An Underwater Passive Electric Field Positioning Method Based on Scalar Potential
Abstract
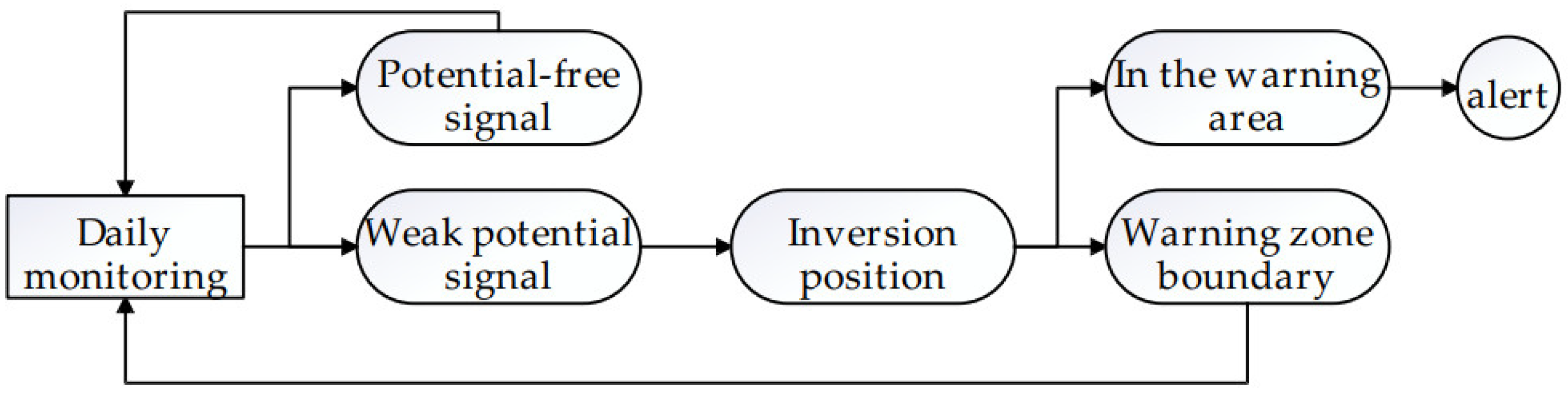
1. Introduction
2. Positioning Method
2.1. Three-Layer Positioning Model
2.2. Selection of and Improvement in Location Algorithm
2.2.1. Basic Differential Evolution Algorithm
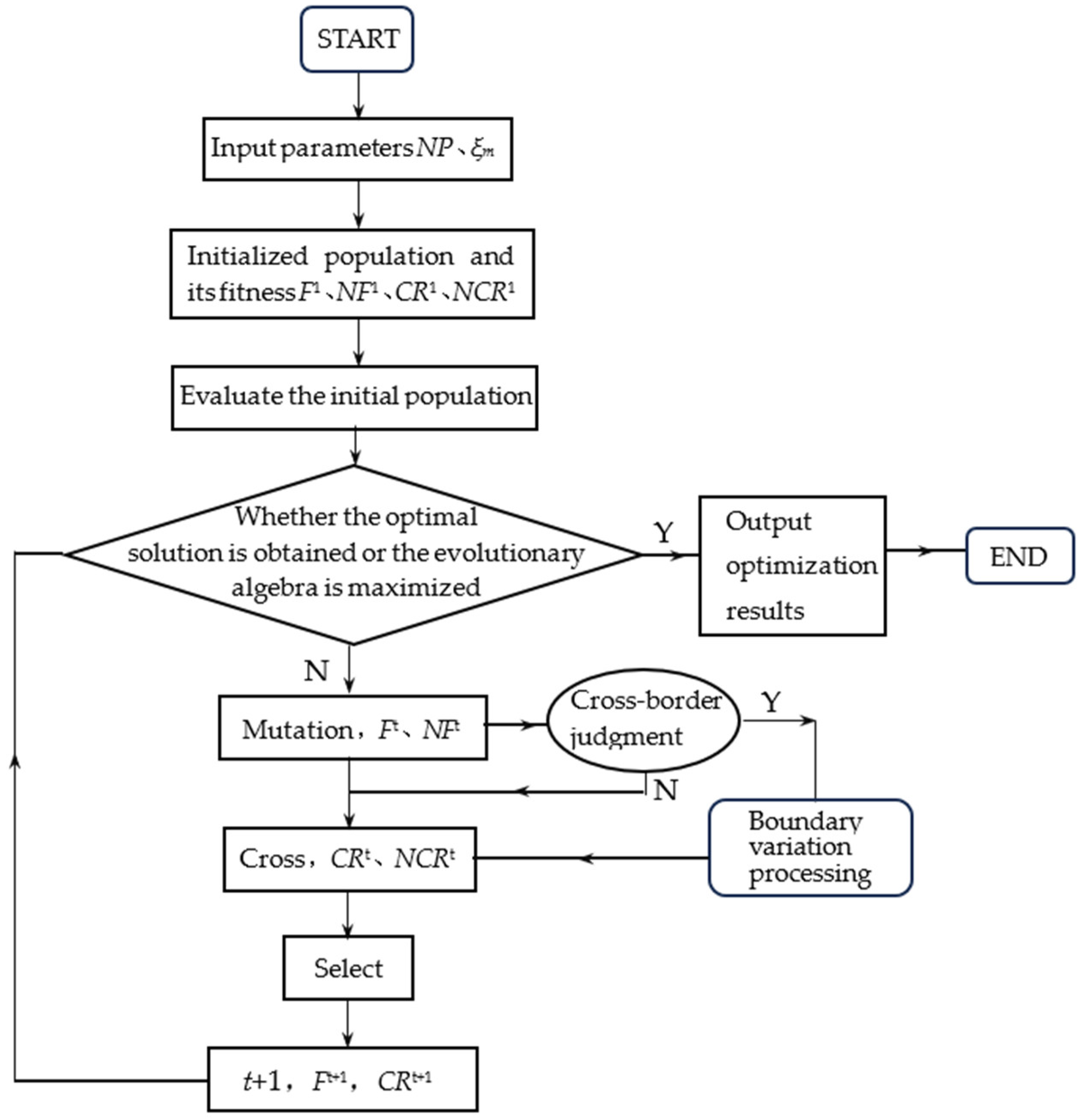
2.2.2. Improved Differential Evolution Algorithm by Introducing a Parameter-Adaptive Strategy
2.2.3. Improved Differential Evolution Algorithm by Introducing a Boundary Mutation Processing Mechanism
3. Simulation Analysis of the Positioning Method
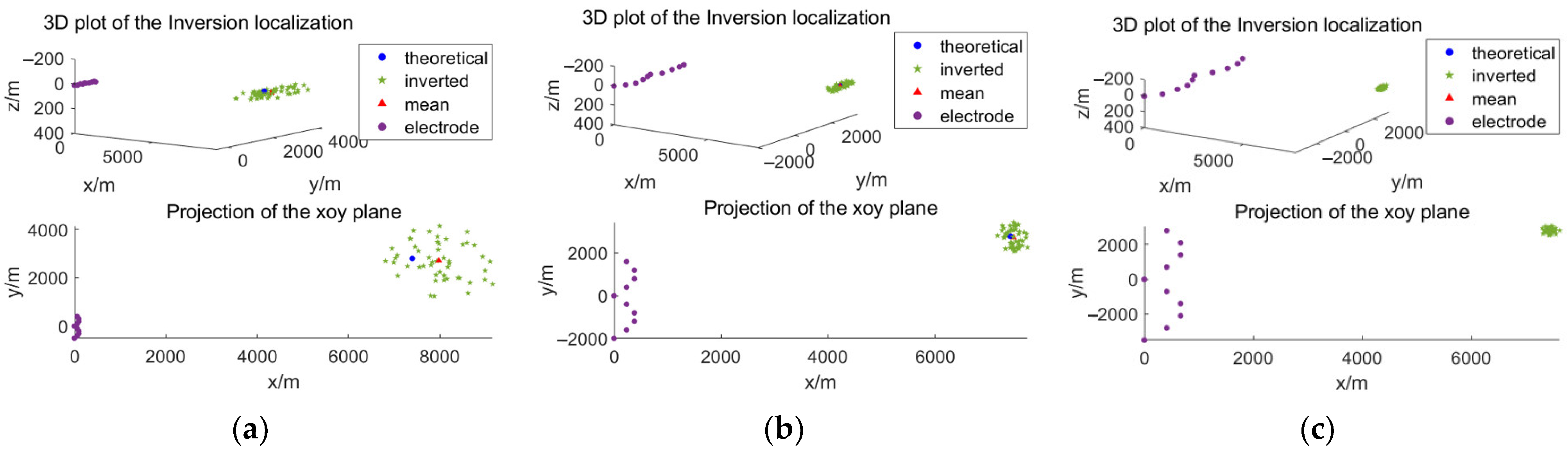
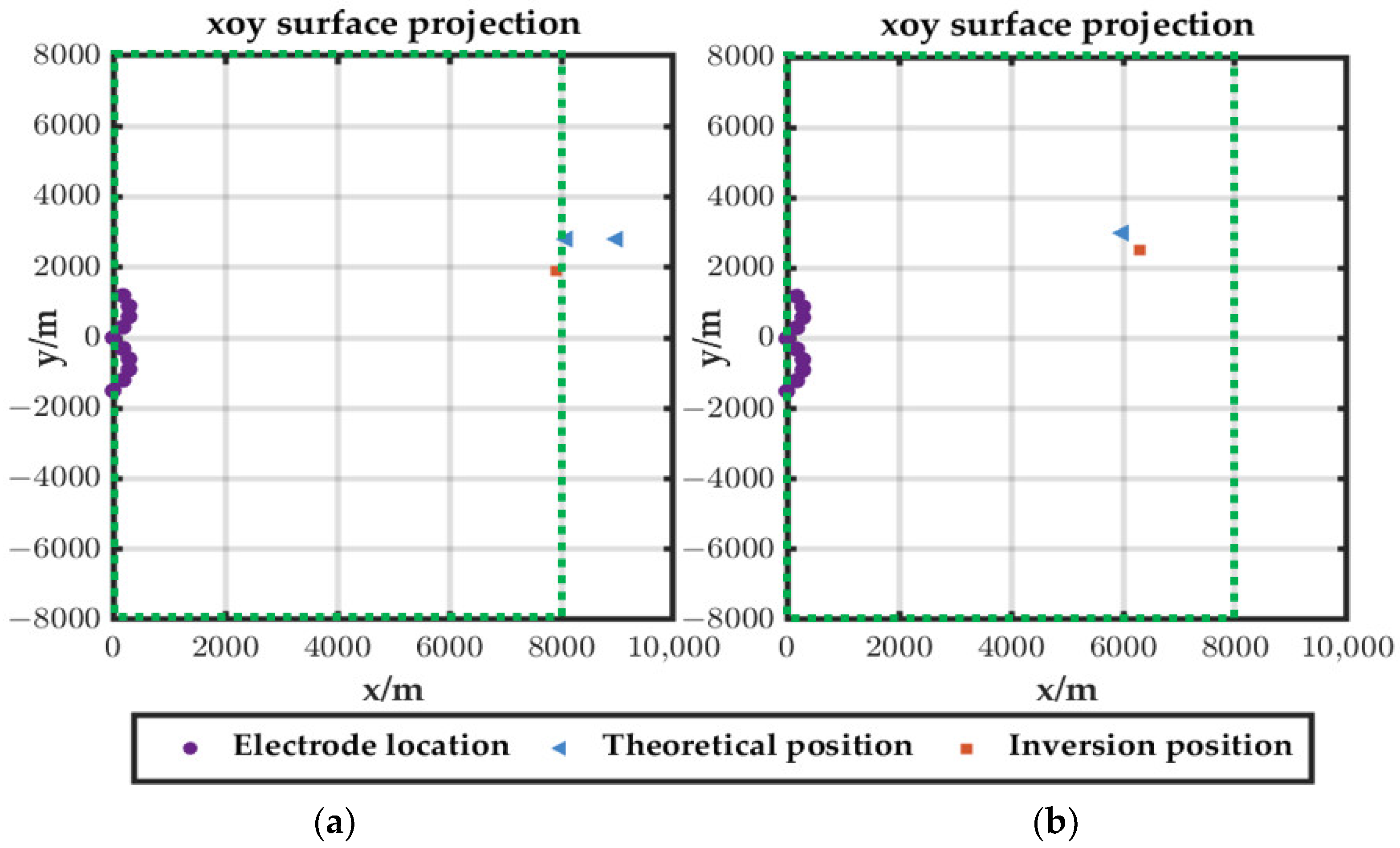
3.1. Simulation Positioning Example
3.2. Optimal Sensor Array Design
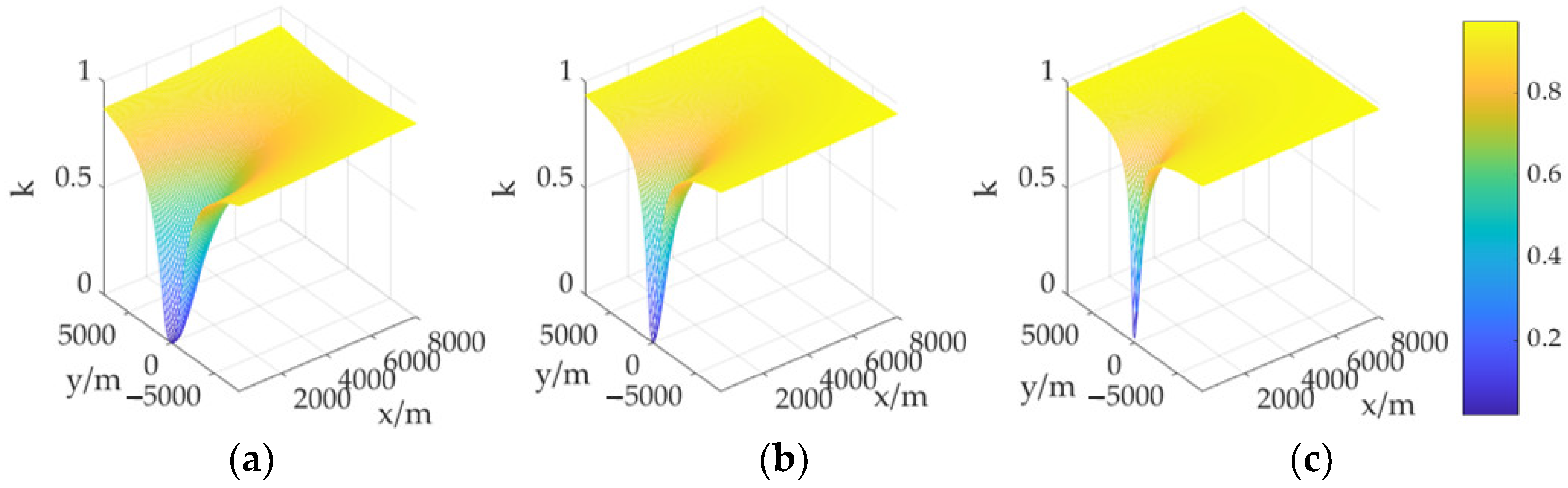
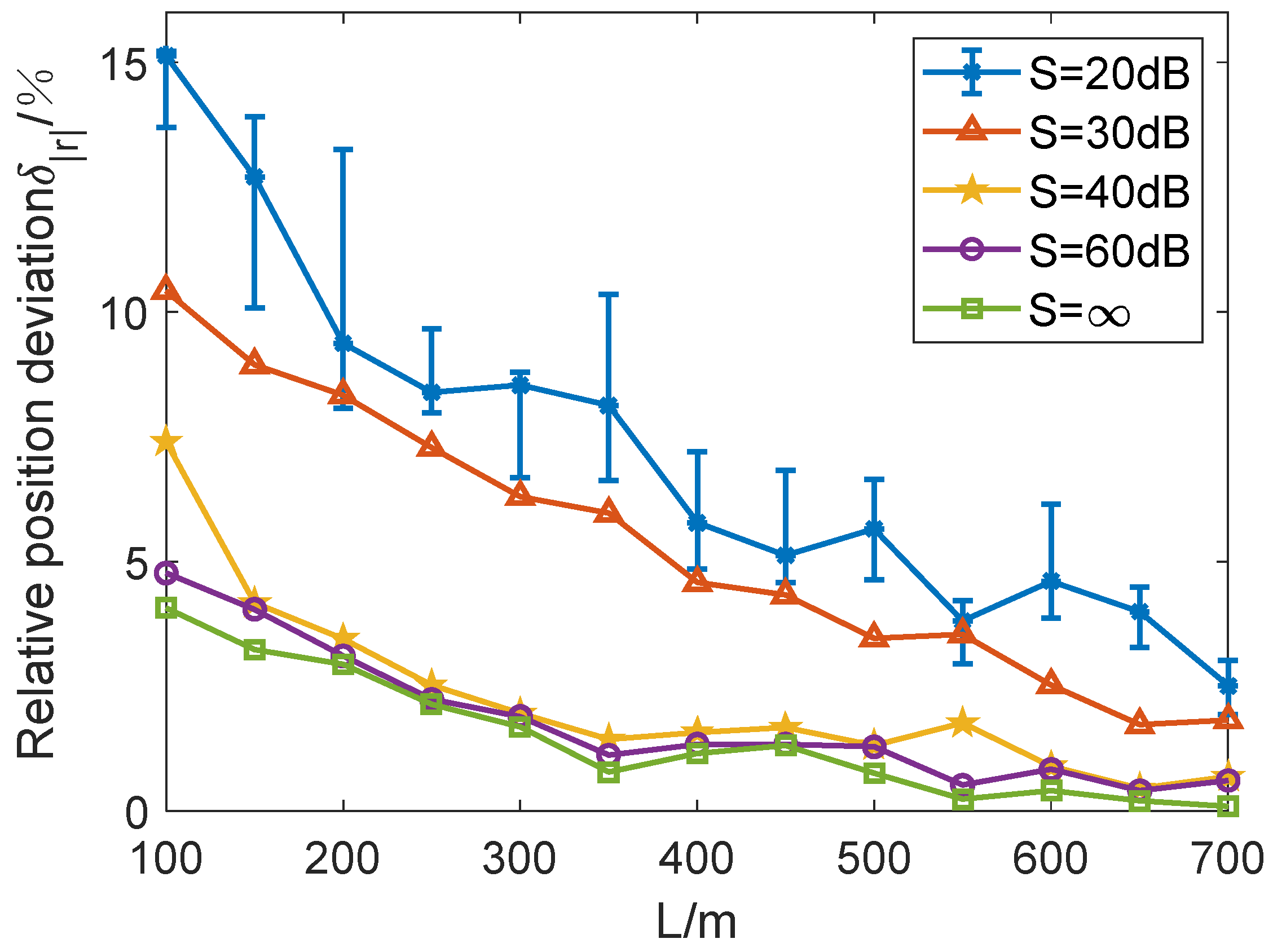
3.2.1. The Influence of Electrode Layout Range
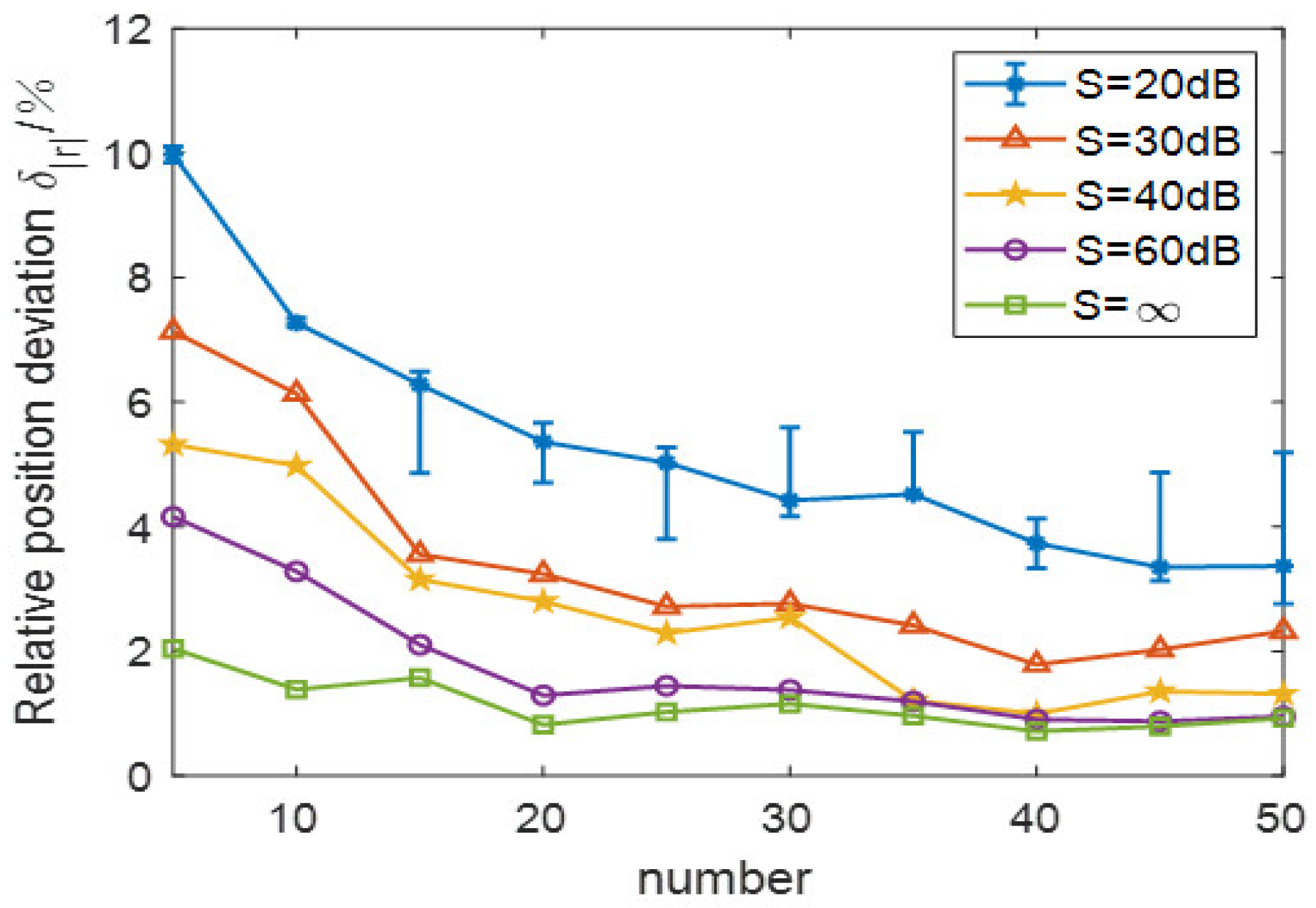
3.2.2. The Influence of the Number of Electrodes
4. Laboratory Verification of the Positioning Method
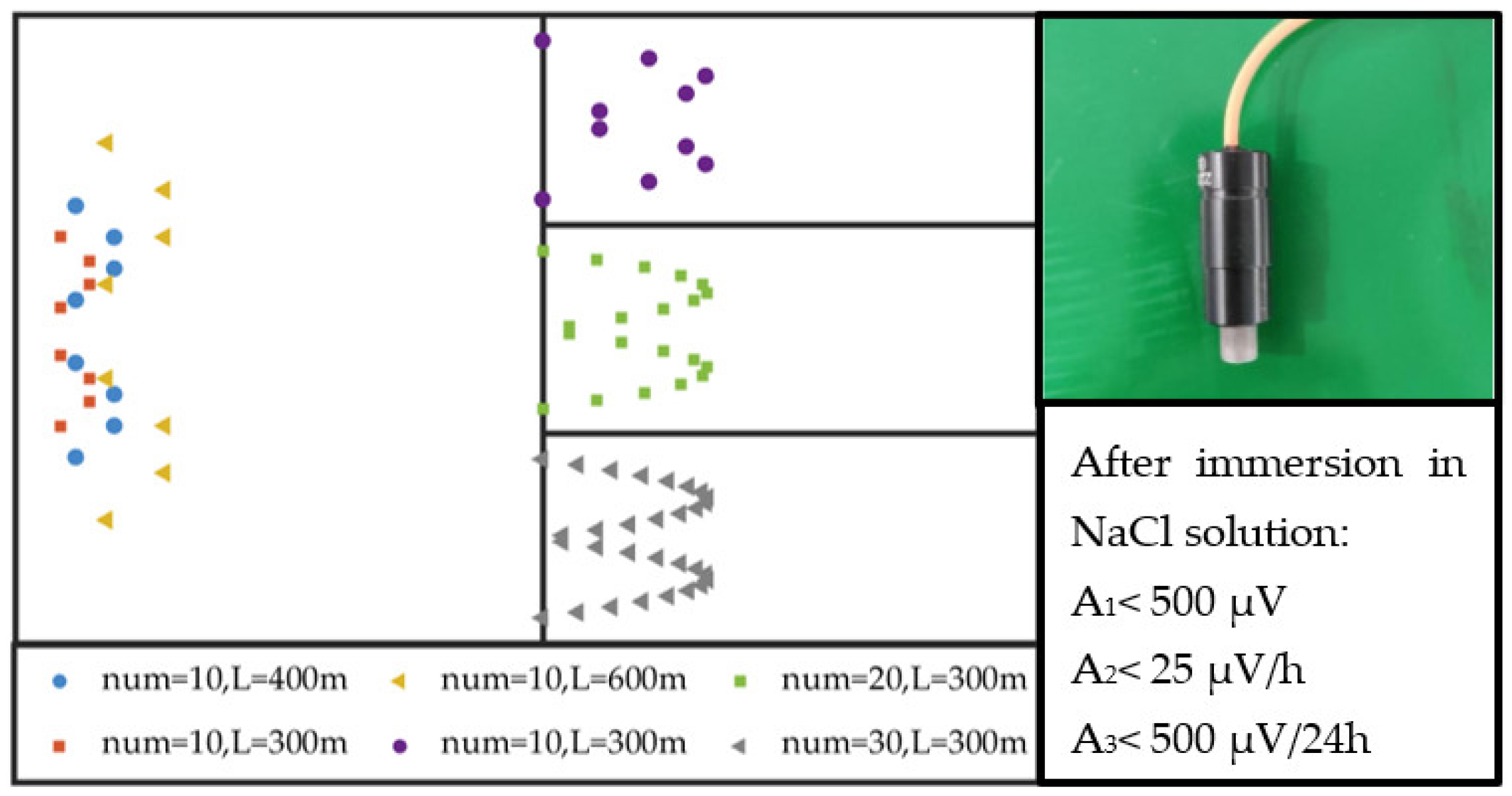
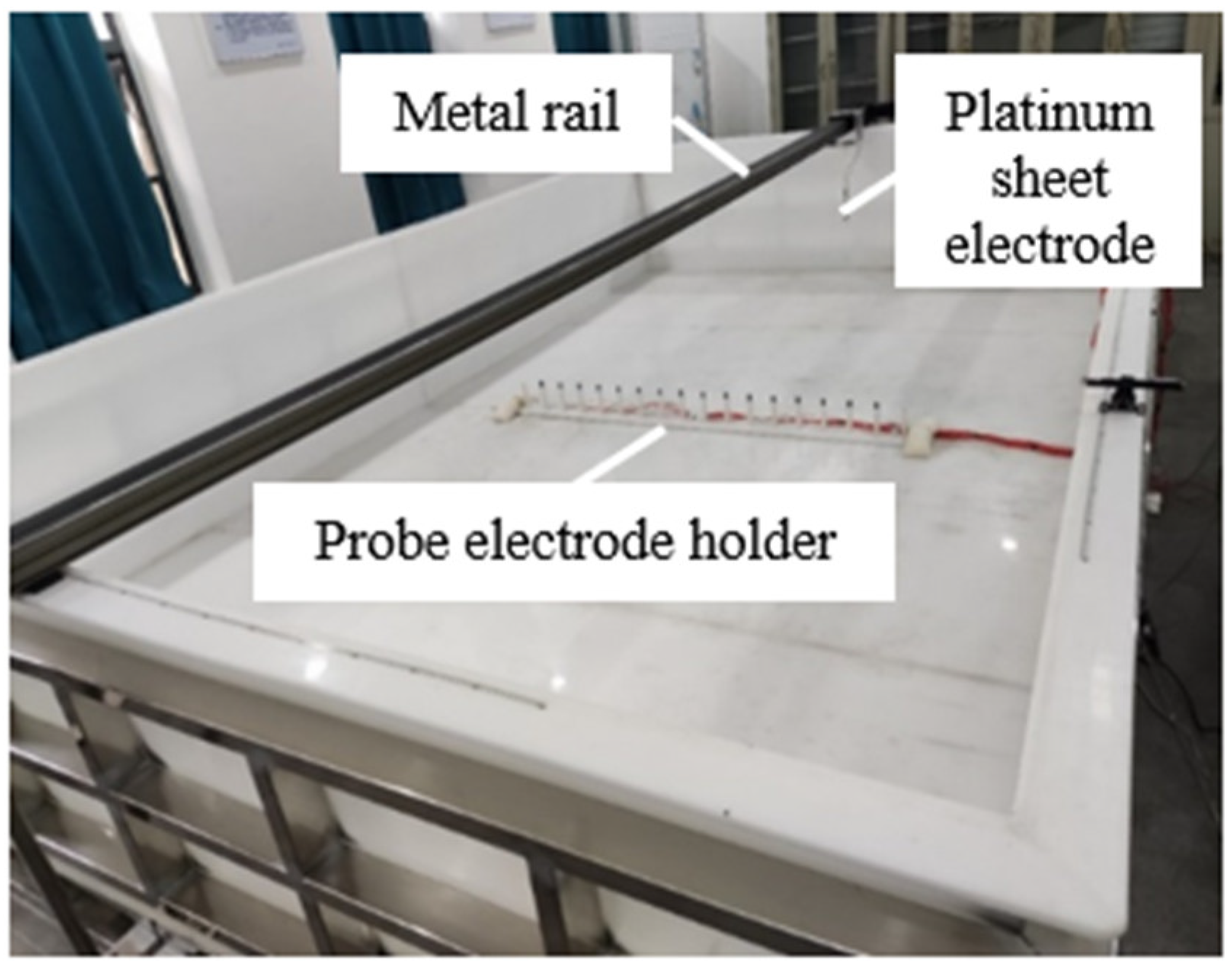
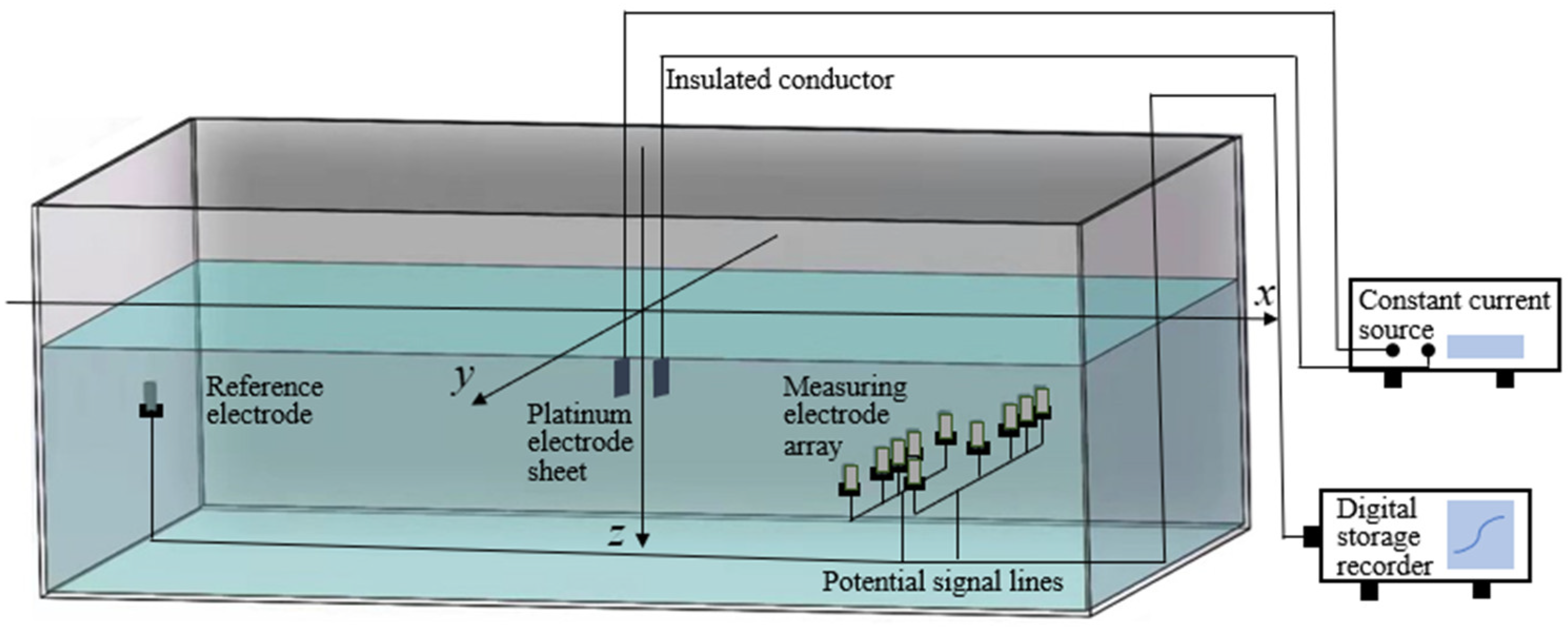
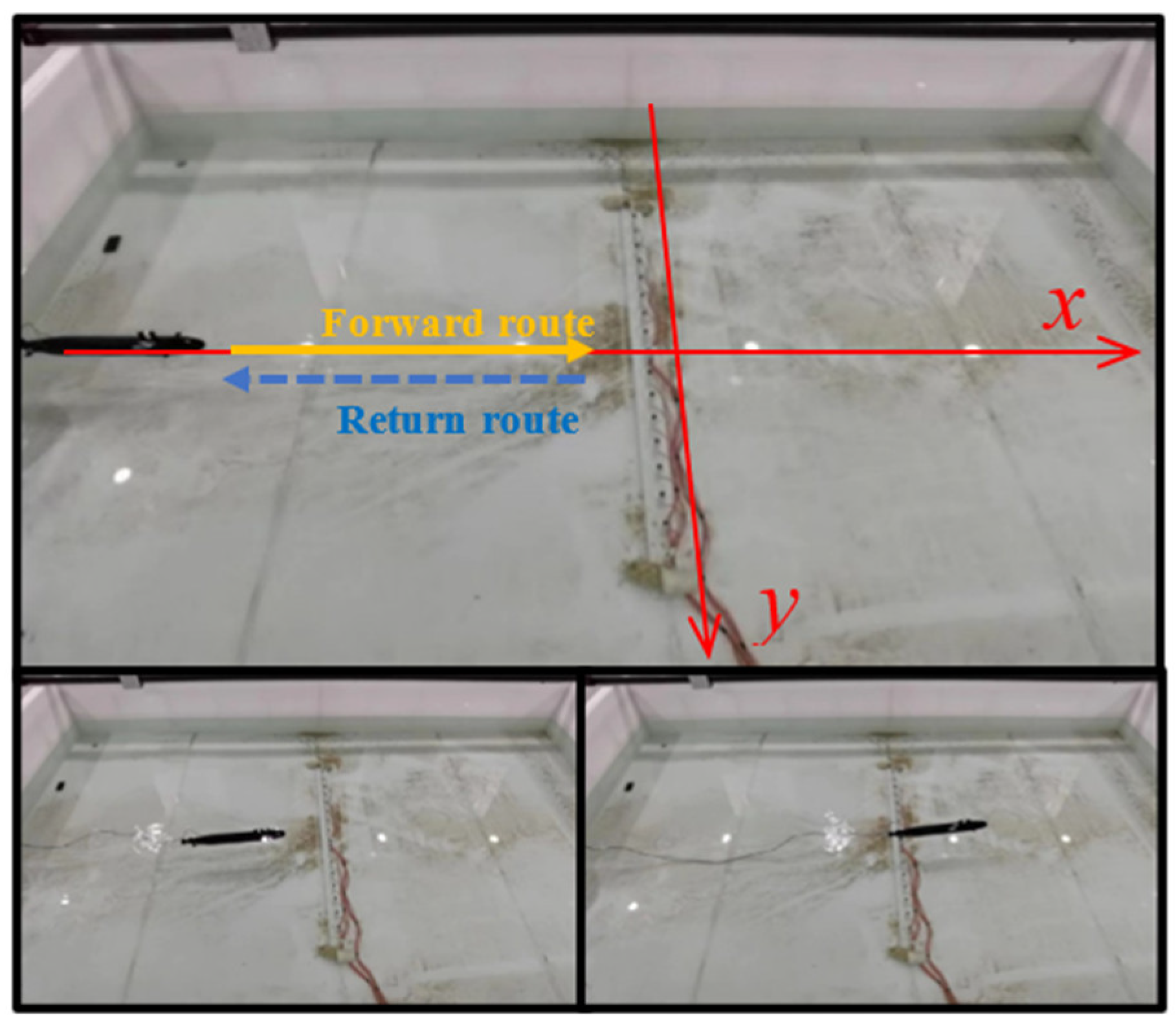
4.1. Current Element Positioning Experiment
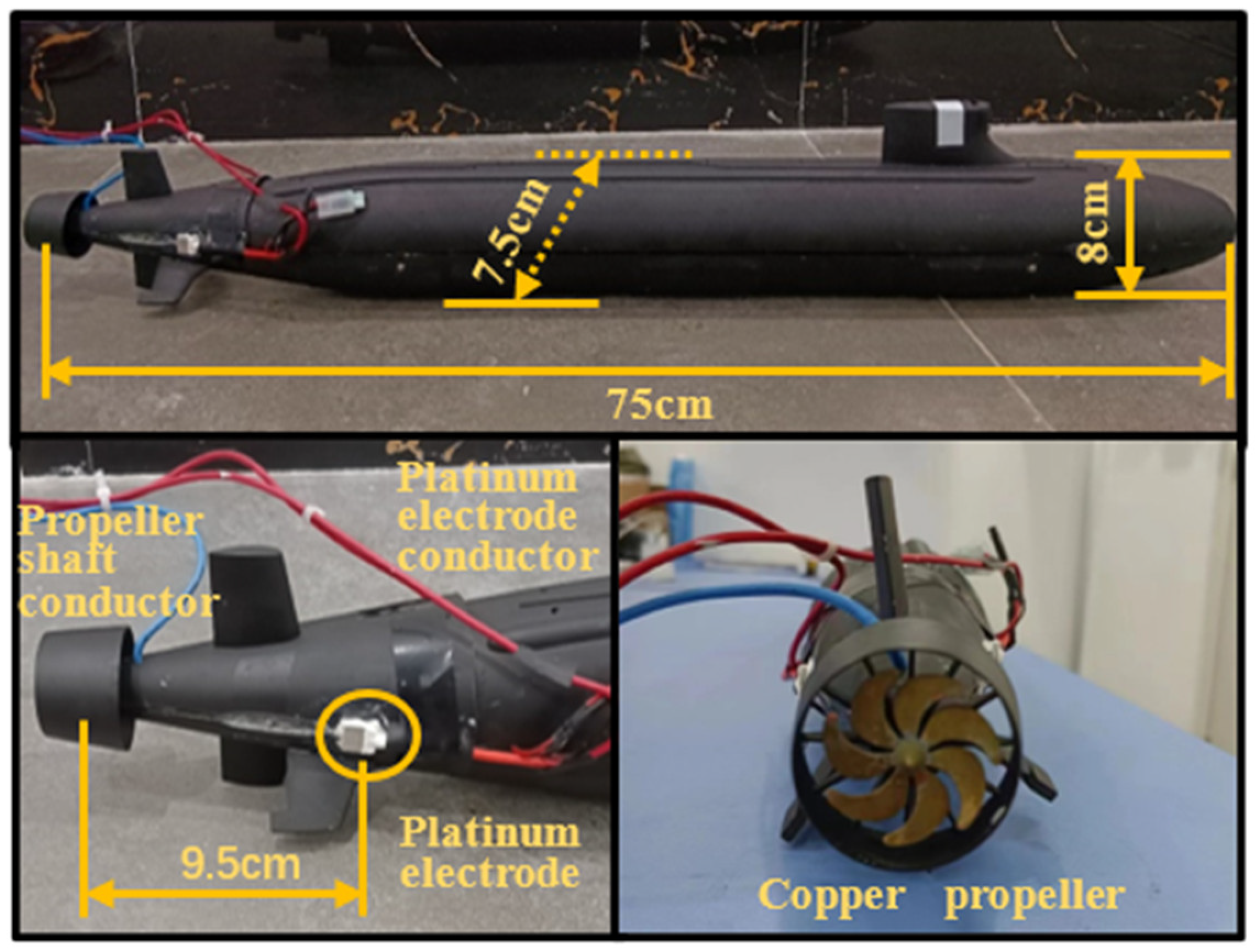
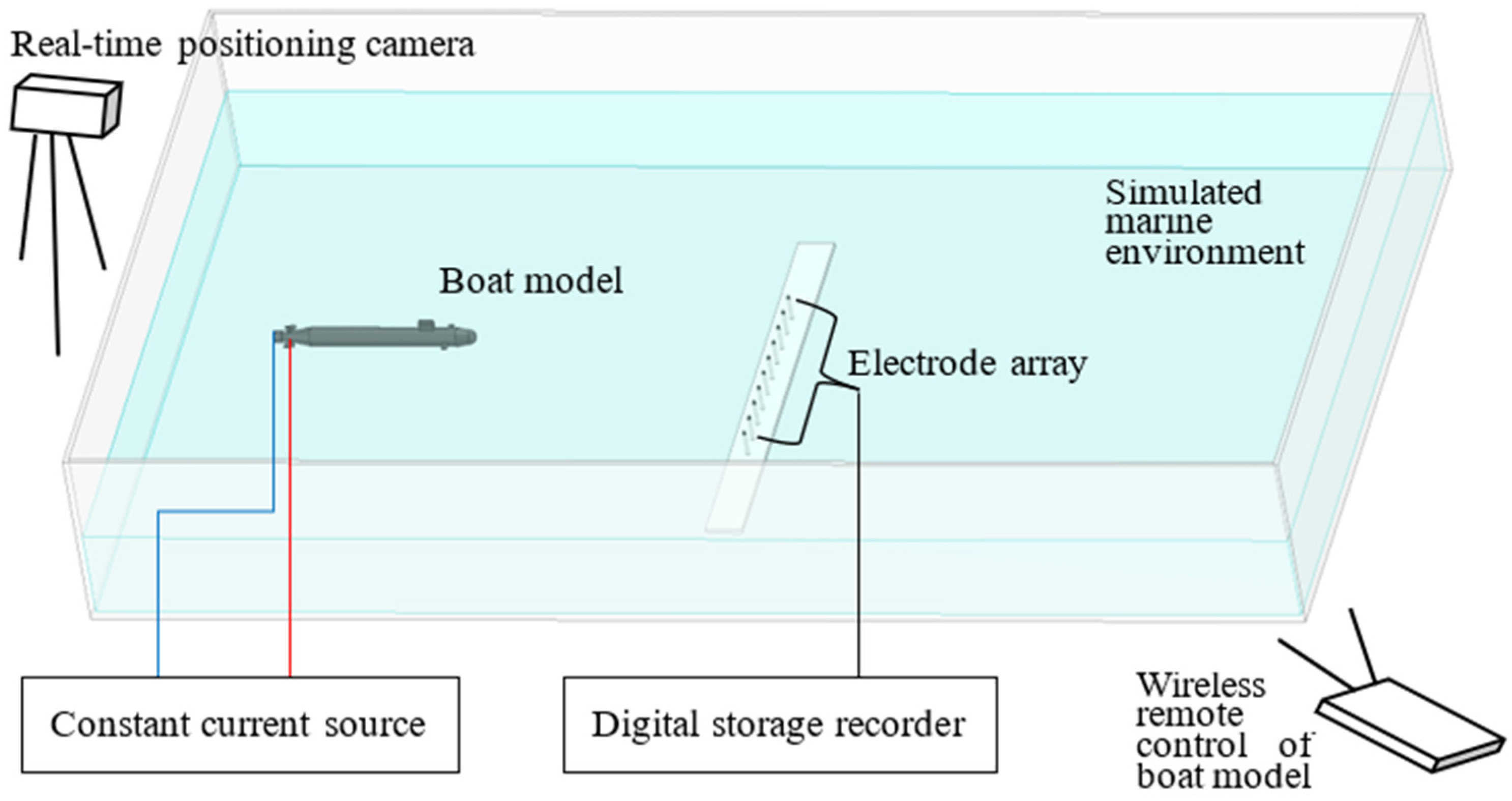
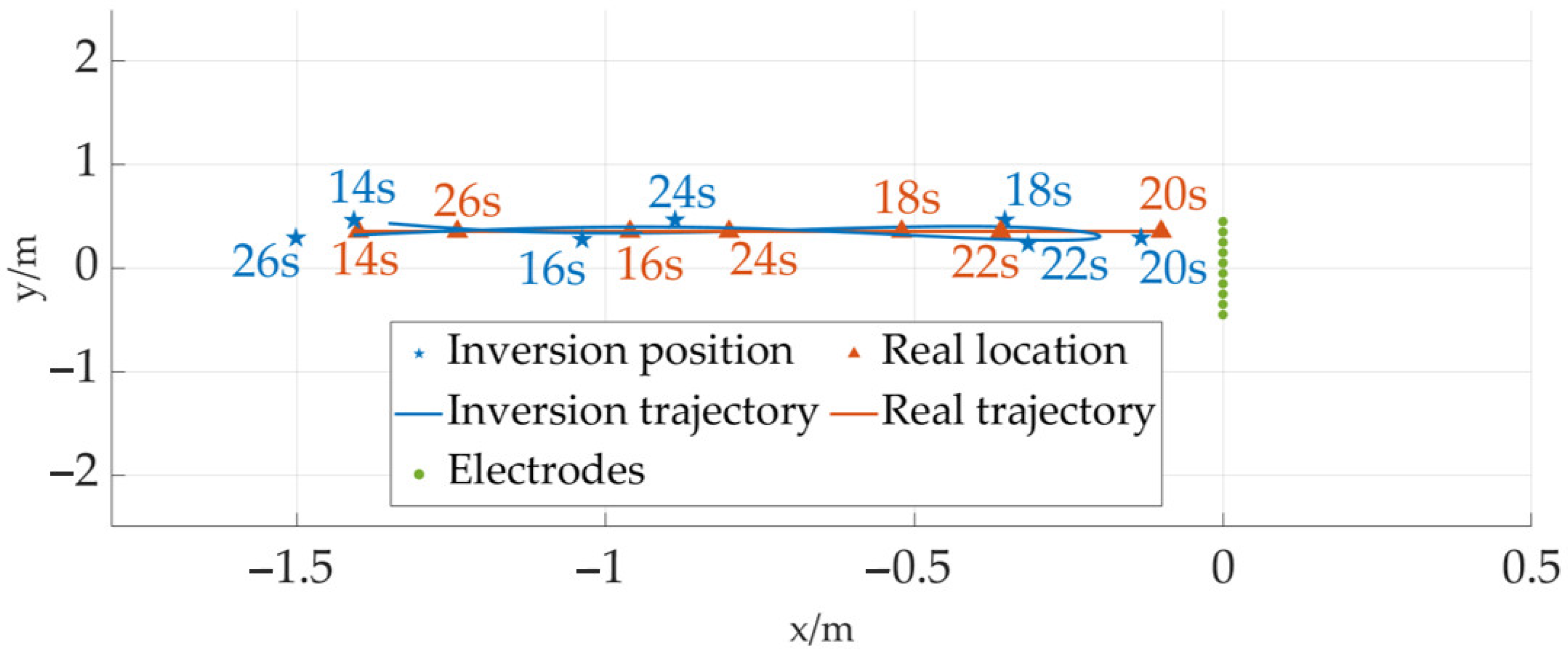
4.2. Positioning Experiment of the Moving Underwater Vehicle
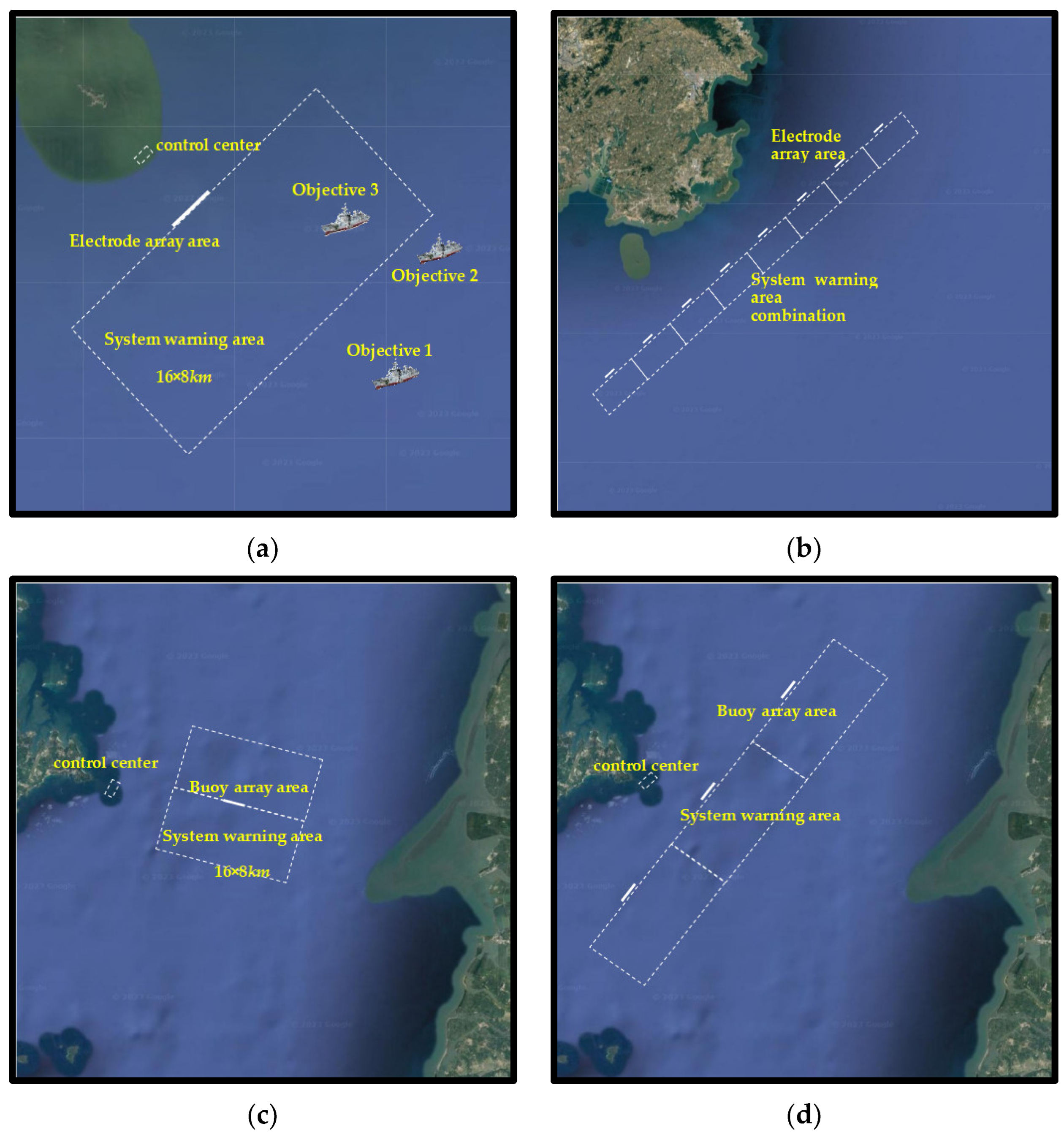
4.3. Discussion and Prospects of Practical Application Scenarios
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, T.A.; Rigby, J. Underwater Radiated Noise from Marine Vessels: A Review of Noise Reduction Methods and Technology. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 266, 112863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H. Underwater Target Localization and Inversion Technology Based on Magnetic Anomaly Detection. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Science & Technology, Nanjing, China, 2022. Available online: https://link.oversea.cnki.net/doi/10.27241/d.cnki.gnjgu.2022.000073 (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Han, R. Development of several key technologies and equipment for high-power and wide-band digital power amplifier. Ph.D. Thesis, Hunan University, Changsha, China, 2022. Available online: https://link.oversea.cnki.net/doi/10.27135/d.cnki.ghudu.2022.000207 (accessed on 3 March 2024).
- Zhang, J.; Yu, P.; Jiang, R.; Xie, T. Real-Time Localization for Underwater Equipment Using an Extremely Low Frequency Electric Field. Def. Technol. 2022, 26, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Q. Influence of mass transfer process on ship electric fieldunder laminar flow condition. J. Nav. Univ. Eng. 2020, 32, 1–6+14. Available online: https://link.oversea.cnki.net/doi/10.7495/j.issn.1009-3486.2020.02.001 (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Kato, R.; Takahashi, M.; Ishii, N.; Chen, Q.; Yoshida, H. Investigation of a 3-D Undersea Positioning System Using Electromagnetic Waves. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2021, 69, 4967–4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duecker, D.-A.; Geist, A.; Hengeler, M.; Kreuzer, E.; Pick, M.-A.; Rausch, V.; Solowjow, E. Embedded Spherical Localization for Micro Underwater Vehicles Based on Attenuation of Electro-Magnetic Carrier Signals. Sensors 2017, 17, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Aris, M.N.; Daud, H.; Mohd Noh, K.A.; Dass, S.C. Stochastic Process-Based Inversion of Electromagnetic Data for Hydrocarbon Resistivity Estimation in Seabed Logging. Mathematics 2021, 9, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Di, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Tian, H.; Gan, L. Enhanced Whale Optimization Algorithm for Improved Transient Electromagnetic Inversion in the Presence of Induced Polarization Effects. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde Mones, J.J.; Hernández Gracidas, C.A.; Morín Castillo, M.M.; Oliveros Oliveros, J.J.; Juárez Valencia, L.H. Stable Numerical Identification of Sources in Non-Homogeneous Media. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yang, J.; Du, C.; Si, L. Distribution Features of Underwater Static Electric Field Intensity of Ship in Typical Restricted Sea Areas. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 2020, 102, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Xue, W.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Xu, Y. An Improved Underwater Electric Field-Based Target Localization Combining Subspace Scanning Algorithm And Meta-EP PSO Algorithm. JMSE 2020, 8, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznichenko, I.; Podržaj, P.; Peperko, A. Calculation of Stationary Magnetic Fields Based on the Improved Quadrature Formulas for a Simple Layer Potential. Mathematics 2023, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhao, S. Study on the localization of the dectric dipole sources. J. Phys. 2007, 56, 5180–5184. Available online: https://link.oversea.cnki.net/doi/10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2007.09.030 (accessed on 31 August 2023).
- Samann, F.; Rausch, A.; Schanze, T. Electrical Dipole Source Localization Using Hybrid Least Squares Method in Combination with ICA. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 5, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ci, L.; Xue, W.; Dang, J.; Jia, P.; Xu, Y.; Gao, J. Underwater Target Electric Field Location Algorithm Based on Electric Dipole. In Proceedings of the IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Image Processing, Electronics and Computers, Dalian, China, 14–16 April 2022; pp. 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, J.; Xu, L.; Jia, P.; Pan, D.; Xue, W. Electromagnetic Fusion Underwater Positioning Technology Based on ElasticNet Regression Method. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 10th International Conference on Information, Communication and Networks (ICICN); IEEE, Zhangye, China, 23 August 2022; pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Chen, C.; Huang, G. Study on location method of electric dipole source in parallel stratified sea area. J. Electron. 2021, 49, 1761–1767. Available online: https://link.oversea.cnki.net/doi/10.12263/DZXB.20200356 (accessed on 30 August 2023).
- Wang, C.; Xu, Y.; Qi, J.; Shang, W.; Liu, M.; Chen, W. Passive Electromagnetic Field Positioning Method Based on BP Neural Network in Underwater 3-D Space. In Advanced Hybrid Information Processing; Liu, S., Ma, X., Eds.; Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switerland, 2022; Volume 416, pp. 292–304. ISBN 978-3-030-94550-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Wu, H.; Peng, J.; Li, K. Long-Range and High-Precision Localization Method for Underwater Bionic Positioning System Based on Joint Active–Passive Electrolocation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wu, X.; Yang, J.; Sun, J. Method for Detecting Electrical Interface in Sea Area Based on Active Electric Field. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2419, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xue, W.; Li, Y.; Guo, L.; Shang, W. Multiple Signal Classification Algorithm Based Electric Dipole Source Localization Method in an Underwater Environment. Symmetry 2017, 9, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y. Research on Electric Field Location Technology of Underwater Target Based on Optimization Theory. Ph.D. Thesis, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chew, W. A quick way to approximate a Sommerfeld-Weyl-type integral (antenna far-field radiation). IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1988, 36, 1654–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, S. Application of the fast Fourier transform to the computation of the Sommerfeld integral for a vertical electric dipole above a half-space. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1992, 40, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Shang, S.; Cai, X.; Zhao, H.; Song, Y.; Xu, J. An Improved Differential Evolution Algorithm and Its Application in Optimization Problem. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 5277–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, B.; Guo, X.; Qi, L.; Li, Z. Self-Adapting Spherical Search Algorithm with Differential Evolution for Global Optimization. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, B. An Improved Differential Evolution Algorithm with Dual Mutation Strategies Collaboration. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 153, 113451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Li, K.; Wang, Y. Differential Evolution with Adaptive Mutation Strategy Based on Fitness Landscape Analysis. Inf. Sci. 2021, 549, 142–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Li, K. Differential Evolution with Mixed Mutation Strategy Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 111, 107678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Gui, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Yu, F.; Wu, H.; Wei, B.; He, G.; Li, Y.; Li, K. A Fitness-Based Adaptive Differential Evolution Algorithm. Inf. Sci. 2021, 549, 116–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, W.; Liu, W.; Zhong, J. Adaptive Differential Evolution Algorithm Based on Population State Information. J. Commun. 2023, 44, 34–46. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Basset, M.; Mohamed, R.; Hezam, I.M.; Alshamrani, A.M.; Sallam, K.M. An Efficient Evolution-Based Technique for Moving Target Search with Unmanned Aircraft Vehicle: Analysis and Validation. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boks, R.; Kononova, A.V.; Wang, H. Quantifying the Impact of Boundary Constraint Handling Methods on Differential Evolution. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference Companion, Lille, France, 7 July 2021; pp. 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanovov, V.; Semenkin, E. Adaptation of the Scaling Factor Based on the Success Rate in Differential Evolution. Mathematics 2024, 12, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
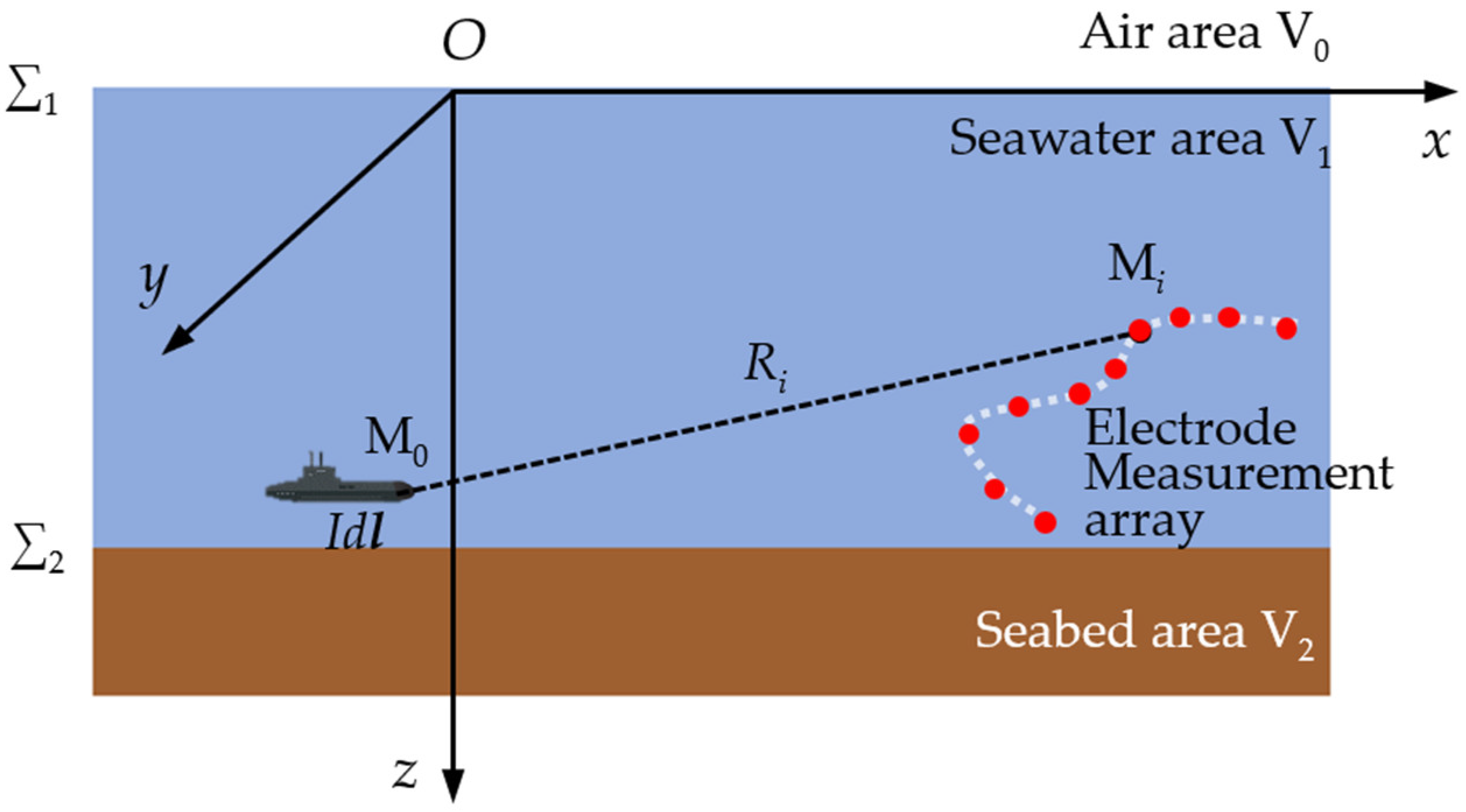



| Group Serial Number | Coordinates | Regarding the Number of Mirror Reflections on the Σ1 Plane | Regarding the Number of Mirror Reflections on the Σ2 Plane | Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | k | k | ||
| 2 | k | k + 1 | ||
| 3 | m | m − 1 | ||
| 4 | m | m |
| S/dB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∞ | (7541, 2853, 78) | 1.90 | (62, 78, 11) | 2.99 |
| 60 | (7576, 2866, 82) | 2.35 | (57, 82, 12) | 4.10 |
| 40 | (7786, 2792, 80) | 2.56 | (58, 76, 8) | 4.87 |
| 30 | (7643, 3050, 77) | 5.33 | (61, 85, 9) | 5.17 |
| 20 | (7551, 2915, 73) | 7.09 | (56, 81, 14) | 5.72 |
| (0.0543, −0.0274, 0.0576) | 5.11 | (0.0091, −0.0005, 0.0004) | 7.2 |
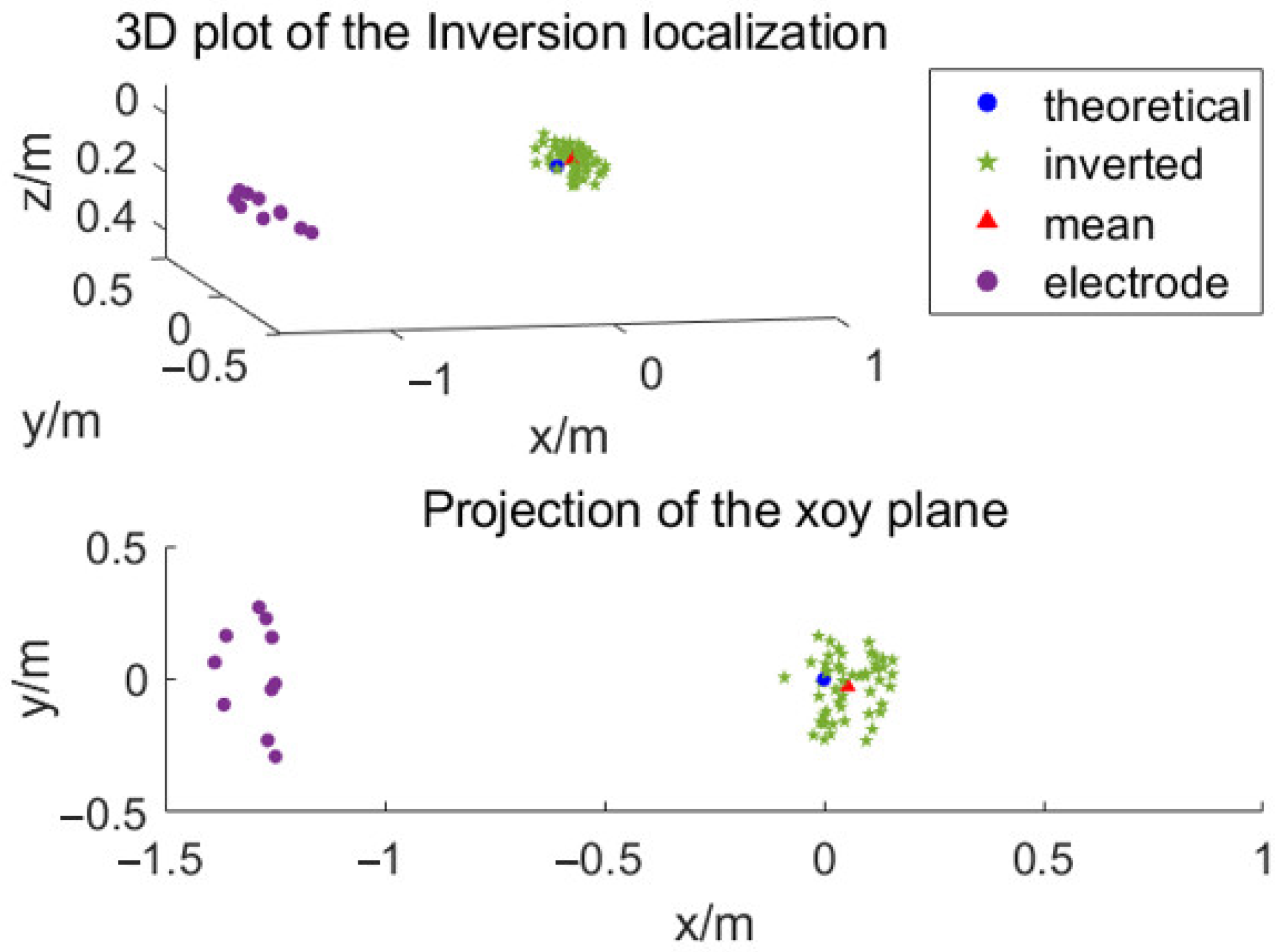
| Moment/s | Theoretical Position/m | Actual Location/m | Absolute Deviation/m |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | (−1.4, 0.36, 0.1) | (−1.41, 0.47, 0.09) | 0.11 |
| 16 | (−0.96, 0.36, 0.1) | (−1.04, 0.28, 0.10) | 0.11 |
| 18 | (−0.52, 0.36, 0.1) | (−0.35, 0.46, 0.10) | 0.20 |
| 20 | (−0.1, 0.36, 0.1) | (−0.13, 0.29, 0.09) | 0.07 |
| 22 | (−0.36, 0.36, 0.1) | (−0.31, 0.23, 0.09) | 0.14 |
| 24 | (−0.80, 0.36, 0.1) | (−0.89, 0.47, 0.09) | 0.14 |
| 26 | (−1.24, 0.36, 0.1) | (−1.50, 0.29, 0.10) | 0.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Sun, J.; Qiu, M.; Wu, X. An Underwater Passive Electric Field Positioning Method Based on Scalar Potential. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1832. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12121832
Zhang Y, Chen C, Sun J, Qiu M, Wu X. An Underwater Passive Electric Field Positioning Method Based on Scalar Potential. Mathematics. 2024; 12(12):1832. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12121832
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yi, Cong Chen, Jiaqing Sun, Mingjie Qiu, and Xu Wu. 2024. "An Underwater Passive Electric Field Positioning Method Based on Scalar Potential" Mathematics 12, no. 12: 1832. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12121832
APA StyleZhang, Y., Chen, C., Sun, J., Qiu, M., & Wu, X. (2024). An Underwater Passive Electric Field Positioning Method Based on Scalar Potential. Mathematics, 12(12), 1832. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12121832






