Empirical Means on Pseudo-Orthogonal Groups
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Function Minimization on Pseudo-Riemannian Smooth Manifolds
2.1. Notes on Pseudo-Riemannian Manifolds
2.2. Gradient-Based Function Minimization on Pseudo-Riemannian Manifolds
3. Function Minimization on the Pseudo-Orthogonal Group
3.1. Pseudo-Riemannian Geometric Structure of the Pseudo-Orthogonal Group
3.2. A Criterion Function Based on the Frobenius Norm over
| Algorithm 1 Pseudocode to implement mean-computation over according to the function minimization rule (7) endowed with the step-size-selection rule in Equation (11) and the stopping criterion in Equation (12). |
|
3.3. A Criterion Function Based on the Geodesic Distance over
| Algorithm 2 Pseudocode to implement mean-computation over according to the function minimization rule in Equation (7). |
|
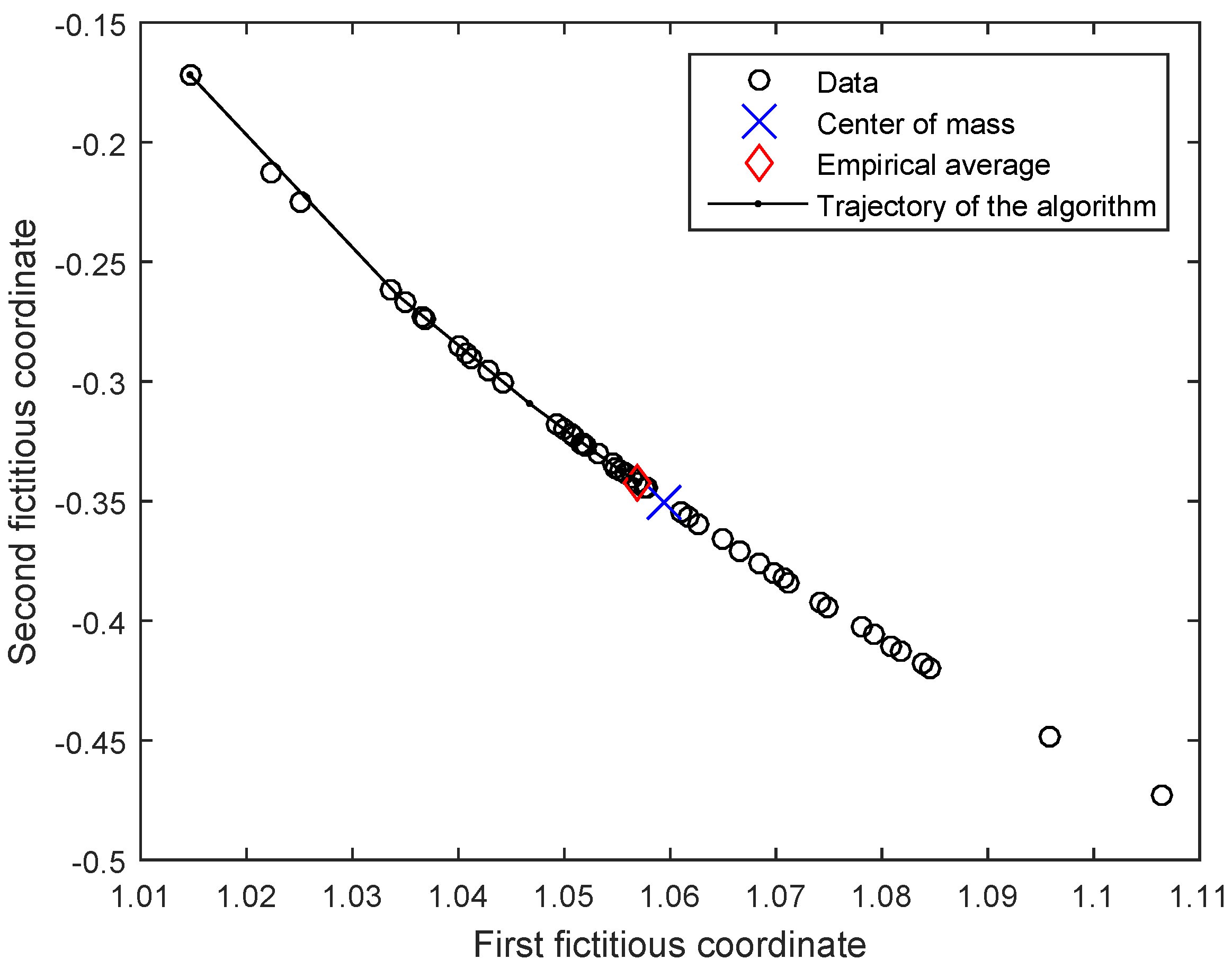
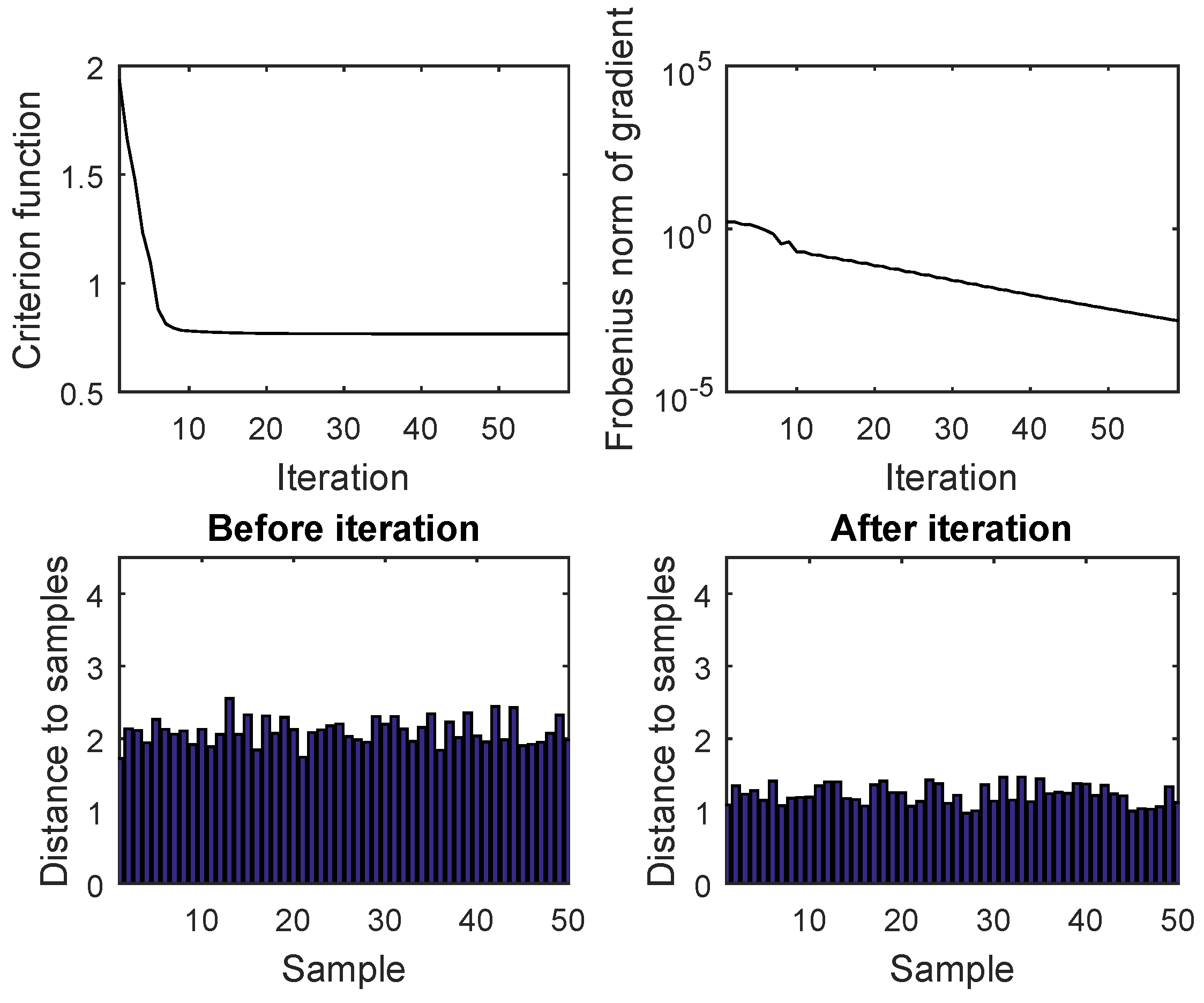
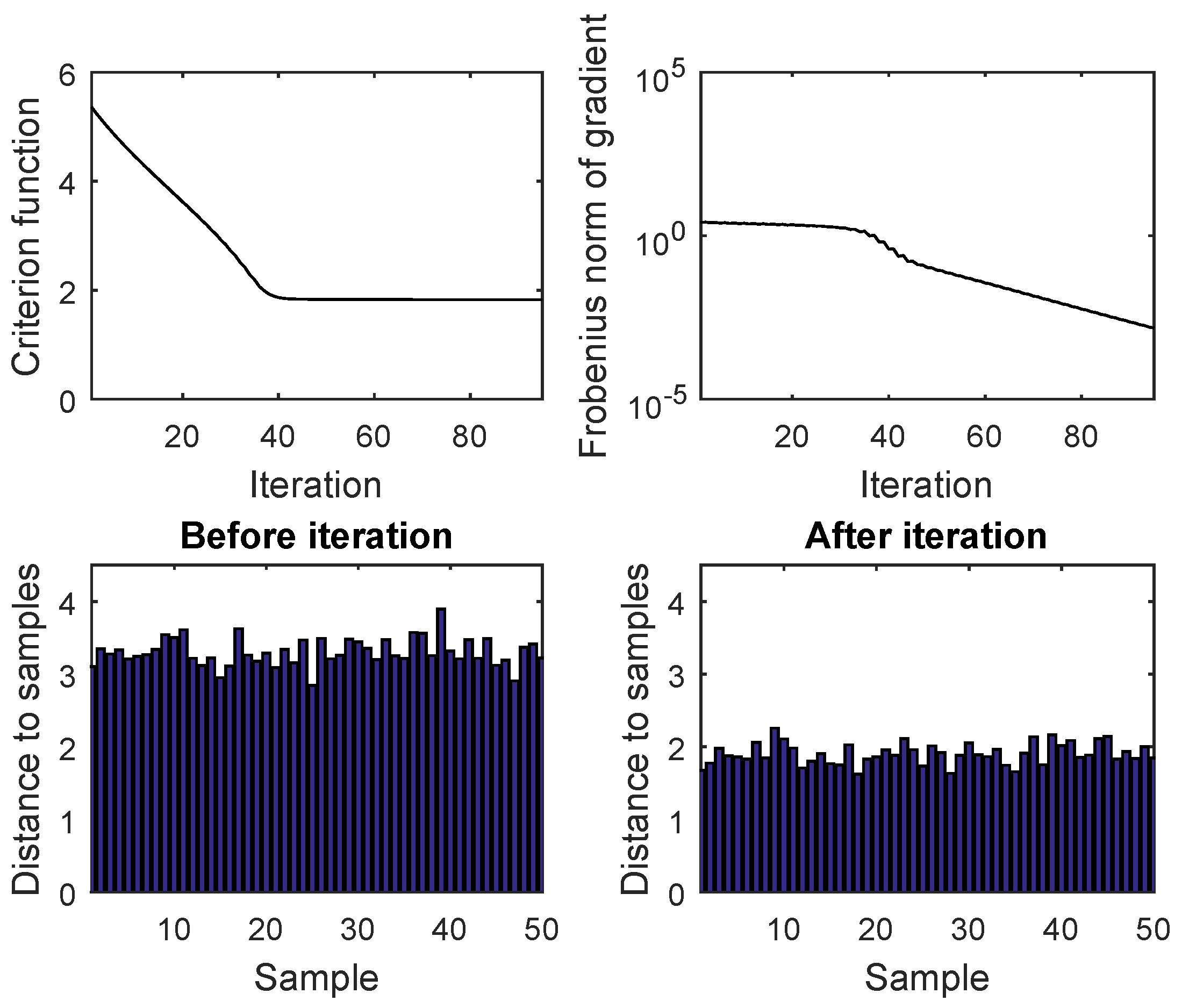
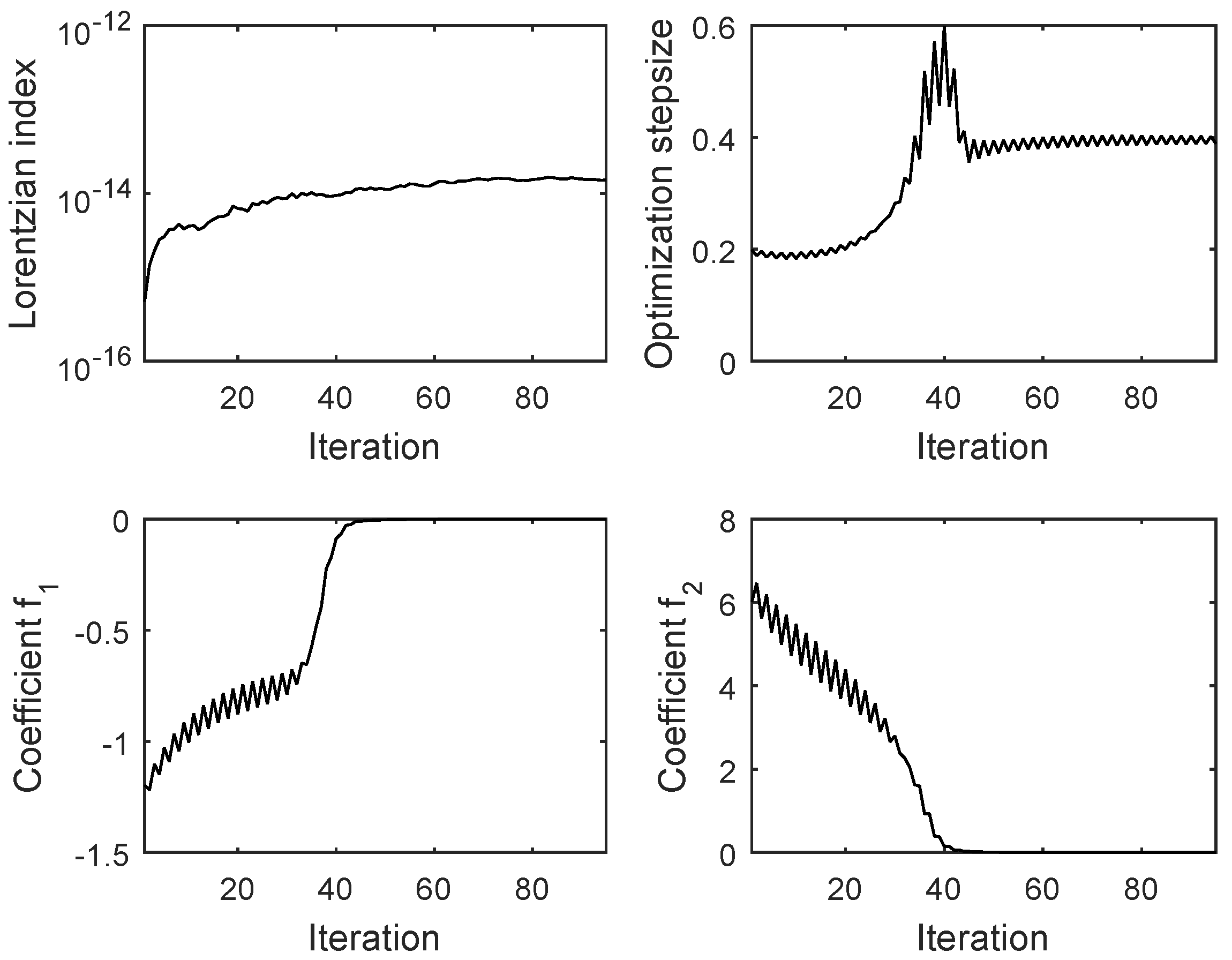
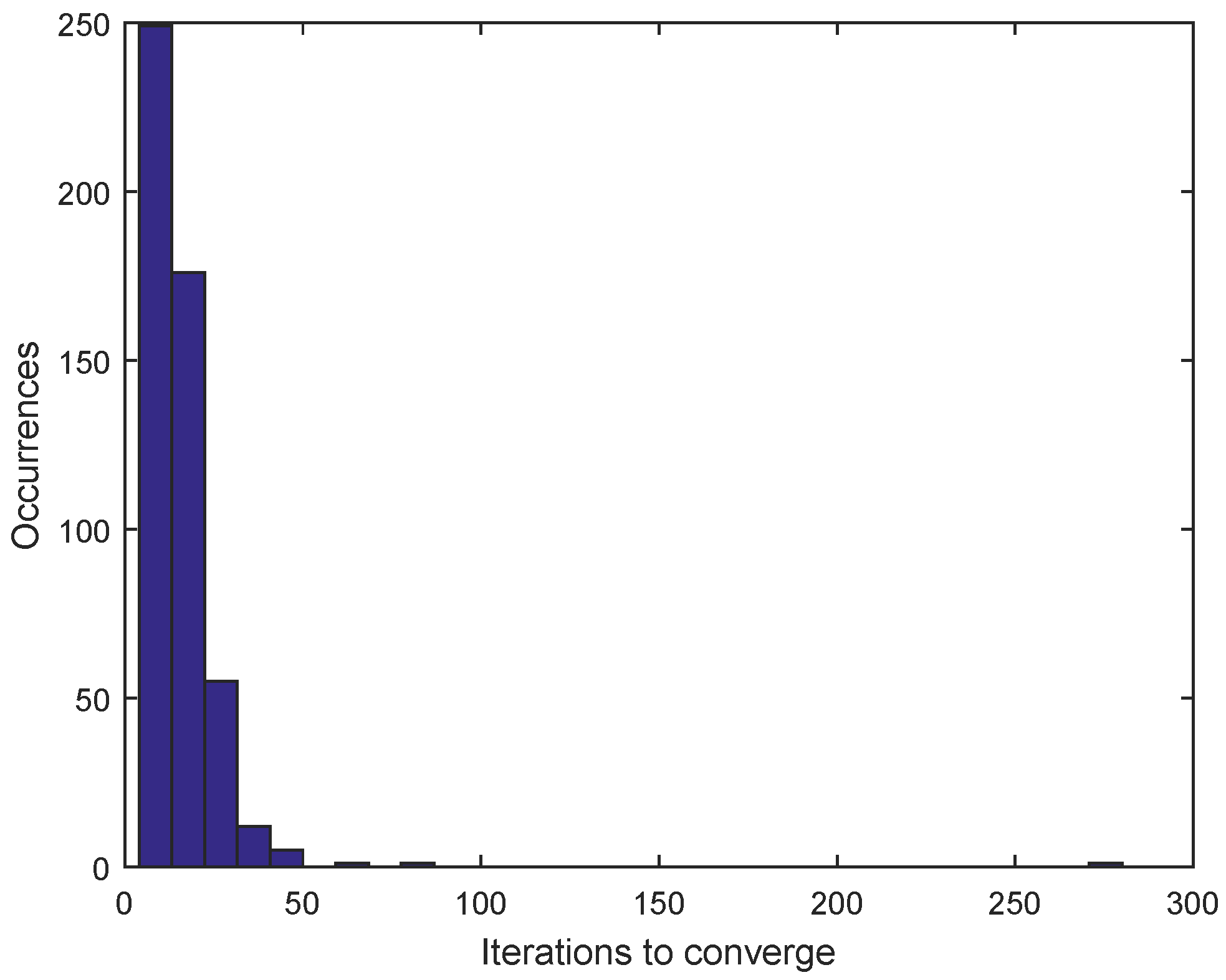
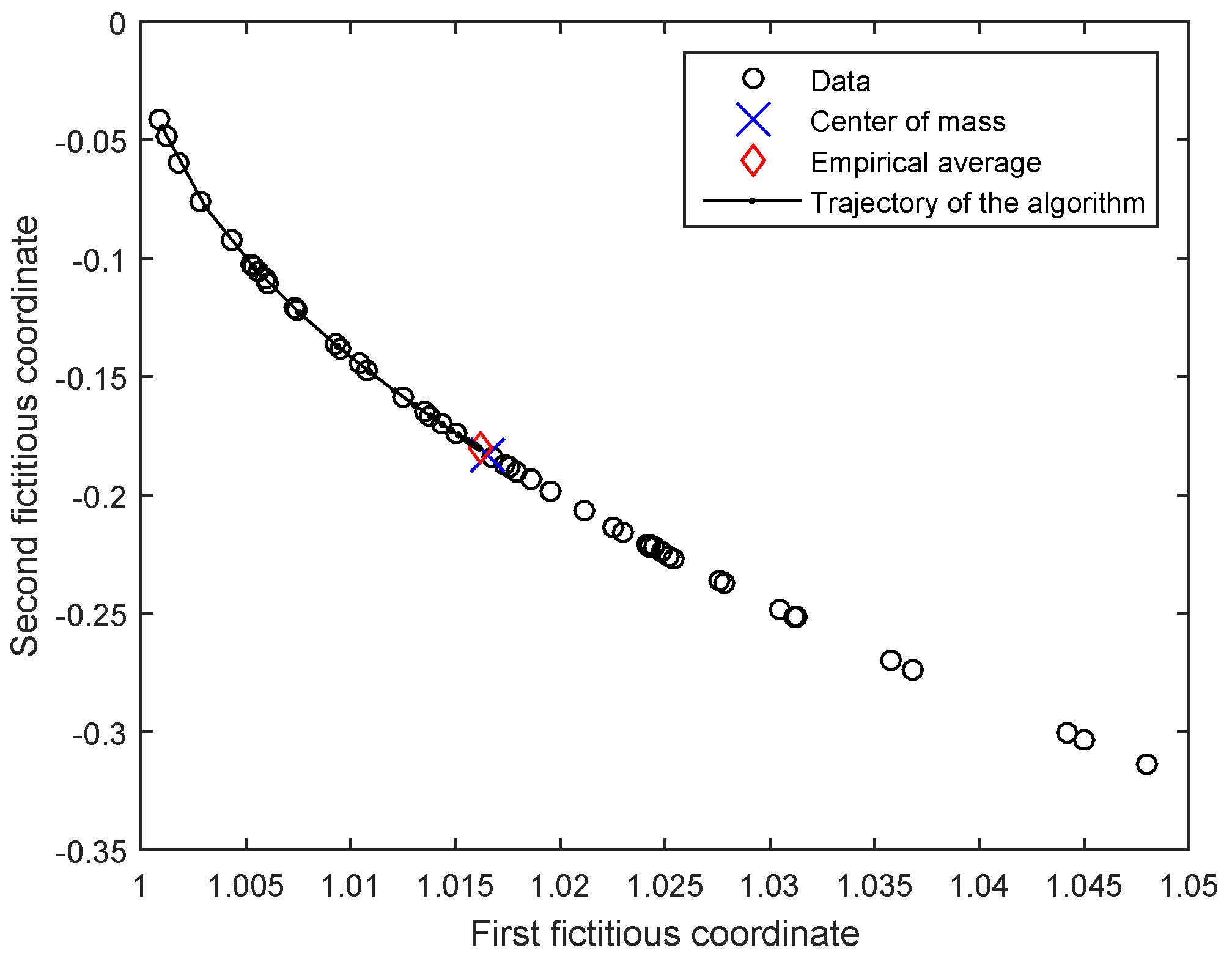
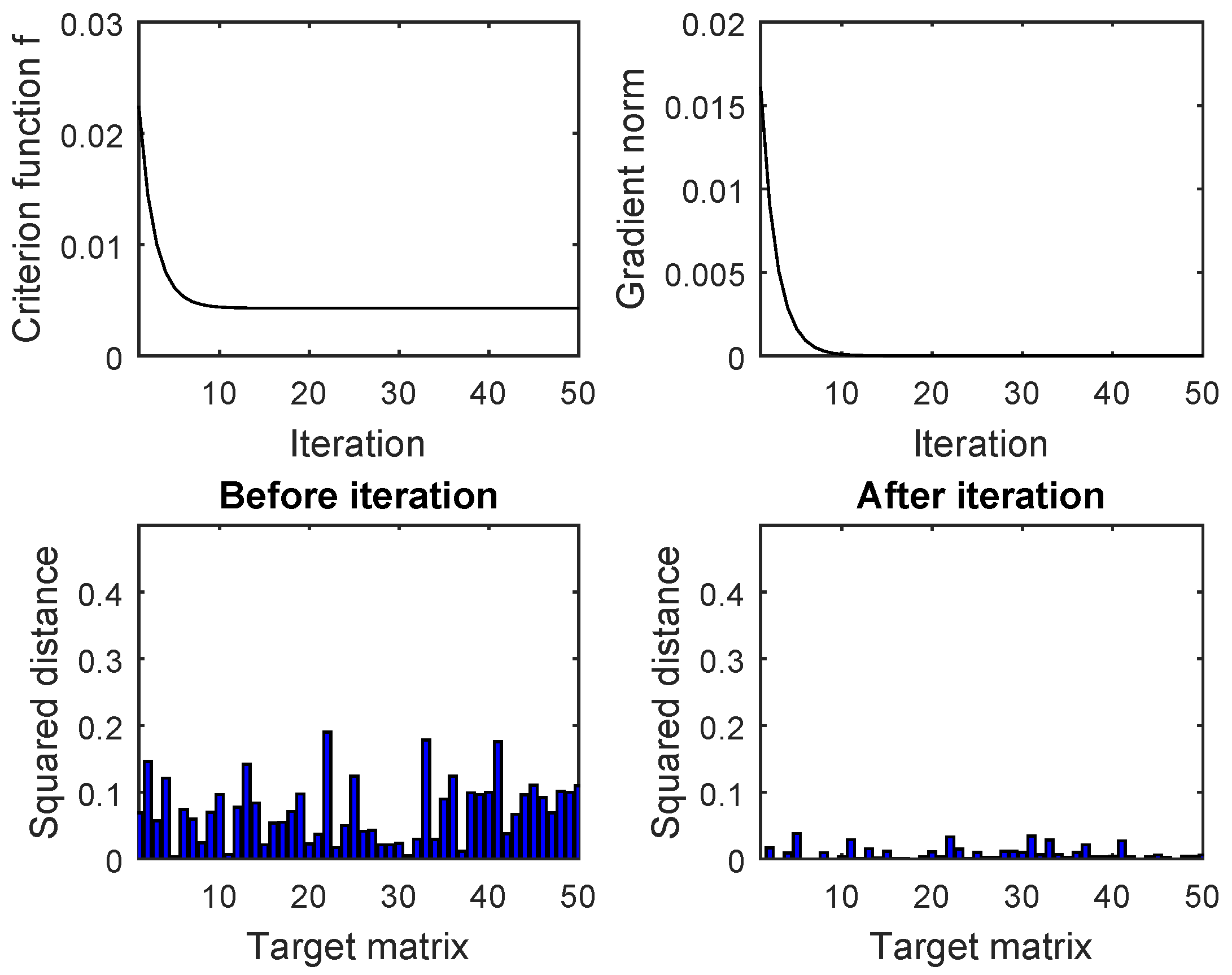
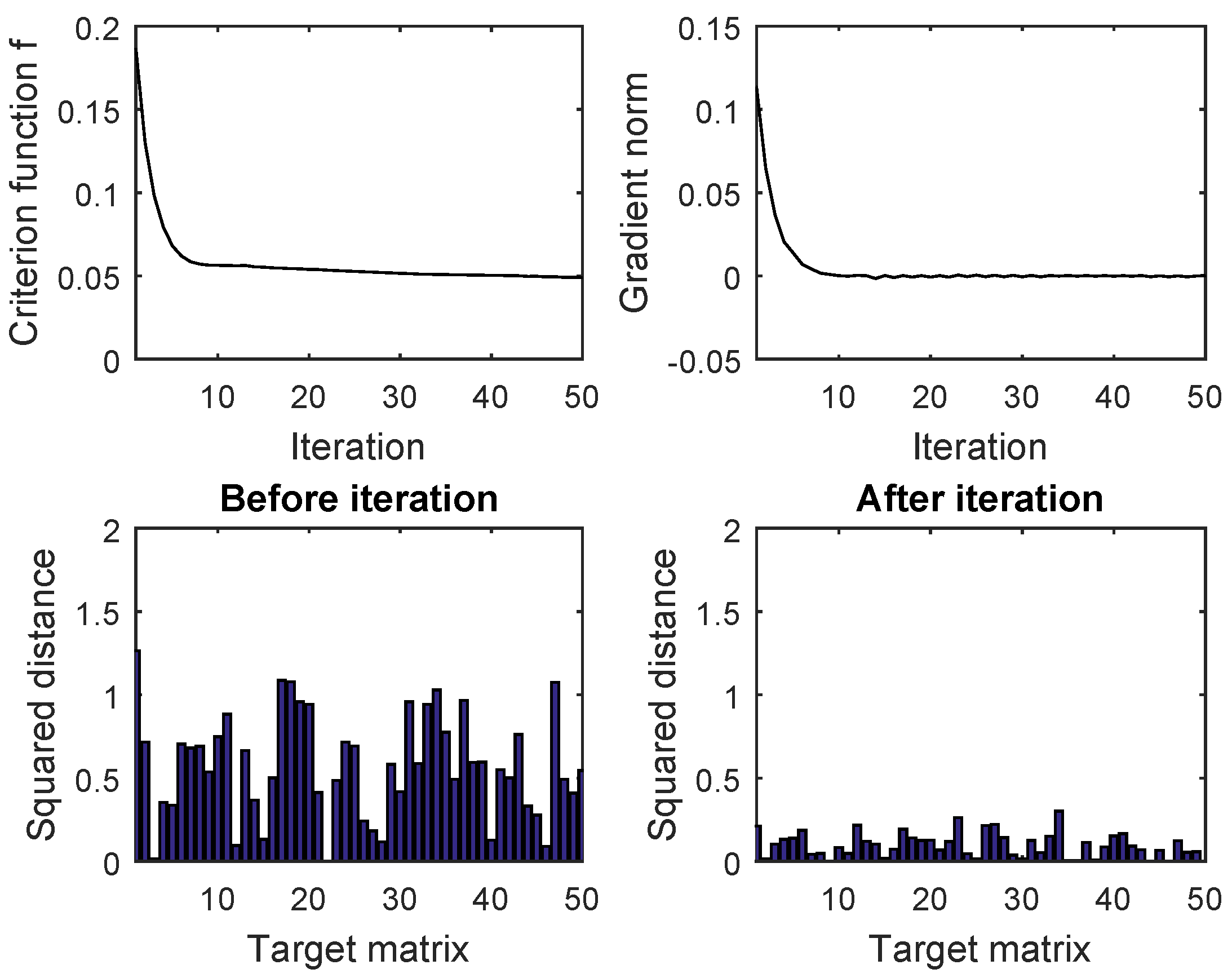
4. Numerical Tests
4.1. Gradient-Based Minimization of a Criterion Function Induced by the Frobenius Norm
4.2. Gradient-Based Minimization of a Criterion Function Induced by the Geodesic Distance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Neill, B. Semi-Riemannian Geometry. With Applications to Relativity. Pure and Applied Mathematics, 103; Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Barachant, A.; Bonnet, S.; Congedo, M.; Jutten, C. Multi-class brain computer interface classification by Riemannian geometry. IEEE Trans. Bio-Med. Eng. 2012, 59, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gariazzo, C.; Pelliccioni, A.; Bogliolo, M.P. Spatiotemporal analysis of urban mobility using aggregate mobile phone derived presence and demographic data: A case study in the city of Rome, Italy. Data 2019, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavareh, M.; Maggioni, V. Application of rough set theory to water quality analysis: A case study. Data 2018, 3, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.K. Classification on Manifolds. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Statistics and Operations Research, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Bhattacharya, R. Nonparametric Statistics on Manifolds with Applications to Shape Spaces. Pushing the Limits of Contemporary Statistics: Contributions in Honor of Jayanta K. Ghosh; Institute of Mathematical Statistics: Beachwood, OH, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Freifeld, O. Statistics on Manifolds with Applications to Modeling Shape Deformations. Ph.D. Thesis, Division of Applied Mathematics, Brown University, Providence, RI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Celledoni, E.; Fiori, S. Descent methods for optimization on homogeneous manifolds. Math. Comput. Simulat. 2008, 79, 1298–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Nie, P. Quadratic problems over the Stiefel manifold. Oper. Res. Lett. 2006, 34, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, D. Minimizing a differentiable function over a differentiable manifold. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1982, 37, 177–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luenberger, D. The gradient projection method along geodesics. Manag. Sci. 1972, 18, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Li, D. A geodesic-based Riemannian gradient approach to averaging on the Lorentz group. Entropy 2017, 19, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Qiu, Y.Y.; Du, K.Q. Conditions for optimal solutions of unbalanced Procrustes problem on Stiefel manifold. J. Comput. Math. 2007, 25, 661–671. [Google Scholar]
- Balande, U.; Shrimankar, D. SRIFA: Stochastic ranking with improved-firefly-algorithm for constrained optimization engineering design problems. Mathematics 2019, 7, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.H.; Han, S. The general least square deviation OWA operator problem. Mathematics 2019, 7, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, E.A.; Yu, B.; Zeng, K. Satisfying bank capital requirements: A robustness approach in a modified Roy safety-first framework. Mathematics 2019, 7, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Li, B.; Zhao, W. Physical layer security and optimal multi-time-slot power allocation of SWIPT system powered by hybrid energy. Information 2017, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, I.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Hagag, A.; Li, X.; Zuo, W. Metric learning with dynamically generated pairwise constraints for ear recognition. Information 2018, 9, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.M.; Sun, H.F.; Peng, L.Y. Riemannian means on special Euclidean group and unipotent matrices group. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 292787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moakher, M. A differential geometric approach to the geometric mean of symmetric positive-definite matrices. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. A 2005, 26, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, T.; Fiori, S.; Tanaka, T. Empirical arithmetic averaging over the compact Stiefel manifold. IEEE Trans. Signal Proces. 2013, 61, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiori, S.; Kaneko, T.; Tanaka, T. Tangent-bundle maps on the Grassmann manifold: Application to empirical arithmetic averaging. IEEE Trans. Signal Proces. 2015, 63, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiori, S. Solving minimal-distance problems over the manifold of real symplectic matrices. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. A 2011, 32, 938–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başkal, S.; Georgieva, E.; Kim, Y.S.; Noz, M.E. Lorentz group in classical ray optics. J. Opt. B Quantum Semiclass. Opt. 2004, 6, S455–S472. [Google Scholar]
- Podleś, P.; Woronowicz, S.L. Quantum deformation of Lorentz group. Commun. Math. Phys. 1990, 130, 381–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, H. Evaluation of the Lorentz group Lie algebra map using the Baker-Cambell-Hausdorff formula. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1999, 35, 1490–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, J. Riemannian Geometry and Geometric Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Armijo, L. Minimization of functions having Lipschitz continuous first partial derivatives. Pac. J. Math. 1966, 16, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A. Matrix Groups: An Introduction to Lie Group Theory; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Khvedelidze, A.; Mladenov, D. Generalized Calogero-Moser-Sutherland models from geodesic motion on GL+(n, R) group manifold. Phys. Lett. A 2002, 299, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrica, D.; Rohan, R.-A. A new way to derive the Rodrigues formula for the Lorentz group. Carpathian J. Math. 2014, 30, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Chakrabarti, R.; Rabitz, H. Critical landscape topology for optimization on the symplectic group. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2010, 145, 387–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Fiori, S. Empirical Means on Pseudo-Orthogonal Groups. Mathematics 2019, 7, 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7100940
Wang J, Sun H, Fiori S. Empirical Means on Pseudo-Orthogonal Groups. Mathematics. 2019; 7(10):940. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7100940
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jing, Huafei Sun, and Simone Fiori. 2019. "Empirical Means on Pseudo-Orthogonal Groups" Mathematics 7, no. 10: 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7100940
APA StyleWang, J., Sun, H., & Fiori, S. (2019). Empirical Means on Pseudo-Orthogonal Groups. Mathematics, 7(10), 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7100940





