Abstract
While English major education is of significant importance in China, there is a lack of comprehensive research that provides a broader perspective, encompassing a thorough exploration and comparison of the diverse program modes employed across different undergraduate English programs in China. The focus of this study is to (1) discern the overarching characteristics of undergraduate English programs in China; (2) identify undergraduate English program modes in China; and (3) delve into the relationship between the identified modes and university discipline evaluation rankings. The dataset includes undergraduate English program handbooks from 50 universities in China and information on 2942 courses extracted from these handbooks. The findings suggest that English programs in universities and colleges in China exhibit a predominantly application-oriented approach. In addition, three modes were identified: Literature and Linguistics, Balanced, and High English Skills. The High English Skill mode was found to be linked with a lower ranking compared to the High Literature and Linguistics mode. The study concludes by offering implications for the design of a future English program based on the insights gained from the analysis.
1. Introduction
The development of English programs plays a crucial role in China’s future international cooperation, given the global prevalence of English as the most widely used language [1]. At present, approximately 82.4% of colleges and universities in China offer foreign language learning programs at the undergraduate level, of which 944 are English programs [2]. However, despite the substantial enrolment in these programs, concerns and criticisms surround the current state of English programs. Some of these concerns stem from the perception that the English programs lack specialization and do not offer substantial knowledge. This is further exacerbated by the challenging employment situation for graduates of English programs, which is characterized by low employment rates and job quality [3].
As a result, some English programs in China have switched to “English + X” modes, wherein “X” represents a subject that is relevant to utilizing English, such as economics, law, social science, or computer science. While this shift is noteworthy, it is equally crucial to take a step back and engage in a more comprehensive assessment of the English program modes in terms of their underlying visions, training goals, and program features. In this pursuit, Hu discussed a compound, research-oriented, and internationally focused training system of English programs, exemplified by the successes at Shanghai Jiao Tong University [4]. Likewise, Huang scrutinized the English program practices at the Huazhong University of Science and Technology based on the Chinese National Standards for Undergraduate Teaching Quality of English Majors in Colleges and Universities [5]. In another study, Zou and Yang studied the curriculum design across 11 universities in Western China [6]. By focusing on individual cases, these studies contribute to the understanding of English program training goals and characteristics in China. However, it has emerged that there is a need for a broader perspective that encompasses a comprehensive exploration and comparison of the diverse modes in practice across various English programs in China.
Indeed, we postulate that such study is necessary. While undergraduate English programs in China adhere to a common guideline and encompass five different course types (i.e., linguistics, literature, translation, English skills, and culture/national and regional studies), inherent differences arise due to the specialized areas that the Chinese National Standards for Undergraduate Teaching Quality of English Majors in Colleges and Universities endorse at each university, due to their specific teaching emphasis. As a result, the design and execution of English programs exhibit variations, leading to the potential existence of diverse combinations of course types among these universities. For instance, certain universities may allocate roughly equal weight to all five types of English program courses, while others may prioritize linguistics-related courses, aligning with the expertise of their faculty members. As such, the distribution and emphasis on various course types can diverge significantly from one institution to another. Given this context, it becomes crucial to ascertain the range of combinations of course types that exist within the current landscape of English programs in China.
Moreover, we postulate that such different combinations of course types in various English programs may also influence the overall reputation of the university. This reputation could potentially be reflected in the institution’s China Discipline Evaluation (CDE) rank—a widely-acknowledged university ranking system in China, published by the China Academic Degrees and Graduate Education Development Centre (CDGDC) once every four years. Thus, investigating the relationship between different combinations of course types and evaluation ranks holds significance—does the evaluation system show a special preference for certain combinations of course types?
Therefore, this study aims to answer the following questions:
- What are the general characteristics of program learning objectives in undergraduate English programs in China?
- How many different combinations of course types (based on the common course types) are there in undergraduate English programs in China?
- What is the relationship between the different combinations of course types and the CDE rank?
This research can offer invaluable insights into the program diversity and priorities present across different universities in China, facilitating a more nuanced understanding of the English program modes in China. In addition, we posit that the findings of this paper could create generalized insights aimed at English program development, reform, and innovation for English educators in other countries. This is especially pertinent in a global context where a noticeable decline in English program enrolment has become a prevailing trend [7].
2. Literature Review
2.1. National Standard of Undergraduate English Programs in China
At the country stepped into the 21st century, under the requirements of the new era, the Ministry of Education introduced the official English Teaching Syllabus for English Majors in Higher Education (Syllabus 2000 hereafter). This syllabus, released in April 2000, marked the introduction of the term interdisciplinary English education within the context of undergraduate English programs. The guiding principles of Syllabus 2000 separated undergraduate English program courses into three categories: English Skills courses (e.g., listening and translation), Content Knowledge courses (e.g., linguistics and British and American literature), and General Education courses (e.g., Diplomacy and Law) [8]. However, although the Syllabus 2000 acknowledged the importance of the integration of English programs with other disciplines, it still had several shortcomings. Notably, it underestimated the importance of literature, grammar, and regional studies in education [9], and placed an excessive emphasis on skill-oriented courses at the expense of creative and open courses [10]. In summary, the training goals outlined in the Syllabus 2000 primarily emphasized the practical application of English as a language, while overlooking its potential as a scholarly pursuit.
By 2012, a significant shift occurred with the issuance of The Catalogue and Introduction of Undergraduate Majors in Higher Education (hereafter, Catalogue). This document brought about adjustments to the training goals of English programs by adding requirements for English language literature knowledge and humanistic qualities. The core courses of the English program were divided into two main categories: English Skills courses and Content Knowledge courses. Compared with the Syllabus 2000, the proportion of learning hours allocated to English Skills courses significantly decreased, while that for Content Knowledge courses increased. Such an adjustment implied a greater focus on advanced content knowledge over basic skills. However, the new Catalogue also retained certain limitations: it continued to overlook courses that combined English with other subjects [11], and there remained an incongruity between the distinct English proficiency levels of students across different universities and the standardized requirements for basic English skills. Consequently, the classification and course design within English programs emerged as challenges in need of resolution.
In the new stage of higher education development, the Ministry of Education in China organized Teaching Guidance Committees for various majors in colleges and universities. This collaborative effort led to the compilation of the National Standards of Teaching Quality for Undergraduate Majors in Colleges and Universities encompassing 92 different undergraduate majors. One outcome of these endeavours was the publication of the National Standards for Undergraduate Teaching Quality of English Majors in Colleges and Universities (hereafter, National Standards) in 2018. In terms of its training goal, this document places paramount importance on fostering “good comprehensive quality”, while simultaneously introducing a new requirement of being “adaptive to the national economic construction and social development” [12]. The National Standards outlines a curriculum structure for English majors comprising five different components: general education courses, compulsory courses, elective courses, teaching practice, and a graduation thesis. In particular, the elective courses fall into four perspectives, Language, Literature, Culture, and Specialty, with the latter being determined independently by each university.
The National Standards has significantly addressed the issue of course classification and circumvented the challenge of segregating English courses into distinct categories of English Skills and Content Knowledge courses [11]. The meticulous classification of elective courses further enriches students’ prospects, allowing them to dive into the areas that pique their interest. Moreover, the introduction of teaching practices and a graduation thesis is conducive to the holistic development of students’ abilities and qualities. The incorporation of the specialty perspective also permits universities to have flexibility in designing distinctive English program courses that align with their unique characteristics.
Although the publishing of the National Standards marks a significant departure from the skill-oriented approach to English programs to embracing the humanistic attributes of the program as its cornerstone, there remains potential for refinement. For example, to enhance the applicability of professional educational guidance derived from the National Standards, it is advisable to formulate guiding principles tailored to English programs within various types of institutions, such as foreign language colleges, teacher education colleges, and comprehensive universities [11]. The National Standards underscores the importance of humanism in English programs and offers distinct categorizations alongside innovative course designs. This not only provides guidelines and requisites but also sets the stage for the sustainable and wholesome advancement of English programs in China [13].
Looking back at the previous official guidelines for English program education in China, it is not surprising to find that issues, such as (1) course categorization, (2) pragmatism versus humanism, and (3) subject-specific knowledge versus interdisciplinary knowledge, have consistently emerged, prompting several adjustments to the original directives. The refinement of the course classification tends to be more detailed and coherent, which has manifested through the introduction of the concept of core courses and elective courses. This resulted in the establishment of the five core course types: linguistics (e.g., Introduction to Linguistics), literature (e.g., American and British Literature), translation (e.g., Interpretation), English skills (e.g., English Writing), and culture/national and regional studies (e.g., American Society and Culture). This delineation affords students greater autonomy in course selection. The dichotomy between English as a tool and English as a subject has found resolution in the resurgence of humanistic dimensions, while practical courses still hold their places. For instance, Tsinghua University has introduced courses such as Selective Reading of Critical Theory and Greek Myths and Civilization, underscoring a heightened focus on humanities-based studies. The incorporation of literature courses and the classification of electives into four fields reveal a growing trend towards a diversified foundation in undergraduate English program education. Last but not least, the concept of interdisciplinary learning, first introduced in Syllabus 2000, has continued to evolve within English program education. This evolution is evident not only in the introduction of new courses, such as Statistical Methods in Language Research and Computer-Aided Translation [14], but also in the refinement of new programs such as Business English [15]. Beijing Foreign Studies University’s establishment of Beiwai College, offering an English (International Organization) program, exemplifies this trend by permitting students to simultaneously study English and a complementary subject, such as Diplomacy, Finance, or Law [16].
2.2. China’s Discipline Evaluation of English Programs
The CDE is a non-profit program organized by the CDGDC, which evaluates the disciplines of universities and scientific research institutions in mainland China in accordance with the Discipline Catalogue of Degree Awarding and Personnel Training. It assigns rankings from A+ to C− to disciplines, aiming to facilitate development, reform, and management through the evaluation of educational institutions.
The CDE was first carried out in 2002 and has undergone five rounds of evaluation to date. Over the past two decades, it has seen the gradual improvement in evaluation content encompassing teaching–research–service, the refinement of evaluation methods involving measurement–description–judgment, and the logical progression in “absolute-relative-stratification” in the evaluation results [17]. A total of 7449 disciplines from 513 institutions participated in the fourth round of the CDE, and English (as Foreign Language and Literature) is certainly one of them. Due to the unpublished status of the fifth round, which was finished in 2022, this study utilized the results of the fourth round for the analyses.
The CDE promotes the standardized construction of disciplines within universities, improves the quality of undergraduate education, and offers insights into the quality of universities and scientific research institutions [18]. Its procedures and methods for data collection, verification, and evaluation have undergone gradual refinement, evolving into a program evaluation system that bears distinctive Chinese attributes and global impact [17]. However, despite its progress, the current evaluation index system still has certain limitations. For instance, it focuses on the benefit of discipline construction while ignoring the measurement of efficiency and sustainability of discipline development. Moreover, it carries out a superimposed evaluation that assesses both the resource input and output of discipline construction. This approach can potentially lead to the inequitable allocation of discipline resources and waste of resources within educational institutions [19]. Therefore, in order to reduce the undue allocation, it is important to determine the relationship between CDE ranks and universities’ program modes. This understanding can facilitate appropriate adjustments to the CDE system and promote a more balanced resource allocation.
3. Methodology
3.1. Sample
In this study, the sample consisted of undergraduate English program handbooks collected from different universities in China. The universities were selected from the fourth round CDE, ranging from the A+ level to B− level. Since programs with a ranking ranging from C+ to C− generally have a limited reference value due to their lower quality, they were excluded from consideration. After accounting for missing information from certain universities, we successfully gathered English program handbooks from a total of 50 universities, encompassing information from 2942 courses, amounting to a total of 6750 credits. Among these 50 universities, 8 belong to the prestigious C9 League (tier 1), 13 are part of the Project 985 universities (tier 2, excluding tier 1 universities), and 14 are categorized as Project 211 universities (tier 3, excluding universities in tier 1 and 2). (The C9 League is a coalition of nine Chinese universities established in 2009 with the aim of advancing the progress and prestige of higher education in China. The Project 985 universities are esteemed academic institutions that select students through a highly competitive process conducted by the National Higher Education system. On the other hand, Project 211, initiated in 1995 by the former State Education Commission of China, was designed to enhance the research capabilities of comprehensive universities and foster strategies for socio-economic development.) In terms of university characteristics, 25 are comprehensive universities, 10 specialize in teacher education, 4 focus on science and engineering, 8 are foreign language universities, and 3 are finance universities. A comprehensive list of the selected universities is shown in the Appendix A.
According to the National Standards, all English program courses were divided into five distinct course types: linguistics, literature, translation, English skills, and culture/national and regional studies.
3.2. Data Collection
The authors collected the program handbooks through searching their official websites and downloading the files. In cases where the university’s website did not provide the required files, we manually copied or printed their curriculum information. For universities that did not upload specific program handbooks, personal connections were leveraged to gather the necessary data.
The CDE data were collected from the official website of the CDGDC, https://www.cdgdc.edu.cn/cde/Latest_Results_of_CDE.htm (accessed on 9 March 2023). Since the latest fifth-round evaluation has not been released to the public, the data of the fourth round (2017) were used instead.
3.3. Data Analysis
Before the data analysis, a thorough review of each university’s program handbook was conducted, and pertinent information regarding the core and orientation courses was collected manually. These data were compiled into a document in preparation for the subsequent analysis.
To answer the first research question, the word frequency count method was used. By calculating the absolute frequency of various words in the program training goals with the help of Weiciyun, https://www.weiciyun.com (accessed on 9 March 2023), a comprehensive understanding of the shared concerns among these universities’ program training goals was gained. Augmented by an analysis of the frequently occurring words, a general description of English programs in China was established.
To tackle the second research question, the K-means clustering analysis method was applied to the data. This algorithm assigns the most similar objects to one group while maximizing the distinctions between different clusters [20]. The total number of core courses and electives within specific course types was aggregated, and the proportion of each course type in the overall curriculum for each university was calculated. This proportion was used as an indicator of the universities’ strength in each course type for the K-means clustering analysis.
To address the third research question, three multiple regression models were developed using the R software. The dependent variable was the CDE rank. For ease of analysis, the CDE ranks were converted into interval variables, ranging from five to one (i.e., A+ = 5, A = 4.5, A− = 4, B+ = 3.5, B = 3, B− = 2.5, C+ = 2, C = 1.5, C− = 1), with increments of 0.5 points for each level. In the subsequent analysis, the predictors included the combination of course types (derived from the second research question), project level, and university type. In the first step of the regression model, the combination of course types were entered, with one of the combination types being chosen as the reference group. In the second step, project level was added as a categorical independent variable (i.e., C9 League, Project 985, Project 211, and None) to control the effect of the universities’ overall strength. Those universities that belong to the None group were used as the reference group. Lastly, in the third step, university type was introduced as a categorical independent variable (i.e., Comprehensive, Teacher Education, Science, Language, and Finance Universities), with universities in the Comprehensive group serving as the reference group.
4. Results
4.1. Features of Undergraduate English Programs in China
The word frequency of the program training goals among the 50 selected universities was calculated. During this process, filler words (e.g., which is equivalent to “of”) and meaningless descriptive words were filtered out. Moreover, the listed words had to be longer than three Chinese characters and were limited to nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs.
As shown in Table 1, cross-cultural ranked first in the word list, indicating the relatively important role of multi-cultural communication in undergraduate English programs. This was followed by content knowledge, basic skill, and language and literature, highlighting the strict requirements for basic English knowledge in English programs. Foreign affairs frequently emerged as the expected career path for English program students. Subsequently, terms such as high-quality, international, and innovative ability underscore the requirements for English programs. English education came next as another expected career path, while responsibility signified the importance of developing appropriate ethical values among English program students. This was followed by subject-matter experts and research ability (i.e., further study).

Table 1.
Top 12 word frequency in program learning objectives.
Therefore, based on this analysis, some general features of English programs in China can be gathered: there is a strong focus on cross-cultural competence, content knowledge, and language skills; an emphasis on appropriate innovative competences and ethical values; and preparation for careers in fields such as English education and foreign affairs. This collectively portrays an application-oriented approach to English programs in China.
4.2. Combinations of Course Types in English Programs
An unsupervised K-means cluster analysis was adopted to identify different combinations of course types in English programs. The optimal number of clusters was determined using the silhouette width method. According to Figure 1, both two and three clusters emerged as potential options, due to the variance stemming from different random seeds. However, the result of the two-combination solution failed to exhibit discernible differentiating characteristics. The number of combinations was finally set to three. With the help of the K-means algorithm, we used the number of courses in the five-course-categories as the five independent variables for each university. Subsequently, the 50 universities were automatically classified into three combinations of course types. The descriptive details for each combination are presented in Table 2.
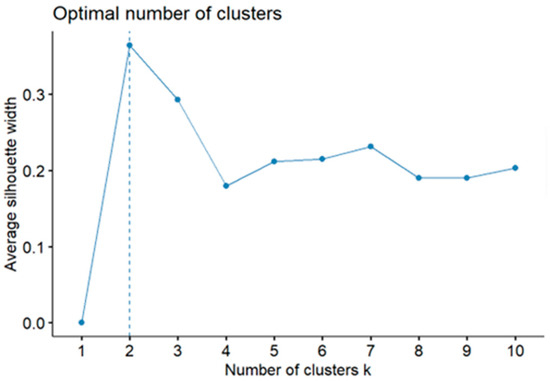
Figure 1.
Average silhouette width plot.

Table 2.
Means of the five course types in each combination.
According to Table 2, there are distinctive features within each combination. The universities in Combination 1 displayed a greater emphasis on Literature and Linguistics courses within their English program. Conversely, universities in Combination 3 demonstrated a pronounced focus on English Skills, placing less emphasis on Literature, Linguistics, and Culture courses. In contrast to the other combinations, the universities in Combination 2 exhibited a relatively even distribution of development modes across all five course types, with English Skills and Translation holding particular significance.
In addition to the differences among the three combinations, a prevailing pattern in English program development can also be discerned. When comparing the mean proportions of the five course types, a notable emphasis on English Skills within English programs becomes evident. In contrast, less focus on Linguistics is apparent, as only 11 universities in Combination 1 prioritize Linguistics as their primary English course. The further scrutiny of individual program handbooks revealed that Linguistics and Culture courses in most universities comprised a single introductory core course, accompanied by two or three elective courses. In contrast, English Skills courses occupy a significant portion of the first-year curriculum. These disparities corroborate the findings from the preceding analysis, thereby aligning with the content derived from the program training objectives and graduation prerequisites.
Consequently, three distinct combinations of course types were identified for the English program in China: (1) High Literature and Linguistics; (2) Balanced; and (3) High English Skills. The universities in each combination tended to skew teaching resources towards course types that are described as high.
4.3. Relationships between Combinations and CDE Rank
Once the combinations of course types for English program modes were determined, the combination information was integrated into the dataset for addressing the third research question. In this context, each university was assigned a combination number, project level, university type, and CDE rank. Subsequently, a multivariate regression analysis was conducted. The regression models included combination, type, and project level as the categorical variables, with CDE rank treated as an interval variable. The outcomes of the regression analysis are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
The effects of factors on CDE ranks.
In Model 1, compared to the combination of “High Literature and Linguistics, Low English Skills”, only the combination of “Low Literature, Linguistics and Culture, High English Skills” demonstrated a significantly lower CDE rank (b = −4.86 × 10−1, p < 0.001). The combination of “Balanced, High Translation, and English Skills” did not show a significant difference in CDE rank compared to the combination of “High Literature and Culture, Low English Skills”. The R-squared of this model was 0.22.
In Model 2, the universities belonging to the three project levels did not show significant differences in CDE rank compared to those not affiliated with Project 211, Project 985, and the C9 League. However, the combination of “Low Literature, Linguistics, and Culture, High English Skills” displayed a significantly lower CDE rank when compared to the “High Literature and Culture, Low English Skills” combination (b = −0.74, p < 0.05). In contrast, the combination of “Balanced, High Translation and English Skills” showed insignificant differences in CDE rank when comparing with the combination of “High Literature and Culture, Low English Skills”. This implies that the evaluation system displays a notable less preference against the specific combination of “Low Literature, Linguistics and Culture, High English Skills” course types when controlling for project levels. The R-squared for Model 2 was 0.28.
In Model 3, with all three independent variables included in the multivariate regression model, the universities belonging to Project 211, Project 985, and the C9 League demonstrated significantly higher CDE ranks compared with universities not belonging to these projects (b = 0.51, p < 0.05, and b = 0.65, p < 0.05, and b = 1.3, p < 0.001, respectively). Language and Finance universities displayed significantly higher CDE ranks in comparison to Comprehensive Universities (b = 1.13, p < 0.001 and b = 0.82, p < 0.05, respectively). Additionally, the combination of “Low Literature, Linguistics and Culture, High English Skills” showed a significant negative difference in CDE rank compared to the combination of “High Literature and Culture, Low English Skills” (b = −0.54, p < 0.05). However, the combination of “Balanced, High Translation and English Skills” showed no significant difference in CDE rank when compared to the combination of “High Literature and Culture, Low English Skills”. Additionally, while the effects of all three project levels on CDE rank were positive, it should be noted that the effect size of belonging to the C9 League (1.3) was greater than that of belonging to Project 985 (0.65), and the effect size of belonging to Project 985 (0.65) was greater than that of Project 211 (0.51). The R-squared of Model 3 reached 0.53.
In summary, there is significant relationship between the CDE rank and certain combinations of course types, when controlling for project level. A nuanced inspection revealed that the CDE system displays a relatively lower preference for combinations of course types that emphasize English Skills compared to other combinations. Furthermore, the universities affiliated with higher project levels, as well as those categorized as Language or Finance Universities, tended to have higher CDE ranks.
5. Discussion
5.1. Features of Undergraduate English Programs in China
The first purpose of this study was to summarize the general features of the program training goals in undergraduate English programs in China. Through a word frequency analysis on program training goals among 50 undergraduate English programs, we identified 12 keywords: cross-cultural, content knowledge, basic skill, language and literature, foreign affairs, high-quality, international, innovative ability, English education, responsibility, subject-matter experts, and research ability. Cross-cultural not only includes the import of culture of English-speaking countries, but it also emphasizes the export of Chinese culture in English. The emphasis of the term cross-cultural in universities’ training goals matches the requirements for English program students in the National Standards [12]. Content knowledge refers to the advanced knowledge related to English, which especially correlates with Linguistics and Literature courses in English majors. On the other hand, basic skill tends to refer to the basic knowledge related to English, which treats English as a communication tool and correlates with Listening, Reading, Speaking, and Writing courses. Together with the keyword language and literature, the high occurrence rate of these three keywords in the training goals meets the requirements for English program students in the three national standards mentioned previously, showing the importance of having a solid knowledge of English. Foreign affairs is the most mentioned target working field for English program students, which includes jobs such as interpreter. The frequent reference of this field reflects the current trend of English programs as application-oriented. High-quality refers to the requirements of excellence for English program students, while international shows another stress on cross-cultural communications, which are common and constant requirements for English program students in each version of the national standards. Nevertheless, innovative ability, as an embodiment of critical thinking and language comprehensive application, was first mentioned in the National Standards (2008) in China, which addresses the shortcomings of the Council of Europe (CEFR, 2001) on which it was based [12]. Its appearance in the top 12 keywords in the training goals shows the fast implementation of the National Standards by Chinese universities. English education refers to another target working field for English program students, which includes jobs such as English teachers. This field also represents English programs’ application-oriented attribute. Responsibility refers to the value that students must have, aiming to train students who are responsible for both themselves and society. Subject-matter experts and research ability together refer to the expectations for English program students’ content knowledge and emphasizing students’ advanced research ability, respectively.
Although the National Standards has promoted a more humanities-based approach to English program education in recent years, the findings from this study suggest that the current state of English programs still seems to be application-oriented, aligning with previous studies that pointed out that language knowledge and ability are always put first by English programs in China [8,13,21]. Two possible explanations could be proposed for the gap between expectation and implementation. The first explanation is that the universities’ curriculum design largely depends on the faculty constitution and current teaching resources, which implies that the transition from conception to realization might take several years and the National Standards was only published five years ago. The second explanation is that actual program training goals are influenced by the demands of the recruitment market. As the official document The Guidelines on Guiding Some Local Colleges and Universities to Transform into Applied Ones published in 2015 has pointed out, ordinary colleges and universities should adapt to the economic developmental trend with a keen consideration for the future employment prospects of their students. In such circumstances, application-oriented program training goals might be beneficial and practical for both ordinary universities and students.
In addition to the lack of humanitarianism, the word frequency of concepts related to fostering one’s ethical values and virtues through foreign language education is far from sufficient. In June 2020, the Ministry of Education issued the Guidelines for Ideological and Political Construction in Higher Education Courses, which called for colleges and universities to “promote ethical education in courses according to the characteristics of different majors” [22]. Given this context, Liu et al. suggested that English program students play an irreplaceable role in China’s initiatives and implementation of “telling China’s story well” and building a “community with a shared future for mankind” [23]. Therefore, it is necessary for Chinese universities to emphasize the requirements of ethical values in their program training goals in the future.
5.2. Combinations of Course Types in English Program Modes
Using the K-means algorithm, the 50 sample universities that ranked above B in the CDE were divided into three combinations of course types, representing three distinct modes for English programs in China: (1) High Literature and Linguistics; (2) Balanced; and (3) High English Skills. Based on the three combinations and their features, it is promising to find that most of the sample universities developed their unique strengths and specialties as the National Standards suggested. However, the large number of universities focused on English Skills (46%) in their English program also implies that the mainstream English program mode is still application-oriented, which is similar to the results achieved in the previous analysis. According to Hu and Sun [24], the preference of resources in basic English is due to the policy of training versatile students in Syllabus 2000. Furthermore, they also blame the predominance of skills training courses for the low and unbalanced level of the students’ English abilities.
On the other hand, universities that specialize in Linguistics are limited (22%), suggesting a large gap in student development in this field in China. Such a limitation bears out the concern of some scholars, who call on Chinese English programs to increase coverage of British and American literature, linguistics, and the study of English-speaking countries (including intercultural studies) [25]. It is understandable that the Linguistics area is not as popular as English Skills in most universities. Nevertheless, as Wang [26] pointed out, Linguistics courses enable students to further develop their language knowledge system, which will lay a good foundation for future language courses and in learning international literature and translation. Therefore, the emphasis on Linguistics courses should also be taken into consideration. Universities could offer more introductory-level linguistics courses tailored to individual universities’ program training goals and available teacher resources.
5.3. Relationships between Combinations of Course Types and the CDE of English Programs
The third purpose of this study was to determine the relationships between combinations of course types and the CDE for English programs. We found that, when controlling for project level, there were significant relationships between the CDE rank and certain combinations of course types. The CDE ranks tend to be lower for combinations of course types that focus on English Skills compared to other combinations, reflecting the official encouragement for universities to develop more humanities-based course types, such as Linguistics and Literature, instead of basic English Skills. Therefore, the CDE rank appears to help to push forward the “more humanities-based” goal in the National Standards: in order to achieve higher CDE ranks, universities need to improve their humanities courses. As Li [17] mentioned, several universities have used the CDE rank result as their strategic guideline to improve program development and reassign resources. Such a preference also matches the reform of English programs that started around 2010, which has positioned English as a humanities discipline [3].
What surprised us is that, when adding the control variables of project level and university type, we found that the combination of “Low Literature, Linguistics and Culture, High English Skills” showed a significant negative difference in the CDE rank compared to the combination of “High Literature and Culture, Low English Skills” (b = −0.54, p < 0.05), while the combination of “Balanced, High Translation and English Skills” still had no significant difference. These findings provide several insights. First, the different significant positive coefficients of the three project levels in Model 3 imply that a university’s overall competence is the basis for its undergraduate programs’ development. A university that belongs to a better project is more likely to be stronger in concrete programs. In other words, although each university has its own strengths and limitations in undergraduate education, those with a stronger comprehensive competence tend to perform better on average. Indeed, this is consistent with previous studies, which point out that there is a significant gap between the English program’s discipline strength in universities not in Project 211 and universities in Project 211, as the universities in Project 211 achieved higher CDE ranks in all the previous evaluation rounds [27,28].
In addition, the greatest significant positive impact of Language universities on the CDE in Model 3 directly suggests that most of the Language universities in China deserve their reputation and that they have a leading role in English language education. Furthermore, the significant positive impact of Finance universities also implies that, in application-oriented universities, such as those focused on finance, English is an important skill to learn. Moreover, it is interesting to find that most of these Language and Finance universities (90.91%) belong to Combinations 2 and 3 (Balanced and High English Skills). This is consistent with previous studies that showed that language-oriented universities have progressively established their superiority in English programs and started to showcase the strength of their English programs [28]. As demonstrated by Xie [27], language-oriented universities have consistently widened the gap compared to other types of universities from the 2009 CDE to the 2017 CDE. Furthermore, this is aligned with research findings related to finance universities, where English proficiency is recognized as a crucial factor in fostering interdisciplinary learning [24]. The high focus on English Skills but less focus on Culture courses is also consistent with the opinion that “Emphasis on language, light on business, light on thinking and light on culture are common problems in current Chinese Business English Program teaching” [29]. Under such circumstances, they suggest integrating the characteristics of cross-cultural and interdisciplinary learning into Business English undergraduate education.
Taking a closer look at the average rank and project level of each cluster, it is not surprising to find that the average rank score and project level for combinations focused on English Skills (Combinations 2 and 3) were 3.19 and 2.05, respectively, while the average rank score and project level for the more humanities-based Combination 1 were 3.91 and 3.09, respectively. This suggests that the growth in humanities-based English courses may require substantial educational resources and students with a strong grasp of fundamental English skills, capable of assimilating advanced English course content. These findings partially support the explanation of the application-oriented program training goals for most universities in the previous parts. Hence, the relatively lower preference for the English Skills-focused mode by the CDE rankings can be partially attributed to the prevalence of this mode in universities at lower project levels, where students may not possess a strong English foundation.
5.4. Limitations
This paper has a few limitations. Due to unavailability of the fifth CDE rank, the rank data used in this study were published in 2017. Although the rankings remain largely the same, some changes in rank score may have occurred in some of the sampled universities. Second, even though we used the most recent available program handbooks, there may be differences among published years. Third, in addition to the proportion of various course categories in the program handbooks, a university’s strengths might also be related to a variety of factors, such as the number of professors who specialize in different fields, the number of published papers in different fields, and students’ achievements. Future studies could consider collecting these data and integrate it into the analyses.
5.5. Implications
The results of this study have several implications. (1) Due to the importance of developing multidimensional abilities and introducing specialized fields within higher education, English programs could consider integrating language skills and professional knowledge into a single course. Course designs can adopt the approach of content-based instruction (CBI), as advocated by Pica [30]. According to Stryker and Leaver [31], teaching meaningful content through a second language can enhance students’ proficiency in the language and subject matter simultaneously. Therefore, it is advisable to combine language skill courses with courses that provide professional knowledge, rather than solely emphasizing basic listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills. As Yuan [32] noted, “We learn languages best by using language as the vehicle for teaching, rather than treating it as the sole focus of instruction” (p. 202).
(2) More research-oriented courses are needed. In our study, almost all of the 50 universities only provide fundamental introductory research-related courses for undergraduate students studying linguistics. Only a select few comprehensive universities systematically offer specialized courses across various branches of linguistics at the undergraduate level. Since research ability was listed as one of the most crucial training goals in the sampled program handbooks, it could be a valuable initiative for English departments to introduce more research-oriented courses.
(3) Universities should explore the development of their unique characteristics based on their distinct features. While the National Standards outlines fundamental directions for English programs, including English language, English literature, translation studies, national and regional studies, comparative literature, and cross-cultural studies, it does not imply that all universities and colleges must offer the same courses in all five directions. English programs can leverage their individual strengths and focus on developing specific and targeted directions based on their distinct features.
(4) There should be an emphasis on incorporating more cross-cultural courses into the curriculum. For example, courses such as “Comparison of Chinese and Foreign Cultures” should be introduced. Additionally, English program students should be encouraged to learn about Chinese culture through courses such as Introduction to Chinese Intellectual Classics, ensuring a well-rounded cultural foundation.
6. Conclusions
As the demand for English professionals grows, undergraduate education in English, which is recognized as the main way of cultivating English students, is subject to increasing requirements and ongoing adjustments from year to year. However, under the same National Standards for undergraduate English Program education, different universities and colleges have implemented different development modes. This study sought to discern the overarching characteristics of English programs in China, the various combinations of English program development modes, and the distinctive features associated with each mode. In addition to the text-based analysis of program training goals and the characteristics of English program education, this study also investigated the relationship between development modes and discipline evaluation rankings. At present, English programs in universities and colleges in China exhibit a predominantly application-oriented approach. In addition, three combinations of development modes were identified: Literature and Linguistics, Balanced, and High English Skills. The High English Skill mode was linked to a lower CDE rank compared to the High Literature and Linguistics mode. The findings from this study not only provide valuable insights into the development of English programs in China, but also inform English program development and reform in other countries.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.C. and Y.Z.; methodology, S.C. and Y.Z.; software, S.C.; formal analysis, S.C.; resources, S.C. and R.L.; data curation, S.C. and R.L.; writing—original draft preparation, S.C.; writing—review and editing, Y.Z.; visualization, S.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is supported by Tsinghua University Initiative Scientific Research Program 2023THZWJC33.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Select subsets of data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
| Rank | University |
| A+ | Peking University, Beijing Foreign Studies University, Shanghai International Studies University |
| A | Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Nanjing University, Zhejiang University, Guangdong University of Foreign Studies |
| A− | Tsinghua University, Beihang University, Beijing Normal University, University of International Business and Economics, Fudan University, East China Normal University, Nanjing Normal University, Shandong University |
| B+ | Renmin University of China, Beijing Language and Culture University, Nankai University, Northeast Normal University, Tongji University, Soochow University, Wuhan University, Hunan University, Hunan Normal University, Sun Yat-Sen University, Sichuan University, Sichuan International Studies University |
| B | University of Science and Technology Beijing, Capital Normal University, Beijing International Studies University, Tianjin Foreign Studies University, Dalian University of Foreign Studies, Jilin University, Shanghai University of International Business and Economics, Zhejiang Gongshang University, Ocean University of China, Henan University, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Central China Normal University, Ningbo University |
| B− | Beijing Jiaotong University, Harbin Institute of Technology, Shanghai Maritime University, Shanghai University, Shandong Normal University, Qufu Normal University, Zhengzhou University, Jinan University, South China University of Technology, South China Normal University, Chongqing University, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Yangzhou University |
References
- Yang, L. Research on Talent Training Model of English Major Based on Core Competency of English Discipline. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, April 2018. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD201901&filename=1018854509.nh (accessed on 26 November 2023).
- Jiang, H. Reflections on developing the Teaching Guide for Undergraduate English Majors. Foreign Lang. World 2019, 5, 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J. A Study on the Current Situation and Path of Teaching Reform in English Majors. Teach. Educ. 2020, 44, 127–129. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K. Training English Majors with Two or More Specialized Expertises, Innovative Consciousness and International Vision: Theoretic Consideration and Practice. Foreign Lang. China 2010, 6, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q. Idea and Practice on the Cultivation of English Majors in Huazhong University of Science and Technology under the Background of New Liberal Arts. Lang. Serv. Res. 2022, 2, 190–202. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, H.; Yang, M. Research and Enlightenment on the Curriculum Setting of English Major in Western Universities. Engl. Campus 2022, 42, 58–60. [Google Scholar]
- Nathan, H. The End of the English Major. The New Yorker. 2023. Available online: https://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2023/03/06/the-end-of-the-english-major (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- English Group of Foreign Language Teaching Steering Committee of Higher Education. Official English Teaching Syllabus for English Majors in Higher Education; Shanghai Foreign Language Education Press: Shanghai, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W. A review and rethinking of the reform of English major teaching in China. Foreign Lang. World 2008, 5, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z. Some reflections on the Official English Teaching Syllabus for English Majors in Higher Education. Kaoshi Zhoukan 2010, 4, 91–92. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J. Some considerations of the course designing for English majors in foreign studies universities within the framework of the National Criteria in China. Foreign Lang. Educ. 2018, 1, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Pan, M. Making National Standards of Teaching Quality for Undergraduate English Majors: Innovation and reflections. Mod. Foreign Lang. 2015, 1, 112–120. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Q. Back to Humanistic Character, Emphasize Humanistic Education--Thoughts on “The National Criteria of Teaching Quality for Undergraduate English Majors”. Guide Sci. Educ. 2017, 32, 129–130. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H. A Study on Construction of Computer Aided Translation Curriculum System for Undergraduates in Context of New Liberal Arts. Teach. For. Reg. 2023, 6, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G. Construction of the Practice Teaching System of Business English Major—A Case Study of Business English Major at CWNU. Technol. Enhanc. Foreign Lang. Educ. 2014, 6, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Pu, S.; Shan, Z. Designing the English plus French curriculum for dual-foreign-language education at the tertiary level: A pilot program at Beijing Foreign Studies University. Foreign Lang. Educ. China 2020, 1, 3–7+86. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S. Reflection on Discipline Evaluation in China for the Past 20 Years. High. Educ. Dev. Eval. 2023, 3, 1–10+119. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X. Thoughts on Practice Countermeasures of The Fifth Round China Discipline Ranking Breaking through the Reality Dilemma. Beijing Educ. 2021, 1, 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, X.; Pan, N. Research on New Orientations of Discipline Evaluation Reform in ChinaFrom Perspectives of Indexes and Methods. Heilongjiang Res. High. Educ. 2022, 40, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.A.; Wichern, D.W. Applied Multivariate Statistical Analysis, 6th ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, W. The innovative development of English majors under the guidance of the National Standards of Teaching Quality for Undergraduate English Majors. Foreign Lang. World 2015, 3, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- The Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China (MOE). Guidelines for Ideological and Political Construction in Higher Education Courses; Scientific Research Publishing Inc.: Irvine, CA, USA, 2020; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Liu, Q.; Shu, M. Research on Social Responsibility Cultivation of Foreign Language Professionals from the Perspective of Curriculum-Based Political Virtuous Awareness. Technol. Enhanc. Foreign Lang. Educ. 2021, 4, 56–60+8. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Sun, Y. On strengthening humanistic education in the English language curriculum. Foreign Lang. Teach. Res. 2006, 5, 243–247+319. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F. The ability composition of undergraduate English majors. China Univ. Teach. 2014, 11, 64–66+92. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. An Analysis of Teaching Methods of English Linguistics under the Background of “Internet +”. Overseas Engl. 2022, 16, 57–58+64. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S. Development of the Discipline of Foreign Languages and Literature of Chinese Education Institutes: A Study Based on China Discipline Ranking. J. Jiangxi Norm. Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2018, 51, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q. A Study on the Competitiveness of China’s First-class Foreign Language and Literature Universities—A Comparative Analysis Based on Four Rounds of Discipline Evaluation Results of the Ministry of Education. J. Chongqing Univ. Sci. Technol. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 3, 75–78+90. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, M. Cultivation of Business English Talents from Multicultural, Interdisciplinary Perspectives. J. Chongqing Jiaotong Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2012, 6, 99–101. [Google Scholar]
- Pica, T. Tradition and transition in English teaching methodology. System 2000, 28, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stryker, S.; Leaver, B. Content-based Instruction in English Education Models and Methods; Georgetown University Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, P. A Study on Content-based Instruction in the Chinese College English Context. J. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. 2008, 202, 22. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).