Dynamic Analysis of Software Systems with Aperiodic Impulse Rejuvenation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. System Formulation
3. Dynamic Analysis
3.1. Well-Posedness
3.2. Approximation System
3.3. Instantaneous Availability
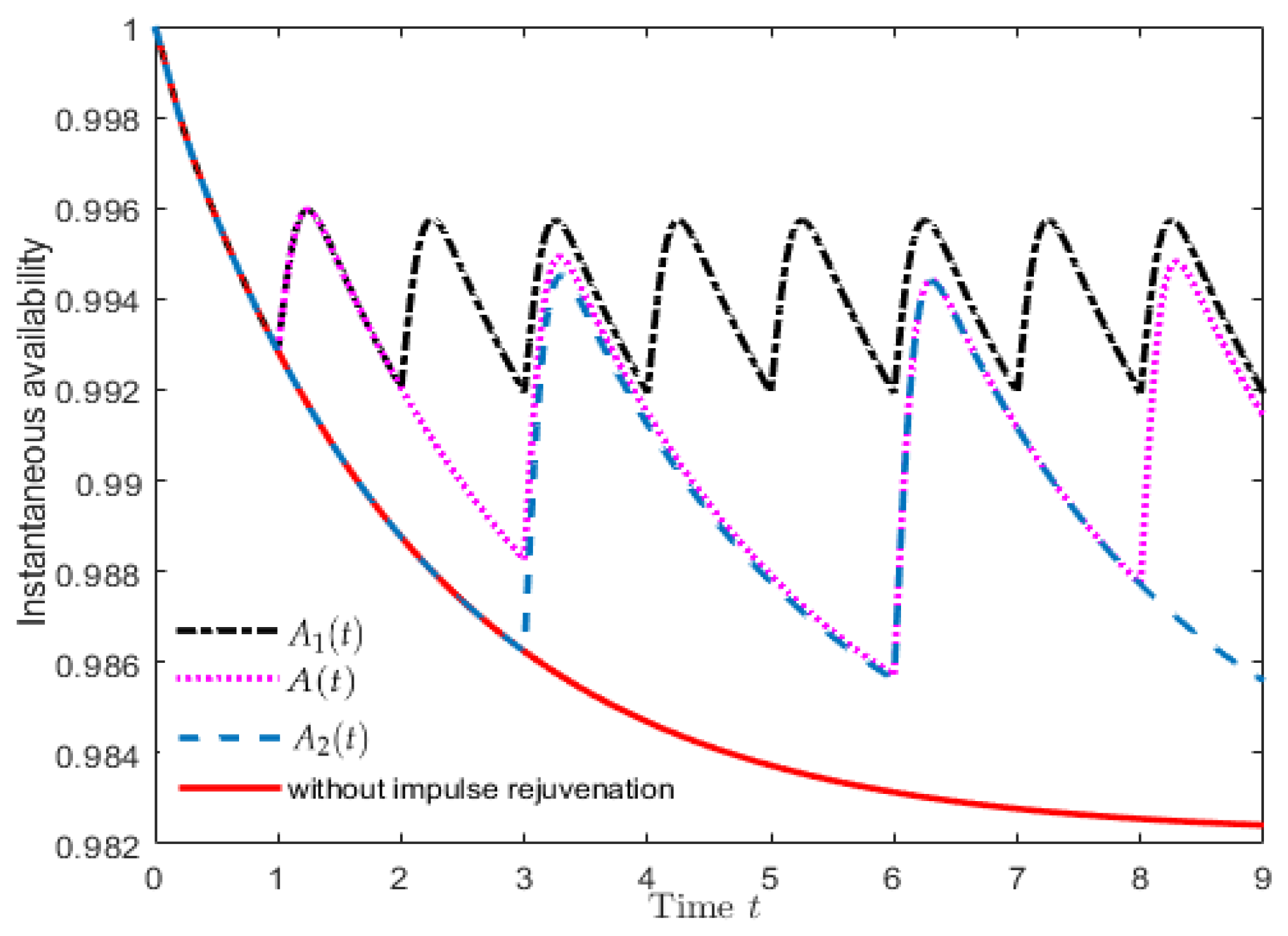
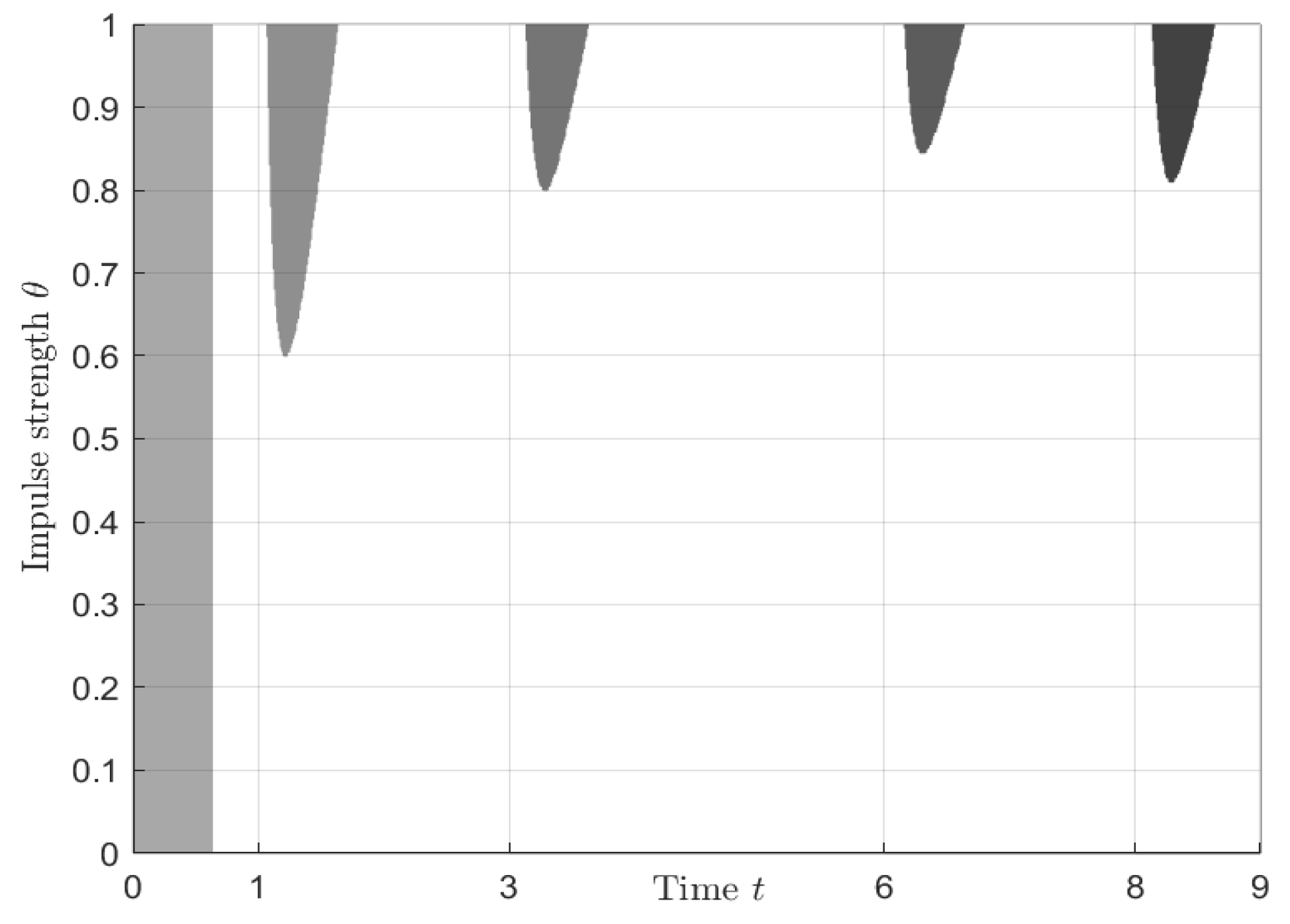
4. Numerical Examples
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grottke, M.; Li, L.; Vaidyanathan, K.; Trivedi, K.S. Analysis of software aging in a web servers. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2006, 55, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.J.; Okamura, H.; Dohi, T. A transient interval reliability analysis for software rejuvenation models with phase expansion. Softw. Qual. J. 2020, 28, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Khomh, F.; Gueheneuc, Y.G. An empirical study of crash-inducing commits in Mozilla Firefox. Softw. Qual. J. 2018, 26, 553–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Puliafito, A.; Telek, M.; Trivedi, K.S. On the analysis of software rejuvenation policies. In Proceedings of the Twelfth Annual Conference on Computer Assurance (ACCA), Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 16–19 June 1997; pp. 88–96. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, H.N.; Liu, J.J.; Hei, X.H. Modeling and optimizing periodically inspected software rejuvenation policy based on geometric sequences. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2015, 133, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, E. Fatal error: How patriot overlooked a scud. Science. 1992, 255, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Kintala, C.; Kolettis, N.; Fulton, N.D. Software rejuvenation: Analysis, module and applications. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth International Symposium on Fault-Tolerant Computing. Digest of Papers, Pasadena, CA, USA, 27–30 June 1995; pp. 381–390. [Google Scholar]
- Dohi, T.; Gos˘eva-Popstojanova, K.; Trivedi, K.S. Estimating software rejuvenation schedules in high-assurance systems. Comput. J. 2001, 44, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.B. Modelling and well-posed analysis for software system with rejuvenation. Math. Comp. Model. Dyn. 2011, 17, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohi, T.; Okamura, H. Dynamic software availability model with rejuvenation. J. Oper. Res. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 59, 270–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Koutras, V.P.; Platis, A.N. On the performance of software rejuvenation models with multiple degradation levels. Softw. Qual. J. 2020, 28, 135–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Okamura, H.; Dohi, T. Availability analysis of software systems with rejuvenation and checkpointing. Mathematics 2021, 9, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmikantham, V.; Bainov, D.; Simeonov, P.S. Theory of Impulsive Differential Equations; World Scientific: Singapore, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Boulbrachene, M. The noncoercive quasi-variational inequalities related to impulse control problems. Comput. Math. Appl. 1998, 35, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nersesov, S.G.; Haddad, W.M. Control vector Lyapunov functions for large-scale impulsive dynamical systems. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst. 2007, 1, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Guan, Z.H.; Yu, X.H.; Luo, Q.M. Multisynchronization of interconnected memristor-based impulsive neural networks with fuzzy hybrid control. IEEE. Trans. Fuzzy. Syst. 2018, 26, 3069–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piunovskiy, A.; Plakhov, A.; Tumanov, M. Optimal impulse control of a SIR epidemic. Optim. Control. Appl. Methods. 2020, 41, 448–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kember, S.A.; Babitsky, V.I. Excitation of vibro-impact system by periodic impulses. J. Sound. Vib. 1999, 227, 427–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Q. Boundedness and periodicity in impulsive ordinary and functional differential equations. Nonlinear. Anal. 2006, 65, 1986–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.J. Existence and multiplicity of positive periodic solutions for a class of higher-dimension functional differential equations with impulses. Comput. Math. Appl. 2009, 58, 1911–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huo, H.X.; Win, T.T.; Xu, H.B. Availability analysis of the software rejuvenation system with impulse control. In Proceedings of the 2019 Chinese Control And Decision Conference (CCDC), Nanchang, China, 3–5 June 2019; pp. 825–829. [Google Scholar]
- Sofiyev, A.H. The stability of functionally graded truncated conical shells subjected to aperiodic impulsive loading. Int. J. Solids. Struct. 2004, 41, 3411–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghshtabrizi, P.; Hespanha, J.P.; Teel, A.R. Exponential stability of impulsive systems with application to uncertain sampled-data systems. Syst. Control. Lett. 2008, 57, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Ho, D.W.C.; Cao, J. A unified synchronization criterion for impulsive dynamical networks. Automatica 2010, 46, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.S.; Li, X.D.; Cao, J.D. Global exponential stability for impulsive systems with infinite distributed delay based on flexible impulse frequency. Appl. Math. Comput. 2020, 386, 125467. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, H.Y.; Yuan, G.X. Sampling dependent stability results for aperiodic sampled-data systems. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2021, 34, 588–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. Exponential stability of a joint-leg-beam system with memory damping. Math. Control. Relat. F. 2015, 5, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.J.; Xu, T.Z. Well-posedness and persistence property for a shallow water wave equation for waves of large amplitude. J. Appl. Anal. 2019, 98, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, J.M.; Li, D.H. Input-to-state stabilization of an ODE-wave system with disturbances. Math. Control. Signal. 2020, 32, 489–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Kappel, F. The Trotter-Kato theorem and approximation of PDEs. Math. Comput. 1998, 67, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.B.; Hu, W.W. Modelling and analysis of repairable systems with preventive maintenance. Appl. Math. Comput. 2013, 224, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.B.; Hu, W.W. Analysis and approximation of a reliable model. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 37, 3777–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, H.X.; Xu, H.B.; Chen, Z.Q.; Win, T.T. Transient analysis of a single server queueing system with infinite buffer. Rairo-Oper. Res. 2021, 55, S2795–S2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, K.; Dohi, T.; Okamura, H.; Kaio, N. Discrete-time cost analysis for a telecommunication billing application with rejuvenation. Comput. Math. Appl. 2006, 51, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sukhwani, H.; Matias, R.; Trivedi, K.S. Monitoring and mitigating software aging on IBM cloud controller system. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering Workshops (ISSREW), Toulouse, France, 23–26 October 2017; pp. 266–272. [Google Scholar]
- Cotroneo, D.; Iannillo, A.K.; Natella, R.; Pietrantuono, R. A comprehensive study on software aging across android versions and vendors. Empir. Softw. Eng. 2020, 25, 3357–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, H.X.; Xu, H.B.; Chen, Z.Q. Modelling and dynamic behavior analysis of the software rejuvenation system with periodic impulse. Math. Comp. Model. Dyn. 2021, 27, 522–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; Qin, G.Q.; Wang, Z.H. The Foundation of the Bounded Linear Operators Semigroup with Application; Liaoning Science and Technology Press: Shenyang, China, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfgang, A. Resolvent positive operators. Proc. Lond. Math. Soc. 1987, 54, 321–349. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Reliability analysis of a cold standby repairable system with repairman extra work. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2015, 28, 1015–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazy, A. Semigroups of Linear Operators and Applications to Partial Differential Equations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.W.; Hu, M.J.; Wang, Y.W.; Chen, W.H. Impulsive positive observers and dynamic output feedback stabilization of positive linear continuous systems. Int. J. Robust. Nonlin. 2017, 27, 2275–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Wang, T.; Rodriguez, R.J.; Zhang, Z. Modeling and analysis of high availability techniques in a virtualized system. Comput. J. 2018, 61, 180–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torquato, M.; Macie, P.; Vieira, M. A model for availability and security risk evaluation for systems with VMM rejuvenation enabled by VM migration scheduling. IEEE Access. 2019, 7, 138315–138326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huo, H.; Xu, H.; Chen, Z. Dynamic Analysis of Software Systems with Aperiodic Impulse Rejuvenation. Mathematics 2022, 10, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10020197
Huo H, Xu H, Chen Z. Dynamic Analysis of Software Systems with Aperiodic Impulse Rejuvenation. Mathematics. 2022; 10(2):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10020197
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuo, Huixia, Houbao Xu, and Zhuoqian Chen. 2022. "Dynamic Analysis of Software Systems with Aperiodic Impulse Rejuvenation" Mathematics 10, no. 2: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10020197
APA StyleHuo, H., Xu, H., & Chen, Z. (2022). Dynamic Analysis of Software Systems with Aperiodic Impulse Rejuvenation. Mathematics, 10(2), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10020197





