Dynamic Analysis of a Pest Management Smith Model with Impulsive State Feedback Control and Continuous Delay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Dynamic Analysis of Impulsive State Feedback Control Model
2.1. Qualitative Analysis of Pest Management Model without Impulsive
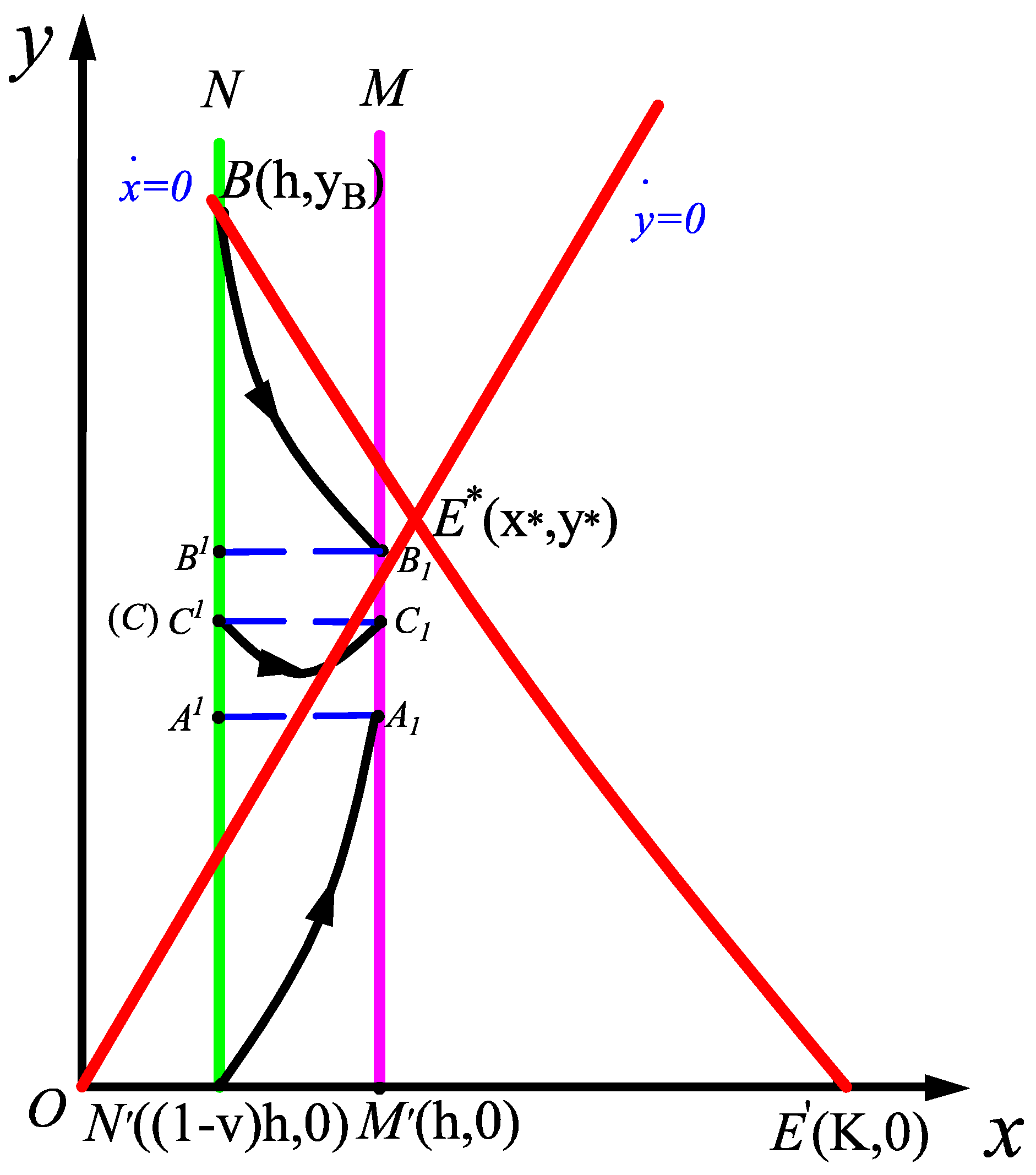
2.2. Existence and Uniqueness of the Order-One Periodic Orbit of Impulsive State Feedback Control Model
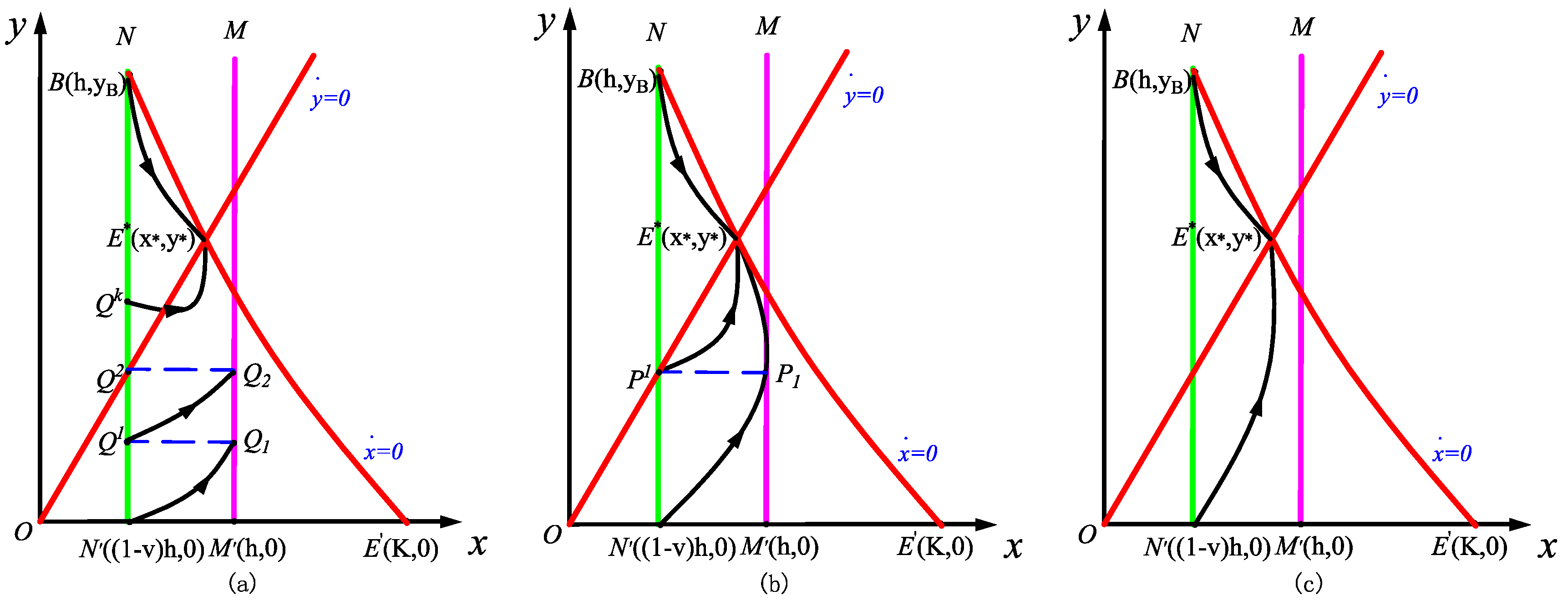
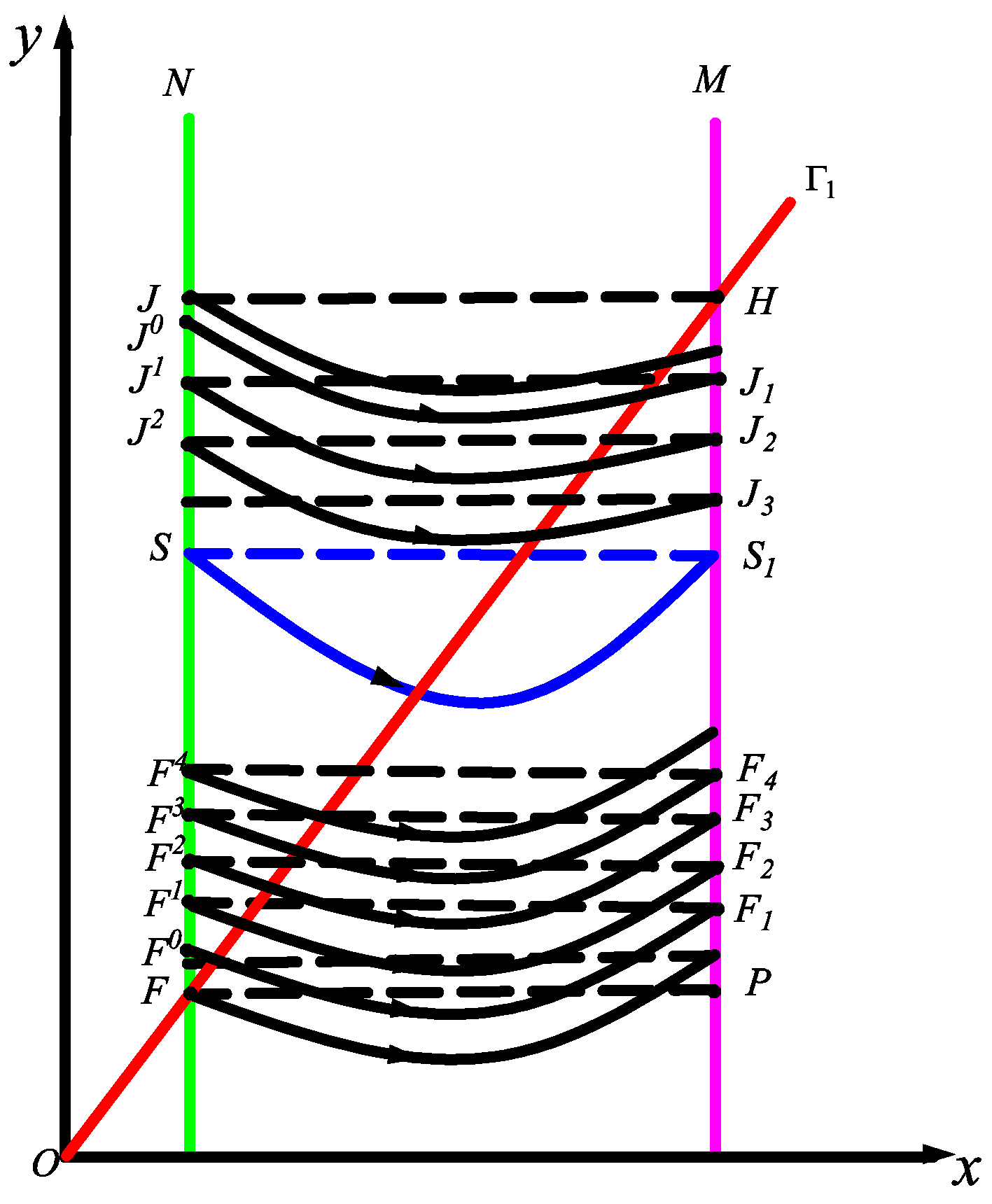
2.3. Stability of the Order-One Periodic Orbit of Impulsive State Feedback Control Model
3. Numerical Simulations and Conclusions
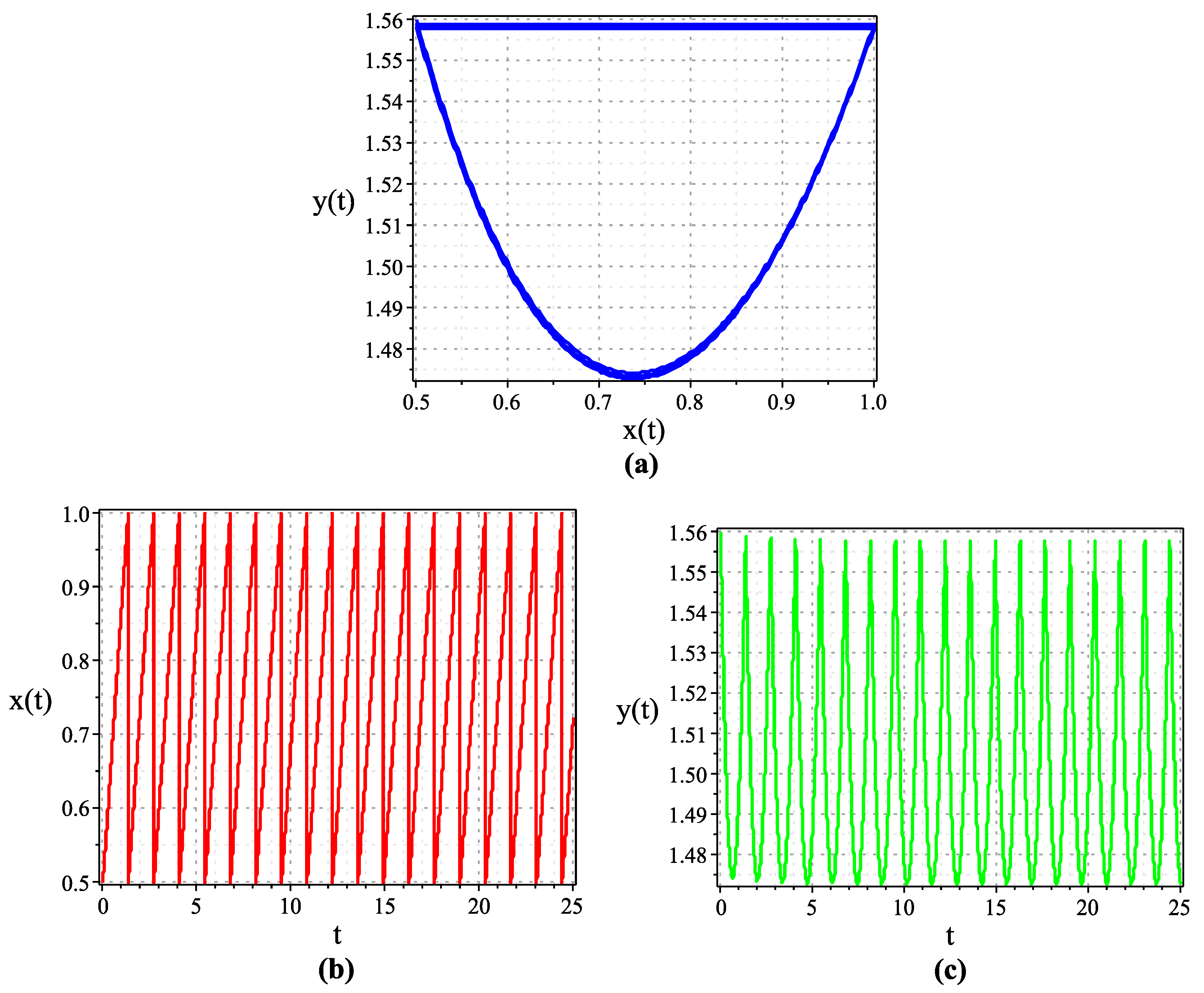
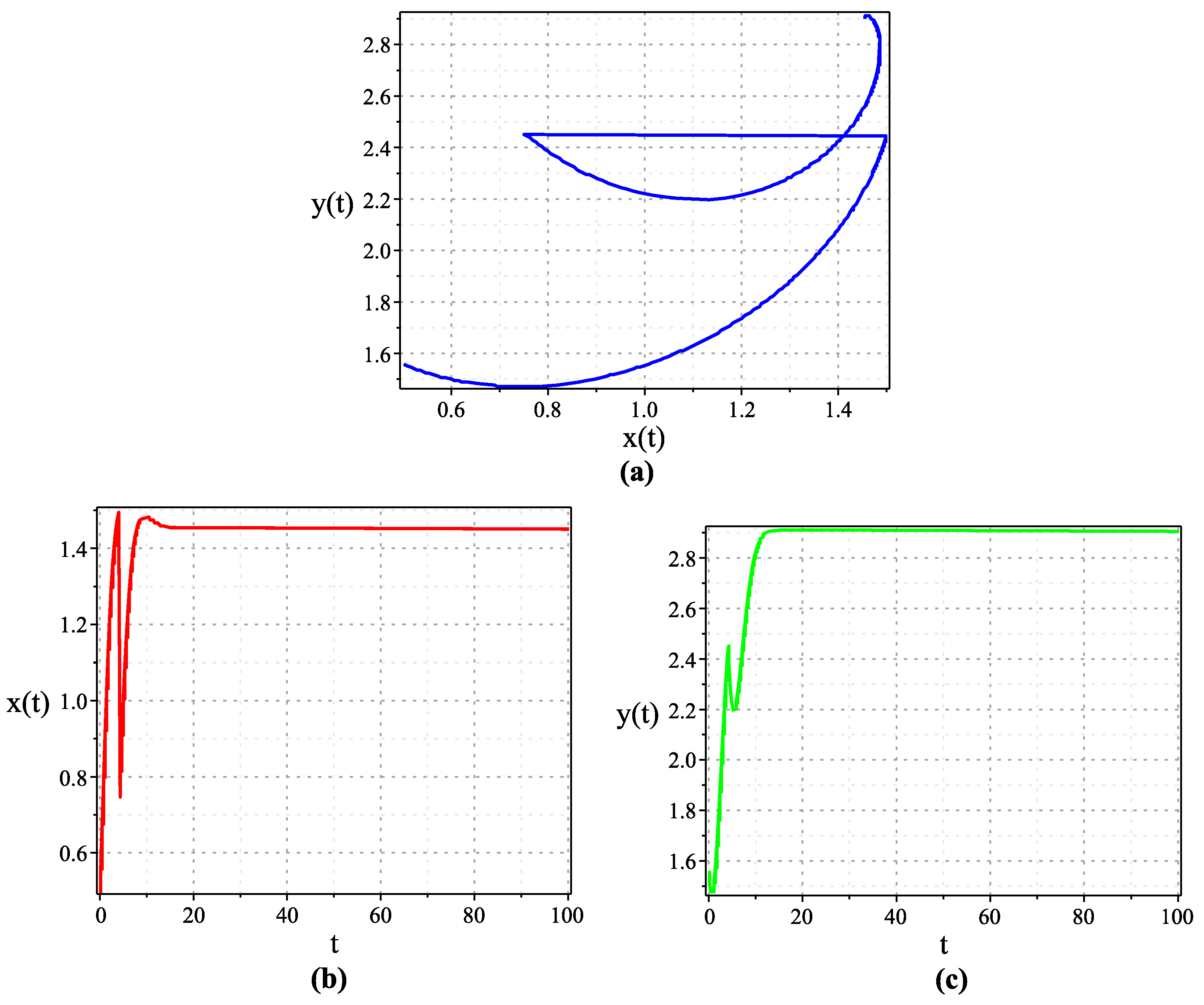
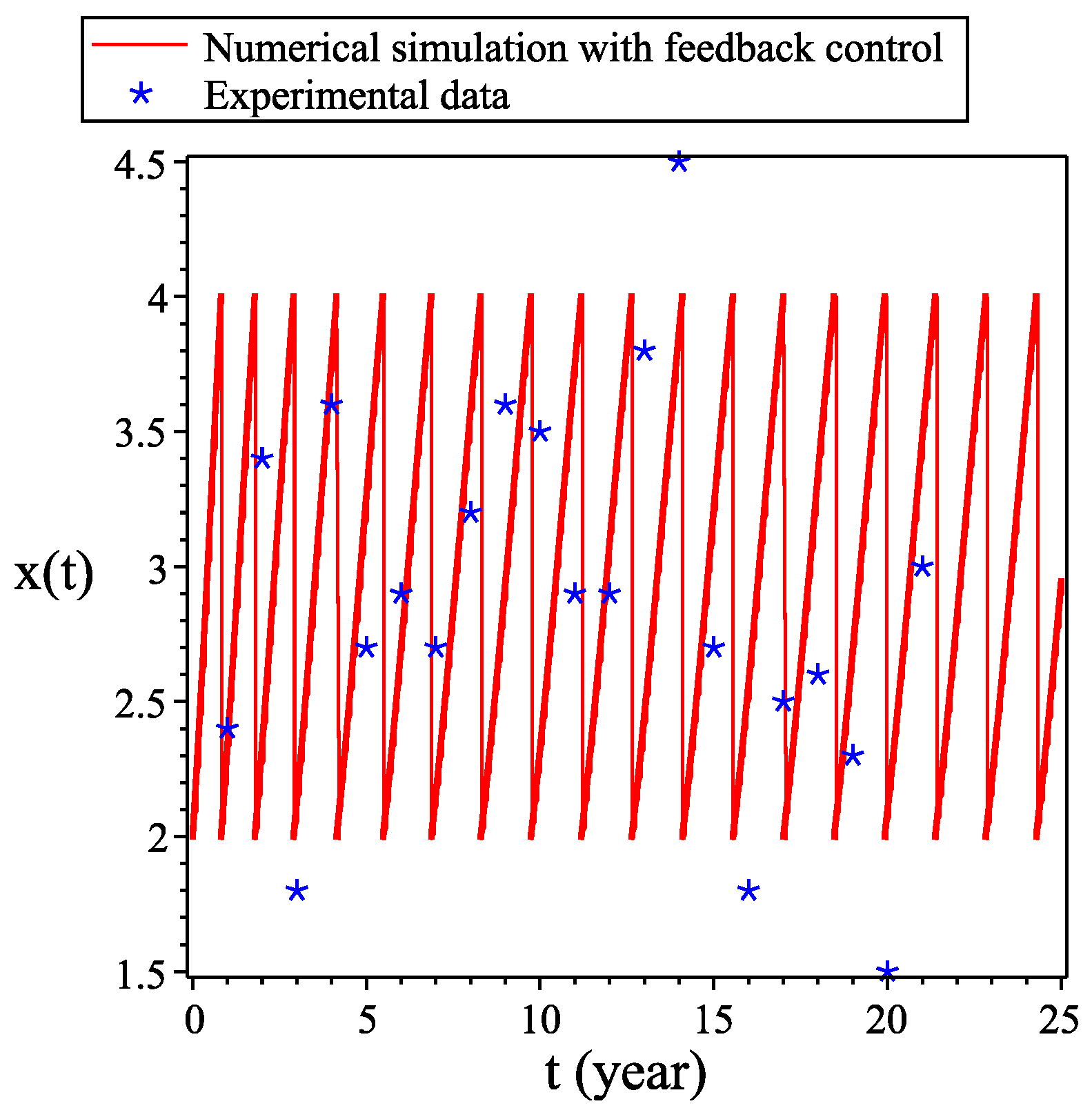
3.1. Numerical Simulations
3.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, T.Q.; Meng, X.Z.; Liu, R.; Zhang, T.H. Periodic solution of a pest management Gompertz model with impulsive state feedback control. Nonlinear Dyn. 2014, 78, 921–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.N.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, H.D. Stability Analysis and Control Optimization of a Prey-Predator Model with Linear Feedback Control. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2018, 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, J.A.; Régnière, J.; Powell, J.A. Assessing the impacts of global warming on forest pest dynamics. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2003, 1, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.S. Pest control and geometric theory of semi-continuous dynamical system. J. Beihua Univ. 2011, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.; Chen, Y.D.; Yang, H.W. A new predator-prey model with a profitless delay of digestion and impulsive perturbation on the prey. Appl. Math. Comput. 2011, 217, 9198–9208. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, L.Z.; Chen, L.S. A pest management model with state feedback control. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2016, 2016, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Y.N.; Cheng, H.D.; Wang, J.M.; Wang, Y.H. Dynamic analysis of unilateral diffusion Gompertz model with impulsive control strategy. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2018, 2018, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Cheng, H.D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.N. The geometrical analysis of a predator-prey model with multi-state dependent impulsive. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 2018, 8, 427–442. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.M.; Cheng, H.D.; Liu, H.X.; Wang, Y.H. Periodic solution and control optimization of a prey-predator model with two types of harvesting. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2018, 2018, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.C.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.Q.; Meng, X.Z.; Zhang, T.H. Persistence and ergodicity of plant disease model with markov conversion and impulsive toxicant input. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2017, 48, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F. Continuity and approximate differentiability of multisublinear fractional maximal functions. Math. Inequal. Appl. 2018, 21, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Song, G.H.; Chen, L.S. A state feedback impulse model for computer worm control. Nonlinear Dyn. 2016, 85, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, G.P.; Chen, L.S. Periodic solution of the system with impulsive state feedback control. Nonlinear Dyn. 2014, 78, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.Z.; Chen, L.S.; Chen, J.F. Persistence and periodic orbits for two-species nonautonomous diffusion lotka-volterra models. Math. Comput. Model. 1994, 20, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.Y.; Chen, L.S. Global attractivity in a food-limited population model with impulsive effects. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2004, 292, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.Z.; Chen, L.S. A stage-structured SI eco-epidemiological model with time delay and impulsive controlling. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2008, 21, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Z.; Wang, J.M.; Li, Q.J.; Cheng, H.D. Control optimization and homoclinic bifurcation of a prey-predator model with ratio-dependent. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2019, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.J.; Chen, L.S.; Song, X.Y. Dynamical properties of a kind of SIR model with constant vaccination rate and impulsive state feedback control. Int. J. Biomath. 2017, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.R.; Pairote, S.; Jiao, J.J. Dynamics of an SIR epidemic model with stage structure and pulse vaccination. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2016, 2016, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, H.H. Dynamic behaviors of interaction solutions of (3+1)-dimensional Shallow Water wave equation. Comput. Math. Appl. 2018, 76, 1408–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.S.; Dong, H.H. The Prolongation Structure of the Modified Nonlinear Schrödinger Equation and Its Initial-Boundary Value Problem on the Half Line via the Riemann-Hilbert Approach. Mathematics 2019, 7, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.B.; Meng, X.Z.; Lu, X. Analysis of a novel stochastic SIRS epidemic model with two different saturated incidence rates. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2017, 472, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.H. Global dynamics analysis of a nonlinear impulsive stochastic chemostat system in a polluted environment. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 2016, 6, 865–875. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.H.; Zhang, T.Q.; Meng, X.Z. Stability analysis of a chemostat model with maintenance energy. Appl. Math. Lett. 2017, 68, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, Y. Adaptive finite time control of nonlinear systems under time-varying actuator failures. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Q.; Ma, W.B.; Meng, X.Z. Global dynamics of a delayed chemostat model with harvest by impulsive flocculant input. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2017, 2017, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.Z.; Li, Z.Q.; Nieto, J.J. Dynamic analysis of michaelis-menten chemosta-type competition models with time delay and pulse in a polluted environment. J. Math. Chem. 2010, 47, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballinger, G.; Liu, X. Permanence of population growth models with impulsive effects. Math. Comput. Model. 1997, 26, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiao, J.J.; Chen, L.S. A Pest management through continuous and impulsive control strategies. Biosystems 2007, 90, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.N.; Cheng, H.D.; Wang, Y.H. A Lycaon pictus impulsive state feedback control model with Allee effect and continuous time delayi equations: The wronskian technique. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2018, 2018, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Wang, Y.; Khalique, C.M.; Bai, Y.Z. Peakon and cuspon solutions of a generalized Camassa-Holm-Novikov equation. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 2018, 8, 1938–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, J.J.; Yang, X.S.; Cai, S.H.; Chen, L.S. Dynamical analysis of a delayed predator-prey model with impulsive diffusion between two patches. Math. Comput. Simul. 2009, 80, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Cheng, H.D.; Meng, X.Z.; Aruna, P.B. Geometrical analysis and control optimization of a predator-prey model with multi state-dependent impulse. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2017, 2017, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.R.; Lu, Q.S. Impulsive state feedback control of a predator-prey model. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2007, 200, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, T.H.; Sun, K.B. Dynamics analysis of a pest management prey-predator model by means of interval state monitoring and control. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst. 2017, 23, 122–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, T.H.; Meng, X.Z.; Zhang, T.Q. Turing-hopf bifurcations in a predator-prey model with herd behavior, quadratic mortality and prey-taxis. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2018, 496, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xue, Q.Y.; Yabuta, K. Rough maximal singular integral and maximal operators supported by subvarieties on Triebel-Lizorkin spaces. Nonlinear Anal. 2018, 171, 41–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, B.; Sun, Y.M.; Lin, C. Finite time control of switched stochastic nonlinear systems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2019, 365, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.C.; Wang, L. Global hopf bifurcation for a predator-prey system with three delays. Int. J. Bifur. Chaos 2017, 27, 1750108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, A.J. Biocontrol in an impulsive predator-prey model. Math. Biosci. 2014, 256, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Grognard, F.; Mailleret, L. Natural enemies deployment in patchy environments for augmentative biological control. Appl. Math. Comput. 2015, 266, 982–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.D.; Wang, X.H.; Meng, X.Z. Extinction and persistence in mean of a novel delay impulsive stochastic infected predator-prey system with jumps. Complexity 2017, 2017, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.M.; Chen, L.S.; Nieto, J.J. The dynamics of an epidemic model for pest control with impulsive effect. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2010, 11, 1374–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M.N.; Zhao, W.C. Dynamical analysis of multi-nutrient and single microorganism chemostat model in a polluted environment. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2018, 2018, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Miao, A.Q.; Zhang, T.Q. Extinction and persistence of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with saturated incidence rate and transfer from infectious to susceptible. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2018, 2018, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, L.S.; Georgescu, P. Impulsive control strategies for pest management. J. Biol. Syst. 2007, 15, 235–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.S.; Wang, F. Adaptive tracking control for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems with infinite number of actuator failures using neural networks. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2017, 2017, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.C.; Chen, L.S.; Zhang, Q.L. The geometrical analysis of a predator-prey model with two state impulses. Math. Biosci. 2012, 238, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.B.; Zhang, T.H.; Tian, Y. Dynamics analysis and control optimization of a pest management predator-prey model with an integrated control strategy. Appl. Math. Comput. 2017, 292, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.D.; Xu, W.J.; Chen, L.S.; Huang, Z.H. A white-headed langurs impulsive state feedback control model with sparse effect and continuous delay. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2017, 50, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.Y.; Wang, K. Economic Harvesting Model with Variabe Price and Cost for Population with Smith Growth and Cui Lawson Growth. J. Biomath. 2004, 19, 328–336. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, F.K. Population dynamics in daphnia magna and a new model for population growth. Ecology 1963, 44, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Z.; Li, Y.; Cheng, H. Dynamic Analysis of a Pest Management Smith Model with Impulsive State Feedback Control and Continuous Delay. Mathematics 2019, 7, 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7070591
Shi Z, Li Y, Cheng H. Dynamic Analysis of a Pest Management Smith Model with Impulsive State Feedback Control and Continuous Delay. Mathematics. 2019; 7(7):591. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7070591
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Zhenzhen, Yaning Li, and Huidong Cheng. 2019. "Dynamic Analysis of a Pest Management Smith Model with Impulsive State Feedback Control and Continuous Delay" Mathematics 7, no. 7: 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7070591
APA StyleShi, Z., Li, Y., & Cheng, H. (2019). Dynamic Analysis of a Pest Management Smith Model with Impulsive State Feedback Control and Continuous Delay. Mathematics, 7(7), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7070591



