The Determinants of FDI in Sub-Saharan Economies: A Study of Data from 1990–2017
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
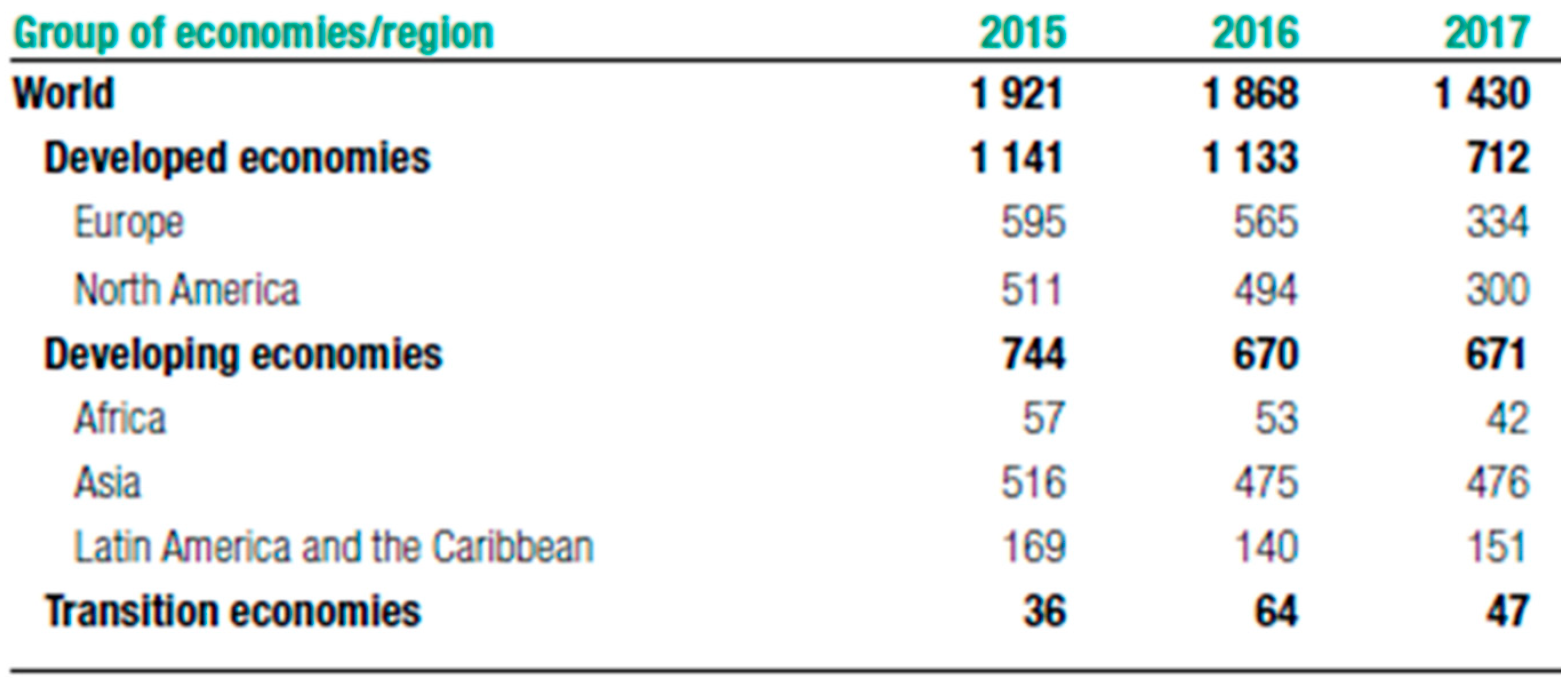
1.2. World FDI Inflows
1.3. Aim of This Paper
1.4. Structure of This Paper
2. Literature Review
2.1. Main Theories of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and their Implications
2.2. Factors Determining FDI Flows from Empirical Research
2.2.1. Inflation, Exchange Rates, Openness
2.2.2. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and GDP Per Capita
2.2.3. Infrastructure
2.2.4. Other Factors Related to an Economy
2.2.5. Summary
3. Research Design
3.1. Problem Statement
3.2. Data Sources
3.3. Method of Analysis
4. Data Description, Analysis, and Findings
4.1. Data Description
4.2. Data Analysis
Interpretation of Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Inflation (INF)
5.2. Exchange Rates (EXRTO$)
5.3. Trade Openness (OPEN)
5.4. Infrastructure (INFRA)
5.5. Market Size (GDP)
5.6. Income Level (GNIPC)
6. Conclusions
Limitations and Recommendations for Further Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Descriptive Statistics for Variables. Source: Authors’ Work
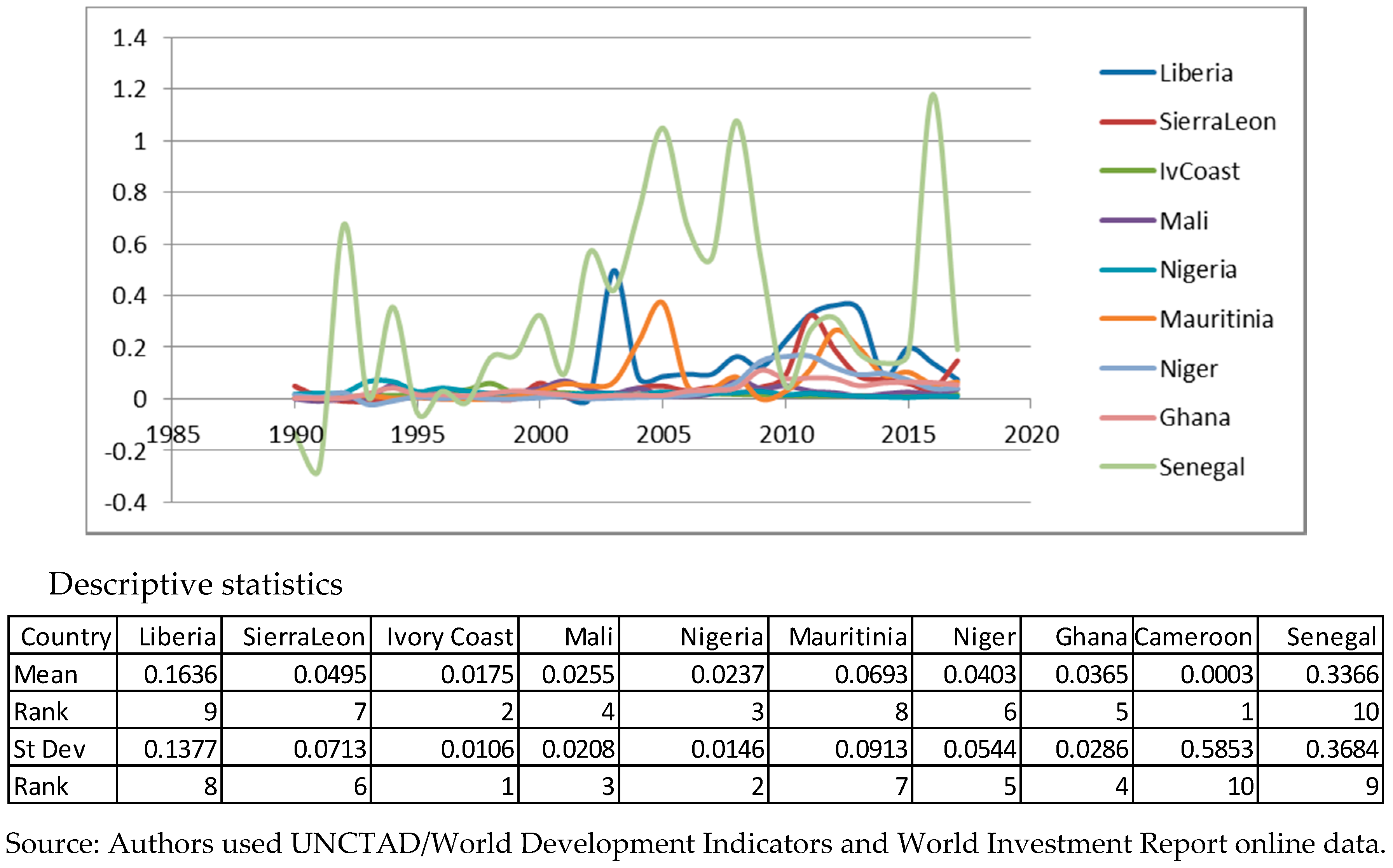
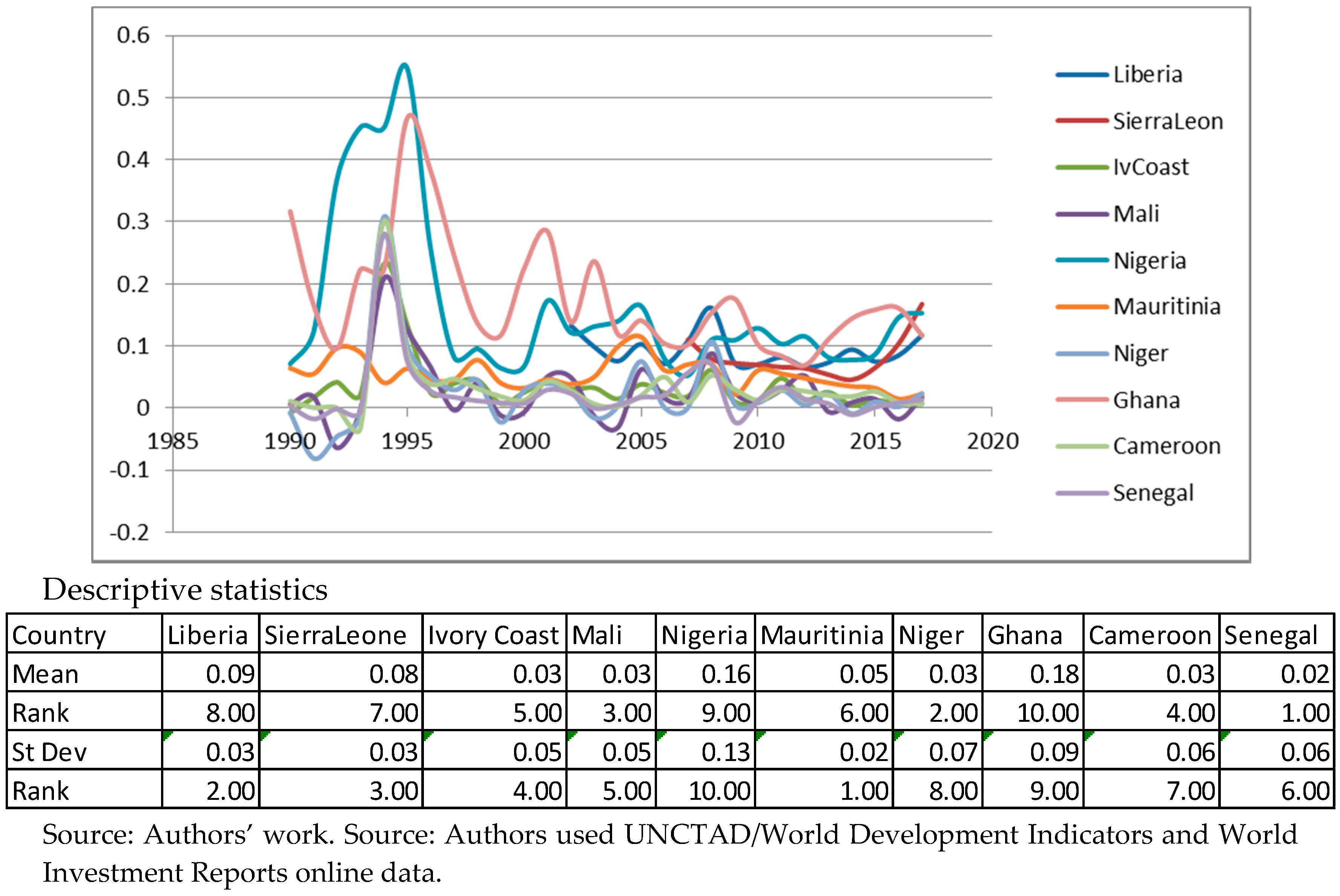
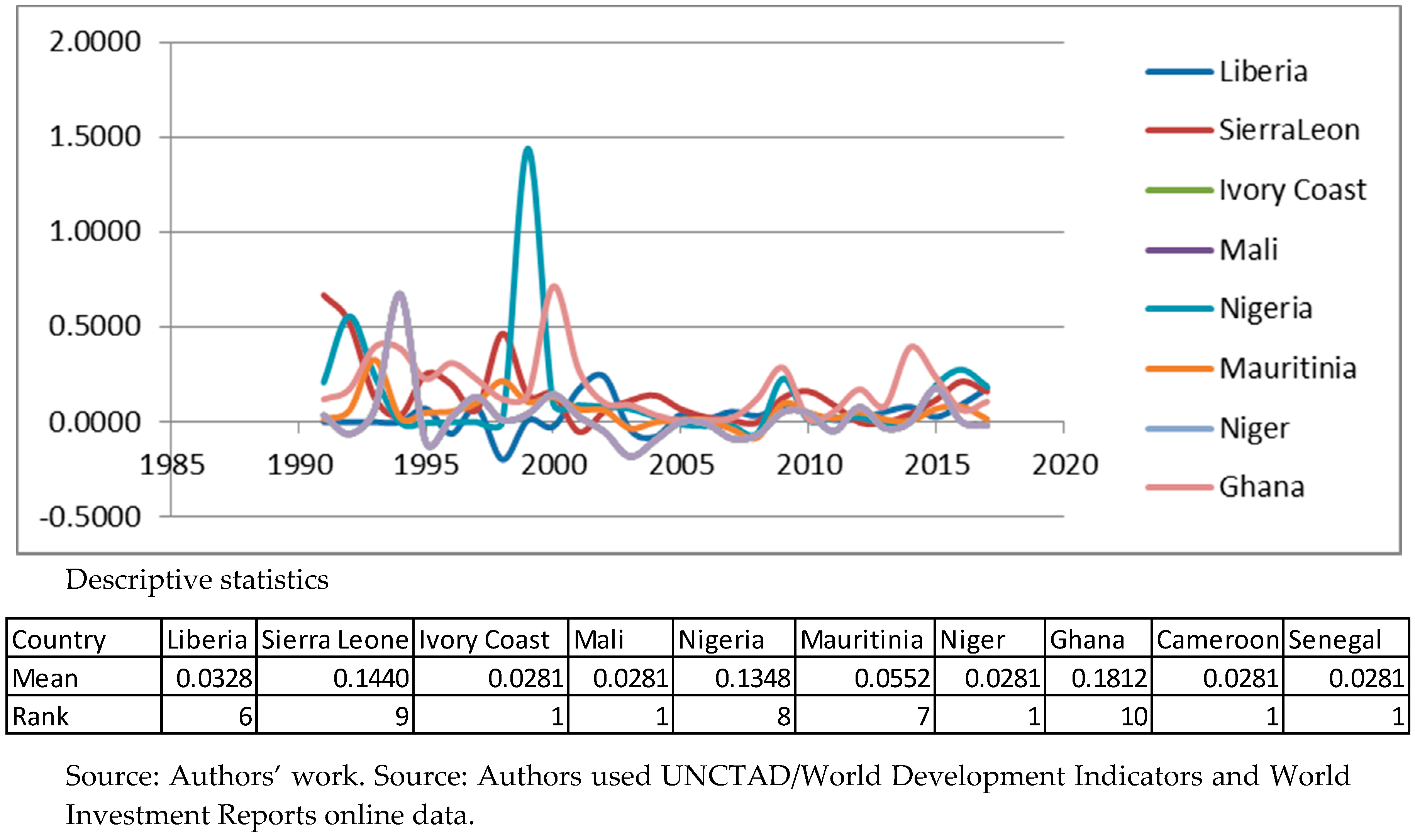
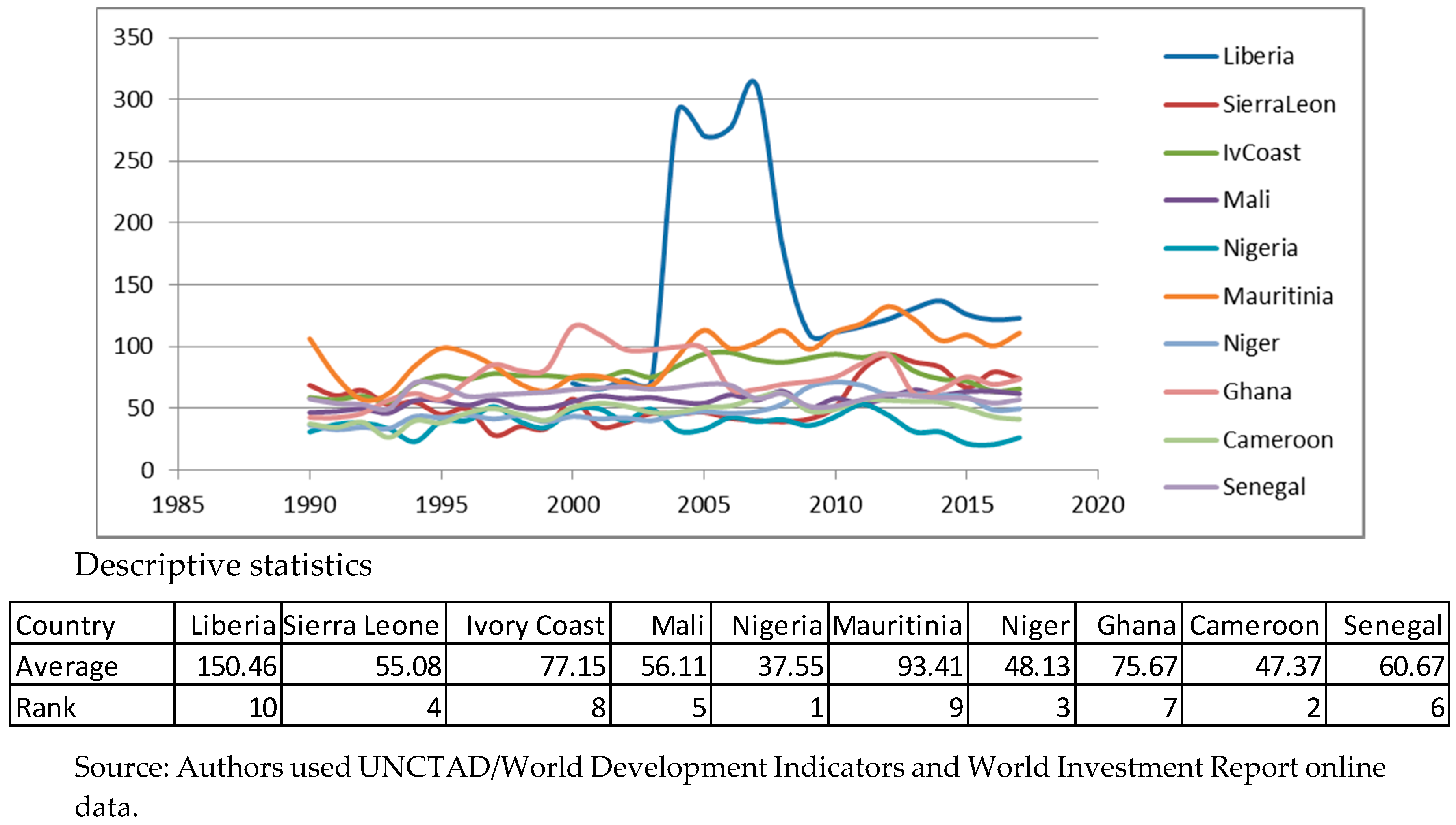
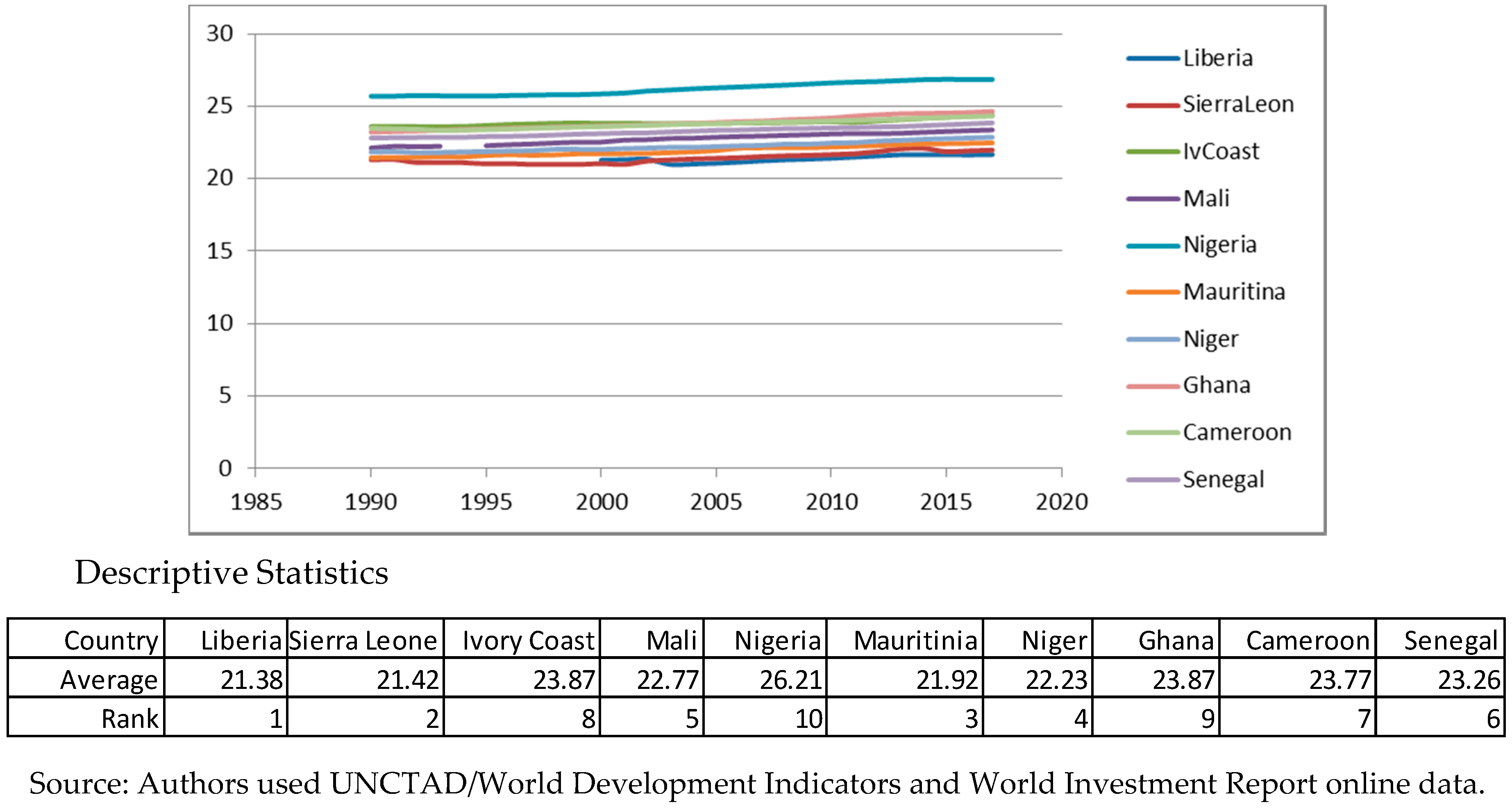

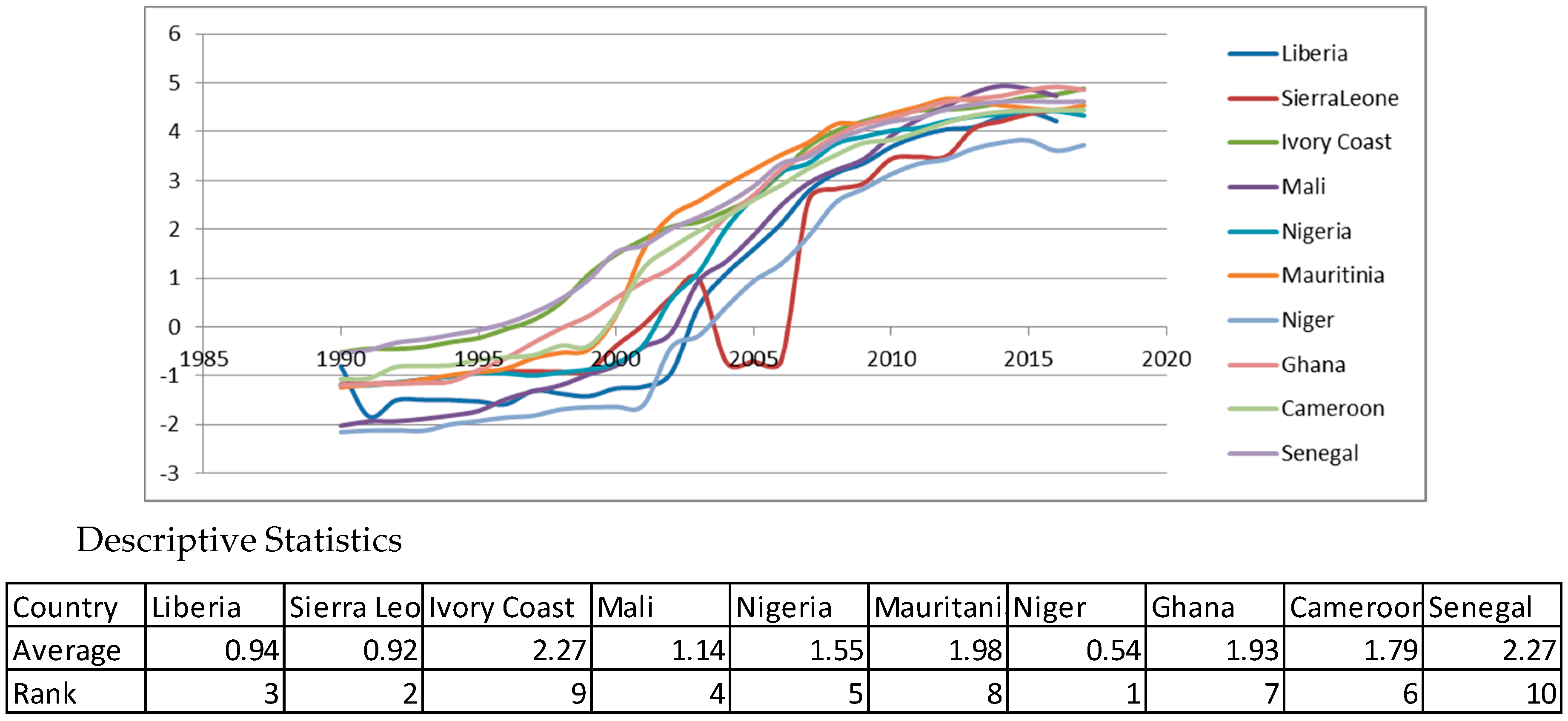
Appendix B. Panel Unit Root Tests for Stationarity. Source: Authors’ Work
| Panel unit root test: Summary | ||||
| Series: FDIGDP | ||||
| Date: 07/18/19 Time: 18:42 | ||||
| Sample: 1990 2017 | ||||
| Exogenous variables: Individual effects | ||||
| User-specified lags: 1 | ||||
| Newey-West automatic bandwidth selection and Bartlett kernel | ||||
| Method | Statistic | Prob.** | Cross-sections | Obs |
| Null: Unit root (assumes common unit root process) | ||||
| Levin, Lin & Chu t * | −3.33783 | 0.0004 | 10 | 250 |
| Null: Unit root (assumes individual unit root process) | ||||
| Im, Pesaran and Shin W-stat | −3.80469 | 0.0001 | 10 | 250 |
| ADF-Fisher Chi-square | 49.4758 | 0.0003 | 10 | 250 |
| PP-Fisher Chi-square | 63.8908 | 0.0000 | 10 | 260 |
| Panel unit root test: Summary | ||||
| Series: INF | ||||
| Date: 07/18/19 Time: 18:45 | ||||
| Sample: 1990 2017 | ||||
| Exogenous variables: Individual effects | ||||
| User-specified lags: 1 | ||||
| Newey-West automatic bandwidth selection and Bartlett kernel | ||||
| Method | Statistic | Prob. ** | Cross-sections | Obs |
| Null: Unit root (assumes common unit root process) | ||||
| Levin, Lin & Chu t * | −2.60546 | 0.0046 | 10 | 231 |
| Null: Unit root (assumes individual unit root process) | ||||
| Im, Pesaran and Shin W-stat | −4.35199 | 0.0000 | 10 | 231 |
| ADF-Fisher Chi-square | 63.7259 | 0.0000 | 10 | 231 |
| PP-Fisher Chi-square | 81.3409 | 0.0000 | 10 | 241 |
| Panel unit root test: Summary | ||||
| Series: DEXRTO$ | ||||
| Date: 07/18/19 Time: 18:38 | ||||
| Sample: 1990 2017 | ||||
| Exogenous variables: Individual effects | ||||
| User-specified lags: 1 | ||||
| Newey-West automatic bandwidth selection and Bartlett kernel | ||||
| Balanced observations for each test | ||||
| Method | Statistic | Prob. ** | Cross-sections | Obs |
| Null: Unit root (assumes common unit root process) | ||||
| Levin, Lin & Chu t * | −7.41623 | 0.0000 | 10 | 250 |
| Null: Unit root (assumes individual unit root process) | ||||
| Im, Pesaran and Shin W-stat | −7.30036 | 0.0000 | 10 | 250 |
| ADF—Fisher Chi-square | 89.7924 | 0.0000 | 10 | 250 |
| PP—Fisher Chi-square | 129.506 | 0.0000 | 10 | 260 |
| Panel unit root test: Summary | ||||
| Series: D(LRGNIPC) | ||||
| Date: 07/18/19 Time: 18:43 | ||||
| Sample: 1990 2017 | ||||
| Exogenous variables: Individual effects | ||||
| User-specified lags: 1 | ||||
| Newey-West automatic bandwidth selection and Bartlett kernel | ||||
| Balanced observations for each test | ||||
| Method | Statistic | Prob. ** | Cross-sections | Obs |
| Null: Unit root (assumes common unit root process) | ||||
| Levin, Lin & Chu t * | −0.75172 | 0.2261 | 10 | 250 |
| Null: Unit root (assumes individual unit root process) | ||||
| Im, Pesaran and Shin W-stat | −5.20462 | 0.0000 | 10 | 250 |
| ADF—Fisher Chi-square | 65.3261 | 0.0000 | 10 | 250 |
| PP—Fisher Chi-square | 155.660 | 0.0000 | 10 | 260 |
| Panel unit root test: Summary | ||||
| Series: OPEN | ||||
| Date: 07/18/19 Time: 18:44 | ||||
| Sample: 1990 2017 | ||||
| Exogenous variables: Individual effects | ||||
| User-specified lags: 1 | ||||
| Newey-West automatic bandwidth selection and Bartlett kernel | ||||
| Method | Statistic | Prob.** | Cross-sections | Obs |
| Null: Unit root (assumes common unit root process) | ||||
| Levin, Lin & Chu t * | −1.57993 | 0.0571 | 10 | 250 |
| Null: Unit root (assumes individual unit root process) | ||||
| Im, Pesaran and Shin W-stat | −1.87251 | 0.0306 | 10 | 250 |
| ADF—Fisher Chi-square | 28.1400 | 0.1061 | 10 | 250 |
| PP—Fisher Chi-square | 32.1728 | 0.0415 | 10 | 260 |
| Panel unit root test: Summary | ||||
| Series: D(LRGDP) | ||||
| Date: 07/18/19 Time: 18:45 | ||||
| Sample: 1990 2017 | ||||
| Exogenous variables: Individual effects | ||||
| User-specified lags: 1 | ||||
| Newey-West automatic bandwidth selection and Bartlett kernel | ||||
| Method | Statistic | Prob. ** | Cross-sections | Obs |
| Null: Unit root (assumes common unit root process) | ||||
| Levin, Lin & Chu t * | −2.93043 | 0.0017 | 10 | 240 |
| Null: Unit root (assumes individual unit root process) | ||||
| Im, Pesaran and Shin W-stat | −4.29968 | 0.0000 | 10 | 240 |
| ADF—Fisher Chi-square | 54.9026 | 0.0000 | 10 | 240 |
| PP—Fisher Chi-square | 108.688 | 0.0000 | 10 | 250 |
Appendix C. Panel Cointegration test. Source: Authors’ Work
| Pedroni Residual Cointegration Test | |||||
| Series: FDIGDP LRGNIPC DEXRTO$ LRGDP OPEN INF | |||||
| Date: 07/18/19 Time: 18:55 | |||||
| Sample: 1990 2017 | |||||
| Included observations: 280 | |||||
| Cross-sections included: 10 | |||||
| Null Hypothesis: No cointegration | |||||
| Trend assumption: No deterministic trend | |||||
| User-specified lag length: 1 | |||||
| Newey-West automatic bandwidth selection and Bartlett kernel | |||||
| Alternative hypothesis: common AR coefs. (within-dimension) | |||||
| Weighted | |||||
| Statistic | Prob. | Statistic | Prob. | ||
| Panel v-Statistic | −3.753281 | 0.9999 | −2.670643 | 0.9962 | |
| Panel rho-Statistic | −1.135354 | 0.1281 | −0.682782 | 0.2474 | |
| Panel PP-Statistic | −9.456912 | 0.0000 | −7.232559 | 0.0000 | |
| Panel ADF-Statistic | −5.213268 | 0.0000 | −3.517866 | 0.0002 | |
| Alternative hypothesis: individual AR coefs. (between-dimension) | |||||
| Statistic | Prob. | ||||
| Group rho-Statistic | 0.933257 | 0.8247 | |||
| Group PP-Statistic | −7.870691 | 0.0000 | |||
| Group ADF-Statistic | −3.103453 | 0.0010 | |||
| Cross section specific results | |||||
| Phillips-Peron results (non-parametric) | |||||
| Cross ID | AR(1) | Variance | HAC | Bandwidth | Obs |
| Liberia | 0.097 | 0.004881 | 0.004881 | 0.00 | 15 |
| Sierra Leone | −0.406 | 0.002000 | 0.000504 | 9.00 | 10 |
| Ivory Coast | −0.175 | 4.50 × 10−5 | 2.49 × 10−5 | 6.00 | 26 |
| Mali | 0.280 | 0.000208 | 0.000235 | 1.00 | 26 |
| Nigeria | −0.100 | 8.52 × 10−5 | 5.31 × 10−5 | 7.00 | 26 |
| Mauritania | 0.254 | 0.003032 | 0.003095 | 3.00 | 26 |
| Niger | 0.037 | 0.000179 | 0.000167 | 1.00 | 26 |
| Ghana | 0.378 | 0.000206 | 0.000206 | 0.00 | 26 |
| Cameroon | −0.051 | 0.333228 | 0.200485 | 6.00 | 26 |
| Senegal | −0.362 | 0.058741 | 0.054414 | 2.00 | 26 |
| Augmented Dickey-Fuller results (parametric) | |||||
| Cross ID | AR(1) | Variance | Lag | Max lag | Obs |
| Liberia | 0.061 | 0.005131 | 1 | -- | 14 |
| Sierra Leone | −1.171 | 0.001676 | 1 | -- | 9 |
| Ivory Coast | −0.587 | 3.99 × 10−5 | 1 | -- | 25 |
| Mali | 0.198 | 0.000197 | 1 | -- | 25 |
| Nigeria | −0.540 | 7.00 × 10−5 | 1 | -- | 25 |
| Mauritania | 0.166 | 0.003013 | 1 | -- | 25 |
| Niger | 0.106 | 0.000156 | 1 | -- | 25 |
| Ghana | 0.272 | 0.000206 | 1 | -- | 25 |
| Cameroon | −0.327 | 0.321532 | 1 | -- | 25 |
| Senegal | −0.572 | 0.054403 | 1 | -- | 25 |
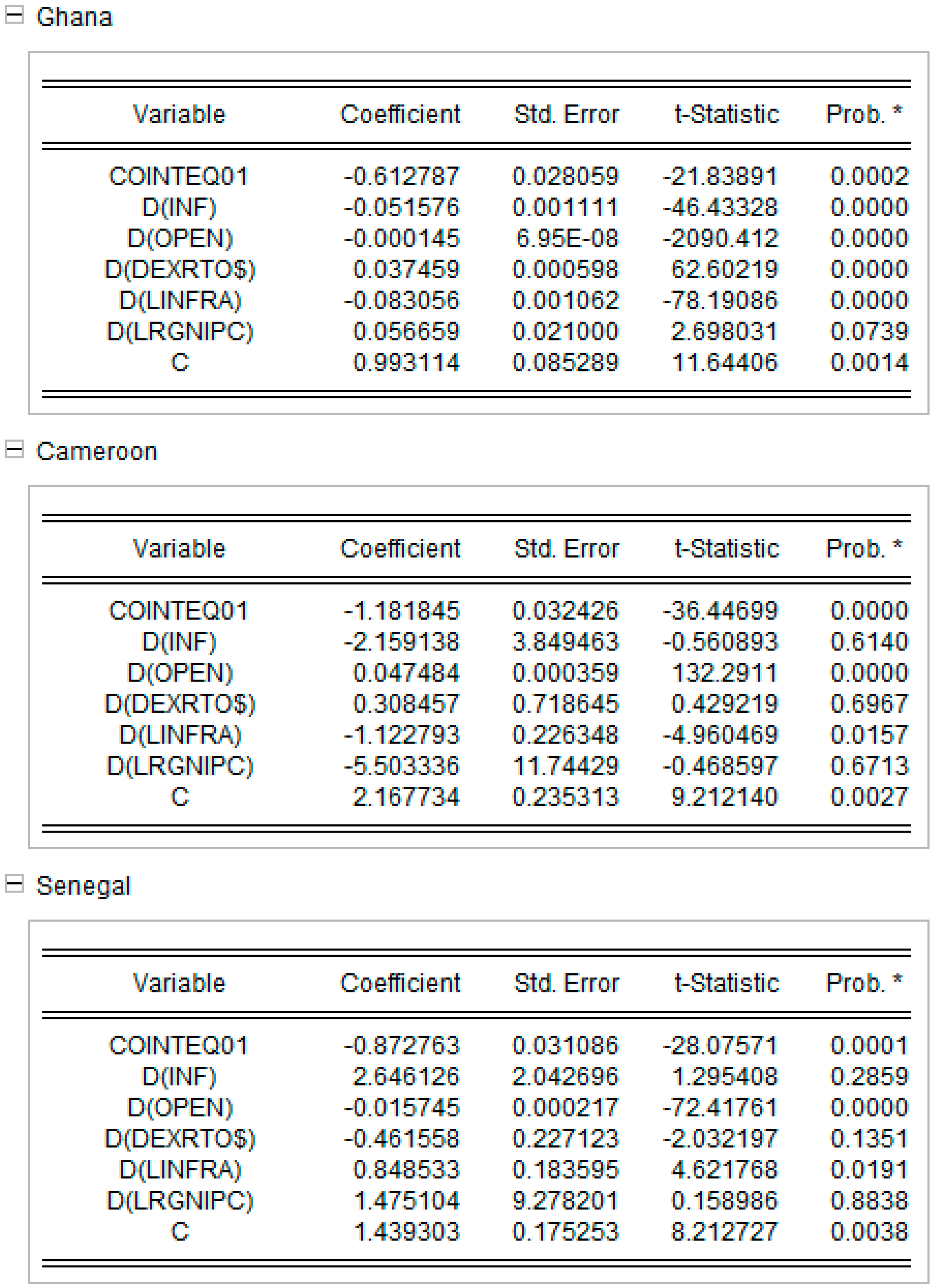
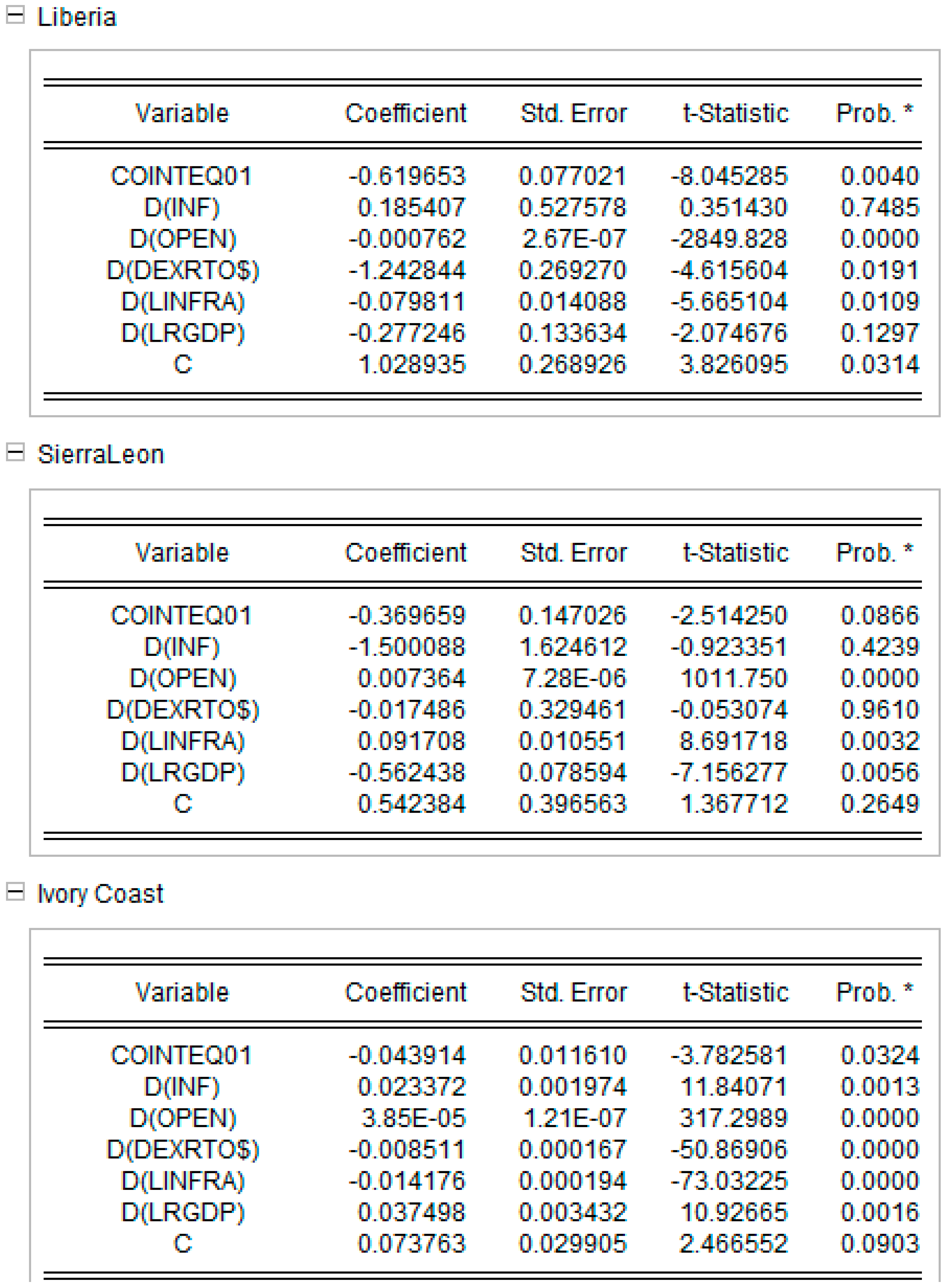
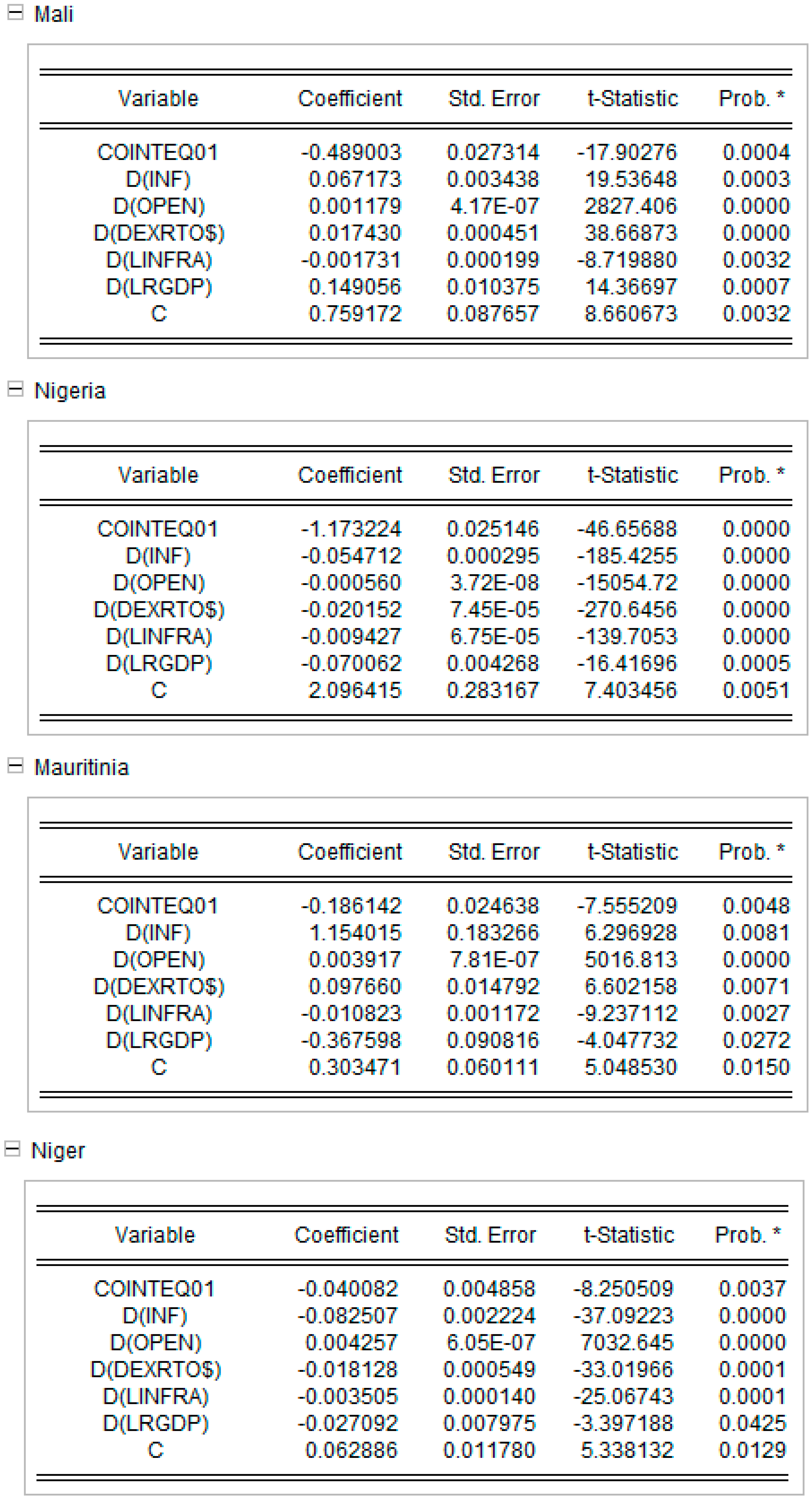
Appendix D. Short-Run Equations for Models 1 and 2. Source: Authors’ Work
Appendix D.1. Short Run equations for Model 1 Model 1
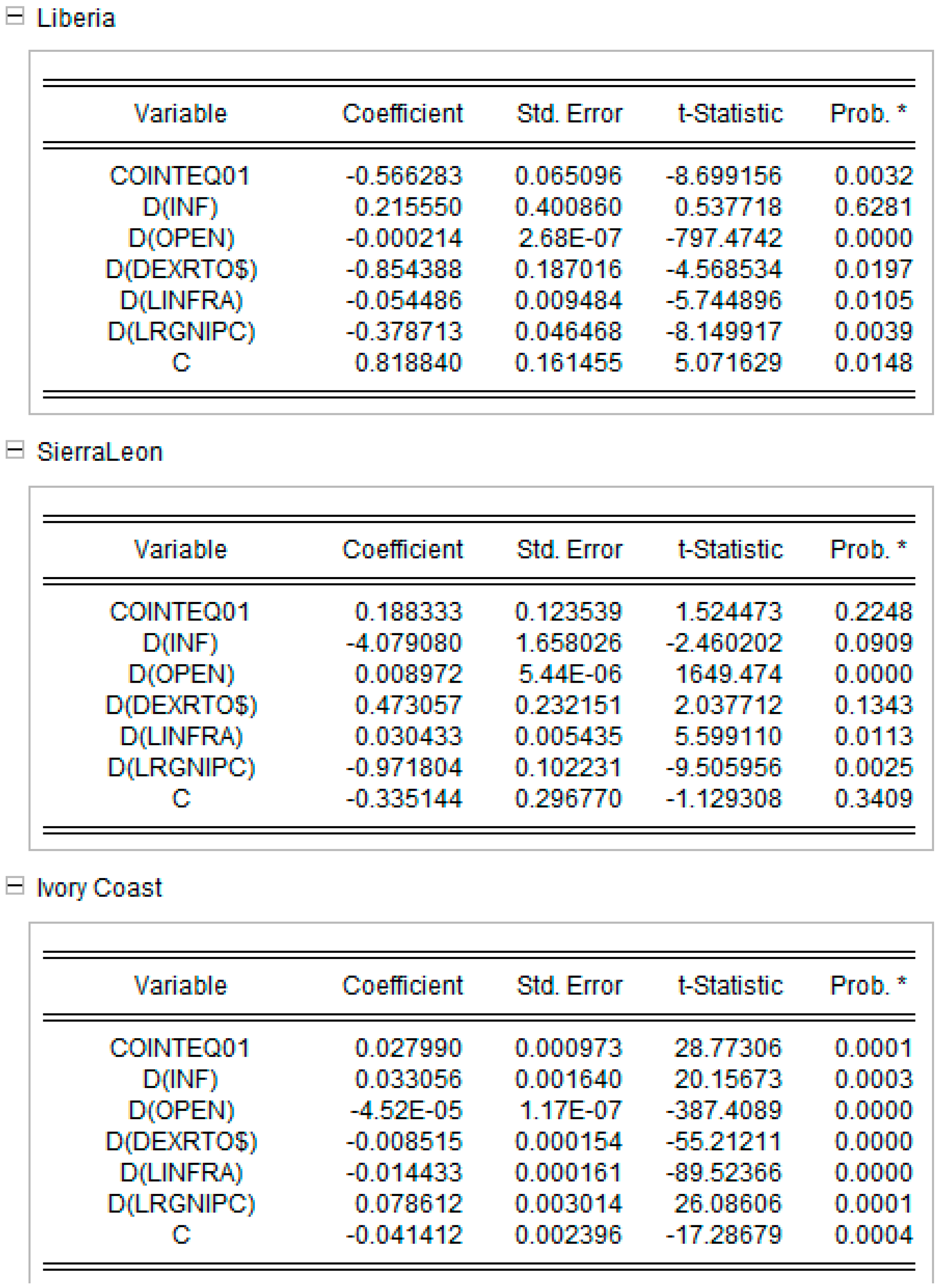
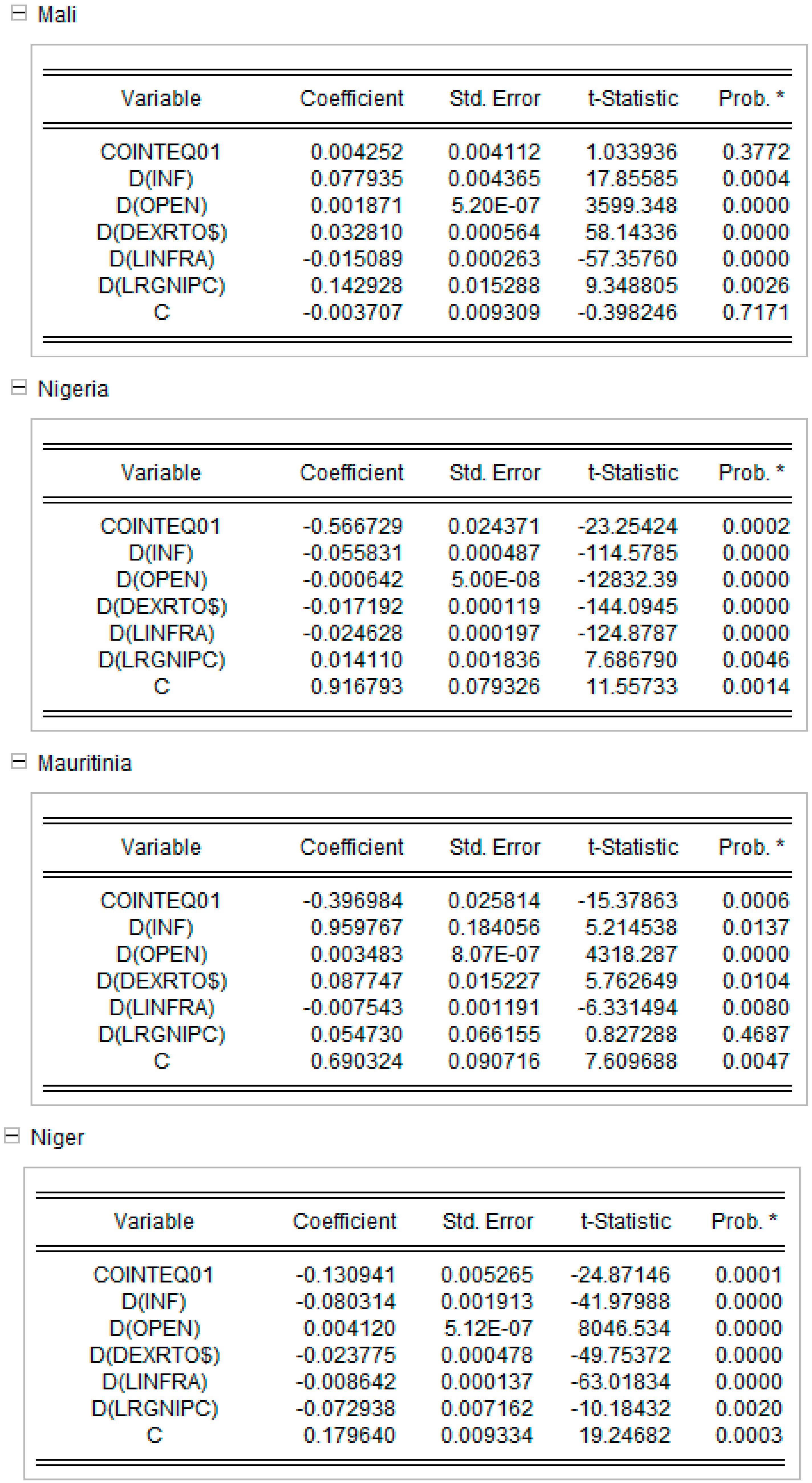
Appendix D.2. Short Run equations for Model 2 Model 2

References
- Abbott, Andrew, David Cushman, and Glauco De Vita. 2012. Exchange rate regimes and foreign direct investment flows to developing countries. Review of International Economics 20: 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, James B. 2008. Determinants of foreign direct investment in Malaysia. Journal of Policy Modeling 30: 185–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyadike, N. O. 2012. Poor Infrastructure: The Hindrance to Foreign Investment and Economic Development in Nigeria. Interdisciplinary Journal of Contemporary Research in Business 4. [Google Scholar]
- Anyanwu, John. 2006. Promoting of investment in Africa. African Development Review 18: 42–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyanwu, John. 2011. Determinants of Foreign Direct Investment Inflows to Africa, 1980–2007. African Development Bank Group Working Paper. September, pp. 1–31. Available online: http://jds.sagepub.com/content/20/1-2/89.short%5Cnhttp://www.afdb.org/fileadmin/uploads/afdb/Documents/Publications/WORKING 136 Determinants of Foreign Direct Investment Inflows To Africa 1980-2007 AS.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2019).
- Asiedu, Elizabeth. 2002. On the Determinants of Foreign Direct Investment to Developing Countries: Is Africa Different? World Development 30: 107–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, Muhammad, and Ling Lukman. 2010. Determinants of Foreign Direct Investment in India, Indonesia and Pakistan: A Quantitative Approach. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273757902_ (accessed on 23 May 2019).
- Aydin, A. 2010. On the interaction between foreign direct investment inflows and international trade: Complementary or substitution? a case study of turkey. International Research Journal of Finance and Economics 48: 130–43. [Google Scholar]
- Babatunde, Abimbola. 2011. Trade Openness, Infrastructure, FDI and Growth in Sub-Saharan African Countries. Journal of Management Policy and Practice 12: 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Bakar, Norazamin, Siti Hadijah Che Mat, and Mukaramah Harun. 2012. The Impact of Infrastructure on Foreign Direct Investment: The Case of Malaysia. Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences 65: 205–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, Johannes, Clemens Fuest, and Nadine Ridel. 2012. Corporate tax effects on the quality and quantity of FDI. European Economic Review 56: 1495–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behname, Mehdi. 2012. Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Growth: Evidence from Southern. Asia Atlantic Review of Economics 2. Available online: http://www.unagaliciamoderna.com/eawp/coldata/uplo... irect_Investment.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2019).
- Callen, Timothy. 2008. Back to Basics. What Is Gross Domestic Product? Finance & Development. Available online: http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fandd/2008/12/pdf/basics.pdf (accessed on 23 February 2019).
- Chakrabarti, Avik. 2001. The Determinants of Foreign Direct Investments: Sensitivity Analyses of Cross-Country Regressions. Kyklos 54: 89–114. Available online: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1111/1467-6435.00142 (accessed on 20 January 2019). [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, Rajesh, Krishnamurthy Subramanian, Sesha Meka, and Kuntluru Sudershan. 2012. Infrastructure and FDI: Evidence from District-Level Data in India. Available online: https://www.isb.edu/faculty/KrishnamurthySubramanian/Images/FDI_infra_20Mar2012_ReStud.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2019).
- Chong, Lee-Lee, and BH Tan. 2008. Exchange rate risk and macroeconomic fundamentals: Evidence from four neighbouring southeast Asian economies. International Research Journal of Finance and Economics 16: 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Culem, Claudy G. 1988. The locational determinants of direct investments among industrialized countries. European Economic Review 32: 885–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, David O. 1985. Real Exchange Rate Risk, Expectations, and the Level of Direct Investment. The Review of Economics and Statistics 67: 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, John H. 1977. Trade, Location of Economic Activity and the MNE: A Search for an Eclectic Approach. In The International Allocation of Economic Activity. London: Palgrave Macmillan. [Google Scholar]
- Dunning, John H. 1980. Towards an Eclectic Paradigm of International Production. Journal of International Business Studies 11: 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, John H. 1993. Multinational Enterprises and the Global Economy. Harlow: Addison Wesley Publishing Co. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, Sebastian. 1990. Capital Flows, Foreign Direct Investment, and Debt-Equity Swaps in Developing Countries. NBER Working Paper No. 3497. Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA: National Bureau of Economic Research. [Google Scholar]
- Essia, Uwem, and Joseph Onyema. 2012. Determinants of Foreign Direct Investment in Nigeria. Journal of Money, Investment and Banking. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/15419113/DETERMINANTS_OF_FOREIGN_DIRECT_INVESTMENT_IN_NIGERIA1 (accessed on 20 February 2019).
- Faroh, Alie, and Hongliang Shen. 2015. Impact of Interest Rates on Foreign Direct Investment: Case Study Sierra Leone Economy. International Journal of Business Management and Economic Research 6: 124–32. [Google Scholar]
- Fedderke, Johannes Wolfgang, and A. T. Romm. 2006. Growth impact and determinants of foreign direct investment into South Africa, 1956–2003. Economic Modelling 23: 738–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldstein, Martin. 2000. Aspects of Global Economic International Integration, Outlook for the Future. NBER Working Paper No. 7899. Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA: National Bureau of Economic Research. [Google Scholar]
- Foellmi, Reto, Sandra Hanslin Grossmann, and Andreas Kohler. 2018. A dynamic North-South model of demand-induced product cycles. Journal of International Economics 110: 63–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, K. C., Alicia Garcia-Herrero, Hitomi Izaka, and Alan Siu. 2005. Hard or Soft? Institutional Reforms and Infrastructure spending as Determinants of foreign direct investment in China. The Japanese Economic Review 56: 408–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakro, Nawaz A., and Abdallah Omezzine. 2011. FDI Flows and Governance in MENA. Countires. Middle Eastern Finance and Economics 12: 143–56. [Google Scholar]
- Hymer, S. 1972. Internationlization of Capital. Journal of Economic Issues 6: 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hymer, Stephen H. 1976. The International Operations of National Firms: A Study of Direct Foreign Investment. Cambridge: MIT Press. [Google Scholar]
- IMF. 1993. Foreign Direct Investment Trends and Statistics: A Summary—IMF. Some Key Concepts and Definitions for the Recording of FDI. Available online: https://www.imf.org/External/np/sta/fdi/eng/2003/102803s1.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2019).
- IMF. n.d. IMF’s International Financial Statistics Base. Available online: http://data.imf.org/?sk=4C514D48-B6BA-49ED-8AB9-52B0C1A0179B (accessed on 15 January 2019).
- Jaspersen, Frederick. Z., Anthony. H. Aylward, and A. David Knox. 2000. Risk and Private Investment: Africa Compared with Other Developing Areas. In Investment and Risk in Africa. Studies on the African Economies. Edited by P. Collier and C. Pattillo. London: Palgrave Macmillan. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, Chris, and Yama Temouri. 2016. The determinants of tax haven FDI. Journal of World Business 51: 237–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordaan, Johannes Cornelius. 2004. Foreign Direct Investment and Neighbouring Influences. Unpublished Doctoral’s thesis, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa. Available online: https://repository.up.ac.za/bitstream/handle/2263/24008/Complete.pdf?sequence=4 (accessed on 20 March 2019).
- Kamath, G. B. 2008. Impact of foreign direct investment in India. The ICFAI University Journal of International Business 3: 16–38. [Google Scholar]
- Karkinsky, Tom, and Nadine Riedel. 2012. Corporate taxation and the choice of patent location within multinational firms. Journal of International Economics 88: 176–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosekahyaoglu, Levent. 2006. A comparative analysis of FDI in Turkey and the CEECS: Is there any link between Fdi and Trade? Journal of Business Economics and Management 7: 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravis, Irving B., and Robert Lipsey. 1982. The location of overseas production and production for export by U.S. multinational firms. Journal of International Economics 12: 201–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurecic, Petar, Goran Luburic, and Goran Kozina. 2015. The influence of the size of the economy and European integration on foreign direct investments in the Central, Southeastern and Eastern European states 1994–2013. Paper presented at 10th International Scientific Conference on Economic and Social Development, Miami, FL, USA, September 25. [Google Scholar]
- Lily, Jaratin, Kogid Mori, Mulok Dullah, Sang Liem Thien, and Rozilee Asid. 2014. Exchange Rate Movement and Foreign Direct Investment in Asean. Economies Economics Research International 2014: 320949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loungani, Prakash, and Assaf Razin. 2001. How beneficial is foreign direct investment for developing countries? Finance and Development 38: 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Obiamaka, Egbo P., Josephat Onwumere, and Chigozie Okpara. 2011. Foreign direct investment and economic growth in Nigeria: A granger causality analysis. International Journal of Current Research 3: 225–32. [Google Scholar]
- Overseas Development Institute, London (UK). 1997. Foreign Direct Investment flows to low-income countries: A review of the evidence. Available online: https://www.odi.org/sites/odi.org.uk/files/odi-assets/publications-opinion-files/2626.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2019).
- OECD. 1990. OECD Benchmark Definition of Foreign Direct Investment. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/daf/inv/investment-policy/2090148.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2019).
- OECD. 2017. Local Content Policies in Minerals-Exporting Countries: The Case of Australia. Trade Policy Note (December). Available online: www.oecd.org/trade (accessed on 10 February 2019).
- Omankhanlen, Alex Ehimare. 2011. The Effect of Exchange Rate and Inflation on Foreign Direct Investment and its relationship with Economic Growth in Nigeria. Economics and Applied Information 1: 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Pärletun, Jana. 2008. The Determinants of Foreign Direct Investment: A Regional Analysis with Focus on Belarus. Lund: Lund University, pp. 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, Abdul, Muhammad Ilyas, Hassan Mobeen Alam, and Muhammad Akram. 2011. The Impact of Infrastructure on Foreign Direct Investment: The Case of Pakistan. International Journal of Business and Management 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, Andrew, and Jurg Bieri. 1972. EEC tariffs and U.S. direct investment. European Economic Review 3: 259–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, Friedrich, and Bruno Frey. 1985. Economic and political determinants of foreign direct investment. World Development 13: 161–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetanah, Boopen. 2009. A Sector-Wise Panel Data Study on the Link between Transport Infrastructure and FDI in Mauritius. Paper presented at 9th Global Conference on Business & Economics, Cambridge, UK, October 17; ISBN 978-0-9742114-2-7. [Google Scholar]
- Sekkat, Khalid, and Marie-Ange Veganzones-Varoudakis. 2007. Openness, investment climate, and FDI in developing countries. Review of Development Economics 11: 607–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, Hira Aijaz Ahmed, and Visarach Aumeboonsuke. 2014. Role of Interest Rate in Attracting the Fdi: Study on Asean 5 Economy. International Journal of Technical Research and Applications 2: 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, P. L. 1994. Determinants of Foreign Direct Investment and Its Impact on Economic Growth. Journal of Economic Development 19: 137–63. [Google Scholar]
- UNCTAD. 2018. World investment Report 2018. Available online: https://unctad.org/en/PublicationsLibrary/wir2018_en.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2019).
- Vernon, Raymond. 1966. International Investment and International Trade in the Product Cycle. The Quarterly Journal of Economics 80: 190. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/qje/article-lookup/doi/10.2307/1880689 (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- Wafure, Obida G., and Abu Nurudeen. 2010. Determinants of Foreign Direct Investment in Nigeria: An Empirical Analysis. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265627570_ (accessed on 20 January 2019).
- Walsh, James P., and Jiangyan Yu. 2010. Determinants of Foreign Direct Investment: A Sectoral and Institutional Approach (July 2010). IMF Working Papers. pp. 1–27. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=1662260 (accessed on 16 January 2019).
- Wheeler, David, and Ashoka Mody. 1992. International investment location decisions: The case of U.S. firms. Journal of International Economics 33: 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. n.d. World Bank’s World Leading Indicators base. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator (accessed on 15 January 2019).
- World Investment Report. 2007. Available online: https://unctad.org/en/Docs/wir2007_en.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2019).
- Xaypanya, Phonesavanh, Poomthan Rangkakulnuwat, and Sasaiwimon Warumsiri Paweenawat. 2015. The determinants of foreign direct investment in ASEAN: The first differencing panel data analysis. International Journal of Social Economics 42: 239–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Yuqing, and Guanghua Wan. 2006. Exchange Rates and Competition for FDI in Asia. The World Economy 29: 419–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Meaning | Data Source |
|---|---|---|
| FDI/GDP | Net Foreign Direct Investment/Gross Domestic Product | World Bank’s World Leading Indicators base |
| RGDP | Real Gross Domestic Product (2010 base) | World Bank’s World Leading Indicators base |
| RGNIPC | Gross National Income per capita (2011 base) | World Bank’s World Leading Indicators base |
| INFRA | Fixed Line and Mobile subscriptions per 100 people | World Bank’s World Leading Indicators base |
| EXRTO$ | Official Exchange Rate: local currency units per US$ | IMF’s International Financial Statistics base |
| INF | Inflation Rate based on Consumer Price Index | World Bank’s World Leading Indicators base |
| OPEN | (Export+Import)/Gross Development Product | World Bank’s World Leading Indicators base |
| Country | FDI/GDP | INF | OPEN | DEXRTO$ | RGDP | RGNIPC | INFRA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liberia | 9 | 8 | 6 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Sierra Leone | 7 | 7 | 9 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| Ivory Coast | 2 | 5 | 1 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 9 |
| Mali | 4 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 |
| Nigeria | 3 | 9 | 8 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 5 |
| Mauritania | 8 | 6 | 7 | 9 | 3 | 9 | 8 |
| Niger | 6 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| Ghana | 5 | 10 | 10 | 7 | 9 | 6 | 7 |
| Cameroon | 1 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 7 | 6 |
| Senegal | 10 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 10 |
| Statistic | LRGNIPC | LINFRA | LRGDP | OPEN% | INF | DEXRTO$ | FDIGD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 7.5878 | 13.8020 | 23.2987 | 68.8472 | 0.0697 | 0.0503 | 0.0797 |
| Median | 7.7579 | 14.0544 | 23.3109 | 60.4673 | 0.0456 | 0.0282 | 0.0277 |
| Maximum | 8.6174 | 18.8557 | 26.8638 | 311.3541 | 0.5472 | 0.7630 | 1.9144 |
| Minimum | 5.8051 | 8.7612 | 20.9898 | 20.7225 | −0.0812 | −0.1992 | −1.2801 |
| Std. Dev. | 0.5646 | 2.5796 | 1.3695 | 37.5945 | 0.0889 | 0.1276 | 0.2596 |
| Observations | 240 | 240 | 240 | 240 | 240 | 240 | 240 |
| Variable | LRGNIPC | LINFRA | LRGDP | OPEN | INF | DEXRTO$ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LRGNIPC | 1 | 0.406312 | 0.679295 | −0.26551 | 0.11505 | 0.073887 |
| LINFRA | 0.406312 | 1 | 0.537931 | 0.011979 | −0.07277 | −0.13281 |
| LRGDP | 0.679295 | 0.537931 | 1 | −0.41589 | 0.277142 | 0.101042 |
| OPEN | −0.26551 | 0.011979 | −0.41589 | 1 | 0.021052 | −0.04142 |
| INF | 0.11505 | −0.07277 | 0.277142 | 0.021052 | 1 | 0.472181 |
| DEXRTO$ | 0.073887 | −0.13281 | 0.101042 | −0.04142 | 0.472181 | 1 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable: D(FDIGDP) | ||||
| Method: ARDL | ||||
| Sample: 2003 2017 | ||||
| Included observations: 230 | ||||
| Dependent lags: 1 (Fixed) | ||||
| Dynamic regressors (1 lag, fixed) | ||||
| Fixed regressors: C | ||||
| Variable | Coefficient | Prob *. | Coefficient | Prob *. |
| Long Run Equation | Long Run Equation | |||
| INF | 0.1124 | 0.0003 | 0.0629 | 0.0000 |
| OPEN | 0.0000 | 0.9206 | 0.0002 | 0.4243 |
| DEXRTO$ | 0.0480 | 0.1308 | 0.0131 | 0.3192 |
| LINFRA | 0.0321 | 0.0000 | 0.0114 | 0.0001 |
| LRGNIPC | −0.2590 | 0.0000 | ||
| LRGDP | −0.0746 | 0.0000 | ||
| Short Run Equation | Short Run Equation | |||
| COINTEQ01 | −0.4108 | 0.0032 | −0.5066 | 0.0002 |
| D(INF) | −0.2494 | 0.6592 | 0.0336 | 0.9369 |
| D(OPEN) | 0.0049 | 0.3402 | 0.0047 | 0.3641 |
| D(DEXRTO$) | −0.0426 | 0.7188 | −0.1188 | 0.4007 |
| D(LINFRA) | −0.0452 | 0.7606 | −0.0357 | 0.8071 |
| D(LRGNIPC) | −0.5105 | 0.3856 | ||
| D(LRGDP) | −0.3598 | 0.4909 | ||
| C | 0.6825 | 0.0052 | 0.8737 | 0.0007 |
| Mean dependent variable | 0.0029 | 0.0029 | ||
| S.E. of regression | 0.2316 | 0.2363 | ||
| Sum squared residuals | 8.8525 | 9.2124 | ||
| Log likelihood | 437.0997 | 437.5212 | ||
| S.D. dependent variable | 0.3269 | 0.3269 | ||
| Akaike info criterion | −3.0175 | −3.0210 | ||
| Schwarz criterion | −1.9298 | −1.9333 | ||
| Hannan−Quinn criterion | −2.5792 | −2.5827 | ||
| Long Run Causality * | Short Run Significance * | M1 | M2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | M1 ** | M2 ** | D(INF) | D(OPEN) | D(EXRTO$) | D(INFRA) | D(LRGNIPC) | D(LRGDP) | ||||
| Liberia | yes | yes | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |||
| Sierra Leone | no | yes | − | − | + | + | + | + | − | − | ||
| Ivory Coast | no | yes | + | + | − | + | − | − | − | − | + | + |
| Mali | no | yes | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | + | + |
| Nigeria | yes | yes | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| Mauritania | yes | yes | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − | |
| Niger | yes | yes | − | − | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Ghana | yes | yes | − | − | − | − | + | + | − | − | + | |
| Cameroon | yes | yes | + | + | − | − | ||||||
| Senegal | yes | yes | − | − | + | + | ||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaiblai, P.; Shenai, V. The Determinants of FDI in Sub-Saharan Economies: A Study of Data from 1990–2017. Int. J. Financial Stud. 2019, 7, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs7030043
Jaiblai P, Shenai V. The Determinants of FDI in Sub-Saharan Economies: A Study of Data from 1990–2017. International Journal of Financial Studies. 2019; 7(3):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs7030043
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaiblai, Prince, and Vijay Shenai. 2019. "The Determinants of FDI in Sub-Saharan Economies: A Study of Data from 1990–2017" International Journal of Financial Studies 7, no. 3: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs7030043
APA StyleJaiblai, P., & Shenai, V. (2019). The Determinants of FDI in Sub-Saharan Economies: A Study of Data from 1990–2017. International Journal of Financial Studies, 7(3), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs7030043




