Spatiality Sensitive Learning for Cancer Metastasis Detection in Whole-Slide Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Is it possible to further improve the performance of cancer metastasis detection through efficiently modeling and exploring the spatial structure information of image patches in WSIs?
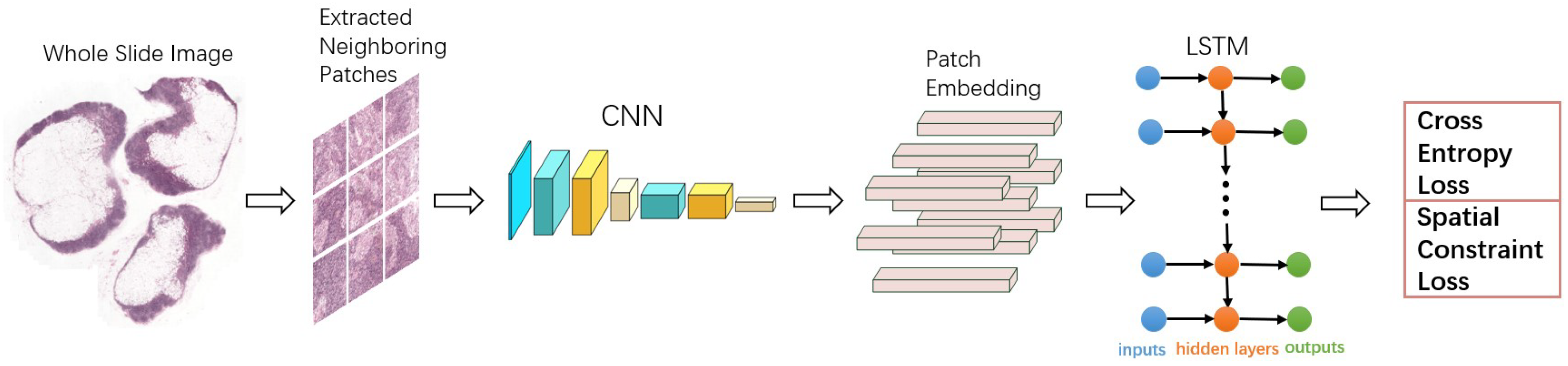
- This paper proposes a new spatially sensitive learning architecture that integrates CNN and long short-term memory (LSTM) in a unified framework to automatically detect the metastasis locations, as shown in Figure 1.
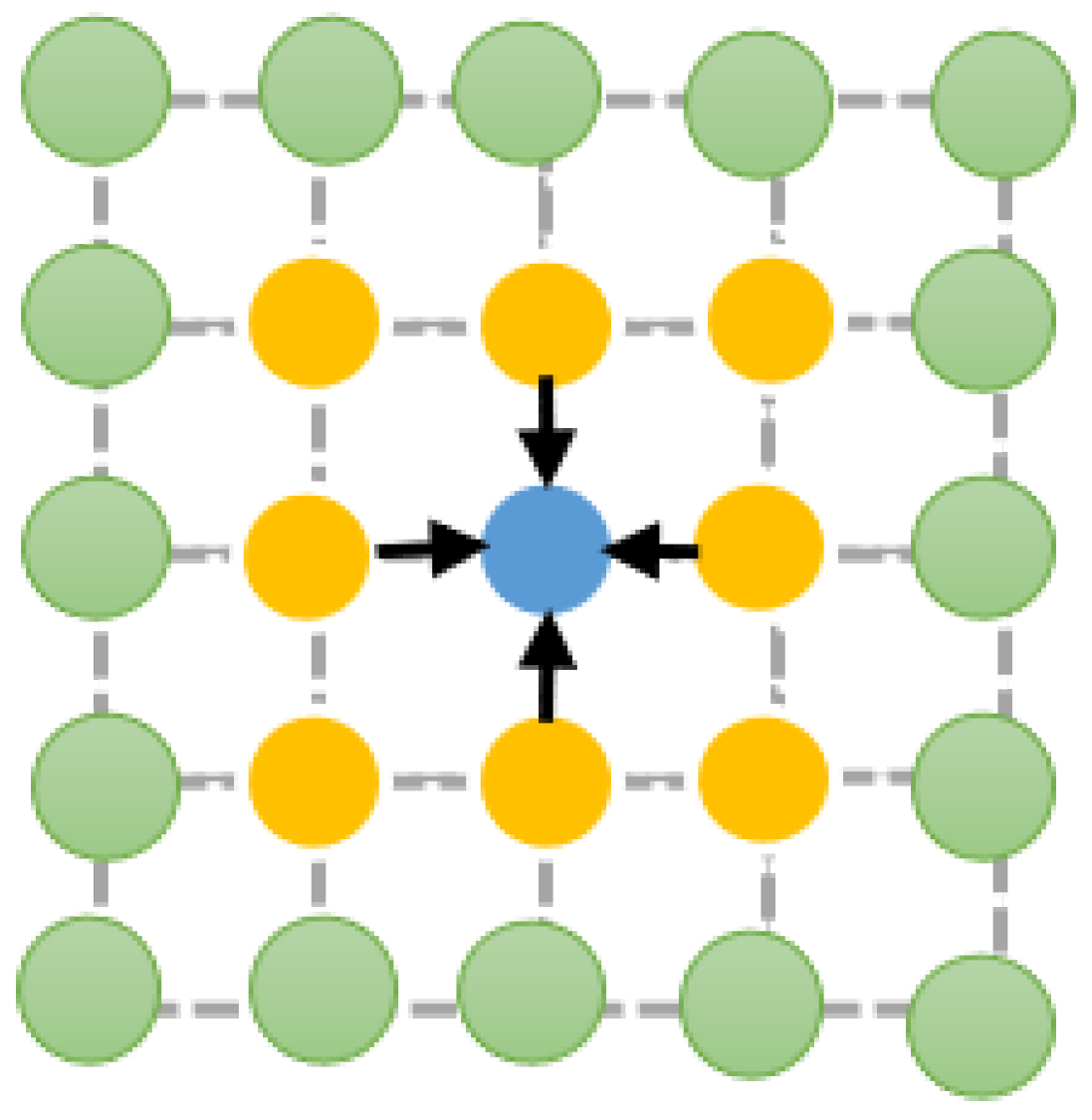
- Inspired by the observation that adjacent regions are interrelated, an LSTM layer is employed to explicitly describe the spatial correlation, at the same time, spatial constraint is also imposed on the loss function to further improve performance.
- Unlike previous approaches, the proposed model not only takes into account the appearance of each patch, but the spatial information between adjacent areas is also embedded into the framework to make better predictions.
2. Related Work
3. Method
3.1. Patch Representation with CNN
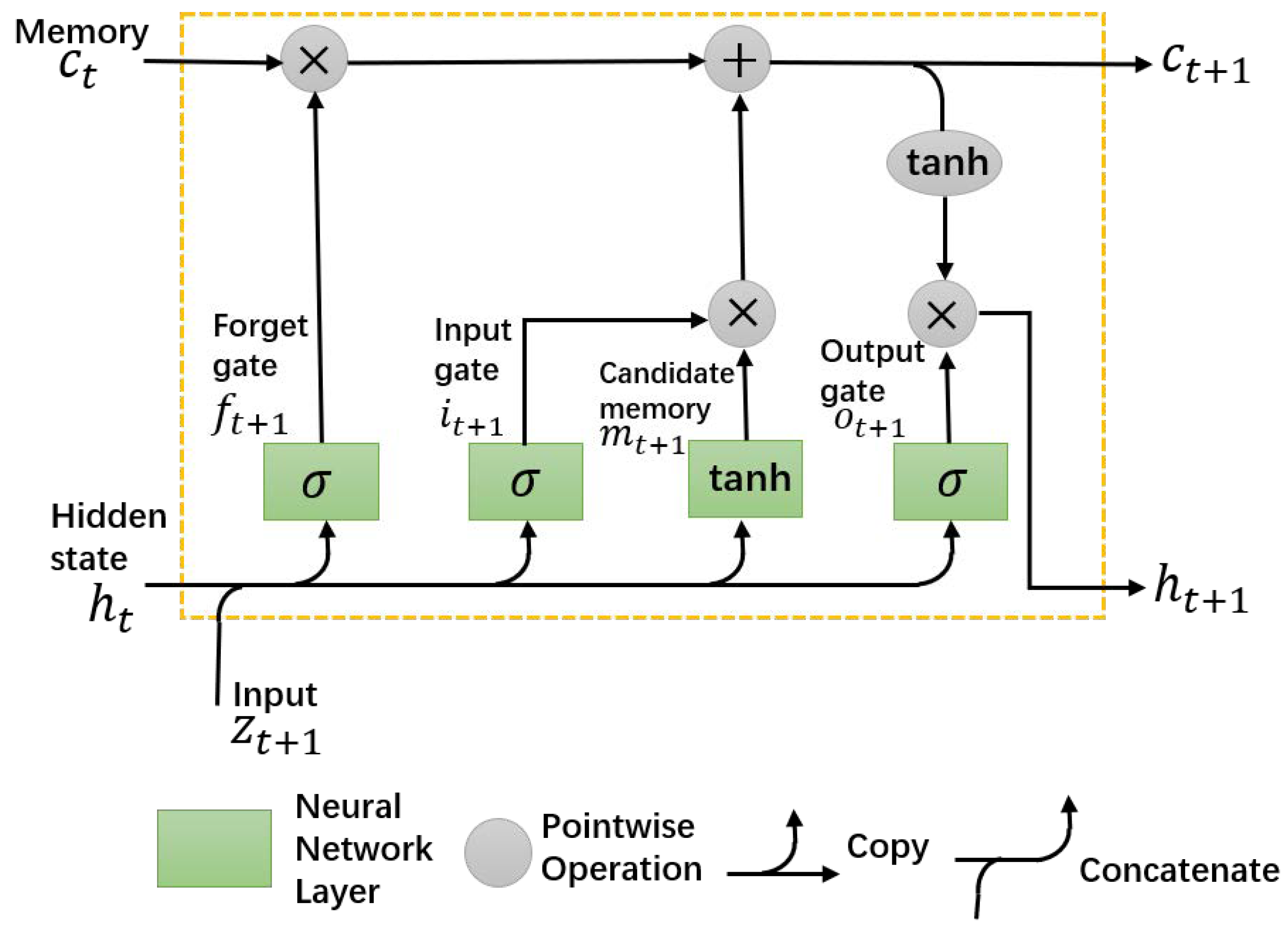
3.2. Spatial Modeling with LSTM
3.3. Optimize with Spatial Constraint
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
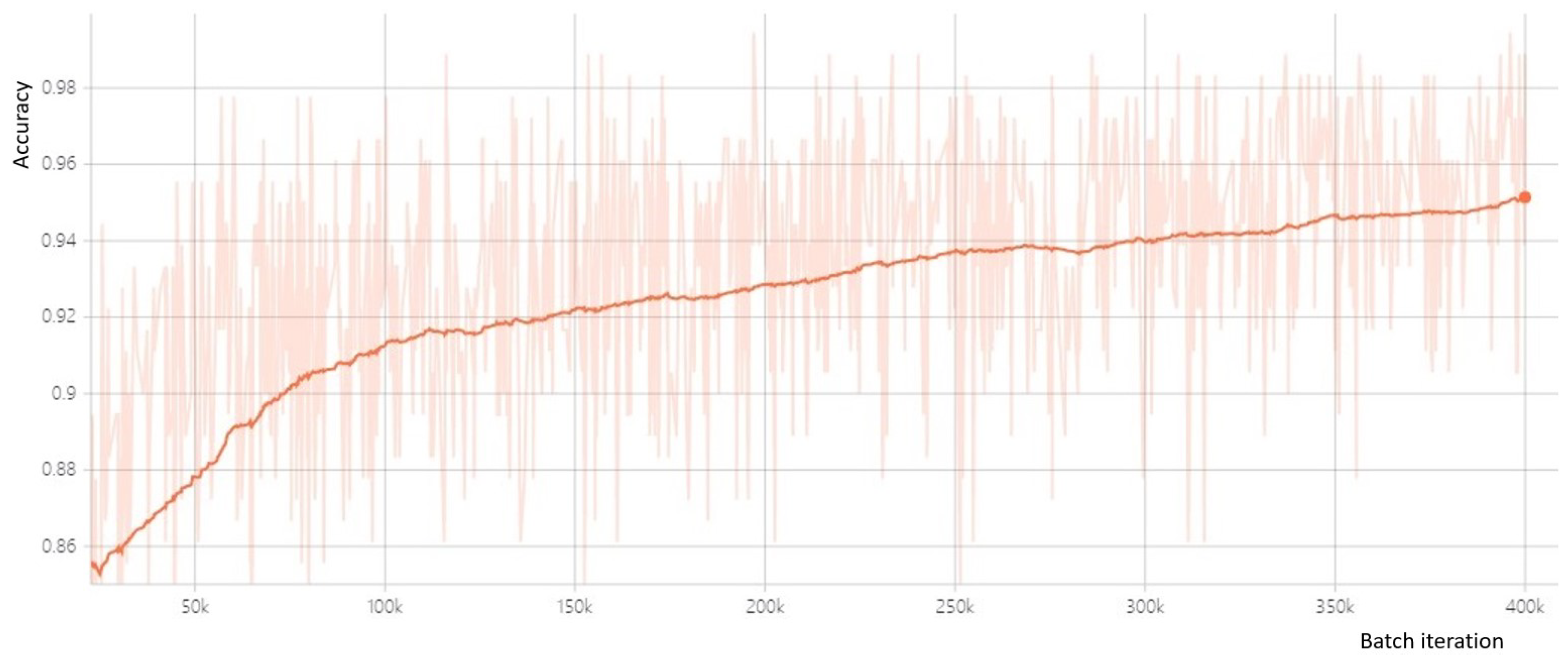
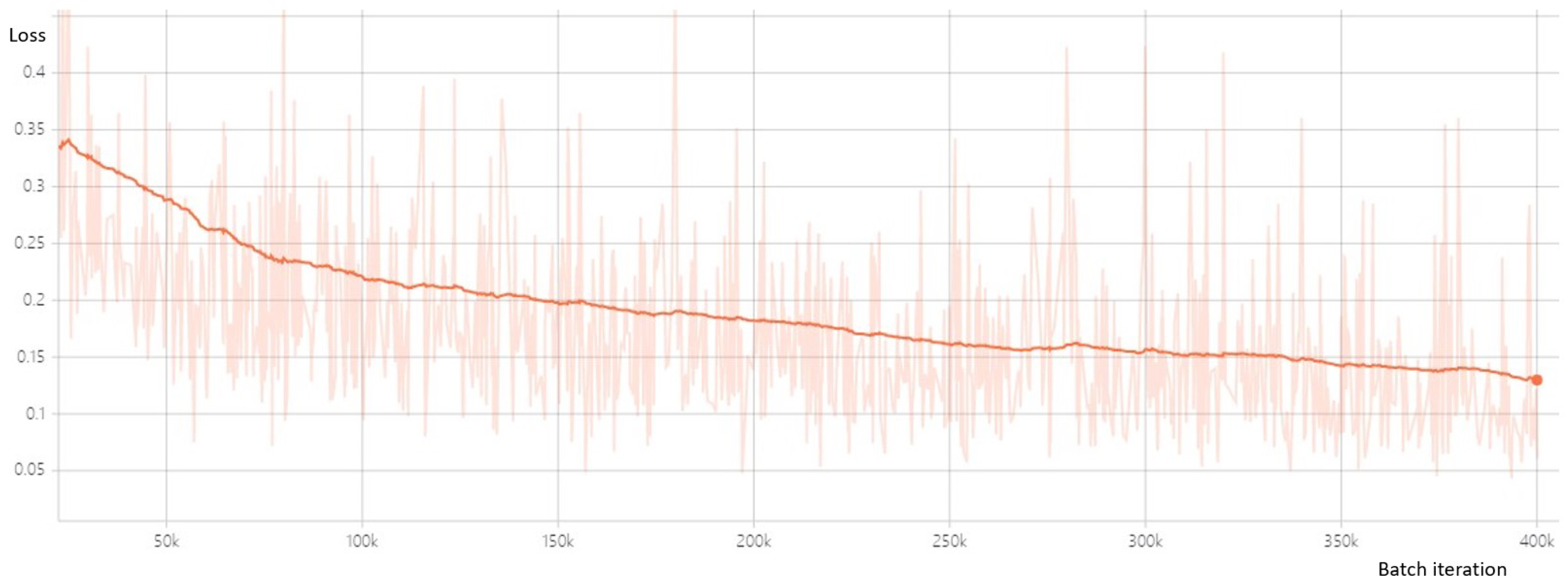
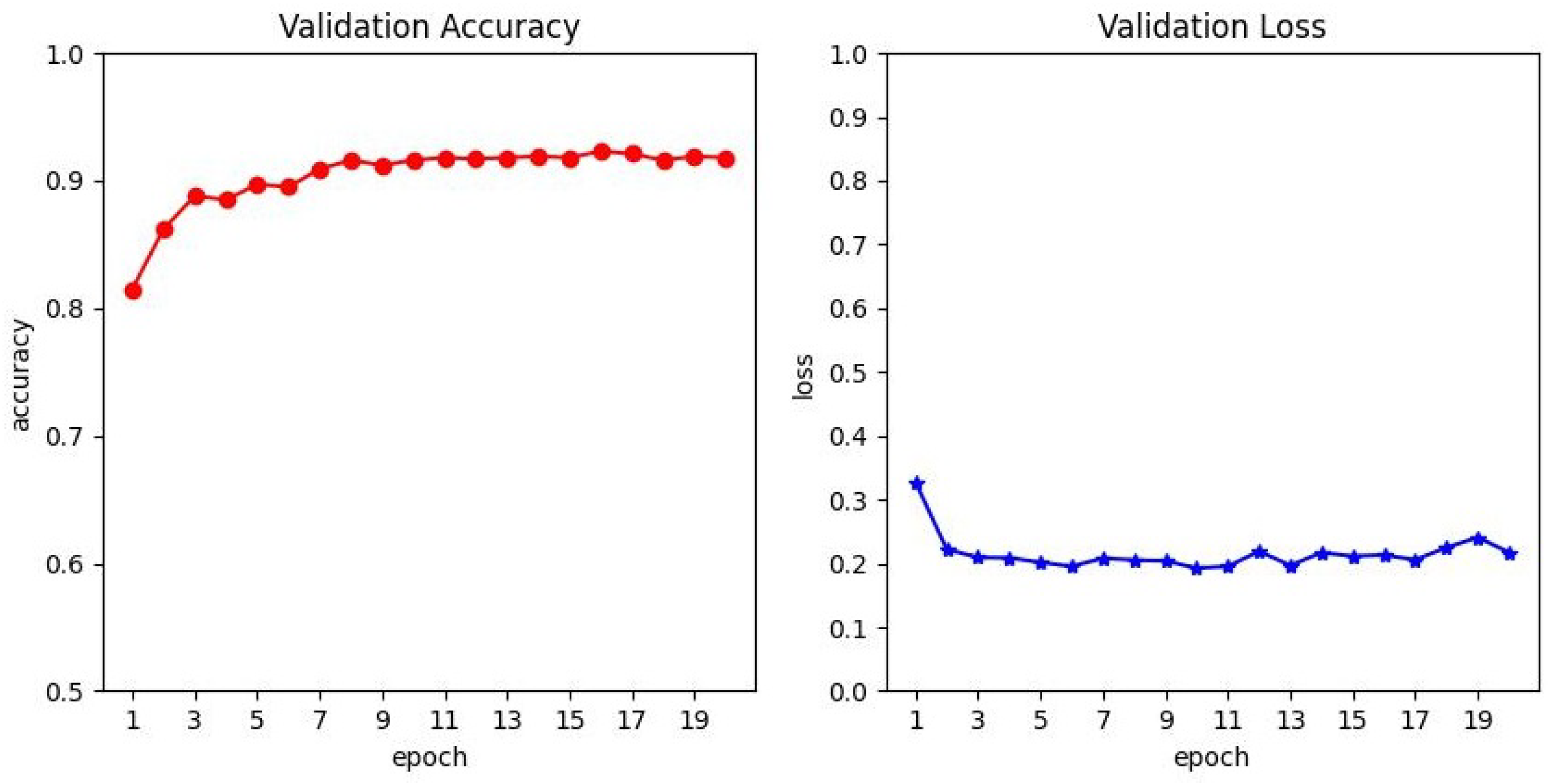
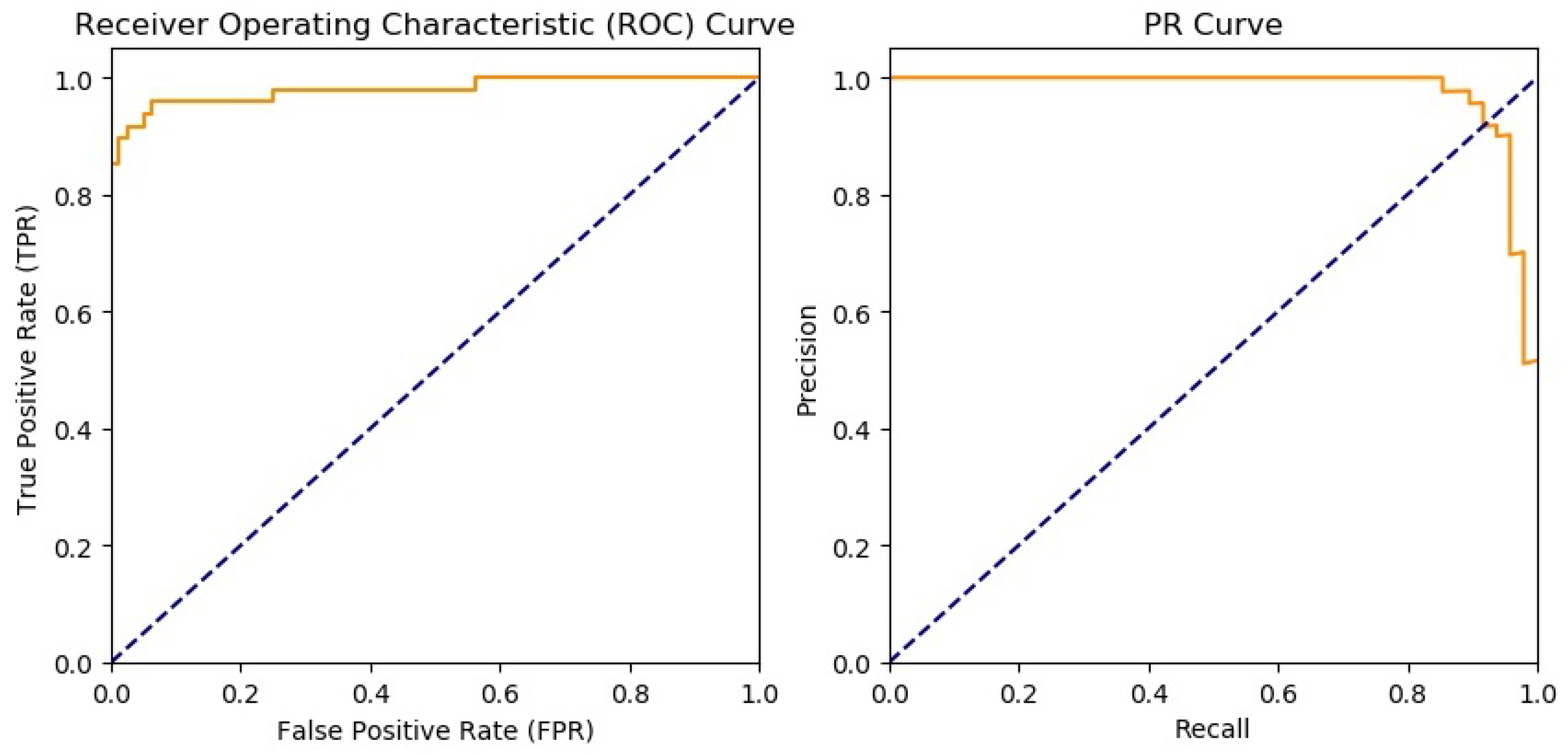
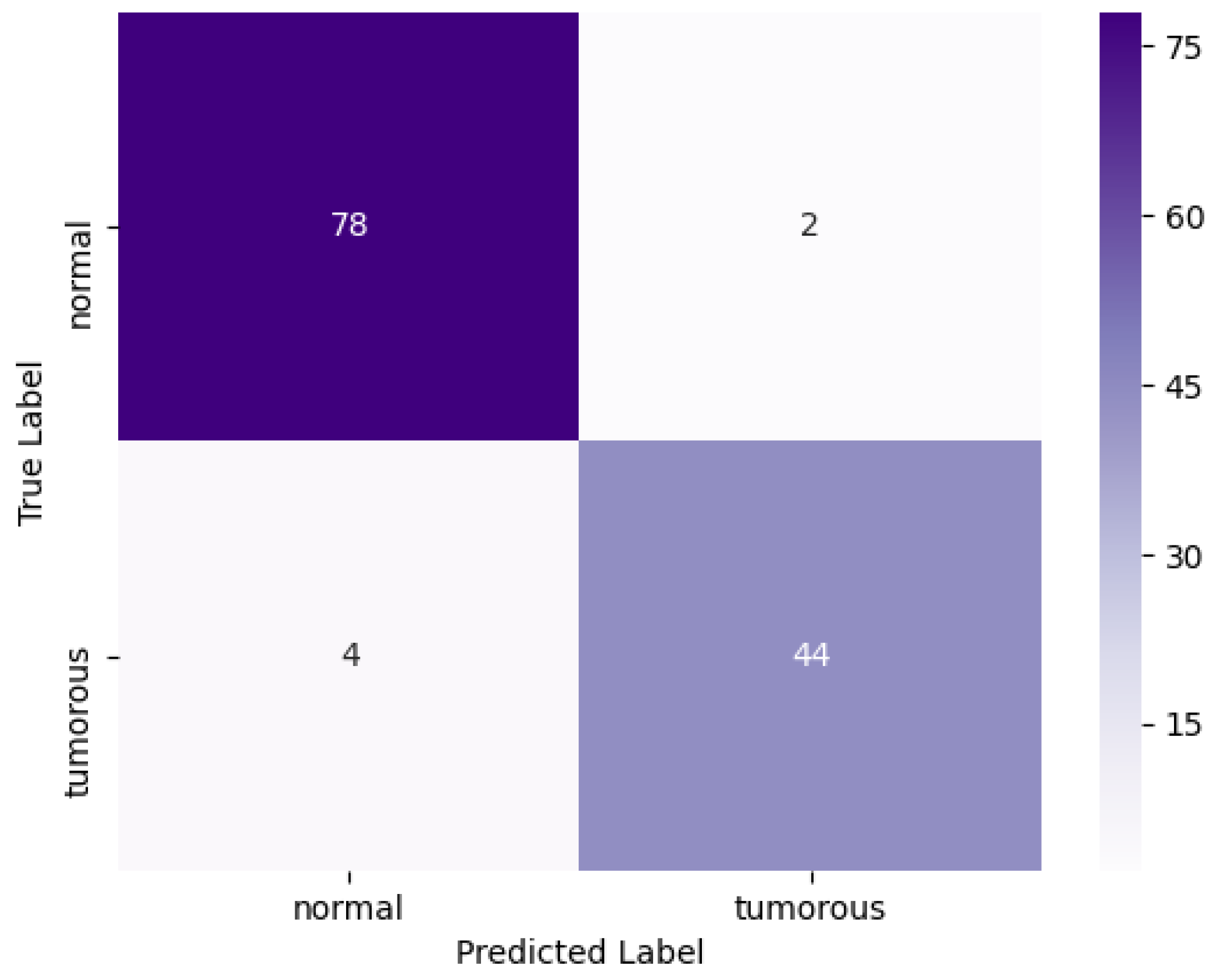
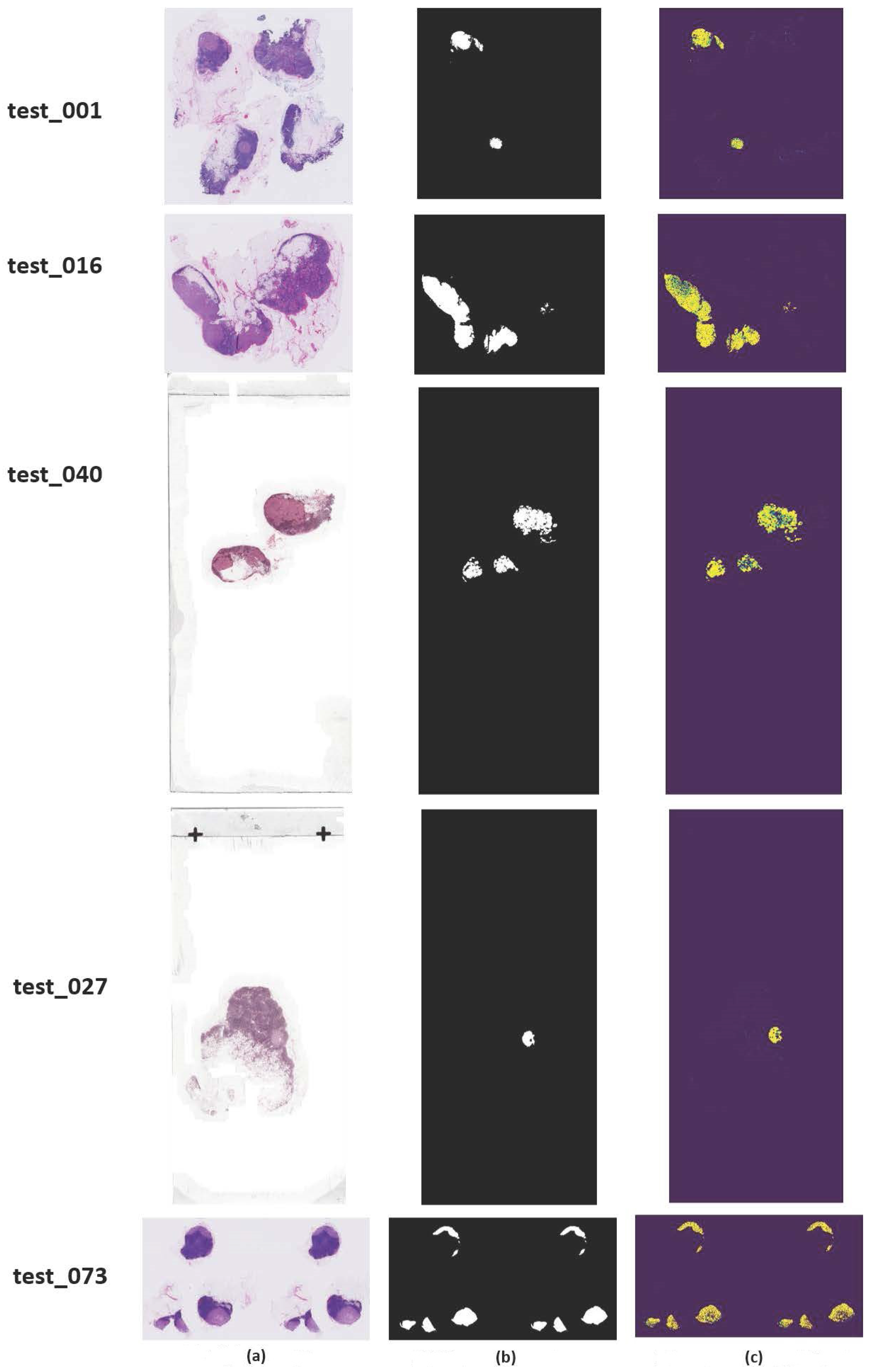
4.3. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Apple, S.K. Sentinel lymph node in breast cancer: Review article from a pathologist’s point of view. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2016, 50, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos-Vara, J.A. Principles and methods of immunohistochemistry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 691, 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys, G.; Ghent, A. World laments loss of pathology service. Bull. World Health Organ. 2010, 88, 564–565. [Google Scholar]
- Litjens, G.; Sánchez, C.; Timofeeva, N.; Hermsen, M.; Nagtegaal, I.; Kovacs, I.; Kaa, H.; Bult, P.; Ginnneken, B.V.; Laak, J. Deep learning as a tool for increased accuracy and efficiency of histopathological diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spanhol, F.A.; Oliveira, L.S.; Petitjean, C.; Heutte, L. A dataset for breast cancer histopathological image classification. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 63, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Roa, A.A.; Ovalle, J.; Madabhushi, A.; Osorio, F. A Deep Learning Architecture for Image Representation, Visual Interpretability and Automated Basal-Cell Carcinoma Cancer Detection. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Nagoya, Japan, 22–26 September 2013; pp. 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Kandemir, M.; Hamprecht, F. Computer-aided diagnosis from weak supervision: A benchmarking study. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2015, 42, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alom, M.Z.; Taha, T.M.; Yakopcic, C.; Westberg, S.; Asari, V.K. The history began from alexnet: A comprehensive survey on deep learning approaches. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.01164. [Google Scholar]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; Laak, J.A.; Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basha, J.; Bacanin, N.; Vukobrat, N.; Zivkovic, M.; Venkatachalam, K.; Hubálovský, S.; Trojovský, P. Chaotic Harris Hawks Optimization with Quasi-Reflection-Based Learning: An Application to Enhance CNN Design. Sensors 2021, 21, 6654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, M.; Pellino, S. Bucket of Deep Transfer Learning Features and Classification Models for Melanoma Detection. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanhol, F.; Oliveira, L.S.; Cavalin, P.R.; Petitjean, C.; Heutte, L. Deep features for breast cancer histopathological image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Banff, AB, Canada, 5–8 October 2017; pp. 1868–1873. [Google Scholar]
- Bayramoglu, N.; Kannala, J.; Heikkilä, J. Deep learning for magnification independent breast cancer histopathology image classification. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Cancun, Mexico, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 2440–2445. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Dong, H.; Song, F.; Zhu, C.; Liu, J. Breast Cancer Histology Image Classification Based on Deep Neural Networks. In International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 10882, pp. 827–836. [Google Scholar]
- Ehteshami Bejnordi, B.; Linz, J.; Glass, B.; Mullooly, M.; Gierach, G.; Sherman, M.; Karssemeijer, N.; van der Laak, J.; Beck, A. Deep learning-based assessment of tumor-associated stroma for diagnosing breast cancer in histopathology images. In Proceedings of the IEEE 14th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 18–21 April 2017; pp. 929–932. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Chen, H.; Dou, Q.; Wang, L.; Qin, J.; Heng, P.A. ScanNet: A Fast and Dense Scanning Framework for Metastatic Breast Cancer Detection from Whole-Slide Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; pp. 539–546. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Chen, H.; Graham, S.; Dou, Q.; Rajpoot, N.; Heng, P.A. Fast scannet: Fast and dense analysis of multi-gigapixel whole-slide images for cancer metastasis detection. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 1948–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, J.; Liu, R.; Luttrell, J.; Zhang, C. Deep Learning Based Analysis of Histopathological Images of Breast Cancer. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 80. [Google Scholar]
- de Matos, J.; de Souza Britto, A.; Oliveira, L.; Koerich, A.L. Double Transfer Learning for Breast Cancer Histopathologic Image Classification. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Budapest, Hungary, 14–19 July 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kassani, S.H.; Kassani, P.H.; Wesolowski, M.J.; Schneider, K.A.; Deters, R. Breast Cancer Diagnosis with Transfer Learning and Global Pooling. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju, Korea, 16–18 October 2019; pp. 519–524. [Google Scholar]
- Zanjani, F.G.; Zinger, S.; With, P. Cancer detection in histopathology whole-slide images using conditional random fields on deep embedded spaces. In Proceedings of the Digital Pathology, Houston, TX, USA, 6 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, B.; Xin, W.; Li, Z.; Qi, S.; Zhang, S. Cancer Metastasis Detection via Spatially Structured Deep Network. In International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 236–248. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NA, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sepp Hochreiter, J.S. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciresan, D.C.; Giusti, A.; Gambardella, L.M.; Schmidhuber, J. Mitosis detection in breast cancer histology images with deep neural networks. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 16, pp. 411–418. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Gadepalli, K.; Norouzi, M.; Dahl, G.E.; Kohlberger, T.; Boyko, A.; Venugopalan, S.; Timofeev, A.; Nelson, P.Q.; Corrado, G.S. Detecting cancer metastases on gigapixel pathology images. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.02442. [Google Scholar]
- Goode, A.; Gilbert, B.; Harkes, J.; Jukie, D.; Satyanarayanan, M. Openslide: A vendor-neutral software foundation for digital pathology. J. Pathol. Inform. 2013, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Khosla, A.; Gargeya, R.; Irshad, H.; Beck, A.H. Deep learning for identifying metastatic breast cancer. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.05718. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, L.; Wei, P. Cancer Metastasis Detection With Neural Conditional Random Field. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.07064. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Chintala, S.; Chanan, G.; Yang, E.; Devito, Z.; Lin, Z.; Desmaison, A.; Antiga, L.; Lerer, A. Automatic Differentiation in PyTorch. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017) Autodiff Workshop, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tijmen, T.; Hinton, G. Lecture 6.5-rmsprop: Divide the gradient by a running average of its recent magnitude. COURSERA Neural Netw. Mach. Learn. 2012, 4, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Hanley, J.A.; Mcneil, B.J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (roc) curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, D.P. Maximum likelihood analysis of free-response receiver operating characteristic (froc) data. Med. Phys. 1989, 16, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
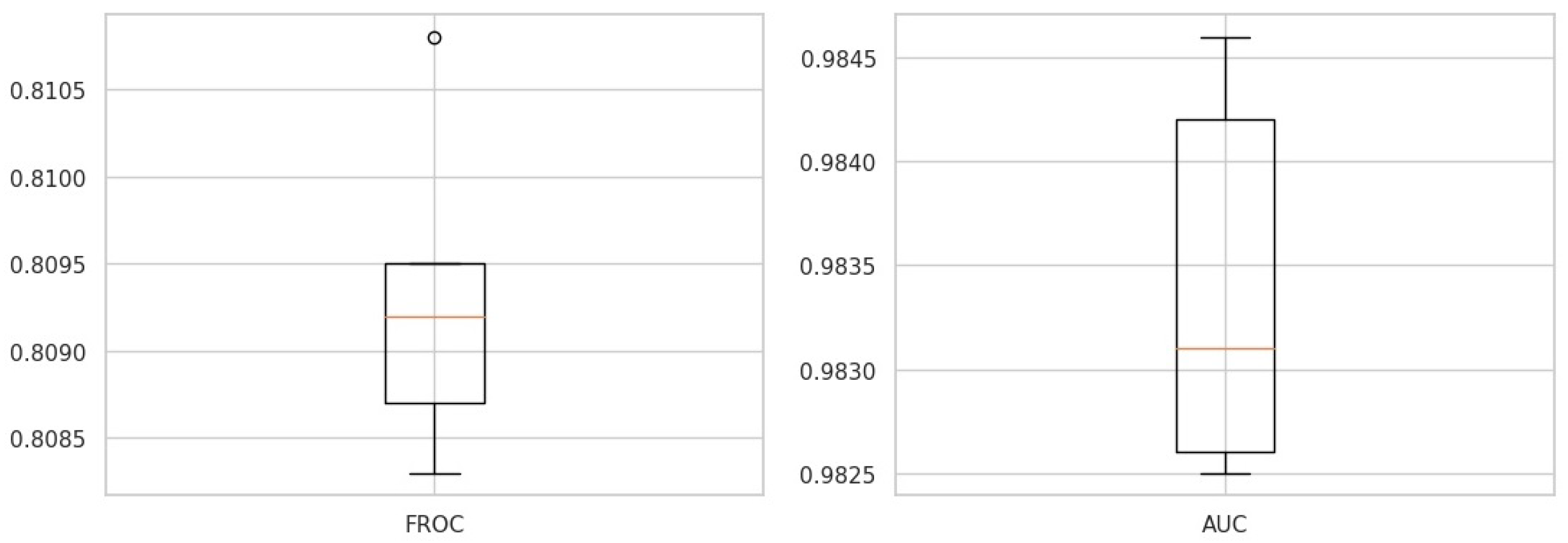
| Methods | FROC Score | AUC Score |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline ResNet-34 | 0.7463 | 0.9524 |
| The proposed framework without spatial constraint loss | 0.7542 | 0.9681 |
| The proposed framework | 0.8093 | 0.9834 |
| Approaches | FROC Score | AUC Score |
|---|---|---|
| Human performance | 0.7325 | 0.9660 |
| C Radboud Uni. (DIAG) | 0.5748 | 0.7786 |
| Middle East Tech. Uni. | 0.3889 | 0.8642 |
| L HMS, Gordan Center, MGH | 0.7600 | 0.9763 |
| NLP LOGIX co. USA | 0.3859 | 0.8298 |
| EXB Research co. | 0.5111 | 0.9156 |
| DeepCare Inc. | 0.2439 | 0.8833 |
| University of Toronto | 0.3822 | 0.8149 |
| The proposed framework | 0.8093 | 0.9834 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, H.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, X. Spatiality Sensitive Learning for Cancer Metastasis Detection in Whole-Slide Images. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10152657
Zheng H, Zhou Y, Huang X. Spatiality Sensitive Learning for Cancer Metastasis Detection in Whole-Slide Images. Mathematics. 2022; 10(15):2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10152657
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Haixia, Yu Zhou, and Xin Huang. 2022. "Spatiality Sensitive Learning for Cancer Metastasis Detection in Whole-Slide Images" Mathematics 10, no. 15: 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10152657
APA StyleZheng, H., Zhou, Y., & Huang, X. (2022). Spatiality Sensitive Learning for Cancer Metastasis Detection in Whole-Slide Images. Mathematics, 10(15), 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10152657






