A p-Refinement Method Based on a Library of Transition Elements for 3D Finite Element Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. p-Refinement Procedure
- 1.
- Creating a set of following Equation (1), and sorting from lowest to the highest;
- 2.
- For each element associated with the sorted , :
- determining all the adjacent elements for ;
- For each adjacent element, obtaining the interelement boundary order;
- If the order of the element boundary > the order of :
- Renaming the node number of to match the interelement boundary;
- Refining the element following the protocol.
2.2. Formulation of Transition Elements
3. Results
3.1. Transition Elements
- Nodal coordinates;
- Shape functions;
- Integration quadrature.
3.2. Verification
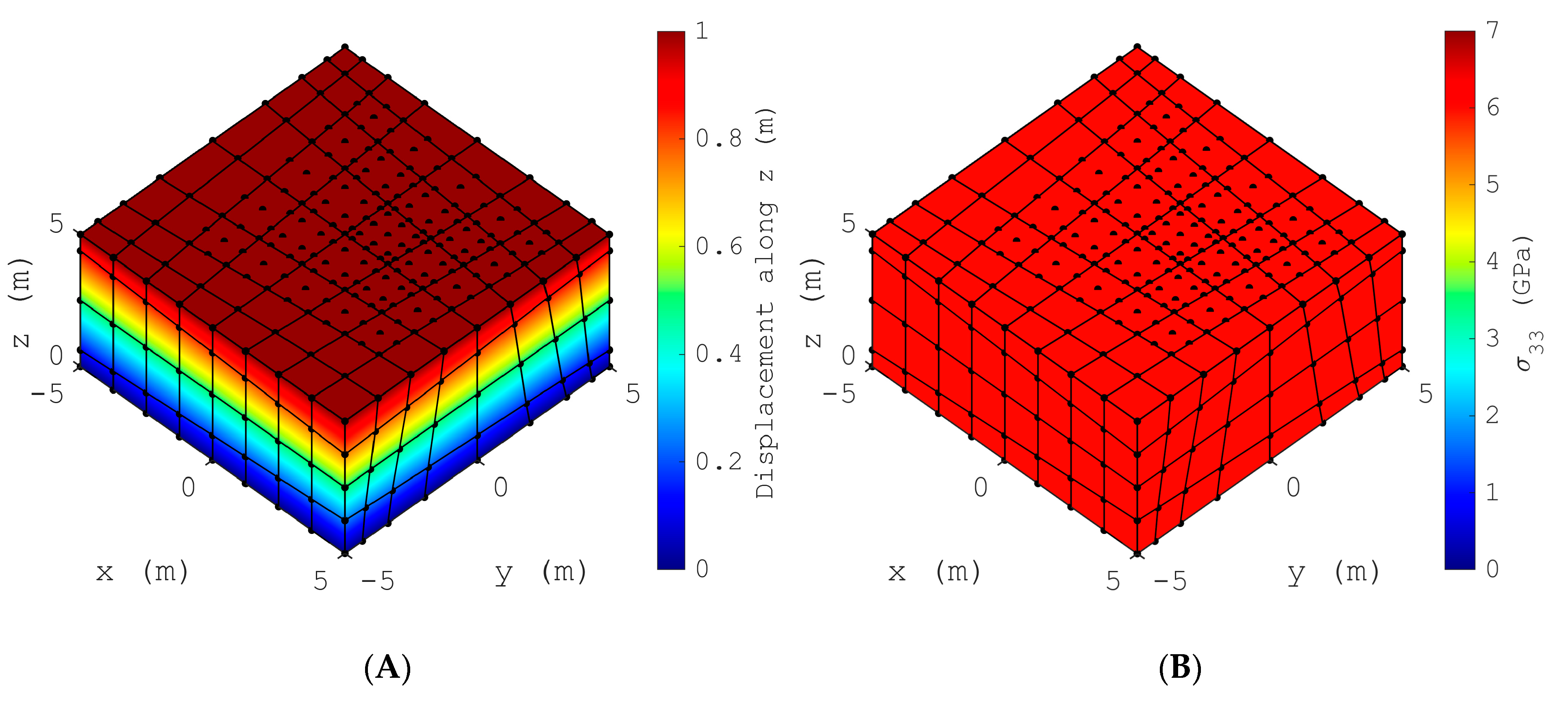
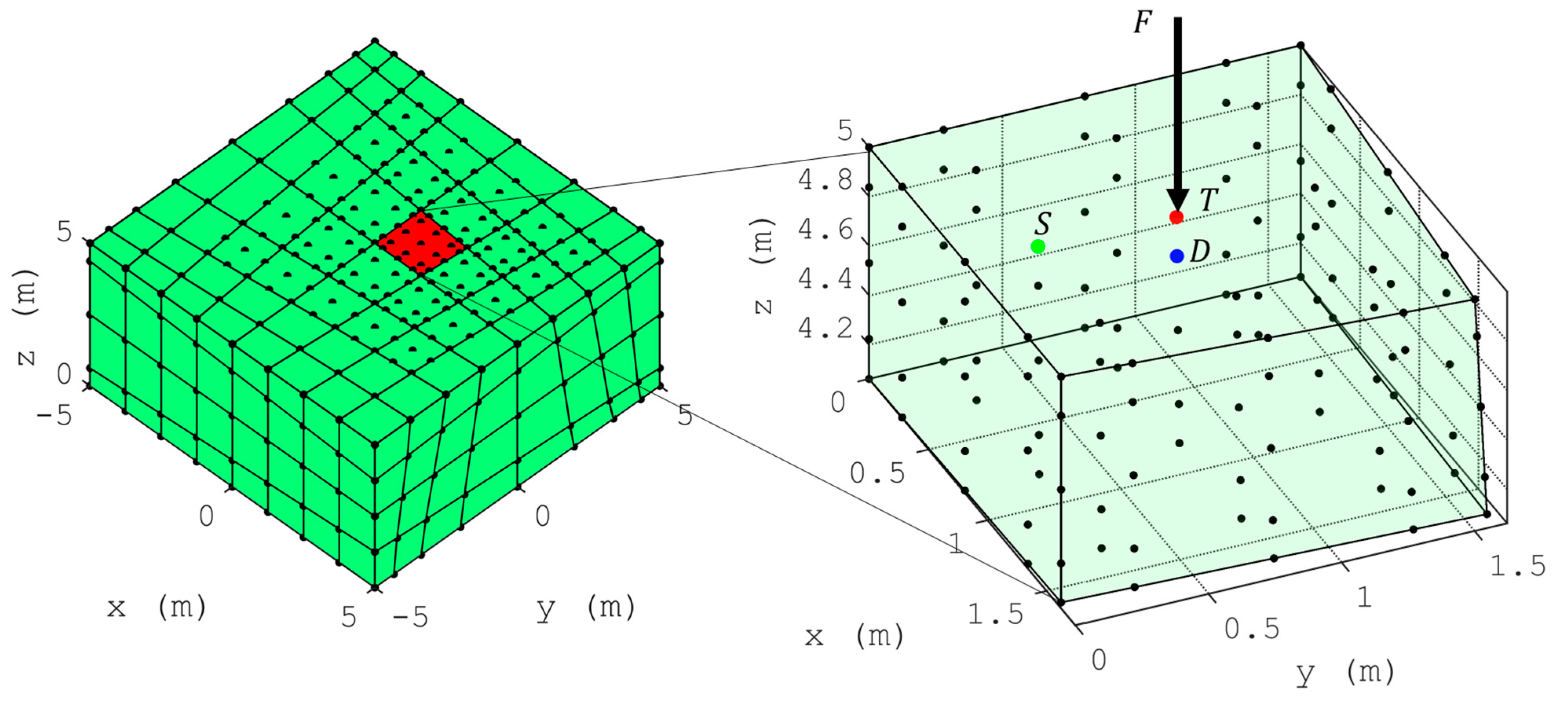
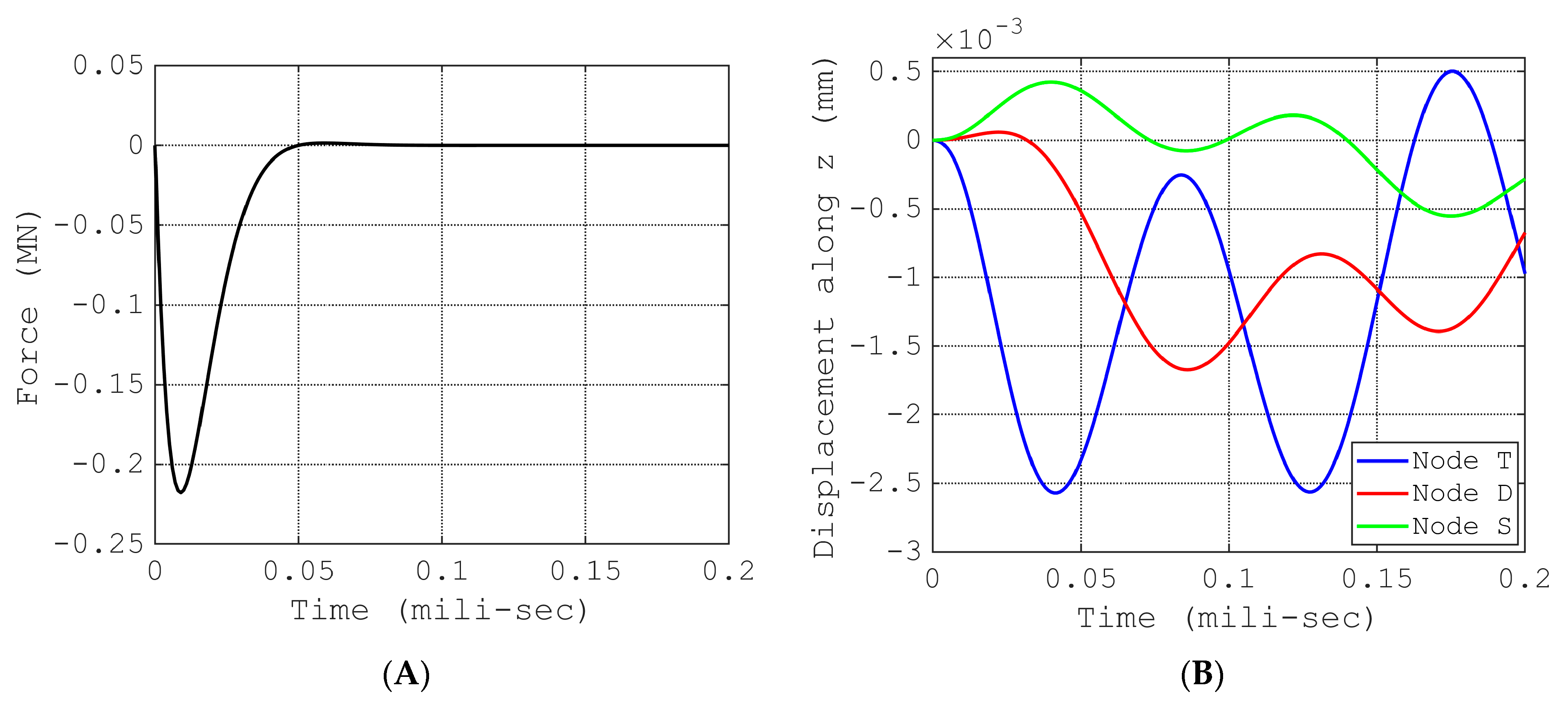
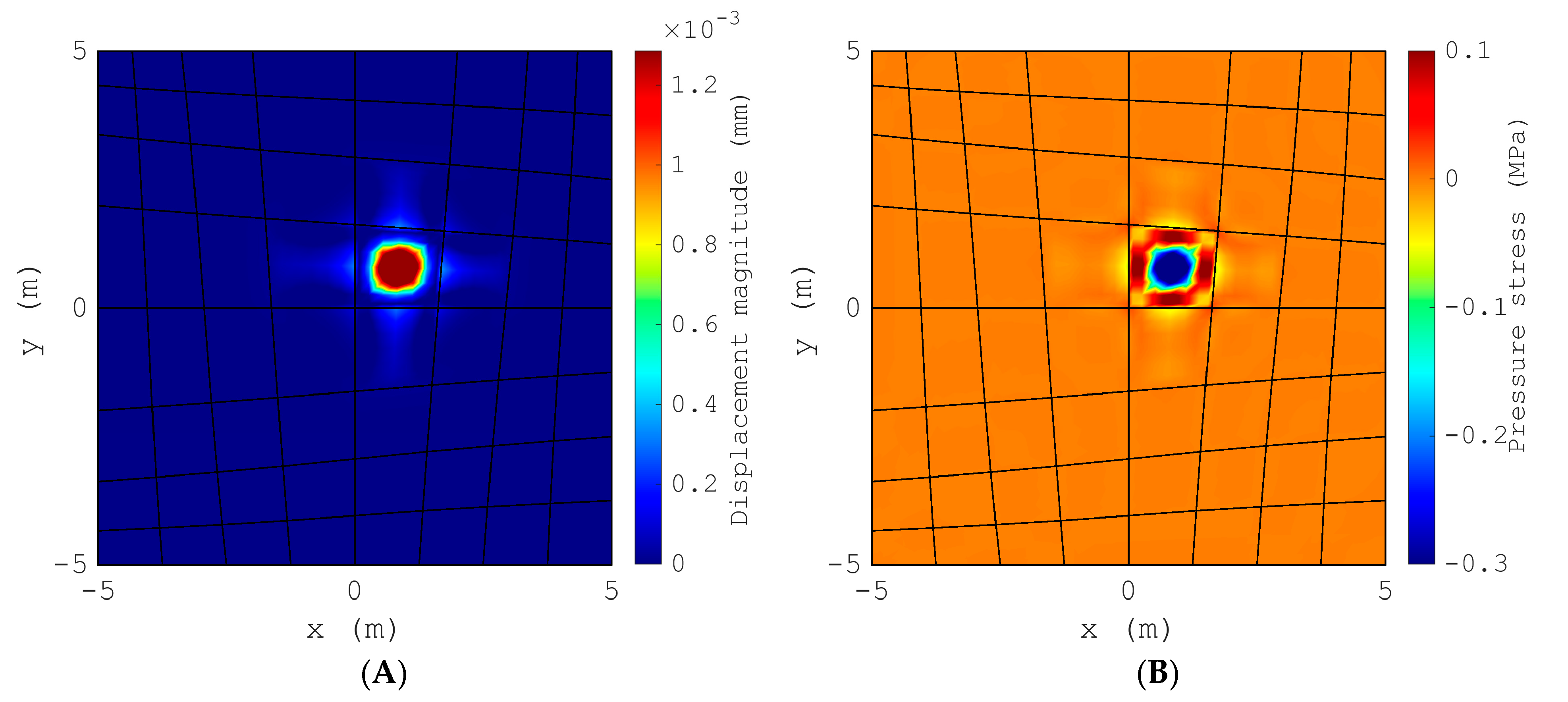
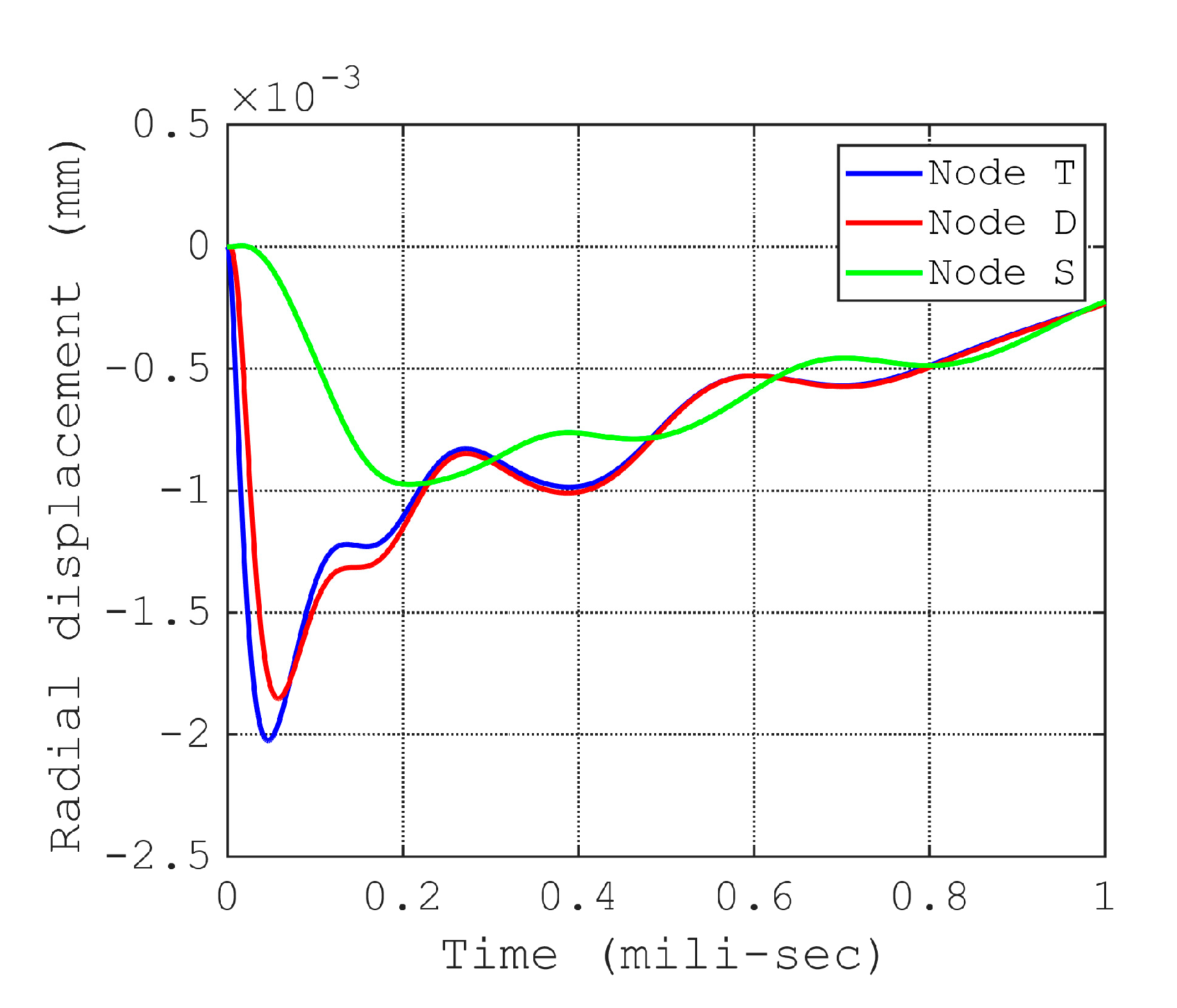
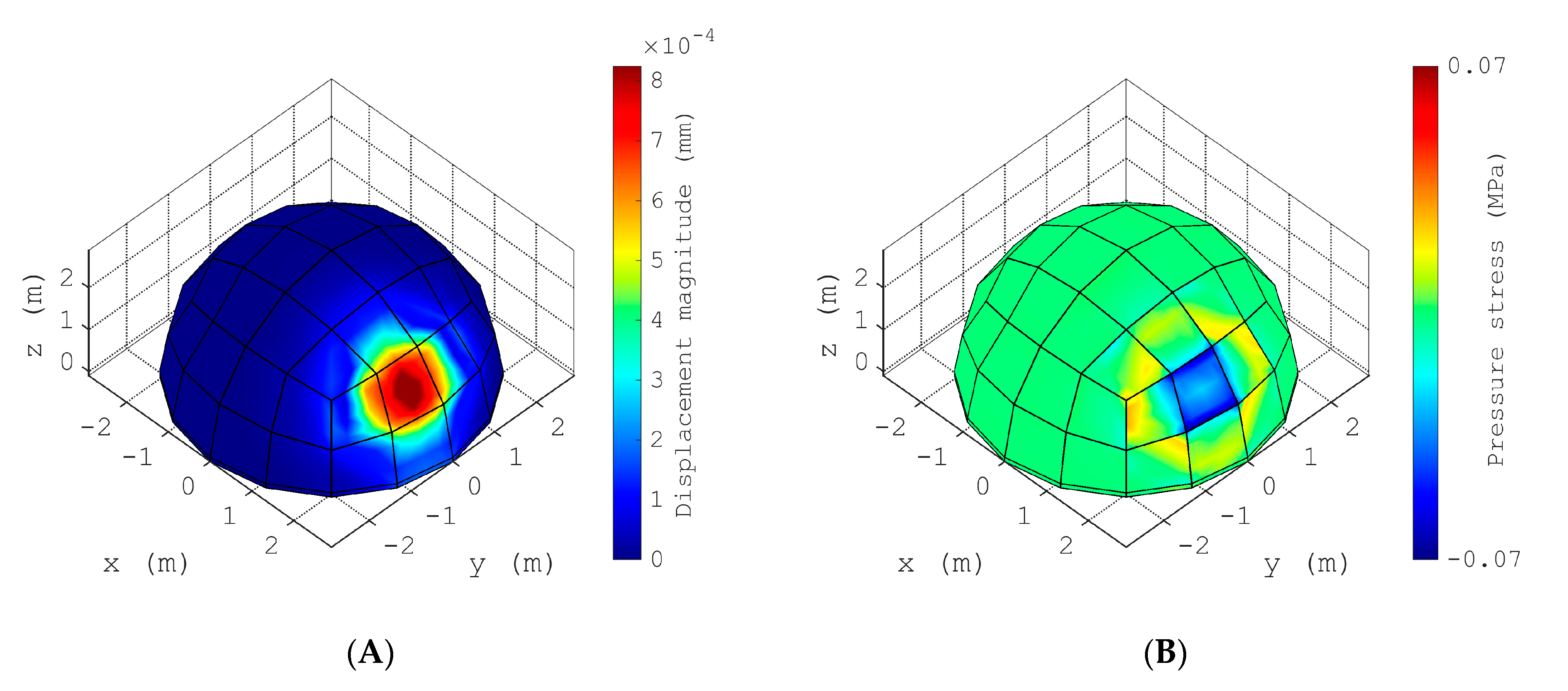
3.3. Implementation of 3D FE Meshes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Node No. | x | y | z |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 |
| 2 | 1 | −1 | −1 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | −1 |
| 4 | 1 | −1 | −1 |
| 5 | −1 | −1 | 1 |
| 6 | 1 | −1 | 1 |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 8 | 1 | −1 | 1 |
| 9 | 0 | −1 | 1 |
| 10 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 11 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 12 | −1 | 0 | 1 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Integration Point No. | Weight | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | |
| 2 | 1 | −1 | −1 | |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | −1 | |
| 4 | −1 | 1 | −1 | |
| 5 | −1 | −1 | 1 | |
| 6 | 1 | −1 | 1 | |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 8 | −1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 9 | 0 | −1 | −1 | |
| 10 | 1 | 0 | −1 | |
| 11 | 0 | 1 | −1 | |
| 12 | −1 | 0 | −1 | |
| 13 | 0 | −1 | 1 | |
| 14 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 15 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 16 | −1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| 18 | 0 | 0 | −1 |
References
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Taylor, R.L.; Zhu, J.Z. The Finite Element Method: Its Basis and Fundamentals; Butterworth Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunting, C.F. Introduction to the finite element method. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility—EMC 2008, Detroit, MI, USA, 18–22 August 2008; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bathe, K.-J. Discontinuous Finite Element Procedures; Springer: London, UK, 2006; pp. 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihlenburg, F.; Babuška, I. Finite element solution of the Helmholtz equation with high wave number part I: The h-version of the FEM. Comput. Math. Appl. 1995, 30, 9–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuska, I.M.; Sauter, S.A. Is the pollution effect of the FEM avoidable for the Helmholtz equation considering high wave numbers? SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 1997, 34, 2392–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccouch, M.; Temimi, H. A high-order space–time ultra-weak discontinuous Galerkin method for the second-order wave equation in one space dimension. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2021, 389, 113331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, K.; Chan, J.; de Hoop, M.V.; Jaiswal, P. A weight-adjusted discontinuous Galerkin method for the poroelastic wave equation: Penalty fluxes and micro-heterogeneities. J. Comput. Phys. 2020, 403, 109061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatitsch, D.; Tromp, J. Spectral-element simulations of global seismic wave propagation-I. Validation. Geophys. J. Int. 2002, 149, 390–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuto, C.; Hussaini, M.Y.; Quarteroni, A.; Zang, T.A. Spectral Approximation. In Spectral Methods in Fluid Dynamics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988; pp. 31–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacz, M.; Krawczuk, M.; Żak, A. Spectral Element Methods for Damage Detection and Condition Monitoring. In Advances in Asset Management and Condition Monitoring; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 549–558. [Google Scholar]
- Ostachowicz, W.; Kudela, P.; Krawczuk, M.; Zak, A. Guided Waves in Structures for SHM: The Time-Domain Spectral Element Method; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patera, A.T. A spectral element method for fluid dynamics: Laminar flow in a channel expansion. J. Comput. Phys. 1984, 54, 468–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihlenburg, F.; Babuska, I. Finite element solution of the helmholtz equation with high wave number part II: The h-p version of the FEM. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 1997, 34, 315–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.-H. P-Refinement Techniques for Vector finite Elements in Electromagnetics. Ph.D. Thesis, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Salazar-Palma, M. Iterative and Self-Adaptive Finite-Elements in Electromagnetic Modeling; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Shahriar, A.; Majlesi, A.; Montoya, A. A General procedure to formulate 3D elements for finite element applications. Computation 2023, 11, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staten, M.L.; Jones, N.L. Local refinement of three-dimensional finite element meshes. Eng. Comput. 1997, 13, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, D.J.; Tyler, J.M.; Dorroh, J.R. A new 3D finite element for adaptive h-refinement in 1-irregular meshes. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1995, 38, 3989–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, W.J.; Hall, C.A. Transfinite element methods: Blending-function interpolation over arbitrary curved element domains. Numer. Math. 1973, 21, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, W.J. Blending-Function Methods of Bivariate and Multivariate Interpolation and Approximation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 1971, 8, 158–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenbach, J.; Scholz, E. Ableitung von Formfunktionen für finite Standard-und Übergangselemente auf der Grundlage der gemischten Interpolation. Tech. Mech. -Eur. J. Eng. Mech. 1987, 8, 18–30. [Google Scholar]
- Duczek, S.; Saputra, A.; Gravenkamp, H. High order transition elements: The xy-element concept—Part I: Statics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020, 362, 112833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Im, S. A new computational approach to contact mechanics using variable-node finite elements. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2008, 73, 1966–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczkowski, R. 21-node hexahedral isoparametric element for analysis of contact problems. Commun. Numer. Methods Eng. 1998, 14, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, I.M.; Kidger, D.J. Elastoplastic analysis using the 14-node brick element family. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1992, 35, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soman, R.; Kudela, P.; Balasubramaniam, K.; Singh, S.K.; Malinowski, P. A study of sensor placement optimization problem for guided wave-based damage detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Winckel, G. Legende-Gauss-Lobatto Nodes and Weights; MathWorks: Natick, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 20. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, D.N.; Awanou, G. The serendipity family of finite elements. Found. Comput. Math. 2011, 11, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, M.; Salon, S. Numerical Methods in Electromagnetism; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; ISBN 9780126157604. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, R.L.; Simo, J.C.; Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Chan, A.C.H. The patch test—A condition for assessing FEM convergence. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1986, 22, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irons, B.M.; Razzaque, A. Experience with the patch test for convergence of finite elements. In The Mathematical Foundations of the Finite Element Method with Applications to Partial Differential Equations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1972; pp. 557–587. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, M.A.; Mansur, M.A.; Paramasivam, P. Correlations between mechanical properties of high-strength concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2002, 14, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, S.; Shahriar, A.; Montoya, A.; Malla, R.B. A finite element approach for simplified 2D nonlinear dynamic contact/impact analysis. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2023, 93, 3511–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shi, C.; Liu, Z.; Wen, D. Theoretical research progress in high-velocity/hypervelocity impact on semi-infinite targets. Shock Vib. 2015, 2015, 265321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfurt, K.J. Accuracy of finite-difference and finite-element modeling of the scalar and elastic wave equations. Geophysics 1984, 49, 533–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

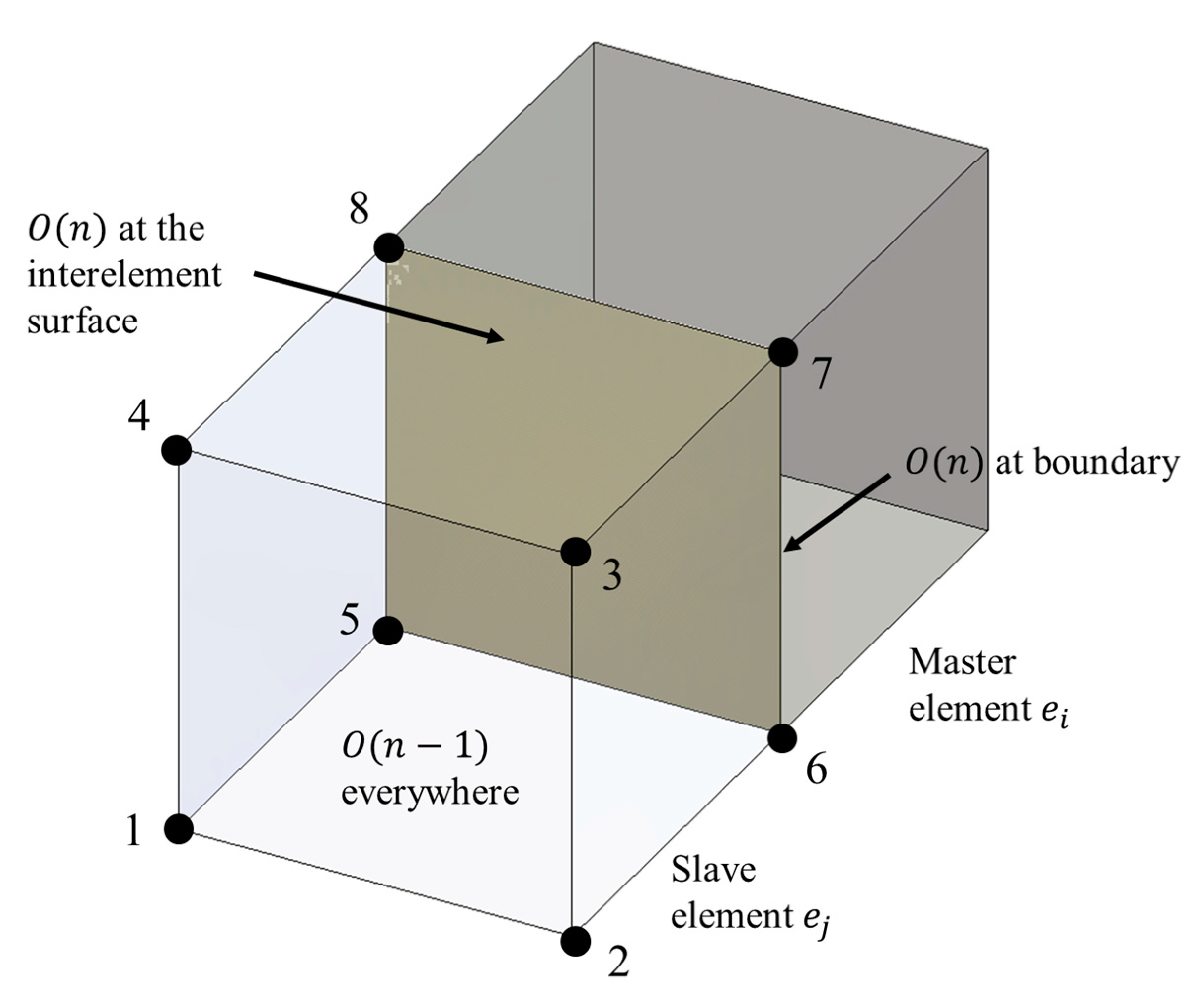
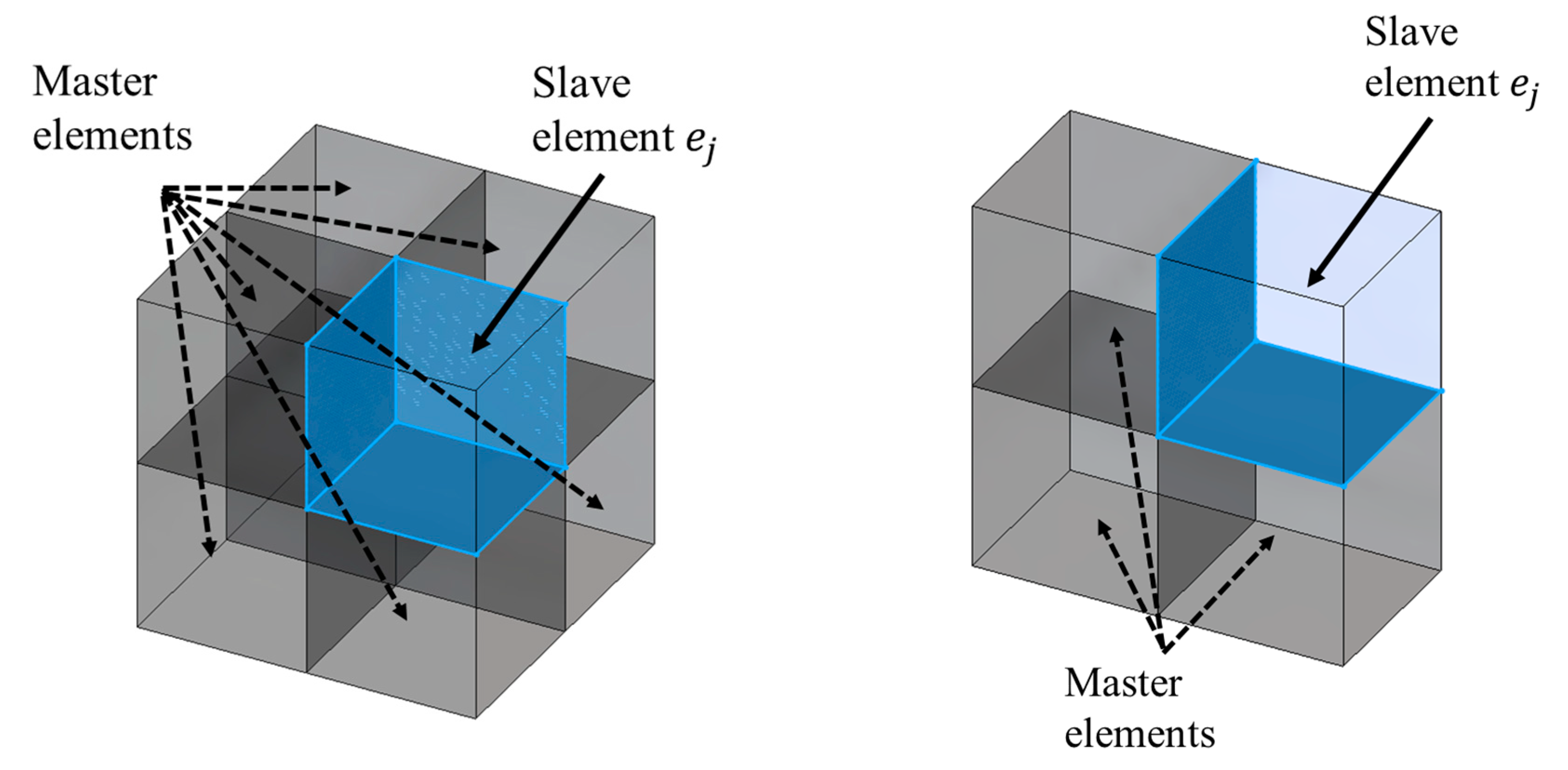
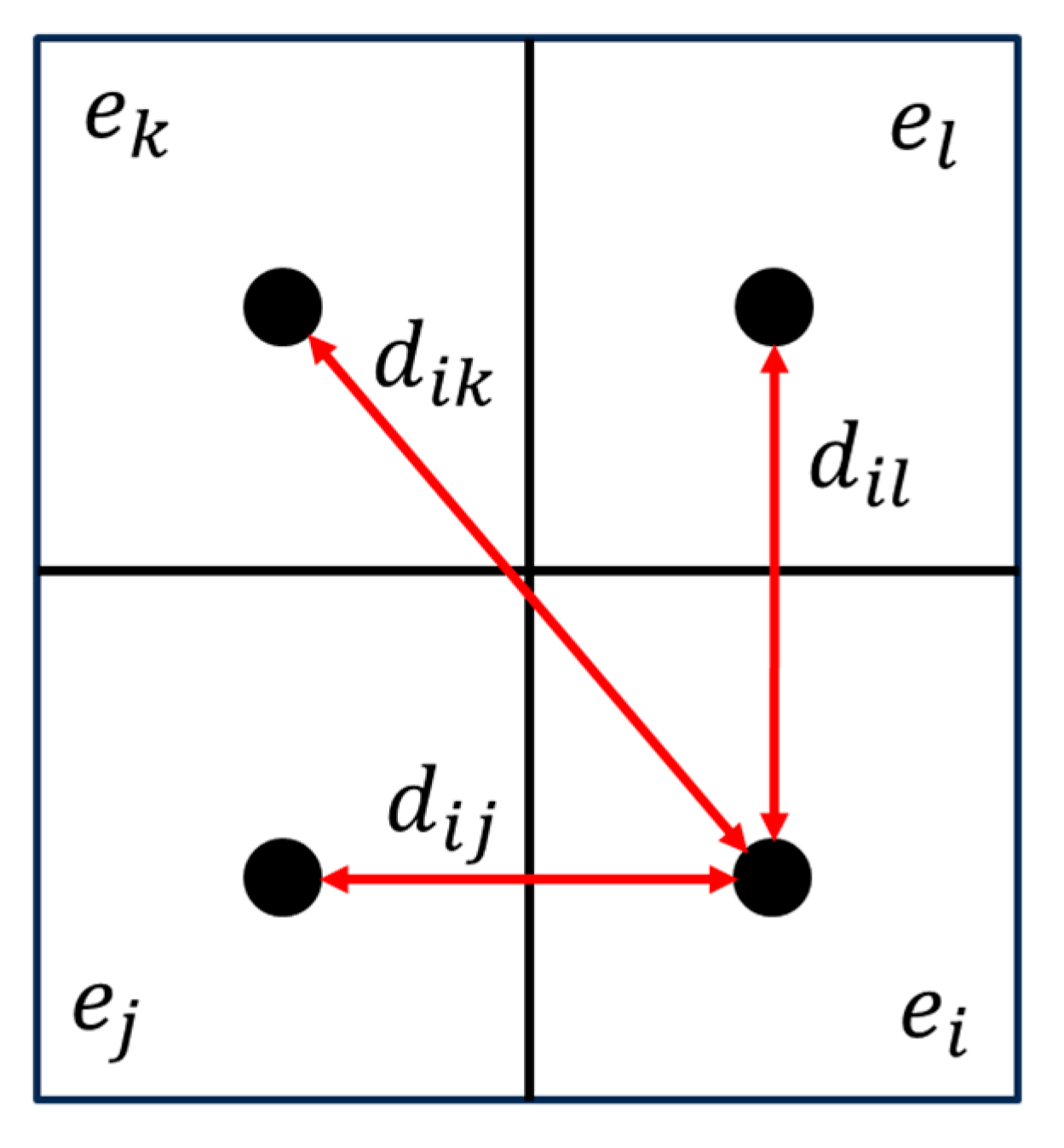
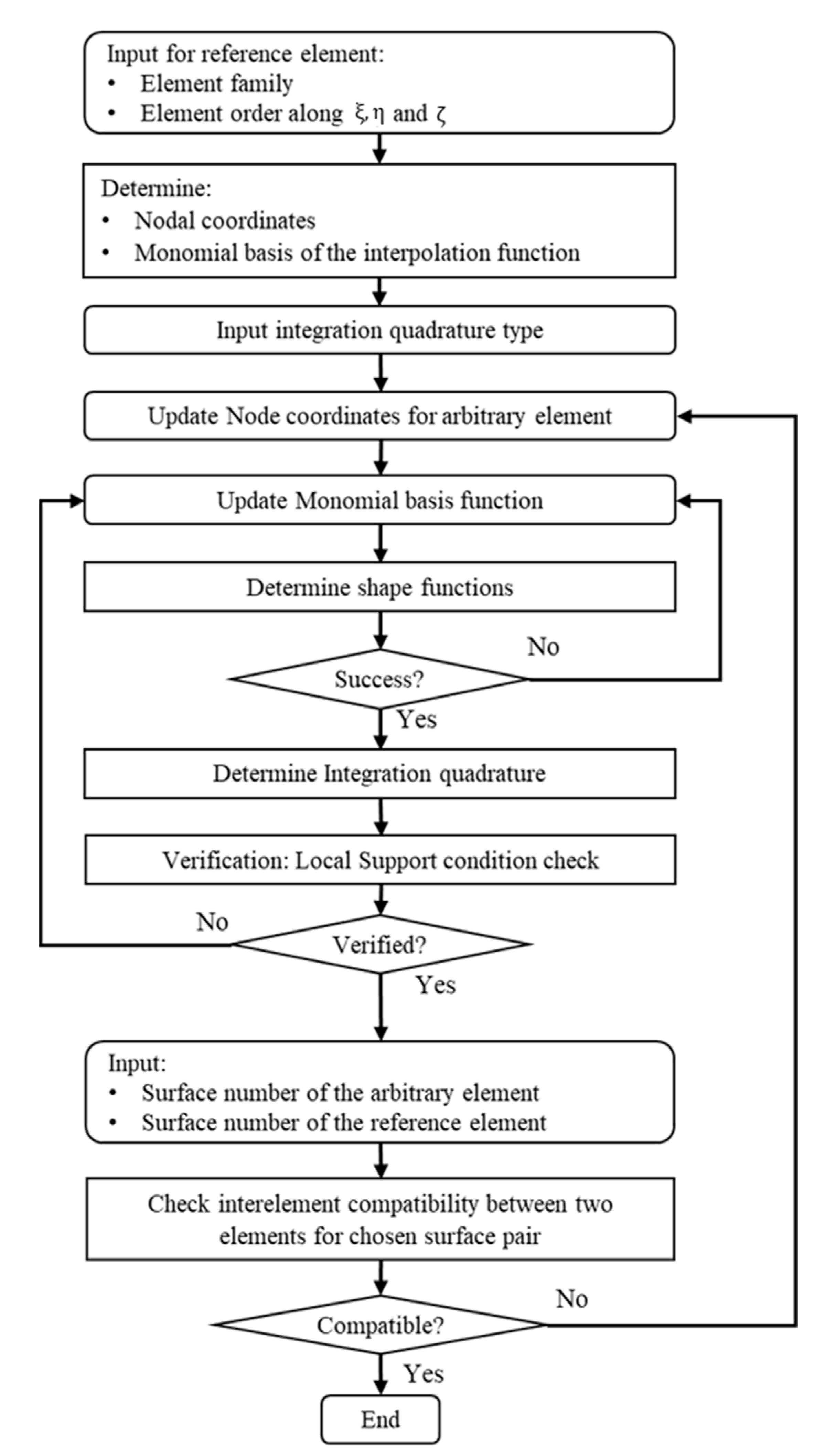

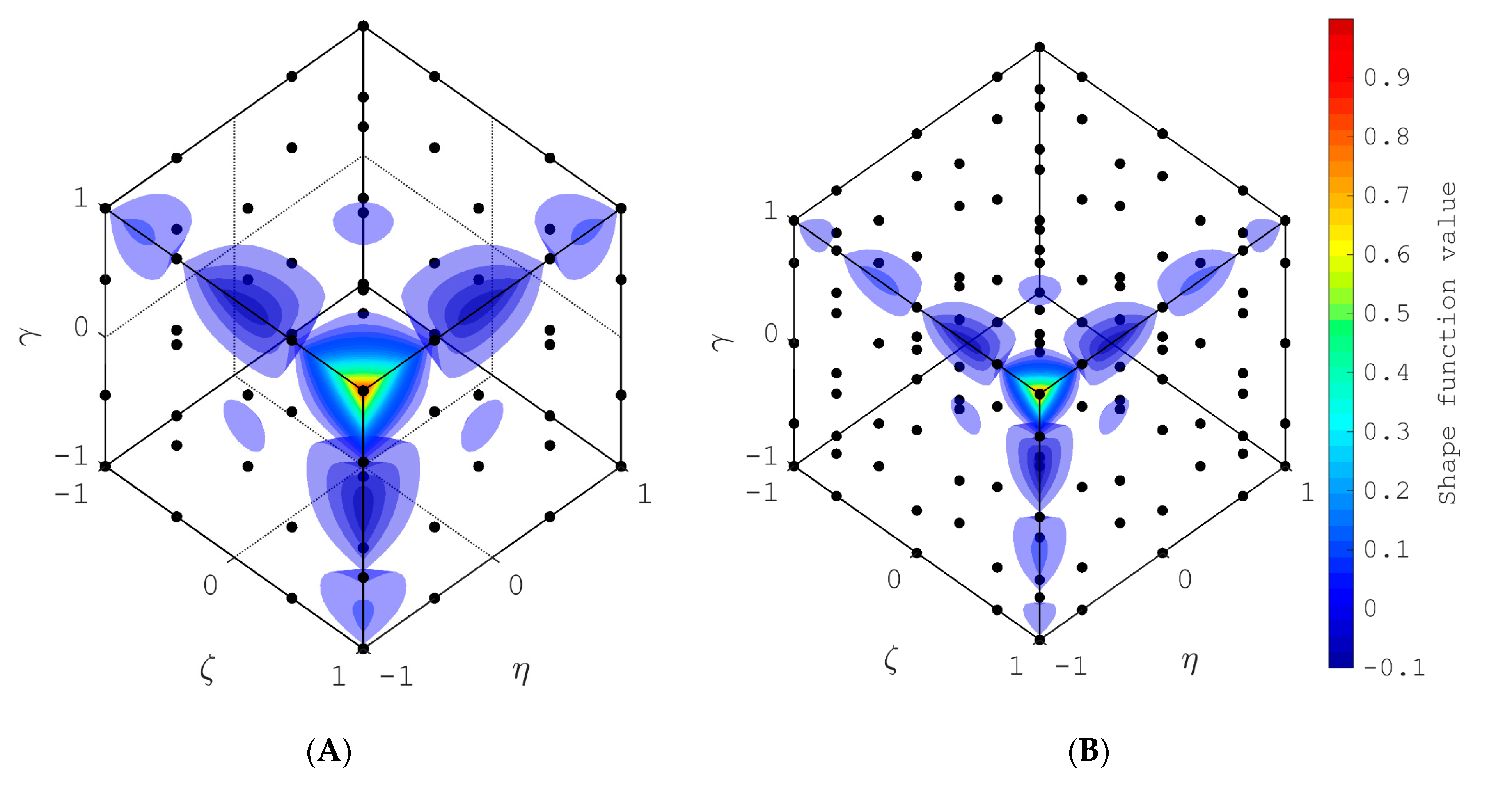
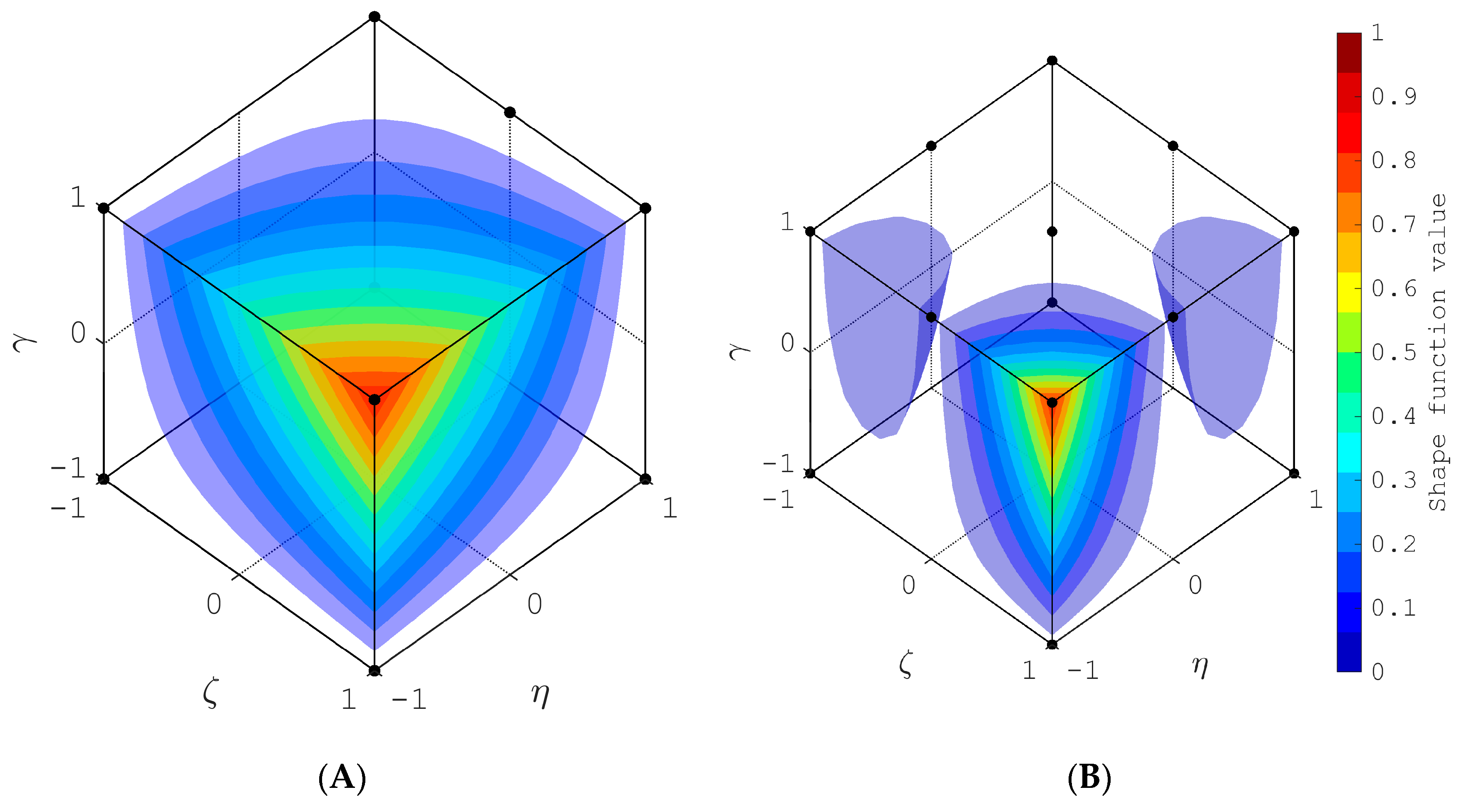
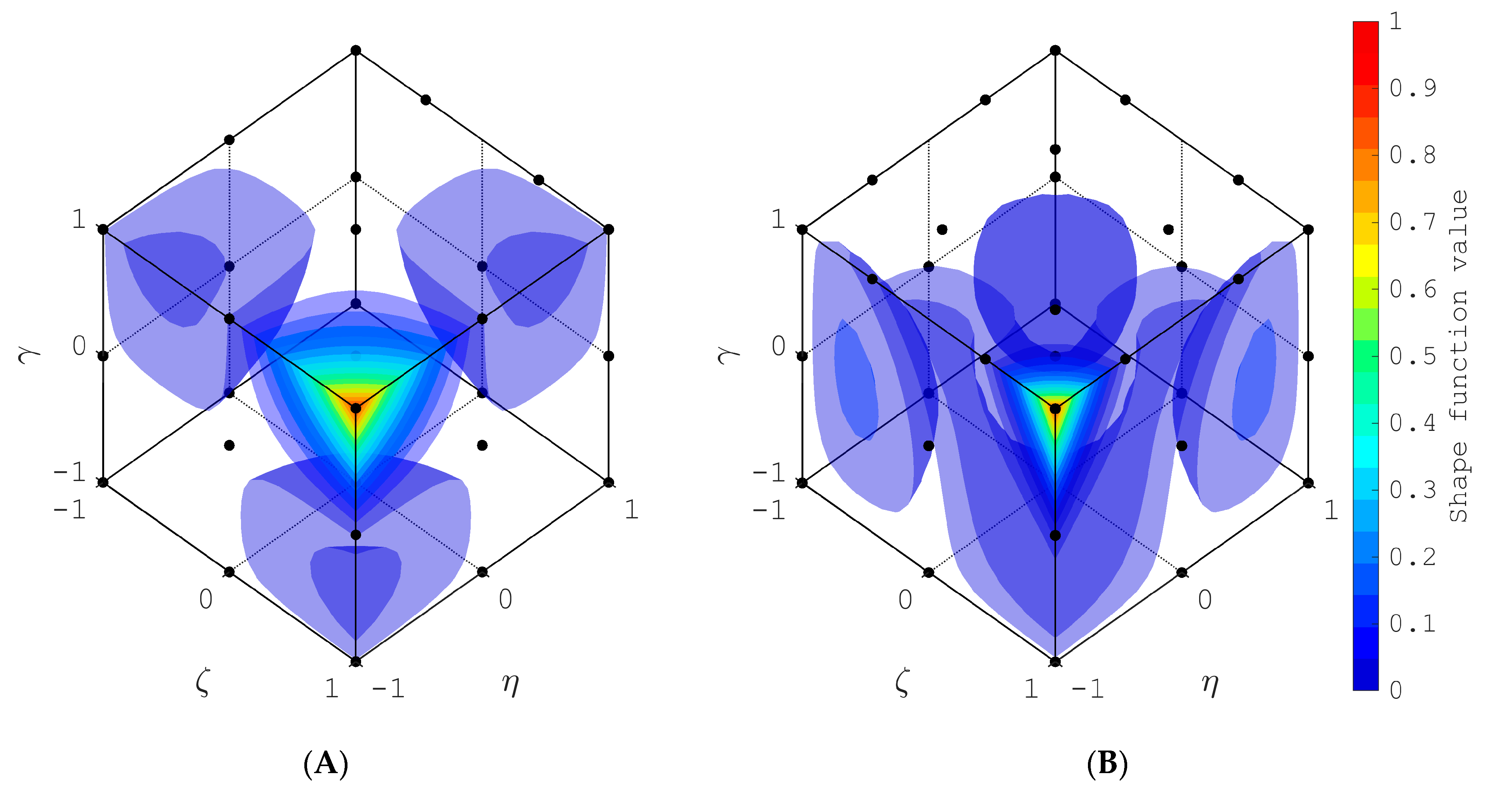
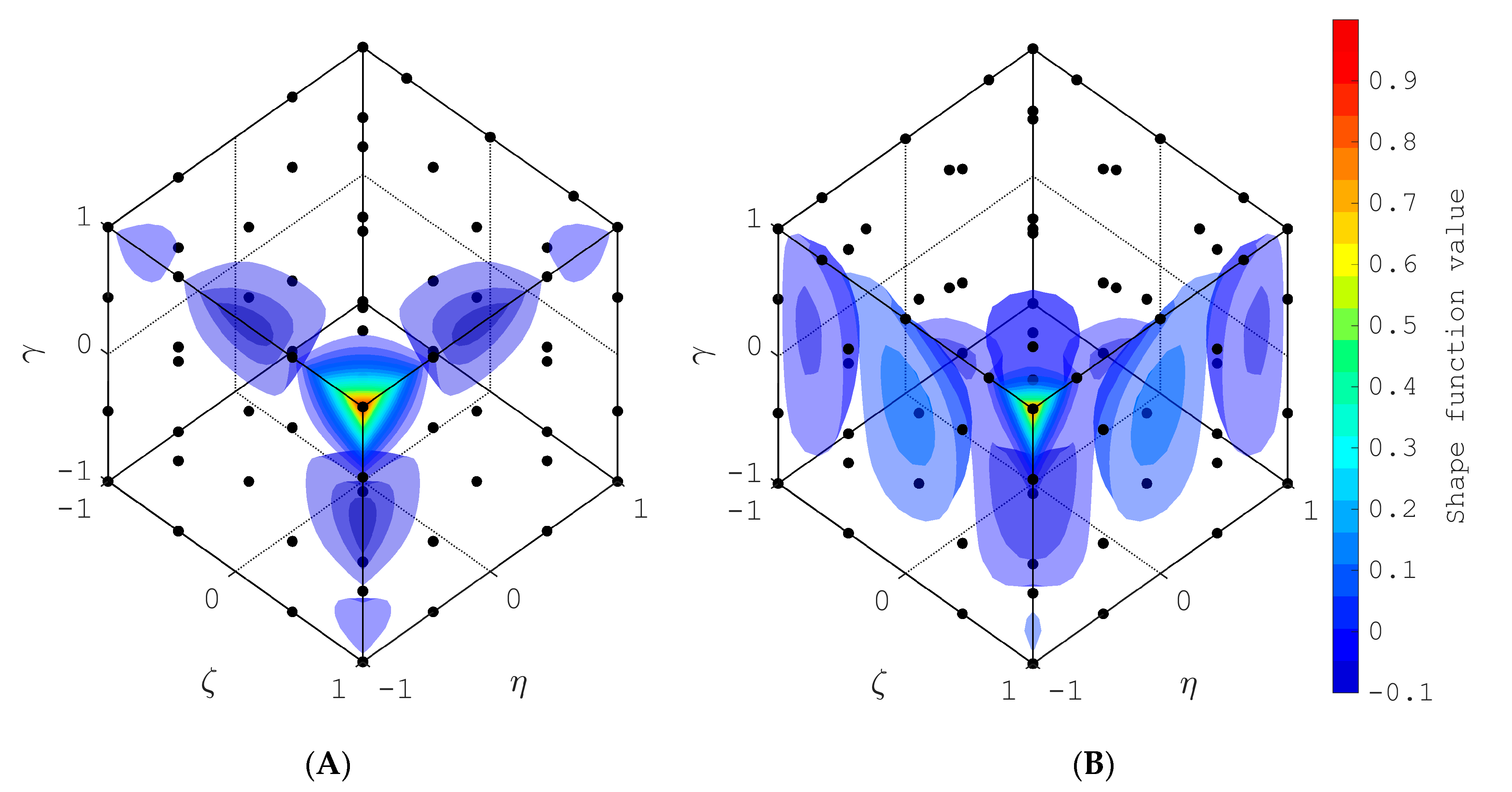



| Element Description | Figure Number | Number of Nodes | Source File Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fourth-order element | Figure 7B | 125 | Fourth_order.txt |
| Fourth-to-third-order transition element for case 1 | Figure 10A | 65 | Transition_4to3_Case1.txt |
| Fourth-to-third-order transition element for case 2 | Figure 10B | 73 | Transition_4to3_Case2.txt |
| Third-order element | Figure 7A | 64 | Third_order.txt |
| Third-to-second-order transition element for case 1 | Figure 9A | 28 | Transition_3to2_Case1.txt |
| Third-to-second-order transition element for case 2 | Figure 9B | 34 | Transition_3to2_Case2.txt |
| Second-order element | Figure 6A | 27 | Second_order.txt |
| Second-to-first-order transition element for case 1 | Figure 8A | 9 | Transition_2to1_Case1.txt |
| Second-to-first-order transition element for case 2 | Figure 8B | 13 | Transition_2to1_Case2.txt |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahriar, A.; Mostafa, A.J. A p-Refinement Method Based on a Library of Transition Elements for 3D Finite Element Applications. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4954. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11244954
Shahriar A, Mostafa AJ. A p-Refinement Method Based on a Library of Transition Elements for 3D Finite Element Applications. Mathematics. 2023; 11(24):4954. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11244954
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahriar, Adnan, and Ahmed Jenan Mostafa. 2023. "A p-Refinement Method Based on a Library of Transition Elements for 3D Finite Element Applications" Mathematics 11, no. 24: 4954. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11244954
APA StyleShahriar, A., & Mostafa, A. J. (2023). A p-Refinement Method Based on a Library of Transition Elements for 3D Finite Element Applications. Mathematics, 11(24), 4954. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11244954




