeem, M., Khattak, H., Khattak, S. J., & Ali, H.
(2019). A Novel Provable Secured Signcryption Scheme




