Abstract
Advances in the development of collision-free path planning algorithms are the main need not only to solve mazes with robotic systems, but also for their use in modern product transportation or green logistics systems and planning merchandise deliveries inside or outside a factory. This challenge increases as the complexity of the task in its structure also increases. This paper deals with the development of a novel methodology for solving mazes with a mobile robot, using image processing techniques and graph theory. The novelty is that the mobile robot can find the shortest path from a start-point to the end-point into irregular mazes with abundant irregular obstacles, a situation that is not far from reality. Maze information is acquired from an image and depending on the size of the mobile robot, a grid of nodes with the same dimensions of the maze is built. Another contribution of this paper is that the size of the maze can be scaled from 1 m × 1 m to 66 m × 66 m, maintaining the essence of the proposed collision-free path planning methodology. Afterwards, graph theory is used to find the shortest path within the grid of reduced nodes due to the elimination of those nodes absorbed by the irregular obstacles. To avoid the mobile robot to travel through those nodes very close to obstacles and borders, resulting in a collision, each image of the obstacle and border is dilated taking into account the size of the mobile robot. The methodology was validated with two case studies with a mobile robot in different mazes. We emphasize that the maze solution is found in a single computational step, from the maze image as input until the generation of the Path vector. Experimental results show the usefulness of the proposed methodology, which can be used in applications such as intelligent traffic control, military, agriculture and so on.
1. Introduction
The solution of a maze consists of reaching the destination point from the starting point, following the most efficient route within the shortest possible time and through a workspace infested with irregular obstacles. On this sense, several methodologies to find the shortest path inside a maze based on graph [1,2,3] and non-graph theory [4,5,6,7] have been reported in the literature. Moreover, robotic systems have been development for performing autonomous and semi-autonomous tasks with human interactions in areas such as industry, intelligent traffic control, military, warehouse and household management, fire fighters, agriculture, rescuing robots and so on [8]. Of all the tasks mentioned before, one very demanding application in the field of robotics is the autonomous navigation. Particularly, maze-solver robots find applications in office buildings, transfer of goods through industry [9], bomb-detection, search and rescue of living beings trapped in natural disasters or dangerous situations [10], etc. In this context, the cell decomposition method along with the potential field method were used to compose a global and local path planning method [11]. However, its drawback is that the mobile robot can fall into local minima due to the negative gradient used in the method. In [2,10], several algorithms based on graphs and non-graphs to solve mazes were studied and compared. According to those papers, the first set presents a better solution in terms of efficiency, reliability and solution time. A weighted shortest path algorithm was introduced in [12] for multi-agent environment. Here, the maze is divided into cells and when robots visit a cell, the number of visits of this cell increases. Because all the robots share memory, when one of them reaches the goal, the information is passed to the other robots and each one of them redirects its trajectory towards the destination point. The main disadvantage is that a lot of hardware is required to solve small mazes. In [13,14], the wall tracking and flood fill algorithms were used to solve small mazes. However, this proposal fails for large mazes. A variant of the Breadth-First Search algorithm was reported in [15]. Here the maze is also divided in cells and the robot movements are stored into a list, where each element of the list is a node of the graph. Its main disadvantage is that this methodology not only consumes a lot of CPU resources when large mazes with many cells are processed, but also the division of the maze into cells is done conveniently, a situation that is very unrealistic.
Moreover, techniques for solving mazes based on image processing have also been proposed. Thus, in [16], several photographs are acquired at different angles of the maze. After processing, a panoramic photo is obtained. However, this work lacks the perspective of the image, since the farthest parts of the maze are not clearer. An image based path planning was proposed in [17], where the image is divided into cells. However, the robot comes to crash with the obstacle when the grid node is very close to it. A similar drawback is found in [18]. In [19] a shorter path finding method in maze images was proposed. Its major disadvantage is related with the noise of the image, which affects the labeling process of the n-blocks. In [20,21,22], image skeletonization was used to find the shortest path within a maze image. A drawback of this method is that morphological pruning is used, which depends on the resolution of the image. As a consequence, the method might not only fail for large and complex mazes, but the memory requirement also increases exponentially. Furthermore other techniques have also been reported, such as resistive grid [23,24,25] and memristive grid [26,27]. However, the main disadvantage of these methods is related with the complexity of the solution algorithm of the system of equations, which depend on the size of the matrix. Therefore, valuable computer resources are wasted in generating large matrices due to the grid and when the shortest path is only searched in a part of the matrix.
As can be seen in the papers reported up to date, all maze-solving methods assume mazes and obstacles without irregular structures and are built according to their convenience. This is a serious drawback since the structure of said mazes differs substantially from reality. Furthermore, each reported methodology may not only fail when the maze is scaled up or down, but in each experimental test, the size of the mobile robot is not taken into account. Therefore, the development of efficient and inexpensive collision-free path planning algorithms is widely needed to solve not only large and complex mazes, but also to be used in the modern product transportation systems and green logistics [9,28]. The main goal of this paper is to describe a novel collision-free maze-solving methodology for mobile robots, based on image processing techniques and graph theory, which improves all the disadvantages described above. The manuscript is organized as follows: Section 2 discusses the processing of an image containing a maze. Section 3 describes path planning using graph theory. Numerical tests of two case studies with different size of the maze and number of cells are discussed. Experimental verification is shown in Section 4. Section 5 presents a brief discussion about the advantages and disadvantages of the developed methodology and the experimental results. Finally, the conclusions are summarized in Section 6.
2. Maze-Image Processing
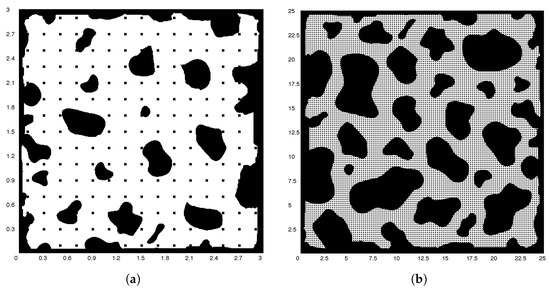
In real applications, a maze with irregular shape is infested with irregular obstacles and a human or machine, such as robots, must be able to find the shortest path between two points in the shortest time possible. These drawbacks make the navigation algorithm a challenging task and particularly, the mobile robot is armed with proximity detection sensors, focused towards the necessary directions to avoid crashing with the obstacles. Unlike the previously described maze solving methods, the proposed methodology is based on image processing techniques and hence, the shortest path between the start-point and end-point is extracted of a maze image. Thus, in each Figure 1a,b, a binarized image of an irregular maze with obstacles and boundaries (all in black color) with irregular shapes is shown. Each image was acquired with natural lighting, using a camera with 17 Mp resolution and f/1.8 illumination aperture. The images were scaled to 500 × 500 pixels using bicubic interpolation, where the black background is represented by a logical 0 and the white background is represented by a logical 1. Whereas the first maze has a size of 3 m × 3 m, the second maze has a dimension of 25 m × 25 m and each of them can be expanded or reduced in the range [1 m × 1 m, 66 m × 66 m]. At the low limit, this depends on the size of the mobile robot to be used, with long L and width W. For the upper limit, it depends on the maximum grid size that can be generated without losing information of the same grid size. Note that if the robot size is smaller, the lower and upper limits can be reduced. On the contrary, if the robot size is larger, both limits can be increased.
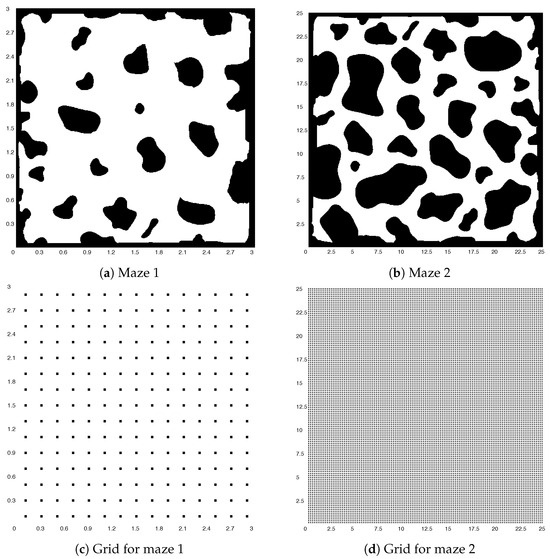
Figure 1.
Mazes with irregular dimensions and obstacles along with their grids.
In the next step, a grid of nodes is automatically generated for each maze, as illustrated in Figure 1c and Figure 1d, respectively. Nodes are stored and enumerated in a matrix in ascending order, from top to bottom and from left to right. The node number is generated as follows
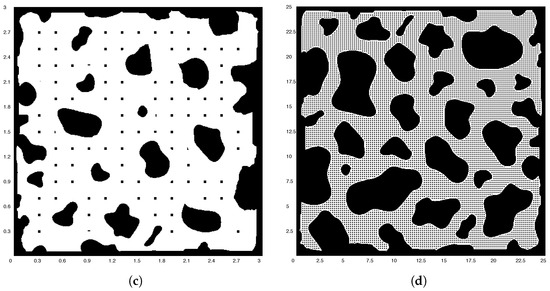
where , indicate the size of the maze-image and ceil(.) round the numeric value to the nearest integer greater than the element. Thus, whereas for Figure 1c the top-left node is number 1 and the bottom-right node is number 225, for Figure 1d the top-left node is number 1 and the bottom-right node is number 15,625. The distance between the grid nodes is L and each node represents a coordinate of a possible position of the autonomous robot. Subsequently, each maze along with its grid are merged as depicted in Figure 2a,b. As a consequence, each obstacle absorbs some nodes and the rest are collision-free nodes. However, in each maze in Figure 2a,b, there are nodes very close to obstacles and boundaries. This is a serious drawback, since the mobile robot can crash. To solve the inconvenient, each obstacle expands at a rate of
where 500 is the number of pixels of the scaled image and min(.) obtains the minimum value. In this way, the nodes closest to each obstacle are absorbed and it ensures that the mobile robot does not crash when navigating near the obstacle or border. All absorbed nodes are listed as zero. The results of this process are shown in Figure 2c and Figure 2d, respectively.
3. Path Planning
Once the collision-free nodes are obtained, the shortest path must be found between the start-point and the end-point, selected by the user in the maze with the grid of reduced nodes. In this sense, an algorithm is developed to built the undirected graph. According to (1) and Figure 2c, the matrix that represents the collision-free nodes is
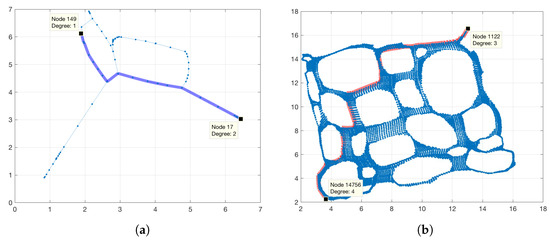
To build the graph, one must verify that in each column of (3), the current and next node must be non-zero. If this occurs, each node is stored in a vector, one for start nodes (s) and other for target nodes (t). This task is repeated for all nodes in each column. A similar process is also performed for each row of (3). As a consequence, the two vectors generated describe the undirected graph, which is only built with horizontal and vertical edges and weights equal to 1. This same procedure is carried out on the matrix that represents the collision-free nodes in Figure 2d, but of size 125 × 125. Moreover, the user must select the start-point and end-point in Figure 2c,d. For the first maze the nodes are: Start = 17 and End = 149 and for the second maze the nodes are: Start = 14,756 and End = 1122, respectively. By executing the Breadth-First Search algorithm in Matlab [1,3,18,19], whose complexity is expressed as where V is the number of vertices and E is the number of edges, one get the collision-free shortest paths through

where the commands between apostrophes specifies the algorithm to use and, in this case, the Breadth-First Search algorithm which is used in graphs with edge weights equal to 1. Additionally, EdgeColor defines the color of the edge on the graph, b = blue and LineWidth defines the width of the line. The shortest path for maze in Figure 2c is illustrated in Figure 3a and for maze in Figure 2d is depicted in Figure 3b. For both cases, the Path vector in the Matlab code mentioned above stores all the collision-free shortest path nodes, respectively.
4. Experimental Verification
MBot Mega is an omnidirectional mobile robot with mecanum wheels [29]. Due to these characteristics, the robot can move in three directions: horizontal, vertical and diagonal, and in four orientations: up, down, left and right. Although the programming language called mBlock is a free and open-source software supporting block-based coding, other platforms can also be used such as Arduino IDE and Raspberry Pi using Python programming. The dimensions of the MBot Mega shown in Figure 4 are L = 0.2 m and W = 0.16 m.
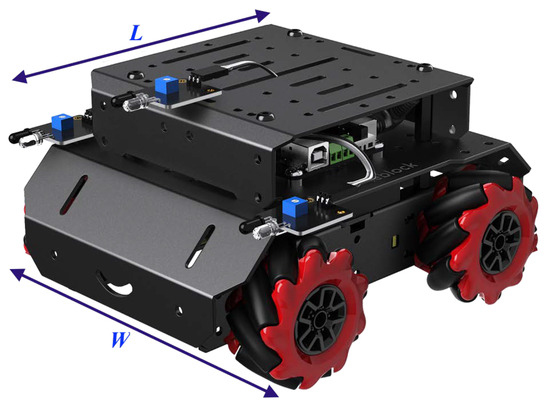
Figure 4.
MBot Mega mobile robot.
According to line 3 of the Matlab code described before, the Path vector stores the position nodes from the start-point until the end-point. To control the movement of the autonomous robot using Arduino IDE platform, each position is transformed into one of the following instructions: up, down, right and left. Diagonal movement is not used in this work. Further, the robot is configured to move at a velocity of = 28 m/min in the up direction and = 35 m/min in the right direction. To move in the other directions, the same velocities are used but with negative sign. These velocities remain active for an instant of time and depending on the distance between nodes. For instance, the time for the up or down direction is computed as
and the time for the right or left direction is obtained as
The instruction transformation algorithm is described as follows. According to (3), the nodes are generated from top to bottom and from left to right in ascending order. Therefore, it can be seen that the numerical value of the difference between two consecutive vertical nodes is ±1, whereas for horizontal nodes the difference is greater than ±1. For the former case, the positive sign indicates a downward movement and the negative sign indicates an upward movement. For the second case, the positive sign indicates a movement to the right and the negative sign indicates a movement to the left. In order to improve the previous description, Algorithm 1 shows the pseudocode of the instruction transformation algorithm.
| Algorithm 1 Instruction transformation algorithm pseudocode. |
Require: Path vector
|
Let us experimentally verify a practical situation. From Figure 3a and the line 3 of the Matlab code mentioned before, the Path vector is obtained as
Then the mobile robot must follow the path shown in Figure 5a. By programming the Algorithm 1 on the Arduino IDE platform and configuring the mobile robot to control each wheel, the experimental evidence is shown in Figure 5b. As can be seen, the mobile robot successfully follows the previously generated collision-free path. A task similar to path in Figure 3b can be performed, where the Path vector only needs to change on the reconfigurable hardware. For this case, the length of the Path vector is 233. Volume and space in the construction of the maze along with the grid nodes illustrated in Figure 2d is not shown, for reasons of complexity. However, performance parameters of the proposed methodology can be obtained as given in Table 1, such as: Processing time, which indicates the time used by the methodology to deduce the shortest path, from the maze image as input until the generation of the Path vector. Travel time, is the time that uses the mobile robot to reach the goal from the start-point. Distance is the path measured in meters that the robot travels from start-point until the end-point and Battery consumption, which is the total energy consumed by the robot. For this work, the battery capacity is 2600 mAh and voltage 9 V. The features of the CPU used to run the methodology are: 1.6 GHz Intel core i5 and memory size 4 GB.
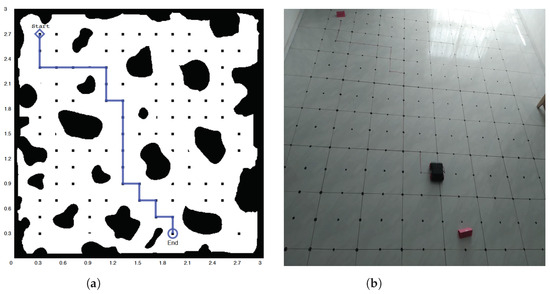

Table 1.
Performance parameters measured during the solution of the mazes.
Moreover, the proposed methodology has only been compared with those methodologies based on image processing, as described in Table 2. It is found that all works reported in the literature do not take into account the dimensions of the robot and fail when the maze is scaled. For this reason, the reported methodologies have been tested in mazes with medium and small dimensions, unlike the proposed methodology that can be scaled in the range described above. As a consequence, some of them report only numerical results and the rest report experimental tests.

Table 2.
Comparison with other methodologies that solve mazes.
5. Discussion
The methodology for solving mazes with the MBot Mega mobile robot, based on graph theory and image processing is relatively simple and easy to encode on reconfigurable hardware. Based on the experimental results obtained using the MBot Mega platform, it can be stated that any maze of size in the range [1 m × 1 m, 66 m × 66 m] with irregular shape, infested with irregular obstacles, can be solved. Unlike the methodologies described above and given in Table 2, here the dimensions of the mobile robot are taken into account in the automatic generation of the node grid and as consequence, the shortest path in very large mazes can be found. Note that the scalability property is included here. Furthermore, the proposed collision-free path planning methodology provides the opportunity to pre-plan the mobile robot travel path and avoids it from getting trapped and falling into infinite loops. However, to improve the performance of the proposed methodology, diagonal movement must be considered and therefore, the setting-up of the undirected graph including this requirement. Another disadvantage observed is related to the case when one or more wheels lose contact with the smooth ground or begin to skid, decreasing the precision and accuracy in the position. This error accumulates during the navigation and is reflected in the final position and orientation of the mobile robot. To reduce this limitation, the floor should be moderately rough. Moreover, an analysis of the battery power consumption when the mobile robot travels on the shortest path is still necessary. However, we ensure that the energy cost is minimal compared if another longer path is used to reach the end-point from the start-point. But also, in future works the charging and discharging modes of the battery in real time should be analyzed. As a consequence, not only battery charge/discharge models could be generated, but the battery life time could also be researched, a very important issue for energy optimization. Furthermore, energy optimization opens the possibility to research the performance of the mobile robot when it travels not only along the shortest path, but also to find and travel along the most optimal path. This is because the shortest path can have several path changes from vertical to horizontal and vice versa. Thus, in each change, the mobile robot must brake slightly and change its speed according to (4) and (5). But also, if long and straight paths are found, the speed of the mobile robot can be increased in order to reduce the travel time and improve the energy efficiency. As a consequence, travel time and energy consumption may be slightly higher in comparison if the most optimal path is used. It is important to highlight that if the maze to be solved is plagued by a large number of irregular obstacles, the developed methodology is more efficient in terms of CPU-time used to find the shortest path, since the number of vertices and edges that make up the graph is reduced. All in all, this navigation methodology can be used in smart applications, agriculture, warehouse and household management and so on.
6. Conclusions
A novel methodology for solving mazes with a mobile robot has been introduced. Unlike the methodologies described above, the autonomous robot can solve the irregular maze infested with irregular obstacles in the range 1 m × 1 m to 66 m × 66 m, where the size of the robot is considered. Therefore, the proposed collision-free path planning methodology includes the scaling property. Furthermore, to generate the collision-free nodes near of each obstacle and boundary, each of them is expanded to a ratio of N, ensuring that the mobile robot does not crash. The node matrix is automatically generated based on (1), taking into account the dimensions of the maze and the autonomous robot. Additionally, we would like to emphasize that the maze solution can be found in a single computational step, from the maze image as input until the generation of the Path vector and the user needs to supply only the start-point and end-point. Regarding to hardware implementation, the Path vector must be updated according to the solved maze. These are the main contributions and hence, the proposed methodology can be used in real applications, as those described before. A shortcoming is related with the constant velocity of the mobile robot. If it is necessary to increase or decrease the velocity and travel a predetermined distance, the time to be used must be updated, as described in (4) and (5). Moreover, the proposed collision-free path planning methodology can be improved by including diagonal motion and thus, smooth movements of the mobile robot can be achieved, mainly when the robot changes its vertical motion to horizontal motion and vice versa. Other future work is related to the efficient use of the battery and hence, establishing energy optimization criteria. Under these criteria, it is possible to research the generation of the most optimal path instead of the shortest path, addressing the aforementioned disadvantages. Numerical simulations were performed in two mazes in order to verify the performance of the proposed collision-free navigation methodology. Experimental results were gathered, as shown in Figure 5, validating the theory. Finally, it is worth mentioning that to the best knowledge of the authors, this type of methodology based on image processing techniques and graph theory has not been developed for mazes and obstacles with irregular shapes, and with the scaling property, until today.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.A.A.-S. and C.S.-L.; methodology, L.A.A.-S., C.H.-M. and C.S.-L.; software, L.A.A.-S. and C.S.-L.; validation, L.A.S.-G. and H.G.G.-H.; formal analysis, R.O.-M., F.M.-G. and C.H.-M.; investigation, L.A.A.-S., F.M.-G. and C.H.-M.; writing—original draft preparation, L.A.S.-G., R.O.-M. and H.G.G.-H.; writing—review and editing, L.A.S.-G. and F.M.-G.; supervision, C.S.-L., R.O.-M. and H.G.G.-H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The second author thanks to CONAHCyT for the sabbatical leave grant at National Institute of Astrophysics, Optics and Electronics (INAOE) during 2022–2023.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gross, J.L.; Yellen, J.; Anderson, M. Graph Theory and Its Applications, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylos & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sadik, A.M.J.; Dhali, M.A.; Farid, H.M.A.B.; Rashid, T.U.; Syeed, A. A Comprehensive and Comparative Study of Maze-Solving Techniques by Implementing Graph Theory. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computational Intelligence, Sanya, China, 23–24 October 2010; pp. 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Kaur, S. A Review of Various Maze Solving Algorithms Based on Graph Theory. Int. J. Sci. Res. Dev. 2019, 6, 431–434. [Google Scholar]
- Niemczyk, R.; Zawiślak, S. Review of Maze Solving Algorithms for 2D Maze and Their Visualisation. In Engineer of the XXI Century. EngineerXXI 2018. Mechanisms and Machine Science; Zawiślak, S., Rysiński, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 70. [Google Scholar]
- Alamri, S.; Alshehri, S.; Alshehri, W.; Alamri, H.; Alaklabi, A.; Alhmiedat, T. Autonomous Maze Solving Robotics: Algorithms and Systems. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Robot. Res. 2021, 10, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, S.; Alamri, H.; Alshehri, W.; Alshehri, S.; Alaklabi, A.; Alhmiedat, T. An autonomous maze-solving robotic system based on an enhanced wall-follower approach. Machines 2023, 11, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, P. Path planning techniques for mobile robots: Review and prospect. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 227, 120254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, X.; Iqbal, S.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J. Applications of chaotic dynamics in robotics. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyushev, N.V.; Malozyomov, B.V.; Sorokova, S.N.; Efremenkov, E.A.; Valuev, D.V.; Qi, M. Review Models and Methods for Determining and Predicting the Reliability of Technical Systems and Transport. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gong, D. A comparative study of A-star algorithms for search and rescue in perfect maze. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electric Information and Control Engineering, Wuhan, China, 15–17 April 2011; pp. 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Huh, D.J.; Park, J.H.; Huh, U.Y.; Kim, H.I. Path planning and navigation for autonomous mobile robot. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual Conference of the Industrial Electronics Society. IECON 02, Seville, Spain, 5–8 November 2002; Volume 2, pp. 1538–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Rahnama, B.; Ozdemir, M.; Kiran, Y.; Elci, A. Design and Implementation of a Novel Weighted Shortest Path Algorithm for Maze Solving Robots. In Proceedings of the 37th International Computer Software and Applications Conference Workshops (COMPSACW), Tokyo, Japan, 22–26 July 2013; pp. 328–332. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.-C.; Zhou, Y.; Shoaib, A.M.; Chu, K.-C.; Izhar, M.; Ullah, S.; Lin, Y.-C. Shortest Distance Maze Solving Robot. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Information Systems (ICAIIS), Dalian, China, 20–22 March 2020; pp. 283–286. [Google Scholar]
- Covaci, R.; Harja, G.; Nascu, I. Autonomous Maze Solving Robot. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Automation, Quality and Testing, Robotics (AQTR), Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 21–23 May 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Pame, Y.G.; Kottawar, V.G.; Mahajan, Y.V. A Novel Approach to Maze Solving Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Emerging Smart Computing and Informatics (ESCI), Pune, India, 1–3 March 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rahnama, B.; Elçi, A.; Metani, S. An Image Processing Approach to Solve Labyrinth Discovery Robotics Problem. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference Workshops, Izmir, Turkey, 16–20 July 2012; pp. 631–636. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, H.N.; Shinde, J.P. An Image Based Path Planning And Motion Planning for Autonomous Robot. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2014, 5, 4844–4847. [Google Scholar]
- Aqel, M.O.A.; Issa, A.; Khdair, M.; ElHabbash, M.; AbuBaker, M.; Massoud, M. Intelligent Maze Solving Robot Based on Image Processing and Graph Theory Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Promising Electronic Technologies (ICPET), Deir El-Balah, Palestine, 16–17 October 2017; pp. 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, Y.; Mitani, Y. A Fast and Shorter Path Finding Method for Maze Images by Image Processing Techniques and Graph Theory. J. Image Graph. 2014, 2, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathe, O.; Turkar, V.; Jagtap, A.; Gidaye, G. Maze solving robot using image processing. In Proceedings of the Bombay Section Symposium (IBSS), Mumbai, India, 10–11 September 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ambeskar, A.; Turkar, V.; Bondre, A.; Gosavi, H. Path finding robot using image processing. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), Coimbatore, India, 26–27 August 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ambeskar, A.; Bondre, A.; Turkar, V.; Gosavi, H. Intuitive solution for Robot Maze Problem using Image Processing. In Proceedings of the Bombay Section Signature Conference (IBSSC), Mumbai, India, 26–28 July 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Althöfer, K.; Fraser, D.A.; Bugmann, G. Rapid path planning for robotic manipulators using an emulated resistive grid. Electron. Lett. 1995, 31, 1960–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Mejía, C.; Vázquez-Leal, H.; Sánchez-González, A.; Corona-Avelizapa, A. A Novel and Reduced CPU Time Modeling and Simulation Methodology for Path Planning Based on Resistive Grids. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 2321–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Mejía, C.; Torres-Muñoz, D.; Inzunza-González, E.; Sánchez-López, C. Exploring Robotical Implementation for Planning of Collision-free Logistical Paths Using RGPPM Algorithm. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. 2023, 47, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pershin, Y.V.; Di Ventra, M. Solving mazes with memristors: A massively parallel approach. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 84, 046703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmiento-Reyes, A.; Rodríguez-Velásquez, Y. Maze-solving with a memristive grid of charge-controlled memristors. In Proceedings of the 9th Latin American Symposium on Circuits & Systems (LASCAS), Puerto Vallarta, Mexico, 25–28 February 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S.; Pyke, D.; Steenhof, P. Electric vehicles: The role and importance of standards in an emerging market. Energy Policy 2010, 28, 3797–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makeblock mBot Mega. Available online: https://www.makeblock.com/pages/mbot-mega-smart-remote-control-robot (accessed on 24 September 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).