Impact of Mask Mandates on K-12 and Higher-Ed Teaching along with the Recommendation for Mask-Wearing during an Infectious Disease Outbreak
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Online Survey
2.2. Online Survey Respondents
2.3. Online Survey Data Analysis
2.4. Follow-Up Questions after the Indoor Mask Mandate Was Lifted
- Please describe all impacts of the mask mandate in your classrooms.
- What difference did you notice after the mask mandate was relaxed?
2.5. Respondents for the Follow-Up Questions
2.6. Data Analysis for the Follow-Up Questionnaire
3. Results
3.1. K-12 Participant’s Classrooms
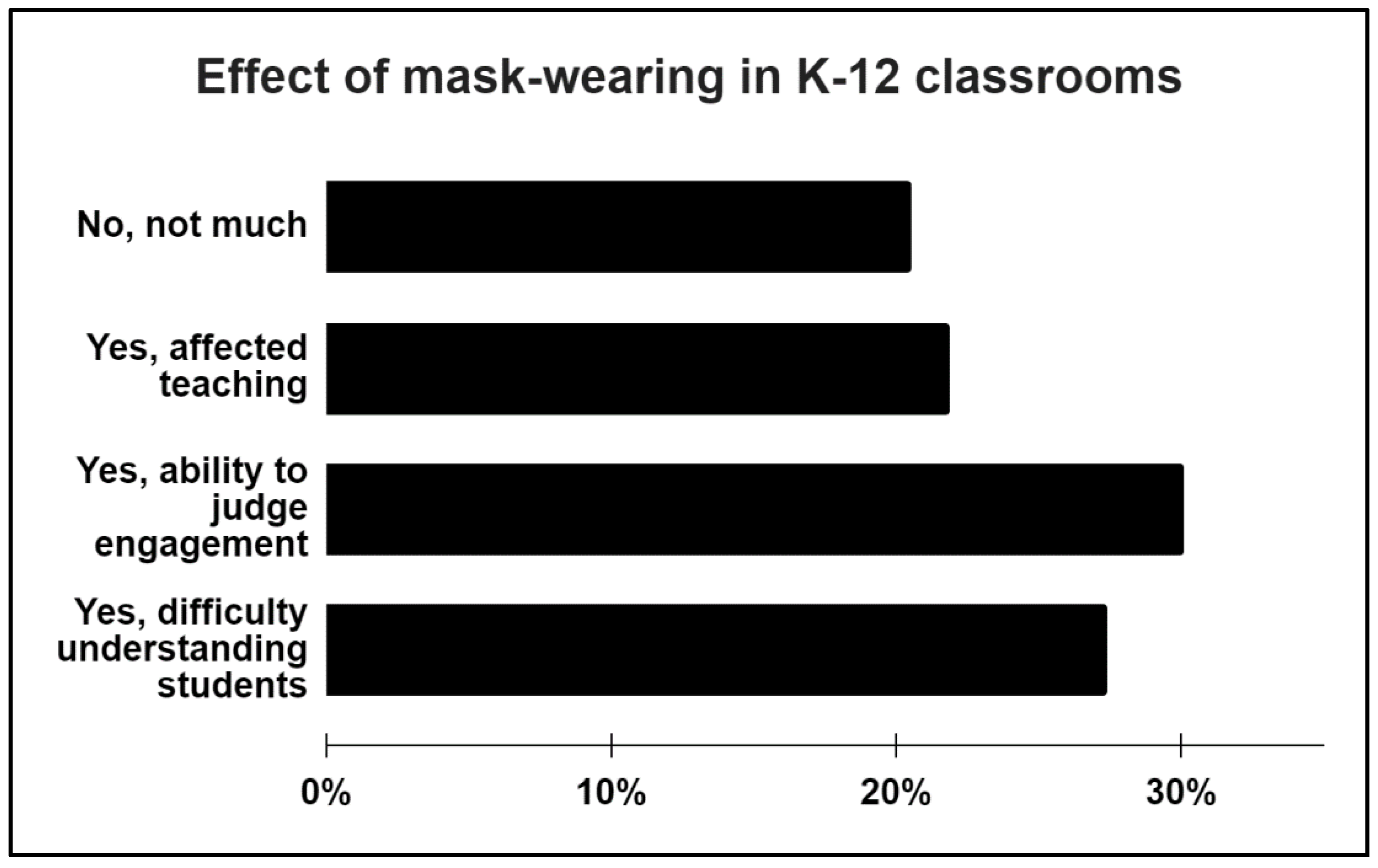
3.2. Effect of Mask-Wearing in K-12 Classrooms
3.3. Effect of Mask-Wearing in Higher-Ed Classrooms
3.4. All Impacts of Mask-Mandate in K-12 Classrooms
3.4.1. No Major Impact on Teaching
3.4.2. Communication and Socializing
3.4.3. Classroom Management and Instructional Strategies
3.4.4. Safety
3.5. Difference in K-12 Classrooms after the Mask-Mandate Was Relaxed
3.5.1. No Major Impact on Teaching
3.5.2. Communication, Socializing and Morale
3.5.3. Safety and Respect of Choice
3.6. All Impacts of Mask-Mandate in Higher-Ed Classrooms
3.6.1. No Major Impact on Teaching
3.6.2. Communication, Socializing and Morale
3.6.3. Classroom Management
3.6.4. Safety
3.7. Difference in Higher-Ed Classrooms after the Mask-Mandate Was Relaxed
3.7.1. No Major Impact on Teaching
3.7.2. Communication, Socializing, and Morale
3.7.3. Classroom Management
3.7.4. Safety Comfort and Respect of Choice
3.8. Unique Perspective from Instructors Who Taught Both in K-12 and Higher-Ed Settings during the Pandemic
3.9. Impact of Masks in the Hearing-Impaired Classroom
3.10. Recommendation for Utilizing Mask-Wearing in the Classrooms
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cucinotta, D.; Vanelli, M. WHO declares COVID-19 a pandemic. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dong, E.; Du, H.; Gardner, L. An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.Y.; Dutra, S.V.O.; Fanfan, D.; Sniffen, S.; Wang, H.; Siddiqui, J.; Song, H.; Bang, S.H.; Kim, D.E.; Kim, S.; et al. Comparative analysis of COVID-19 guidelines from six countries: A qualitative study on the US, China, South Korea, the UK, Brazil, and Haiti. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabari, P.; Amini, M.; Moghadami, M.; Moosavi, M. International Public Health Responses to COVID-19 Outbreak: A Rapid Review. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 45, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pokhrel, S.; Chhetri, R. A Literature Review on Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Teaching and Learning. High. Educ. Future 2021, 8, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawrilenko, M.; Kroshus, E.; Tandon, P.; Christakis, D. The Association Between School Closures and Child Mental Health During COVID-19. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, 2124092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Solomon, M.; Stead, T.; Kwon, B.; Ganti, L. Impact of COVID-19 on the mental health of US college students. BMC Psychol. 2021, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliburton, A.E.; Hill, M.B.; Dawson, B.L.; Hightower, J.M.; Rueden, H. Increased Stress, Declining Mental Health: Emerging Adults’ Experiences in College During COVID-19. Emerg. Adulthood 2021, 9, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, G.; Buonomo, I.; Benevene, P.; Consiglio, P.; Romano, L.; Fiorilli, C. The Burnout Assessment Tool (BAT): A contribution to Italian validation with teachers’. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorilli, C.; Pepe, A.; Buonomo, I.; Albanese, O. At-risk teachers: The association between burnout levels and emotional appraisal processes. Open Psychol. J. 2017, 10, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pyhältö, K.; Pietarinen, J.; Haverinen, K.; Tikkanen, L.; Soini, T. Teacher burnout profiles and proactive strategies. Eur. J. Psychol. Educ. 2021, 36, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adjodah, D.; Dinakar, K.; Chinazzi, M.; Fraiberger, S.P.; Pentland, A.; Bates, S.; Staller, K.; Vespignani, A.; Bhatt, D.L. Association between COVID-19 outcomes and mask mandates, adherence, and attitudes. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jehn, M.; Mac McCullough, J.; Dale, A.P.; Gue, M.; Eller, B.; Cullen, T.; Scott, S.E. Association Between K–12 School Mask Policies and School-Associated COVID-19 Outbreaks—Maricopa and Pima Counties, Arizona, July–August 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1372–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budzyn, S.E.; Panaggio, M.J.; Parks, S.E.; Papazian, M.; Magid, J.; Eng, M.; Barrios, L.C. Pediatric COVID-19 Cases in Counties with and Without School Mask Requirements—United States, July 1–September 4, 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1377–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, S.E.; Zviedrite, N.; Budzyn, S.E.; Panaggio, M.J.; Raible, E.; Papazian, M.; Magid, J.; Ahmed, F.; Uzicanin, A.; Barrios, L.C. COVID-19–Related School Closures and Learning Modality Changes—United States, August 1–September 17, 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1374–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutzoukas, A.E.; Zimmerman, K.O.; Inkelas, M.; Brookhart, M.A.; Benjamin, J.D.K.; Butteris, S.; Koval, M.S.; DeMuri, G.P.; Manuel, V.G.; Smith, M.J.; et al. School Masking Policies and Secondary SARS-CoV-2 Transmission. Pediatrics 2022, 149, 2022056687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, M. Masked education? The benefits and burdens of wearing face masks in schools during the current Corona pandemic. Trends Neurosci. Educ. 2020, 20, 100138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbon, C.-C.; Serrano, M. The Impact of Face Masks on the Emotional Reading Abilities of Children—A Lesson from a Joint School–University Project. i-Perception 2021, 12, 20416695211038265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.L.; Beck, S.D.; Weber, A. The impact of face masks on the recall of spoken sentences. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 149, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, K.; Buss, E.; Miller, M.K.; Leibold, L.J. Face Masks Impact Auditory and Audiovisual Consonant Recognition in Children with and Without Hearing Loss. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Enacts Further Restrictions to Stop Spread, Including Stay-at-Home Instruction. Available online: https://www.governor.state.nm.us/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/COVID-19-DOH-Order-fv.pdf (accessed on 8 March 2022).
- N.M. to Lift Pandemic Restrictions Thursday. Available online: https://www.governor.state.nm.us/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/063021-PHO.pdf (accessed on 8 March 2022).
- COVID-19 (Coronavirus). Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32196406/ (accessed on 8 March 2022).
- New Mexico to Re-Implement Indoor Mask Mandate; Vaccinations Required in Hospitals, Congregate Settings. Available online: https://www.governor.state.nm.us/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/081721-PHO-Masks.pdf (accessed on 8 March 2022).
- New Mexico Indoor Mask Mandate Lifted. Available online: https://www.governor.state.nm.us/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/021722-PHO-Masksfv.pdf (accessed on 8 March 2022).
- Kahane, L.H. Politicizing the Mask: Political, Economic and Demographic Factors Affecting Mask Wearing Behavior in the USA. East. Econ. J. 2021, 47, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graduate Programs: New Mexico Tech. Available online: https://www.nmt.edu/academics/psych-ed/graduate.php (accessed on 17 March 2022).
- Title I, Part A Program. Available online: https://www2.ed.gov/programs/titleiparta/index.html (accessed on 11 March 2022).
- Shaw, K.; Butcher, S.; Ko, J.; Zello, G.A.; Chilibeck, P.D. Wearing of Cloth or Disposable Surgical Face Masks has no Effect on Vigorous Exercise Performance in Healthy Individuals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhart, M.; Orthaber, S.; Kerbl, R. The impact of face masks on children—A mini review. Acta Paediatr. 2021, 110, 1778–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Sign Language. Available online: https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/american-sign-language (accessed on 18 March 2022).


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khandelwal, M.; Apodaca, T. Impact of Mask Mandates on K-12 and Higher-Ed Teaching along with the Recommendation for Mask-Wearing during an Infectious Disease Outbreak. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12080509
Khandelwal M, Apodaca T. Impact of Mask Mandates on K-12 and Higher-Ed Teaching along with the Recommendation for Mask-Wearing during an Infectious Disease Outbreak. Education Sciences. 2022; 12(8):509. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12080509
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhandelwal, Megha, and Theresa Apodaca. 2022. "Impact of Mask Mandates on K-12 and Higher-Ed Teaching along with the Recommendation for Mask-Wearing during an Infectious Disease Outbreak" Education Sciences 12, no. 8: 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12080509
APA StyleKhandelwal, M., & Apodaca, T. (2022). Impact of Mask Mandates on K-12 and Higher-Ed Teaching along with the Recommendation for Mask-Wearing during an Infectious Disease Outbreak. Education Sciences, 12(8), 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12080509




