Siamese-Derived Attention Dense Network for Seismic Impedance Inversion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Theory
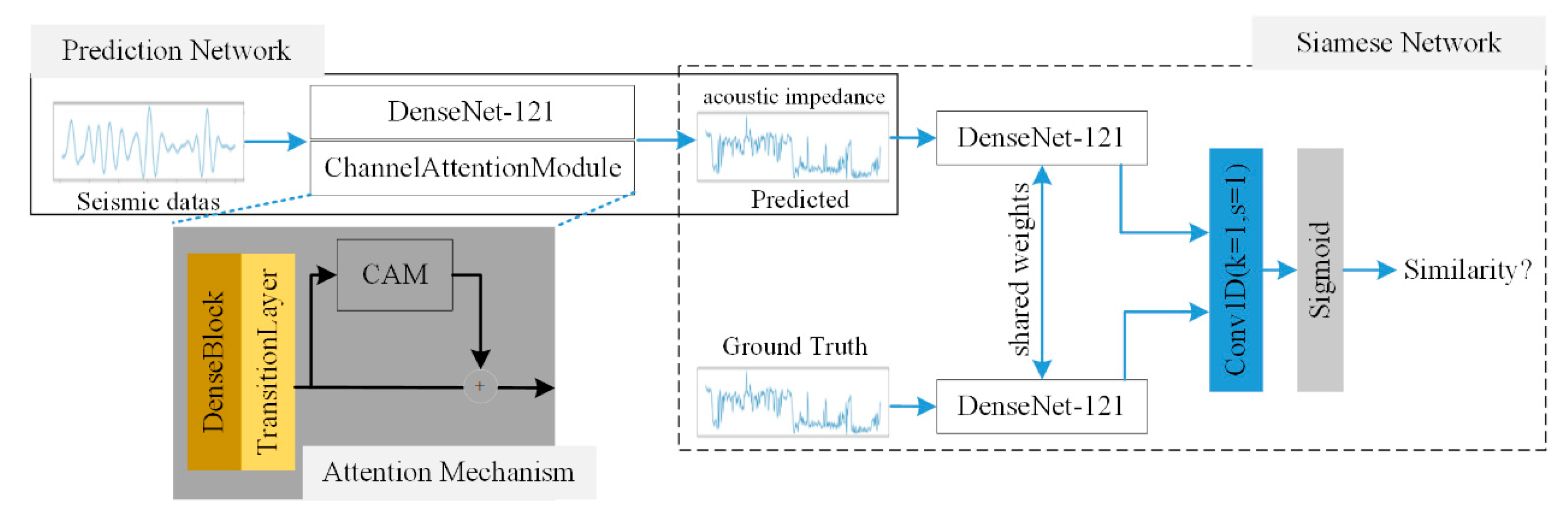
2.2. Network
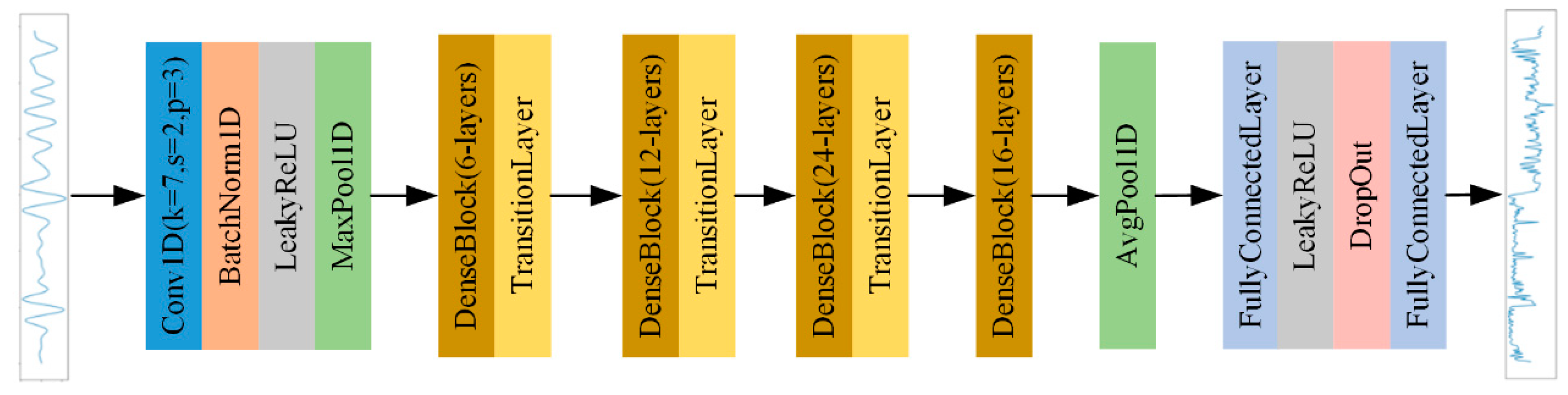
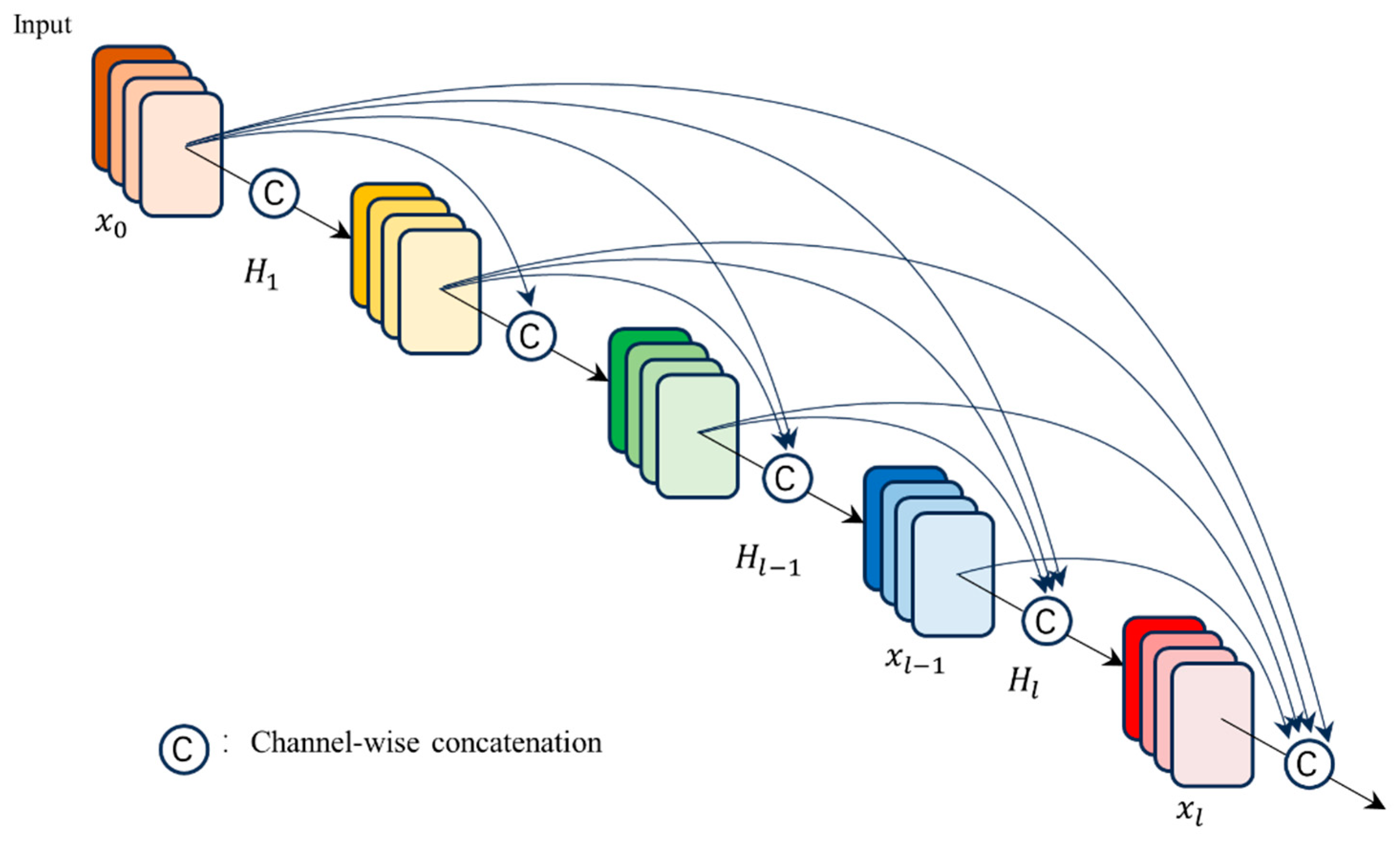
2.2.1. Backbone of the Prediction Network
2.2.2. Attention Block
2.2.3. Revised Siamese Network
2.2.4. Loss Function
2.3. Evaluation Metrics
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. Datasets
3.2. Network Training
3.3. Comparative Experiment
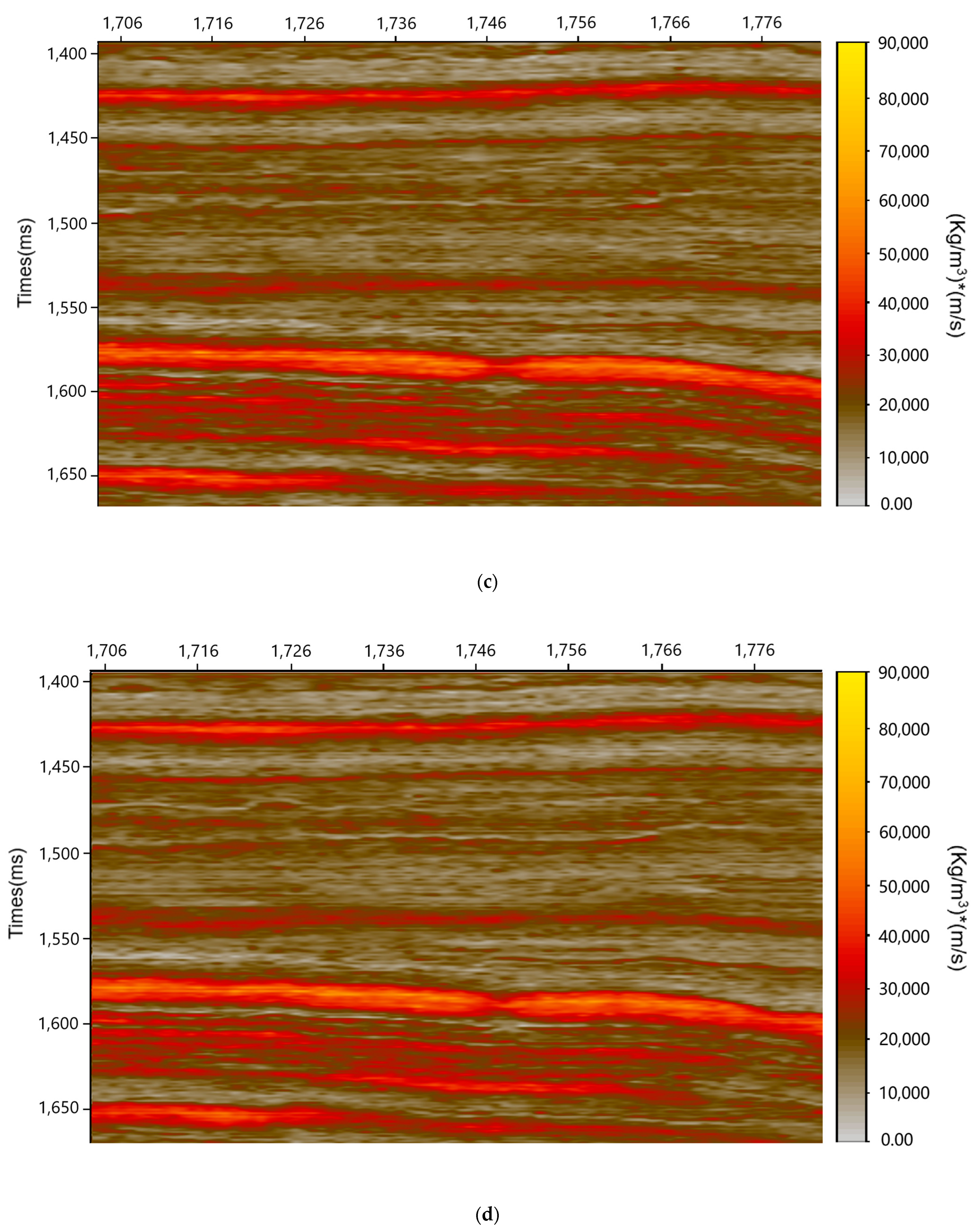
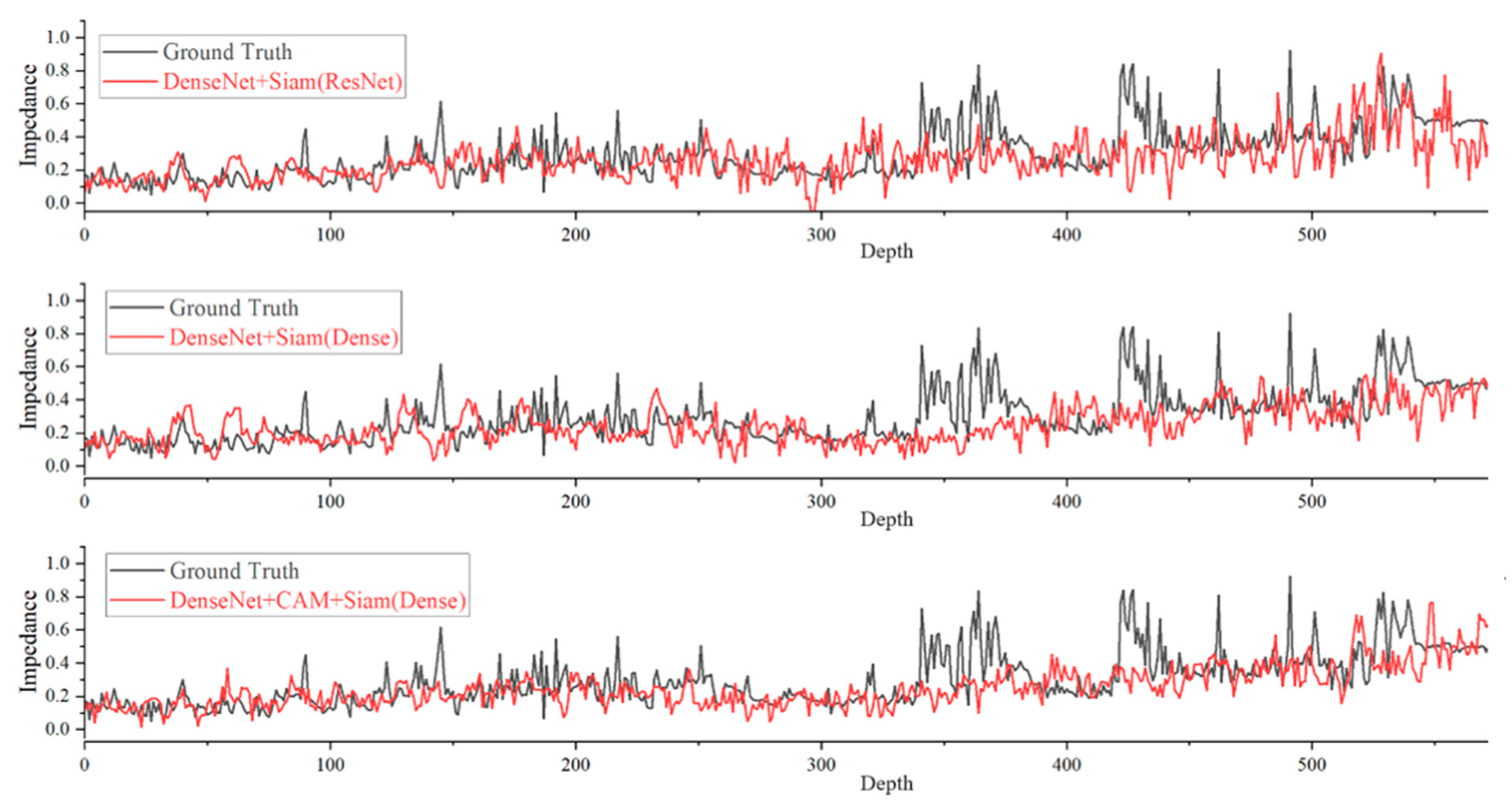
3.4. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ray, A.K.; Chopra, S. Building more robust low-frequency models for seismic impedance inversion. First Break 2016, 34, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ao, Y.; Lu, W. Seismic inversion based on 2D-CNNs and domain adaption. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5921512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Tang, G.; Wang, S.; Lin, K.; Peng, R. Deep learning for irregularly and regularly missing 3-D data reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 6244–6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomel, S. Seismic reflection data interpolation with differential offset and shot continuation. Geophysics 2003, 68, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghizadeh, M.; Sacchi, M.D. f-x adaptive seismic-trace interpolation. Geophysics 2009, 74, V9–V16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Fu, L.; Liu, S.; Li, H. Dealiased seismic data interpolation using a deep-learning-based prediction-error filter. Geophysics 2021, 86, V317–V328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Plonka, G.; Chauris, H. A new sparse representation of seismic data using adaptive easy-path wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 7, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghizadeh, M.; Sacchi, M.D. Beyond alias hierarchical scale curvelet interpolation of regularly and irregularly sampled seismic data. Geophysics 2010, 75, WB189–WB202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J. Three-dimensional irregular seismic data reconstruction via low-rank matrix completion. Geophysics 2013, 78, V181–V192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghizadeh, M.; Sacchi, M. Multidimensional de-aliased Cadzow reconstruction of seismic records. Geophysics 2013, 78, A1–A5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, D. Seismic data reconstruction via wavelet-based residual deep learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4508213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, N.; Lu, W.; Wang, J. Deep-learning-based seismic data interpolation: A preliminary result. Geophysics 2019, 84, V11–V20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, B.; Lin, T.; Cao, D.; Lou, Y. Semiautomated seismic horizon interpretation using the encoder-decoder convolutional neural network. Geophysics 2019, 84, B403–B417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zhang, B.; Lyu, B.; Marfurt, K. Seismic attribute selection for machine-learning-based facies analysis. Geophysics 2020, 85, O17–O35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gao, J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, P. Seismic acoustic impedance inversion via optimization-inspired semisupervised deep learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5906611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Shi, Y.; Fomel, S.; Liang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yusifov, A.Z. FaultNet3D: Predicting fault probabilities, strikes, and dips with a single convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 9138–9155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; He, T.; Tian, Y.; Wu, B.; Gao, J.; Xu, Z. Common-azimuth seismic data fault analysis using residual UNet. Interpretation 2020, 8, SM25–SM37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xue, H. Seismic facies analysis based on deep learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 17, 1119–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X. ADDCNN: An attention-based deep dilated convolutional neural network for seismic facies analysis with interpretable spatial–spectral maps. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 1733–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Li, H.; Liu, N.; Gao, J.; Li, Z. Automatic lithology identification by applying LSTM to logging data: A case study in X tight rock reservoirs. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 18, 1361–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Huang, T.; Gao, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, F. Quantum-enhanced deep learning-based lithology interpretation from well logs. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 4503213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.; Araya-Polo, M.; Poggio, T. Deep learning for seismic inverse problems: Toward the acceleration of geophysical analysis workflows. IEEE Signal Proc. Mag. 2021, 38, 89–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Fu, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z. Seismic data interpolation based on U-net with texture loss. Geophysics 2021, 86, V41–V54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.; Yeeh, Z.; Byun, J. Seismic data reconstruction using deep bidirectional long short-term memory with skip connections. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 18, 1298–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Li, X.; Song, M. Reconstruction of irregular missing seismic data using conditional generative adversarial networks. Geophysics 2021, 86, V471–V488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.B.; Si, H.J.; Wu, X.M.; Yan, S.S. A comparison of deep learning methods for seismic impedance inversion. Petrol. Sci. 2022, 19, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liao, S.; Pan, S.; Hu, G. DTAE: Deep tensor autoencoder for 3-D seismic data interpolation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 4503213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, V.; Pollack, A.; Wollner, U.; Mukerji, T. Convolutional neural network for seismic impedance inversion. Geophysics 2019, 84, R869–R880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfarraj, M.; AlRegib, G. Semi-supervised learning for acoustic impedance inversion. In Proceedings of the 2019 SEG International Exposition and Annual Meeting, San Antonio, TX, USA, 15–20 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, X.; Cui, L.; Wu, Z.; Chen, K.; Wang, D.; Liu, Q.H. Imaging hydraulic fractures under energized steel casing by convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 8831–8839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Luo, Y. Using GAN priors for ultrahigh resolution seismic inversion. In Proceedings of the 2019 SEG International Exposition and Annual Meeting, San Antonio, TX, USA, 15–20 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ge, Q.; Lu, W.; Yan, X. Well-logging constrained seismic inversion based on closed-loop convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 5564–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, J.; Lunz, S. Banach wasserstein gan. In Proceedings of the 2018 the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Montréal, Quebec province, Canada, 3–8 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, K.; Lin, L.; Zuo, W. Multi-level wavelet-CNN for image restoration. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Xie, Q.; Wu, B. Seismic impedance inversion based on residual attention network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4511117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Diego, CA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, H.; Weng, C.; Shi, X. Video Human Action Recognition with Channel Attention on ST-GCN. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Computer Information Science and Application Technology (CISAT), Lanzhou, China, 30 July–1 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Benesty, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Cohen, I. Pearson correlation coefficient. In Noise Reduction in Speech Processing, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 2, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]




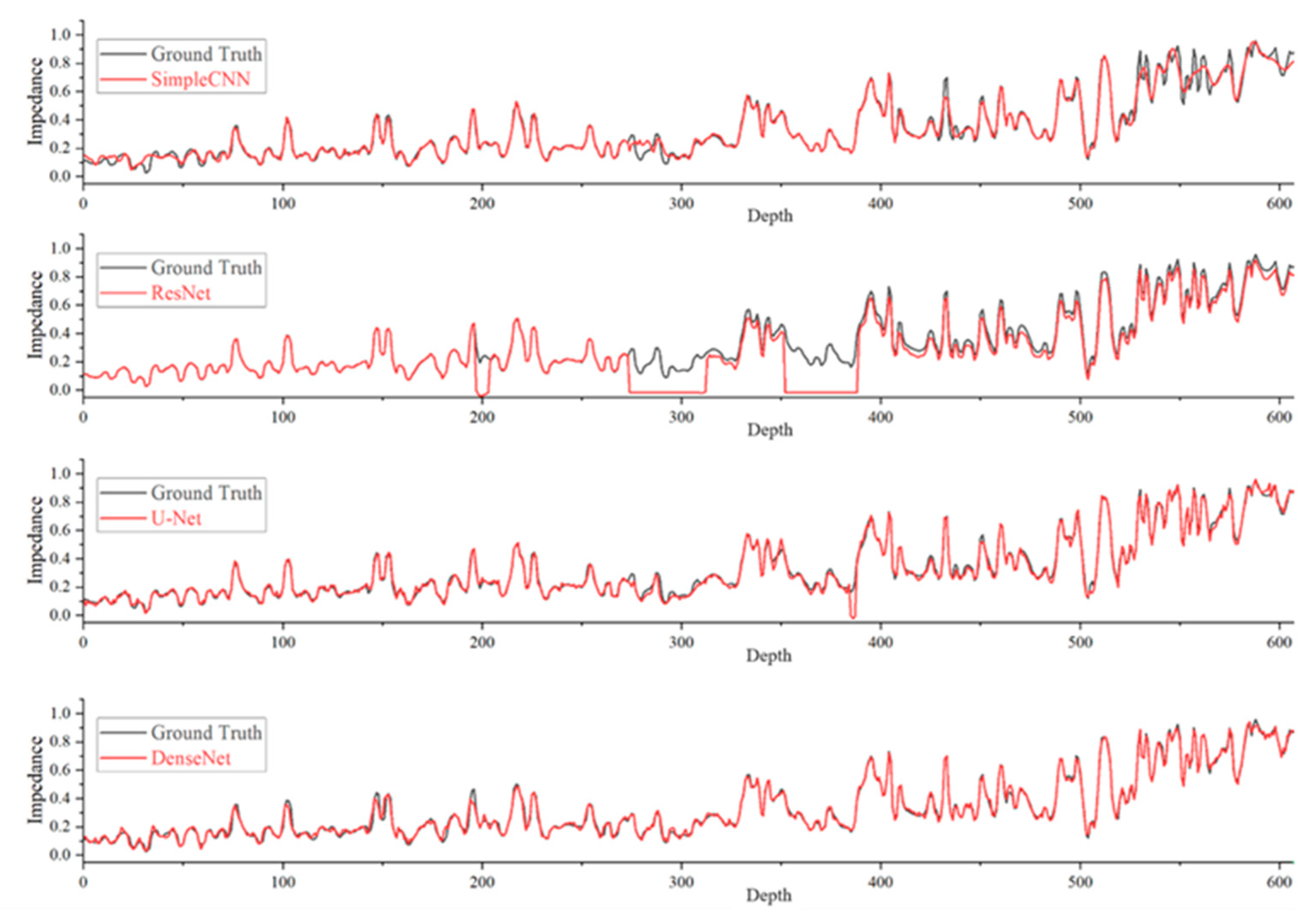
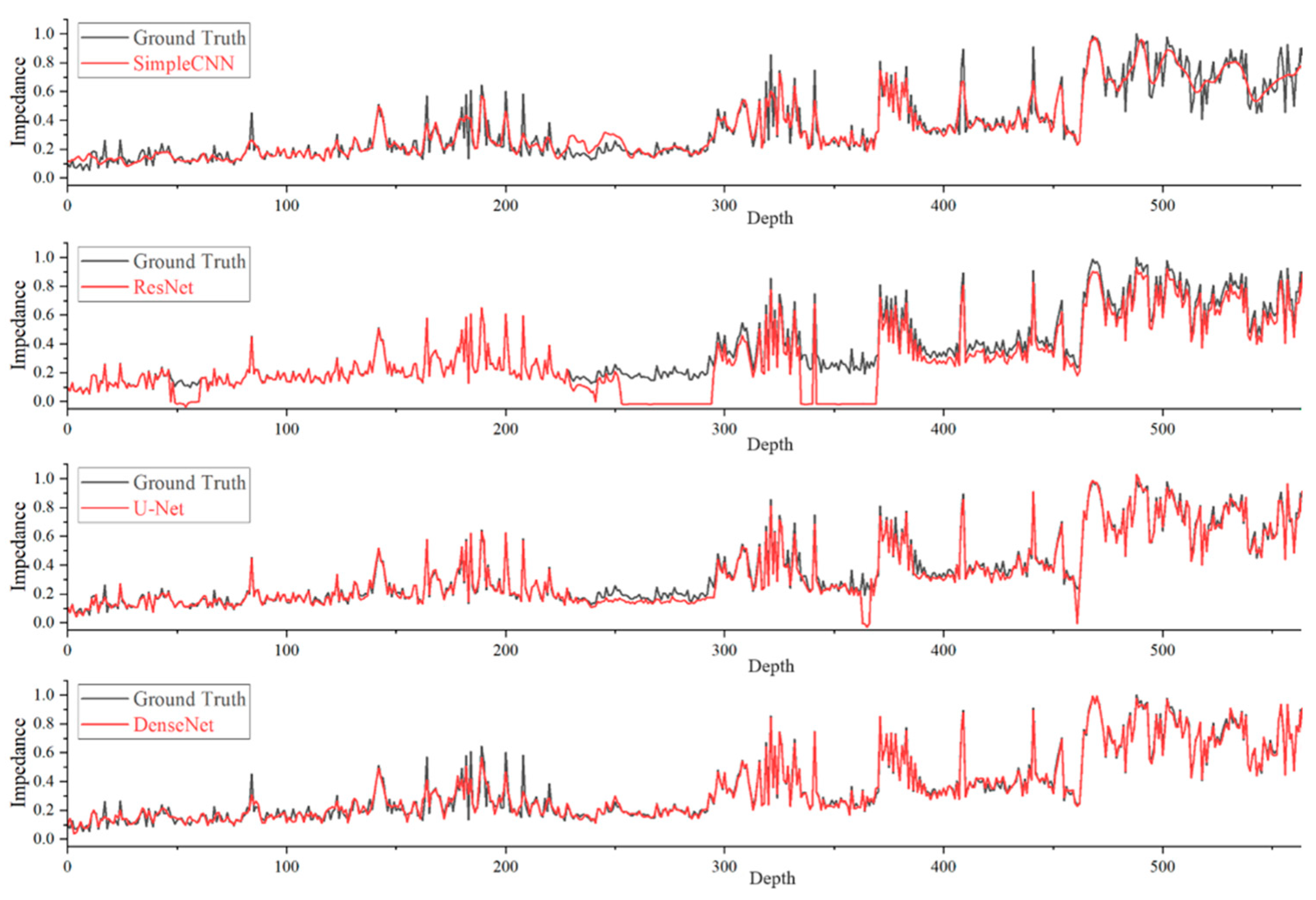
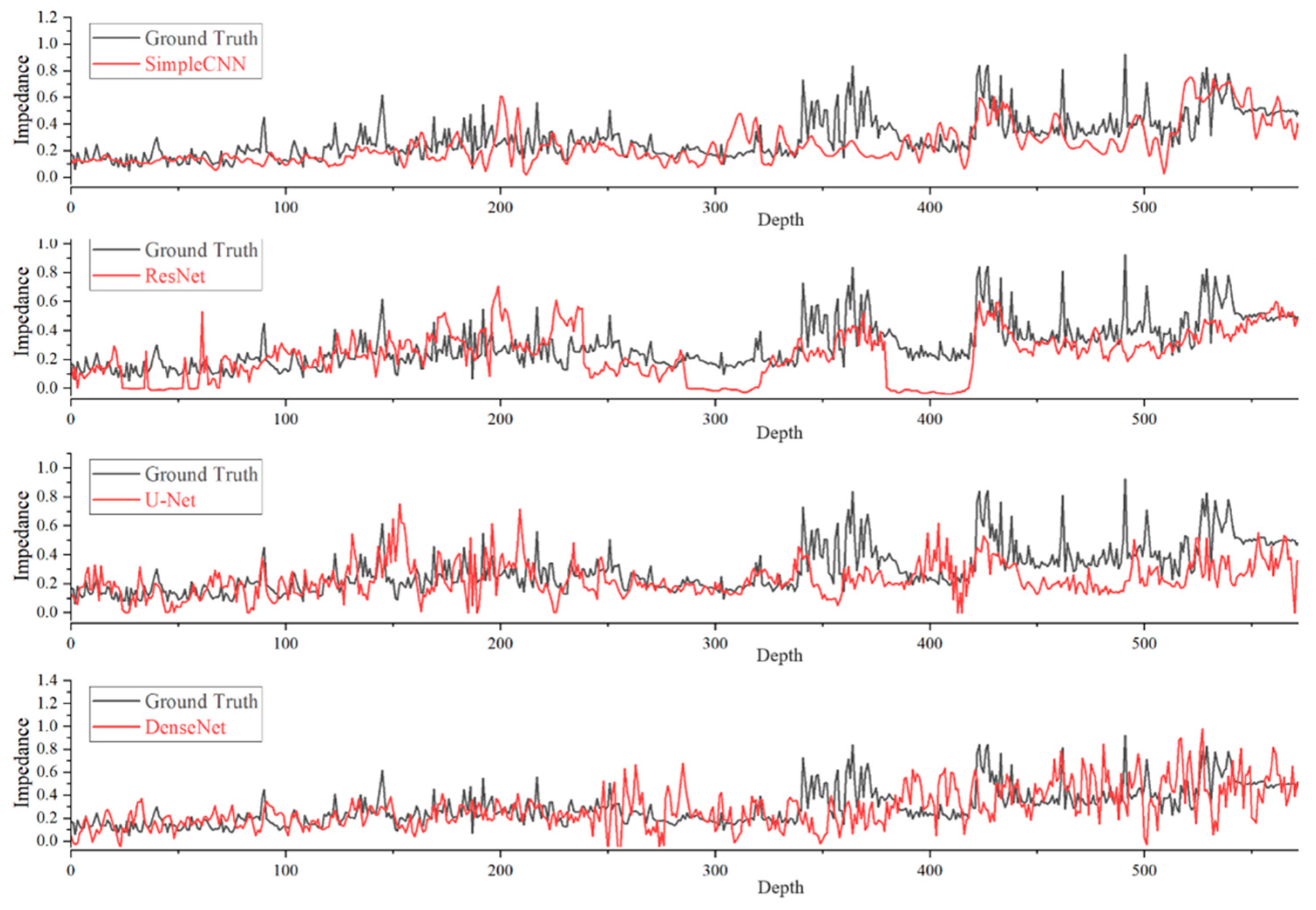
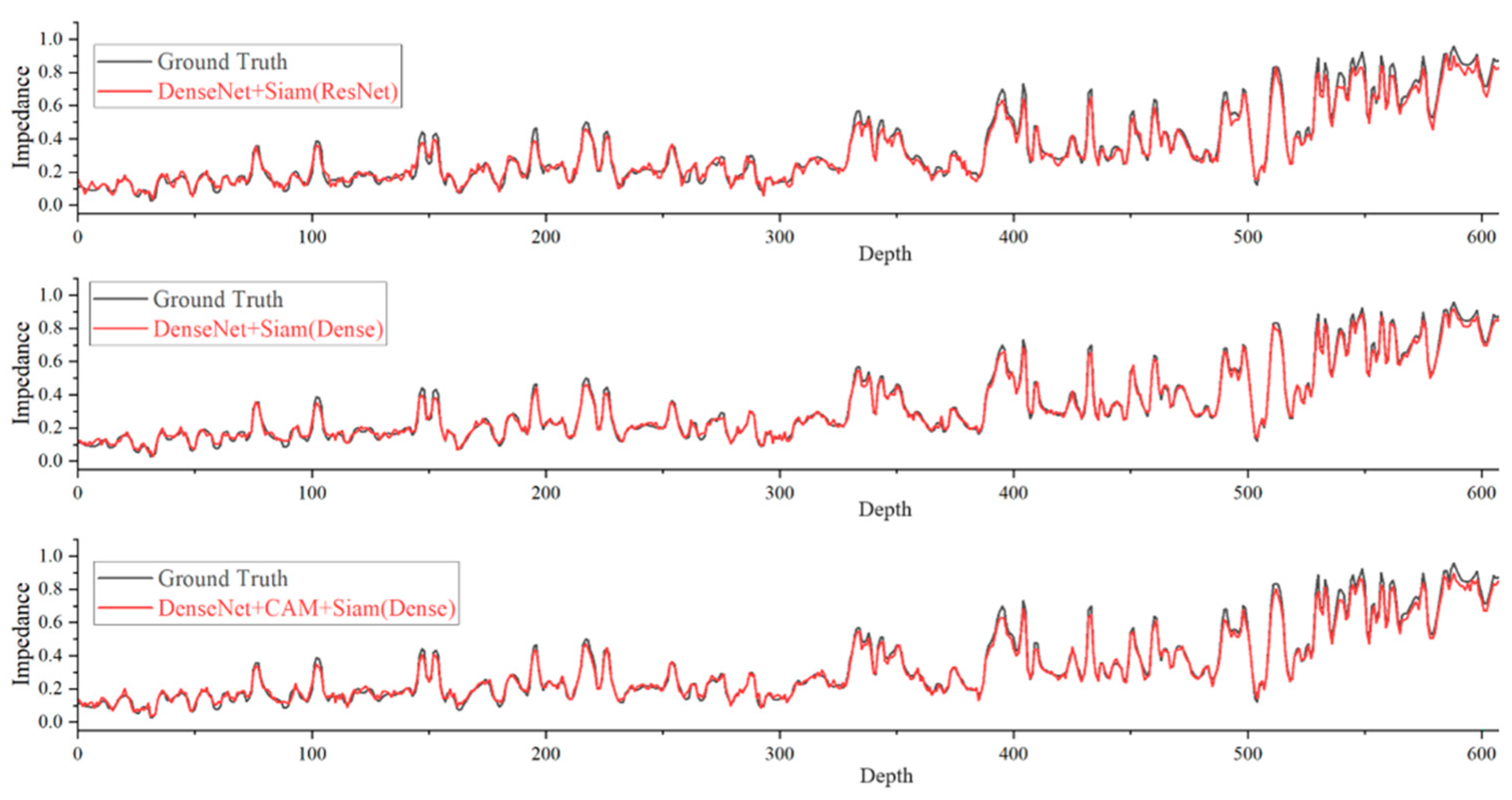


| Networks | MSE | MAE | PCC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple CNN | 0.45464 | 0.0292 | 0.1273 | 0.6063 |
| ResNet | 0.89146 | 0.0267 | 0.1265 | 0.5387 |
| U-Net | 0.15672 | 0.0285 | 0.1263 | 0.5764 |
| DenseNet | 0.43863 | 0.0198 | 0.1027 | 0.6179 |
| Networks | MSE | MAE | PCC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DenseNet+Siam (Res) | 0.13761 | 0.0199 | 0.1006 | 0.6657 |
| DenseNet+ Siam (Dense) | 0.05668 | 0.0203 | 0.1023 | 0.6620 |
| DenseNet+CAM+Siam (Dense) | 0.05168 | 0.0188 | 0.1004 | 0.7464 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J. Siamese-Derived Attention Dense Network for Seismic Impedance Inversion. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12182824
Wu J. Siamese-Derived Attention Dense Network for Seismic Impedance Inversion. Mathematics. 2024; 12(18):2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12182824
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jiang. 2024. "Siamese-Derived Attention Dense Network for Seismic Impedance Inversion" Mathematics 12, no. 18: 2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12182824
APA StyleWu, J. (2024). Siamese-Derived Attention Dense Network for Seismic Impedance Inversion. Mathematics, 12(18), 2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12182824





