Rethinking I/O Caching for Large Language Model Inference on Resource-Constrained Mobile Platforms
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Characterization of on-device LLM I/O behavior. We analyze file-access traces of mobile on-device LLM workloads, identifying distinctive I/O patterns such as recurring loop and hot-block accesses, in contrast to remote inference LLMs.
- Design of an LLM-aware buffer caching strategy. We propose a lightweight caching mechanism that accounts for loop and hot-set accesses in LLM workloads, sustaining stable inference performance under limited memory and bandwidth conditions.
- Cache-size modeling and hardware-specific validation. We formulate a cache-sizing model that quantifies feasible cache capacities and validate the proposed strategy through empirical evaluation on smartphone and smartwatch platforms, providing design guidelines for LLM-aware buffer caching in practical device classes.
2. Related Work
2.1. Internal KV Caching
2.1.1. Prefix-Aware KV Caching
2.1.2. Prompt- and RAG-Level Caching
2.1.3. Workload-Aware Cache Eviction
2.1.4. Memory Reduction and Compression
2.1.5. Joint Optimization of Caching and Scheduling
2.2. External Semantic Caching
2.3. System-Level File-Block Caching
3. File-Access Characteristics of LLM Workloads
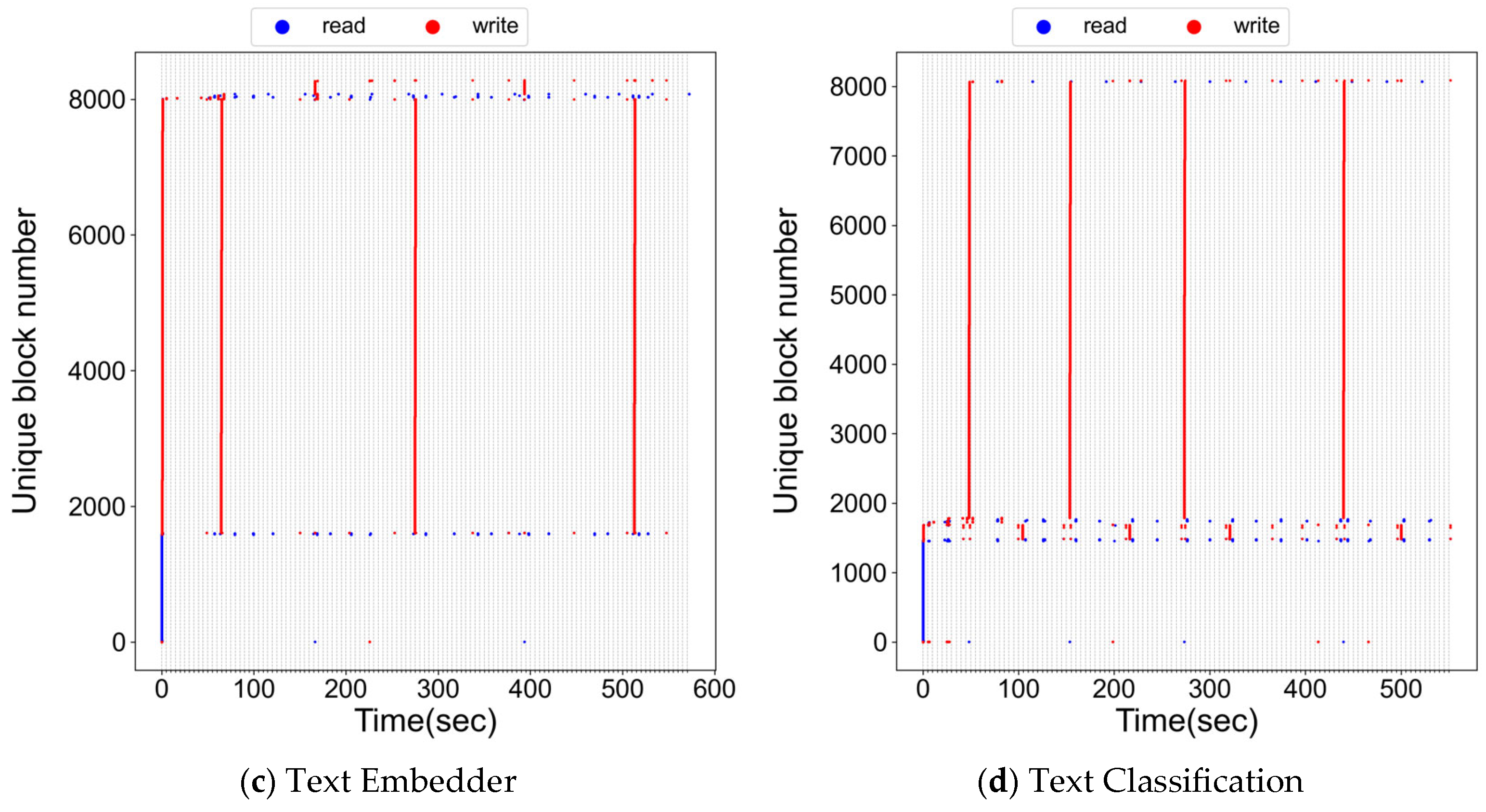
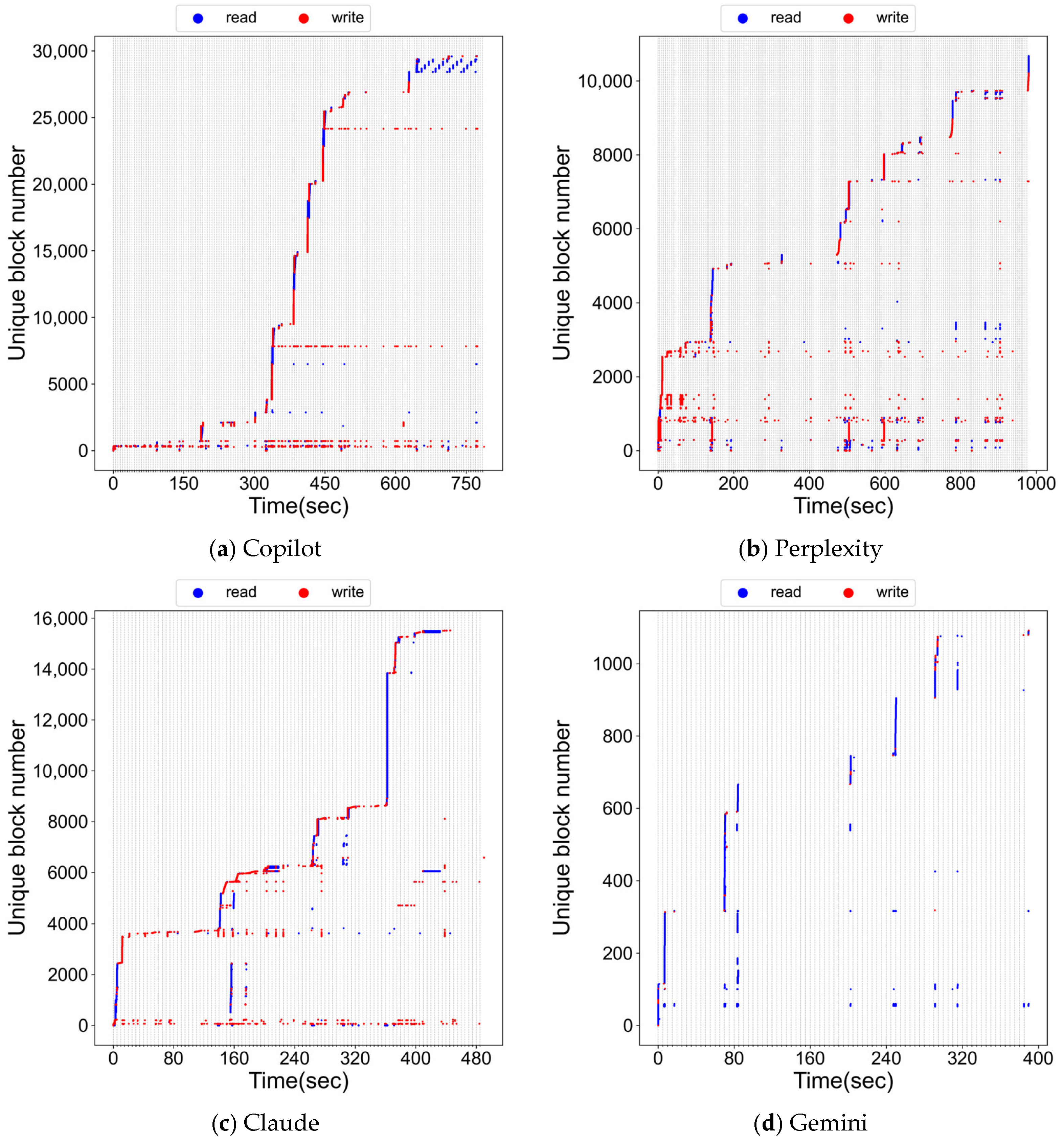
3.1. On-Device Inference
3.2. Remote Inference
3.3. Summary
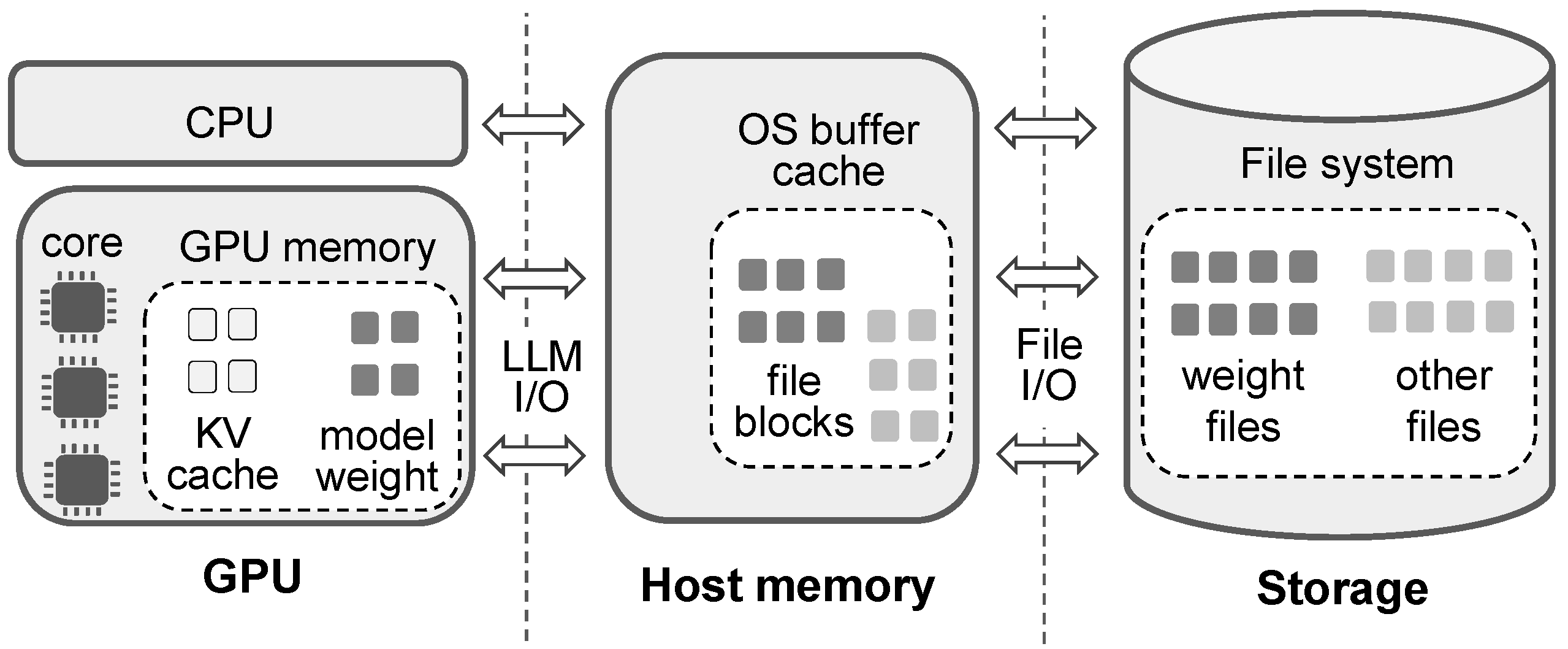
4. Buffer Cache Model for LLM and Implications
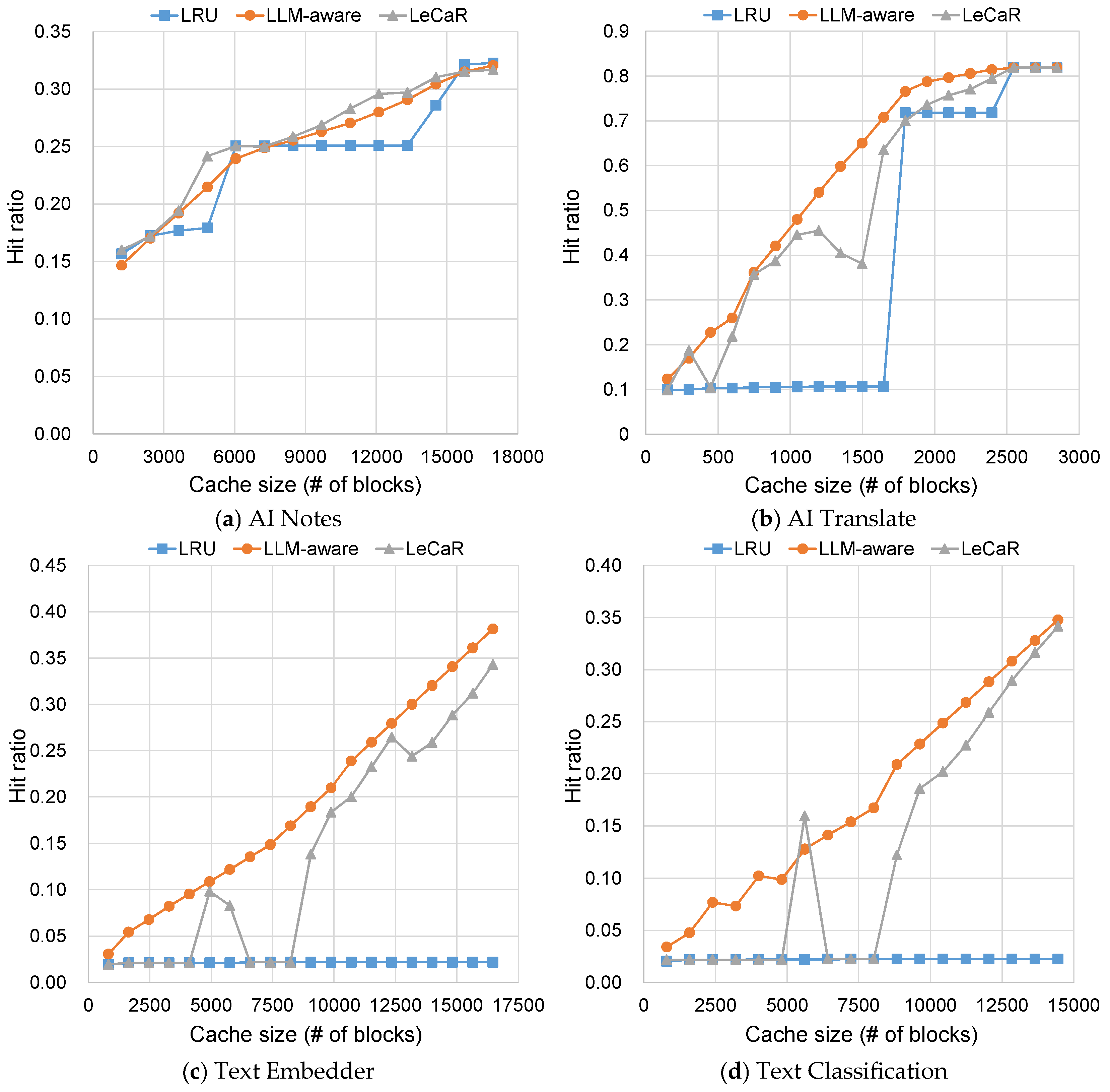
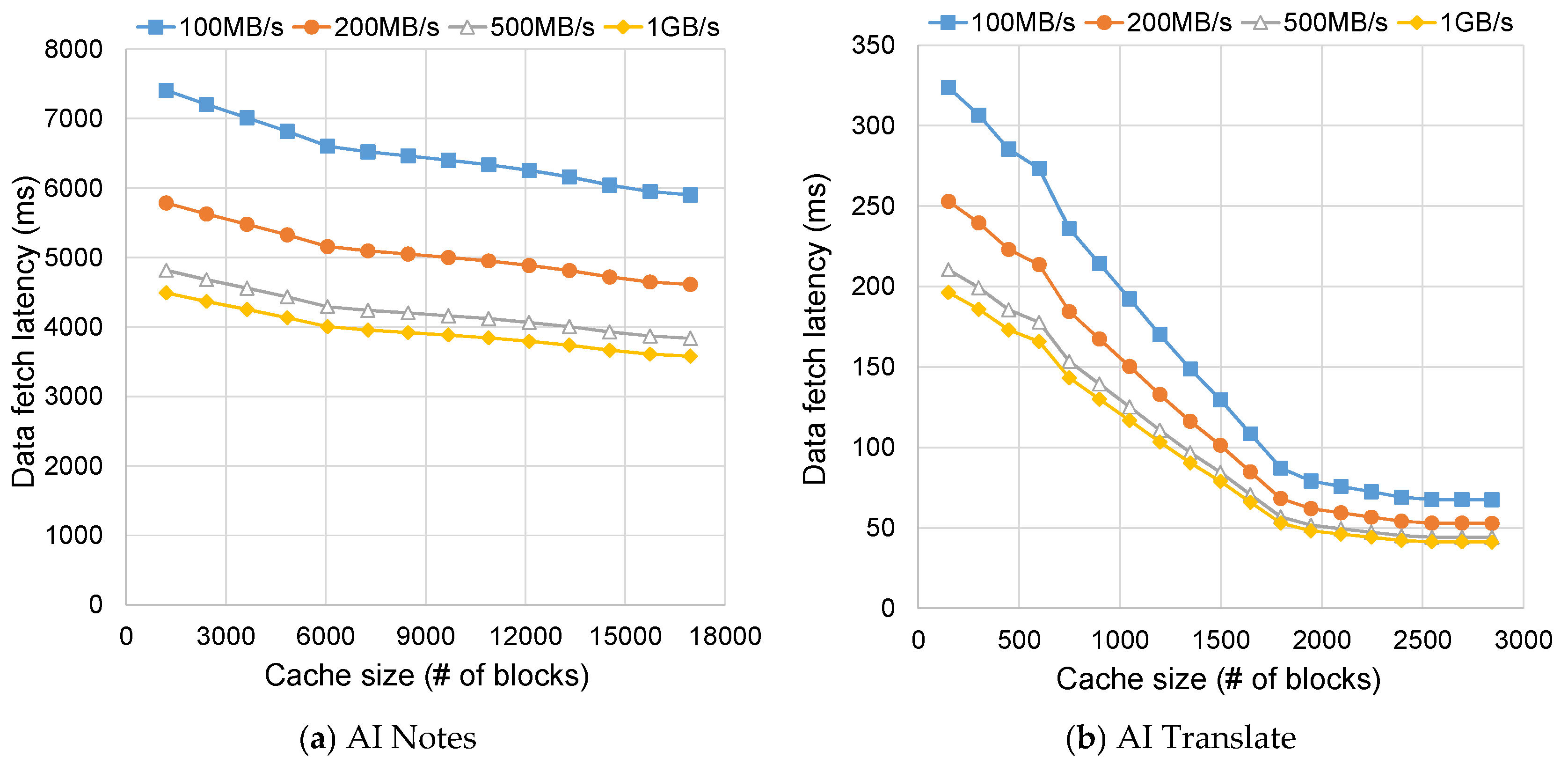
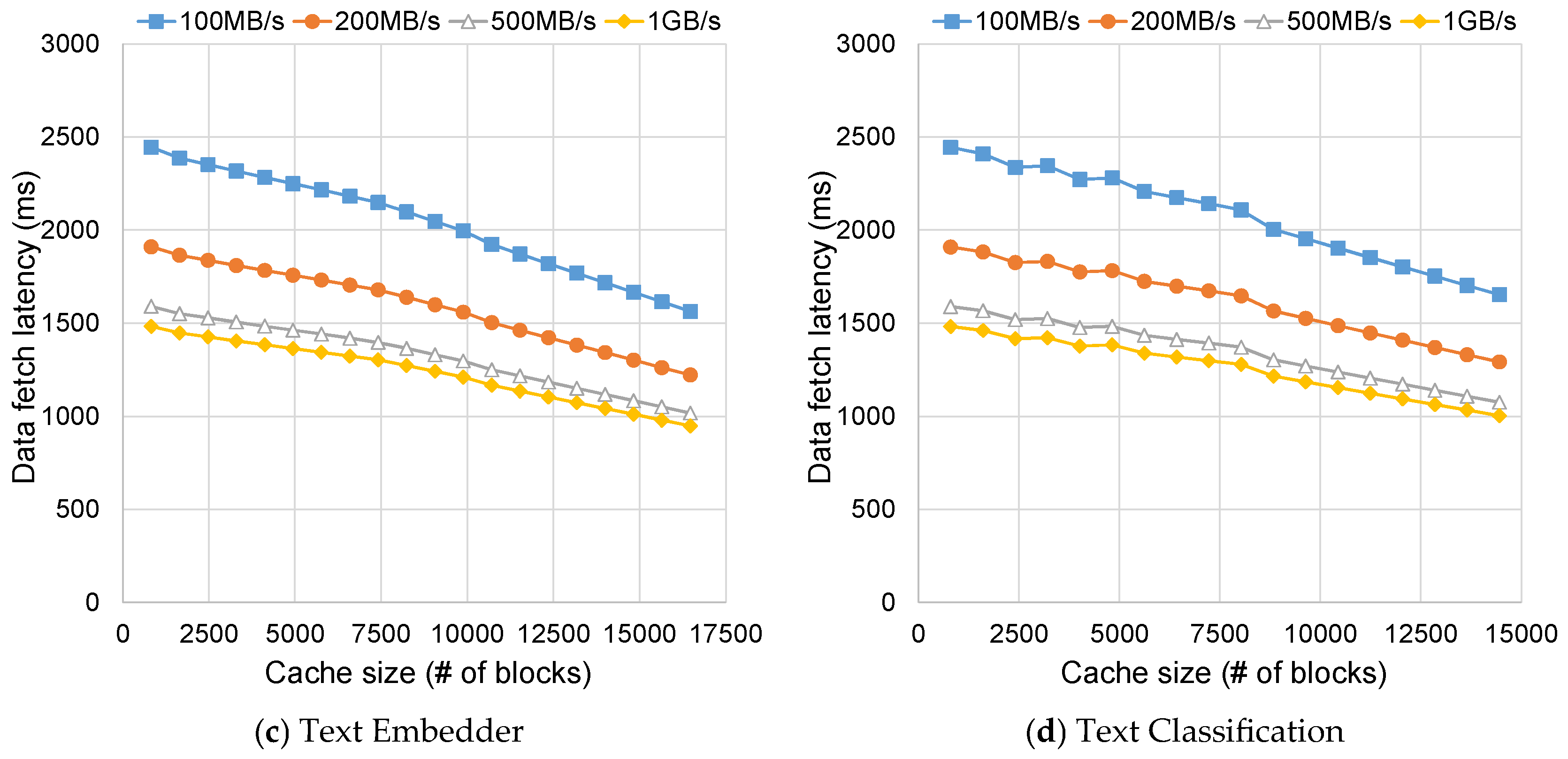
4.1. Cache Size Model
| Algorithm 1. Pseudocode of the LLM-aware cache management policy |
| Block sequence BS is consecutive blocks {B, B + 1, …}; Each BS belongs to one of SEQ, LOOP, or HOT; BS(B) returns BS that contains block B (if any); procedure Access(B) if previous access is B − 1 then add B to BS(B − 1); if BS(B) ∈ HOT then remove BS(B) from HOT; insert BS(B) into SEQ; end if else if BS(B) ∈ SEQ or LOOP then BS’ ← {B}; insert BS’ into LOOP; else if BS(B) is undefined then // B accessed first BS’ ← {B}; insert BS’ into HOT; end if end if end procedure procedure Evict( ) if SEQ is not empty then evict highest-numbered block from oldest BS in SEQ; else if HOT is full then evict the least-recently-used block from HOT; else // LOOP is full evict highest-numbered block from longest-period BS; end if end procedure |
4.2. Discussion on Hardware Specifications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Du, Y.; Xiang, S.; Yue, Z.; Zhang, N.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, Z. Understanding the Potential of FPGA-based Spatial Acceleration for Large Language Model Inference. ACM Trans. Reconfigurable Technol. Syst. 2024, 18, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Oliaro, G.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, X.; Jin, H.; Chen, T.; Jia, Z. Towards Efficient Generative Large Language Model Serving: A Survey from Algorithms to Systems. ACM Comput. Surv. 2025, 58, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Feng, D.; Feng, E.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Xia, Y.; Xu, P.; Chen, H. Characterizing Mobile SoC for Accelerating Heterogeneous LLM Inference. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGOPS 31st Symposium on Operating Systems Principles, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 13–16 October 2025; pp. 359–374. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, S.; Bahn, H. Memory Reference Analysis and Implications for Executing AI Workloads in Mobile Systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Electrical and Information Technology, Malang, Indonesia, 14–15 September 2023; pp. 281–285. [Google Scholar]
- Apple A17 Pro 3nm iPhone 15 Pro. Available online: https://www.tomshardware.com/news/apple-a17-pro-3nm-iphone-15-pro (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Qualcomm. Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 Mobile Platform Product Brief. Available online: https://docs.qualcomm.com/bundle/publicresource/87-71408-1_REV_C_Snapdragon_8_gen_3_Mobile_Platform_Product_Brief.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Samsung Revamped NPU Architecture in Exynos 2400 for AI Boost. Available online: https://www.androidheadlines.com/2023/10/samsung-revamped-npu-architecture-in-exynos-2400-for-ai-boost.html (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Apple Machine Learning Research. Core ML On-Device Llama. Available online: https://machinelearning.apple.com/research/core-ml-on-device-llama (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- PyTorch. ExecuteTorch Llama Demo for Android. Available online: https://docs.pytorch.org/executorch/0.7/llm/llama-demo-android.html (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Das, B.; Amini, M.; Wu, Y. Security and Privacy Challenges of Large Language Models: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2025, 57, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Qian, X.; Xing, S.; Jiang, X.; Lv, C.; Zhang, S. MNN-LLM: A Generic Inference Engine for Fast Large Language Model Deployment on Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the 6th ACM International Conference on Multimedia in Asia Workshops, Auckland, New Zealand, 3–6 December 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, G.; Bahn, H. Quantifying the Effectiveness of Cloud and Edge Offloading: An Optimization Study on Energy Efficiency of Mobile Real-Time Systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication, Fukuoka, Japan, 18–21 February 2025; pp. 427–432. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Lim, S.; Bahn, H. Analyzing Data Access Characteristics of AIoT Workloads for Efficient Write Buffer Management. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 31601–31614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Bahn, H. WANE: Workload Adaptive Neuro-Genetic Engine for Container Usage Prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advances in Electrical Engineering and Computer Applications, Dalian, China, 16–18 August 2024; pp. 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Yuan, J.; Jin, H.; Zhong, S.; Xu, Z.; Braverman, V.; Chen, B.; Hu, X. KIVI: A Tuning-Free Asymmetric 2bit Quantization for KV Cache. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.02750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Han, J.; Wei, X.; Shen, S.; Zhang, D.; Fang, C.; Chen, R.; Yu, W.; Chen, H. KVCache Cache in the Wild: Characterizing and Optimizing KVCache Cache at a Large Cloud Provider. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.02634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, W.; Li, Z.; Zhuang, S.; Sheng, Y.; Zheng, L.; Yu, C.; Gonzalez, J.; Zhang, H.; Stoica, I. Efficient Memory Management for Large Language Model Serving with PagedAttention. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM Symposium on Operating Systems Principles (SOSP), Koblenz, Germany, 23–26 October 2023; pp. 611–626. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Huang, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Hu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, H.; Chen, X.; Shan, Y.; Xie, T. EPIC: Efficient Position-Independent Caching for Serving Large Language Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.15332. [Google Scholar]
- Gim, I.; Chen, G.; Lee, S.; Sarda, N.; Khandelwal, A.; Zhong, L. Prompt Cache: Modular Attention Reuse for Low-Latency Inference. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning and Systems (MLSys), Santa Clara, CA, USA, 13–16 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Ray, S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Du, K.; Lu, S.; Jiang, J. CacheBlend: Fast Large Language Model Serving for RAG with Cached Knowledge Fusion. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM European Conference on Computer Systems (EuroSys), Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 30 March–3 April 2025; pp. 94–109. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, C.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Liu, F.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Jin, X. RAGCache: Efficient Knowledge Caching for Retrieval-Augmented Generation. ACM Trans. Comput. Syst. 2025, 44, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Lin, B.; Hou, T.; Zhang, H.; Deng, Z. In-Context KV-Cache Eviction for LLMs via Attention-Gate. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.12876. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Jones, D.; Morse, M.; Goel, R.; Lee, M.; Lott, C. KeyDiff: Key Similarity-Based KV Cache Eviction for Long-Context LLM Inference in Resource-Constrained Environments. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.15364. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Huang, H.; Hu, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, X.; Xie, T.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Bao, Y.; Sun, N.; et al. MemServe: Context Caching for Disaggregated LLM Serving with Elastic Memory Pool. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.17565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Falahati, A.; Yang, D.; Amiri, M. SentenceKV: Efficient LLM Inference via Sentence-Level Semantic KV Caching. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.00970,. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Chang, L.; Bao, W.; Zheng, S.; Zheng, N. ShadowKV: KV Cache in Shadows for High-Throughput Long-Context LLM Inference. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.21465. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Kwon, S.; Lee, J.; Yun, S.; Song, H. KVzip: Query-Agnostic KV Cache Compression with Context Reconstruction. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.23416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Yuan, A.; Wang, Z.; Yi, B.; Liu, X.; Cui, Y.; Yang, T. KeepKV: Eliminating Output Perturbation in KV Cache Compression for Efficient LLMs Inference. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.09936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Lv, J.; Cao, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhou, S. Identify Critical KV Cache in LLM Inference from an Output Perturbation Perspective. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.03805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaillet, P.; Jiang, J.; Mellou, K.; Molinaro, M.; Podimata, C.; Zhou, Z. Online Scheduling for LLM Inference with KV Cache Constraints. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.07115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, F. GPTCache: An Open-Source Semantic Cache for LLM Applications Enabling Faster Answers and Cost Savings. In Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop for Natural Language Processing Open Source Software (NLP-OSS), Singapore, 6 December 2023; pp. 212–218. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, W.; Elidrisi, M.; Kalapatapu, P.; Ahmed, A.; Anwar, A.; Gulzar, M.A. MeanCache: User-Centric Semantic Caching for LLM Web Services. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium (IPDPS), Milano, Italy, 3–7 June 2025; pp. 1298–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, F.; Riedemann, I.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J. SCALM: Towards Semantic Caching for Automated Chat Services with Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM 32nd International Symposium on Quality of Service (IWQoS), Guangzhou, China, 19–21 June 2024; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Ni, W.; Chen, L.; Lin, X.; Cheng, P.; Qin, Z.; Ren, K. ContextCache: Context-Aware Semantic Cache for Multi-Turn Queries in Large Language Models. Proc. VLDB Endow. 2025, 18, 5391–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, W.; Cechmanek, J.; Hutcherson, T.; Rajamohan, S.; Agarwal, J.; Gulzar, M.; Singh, M.; Dion, B. Advancing Semantic Caching for LLMs with Domain-Specific Embeddings and Synthetic Data. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.02268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Atalar, B.; Dai, X.; Zuo, J.; Wang, S.; Lui, J.; Chen, W.; Joe-Wong, C. Semantic Caching for Low-Cost LLM Serving: From Offline Learning to Online Adaptation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2508.07675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haqiq, K.; Jahan, M.; Farimani, S.; Masoom, S. MinCache: A Hybrid Cache System for Efficient Chatbots with Hierarchical Embedding Matching and LLM. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2025, 170, 107822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, A.; Kundu, A.; Kompella, R.; Mamidi, S. A Generative Caching System for Large Language Models. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.17603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsung Mobile Press. Galaxy S22. Available online: https://www.samsungmobilepress.com/media-assets/galaxy-s22 (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Samsung Galaxy AI. Available online: https://www.samsung.com/us/galaxy-ai (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Google Mediapipe Samples. Available online: https://github.com/google-ai-edge/mediapipe-samples (accessed on 8 November 2025).
- Apple S9 Technical Specifications. Available online: https://support.apple.com/en-us/111833 (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Samsung Exynos W1000 Wearable Processor. Available online: https://semiconductor.samsung.com/processor/wearable-processor/exynos-w1000/ (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Qualcomm Snapdragon W5+ Gen 1 Wearable Platform. Available online: https://www.qualcomm.com/products/mobile/snapdragon/wearables/snapdragon-w5-plus-gen-1-wearable-platform (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Lee, J.; Lim, S.; Bahn, H. Analyzing File Access Characteristics for Deep Learning Workloads on Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE International Conference on Advances in Electrical Engineering and Computer Applications, Dalian, China, 16–18 August 2024; pp. 417–422. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Choi, J.; Kim, J.; Noh, S.H.; Min, S.; Cho, Y.; Kim, C. A Low-Overhead High-Performance Unified Buffer Management Scheme That Exploits Sequential and Looping References. In Proceedings of the 4th USENIX Conference on Operating System Design & Implementation (OSDI), San Diego, CA, USA, 22–25 October 2000; pp. 119–134. [Google Scholar]
- Vietri, G.; Rodriguez, L.; Martinez, W.; Lyons, S.; Liu, J.; Rangaswami, R.; Zhao, M.; Narasimhan, G. Driving Cache Replacement with ML-based LeCaR. In Proceedings of the 10th USENIX Workshop on Hot Topics in Storage and File Systems (HotStorage), Boston, MA, USA, 9–10 July 2018. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Bahn, H. Rethinking I/O Caching for Large Language Model Inference on Resource-Constrained Mobile Platforms. Mathematics 2025, 13, 3689. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13223689
Kim H, Lee J, Bahn H. Rethinking I/O Caching for Large Language Model Inference on Resource-Constrained Mobile Platforms. Mathematics. 2025; 13(22):3689. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13223689
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Heejin, Jeongha Lee, and Hyokyung Bahn. 2025. "Rethinking I/O Caching for Large Language Model Inference on Resource-Constrained Mobile Platforms" Mathematics 13, no. 22: 3689. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13223689
APA StyleKim, H., Lee, J., & Bahn, H. (2025). Rethinking I/O Caching for Large Language Model Inference on Resource-Constrained Mobile Platforms. Mathematics, 13(22), 3689. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13223689







