Advanced Mathematical Modeling of Hydrogen and Methane Production in a Two-Stage Anaerobic Co-Digestion System
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- New mathematical models of an anaerobic co-digestion process are developed and validated. To our knowledge, no such models have been published so far, considering the specific substrate utilized in the suggested digestion process.
- (2)
- The model’s parameters are identified based on the deterministic active-set algorithm and metaheuristic algorithms–GA, COA, and MPA.
- (3)
- This work marks the first application of the MPA for model parameter identification of a two-stage anaerobic co-digestion system.
- (4)
- The developed mathematical models, once validated, offer a powerful tool for in-depth process analysis and optimization.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Study
2.2. Mathematical Model of the Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion Process
2.3. Active-Set Algorithm
2.4. Genetic Algorithm
2.5. Coyote Optimization Algorithm
- For each pack:
- (1)
- Find the alpha-coyote (best solution)
- (2)
- Find the social tendency of the pack cult.
- (3)
- For each coyote, update the possible new candidate’s social value as:
- Pack dynamics involve births and deaths.
- ✓
- A newborn pup’s characteristics (soc) are determined by its parents.
- ✓
- The pup survives if the pack contains at least one coyote with lower fitness (worse adaptation); in such cases, the least fit coyote dies.
- ✓
- If multiple coyotes have lower fitness, the oldest among them dies to make space for the pup.
- ✓
- Otherwise, the pup does not survive.
- Migration between packs.
- The age of the coyotes is updated.
2.6. Marine Predators Algorithm
- Phase 1. High Velocity Ratio (Prey Faster than Predator)
- Phase 2. Unit Velocity Ratio (Predator and Prey Similar Speed)
- first half of the population
- second half of the population
- Phase 3. Low Velocity Ratio (Predator Faster than Prey)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Studies
3.2. Mathematical Modeling
3.2.1. Setup of Numerical Experiments
| GA parameters | |
| population size n | 100 |
| generation gap | 0.97 |
| crossover rate | 0.85 |
| mutation rate | 0.1 |
| COA parameters | |
| number of packs Np | 50 |
| number of coyotes Nc | 100 |
| probability of eviction of a coyote leave. | 0.0005 × Nc2 |
| scatter probability Ps | 1/D |
| association probability Pa | (1 − Ps)/2 |
| MPA parameters | |
| number of predators | 100 |
| P | 0.5 |
| FADs | 0.1 |
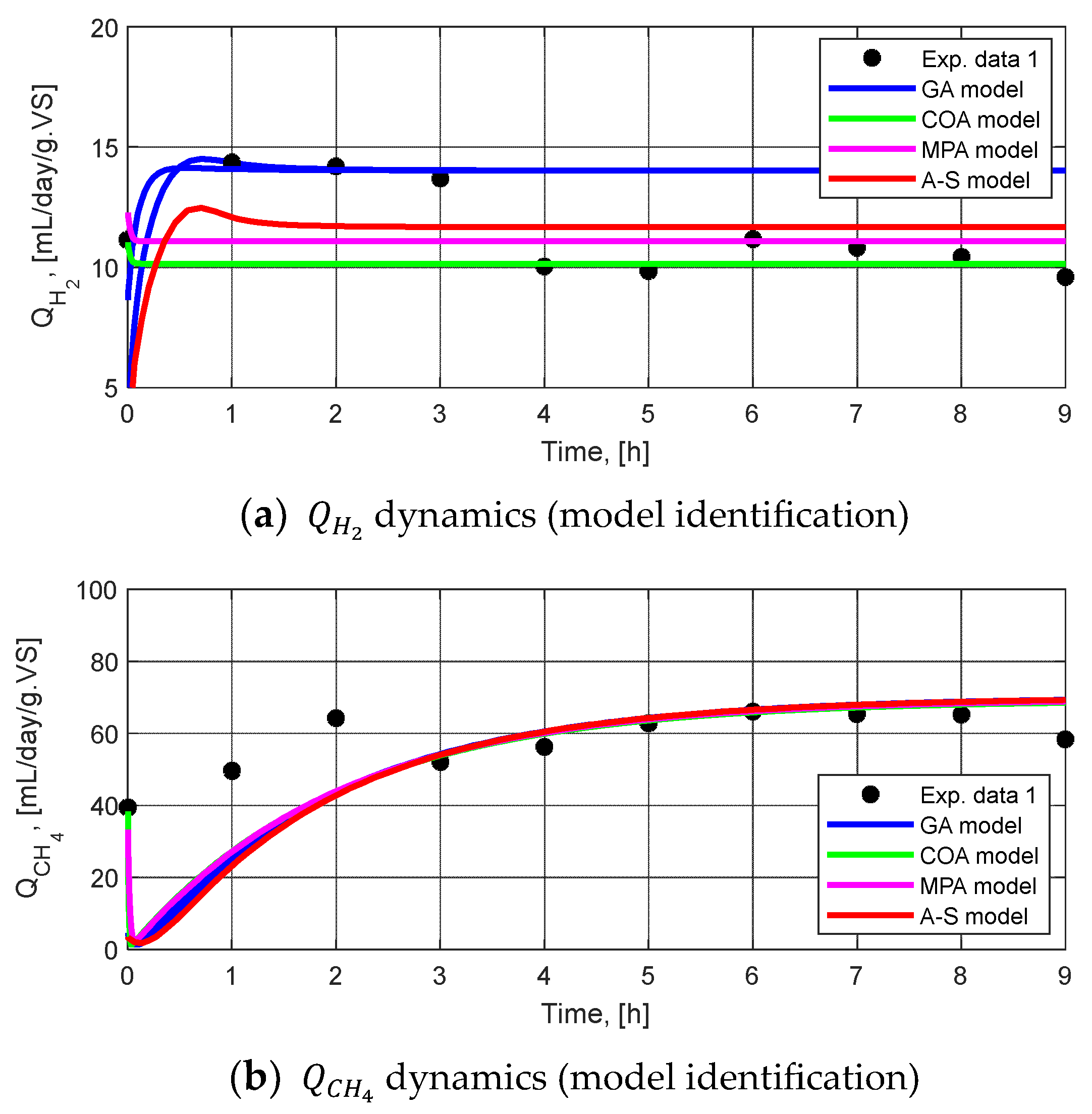
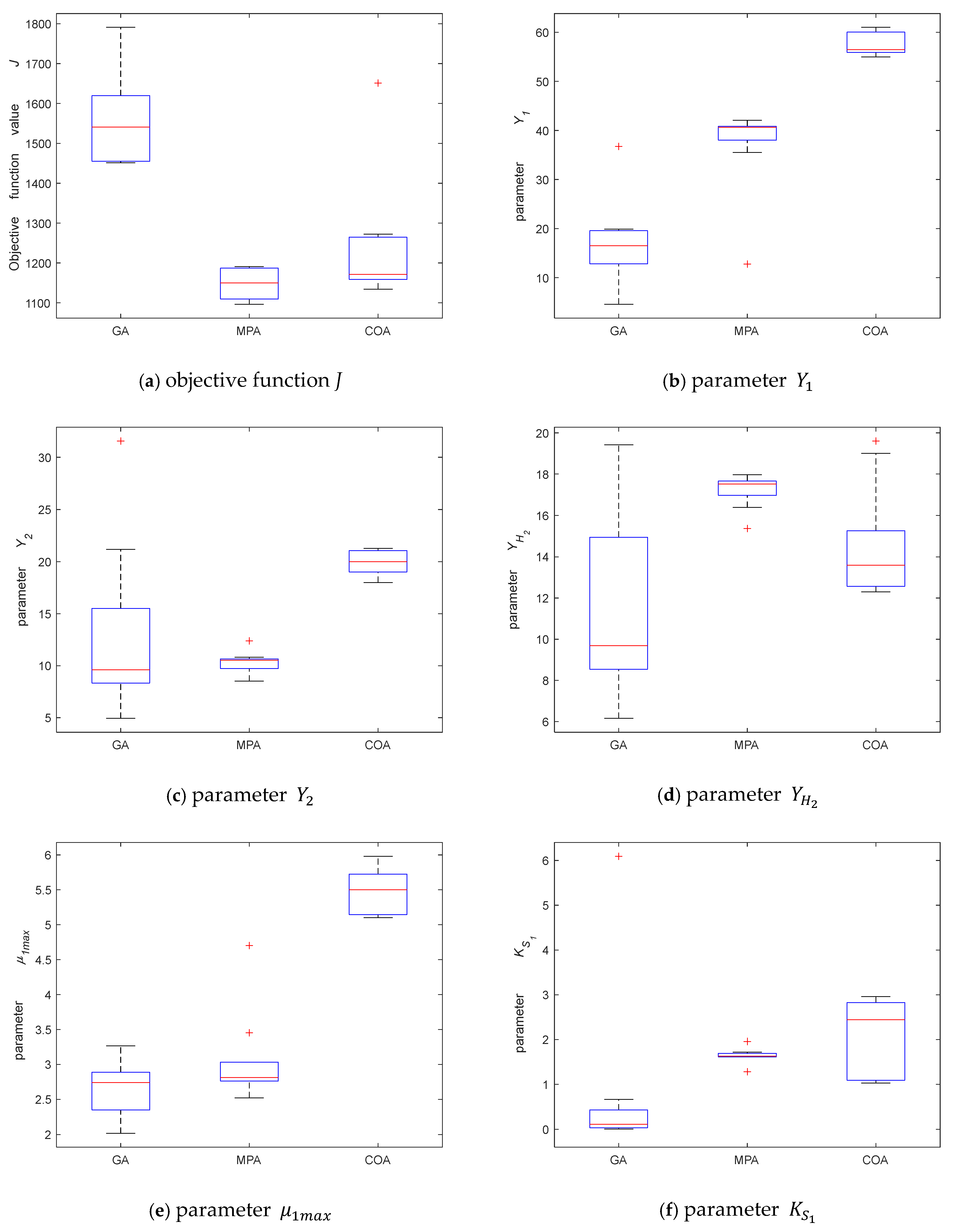
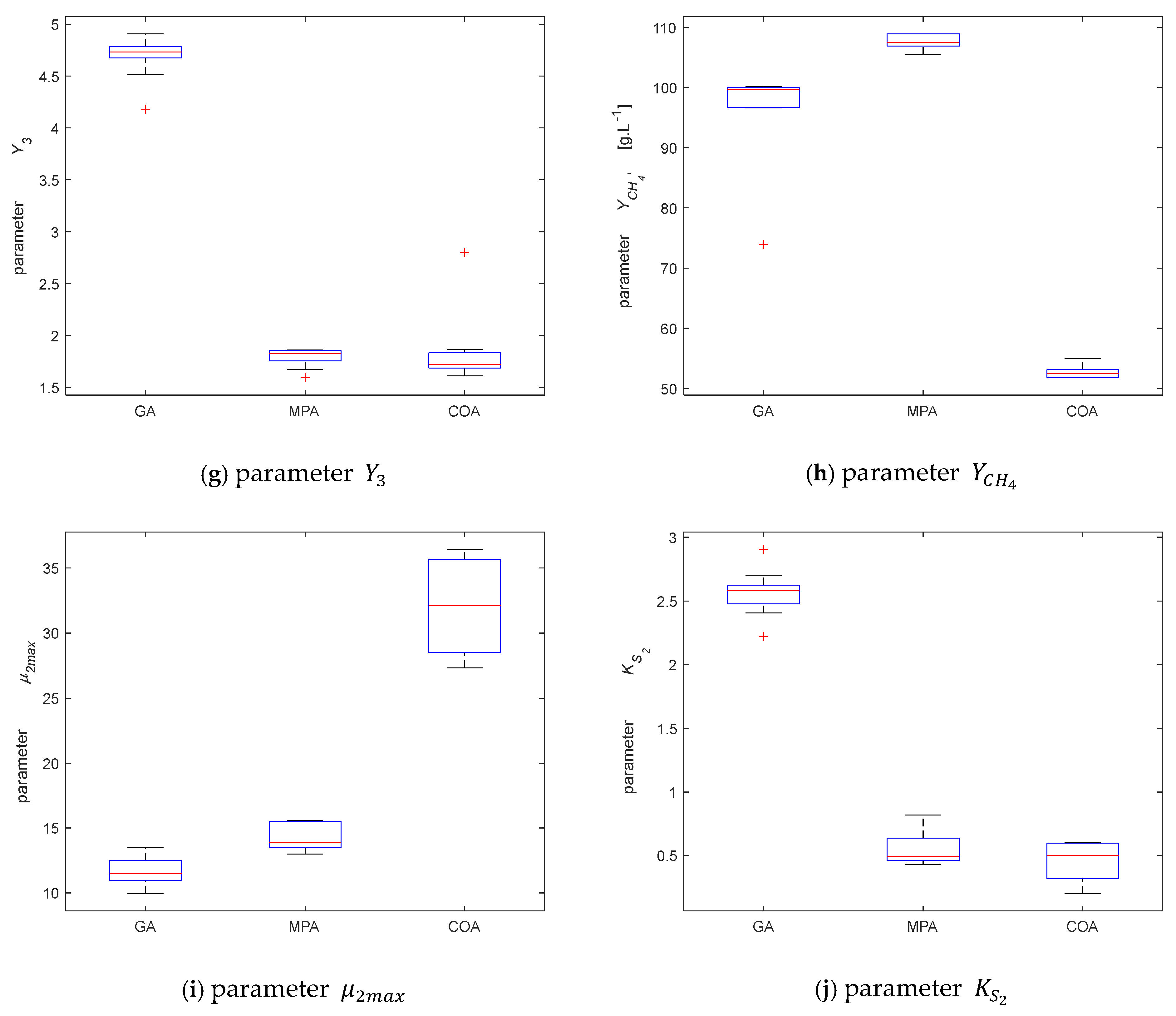
3.2.2. Parameter Identification
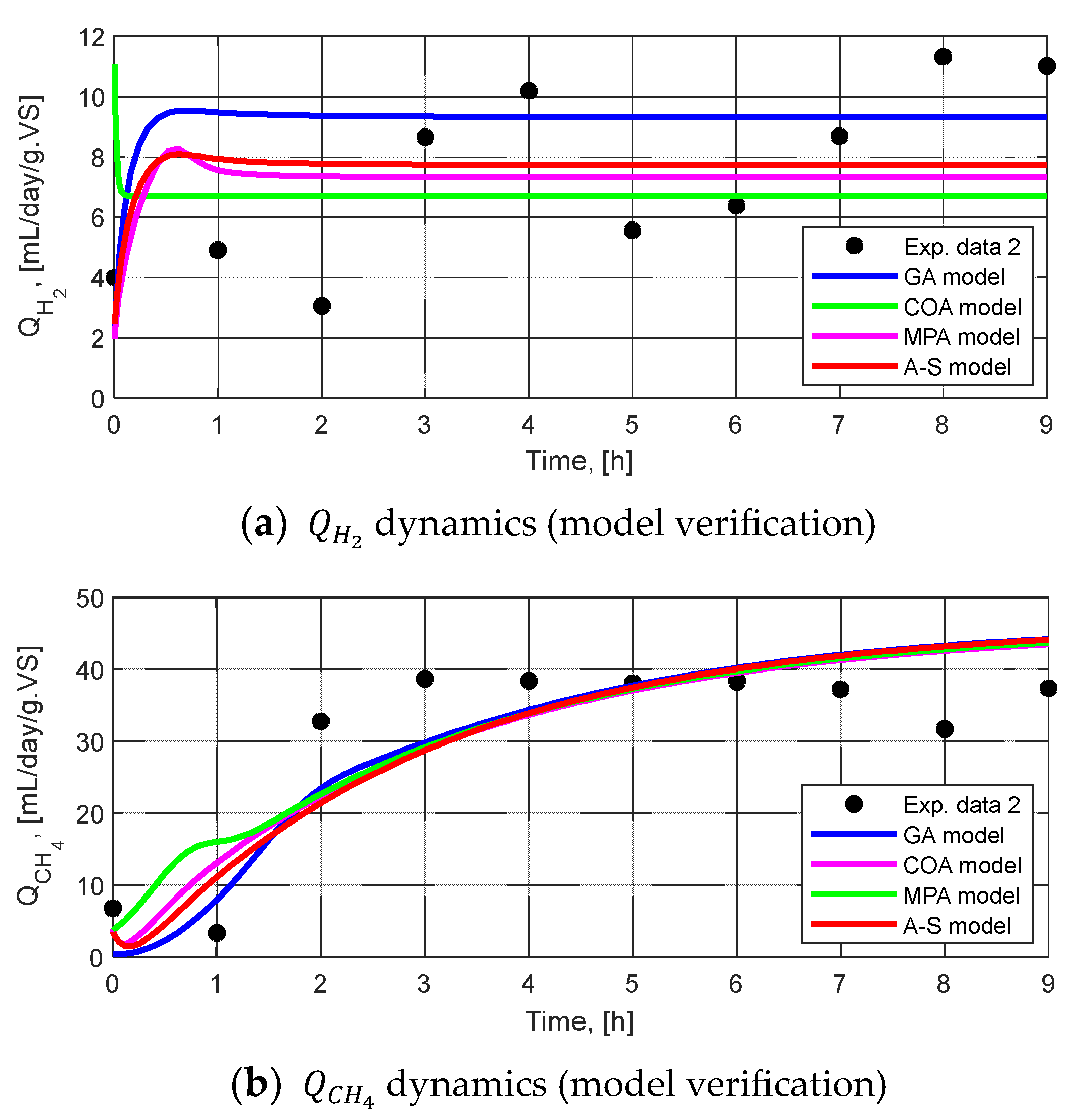
3.2.3. Model Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Srisowmeya, G.; Chakravarthy, M.; Nandhini Devi, G. Critical considerations in two-stage anaerobic digestion of food waste—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 119, 109587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, A.; Bernardi, B.; Zimbalatti, G.; Benalia, S. An Overview of Anaerobic Digestion of Agricultural By-Products and Food Waste for Biomethane Production. Energies 2023, 16, 6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerabadhran, M.; Gnanasekaran, D.; Wei, J.; Yang, F. Anaerobic digestion of microalgal biomass for bioenergy production, removal of nutrients and microcystin: Current status. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Mahar, R.B.; Panhwar, S.; Keerio, H.A.; Khokhar, N.H.; Suja, F.; Rundong, L. Generation of green renewable energy through anaerobic digestion technology (ADT): Technical insights review. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 14, 663–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.; Rathore, S.S.; Singh, R.; Kumar, S.; Singh, V.K.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, V.; Raj, R.; Yadav, D.; Shekhawat, K.; et al. Exploring agricultural waste biomass for energy, food and feed production and pollution mitigation: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajji, M.; Mazenc, F.; Harmand, J. A mathematical study of a syntrophic relationship of a model of anaerobic digestion process. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2010, 7, 641–656. [Google Scholar]
- Abilmazhinov, Y.; Shakerkhan, K.; Meshechkin, V.; Shayakhmetov, Y.; Nurgaliyev, N.; Suychinov, A. Mathematical Modeling for Evaluating the Sustainability of Biogas Generation through Anaerobic Digestion of Livestock Waste. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaki, M.; Harmand, J.; Mghazli, Z.; Rapaport, A.; Sari, T.; Ugalde, P. Mathematical Study of a Two-Stage Anaerobic Model When the Hydrolysis Is the Limiting Step. Processes 2021, 9, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeva, O.; Chorukova, E. Metaheuristic algorithms to optimal parameters estimation of a model of two-stage anaerobic digestion of corn steep liquor. Appl. Sci. 2022, 13, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocedal, J.; Wright, S.J. Numerical Optimization; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, R.E. Optimization: Foundations and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Spettel, P.; Ba, Z.; Arnold, D.V. Active Sets for Explicitly Constrained Evolutionary Optimization. Evol. Comput. 2022, 30, 531–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, F.; Castelli, M. Combinatorial Optimization Problems and Metaheuristics: Review, Challenges, Design, and Development. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, L.; Guerrero, H.; Hospitaler, A. A literature review and critical analysis of metaheuristics recently developed. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2024, 31, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, A.; Verma, N.K.; Aziz, R.M. Metaheuristic algorithms and their applications in different fields: A comprehensive review. In Metaheuristics for Machine Learning: Algorithms and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Zhang, T.; Tsai, C.Y.; Yao, L.; Lu, Y.; Tang, J. Review of the metaheuristic algorithms in applications: Visual analysis based on bibliometrics (1994–2023). Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 255, 124857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, L.; Li, G.; Xiao, W.; Tan, L.; Xu, D.; Guo, J. AI-based 3D pipe automation layout with enhanced ant colony optimization algorithm. Autom. Constr. 2024, 167, 105689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, L.; Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, W.; Xu, D.; Guo, J.; Li, W. Improved multi-search strategy A* algorithm to solve three-dimensional pipe routing design. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 240, 122313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, C.; Wu, L.; Xiao, W. A mixing algorithm of ACO and ABC for solving path planning of mobile robot. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 148, 110868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierezan, J.; Coelho, L.D.S. Coyote Optimization Algorithm: A New Metaheuristic for Global Optimization Problems. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faramarzi, A.; Heidarinejad, M.; Mirjalili, S.; Gandomi, A.H. Marine Predators Algorithm: A nature-inspired metaheuristic. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 152, 113377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, Y.; Hua, X.; Qi, C.; Yao, Y.X. Improved marine predators algorithm for engineering design optimization problems. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Prakash, S. Implementation of Marin predators algorithm for optimizing the position of multiple optical network units in fiber wireless access networks. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2022, 72, 102971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousri, D.; Fathy, A.; Rezk, H.; Babu, T.S.; Berber, M.R. A reliable approach for modeling the photovoltaic system under partial shading conditions using three diode model and hybrid marine predators-slime mould algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 243, 114269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, M.A.; Yousri, D.; Fathy, A.; Hasanien, H.M.; Alkuhayli, A.; Muyeen, S.M. A novel application of improved marine predators algorithm and particle swarm optimization for solving the ORPD problem. Energies 2020, 13, 5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Betar, M.A.; Awadallah, M.A.; Makhadmeh, S.N.; Alyasseri, Z.A.A.; Al-Naymat, G.; Mirjalili, S. Marine predators algorithm: A review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 3405–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugemanyi, S.; Qu, Z.; Rugema, F.X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, L.; Bananeza, C.; Nshimiyiman, A.; Mutabazi, E. Marine predators algorithm: A comprehensive review. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2023, 12, 100471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R.; Dhal, K.G.; Das, A.; Ray, S. An inclusive survey on marine predators algorithm: Variants and applications. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 3133–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Meng, Z.; Ma, H.; Liu, L. An adaptive marine predators algorithm for optimizing a hybrid PV/DG/Battery system for a remote area in China. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Saha, S.K.; Kar, R.; Mandal, D. EEG/ERP signal enhancement through an optimally tuned adaptive filter based on marine predators algorithm. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 73, 103427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.V.; Nguyen, D.H.; Mousavi, M.; De Roeck, G.; Bui-Tien, T.; Gandomi, A.H.; Wahab, M.A. A hybrid computational intelligence approach for structural damage detection using marine predator algorithm and feedforward neural networks. Comput. Struct. 2021, 252, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, J.; Si, T. Artificial neural network training using marine predators algorithm for medical data classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Intelligence, Maharashtra, India, 29–30 December 2022; Algorithms for Intelligent Systems. Tiwari, R., Mishra, A., Yadav, N., Pavone, M., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milenković, B.N.; Krstić, M.T. Marine predators’ algorithm: Application in applied mechanics. Tehnika 2021, 76, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elaziz, M.; Thanikanti, S.B.; Ibrahim, I.A.; Lu, S.; Nastasi, B.; Alotaibi, M.A.; Hossain, A.; Yousri, D. Enhanced marine predators algorithm for identifying static and dynamic photovoltaic models parameters. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 236, 113971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhafiz, S.M.; AbdelAty, A.M.; Fouda, M.E.; Radwan, A.G. Parameter identification of commercial li-ion batteries with marine predator algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Lansing, MI, USA, 9–11 August 2021; pp. 208–211. [Google Scholar]
- Neumaier, A.; Azmi, B.; Kimiaei, M. An active set method for bound-constrained optimization. Optim. Methods Softw. 2024, 39, 1216–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharon, B.-T.; Nemirovski, A. Lecture Notes Optimization III. Convex Analysis. Nonlinear Programming Theory. Nonlinear Programming Algorithms. 2023. Available online: https://www2.isye.gatech.edu/~nemirovs/OPTIIILN2023Spring.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- Alhijawi, B.; Awajan, A. Genetic algorithms: Theory, genetic operators, solutions, and applications. Evol. Intell. 2024, 17, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuptametee, C.; Michalopoulou, Z.H.; Aunsri, N. A review of efficient applications of genetic algorithms to improve particle filtering optimization problems. Measurement 2024, 224, 113952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, A.; Hajji, A.; Rekik, M.; Pellerin, R. Genetic algorithms for planning and scheduling engineer-to-order production: A systematic review. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 62, 2888–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Sun, L.; Han, Y.; Tian, H. Research on Competitive Evaluation Based on Genetic Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Signal Processing, Communications and Engineering Management Conference (ISPCEM), Montreal, QC, Canada, 28–30 November 2024; pp. 760–767. [Google Scholar]
- Diop, S.; Simeonov, I. On the Biomass Specific Growth Rates Estimation for Anaerobic Digestion using Differential Algebraic Techniques. Int. J. Bioautom. 2009, 13, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Noykova, N.; Muller, T.G.; Gyllenberg, M.; Timmer, J. Quantitative Analyses of Anaerobic Wastewater Treatment Processes: Identifiability and Parameter Estimation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2002, 78, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Menezes, L.H.S.; Carneiro, L.L.; de Carvalho Tavares, I.M.; Santos, P.H.; das Chagas, T.P.; Mendes, A.A.; da Silva, E.G.P.; Franco, M.; de Oliveira, J.R. Artificial Neural Network Hybridized with a Genetic Algorithm for Optimization of Lipase Production from Penicillium roqueforti ATCC 10110 in Solid-State Fermentation. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 101885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ma, X.; He, C.; Pan, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Awasth, M.K. Exergy analysis and optimization of bio-hydrogen and bio-methane cogeneration from corn stover based on genetic algorithm. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 18, 101113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mestari, W.; Cheggaga, N.; Adli, F.; Benallal, A.; Ilinca, A. Tuning Parameters of Genetic Algorithms for Wind Farm Optimization Using the Design of Experiments Method. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Yildizbasi, A. Developed Coyote Optimization Algorithm and Its Application to Optimal Parameters Estimation of PEMFC Model. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.S.; Abd Elazim, S.M.; Balobaid, A.S. Implementation of Coyote Optimization Algorithm for Solving Unit Commitment Problem in Power Systems. Energy 2022, 263, 125697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, G.I.; Khoriba, G.; Haggag, M.H. The novel multi-swarm coyote optimization algorithm for automatic skin lesion segmentation. Evol. Intell. 2024, 17, 679–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elminaam, D.S.; Nabil, A.; Ibraheem, S.A.; Houssein, E.H. An efficient marine predators algorithm for feature selection. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 60136–60153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Basset, M.; El-Shahat, D.; Chakrabortty, R.K.; Ryan, M. Parameter estimation of photovoltaic models using an improved marine predators algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 227, 113491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.A.; Khan, T.A.; Waqar, M.; Chaudhary, N.I.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Shu, C.M. Nonlinear Marine Predator Algorithm for Robust Identification of Fractional Hammerstein Nonlinear Model under Impulsive Noise with Application to Heat Exchanger System. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2025, 146, 108809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, G.; Houssein, E.H.; Zhong, R. Multi-strategy enhanced marine predator algorithm: Performance investigation and application in intrusion detection. J. Big Data 2025, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Bu, X.; Zhan, Z.H.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. An efficient optimization state-based coyote optimization algorithm and its applications. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 147, 110827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batstone, D.J.; Puyol, D.; Flores-Alsina, X.; Rodrigues, J. Mathematical modelling of anaerobic digestion processes: Applications and future needs. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 595–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlamine, I.; Alla, A.; Khattabi, N.E. Mathematical analysis of an anaerobic digestion model for biogas production from solid waste. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasear, S.A. Adaptive crossover-based marine predators algorithm for global optimization problems. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2024, 11, 124–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehkordi, A.A.; Etaati, B.; Neshat, M.; Mirjalili, S. Adaptive Chaotic Marine Predators Hill Climbing Algorithm for Large-Scale Design Optimizations. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 39269–39294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model Variables | |
| Dilution rates (day−1) | |
| Inlet cellulose concentration in BR1 (g/L) | |
| Substrate concentration (g/L) | |
| Biomass concentrations (g/L) | |
| Acetate concentrations (g/L) | |
| Hydrogen yield (mL/day/g VS) | |
| Methane yield (mL/day/g VS) | |
| Model Parameters | |
| Monod kinetic coefficients (day−1) | |
| Saturation coefficients (g/L) | |
| Yield coefficients (g/g) | |
| Yield coefficient for hydrogen (g/g) | |
| Yield coefficient for methane (g/g) | |
| Duration, day | Dilution Rate, day−1 | Hydrogen, mL/day/g VS. | Dilution Rate, day−1 | Methane, mL/day/g VS. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.5 | 11.14 | 0.1 | 39.45 |
| 1 | 0.5 | 14.35 | 0.1 | 49.58 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 14.20 | 0.1 | 64.25 |
| 3 | 0.5 | 13.69 | 0.1 | 52.00 |
| 4 | 0.5 | 10.04 | 0.1 | 56.23 |
| 5 | 0.5 | 9.84 | 0.1 | 62.86 |
| 6 | 0.5 | 11.17 | 0.1 | 65.99 |
| 7 | 0.5 | 10.82 | 0.1 | 65.36 |
| 8 | 0.5 | 10.43 | 0.1 | 65.14 |
| 9 | 0.5 | 9.60 | 0.1 | 58.33 |
| Duration, day | Dilution Rate, day−1 | Hydrogen, mL/day/g VS. | Dilution Rate, day−1 | Methane, mL/day/g VS. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.33 | 4.00 | 0.067 | 6.81 |
| 1 | 0.33 | 4.91 | 0.067 | 3.34 |
| 2 | 0.33 | 3.06 | 0.067 | 32.73 |
| 3 | 0.33 | 8.65 | 0.067 | 38.64 |
| 4 | 0.33 | 10.20 | 0.067 | 38.40 |
| 5 | 0.33 | 5.57 | 0.067 | 38.08 |
| 6 | 0.33 | 6.38 | 0.067 | 38.32 |
| 7 | 0.33 | 8.69 | 0.067 | 37.25 |
| 8 | 0.33 | 11.33 | 0.067 | 31.69 |
| 9 | 0.33 | 11.00 | 0.067 | 37.40 |
| Algorithm | Model Parameters | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-S | 3.00 | 3.55 | 14.16 | 5.52 | 6.70 | 5.03 | 1.59 | 3.02 | 110.00 |
| GA | 2.81 | 4.56 | 19.92 | 13.50 | 11.41 | 11.89 | 2.59 | 4.73 | 99.66 |
| COA | 5.10 | 2.95 | 36.66 | 18.14 | 14.95 | 35.56 | 0.47 | 1.86 | 52.43 |
| MPA | 2.89 | 1.61 | 40.06 | 9.70 | 17.88 | 15.57 | 0.50 | 1.88 | 108.92 |
| Algorithm | Objective Function | Value | Rank | Total Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-S | 103.13 | 4 | 16 | |
| 2614.09 | 4 | |||
| 2717.22 | 4 | |||
| GA | 90.87 | 3 | 9 | |
| 2360.93 | 3 | |||
| 1451.80 | 3 | |||
| COA | 33.76 | 1 | 5 | |
| 1100.44 | 2 | |||
| 1134.20 | 2 | |||
| MPA | 48.83 | 2 | 4 | |
| 1050.10 | 1 | |||
| 1098.93 | 1 |
| Algorithm | Objective Function | Value | Rank | Total Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-S | 71.56 | 1 | 8 | |
| 519.85 | 4 | |||
| 591.41 | 3 | |||
| GA | 96.11 | 3 | 6 | |
| 449.39 | 2 | |||
| 545.50 | 1 | |||
| COA | 137.57 | 4 | 11 | |
| 486.71 | 3 | |||
| 624.28 | 4 | |||
| MPA | 83.42 | 2 | 5 | |
| 499.25 | 1 | |||
| 582.67 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roeva, O.; Chorukova, E.; Kabaivanova, L. Advanced Mathematical Modeling of Hydrogen and Methane Production in a Two-Stage Anaerobic Co-Digestion System. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13101601
Roeva O, Chorukova E, Kabaivanova L. Advanced Mathematical Modeling of Hydrogen and Methane Production in a Two-Stage Anaerobic Co-Digestion System. Mathematics. 2025; 13(10):1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13101601
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoeva, Olympia, Elena Chorukova, and Lyudmila Kabaivanova. 2025. "Advanced Mathematical Modeling of Hydrogen and Methane Production in a Two-Stage Anaerobic Co-Digestion System" Mathematics 13, no. 10: 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13101601
APA StyleRoeva, O., Chorukova, E., & Kabaivanova, L. (2025). Advanced Mathematical Modeling of Hydrogen and Methane Production in a Two-Stage Anaerobic Co-Digestion System. Mathematics, 13(10), 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13101601







