Personalized Image Aesthetics Assessment via Multi-Attribute Interactive Reasoning
Abstract
1. Introduction
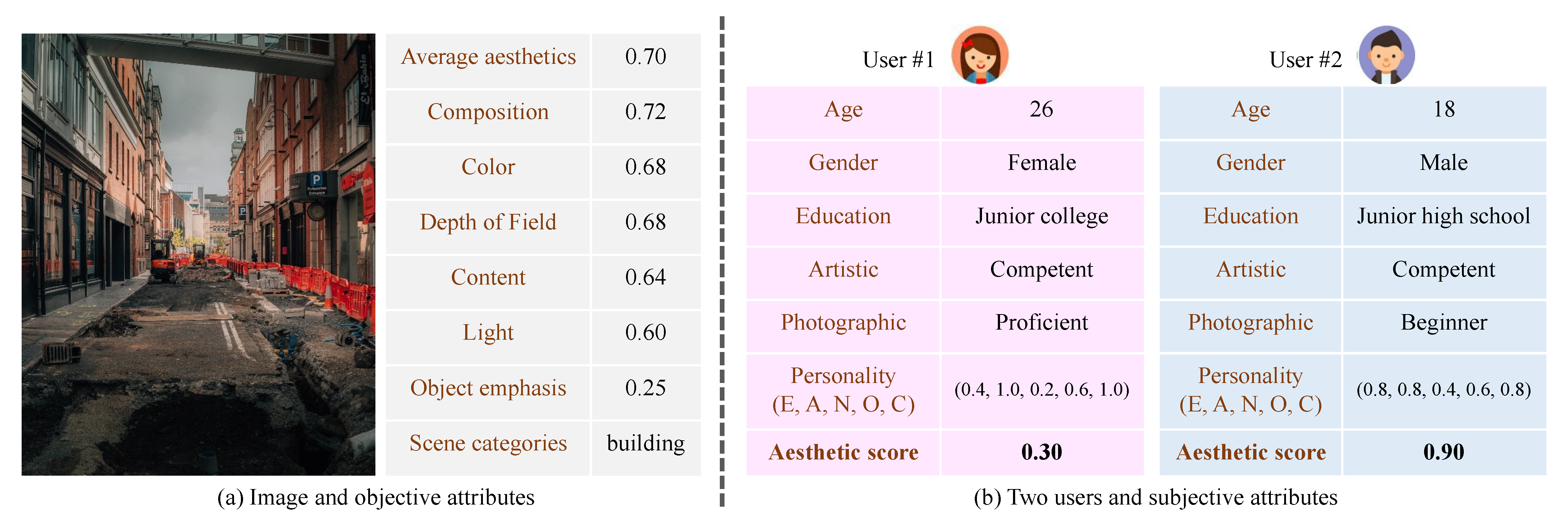
- We excavated the fundamental factors of users’ personalized aesthetic preferences for images by constructing a multi-attribute interaction, which alleviates the insufficient problem of directly obtaining prior knowledge only from the generic aesthetics of images or the personalized aesthetics of a large number of individual users.
- We propose a generic aesthetics extraction module that can simultaneously predict multiple attributes and aesthetic distributions of images. In the multi-attribute interactive reasoning network, we can not only leverage multiple attributes of images and users to construct an effective interaction, but also further use the multi-attribute interactive features and aesthetic score distribution to jointly model personalized aesthetic scores.
- We propose a personalized image aesthetics assessment method via multi-attribute interactive reasoning (PIAA-MIR), whose experimental results on several PIAA databases demonstrated that the proposed PIAA-MIR outperformed state-of-the-art PIAA methods. Besides, ablation studies also showed the effectiveness of our method in learning a personalized aesthetic prior model.
2. Related Works
2.1. Generic Image Aesthetics Assessment
2.2. Personalized Image Aesthetics Assessment
3. Proposed Method
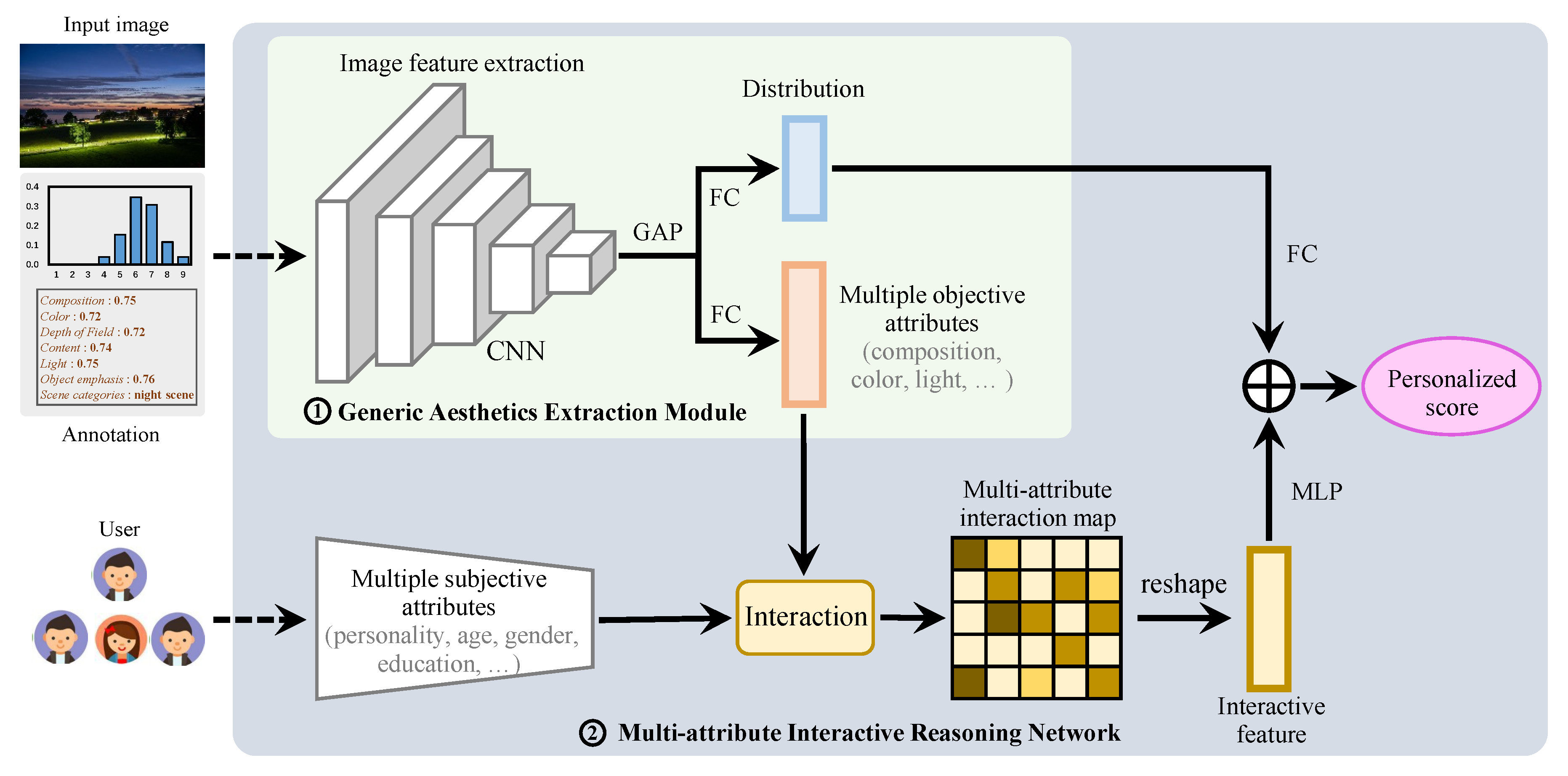
3.1. Generic Aesthetics Extraction
3.2. Multi-Attribute Interaction Reasoning
3.3. PIAA Fine-Tuning for a Specific User
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Databases
4.2. Experimental Settings
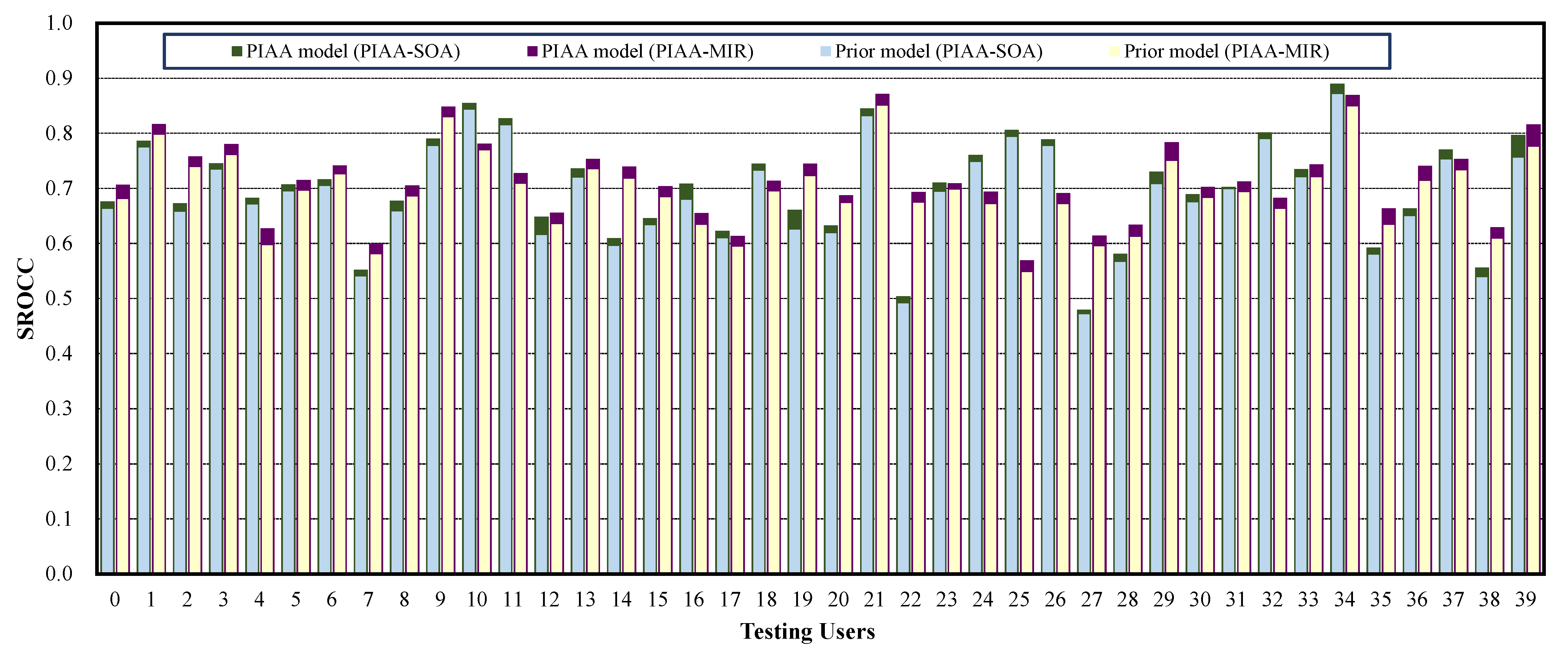
4.3. Comparing with the State-of-the-Art PIAA Methods
4.4. Ablation Study
4.5. Visual Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, Y.; Chen, C.L.; Tang, X. Image Aesthetic Assessment: An Experimental Survey. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2017, 34, 80–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, H.; Milanfar, P. NIMA: Neural Image Assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 3998–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Qin, J.; Xiang, X.; Tan, Y.; He, Z. Searchable Encrypted Image Retrieval Based on Multi-Feature Adaptive Late-Fusion. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, K.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, D.Q. Mobile photo album management with multiscale timeline. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Orlando, FL, USA, 3–7 November 2014; pp. 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Vázquez, L.V.; Miura, J.; Rosales-Silva, A.J.; Luviano-Juárez, A.; Mújica-Vargas, D. Analysis of Different Image Enhancement and Feature Extraction Methods. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, P.; Rombach, R.; Ommer, B. Taming Transformers for High-Resolution Image Synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 12873–12883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yamasaki, T. Style-Aware Image Recommendation for Social Media Marketing. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual, China, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 3106–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, S.; Ding, G.; Lin, W. Personality-Assisted Multi-Task Learning for Generic and Personalized Image Aesthetics Assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 3898–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, G. Theme-Aware Semi-Supervised Image Aesthetic Quality Assessment. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, L.; Qie, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Guo, Y. Personalized Image Aesthetics Assessment With Rich Attributes. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; pp. 19861–19869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, N.; Marchesotti, L.; Perronnin, F. AVA: A large-scale database for aesthetic visual analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 2408–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.; He, R.; Huang, K. Deep Aesthetic Quality Assessment With Semantic Information. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 1482–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Shen, X.; Lin, Z.; Mech, R.; Fowlkes, C. Photo Aesthetics Ranking Network with Attributes and Content Adaptation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 662–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Q. Image Aesthetic Assessment Assisted by Attributes through Adversarial Learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January 27–1 February 2019; pp. 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, X.; Lu, W.; He, L. A Gated Peripheral-Foveal Convolutional Neural Network for Unified Image Aesthetic Prediction. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2019, 21, 2815–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Bovik, A.C. A Unified Probabilistic Formulation of Image Aesthetic Assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 1548–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, D.; Lai, Y.K.; Yi, G.; Xu, K. Hierarchical Layout-Aware Graph Convolutional Network for Unified Aesthetics Assessment. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 8475–8484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Q.; Liu, G. Multimodal Image Aesthetic Prediction with Missing Modality. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhuo, L.; Tian, Q.; Liang, X. Personalized Recommendation of Social Images by Constructing a User Interest Tree with Deep Features and Tag Trees. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2019, 21, 2762–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.C.; Kim, B.; KIM, G. Towards Personalized Image Captioning via Multimodal Memory Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, S.; Cusano, C.; Piccoli, F.; Schettini, R. Personalized Image Enhancement Using Neural Spline Color Transforms. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 6223–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Shen, X.; Lin, Z.; Mech, R.; Foran, D.J. Personalized Image Aesthetics. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Peng, Z.; Sun, J.; Su, S.; Zhou, B.; Xu, M. USAR: An Interactive User-Specific Aesthetic Ranking Framework for Images. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seoul, Korea, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 1328–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yan, J.; Qin, Z. Collaborative and Attentive Learning for Personalized Image Aesthetic Assessment. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; pp. 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Su, J.; Li, L.; Xu, X.; Luo, J. Meta-Learning Perspective for Personalized Image Aesthetics Assessment. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 1875–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Fan, J.; Nie, X.; Dong, W.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, B.; Xu, M.; Xu, C. User-Guided Personalized Image Aesthetic Assessment based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y. Learning Personalized Image Aesthetics from Subjective and Objective Attributes. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Li, L.; Wu, J.; Zhao, S.; Ding, G.; Shi, G. Personalized Image Aesthetics Assessment via Meta-Learning with Bilevel Gradient Optimization. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 1798–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Lin, W.; Yue, G.; Liu, W.; Zhao, B. Interaction-Matrix Based Personalized Image Aesthetics Assessment. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucer, M.; Loui, A.C.; Messinger, D.W. Leveraging Expert Feature Knowledge for Predicting Image Aesthetics. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 5100–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinciarelli, A.; Mohammadi, G. A Survey of Personality Computing. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2014, 5, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Du, X.; Wang, X.; Tian, F.; Tang, J.; Chua, T. Outer Product-based Neural Collaborative Filtering. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; pp. 2227–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeki, S. Clive Bell’s “Significant Form” and the neurobiology of aesthetics. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perona, F.R.; Gallego, M.J.F.; Callejón, J.M.P. An Application for Aesthetic Quality Assessment in Photography with Interpretability Features. Entropy 2021, 23, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelli, F.; Uricchio, T.; He, X.; Del Bimbo, A.; Chua, T.S. Learning Subjective Attributes of Images from Auxiliary Sources. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 2263–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.H.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, J.S. Objectivity and Subjectivity in Aesthetic Quality Assessment of Digital Photographs. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2020, 11, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, B.; Ye, J.; Yang, M.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, R.; Qiao, Y. A Multi-task Learning Approach for Image Captioning. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; pp. 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levina, E.; Bickel, P. The Earth Mover’s distance is the Mallows distance: Some insights from statistics. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–14 July 2001; Volume 2, pp. 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, S.; Jiang, H. Evaluating attributed personality traits from scene perception probability. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2018, 116, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammstedt, B.; John, O.P. Measuring personality in one minute or less: A 10-item short version of the Big Five Inventory in English and German. J. Res. Pers. 2007, 41, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Methods | 10 Images | 100 Images |
|---|---|---|
| PAPA (unconditional) [10] | 0.681 ± 0.0015 | 0.695 ± 0.0014 |
| PAPA (artistic) [10] | 0.686 ± 0.0016 | 0.698 ± 0.0012 |
| PAPA (photographic) [10] | 0.683 ± 0.0014 | 0.698 ± 0.0010 |
| PAPA (personality) [10] | 0.691 ± 0.0009 | 0.705 ± 0.0015 |
| PA_IAA [8] | 0.683 ± 0.0013 | 0.690 ± 0.0016 |
| BLG-PIAA [28] | 0.688 ± 0.0015 | 0.697 ± 0.0013 |
| PIAA-SOA [27] | 0.692 ± 0.0014 | 0.703 ± 0.0012 |
| PIAA-MIR | 0.702 ± 0.00010 | 0.716 ± 0.0008 |
| Methods | 10 Images | 100 Images |
|---|---|---|
| PAM (attribute) [22] | 0.518 ± 0.003 | 0.539 ± 0.013 |
| PAM (content) [22] | 0.515 ± 0.004 | 0.535 ± 0.017 |
| PAM (content and attribute) [22] | 0.520 ± 0.003 | 0.553 ± 0.012 |
| USAR_PPR [23] | 0.521 ± 0.002 | 0.544 ± 0.007 |
| USAR_PAD [23] | 0.520 ± 0.003 | 0.537 ± 0.003 |
| USAR_PPR&PAD [23] | 0.525 ± 0.004 | 0.552 ± 0.015 |
| ML-PIAA [25] | 0.522 ± 0.005 | 0.562 ± 0.015 |
| PA_IAA [8] | 0.543 ± 0.003 | 0.639 ± 0.011 |
| BLG-PIAA [28] | 0.561 ± 0.005 | 0.669 ± 0.013 |
| UG-PIAA [26] | 0.559 ± 0.002 | 0.660 ± 0.013 |
| PIAA-SOA [27] | 0.618 ± 0.006 | 0.691 ± 0.015 |
| PIAA-MIR | 0.621 ± 0.005 | 0.713 ± 0.00016 |
| Methods | 10 Images | 100 Images |
|---|---|---|
| PA_IAA [8] | 0.443 ± 0.004 | 0.562 ± 0.013 |
| BLG-PIAA [28] | 0.448 ± 0.007 | 0.578 ± 0.015 |
| PIAA-SOA [27] | 0.487 ± 0.006 | 0.589 ± 0.014 |
| PIAA-MIR | 0.498 ± 0.008 | 0.606 ± 0.013 |
| Methods | 10 Images | 100 Images |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline (generic) | 0.679 ± 0.0014 | 0.692 ± 0.0015 |
| Baseline (personalized) | 0.682 ± 0.0015 | 0.698 ± 0.0016 |
| PIAA-MIR w/o objective | 0.689 ± 0.0011 | 0.700 ± 0.0011 |
| PIAA-MIR w/o subjective | 0.684 ± 0.0013 | 0.693 ± 0.0014 |
| PIAA-MIR w/o interaction | 0.696 ± 0.0012 | 0.707 ± 0.0010 |
| PIAA-MIR | 0.702 ± 0.00010 | 0.716 ± 0.0008 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Shao, Z.; Du, W.; Wang, G.; Li, Q. Personalized Image Aesthetics Assessment via Multi-Attribute Interactive Reasoning. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4181. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10224181
Zhu H, Zhou Y, Shao Z, Du W, Wang G, Li Q. Personalized Image Aesthetics Assessment via Multi-Attribute Interactive Reasoning. Mathematics. 2022; 10(22):4181. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10224181
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Hancheng, Yong Zhou, Zhiwen Shao, Wenliang Du, Guangcheng Wang, and Qiaoyue Li. 2022. "Personalized Image Aesthetics Assessment via Multi-Attribute Interactive Reasoning" Mathematics 10, no. 22: 4181. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10224181
APA StyleZhu, H., Zhou, Y., Shao, Z., Du, W., Wang, G., & Li, Q. (2022). Personalized Image Aesthetics Assessment via Multi-Attribute Interactive Reasoning. Mathematics, 10(22), 4181. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10224181





