Eulerian–Eulerian RSTM-PDF Modeling of Turbulent Particulate Flow
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Numerical Method and Assumptions
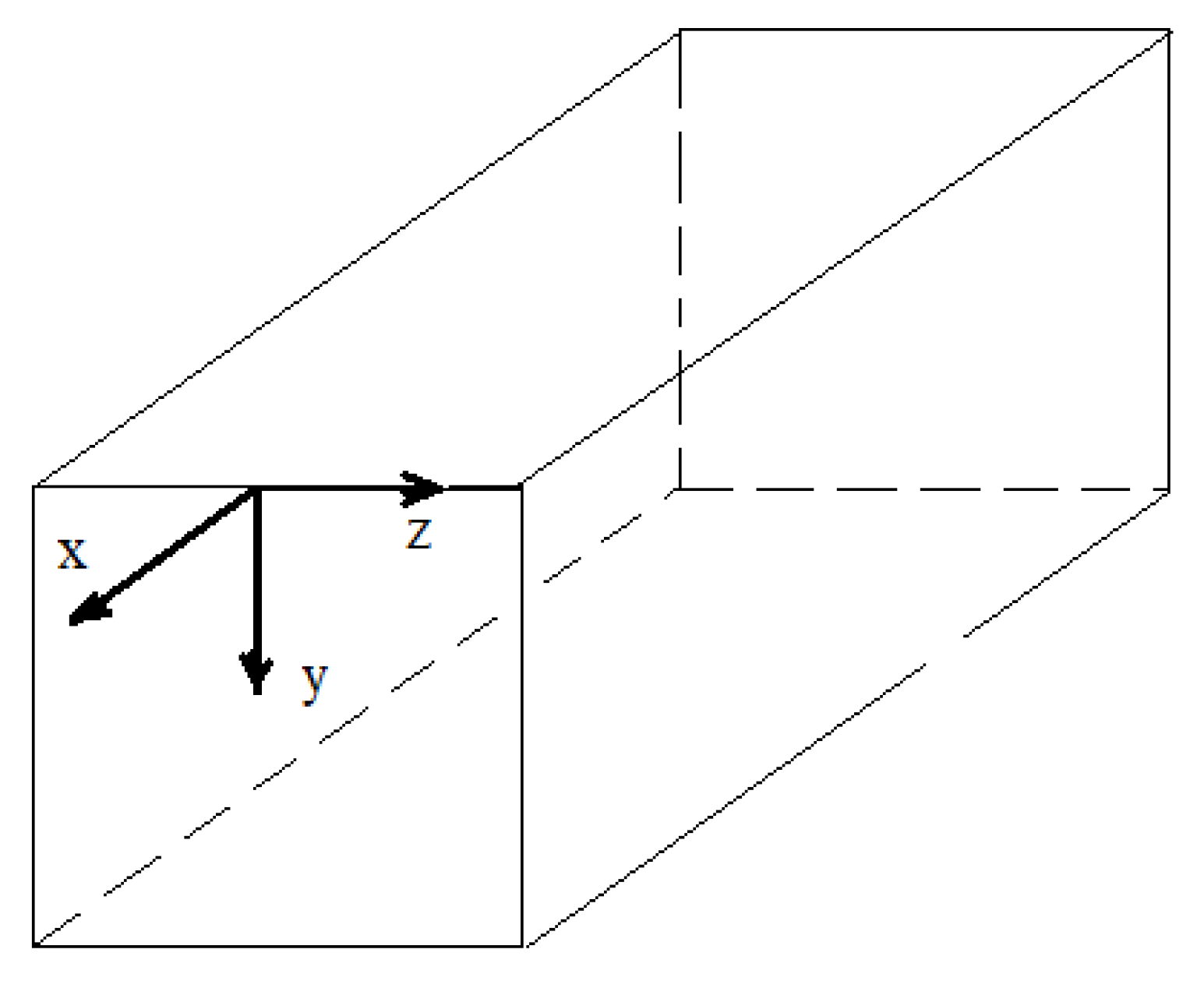
2.1. Scale of the Investigation
2.2. Computational Method
2.3. Governing Equations for the Carrier Fluid
2.4. Governing Equations for the Particulate Phase
2.5. Boundary Conditions
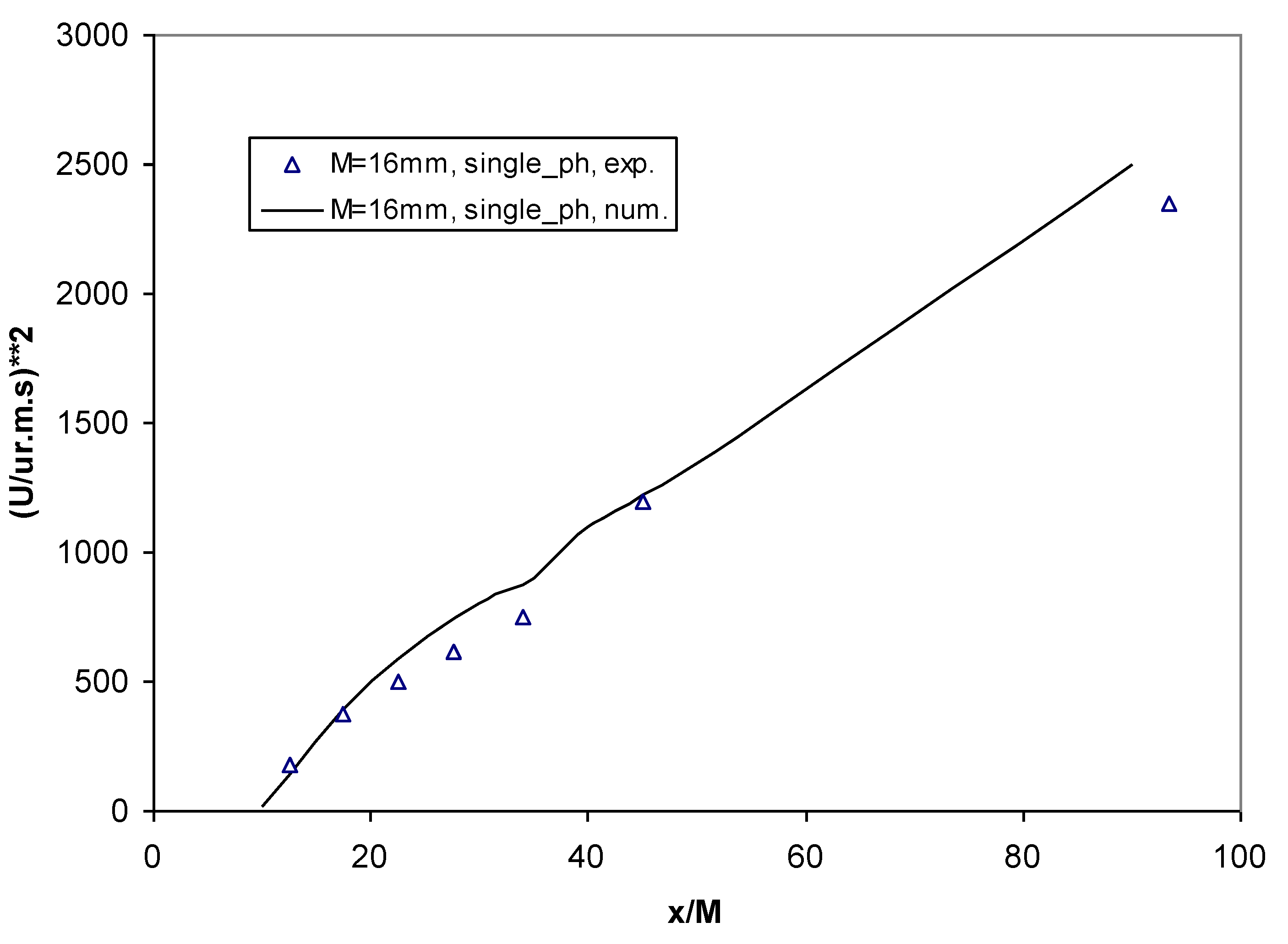
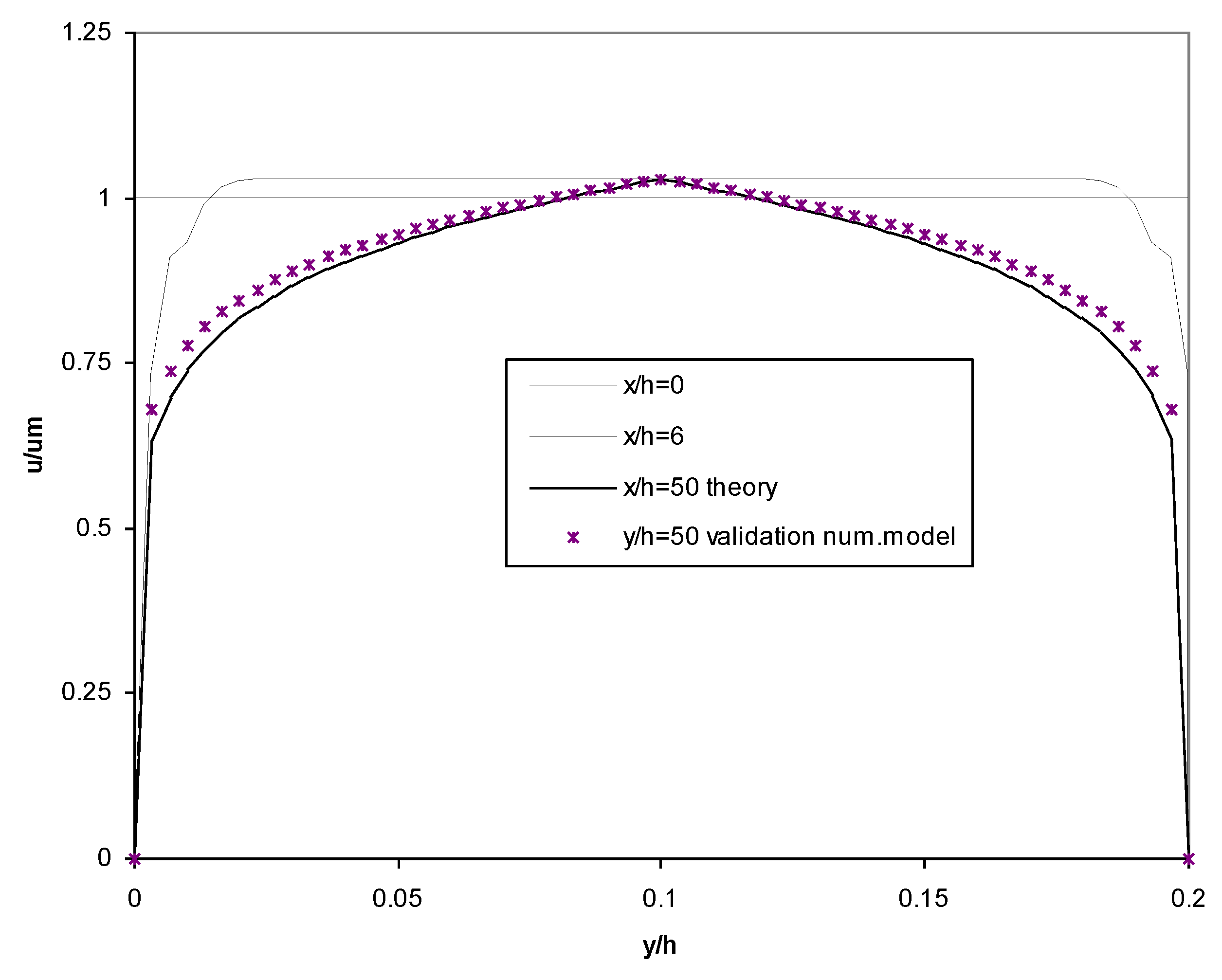
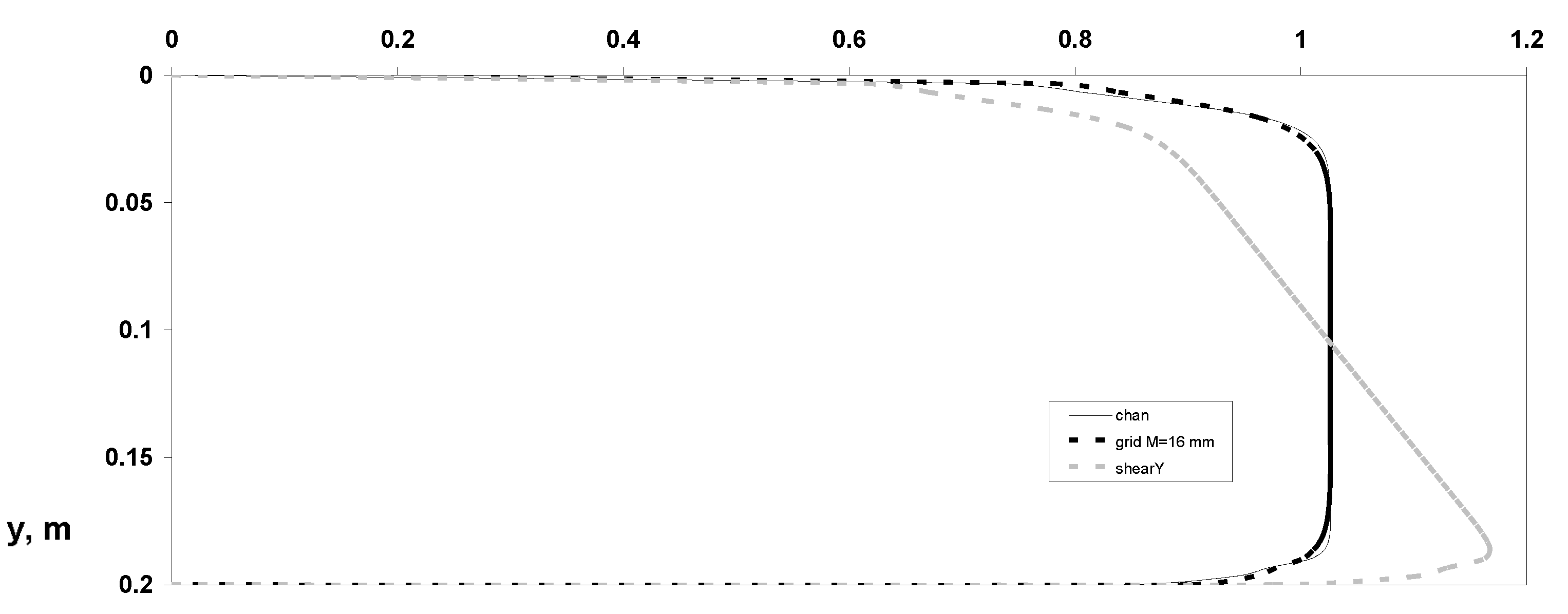
2.6. Validation
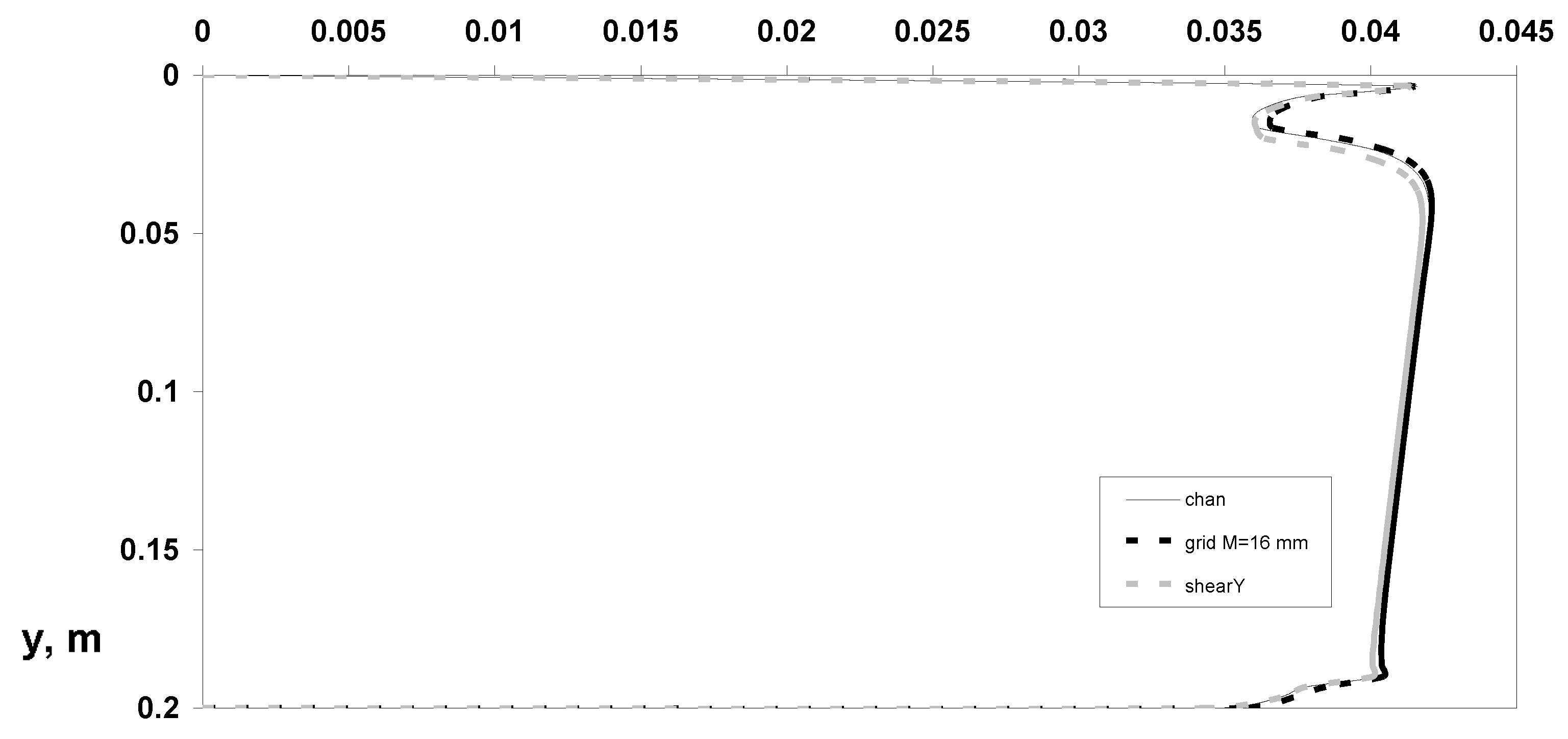
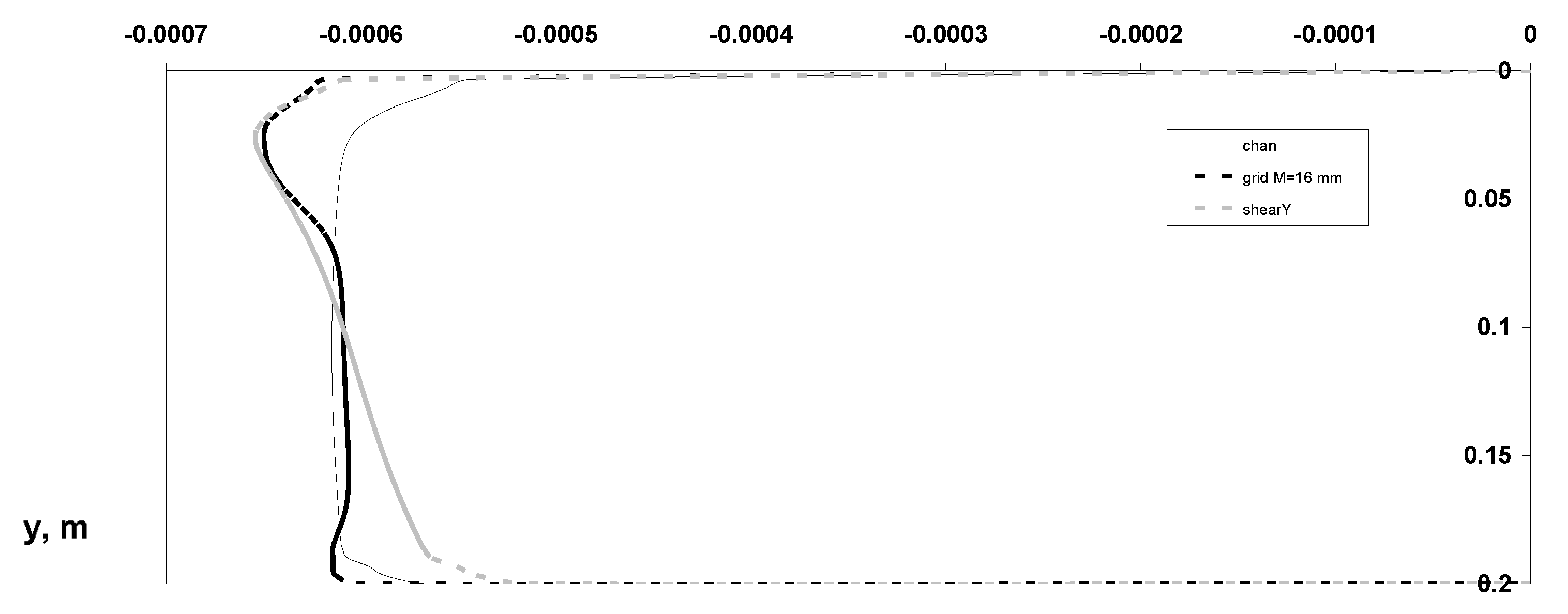
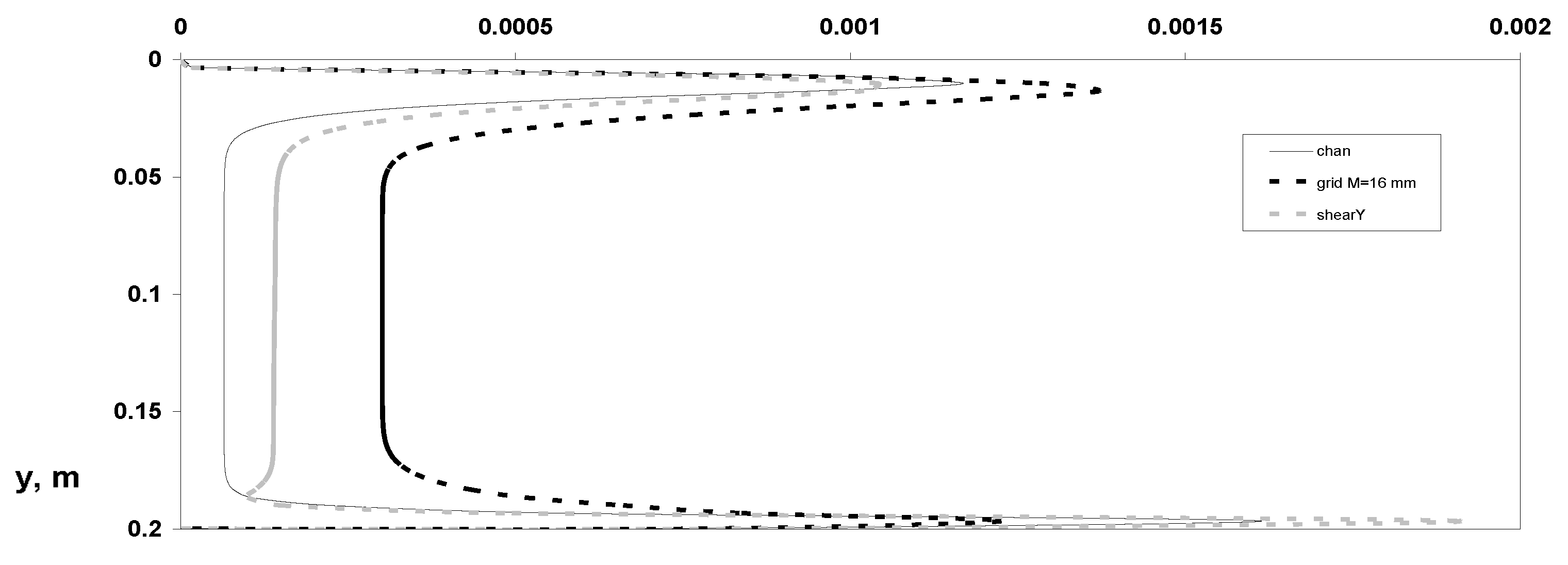
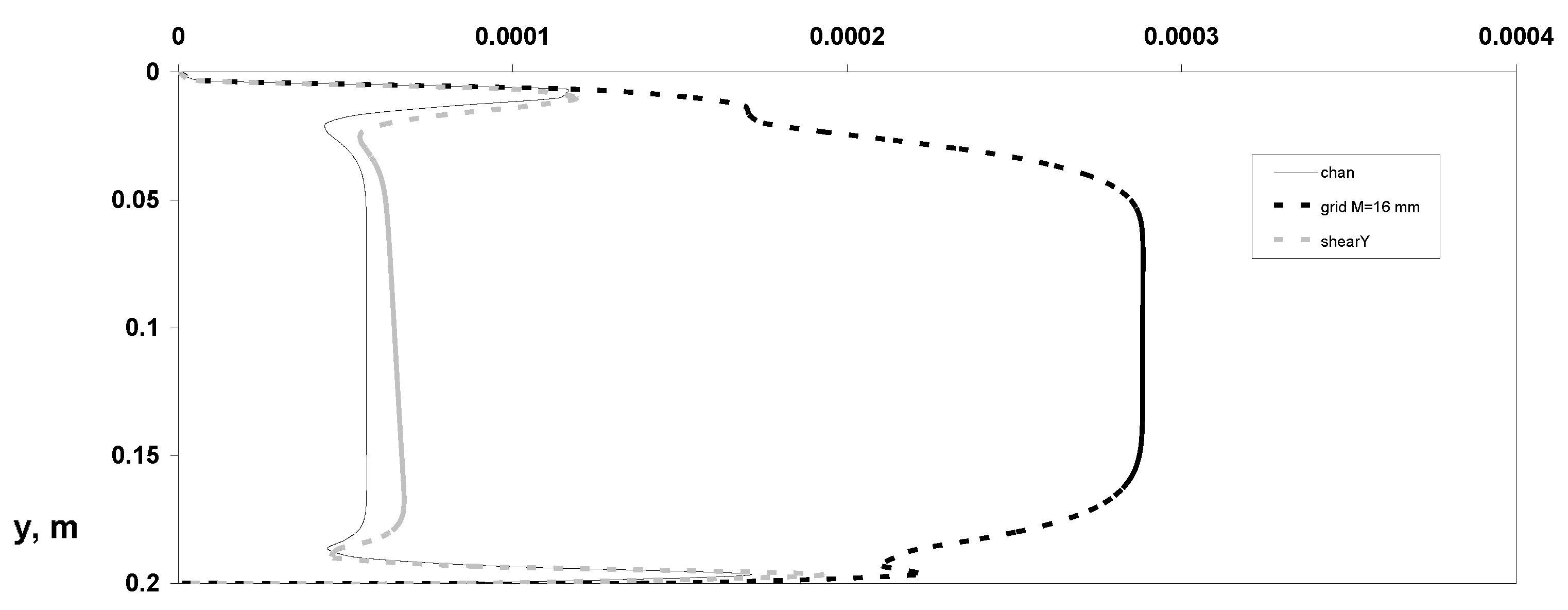
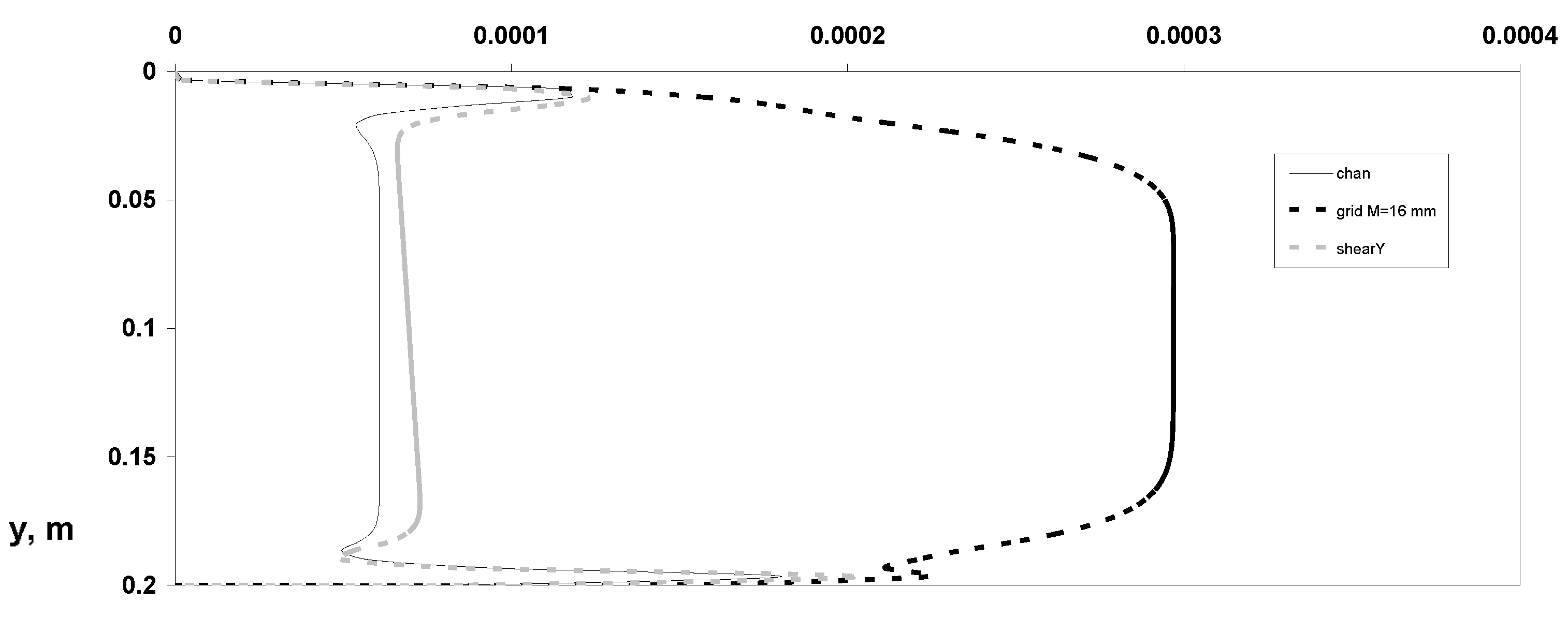
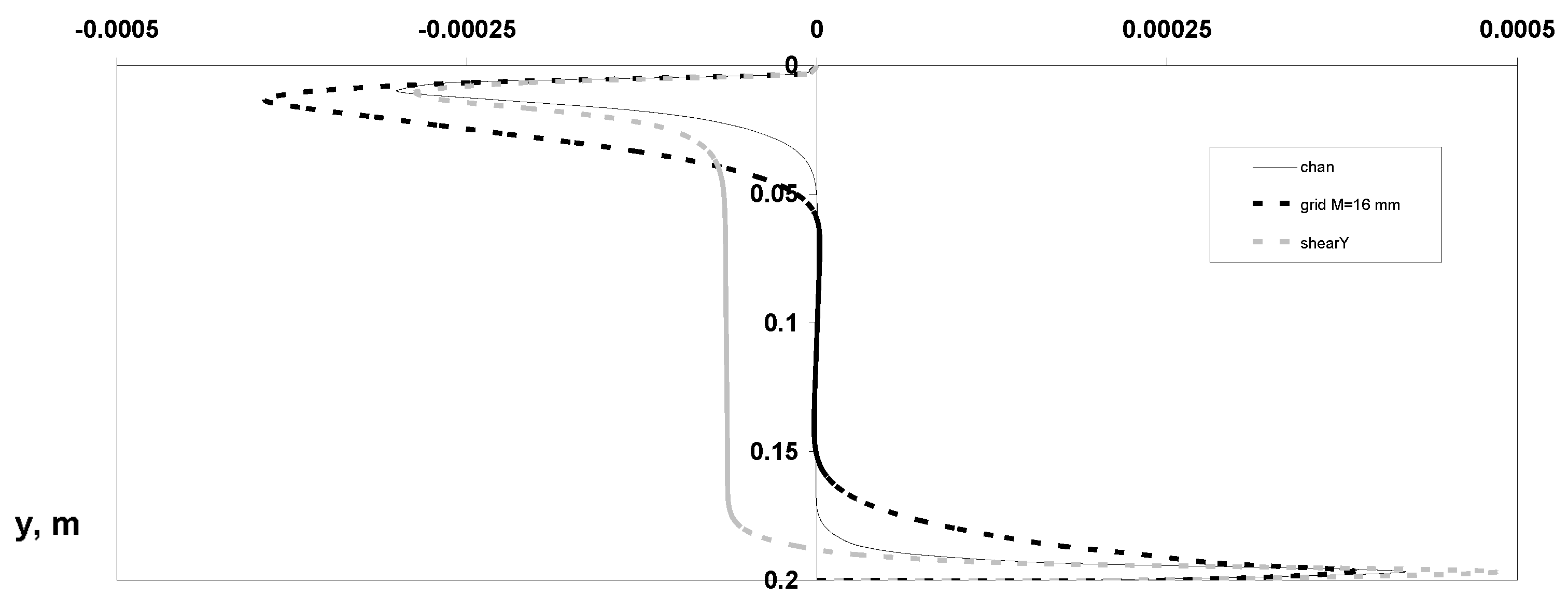
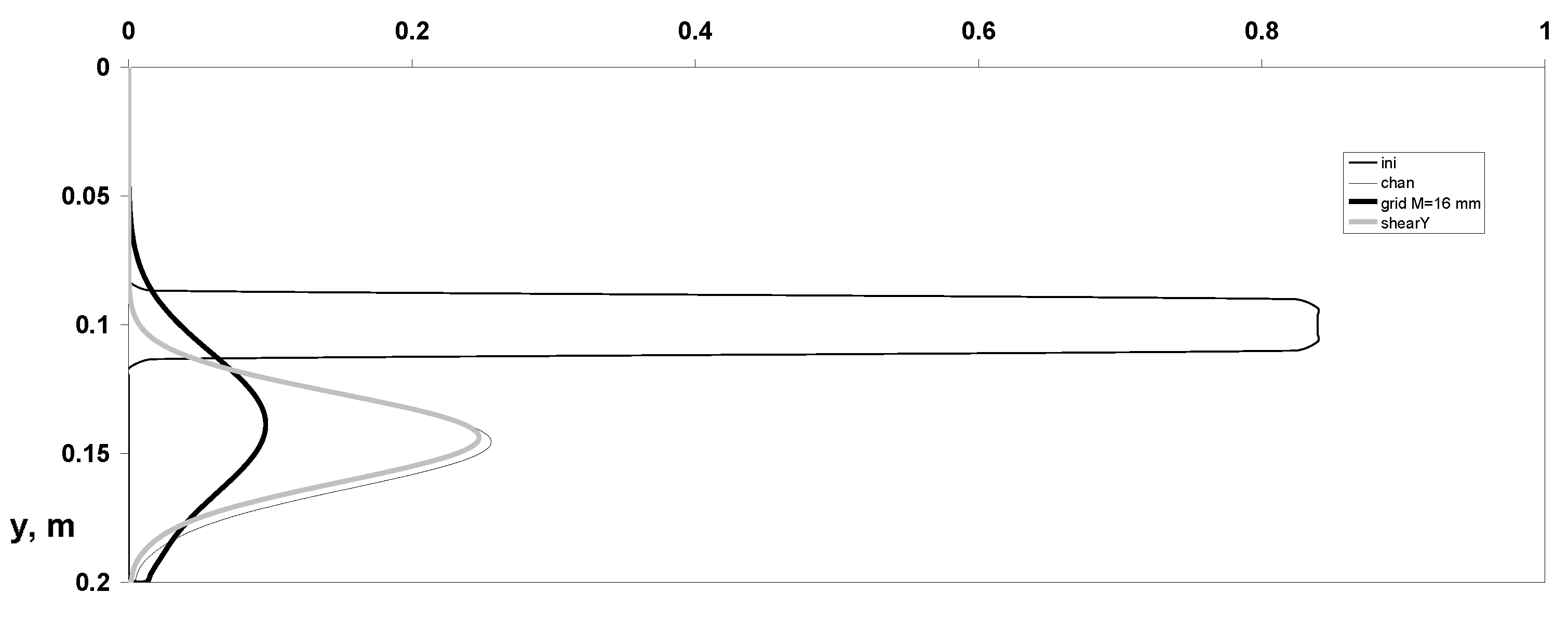
3. Results and Discussions
- -
- Distributions of dynamic parameters of the particulate phase for averaged various velocity components;
- -
- Reynolds stresses’ components;
- -
- Particle mass concentration, omitting distributions of parameters of the carrier gas-phase flow for its simplicity.
4. Conclusions
- Grid-generated turbulent flow;
- Channel turbulent flow.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Pfeffer, R.; Rosetti, S.; Licklein, S. Analysis and Correlation of Heat Transfer Coefficient and Heat Transfer Data for Dilute Gas–Solid Suspensions; NASA ReportTND3603; 1966. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/19660026357/downloads/19660026357.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Michaelides, E.E. A model for the flow of solid particles in gases. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1984, 10, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghobashi, S.; Abou-Arab, T.W. A two-equation turbulence model for twophase flows. Phys. Fluids 1983, 26, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, L.P.; Hetsroni, G. Turbulence intensity in dilute two-phase flows, Parts I, II and III. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1994, 20, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Michaelides, E.E. Turbulence modulation in particulate flows—A theoretical approach. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1992, 18, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, C.T.; Gillandt, I. Turbulence modulation of fluid-particle flows—A basic approach. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Multiphase Flows, Lyon, France, 8–12 June 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zaichik, L. A statistical model of particle transport and heat transfer in turbulent shear flows. Phys. Fluids 1999, 11, 1521–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukin, R.V.; Zaichik, L.I. Nonlinear algebraic Reynolds stress model for two-phase turbulent flows laden with small heavy particles. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2012, 33, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaichik, L.I.; Alipchenkov, V.M. Statistical models for predicting particle dispersion and preferential concentration in turbulent flows. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2005, 26, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaichik, L.I.; Vinberg, A.A. Modeling of particle dynamics and heat transfer in turbulent flows using equations for first and second moments of velocity and temperature fluctuations. In Proceedings of the 8th Symposium on Turbulent Shear Flows, Munich, Germany, 9–11 September 1991; Volume 1, pp. 10-2-1–10-2-6. [Google Scholar]
- Zaichik, L.I.; Alipchenkov, V.M. Refinement of the probability density function model for preferential concentration of aerosol particles in isotropic turbulence. Phys. Fluids 2007, 19, 113308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taulbee, D.B.; Mashayek, F.; Barré, C. Simulation and Reynolds stress modeling of particle-laden turbulent shear flows. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 1999, 20, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerolymos, G.A.; Vallet, I. Contribution to Single-Point-Closure Reynolds-Stress Modelling of Inhomogeneous Flows. In Proceedings of the ASME/JSME 2003 4th Joint Fluids Summer Engineering Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 6–10 July 2003; American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 1989–1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-Y.; Cho, C.-H. Performance of Reynolds stress turbulence closures in the calculation of three-dimensional transonic flows. In Proceedings of the ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting ASME FEDSM, New Orleans, LA, USA, 29 May–1 June 2001. FEDSM2001-18239, CD-ROM. [Google Scholar]
- Abouali, O.; Ahmadi, G.; Rabiee, A. Computational simulation of supersonic flow using Reynolds stress model. In Proceedings of the ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting ASME FEDSM, Houston, TX, USA, 19–23 June 2005. FEDSM2005-77434, CD-ROM. [Google Scholar]
- Leighton, R.; Walker, D.T.; Stephens, T.; Garwood, G. Reynolds stress modeling for drag reducing viscoelastic flows. In Proceedings of the 4th ASME/JSME Joint Fluids Summer Engineering Conference FEDSM, Honolulu, HI, USA, 6–10 June 2003. FEDSM2003-45655, CD-ROM. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Yu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Guo, Y. Imporved modeling of interface terms in the second- moment closure for particle-laden flows based on interface-resolved simulation data. J. Fluid Mech. 2022, 952, A25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeks, M.W. On a Kinetic Equation for the Transport of Particles in Turbulent flows. Phys. Fluids A Fluid Dyn. 1991, 3, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeks, M.W. On the Continuum Equations for Dispersed Particles in Nonuniform Flows. Phys. Fluids A Fluid Dyn. 1992, 4, 1290–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauk, P.; Kartushinsky, A.; Hussainov, M.; Polonsky, A.; Rudi, Ü.; Shcheglov, I.; Tisler, S.; Seegel, K.E. Two-Fluid RANS-RSTM-PDF Model for Turbulent Particulate Flows. In Numerical Simulation: From Brain Imaging to Turbulent Flows; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; pp. 339–363. [Google Scholar]
- Kartushinsky, A.; Rudi, Y.; Stock, D.; Hussainov, M.; Shcheglov, I.; Tisler, S.; Shablinsky, A. Numerical simulation of grid-generating turbulent particulate flow by three-dimensional Reynolds stress. Proc. Est. Acad. Sci. 2013, 62, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartushinsky, A.; Tisler, S.; Oliveira, J.L.G.; van der Geld, C.W.M. Eulerian-Elerian modeling of particle-laden two-phase flows. Powder Techol. 2016, 301, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartushinsky, A.; Rudi, Y.; Hussainov, M.; Shcheglov, I.; Tisler, S.; Krupenski, I.; Stock, D. RSTM numerical simulation of channel particulate flow with rough wall. In Computational and Numerical Simulations; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2014; pp. 41–63. [Google Scholar]
- Pourahmadi, F.; Humphrey, J.A. Prediction of curved channel flow with an extended k-epsilon model of turbulence. AIAA J. 1983, 21, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, M.A.; Elghobashi, S.E. A two-equation turbulence model for dispersed dilute confined two-phase flows. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1989, 15, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonin, O.; Viollet, P.L. Modelling of turbulent two-phase jets loaded with discrete particles. Phenom. Multiph. Flows 1990, 259–269. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch, E.; Simonin, O. Large Eddy Simulation Applied to the Modelling of Particulate Transport Coefficients in Turbulent Two-Phase Flows. 1991, pp. 1011–1016. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1991tsf.....1Q..10D/abstract (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Shraĭber, A.A. Turbulent Flows in Gas Suspensions; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzkopf, J.D.; Crowe, C.T.; Dutta, P. A model for particle laden turbulent flows. In Proceedings of the ASME FEDSM2009-7838, Vail, CO, USA, 2–6 August 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Crowe, C.T. On models for turbulence modulation in fluid–particle flows. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2000, 26, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, Z.; Chrigui, M.; Sadiki, A.; Dreizler, A.; Geiss, S.; Janicka, J. Expermental investigation and modeling of turbulence modification in a dilute two-phase turbulent flow. In Proceedings of the 10th Workshop on Two-Phase Flow Prediction, Merseburg, Germany, 9–12 April 2002; pp. 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Geiss, S.; Dreizler, A.; Stojanovic, Z.; Chrigui, M.; Sadiki, A.; Janicka, J. Investigation of turbulence modification in a non-reactive two-phase flow. Exp. Fluids 2004, 36, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussainov, M.; Kartushinsky, A.; Rudi, Ü.; Shcheglov, I.; Kohnen, G.; Sommerfeld, M. Experimental investigation of turbulence modulation by solid particles in a grid-generated vertical flow. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2000, 21, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussainov, M.; Kartushinsky, A.; Rudi, Y.; Shcheglov, I.; Tisler, S. Experimental study of the effect of velocity slip and mass loading on the modification of grid-generated turbulence in gas-solid particles flows. Proc. Estonian Acad. Sci. Eng. 2005, 11, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karman, T.V. The fundamentals of the statistical theory of turbulence. J. Aeronaut. Sci. 1937, 4, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, F.H.; Harris, V.G.; Corrsin, S. Experiments on nearly homogeneous turbulent shear flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1970, 41, 81–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, V.G.; Graham, J.A.; Corrsin, S. Further experiments in nearly homogeneous turbulent shear flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1977, 81, 657–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.M.; Elghobashi, S. On the mechanisms of modifying the structure of turbulent homogeneous shear flows by dispersed particles. Phys. Fluids 2000, 12, 2906–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perić, M.; Scheuerer, G. CAST: A Finite Volume Method for Predicting Two-Dimensional Flow and Heat Transfer Phenomena; GRS—Technische Notiz SRR–89–01; GRS: Koeln, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Fertziger, J.H.; Perić, M. Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2002; 426p. [Google Scholar]
- Pope, S.B. Turbulent Flows; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; 771p. [Google Scholar]
- Kartushinsky, A.I.; Rudi, Y.u.A.; Tisler, S.V.; Hussainov, M.T.; Shcheglov, I.N. Application of particle tracking velocimetry for studying the dispersion of particles in a turbulent gas flow. High Temp. 2012, 50, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.C.; Thomas, N.H.; Perkins, R.J.; Miller, P.C.H. Wind tunnel velocity profiles generated by differentially spaced flat plates. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1999, 80, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlichting, H. Boundary Layer Theory; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kartushinsky, A.; Michaelides, E.E.; Hussainov, M.; Shcheglov, I.; Akhmadullin, I. Eulerian–Eulerian RSTM-PDF Modeling of Turbulent Particulate Flow. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11122647
Kartushinsky A, Michaelides EE, Hussainov M, Shcheglov I, Akhmadullin I. Eulerian–Eulerian RSTM-PDF Modeling of Turbulent Particulate Flow. Mathematics. 2023; 11(12):2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11122647
Chicago/Turabian StyleKartushinsky, Aleaxander, Efstathios E. Michaelides, Medhat Hussainov, Igor Shcheglov, and Ildar Akhmadullin. 2023. "Eulerian–Eulerian RSTM-PDF Modeling of Turbulent Particulate Flow" Mathematics 11, no. 12: 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11122647
APA StyleKartushinsky, A., Michaelides, E. E., Hussainov, M., Shcheglov, I., & Akhmadullin, I. (2023). Eulerian–Eulerian RSTM-PDF Modeling of Turbulent Particulate Flow. Mathematics, 11(12), 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11122647






