Jordan Canonical Form for Solving the Fault Diagnosis and Estimation Problems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diagnostic Observer Design
3. Virtual Sensor Design
4. Interval Observer Design
5. Sliding Mode Observer Design
6. Nonlinear Systems
7. Robust Solution
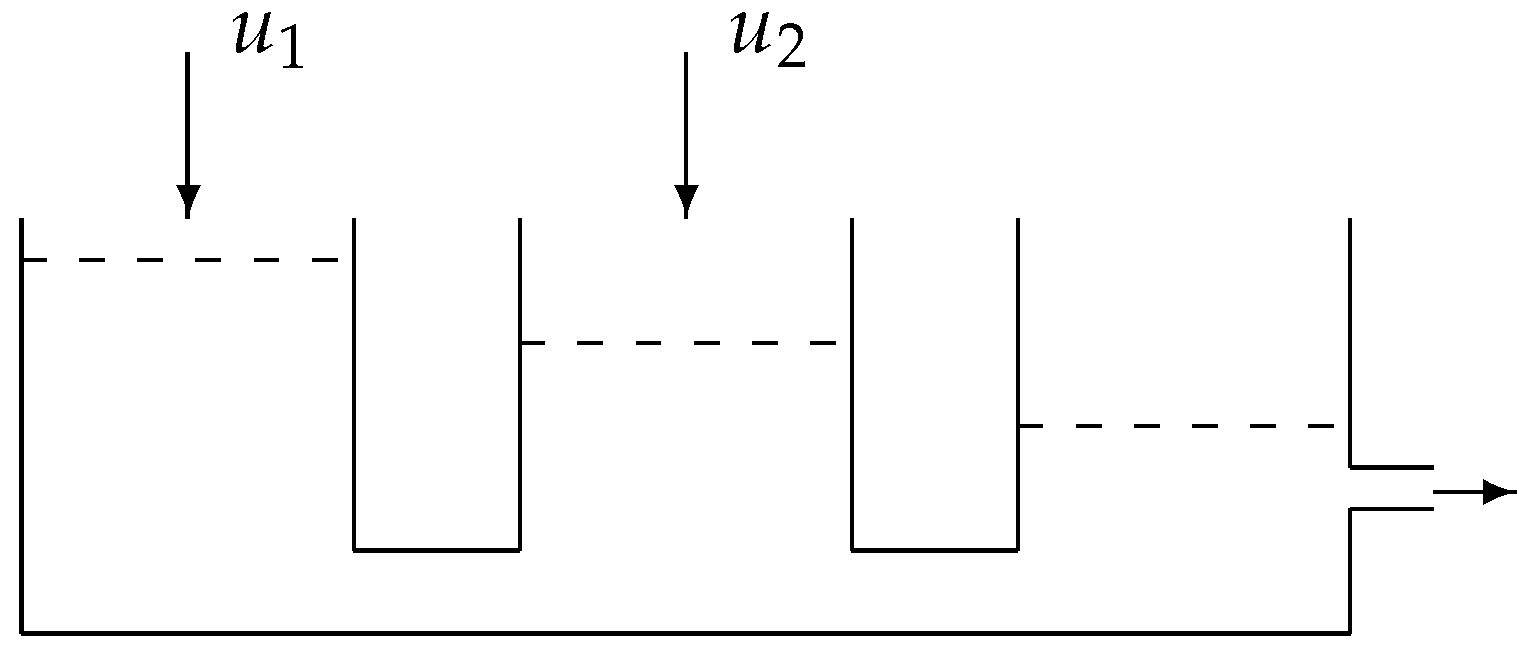
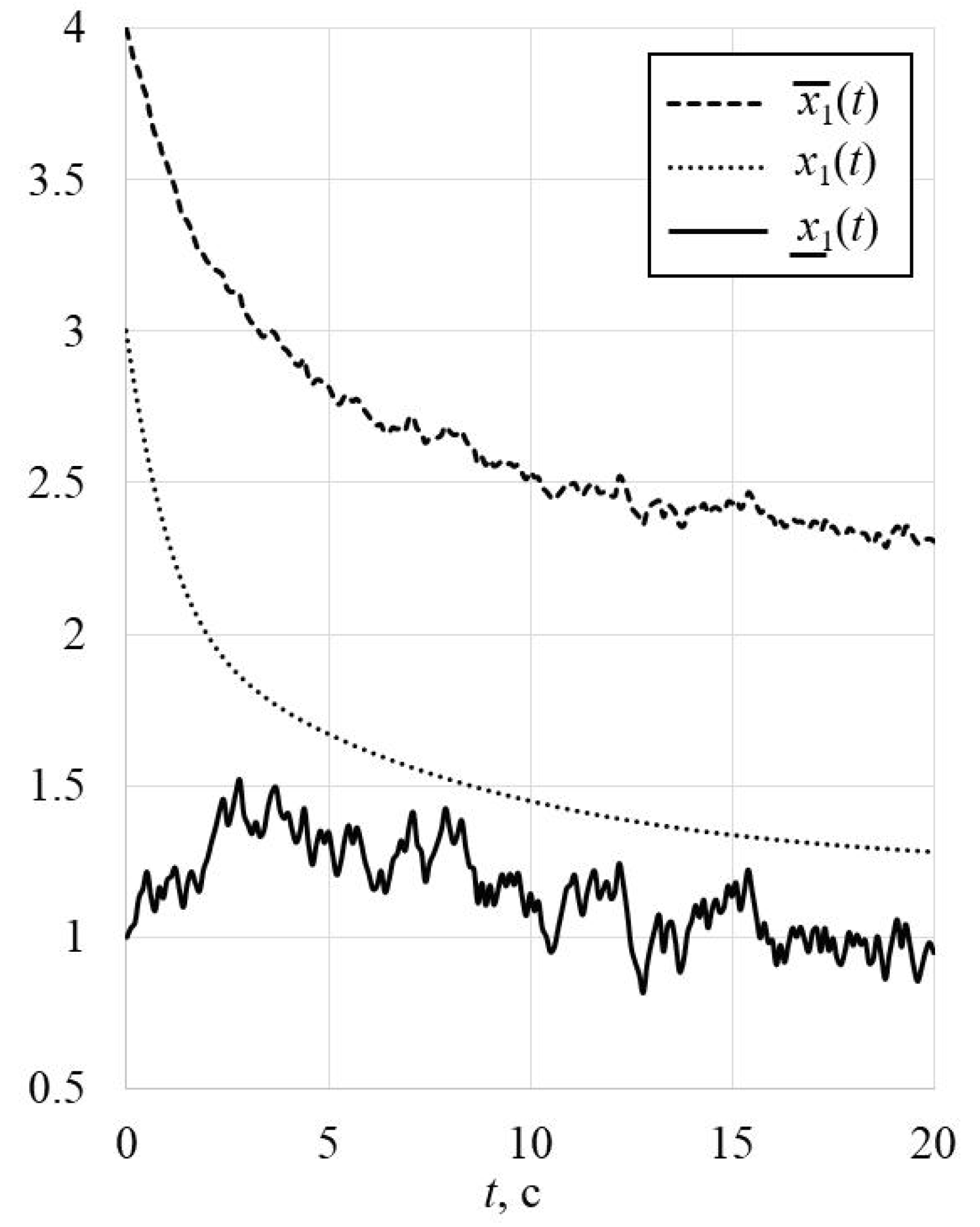
8. Example
9. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICF | identification canonical form |
| JCF | Jordan canonical form |
| SMO | sliding mode observers |
References
- Blanke, M.; Kinnaert, M.; Lunze, J.; Staroswiecki, M. Diagnosis and Fault-Tolerant Control; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Efimov, D.; Raissi, T. Design of interval state observers for uncertain dynamical systems. Autom. Remote Control 2016, 77, 191–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakernaak, H.; Sivan, R. Linear Optimal Control Systems; Wiley-Interscience: London, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Misawa, E.; Hedrick, J. Nonlinear observers—A state of the art survey. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 1989, 111, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhirabok, A.; Shumsky, A.; Pavlov, S. Diagnosis of linear dynamic systems by the nonparametric method. Autom. Remote Control 2017, 78, 1173–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimov, D.; Polyakov, A.; Richard, J. Interval observer design for estimation and control of time-delay descriptor systems. Eur. J. Control 2015, 23, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Xie, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L. Design and applications of interval observers for uncertain dynamical systems. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 2020, 14, 721–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesov, N.V.; Gruzlikov, A.M.; Lukoyanov, E.V. Using fuzzy interacting observers for fault diagnosis in systems with parametric uncertainty. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 103, 499–504. [Google Scholar]
- Mazenc, F.; Dinh, T.; Niculescu, S. Interval observers for discrete-time systems. Inter. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2014, 24, 2867–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raissi, T.; Efimov, D.; Zolghadri, A. Interval state estimation for a class of nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2012, 57, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, D.; Fernanez-Canti, R.; Tornil-Sin, S. Robust fault diagnosis of proton exchange membrane fuel cells using a Takagi-Sugeno interval observer approach. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 2875–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Jiang, B.; Yan, X.; Edwards, C. Interval sliding mode based fault accommodation for non-minimal phase LPV systems with online control application. Intern. J. Control 2019, 93, 2675–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhirabok, A. Error selfcorrection in discrete dynamic systems. Autom. Remote Control 2006, 67, 868–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witczak, M. Fault Diagnosis and Fault Tolerant Control Strategies for Nonlinear Systems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhirabok, A.; Shumsky, A.; Solyanik, S.; Suvorov, A. Fault detection in nonlinear systems via linear methods. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 2017, 27, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blesa, J.; Rotondo, D.; Puig, V. FDI and FTC of wind turbines using the interval observer approach and virtual actuators/sensors. Control Eng. Pract. 2014, 24, 138–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jove, E.; Casteleiro-Roca, J.; Quntian, H.; Mendez-Perez, J.; Calvo-Rolle, J. Virtual sensor for fault detection, isolation and data recovery for bicomponent mixing machine monitoring. Informatica 2019, 30, 671–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpoor, Z.; Arefi, M.; Razavi-Far, R.; Mozafari, N.; Hazbavi, S. Virtual sensors for fault diagnosis: A case of induction motor broken rotor bar. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 5044–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhirabok, A.; Kim, C. Virtual sensors for the functional diagnosis of nonlinear systems. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. Int. 2022, 61, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degue, K.; Efimov, D.; Richard, J. Interval observers for linear impulsive systems. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, N.; Mazenc, F.; Niculescu, S. Interval observer composed of observers for nonlinear systems. In Proceedings of the 2014 European Control Conference (ECC), Strasbourg, France, 24–27 June 2014; pp. 660–665. [Google Scholar]
- Mazenc, F.; Bernard, O. Interval observers for linear time-invariant systems with disturbances. Automatica 2011, 47, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimov, D.; Perruquetti, W.; Raissi, T.; Zolghadri, A. Interval observers for time-varying discrete-time systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2013, 58, 3218–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergiyenko, O.; Zhirabok, A.; Ibraheem, I.; Zuev, A.; Filaretov, V.; Azar, A.; Hameed, I. Interval observers for discrete-time linear systems with uncertainties. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Tan, C.; Trinh, H.; Kamal, M. State and fault estimation for a class of non-infinitely observable descriptor systems using two sliding mode observers in cascade. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 356, 3010–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.; Spurgeon, S.; Patton, R. Sliding mode observers for fault detection and isolation. Automatica 2000, 36, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, L.; Levant, A.; Davila, J. Observation of linear systems with unknown inputs via high-order sliding-modes. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2007, 38, 773–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergiyenko, O.; Tyrsa, V.; Zhirabok, A.; Zuev, A. Sensor fault identification in linear and nonlinear dynamic systems via sliding mode observers. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 10173–10182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtessel, Y.; Edwards, C.; Fridman, L.; Levant, A. Sliding Mode Control and Observation; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Tan, C.; Zhou, D. A novel sliding mode observer for state and fault estimation in systems not satisfing maching and minimum phase conditions. Automatica 2017, 79, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Edwards, C. Nonlinear robust fault reconstruction and estimation using a sliding modes observer. Automatica 2007, 43, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhirabok, A.; Shumsky, A.; Zuev, A. Fault diagnosis in linear systems via sliding mode observers. Int. J. Control 2021, 94, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhirabok, A.; Zuev, A.; Seriyenko, O.; Shumsky, A. Fault identificaition in nonlinear dynamic systems and their sensors based on sliding mode observers. Autom. Remote Control 2022, 83, 214–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, I.; Fridman, L.; Moreno, J. Super-twisting algorithm in presence of time and state dependent perturbations. Int. J. Control 2018, 91, 2535–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Edwards, C. Sliding mode observers for robust detection and reconstruction of actuator and sensor faults. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2003, 13, 443–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhirabok, A.; Zuev, A.; Filaretov, V.; Shumsky, A. Sliding mode observers for fault identification in linear systems not satisfying matching and minimum phase conditions. Arch. Control Sci. 2021, 31, 253–266. [Google Scholar]
- Low, X.; Willsky, A.; Verghese, G. Optimally robust redundancy relations for failure detection in uncertain systems. Automatica 1996, 22, 333–344. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sergiyenko, O.; Zhirabok, A.; Mercorelli, P.; Zuev, A.; Filaretov, V.; Tyrsa, V. Jordan Canonical Form for Solving the Fault Diagnosis and Estimation Problems. Technologies 2023, 11, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies11030072
Sergiyenko O, Zhirabok A, Mercorelli P, Zuev A, Filaretov V, Tyrsa V. Jordan Canonical Form for Solving the Fault Diagnosis and Estimation Problems. Technologies. 2023; 11(3):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies11030072
Chicago/Turabian StyleSergiyenko, Oleg, Alexey Zhirabok, Paolo Mercorelli, Alexander Zuev, Vladimir Filaretov, and Vera Tyrsa. 2023. "Jordan Canonical Form for Solving the Fault Diagnosis and Estimation Problems" Technologies 11, no. 3: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies11030072
APA StyleSergiyenko, O., Zhirabok, A., Mercorelli, P., Zuev, A., Filaretov, V., & Tyrsa, V. (2023). Jordan Canonical Form for Solving the Fault Diagnosis and Estimation Problems. Technologies, 11(3), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies11030072







