Survival Analysis of a Predator–Prey Model with Seasonal Migration of Prey Populations between Breeding and Non-Breeding Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
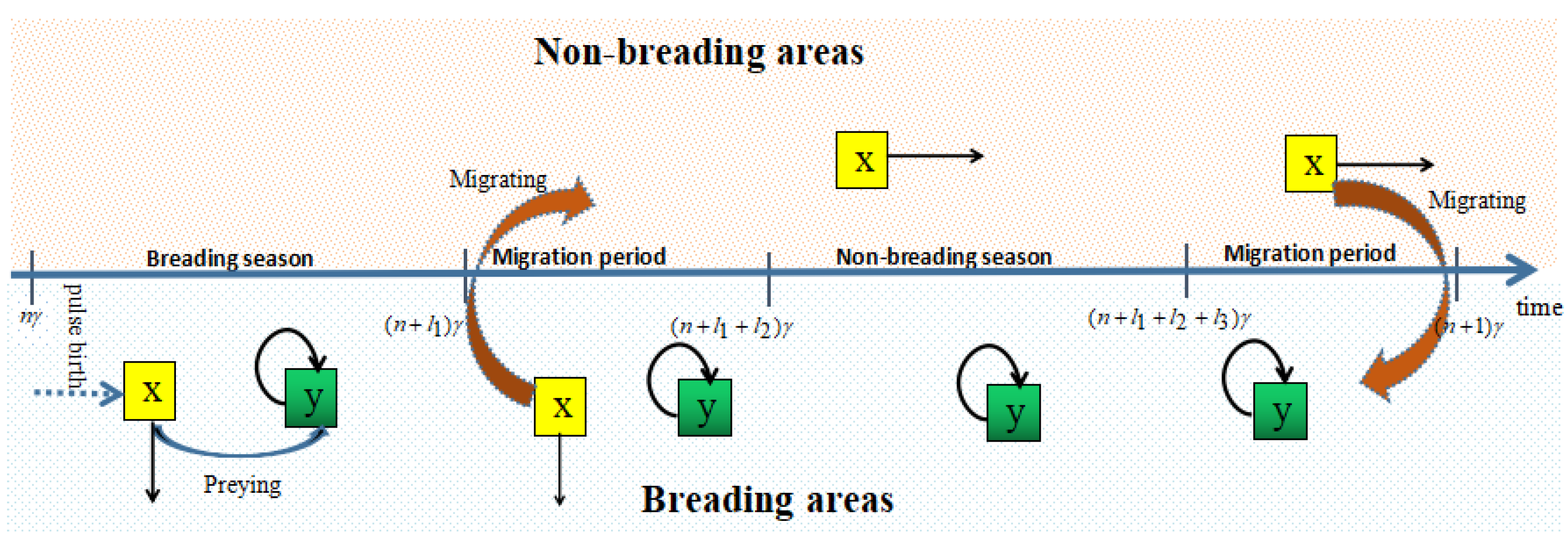
2. Model Formulation
3. Preliminaries
4. Main Results
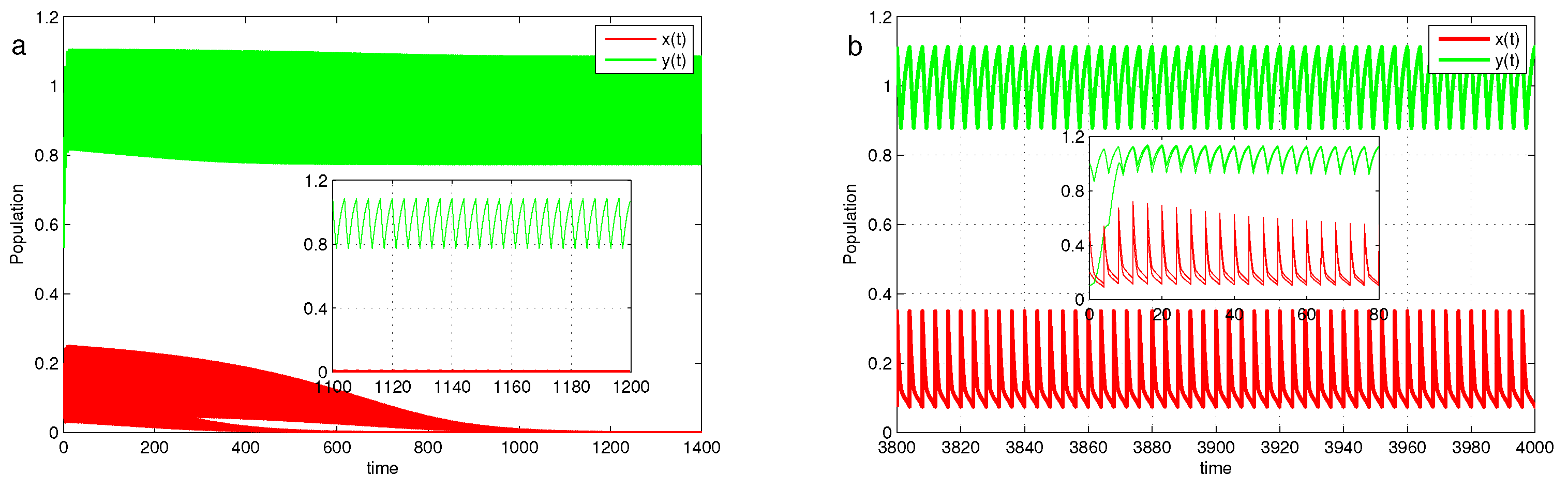
4.1. Stability of Prey-Extinction Periodic Solution
4.2. Permanence
5. Numerical Simulations
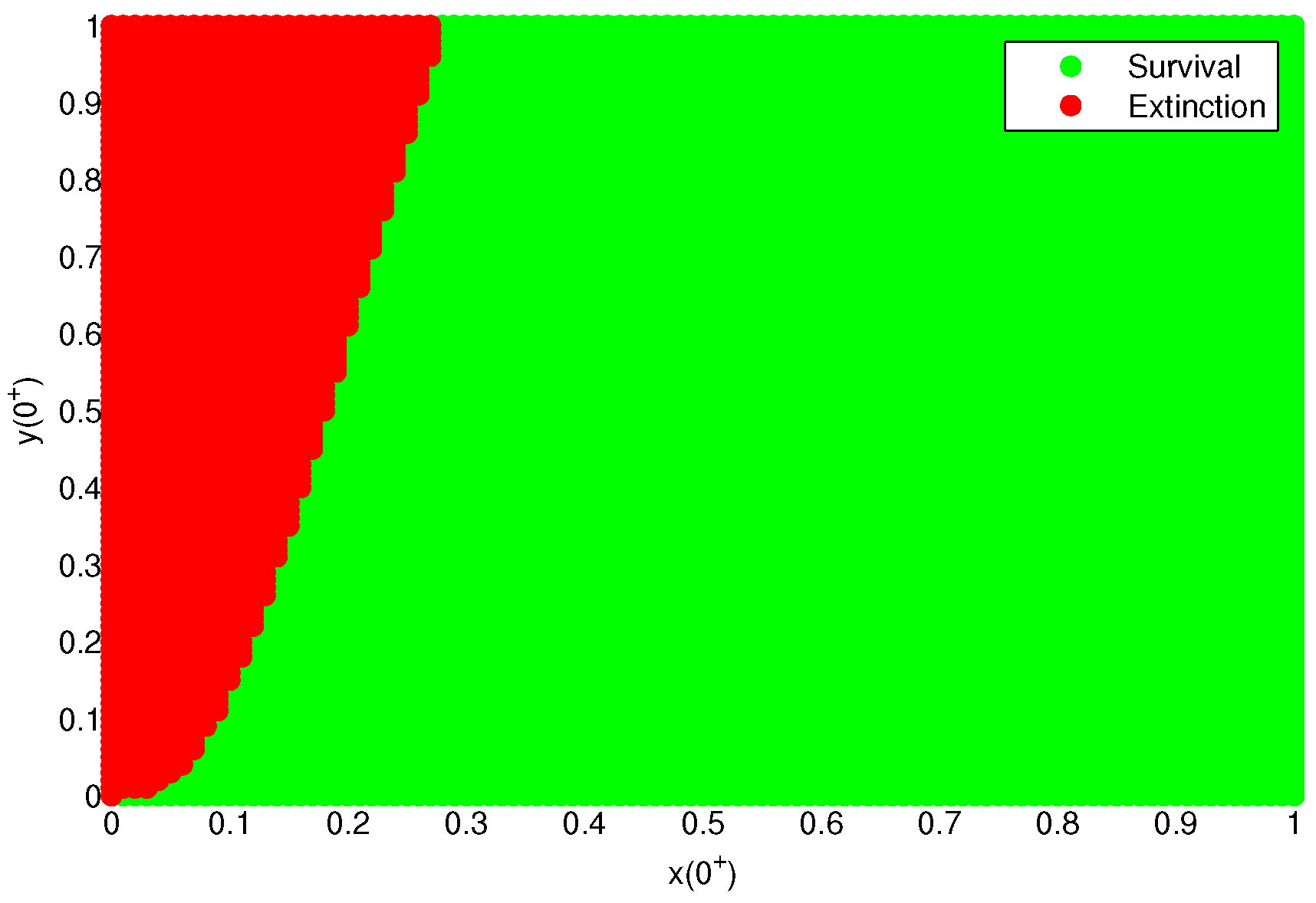
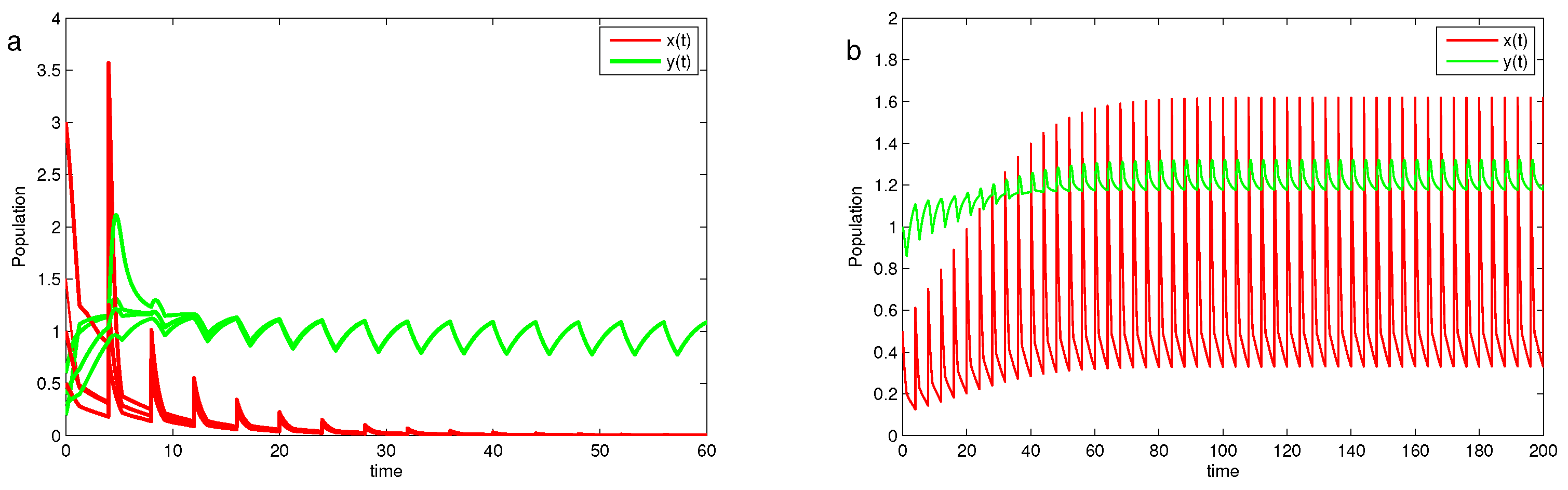
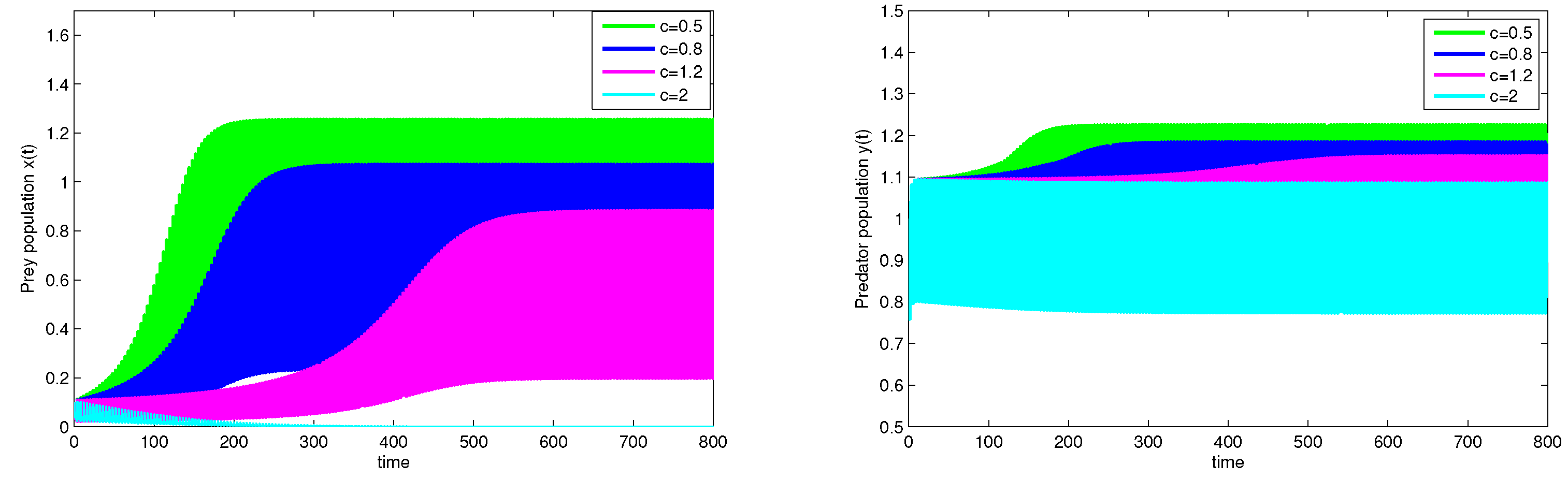
5.1. The Role of the Refuge Effect
5.2. The Role of the Fear Effect
5.3. The Dynamic Behaviors of System (20)
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dingle, H. Migration: The Biology of Life on the Move, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, R.A.; Wikelski, M.; Wilcove, D.S. How and why do insects migrate? Science 2006, 313, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrish, B.B. Fish Migration. Nature 1968, 220, 1008–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, L.M.; Talbot, M.H. The wildebeest in western masailand, east africa. Wildl. Monogr. 1963, 12, 3–88. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, L.J.S. Persistence and extinction in single-species reaction-diffusion models. Bull. Math. Biol. 1983, 45, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.S.; Murray, J.D. A generalized diffusion model for growth and dispersal in a population. J. Math. Biol. 1981, 12, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.Z.; Chen, L.S.; Chen, J.F. Persistence and periodic orbits for two-species nonautonomous diffusion lotka-volterra models. Math. Comput. Model. 1994, 20, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Takeuchi, Y.; Lin, Z. Permanence and extinction for dispersal population systems. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2004, 298, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Lu, Q.; Yang, Z. The effect of diffusion on the permanence of Smith population model in a polluted patch. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 2001, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takigawa, S. A predator–prey diffusion model in age-dependent population dynamics. Hiroshima Math. J. 1989, 19, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, H.I. Single species migration in two habitats: Persistence and extinction. Math. Model. 1987, 8, 778–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Gao, S. Analysis of a nonautonomous Gompertz population growth model with dispersal in a polluted environment. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 2012, 39, 459–472. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.; Wang, K. A robustness analysis of biological population models with protection zone. Appl. Math. Model. 2011, 35, 5553–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovaskainen, O.; Meerson, B. Stochastic models of population extinction. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, L.; Jiang, D.; O’egan, D. Stochastic permanence, stationary distribution and extinction of a single-species nonlinear diffusion system with random perturbation. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2014, 2014, 320460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Fan, D.; Wang, K. Effects of dispersal for a logistic growth population in random environments. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2013, 2013, 912579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, M. Can protection zone potentially strengthen protective effects in random environments ? Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 231, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Wang, K. Dynamical properties of a biological population with a protected area under ecological uncertainty. Appl. Math. Model. 2015, 39, 6273–6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.Y.; Wang, C.J. Survival analysis of a single-species population model with fluctuations and migrations between patches. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 81, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Deng, M.; Du, B. Analysis of a stochastic logistic model with diffusion. Appl. Math. Comput. 2015, 266, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.Y.; Chen, L.H. Psychological effect on single-species population models in a polluted environment. Math. Biosci. 2017, 290, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Wang, S.; Xiong, W. Survival analysis of a stochastic delay single-species system in polluted environment with psychological effect and pulse toxicant input. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2020, 2020, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggriani, N.; Panigoro, H.; Rahmi, E.; Peter, O.J.; Jose, S.A. A predator–prey model with additive Allee effect and intraspecific competition on predator involving Atangana-Baleanu-Caputo derivative. Results Phys. 2023, 49, 106489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, D.; Ramachandran, R.; Alzabut, J.; Jose, S.A.; Khan, H. A fractional-order density-dependent mathematical model to find the better strain of wolbachia. Symmetry 2023, 15, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yang, Z. Dynamical behaviors of a stage-structured predator–prey model with harvesting effort and impulsive diffusion. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2015, 2015, 371852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Jing, H.; Cheng, L. Impulsive diffusion in single species model. Chaos Solitons Fract. 2007, 33, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Yang, X.; Cai, S.; Cheng, L. Dynamical analysis of a delayed predator–prey model with impulsive diffusion between two patches. Math. Comput. Simulat. 2010, 80, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Cai, S. Dynamics of a new delayed stage-structured predator–prey model with impulsive diffusion and releasing. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2016, 2016, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Teng, Z.; Zhang, L. Two patches impulsive diffusion periodic single-species logistic model. Int. J. Biomath. 2010, 3, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y. Analysis of a delayed predator–prey system with impulsive diffusion between two patches. Math. Comput. Model. 2010, 52, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, C. Permanence and periodic solutions for a two-patch impulsive migration periodic N-species Lotka-Volterra competitive system. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2015, 2015, 293050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhong, S.; Yin, C. Two-patches prey impulsive diffusion periodic predator–prey model. Commun. Nonlinear. Sci. 2011, 16, 2641–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Teng, Z. The dynamical behavior of a predator–prey system with Gompertz growth function and impulsive dispersal of prey between two patches. Math. Method. Appl. Sci. 2016, 39, 3623–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Jiang, H. Dynamical behaviors of a predator–prey system with prey impulsive diffusion and dispersal delay between two patches. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2019, 2019, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.A.; Ramachandran, R.; Cao, J.; Alzabut, J.; Niezabitowski, M.; Balas, V. Stability analysis and comparative study on different eco-epidemiological models: Stage structure for prey and predator concerning impulsive control. Optim. Control Appl. Meth. 2022, 43, 842–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, B. Animal Migration: Remarkable Journeys in the Wild; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, D.L.; Boersma, P.D.; Javier, L. Conservation of migratory Magellanic penguins requires marine zoning. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 170, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, A.E.; Levey, D.J.; Smith, K.G. Reflections across hemispheres: A system-wide approach to new world bird migration. Auk 2004, 121, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zanette, L.; Zou, X. Modelling the fear effect in predator–prey interactions. J. Math. Biol. 2016, 73, 1179–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasmal, S.K. Population dynamics with multiple allee effects induced by fear factors-a mathematical study on prey-predator interactions. Appl. Math. Model. 2018, 64, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zou, X. Modeling the fear effect in predator–prey interactions with adaptive avoidance of predators. Bull. Math. Biol. 2017, 79, 1325–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmikantham, V. Theory of Impulsive Differential Equations; World Scientific: Singapore, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, J.; Cai, S.; Li, L. Dynamics of a periodic switched predator–prey system with impulsive harvesting and hibernation of prey population. J. Frankl. Inst. 2016, 353, 3818–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, X.; Jiao, H.; Jiao, J.; Quan, Q. Survival Analysis of a Predator–Prey Model with Seasonal Migration of Prey Populations between Breeding and Non-Breeding Regions. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3838. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11183838
Dai X, Jiao H, Jiao J, Quan Q. Survival Analysis of a Predator–Prey Model with Seasonal Migration of Prey Populations between Breeding and Non-Breeding Regions. Mathematics. 2023; 11(18):3838. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11183838
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Xiangjun, Hui Jiao, Jianjun Jiao, and Qi Quan. 2023. "Survival Analysis of a Predator–Prey Model with Seasonal Migration of Prey Populations between Breeding and Non-Breeding Regions" Mathematics 11, no. 18: 3838. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11183838
APA StyleDai, X., Jiao, H., Jiao, J., & Quan, Q. (2023). Survival Analysis of a Predator–Prey Model with Seasonal Migration of Prey Populations between Breeding and Non-Breeding Regions. Mathematics, 11(18), 3838. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11183838




