Dance Pose Identification from Motion Capture Data: A Comparison of Classifiers †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Data Capturing and Dance Representation
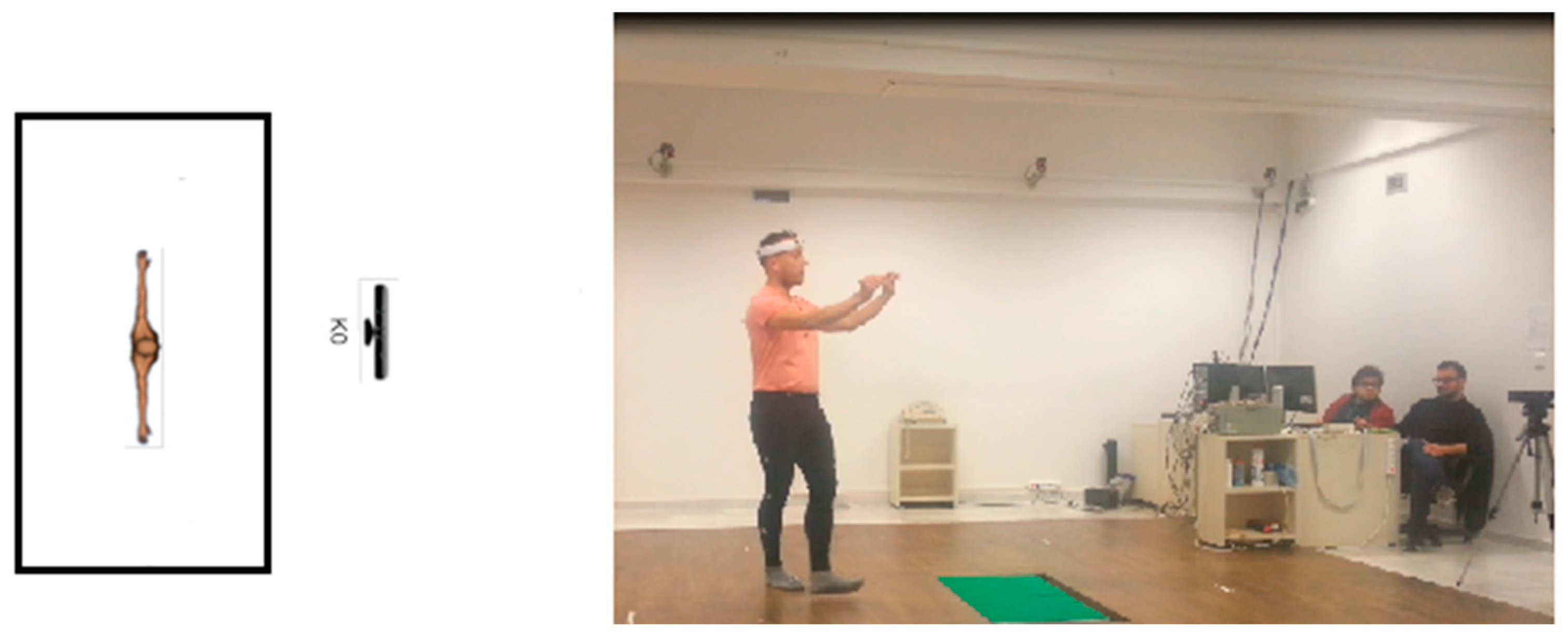
3.1. Capturing Dance Poses
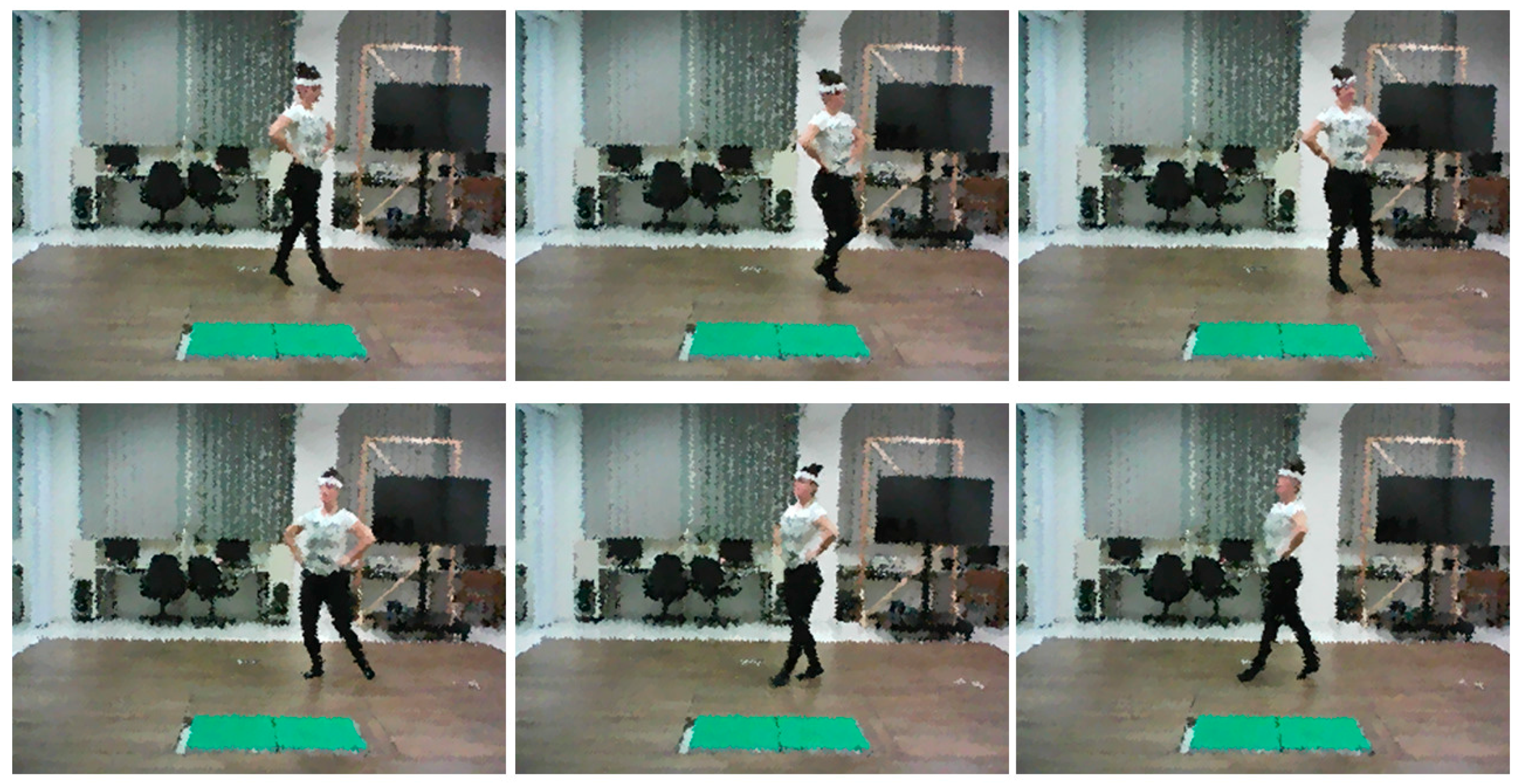
3.2. Identifying Key Poses
4. Classifiers for Dance Pose Identification
4.1. k Nearest Neighbors
4.2. Naïve Bayes
4.3. Discriminant Analysis
4.4. Classification Trees
4.5. Ensemble Methods
4.6. Support Vector Machines
5. Experimental Results
- Classifier input type: related to the input features’ values. The possible alternatives for the creation of input features are four: (i) leg joints per frame (1Fr Legs), (ii) leg joints and frame difference (FrDiff Legs), (iii) all joints per frame (1Fr All) and, (iv) all joints and frame difference (FrDiff All).
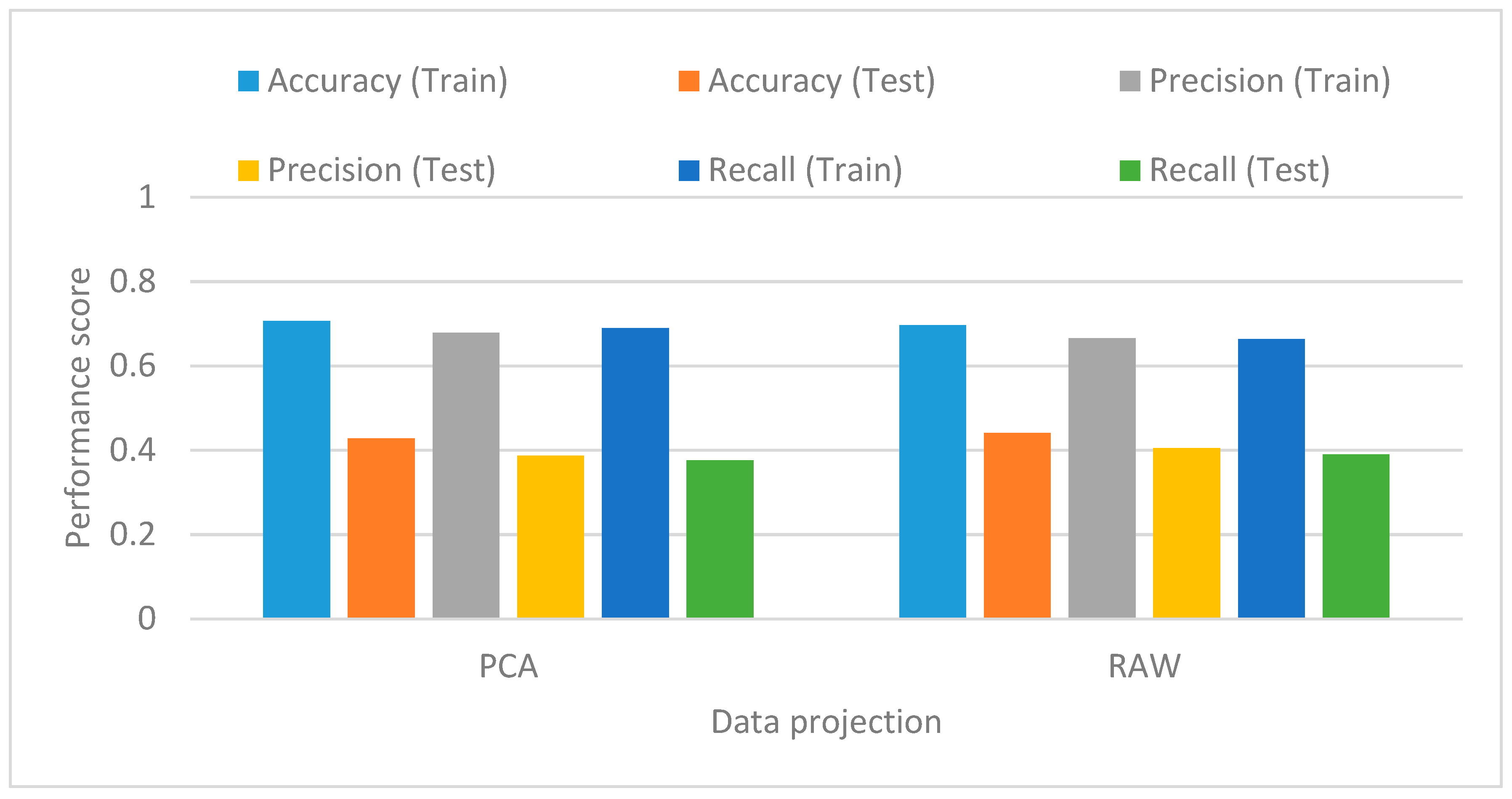
- Projection techniques: related to the dimensionality of inputs. There are two alternatives: PCA or raw data.
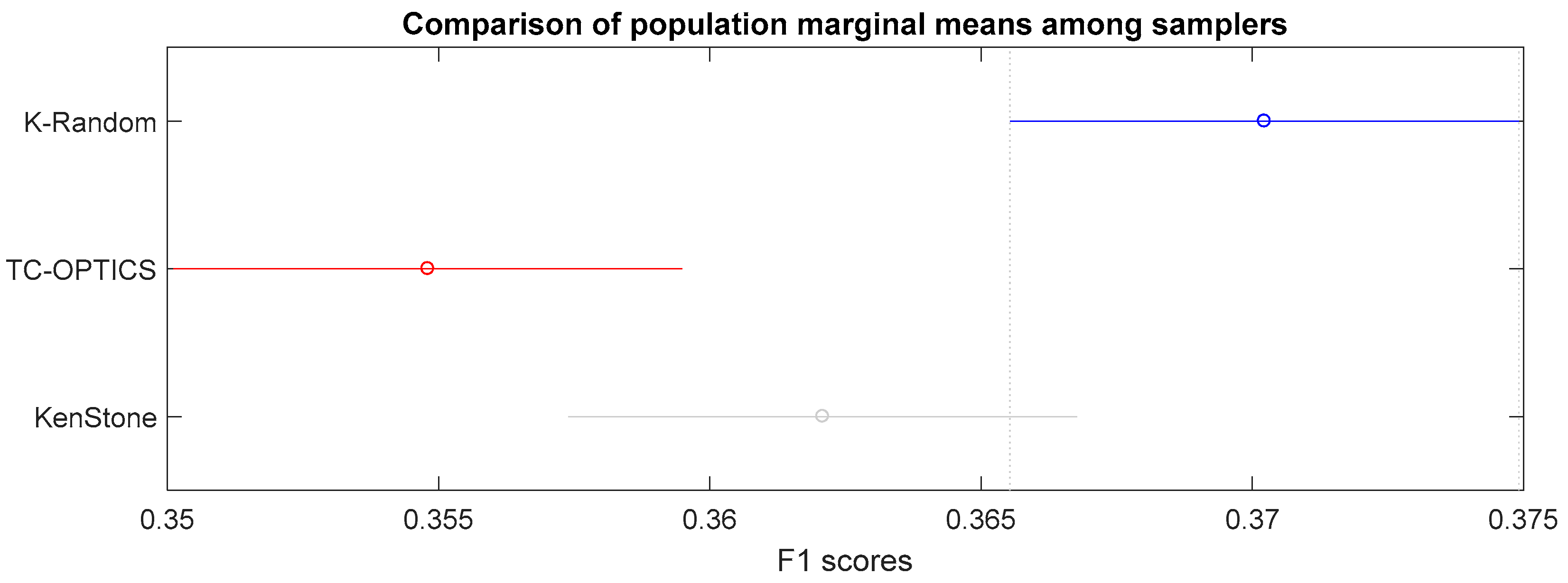
- Sampling approaches: related to training sets creation. There are three approaches: (i) random sampling over kmeans clusters (K-random), (ii) time constrained OPTICS (TC-OPTICS), and (iii) Kennard Stone (KenStone).
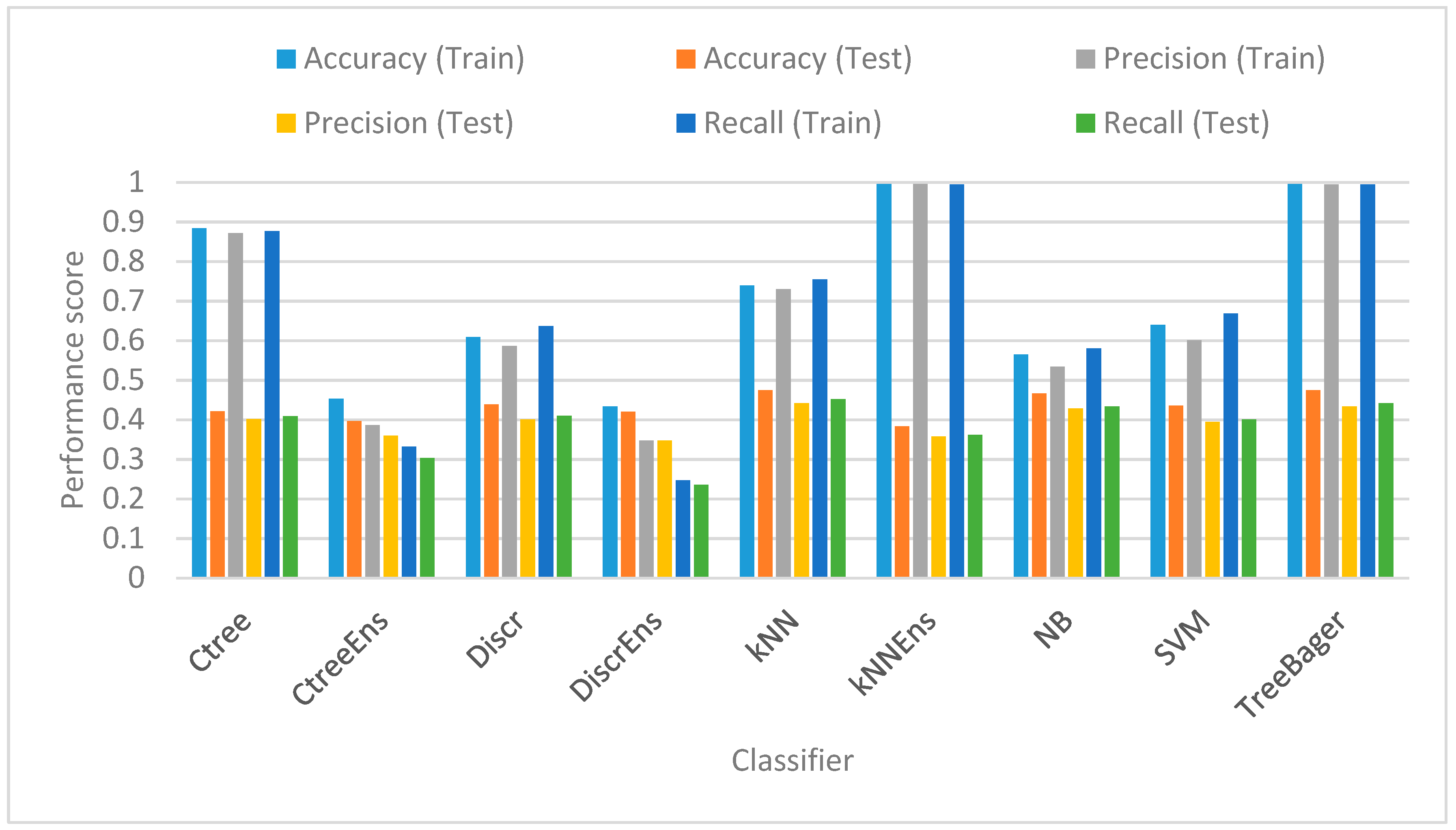
- Classifier: i.e., the classification technique used, i.e., k-nearest neighbors (k-NN), naïve Bayes (NB), classification trees (CT), linear kernel support vector machines (SVMs), a random forest approach (TreeBagger), as well as Ensemble (Ens) versions.
5.1. Dataset Description
5.2. Feature Extraction
5.3. Variation, Space, and Noise Handling
5.4. Algorithms Setup
5.5. Classification Scores
5.6. Statistical Analysis
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shay, A.; Sellers-Young, B. The Oxford Handbook of Dance and Ethnicity; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Voulodimos, A.S.; Patrikakis, C.Z. Quantifying privacy in terms of entropy for context aware services. Identity Inf. Soc. 2009, 2, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmopoulos, D.I.; Voulodimos, A.S.; Doulamis, A.D. A System for Multicamera Task Recognition and Summarization for Structured Environments. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulodimos, A.S.; Doulamis, N.D.; Kosmopoulos, D.I.; Varvarigou, T.A. Improving Multi-Camera Activity Recognition by Employing Neural Network Based Readjustment. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2012, 26, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulamis, N.D.; Voulodimos, A.S.; Kosmopoulos, D.I.; Varvarigou, T.A. Enhanced Human Behavior Recognition Using HMM and Evaluative Rectification. In Proceedings of the First ACM International Workshop on Analysis and Retrieval of Tracked Events and Motion in Imagery Streams, New York, NY, USA, 21–25 October 2010; pp. 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Voulodimos, A.; Kosmopoulos, D.; Veres, G.; Grabner, H.; van Gool, L.; Varvarigou, T. Online classification of visual tasks for industrial workflow monitoring. Neural Netw. 2011, 24, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protopapadakis, E.; Voulodimos, A.; Doulamis, A.; Camarinopoulos, S. A Study on the Use of Kinect Sensor in Traditional Folk Dances Recognition via Posture Analysis. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments, New York, NY, USA, 21–23 June 2017; pp. 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Felzenszwalb, P.F.; Huttenlocher, D.P. Pictorial Structures for Object Recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2005, 61, 55–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulodimos, A.; Doulamis, N.; Doulamis, A.; Protopapadakis, E. Deep Learning for Computer Vision: A Brief Review. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, 7068349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshev, A.; Szegedy, C. DeepPose: Human Pose Estimation via Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1653–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yuille, A. Articulated Pose Estimation by a Graphical Model with Image Dependent Pairwise Relations. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Cambridge, MA, USA, 8–13 December 2014; Volume 1, pp. 1736–1744. [Google Scholar]
- Tompson, J.; Jain, A.; LeCun, Y.; Bregler, C. Joint Training of a Convolutional Network and a Graphical Model for Human Pose Estimation. arXiv, 2014; arXiv:14062984. [Google Scholar]
- Raptis, M.; Kirovski, D.; Hoppe, H. Real-time Classification of Dance Gestures from Skeleton Animation. In Proceedings of the 2011 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, New York, NY, USA, 26–28 September 2011; pp. 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Zanfir, M.; Leordeanu, M.; Sminchisescu, C. The Moving Pose: An Efficient 3D Kinematics Descriptor for Low-Latency Action Recognition and Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 2752–2759. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, A.; Rye, D.; Ramos, F.; Velonaki, M. Unsupervised Clustering of People from ‘Skeleton’ Data. In Proceedings of the Seventh Annual ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction, New York, NY, USA, 5–8 March 2012; pp. 225–226. [Google Scholar]
- Rallis, I.; Georgoulas, I.; Doulamis, N.; Voulodimos, A.; Terzopoulos, P. Extraction of key postures from 3D human motion data for choreography summarization. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Virtual Worlds and Games for Serious Applications (VS-Games), Athens, Greece, 6–8 September 2017; pp. 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Kitsikidis, A.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Yilmaz, E.; Douka, S.; Grammalidis, N. Multi-sensor Technology and Fuzzy Logic for Dancer’s Motion Analysis and Performance Evaluation within a 3D Virtual Environment. In Proceedings of the Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction. Design and Development Methods for Universal Access, Heraklion, Greece, 22–27 June 2014; pp. 379–390. [Google Scholar]
- Kitsikidis, A.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Uğurca, D.; Bayçay, C.; Yilmaz, E.; Tsalakanidou, F.; Douka, S.; Grammalidis, N. A Game-like Application for Dance Learning Using a Natural Human Computer Interface. In Proceedings of the Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction. Access to Learning, Health and Well-Being, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2–7 August 2015; pp. 472–482. [Google Scholar]
- Kitsikidis, A.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Douka, S.; Grammalidis, N. Dance analysis using multiple Kinect sensors. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP), Lisbon, Portugal, 5–8 January 2014; Volume 2, pp. 789–795. [Google Scholar]
- Kitsikidis, A.; Boulgouris, N.V.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Grammalidis, N. Unsupervised Dance Motion Patterns Classification from Fused Skeletal Data Using Exemplar-Based HMMs. Int. J. Herit. Digit. Era 2015, 4, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitropoulos, K.; Barmpoutis, P.; Kitsikidis, A.; Grammalidis, N. Classification of Multidimensional Time-Evolving Data using Histograms of Grassmannian Points. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protopapadakis, E.; Grammatikopoulou, A.; Doulamis, A.; Grammalidis, N. Folk Dance Pattern Recognition over Depth Images Acquired via Kinect Sensor. In Proceedings of the 3D Virtual Reconstruction and Visualization of Complex Architectures, Nafplio, Greece, 1–3 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kinect—Windows App Development, 2017. Available online: https://developer.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/kinect (accessed on 15 January 2017).
- Webb, J.; Ashley, J. Beginning Kinect Programming with the Microsoft Kinect SDK; Apress: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Protopapadakis, E.; Doulamis, A. Semi-Supervised Image Meta-Filtering Using Relevance Feedback in Cultural Heritage Applications. Int. J. Herit. Digit. Era 2014, 3, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandana, N.B. Survey of Nearest Neighbor Techniques. arXiv, 2010; arXiv:10070085. [Google Scholar]
- Farid, D.M.; Zhang, L.; Rahman, C.M.; Hossain, M.A.; Strachan, R. Hybrid decision tree and naïve Bayes classifiers for multi-class classification tasks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 1937–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.S.; Borba, F.d.L.; Pimentel, M.F.; Pontes, M.J.C.; Honorato, R.S.; Pasquini, C. Classification of blue pen ink using infrared spectroscopy and linear discriminant analysis. Microchem. J. 2013, 109, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokach, L.; Schclar, A.; Itach, E. Ensemble methods for multi-label classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 7507–7523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, S. Support Vector Machines for Pattern Classification; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitropoulos, K.; Manitsaris, S.; Tsalakanidou, F.; Nikolopoulos, S.; Denby, B.; Al Kork, S.; Crevier-Buchman, L.; Pillot-Loiseau, C.; Adda-Decker, M.; Dupont, S. Capturing the intangible an introduction to the i-Treasures project. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP), Lisbon, Portugal, 5–8 January 2014; Volume 2, pp. 773–781. [Google Scholar]
- Protopapadakis, E.; Doulamis, A.; Makantasis, K.; Voulodimos, A. A Semi-Supervised Approach for Industrial Workflow Recognition. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Advanced Communications and Computation (INFOCOMP 2012), Venice, Italy, 21–26 October 2012; pp. 155–160. [Google Scholar]







| KalCirc | KalStr8 | MakCirc | MakStr8 | Syrt2Circ | Syrt2Str8 | Syrt3Circ | Syrt3Str8 | Syrt11Str8 | TrehCirc | TrehStr8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Frame Legs Only | |||||||||||
| D1 | 18 | 10 | 11 | 7 | 21 | 19 | 44 | 24 | 19 | 34 | 10 |
| D2 | 19 | 11 | 19 | 10 | 17 | 19 | 31 | 21 | 22 | 22 | 10 |
| D3 | 18 | 14 | 11 | 15 | 9 | 10 | 30 | 16 | 25 | 16 | 11 |
| Frame Difference Legs Only | |||||||||||
| D1 | 17 | 8 | 14 | 8 | 19 | 18 | 39 | 21 | 18 | 28 | 10 |
| D2 | 16 | 11 | 18 | 11 | 15 | 17 | 32 | 21 | 18 | 17 | 8 |
| D3 | 16 | 14 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 9 | 32 | 16 | 18 | 12 | 10 |
| Frame Difference All Joints | |||||||||||
| D1 | 18 | 8 | 14 | 8 | 18 | 18 | 44 | 20 | 18 | 27 | 8 |
| D2 | 18 | 10 | 16 | 8 | 15 | 21 | 30 | 21 | 22 | 17 | 8 |
| D3 | 17 | 13 | 9 | 11 | 9 | 9 | 34 | 16 | 21 | 12 | 9 |
| Row Labels | Frame_Diff_Legs | FrameDiff_All_Joints | Single_Frame_Legs | Single_Frame_All |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KenStone | ||||
| D1 | 180 | 180 | 189 | 189 |
| D2 | 171 | 171 | 180 | 180 |
| D3 | 146 | 146 | 155 | 155 |
| K-Random | ||||
| D1 | 186 | 186 | 196 | 196 |
| D2 | 176 | 177 | 186 | 187 |
| D3 | 151 | 152 | 160 | 161 |
| TC-OPTICS | ||||
| D1 | 56 | 56 | 58 | 60 |
| D2 | 56 | 56 | 57 | 60 |
| D3 | 52 | 52 | 51 | 54 |
| Dance | Variation | Short Name | Duration (Frames) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | D2 | D3 | |||
| Enteka | Straight | Syrt_11_Str8 | 749 | 807 | 858 |
| Kalamatianos | Circular | Kal_Circ | 655 | 593 | 561 |
| Straight | Kal_Str8 | 304 | 378 | 455 | |
| Makedonitikos | Circular | Mak_Circ | 424 | 582 | 409 |
| Straight | Mak_Str8 | 283 | 367 | 418 | |
| Syrtos 2 | Circular | Syrt_2_Circ | 608 | 543 | 352 |
| Straight | Syrt_2_Str8 | 623 | 639 | 334 | |
| Syrtos 3 | Circular | Syrt_3_Circ | 608 | 964 | 947 |
| Straight | Syrt_3_Str8 | 1366 | 678 | 511 | |
| Trehatos | Circular | Treh_Circ | 991 | 723 | 443 |
| Straight | Treh_Str8 | 315 | 295 | 355 | |
| Source | Sum Sq. | d.f. | Mean Sq. | F | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projection | 0.0232 | 1 | 0.0232 | 13.3600 | 0.0003 |
| Sampling | 0.0261 | 2 | 0.0130 | 7.5000 | 0.0006 |
| Classifier | 2.2686 | 8 | 0.2836 | 163.3000 | 0.0000 |
| InputType | 0.2790 | 3 | 0.0930 | 53.5600 | 0.0000 |
| Projection × Sampling | 0.0064 | 2 | 0.0032 | 1.8400 | 0.1590 |
| Projection × Classifier | 0.0118 | 8 | 0.0015 | 0.8500 | 0.5621 |
| Projection × InputType | 0.0226 | 3 | 0.0075 | 4.3400 | 0.0049 |
| Sampling × Classifier | 0.0818 | 16 | 0.0051 | 2.9400 | 0.0001 |
| Sampling × InputType | 0.0147 | 6 | 0.0025 | 1.4100 | 0.2073 |
| Classifier × InputType | 0.2830 | 24 | 0.0118 | 6.7900 | 0.0000 |
| Error | 0.9967 | 574 | 0.0017 | ||
| Total | 4.0138 | 647 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Protopapadakis, E.; Voulodimos, A.; Doulamis, A.; Camarinopoulos, S.; Doulamis, N.; Miaoulis, G. Dance Pose Identification from Motion Capture Data: A Comparison of Classifiers. Technologies 2018, 6, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies6010031
Protopapadakis E, Voulodimos A, Doulamis A, Camarinopoulos S, Doulamis N, Miaoulis G. Dance Pose Identification from Motion Capture Data: A Comparison of Classifiers. Technologies. 2018; 6(1):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies6010031
Chicago/Turabian StyleProtopapadakis, Eftychios, Athanasios Voulodimos, Anastasios Doulamis, Stephanos Camarinopoulos, Nikolaos Doulamis, and Georgios Miaoulis. 2018. "Dance Pose Identification from Motion Capture Data: A Comparison of Classifiers" Technologies 6, no. 1: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies6010031
APA StyleProtopapadakis, E., Voulodimos, A., Doulamis, A., Camarinopoulos, S., Doulamis, N., & Miaoulis, G. (2018). Dance Pose Identification from Motion Capture Data: A Comparison of Classifiers. Technologies, 6(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies6010031







