Behavioral Pattern Analysis between Bilingual and Monolingual Listeners’ Natural Speech Perception on Foreign-Accented English Language Using Different Machine Learning Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Data Acquisition and Methods
3.1. Data Acquisition
3.2. Methodology
- Independent variables: Language (monolingual, bilingual)—2 factors
- Dependent variables: Speech sound (quiet, white noise, bubble noise)—3 factors.
4. Results
4.1. Correlation Analysis
4.2. Machine Learning Algorithm
4.3. Behavioral Pattern Recognition Using a Deep Learning Approach
Proposed Model
5. Discussion
- During this study, only a limited number of individuals (12 participants) were considered.
- We did not consider other widely bilingual people who speak English–Arabic, Hindi–English who need to be taken into account for the proper evaluation of the effect of noise on bilingual people on a large scale.
- The performance of the proposed deep neural network may fluctuate when applied to a larger data set.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gordon-Salant, S.; Yeni-Komshian, G.H.; Fitzgibbons, P.J. Recognition of Accented English in Quiet and Noise by Younger and Older Listeners. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 3152–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nábělek, A.K.; Robinson, P.K. Monaural and Binaural Speech Perception in Reverberation for Listeners of Various Ages. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1982, 71, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbab, H.; Moossavi, A.; Javanbakht, M.; Arbab Sarjoo, H.; Bakhsh, E.; MahmoodiBakhtiari, B.; Lotfi, Y. Development and Psychometric Evaluation of Persian Version of the Quick Speech in Noise Test in Persian Speaking 18–25 Years Old Normal Adults. J. Rehabil. Sci. Res. 2016, 3, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandell, C.C.; Smaldino, J.J. Classroom Acoustics for Children with Normal Hearing and with Hearing Impairment. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 2000, 31, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabelek, A.K.; Mason, D. Effect of Noise and Reverberation on Binaural and Monaural Word Identification by Subjects with Various Audiograms. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 1981, 24, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon-Salant, S.; Fitzgibbons, P.J. Temporal Factors and Speech Recognition Performance in Young and Elderly Listeners. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 1993, 36, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.H.; Jongman, A.; Sereno, J.A.; Keum, K. Intelligibility of Foreign-Accented Speech for Older Adults with and without Hearing Loss. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2010, 21, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, R.A.; Flege, J.E.; Munro, M.J. The Perception of English and Spanish Vowels by Native English and Spanish Listeners: A Multidimensional Scaling Analysis. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1995, 97, 2540–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKay, I.R.; Flege, J.E.; Piske, T. Persistent Errors in the Perception and Production of Word-Initial English Stop Consonants by Native Speakers of Italian. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 107, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burda, A.N.; Hageman, C.F.; Scherz, J.A.; Edwards, H.T. Age and Understanding Speakers with Spanish or Taiwanese Accents. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2003, 97, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon-Salant, S.; Yeni-Komshian, G.H.; Fitzgibbons, P.J. Recognition of Accented English in Quiet by Younger Normal-Hearing Listeners and Older Listeners with Normal-Hearing and Hearing Loss. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Yoho, S.E.; Wang, D.; Healy, E.W. Large-Scale Training to Increase Speech Intelligibility for Hearing-Impaired Listeners in Novel Noises. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 139, 2604–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, E.W.; Yoho, S.E.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D. An Algorithm to Improve Speech Recognition in Noise for Hearing-Impaired Listeners. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 3029–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, E.W.; Yoho, S.E.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D. An Algorithm to Increase Speech Intelligibility for Hearing-Impaired Listeners in Novel Segments of the Same Noise Type. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 138, 1660–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Lu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Loizou, P.C. An Algorithm That Improves Speech Intelligibility in Noise for Normal-Hearing Listeners. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 126, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, T.; Dau, T. Requirements for the Evaluation of Computational Speech Segregation Systems. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 136, EL398–EL404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, J. Supervised Speech Separation Based on Deep Learning: An Overview. IEEE ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2018, 26, 1702–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, D. Dnn based mask estimation for supervised speech separation. In Audio Source Separation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 207–235. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.B.; Kominski, R. Language Use in the United States, 2007; US Department of Commerce, Economics and Statistics Administration, USA Census Bureau: Suitland, MD, USA, 2010.
- Krogstad, J.M. With Fewer New Arrivals, Census Lowers Hispanic Population Projections. Pew Res. Cent. 2014, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, H.J.; Dobie, R.A.; Losonczy, K.G.; Themann, C.L.; Flamme, G.A. Declining Prevalence of Hearing Loss in US Adults Aged 20 to 69 Years. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 143, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takata, Y.; Nábělek, A.K. English Consonant Recognition in Noise and in Reverberation by Japanese and American Listeners. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1990, 88, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristia, A.; Seidl, A.; Vaughn, C.; Schmale, R.; Bradlow, A.; Floccia, C. Linguistic Processing of Accented Speech Across the Lifespan. Front. Psychol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grey, S.; van Hell, J.G. Foreign-Accented Speaker Identity Affects Neural Correlates of Language Comprehension. J. Neurolinguistics 2017, 42, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabri, D.; Chacra, K.M.S.A.; Pring, T. Speech Perception in Noise by Monolingual, Bilingual and Trilingual Listeners. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2011, 46, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotfi, Y.; Chupani, J.; Javanbakht, M.; Bakhshi, E. Evaluation of Speech Perception in Noise in Kurd-Persian Bilinguals. Audit. Vestib. Res. 2019, 28, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizman, J.; Bradlow, A.R.; Lam, S.S.-Y.; Kraus, N. How Bilinguals Listen in Noise: Linguistic and Non-Linguistic Factors. Biling. Lang. Cogn. 2017, 20, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoe, E.; Karayanidi, K. Bilingualism and Speech Understanding in Noise: Auditory and Linguistic Factors. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2019, 30, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, B.A.; Coles-White, D.; Regal, D.; Kijai, J. Analysis of Language Errors in Speakers Who Are Bilingual Under Quiet and Background Noise Conditions. Perspect. ASHA Spec. Interest Groups 2020, 5, 1687–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidelman, G.M.; Dexter, L. Bilinguals at the “Cocktail Party”: Dissociable Neural Activity in Auditory–Linguistic Brain Regions Reveals Neurobiological Basis for Nonnative Listeners’ Speech-in-Noise Recognition Deficits. Brain Lang. 2015, 143, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoe, E. Turn up the Volume: Speech Perception in Noise for Bilingual Listeners. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 145, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidtke, J. The Bilingual Disadvantage in Speech Understanding in Noise Is Likely a Frequency Effect Related to Reduced Language Exposure. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuipers, J.R.; Thierry, G. Bilingualism and Increased Attention to Speech: Evidence from Event-Related Potentials. Brain Lang. 2015, 149, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reetzke, R.; Lam, B.P.-W.; Xie, Z.; Sheng, L.; Chandrasekaran, B. Effect of Simultaneous Bilingualism on Speech Intelligibility across Different Masker Types, Modalities, and Signal-to-Noise Ratios in School-Age Children. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, V.; Hayakawa, S.; Lam, T.Q.; Schroeder, S.R. Language Experience Changes Audiovisual Perception. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosdi, F.; Salim, S.S.; Mustafa, M.B. An FPN-Based Classification Method for Speech Intelligibility Detection of Children with Speech Impairments. Soft Comput. 2019, 23, 2391–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ahad, M.T.; Gupta, K.D. Evaluating the Performance of Eigenface, Fisherface, and Local Binary Pattern Histogram-Based Facial Recognition Methods under Various Weather Conditions. Technologies 2021, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ahad, M.T.; Yazdan, M.M.S. Face Recognition in an Unconstrained and Real-Time Environment Using Novel BMC-LBPH Methods Incorporates with DJI Vision Sensor. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2020, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fook, C.Y.; Muthusamy, H.; Chee, L.S.; Yaacob, S.B.; Adom, A.H.B. Comparison of Speech Parameterization Techniques for the Classification of Speech Disfluencies. Turk. J. Elec. Eng. Comp. Sci. 2013, 21, 1983–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kumar, N.; Tsiartas, A.; Li, M.; Narayanan, S.S. Automatic Intelligibility Classification of Sentence-Level Pathological Speech. Comput. Speech Lang 2015, 29, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfahal, M.O.E. Supervisor, -Mohammed Elhafiz Mustafa; Co-Supervisor, -Rashid A. Saeed Automatic Recognition and Identification for Mixed Sudanese Arabic–English Languages Speech. Ph.D Thesis, Sudan University of Science & Technology, Khartoum, Sudan, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yemmene, P.; Besacier, L. Motivations, Challenges, and Perspectives for the Development of an Automatic Speech Recognition System for the under-Resourced Ngiemboon Language. In Proceedings of the First International Workshop on NLP Solutions for Under Resourced Languages (NSURL 2019) Co-Located with ICNLSP 2019-Short Papers, Trento, Italy, 11–12 September 2019; pp. 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Díaz, M.; Gallardo-Antolín, A. An Attention Long Short-Term Memory Based System for Automatic Classification of Speech Intelligibility. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 96, 103976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghini, G.; Hazan, V. Listening Effort During Sentence Processing Is Increased for Non-Native Listeners: A Pupillometry Study. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D. Towards Scaling Up Classification-Based Speech Separation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2013, 21, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D. Noise Perturbation for Supervised Speech Separation. Speech Commun. 2016, 78, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bolner, F.; Goehring, T.; Monaghan, J.; Van Dijk, B.; Wouters, J.; Bleeck, S. Speech Enhancement Based on Neural Networks Applied to Cochlear Implant Coding Strategies. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 November 2016; pp. 6520–6524. [Google Scholar]
- Goehring, T.; Bolner, F.; Monaghan, J.J.; Van Dijk, B.; Zarowski, A.; Bleeck, S. Speech Enhancement Based on Neural Networks Improves Speech Intelligibility in Noise for Cochlear Implant Users. Hear. Res. 2017, 344, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahad, M.T. An EEG-Based Comparative Analysis of Natural Speech Perception by Native Speakers of American English vs. Bilingual Individuals; Lamar University-Beaumont ProQuest: Beaumont, TX, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Keras: The Python Deep Learning API. Available online: https://keras.io/ (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Brownlee, J. Deep Learning with Python: Develop Deep Learning Models on Theano and TensorFlow Using Keras; Machine Learning Mastery, 2016. Available online: https://books.google.com.hk/books/about/Deep_Learning_With_Python.html?id=K-ipDwAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&source=kp_read_button&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false (accessed on 22 July 2021).
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Ahsan, M.M.; Alam, T.E.; Trafalis, T.; Huebner, P. Deep MLP-CNN Model Using Mixed-Data to Distinguish between COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 Patients. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.M.; Ahad, M.T.; Soma, F.A.; Paul, S.; Chowdhury, A.; Luna, S.A.; Yazdan, M.M.S.; Rahman, A.; Siddique, Z.; Huebner, P. Detecting SARS-CoV-2 From Chest X-Ray Using Artificial Intelligence. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 35501–35513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.M.; Gupta, K.D.; Islam, M.M.; Sen, S.; Rahman, M.L.; Shakhawat Hossain, M. COVID-19 Symptoms Detection Based on NasNetMobile with Explainable AI Using Various Imaging Modalities. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2020, 2, 490–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Participants | Bubble Noise | White Noise | Quiet level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monolingual | 5.4 | 4.2 | 9.94 |
| Monolingual | 3.875 | 3.2 | 6.4 |
| Monolingual | 4.67 | 3.68 | 9.1 |
| Monolingual | 4.45 | 3.8 | 9.58 |
| Monolingual | 4.25 | 2.6 | 6.83 |
| Monolingual | 6.17 | 7.76 | 6.54 |
| Bilingual | 7.79 | 7.64 | 7.875 |
| Bilingual | 4.29 | 3.56 | 3.16 |
| Bilingual | 5.25 | 6.24 | 5.45 |
| Bilingual | 5.41 | 5 | 4.16 |
| Bilingual | 5.79 | 6.4 | 5.5 |
| Bilingual | 6.625 | 6.28 | 6.04 |
| Effect | Value | F | Hypothesis df | Error df | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | Pillai’s Trace | 0.974 | 101.331 b | 3.000 | 8.000 | 0.000 |
| Wilks’ Lambda | 0.026 | 101.331 b | 3.000 | 8.000 | 0.000 | |
| Hotelling’s Trace | 37.999 | 101.331 b | 3.000 | 8.000 | 0.000 | |
| Roy’s Largest Root | 37.999 | 101.331 b | 3.000 | 8.000 | 0.000 | |
| Language | Pillai’s Trace | 0.744 | 7.740 b | 3.000 | 8.000 | 0.009 |
| Wilks’ Lambda | 0.256 | 7.740 b | 3.000 | 8.000 | 0.009 | |
| Hotelling’s Trace | 2.903 | 7.740 b | 3.000 | 8.000 | 0.009 | |
| Roy’s Largest Root | 2.903 | 7.740 b | 3.000 | 8.000 | 0.009 | |
| Bubble Noise Speech | Gaussian or White Noise Speech | Quiet Speech | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bubble Noise Speech | Pearson Correlation | 1 | 0.883 ** | 0.051 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.000 | 0.876 | ||
| N | 12 | 12 | 12 | |
| Gaussian or White noise Speech | Pearson Correlation | 0.883 ** | 1 | −0.130 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.000 | 0.688 | ||
| N | 12 | 12 | 12 | |
| Quiet Speech | Pearson Correlation | 0.051 | −0.130 | 1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.876 | 0.688 | ||
| N | 12 | 12 | 12 |
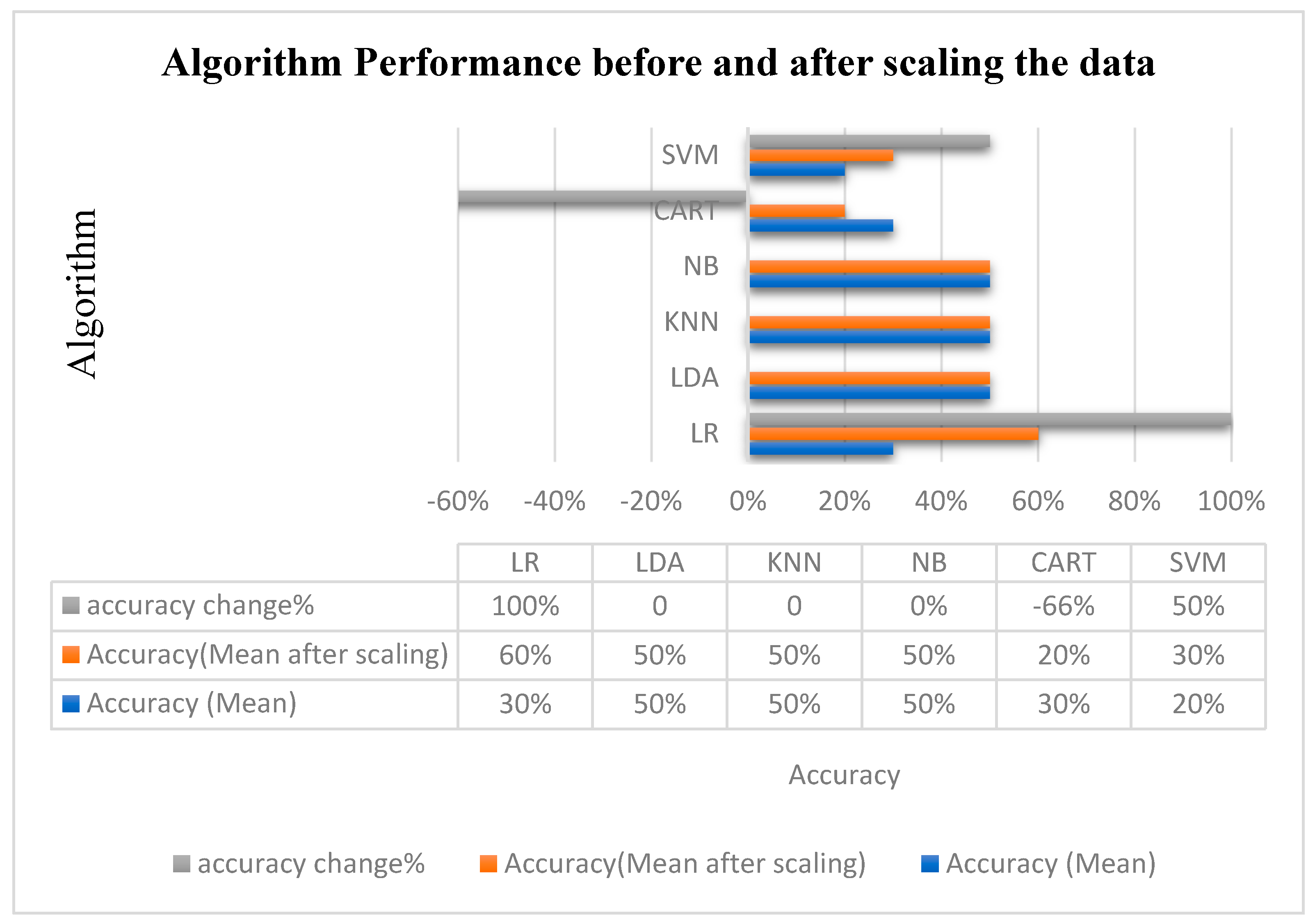
| Algorithm | Accuracy (Avg) | Std |
|---|---|---|
| LR | 0.30 | 0.24 |
| LDA | 0.50 | 0.44 |
| KNN | 0.50 | 0.44 |
| NB | 0.50 | 0.316 |
| CART | 0.30 | 0.4 |
| SVM | 0.20 | 0.244 |
| Algorithm (Scaled) | Accuracy (Avg) | Std |
|---|---|---|
| LR | 0.60 | 0.37 |
| LDA | 0.50 | 0.44 |
| KNN | 0.50 | 0.44 |
| CART | 0.20 | 0.24 |
| NB | 0.50 | 0.32 |
| SVM | 0.30 | 0.244 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahad, M.T.; Ahsan, M.M.; Jahan, I.; Nazim, R.; Yazdan, M.M.S.; Huebner, P.; Siddique, Z. Behavioral Pattern Analysis between Bilingual and Monolingual Listeners’ Natural Speech Perception on Foreign-Accented English Language Using Different Machine Learning Approaches. Technologies 2021, 9, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies9030051
Ahad MT, Ahsan MM, Jahan I, Nazim R, Yazdan MMS, Huebner P, Siddique Z. Behavioral Pattern Analysis between Bilingual and Monolingual Listeners’ Natural Speech Perception on Foreign-Accented English Language Using Different Machine Learning Approaches. Technologies. 2021; 9(3):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies9030051
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhad, Md Tanvir, Md Manjurul Ahsan, Ishrat Jahan, Redwan Nazim, Munshi Md. Shafwat Yazdan, Pedro Huebner, and Zahed Siddique. 2021. "Behavioral Pattern Analysis between Bilingual and Monolingual Listeners’ Natural Speech Perception on Foreign-Accented English Language Using Different Machine Learning Approaches" Technologies 9, no. 3: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies9030051
APA StyleAhad, M. T., Ahsan, M. M., Jahan, I., Nazim, R., Yazdan, M. M. S., Huebner, P., & Siddique, Z. (2021). Behavioral Pattern Analysis between Bilingual and Monolingual Listeners’ Natural Speech Perception on Foreign-Accented English Language Using Different Machine Learning Approaches. Technologies, 9(3), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies9030051








