Valorization of Steelmaking Slag for Circular Economy Applications: Adsorptive Removal and Recovery of Ni(II) and Cu(II) from Aqueous Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
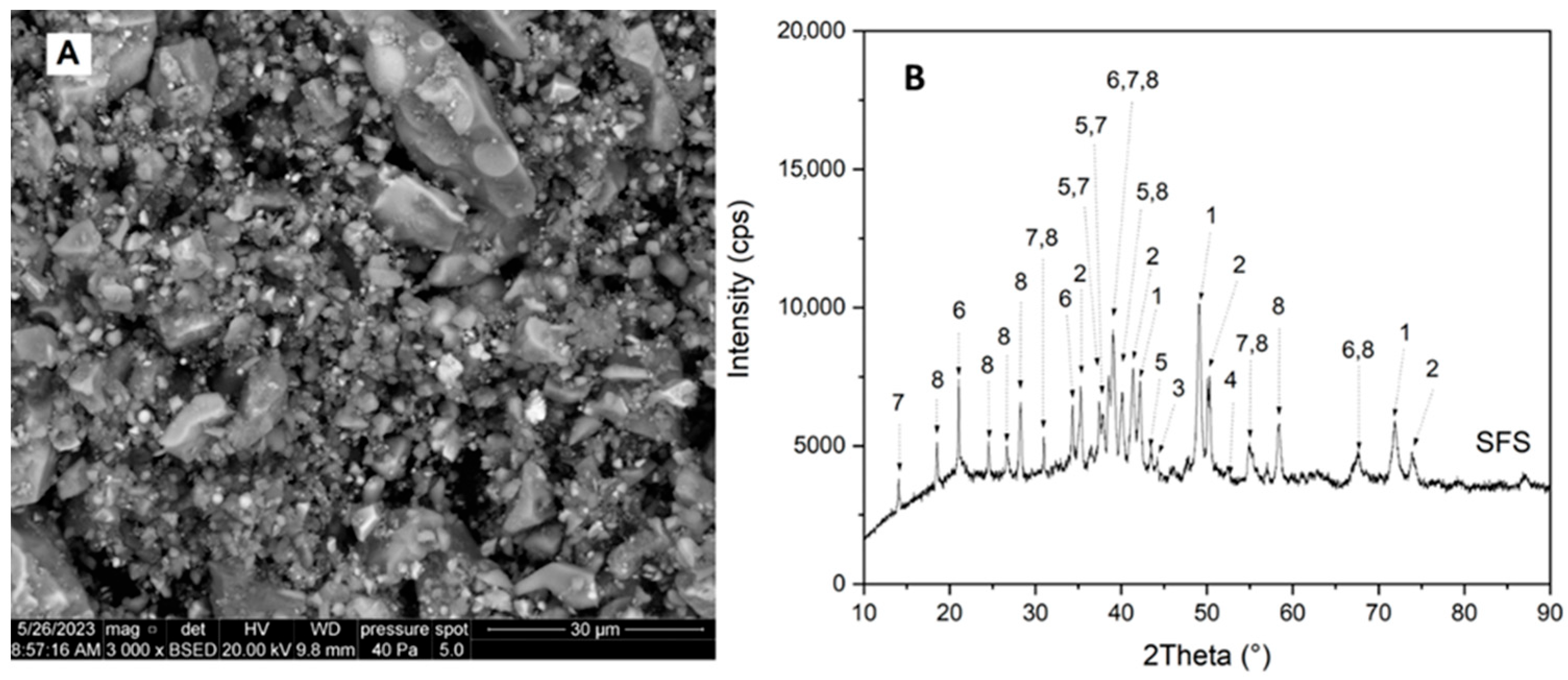
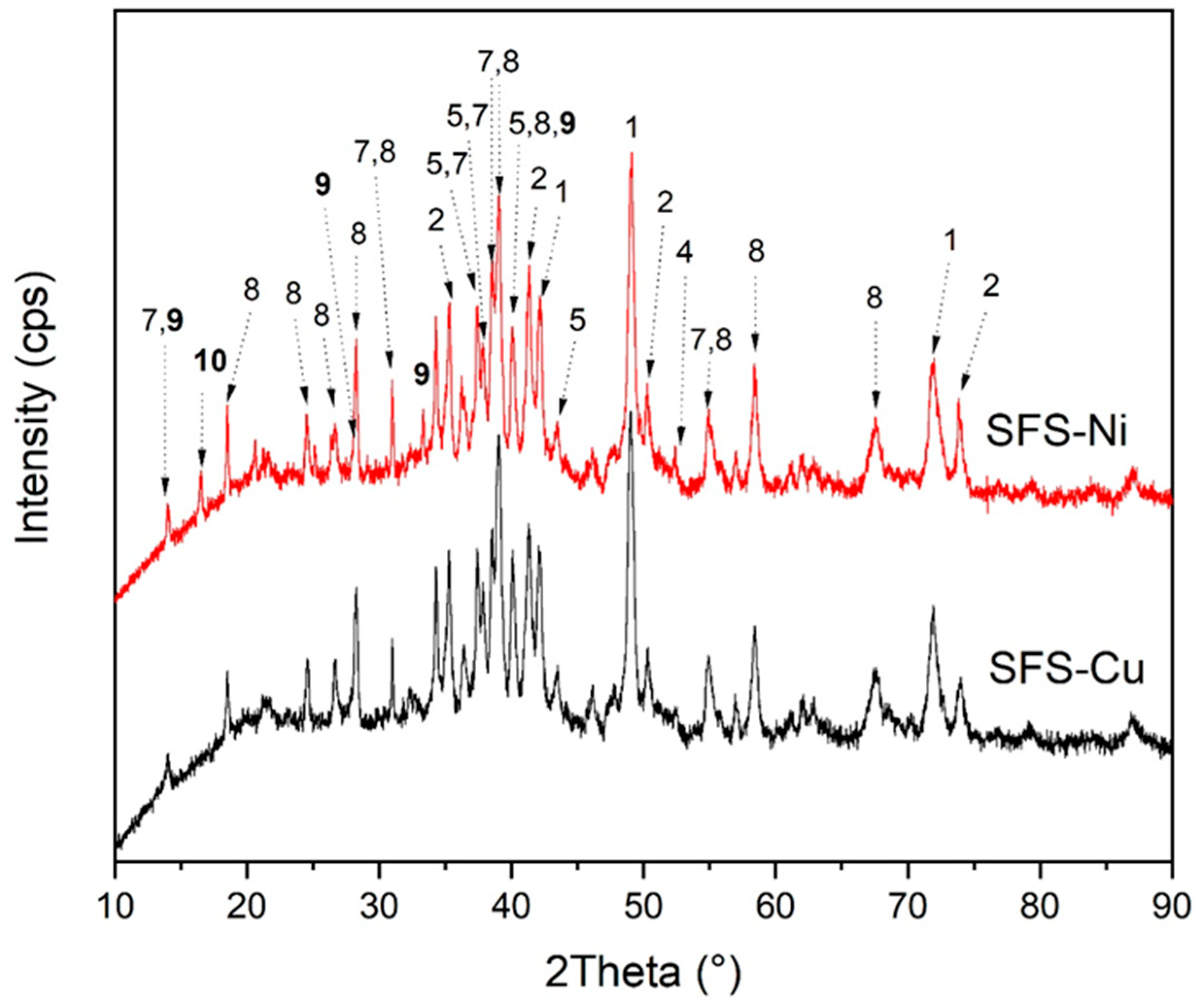
3.1. Chemical and Structural Characteristics of the Slag
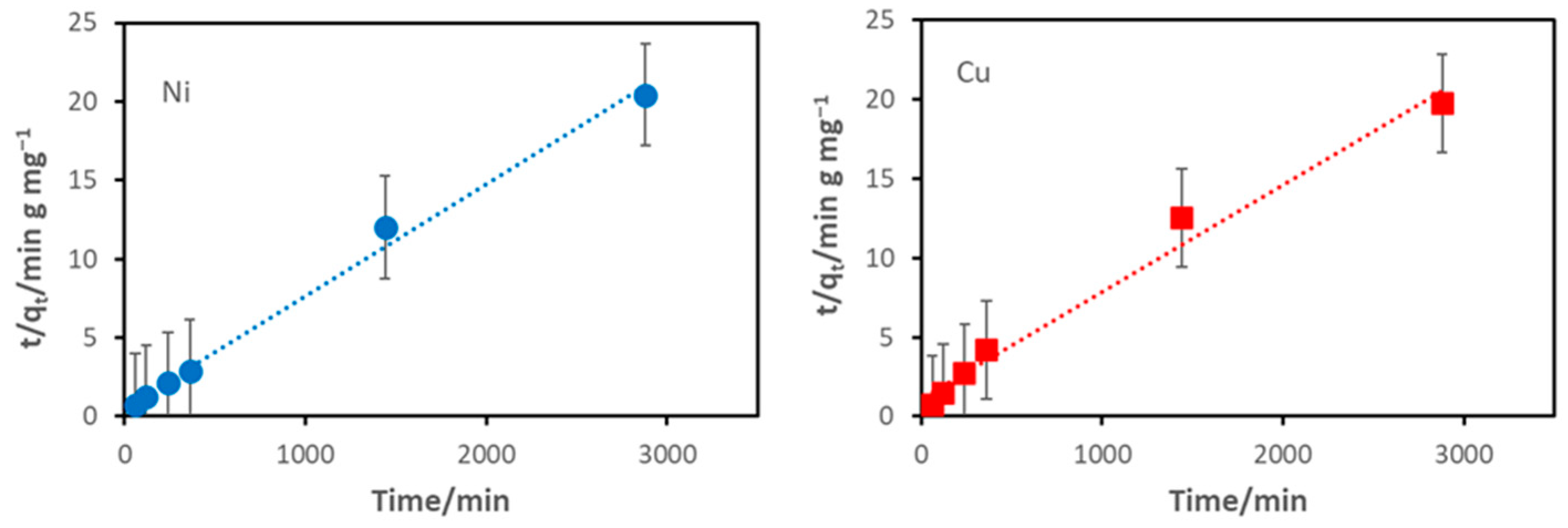
3.2. Adsorption Capacity and Modelling
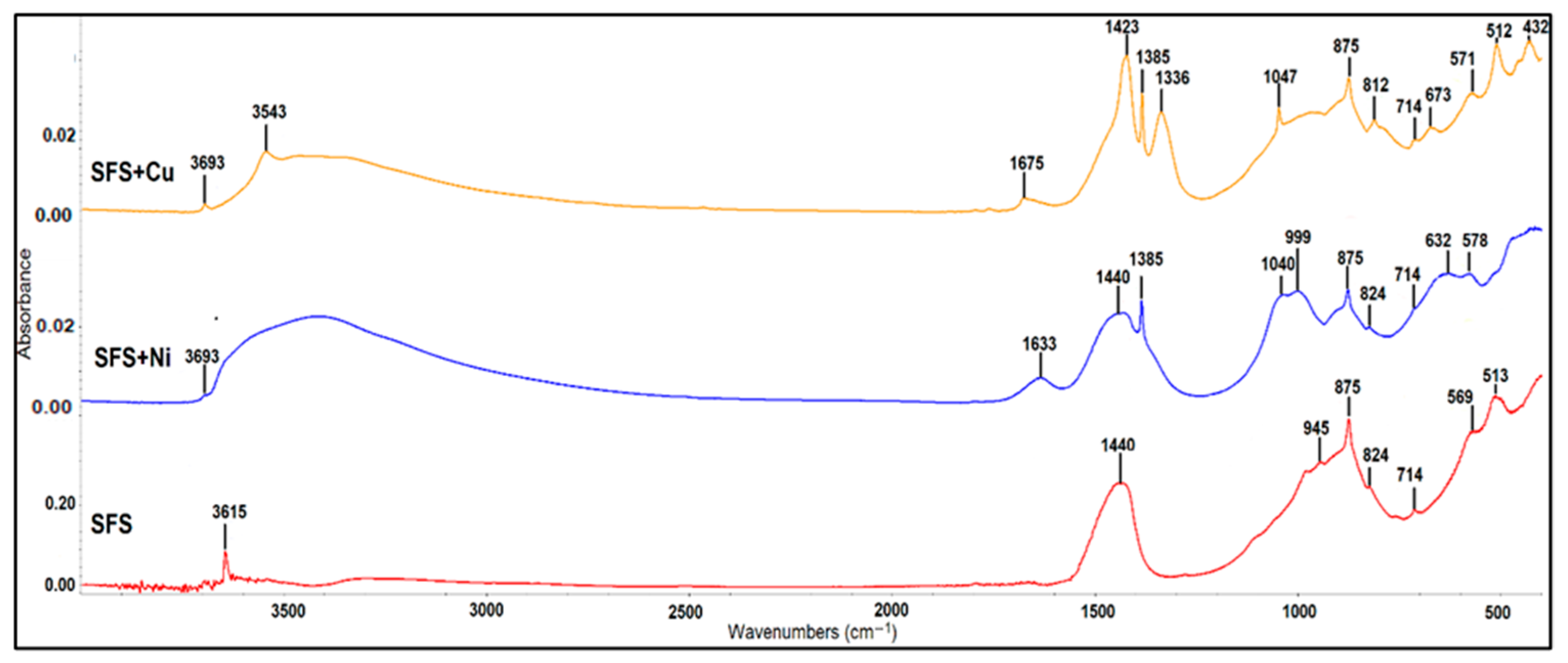
3.3. Surface Mechanisms and Spectroscopic Evidence
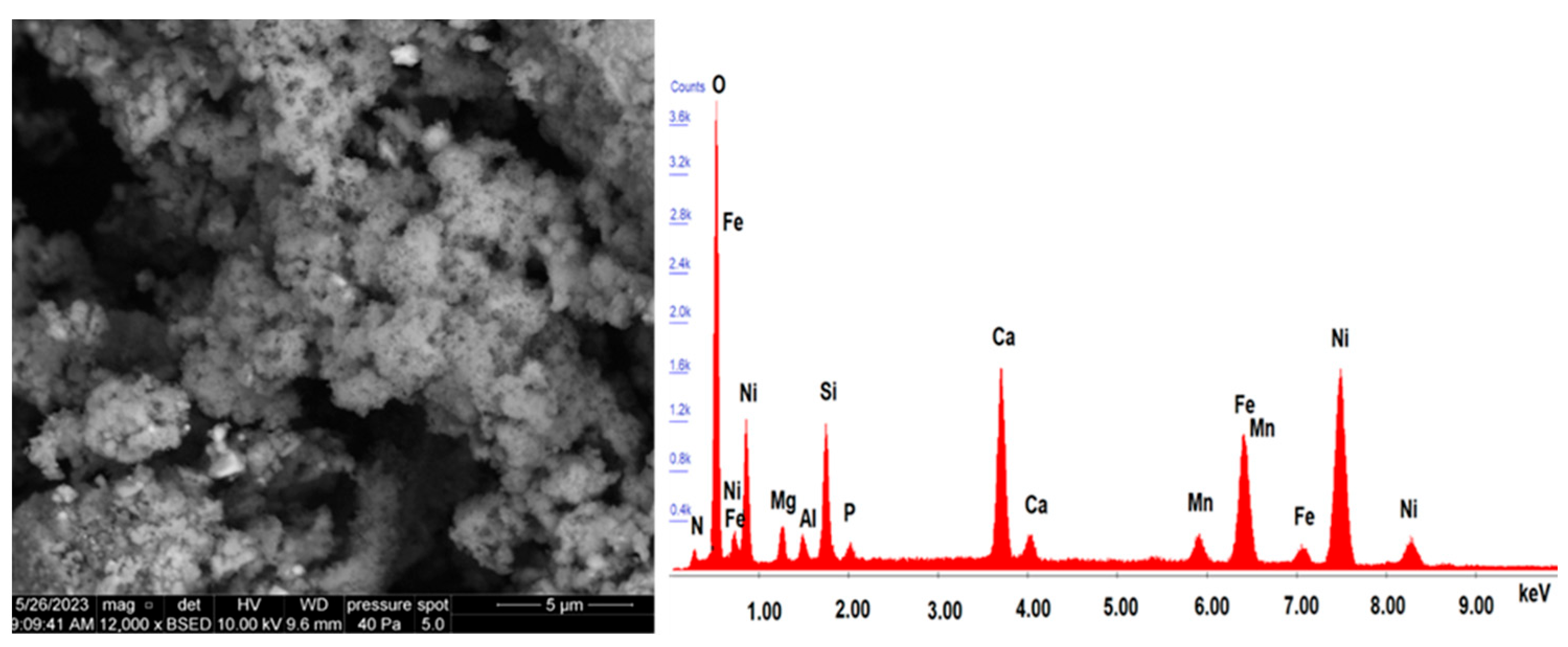
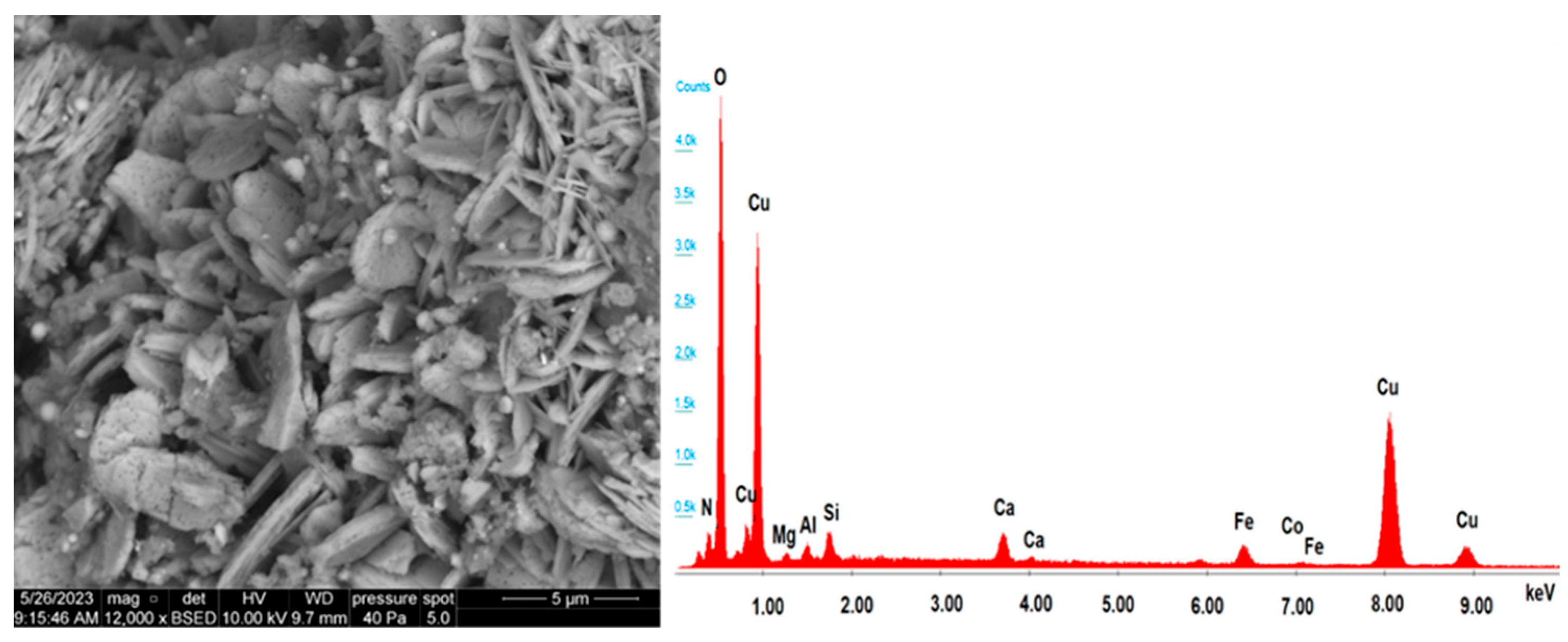
3.4. Morphological and Structural Transformations
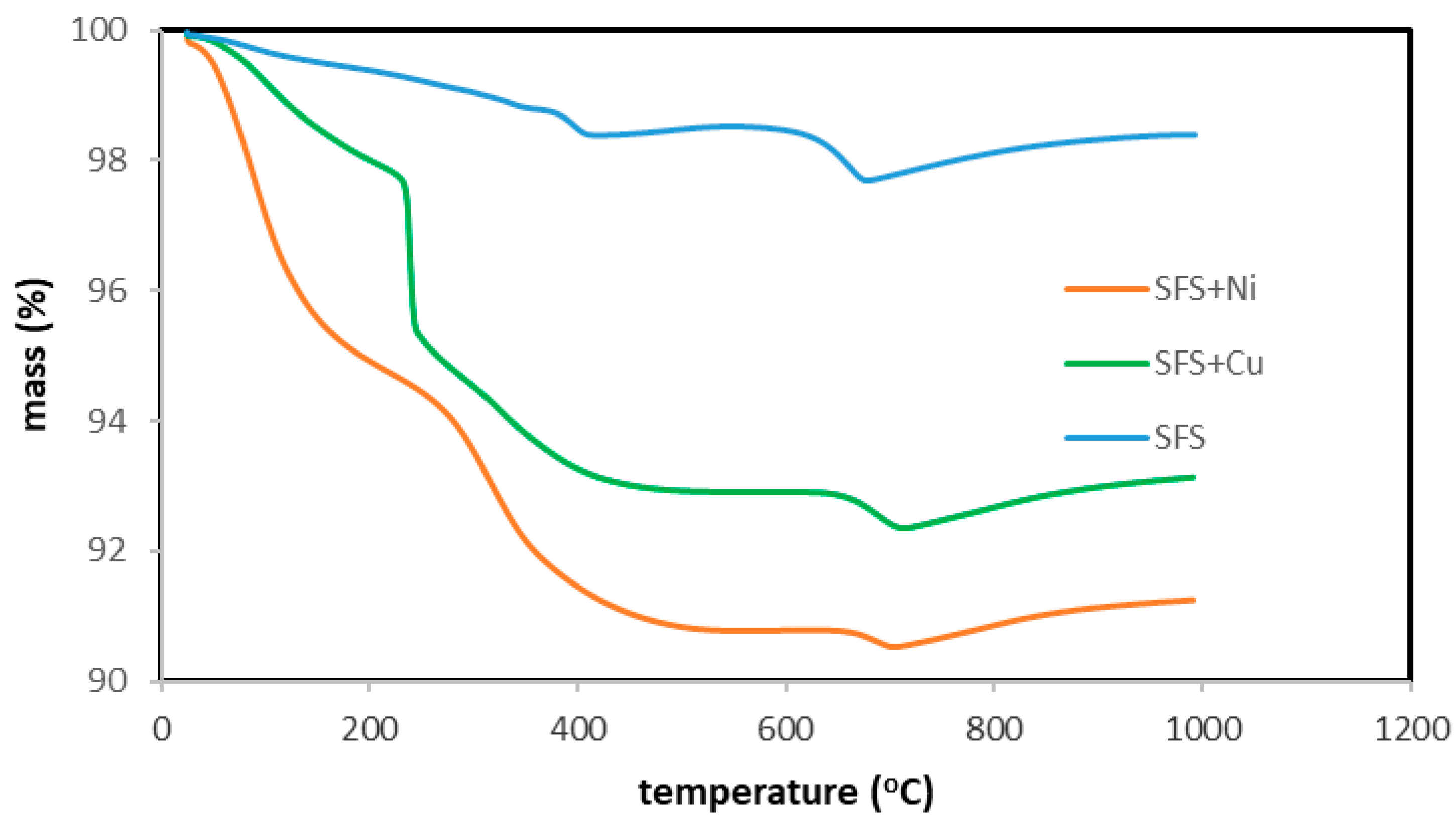
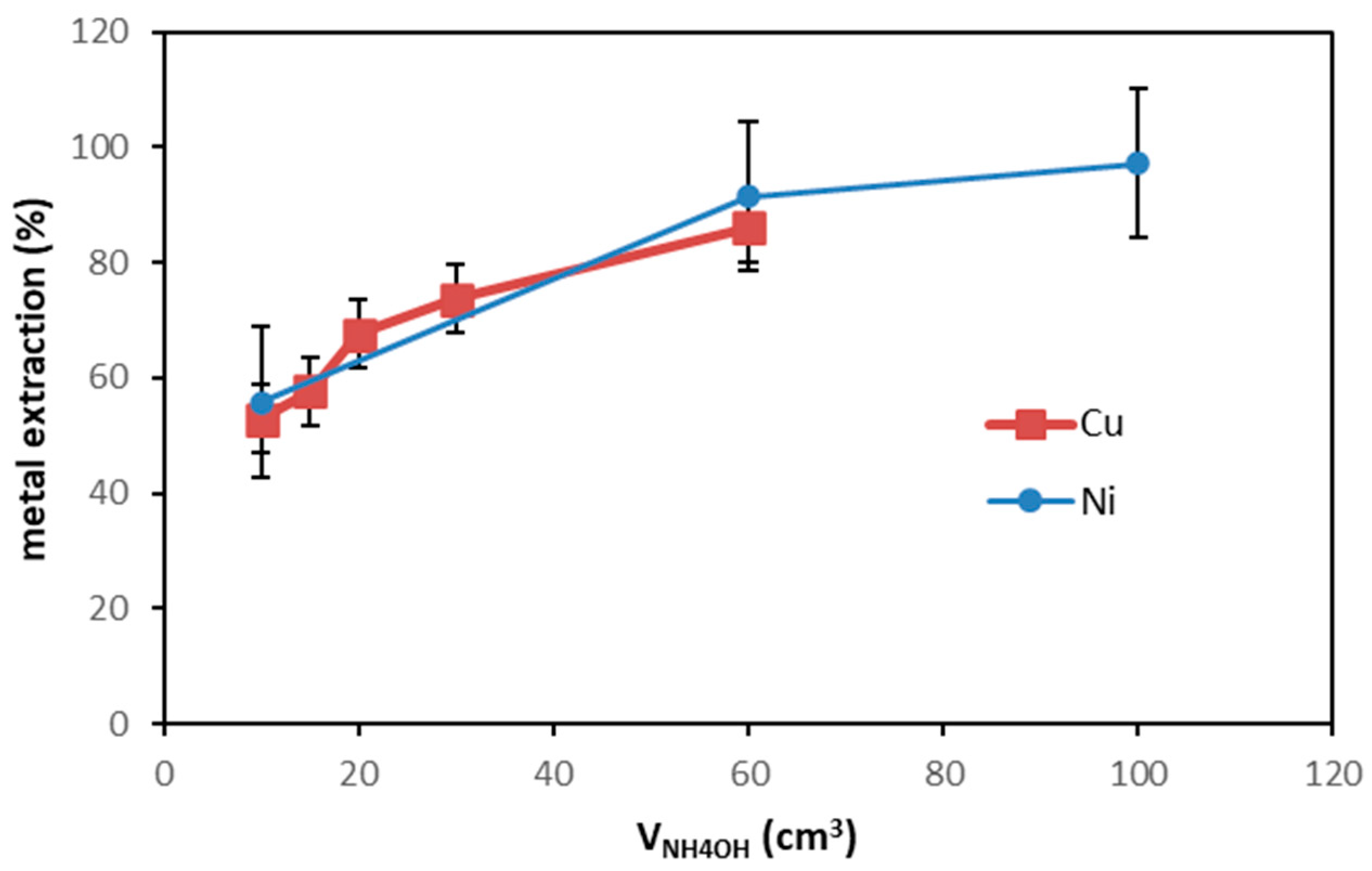
3.5. Thermal Behaviour and Metal Recovery
3.6. Environmental and Economic Implications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barakat, M.A. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehrenheim, E.; Gustafsson, J.P. Kinetic sorption modelling of Cu, Ni, Zn, Pb and Cr ions to pine bark and blast furnace slag by using batch experiments. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1571–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holappa, L.; Kekkonen, M.; Jokilaakso, A.; Koskinen, J. A Review of Circular Economy Prospects for Stainless Steelmaking Slags. J. Sustain. Metall. 2021, 7, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbelin, M.; Bascou, J.; Lavastre, V.; Guillaume, D.; Benbakkar, M.; Peuble, S.; Baron, J.-P. Steel Slag Characterisation—Benefit of Coupling Chemical, Mineralogical and Magnetic Techniques. Minerals 2020, 10, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsafi, M.; Fornasiero, R. Explorative Multiple-Case Research on the Scrap-Based Steel Slag Value Chain: Opportunities for Circular Economy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, S.K.; AlSharif, M.A. Copper (Cu) an Essential Redox-Active Transition Metal in Living System—A Review Article. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 9, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardhan, K.H.; Kumar, P.S.; Panda, R.C. A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: Current trends and future perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.A.; Adlan, M.N.; Ariffin, K.S. Heavy metals (Cd, Pb, Zn, Ni, Cu and Cr(III)) removal from water in Malaysia: Post treatment by high quality limestone. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiya, T.K.; Bhattacharya, A.K.; Das, S.K. Removal of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions using clarified sludge. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 325, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Hofmann, A.; Wolthers, M.; Thomas, P. Reversibility of cadmium sorption to calcite revisited. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 368, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Tian, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, G. Comparison of adsorption properties for cadmium removal from aqueous solution by Enteromorpha prolifera biochar modified with different chemical reagents. Environ. Res. 2020, 186, 109502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kołodyńska, D.; Wnetrzak, R.; Leahy, J.J.; Hayes, M.H.B.; Kwapiński, W.; Hubicki, Z. Kinetic and adsorptive characterization of biochar in metal ions removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang, H.I.; Onwawoma, A.; Bae, S. The Elovich equation as a predictor of lead and cadmium sorption rates on contaminant barrier minerals. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.; Manocha, S. Sorption of cadmium ions onto synthetic hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Mater. Today-Proc. 2017, 4, 10460–10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiar, N.; Suri, R.; McKenzie, E.R. Competitive sorption of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn from stormwater runoff by five low-cost sorbents; Effects of co-contaminants, humic acid, salinity and pH. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 126938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czech, B.; Hojamberdiev, M.; Bogusz, A. Impact of thermal treatment of calcium silicate-rich slag on the removal of cadmium from aqueous solution. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 200, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Su, B. Removal characteristics of Cd(II) from acidic aqueous solution by modified steel-making slag. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 246, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langová, S.; Kostura, B.; Matějka, V.; Ritz, M.; Krčmář, J. Cadmium sorption on to basic oxygen furnace slag. Arch. Mater. Sci. 2022, 2, 1–9. Available online: https://www.stechnolock.com/article/Cadmium-Sorption-on-to-Basic-Oxygen.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Xue, Y.; Hu, Z.; Niu, Y. Single and coadsorption of copper, cadmium, lead and zinc onto basic oxygen furnace slag. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 179, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Chung, H.; Jeong, S.; Nam, K. Identification of pH-dependent removal mechanisms of lead and arsenic by basic oxygen furnace slag: Relative contribution of precipitation and adsorption. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Circular Economy Action Plan: For a Cleaner and More Competitive Europe; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bogacka, M.; Iluk, T.; Pikoń, K.; Ściążko, M.; Stec, M.; Czaplicki, A.; Wajda, A. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of the Use of Metallurgical Process Gas for Heat and Electricity, Combined with Salt Removal from Discarded Water. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasiuk, D.; Daigo, I.; Hoshino, T.; Hayashi, H.; Yamasue, E.; Tran, D.H.; Sprecher, B.; Shi, F.; Shatokha, V. International comparison of impurities mixing and accumulation in steel scrap. J. Ind. Ecol. 2022, 26, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, R.; Nekouei, R.K.; Al Mahmood, A.; Sahajwalla, V. Value-added fabrication of NiO-doped CuO nanoflakes from waste flexible printed circuit board for advanced photocatalytic application. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xie, H.; Han, B. The Utilization of the Copper Smelting Slag: A Critical Review. Minerals 2025, 15, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horák, M.; Papoušek, D. Infrared Spectroscopy and Structure Molecules; Academia: Prague, Czechoslovakia, 1976. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Peng, X.; Tang, L.; Zeng, L.; Lan, C. Influence of inorganic admixtures on the 11 Å-tobermorite formation prepared from steel slags: XRD and FTIR analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 60, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G.; Wase, D.A.J.; Forster, C.F. Study of the Sorption of Divalent Metal Ions on to Peat. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2000, 18, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, Z.; Chen, L.; Sun, Y. The sorption of Cd(II) and U(VI) on sepiolite: A combined experimental and modeling studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 209, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.C.; Moura, D.; Costa, A.P.; Yokoyama, L.; da Fonseca Araujo, F.V.; Cammarota, M.C.; Cardillo, L. Evaluation of pH, alkalinity and temperature during air stripping process for ammonia removal from landfill leachate. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. Part A 2013, 48, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, S.; Chen, F.; Guo, Z.; Qiu, M. Technical progress in removal of ammonia nitrogen from landfill leachate by air stripping. Mod. Chem. Ind. 2019, 39, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazkova, E.A.; Bakina, O.V.; Rodkevich, N.G.; Mosunov, A.A.; Vornakova, E.A.; Chzhou, V.R.; Lerner, M.I. Copper ferrite/copper oxides (I, II) nanoparticles synthesized by electric explosion of wires for high performance photocatalytic and antibacterial applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2022, 283, 115845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, S.; Warsi, M.F.; Zulfiqar, S.; Ayman, I.; Haider, S.; Alsafari, I.A.; Agboola, P.O.; Shakir, I. Nickel ferrite/zinc oxide nanocomposite: Investigating the photocatalytic and antibacterial properties. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouras, D.; Mecif, A.; Barillé, R.; Harabi, A.; Rasheed, M.; Mahdjoub, A.; Zaabat, M. Cu:ZnO deposited on porous ceramic substrates by a simple thermal method for photocatalytic application. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 21546–21555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.F.; Roush, T.L.; Morris, R.V. Mid-infrared transmission spectra of crystalline nanophase iron oxides/oxyhydroxides and implications for remote sensing of Mars. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 5297–5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckler, B.; Lutz, H.D. Lattice vibration spectra. Part XCV. Infrared spectroscopic studies on the iron oxide hydroxides goethite (α), akaganéite (β), lepidocrocite (γ), and feroxyhite (δ). Eur. J. Solid State Inorg. Chem. 1988, 35, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ca | Mg | Fe | Mn | Al | Si | Zn | Cr | Pb | Cd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21.8 | 4.1 | 28.3 | 4.4 | 1.4 | 6.7 | 0.10 | 0.28 | 0.028 | 0.0014 |
| Ion | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax [mg·g−1] | b [dm3·mg−1] | R2 | K | n | R2 | |
| Cu(II) | 146.57 | 0.0385 | 0.9903 | 15.001 | 2.594 | 0.6582 |
| Ni(II) | 147.23 | 0.0249 | 0.9989 | 63.156 | 7.519 | 0.5341 |
| Ion | Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 [min−1] | R2 | K2 [g·mg·min−1] | R2 | |
| Cu(II) | 3.00·10−4 | 0.6345 | 3.86·10−5 | 0.9836 |
| Ni(II) | 7.00·10−4 | 0.9480 | 6.21·10−5 | 0.9932 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kostura, B.; Matějka, V.; Ritz, M.; Sabovčík, T.; Vlček, J. Valorization of Steelmaking Slag for Circular Economy Applications: Adsorptive Removal and Recovery of Ni(II) and Cu(II) from Aqueous Systems. Technologies 2025, 13, 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13120552
Kostura B, Matějka V, Ritz M, Sabovčík T, Vlček J. Valorization of Steelmaking Slag for Circular Economy Applications: Adsorptive Removal and Recovery of Ni(II) and Cu(II) from Aqueous Systems. Technologies. 2025; 13(12):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13120552
Chicago/Turabian StyleKostura, Bruno, Vlastimil Matějka, Michal Ritz, Tomáš Sabovčík, and Jozef Vlček. 2025. "Valorization of Steelmaking Slag for Circular Economy Applications: Adsorptive Removal and Recovery of Ni(II) and Cu(II) from Aqueous Systems" Technologies 13, no. 12: 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13120552
APA StyleKostura, B., Matějka, V., Ritz, M., Sabovčík, T., & Vlček, J. (2025). Valorization of Steelmaking Slag for Circular Economy Applications: Adsorptive Removal and Recovery of Ni(II) and Cu(II) from Aqueous Systems. Technologies, 13(12), 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies13120552







