Financial Performance and Corporate Governance on Firm Value: Evidence from Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Trade-Off Theory
2.2. Pecking Order Theory
2.3. Signaling Theory
2.4. Agency Theory
2.5. Corporate Governance in SMEs
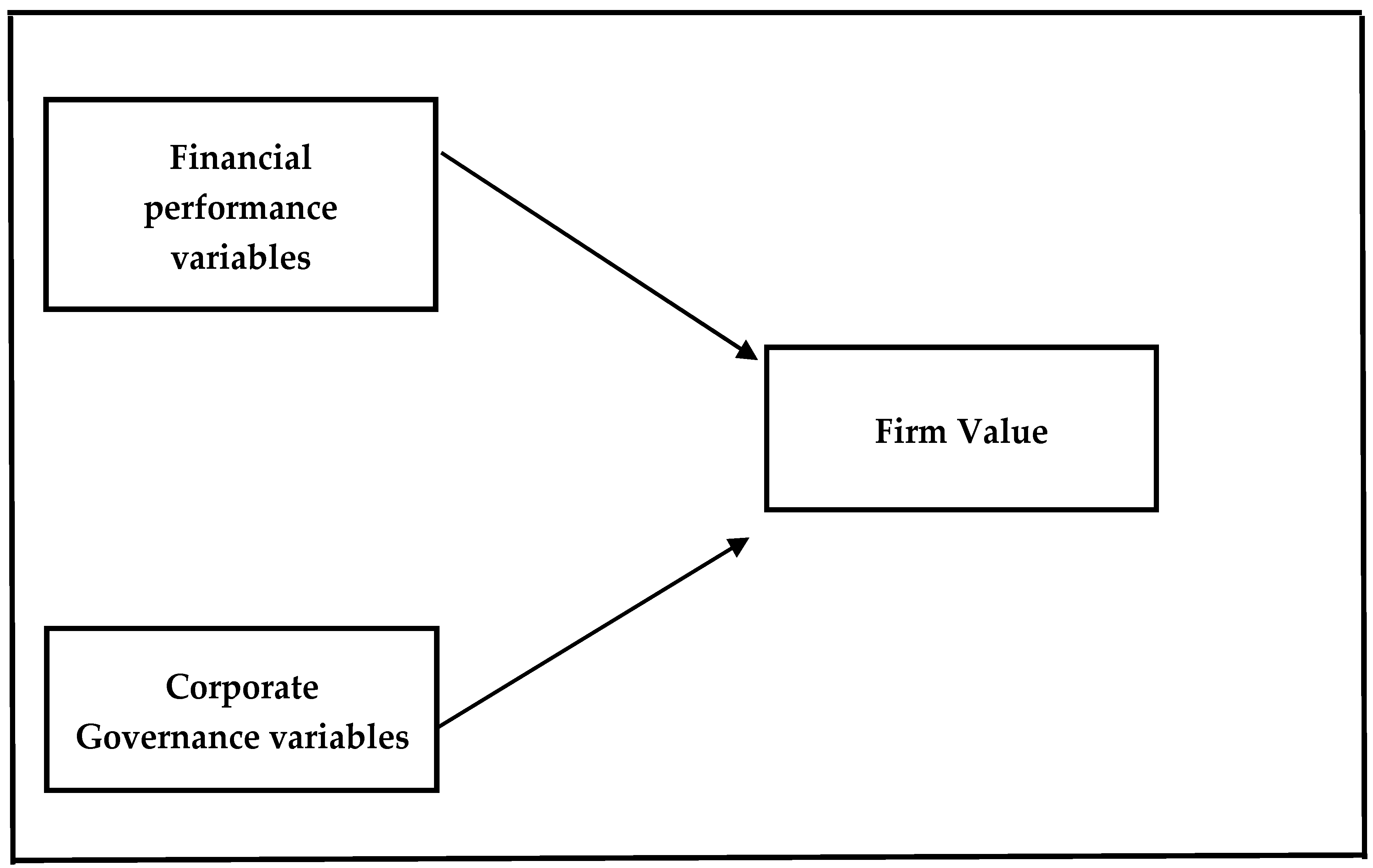
2.6. Study Framework
3. Methodology
3.1. Data
3.2. Variable Description and Measurement
3.2.1. Dependent Variable: Firm Valuation
3.2.2. Control Variables
3.2.3. Financial Performance
3.2.4. Corporate Governance Variables
3.3. Hypothesis Testing
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Descriptive Statistics and Correlations
4.2. Cross-Sectional Time Series Fixed Effects Regression Results
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | BME: Bolsas y Mercados Españoles. |
References
- Abdalmuttaleb, M. A.-S., & Sameh, R. (2018). Signaling theory and the determinants of online financial disclosure. Journal of Economic and Administrative Sciences, 34(3), 237–247. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera, R. V., & Jackson, G. (2010). Comparative and international corporate governance. The Academy of Management Annals, 4(1), 485–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyei, J., Sun, S., & Abrokwah, E. (2020). Trade-off theory versus pecking order theory: Ghanaian evidence. Sage Open, 10(3). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S., & Shrestha, K. (2013). The differential effects of classified boards on firm value. Journal of Banking and Finance, 37, 3993–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerlof, G. (1970). The market for “lemons”: Qualitative uncertainty and the market mechanism. Quarterly Journals of Economics, 84, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, S., & Oliver, B. (2009). Determinants of capital structure for Japanese multinational and domestic corporations. International Review of Finance, 9(1–2), 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R. C., & Reeb, D. M. (2004). Board composition: Balancing family influence in S&P 500 firms. Administrative Science Quarterly, 49(2), 209–237. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, J. C. (2000). Agency costs and ownership structure. The Journal of Finance, 55(1), 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifianto, M., & Chabachib, M. (2016). Analysis of factors affecting firm value (a case study of companies listed on the LQ-45 Index for the 2011–2014 period). Diponegoro Journal of Management, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.-E. L. (2004). Corporate governance and market valuation in China. Journal of Comparative Economics, 32(4), 599–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, N. P., & Rahnamaei, M. (2016). Multiple blockholders, power, and firm value. Journal of Banking & Finance, 66, 66–78. [Google Scholar]
- Black, F., & Scholes, M. (1974). From theory to a new financial product. The Journal of Finance, 29(2), 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BME Growth. (2025). Obtenido de. Available online: https://www.bmegrowth.es/ (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Bonaventura, M., Giudici, G., & Vismara, S. (2017). Valuation and performance of reallocated IPO shares. Journal of International Financial Markets, 54, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigham, E., & Houston, J. (2021). Fundamentals of financial management (16th ed.). Cengage Learning. [Google Scholar]
- Buigut, K., Soi, N., Koskei, I., & Kibet, J. (2013). The Effect of Capital Structure on Share Price on Listed Firms in Kenya. European Journal of Business and Management, 5(9), 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Cetorelli, N., & Peristiani, S. (2015). Firm value and cross listings: The impact of stock market prestige. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 8(1), 150–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charumanithi, B., & Krishnan, M. (2016). On the determinants of the firm value of Indian companies. Global Business Review, 13(2), 251–267. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L. J. (2011). The influence of profitability on firm value with capital structure as the mediator and firm size and industry as moderators. Investment Management and Financial Innovations, 8(3), 120–129. [Google Scholar]
- Churchill, G., & Iacobucci, D. (2006). Marketing research: Methodological foundations (5th ed.). The Dryden Press. [Google Scholar]
- Colli, A., García-Canal, E., & Guillén, M. F. (2013). Family character and international entrepreneurship: A historical comparison of Italian and Spanish ‘new multinationals’. Business History, 55(1), 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, B. L., Certo, S. T., Reutzel, C. R., DesJardine, M. R., & Zhou, Y. S. (2024). Signaling theory: State of the theory and its future. Journal of Management, 51(1), 24–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, D., Karoly, A., & Stulz, R. (2004). Why are foreign firms listed in the U.S. worth more? Journal of Financial Economics, 71(2), 205–238. [Google Scholar]
- Damodaran, A. (2012). Investment Valuation. John Wiley and Sons, Inc. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, H. (2015). The effect of internal factors on stock price of the company LQ 45. EMBA Journals, 3(1), 45–59. [Google Scholar]
- DeAngelo, H., & Masulis, R. (1980). Capital structure under corporate and personal taxation. Journal of Financial Economics, 8, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitiana, T. (2013). Influence of Current Ratio, Return on Equity and Total Asset Turn Over against Dividend Payout Ratio and Implication on Stock Price Company LQ 45. Journal of Business and Accounting, 15(1), 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Dewi, P. A., & Suaryana, I. (2013). Effect of EPS, DER, and PBV on Share Price. Journal of Accounting Udayana University, 7(2), 100–110. [Google Scholar]
- Dewi, S., & Hidayat, R. (2014). Effect of net profit margin and return on assets on stock prices on automotive companies listed in indonesia stock exchange. ILMAN, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dinh, H., & Pham, C. (2010). The effect of capital structure on the financial performance of Vietnamese listing pharmaceutical enterprises. Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 7(9), 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, G. (1961). Corporate debt capacity: A study of corporate debt policy and the determination of corporate debt capacity. Division of Research, Graduate School of Business Administration, 113, 387–432. [Google Scholar]
- Edmans, A. (2014). Blockholders and corporate governance. Annual Review of Finance and Economics, 6(1), 23–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmans, A., Fang, V., & Zur, E. (2013). The effect of liquidity on governance. Review of Financial Studies, 26(6), 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmans, A., & Manso, G. (2011). Governance through trading and intervention: A theory of multiple blockholders. Review of Financial Studies, 24(7), 2395–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt, M., & Brigham, E. (2011). Financial management: Theory and practice. Cengage Learning. [Google Scholar]
- Fama, E. (1980). Agency problems and the theory of the firm. Journal of Politics Economics, 88, 288–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fama, E., & Jensen, M. (1983). Separation of ownership and control. The Journal of Law & Economics, 26(2), 301–325. [Google Scholar]
- Farag, H., & Mallin, C. (2019). Monitoring corporate boards: Evidence from China. European Journal of Finance, 25, 524–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florackis, C., Kostakis, A., & Ozkan, A. (2009). Managerial ownership and performance. Journal of Business Research, 62(12), 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosu, S., Danso, A., Ahmad, W., & Coffie, W. (2016). Information asymmetry, leverage and firm value: Do crisis and growth matter? International Review of Financial Analysis, 46, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friend, I., & Lang, L. (1988). An empirical test of the impact of managerial self-interest on corporate capital structure. Journal of Finance, 43(2), 271–281. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, S. (2013). Venture boards: Distinctive monitoring and implications for firm performance. Academy of Management Review, 38(1), 90–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gompers, P., Ishii, J., & Metrick, A. (2003). Corporate governance and equity prices. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 118(1), 107–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujarati, D., & Porter, D. (2010). Econometría (5th ed.). McGraw Hill. [Google Scholar]
- Gujarati, D. N. (2004). Applied econometrics. McGraw-Hill. [Google Scholar]
- Hamidah, G., & Umdiana, N. (2017). The effect of profitability and investment opportunity set (IOS) on firm value with stock price as an intervening variable. Accounting Journal, 2, 90–106. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, M., & Raviv, A. (1991). The theory of capital structure. The Journal of Finance, 46(1), 297–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, D. C., Montalvo, C. M., & Valencia, L. R. (2017). Prueba de la teoría del intercambio y la teoría del orden jerárquico de la estructura de capital, evidencia ecuatoriana. Revista Ciencias Pedagógicas e Innovación, 5(3), 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Hirdinis, M. (2019). Capital structure and firm size on firm value moderated by profibility. International Journal of Economics and Business Administration, 7(1), 174–191. [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman, A. (1982). Rival interpretation of market society: Covilizing, destructure, or feeble? Journal of Economics Literature, 20(1), 1463–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, S., & Wong, K. (2001). A study of the relationship between corporate governance structures and the extent of voluntary disclosure. Journal of International Accounting, Auditing & Taxation, 10(2), 139–157. [Google Scholar]
- Idawati, W., & Wahyudi, A. (2015). Effect of earning per shares (EPS) and return on assets (ROA) against share price on coal mining company listed in indonesia stock exchange. Journal of Resources Development and Management, 7, 79–91. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, M. (1994). Self-interest, altruism, incentives, and agency theory. Journal of Applied Corporate Finance, 7(2), 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M., & Meckling, W. (1976). Theory of the firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs and ownership structure. Journal of Financial Economics, 3(4), 305–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeroh, E. (2020). Corporate financial tarributes and the value of listed financial services firms: The Nigerian evidence. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 24(2), 45–60. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R., Dharwadkar, R., & Brandes, P. (2005). Institutional ownership and CEO compensation: A longitudinal examination. Journal of Business Research, 58(8), 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E. (1978). A Mean-variance theory of capital structure and corporate debt capacity. The Journal of Finance, 33, 45–63. [Google Scholar]
- Klapper, L. F., & Love, I. (2004). Corporate governance, investor protection, and performance in emerging markets. Journal of Corporate Finance, 10(3), 703–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A. (2022). Shareholder withdrawal in close corporations: An Anglo-German comparative analysis. Journal of Corporate Law Studies, 22(1), 97–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohansal, M., Dadrasmoghaddam, A., Karmozdi, K., & Mohseni, A. (2013). Relationship between financial ratios and stock prices for the food industry firms in stock exchange of Iran. World Applied Programming, 10, 512–521. [Google Scholar]
- Kraus, A., & Litzenberger, R. (1973). A state-preference model of financial leverage. The Journal of Finance, 28, 911–922. [Google Scholar]
- Kurnia, P., Darlis, E., & Putra, A. (2020). Carbon emission disclosure, good corporate governance, financial performance, and firm value. Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 7(12), 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laim, W., Nangoy, S., & Murni, S. (2015). Analysis of factors that influencing dividend payout ratio on companies that listed in LQ-45 index stock exchange Indonesia. Jurnal EMBA, 3(1), 1129–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, L., & Stulz, R. (1994). Tobin’s q, corporate diversification, and firm performance. Journal of Political Economy, 102(6), 1248–1280. [Google Scholar]
- La Porta, R., Lopez-de-Silanes, F., Shleifer, A., & Vishny, R. (2000). Investor protection and corporate governance. Journal of Financial Economics, 58(1–2), 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, E. (2023). Debt to equity ratio (DER) and firm size toward firm value: The mediating role of return on asset. Return: Study of Management, Economic and Bussines, 2(11), 1095–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H., Terjesen, S., & Uman, T. (2020). Corporate governance in entrepreneurial firms: A systematic review and research agenda. Small Busess Economics, 54, 43–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W., Lu, C., & Wang, H. (2014). Venture capital, corporate governance, and financial stability of IPO firms. Emerging Markets Review, 18, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindayani, N. W., & Dewi, S. K. S. (2016). Dampak struktur modal dan inflasiterhadap profitabilitas dan return saham perusahaan keuangan sektor perbankan. E-Jurnal Manajemen Uuud, 5(8), 123–135. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, Y. T., & Kusnadi, Y. (2005). Size really matters: Further evidence on the negative relationship between board size and firm value. Pacific-Basin Finance Journal, 13(3), 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoppo, H., & Arie, F. (2016). The influence of capital structure, company size and profitability towards automotive company value of IDX Period 2011–2014. Journal EMBA, 4(2), 485–497. [Google Scholar]
- Mateev, M., Poutziourisb, P., & Ivanovc, K. (2013). On the determinants of SME capital structure in Central and Eastern Europe: A dynamic panel analysis. Research in International Business and Finance, 27, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maury, B., & Pajuste, A. (2005). Multiple large shareholders and firm value. Journal of Banking & Finance, 29(7), 1813–1834. [Google Scholar]
- Merton, R. C. (1974). On the pricing of corporate debt: The risk structure of interest rates. The Journal of Finance, 29(2), 449–470. [Google Scholar]
- Meythi, E., & Rusli, L. (2011). The influence of liquidity and profitability on stock price of manufacturing companies listed on Indonesia stock exchange. Journal of Business Management and Economics, 10(2), 2671–2684. [Google Scholar]
- Modigliani, F., & Miller, M. (1963). Corporate income taxes and the cost of capital: A correction. The American Economic Review, 53(3), 433–443. [Google Scholar]
- Modigliani, F., & Miller, M. H. (1958). The cost of capital, corporation finance and the theory of investment. The American Economic Review, 261–296. [Google Scholar]
- Mortazian, M., Tabaghdehi, S., & Mase, B. (2019). Large shareholding and firm value in the Alternative Investment Market (AIM). Asia-Pacific Financial Markets, 26(2), 229–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P. (2022). Revisitng the Indian Financial Sector. In Recent issues ans perspectives. Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, S., & Majluf, N. (1984). Corporate financing and investment decisions when firm s have information that investors do not have. Journal of Financial Economics, 13(2), 187–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, S. C. (1977). Determinants of corporate borrowing. Journal of Financial Economics, 5, 147–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A., Gunessee, S., & Hilton, B. (2012). The applicability of financial theories of capital structure to the Chinese cultural context: A study of privately-owned SMEs. International Small Business Journal, 30, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P., Rahman, N., Tong, A., & Yusof, M. (2016). Board size and firm value: Evidence from Australia. Journal of Management & Governance, 20(4), 851–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandansari, F. (2012). Analysis of fundamental factors against stock price. Accounting Analysis Journal, 1(2), 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Perfect, S., & Wiles, K. (1994). Alternative constructions of Tobin’s Q: An empirical comparison. Journal of Empirical Finance, 1, 313–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permana, D. (2017). Toward the best model of strategy implementation in Indonesian islamic banking from the lens of strategic clarity. European Research Studies Journal, 4B, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polii, P., Saerang, I., & Mandagie, Y. (2014). The influence of financial ratios on stock price in national private foreign-exchange commercial bank listed on indonesia stock exchange. EMBA Journals, 2, 993–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Prasetiyo, Y. (2022). Analysis of company size, profitability, and solvency on firm value at BUMN IDX20. Formosa Journal of Science and Technology, 1(7), 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purba, J., & Africa, L. (2019). The effect of capital structure, institutional ownership, managerial ownership, and profitability on company value in manufacturing companies. The Indonesian Accounting Review, 9(1), 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, S. (2014). The role of intellectual capital in determining differences between stock market and financial performance. International Research Journal of Finance and Economics, 89, 46–77. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, R. G., & Zingales, L. (1995). What do we know about capital structure? Some evidence from international data. The Journal of Finance, 50(5), 1421–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, O. (2016). Impact of capital structure and dividend policy on firm value. Journal of Poverty, Investment and Development, 21, 45–60. [Google Scholar]
- Reuer, J., Tong, T., & Cheng-Wei, W. (2012). A signaling theory of acquisition premiums: Evidence from IPO targets. Academy of Management Journal, 55(3), 667–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Valencia, L., & Lamothe Fernández, P. (2022). Insights into alternative stock markets: A systematic review of academic literature. Modern Economy, 13(06), 789–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Valencia, L., & Lamothe Fernández, P. (2023). Managerial concentration, ownership concentration, and firm value: Evidence from Spanish SMEs. Small Business International Review, 7(1), e541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Valencia, L., Lamothe-Fernández, P., & Alaminos, D. (2023). The market value of SMEs: A comparative study between private and listed firms in alternative stock markets. Annals of Finance, 19(1), 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rompas, G. P. (2013). Likuiditas solvabilitas dan rentabilitas terhadap nilai perusahaan bumn yang terdaftar dibursa efek Indonesia. Jurnal EMBA, 1(3), 252–262. [Google Scholar]
- Safitri, A. (2013). Influence of earning per share, price earnings ratio, return on asset, debt to equity ratio and market value added on stock price of the jakarta islamic index. Management Analysis Journal, 2(2), 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Schulze, W., Lubatkin, M., Dino, R., & Buchholtz, A. (2001). Agency relationships in family firms: Theory and evidence. Organization Science, 12(2), 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A., & Khan, S. (2007). Determinants of capital structure: Evidence from Pakistani panel data. International Review of Business Research Papers, 3(4), 265–282. [Google Scholar]
- Simamora, H. (2000). Accounting base for business decision making. Salemba Empat. [Google Scholar]
- Simatupang, H. J., Purwanti, L., & Mardiati, E. (2019). Determinants of capital structures based on the pecking order theory and trade-off theory. Jurnal Keuangan dan Perbankan, 23(1), 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondakh, F., Tommy, P., & Mangantar, M. (2015). Current ratio, debt to equity ratio, return on asset, return on equity effect on stock prices of LQ 45 index in BEI period 2010–2014. EMBA Journals, 3, 749–756. [Google Scholar]
- Spence, A. (1973). Job market signaling. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 87(3), 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, A. (1974). Market signaling: Informational transfer in hiring and related screening processes. Harvard University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Stiglitz, J. (2000). The contributions of the economics of information to twentieth century economics. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 115(4), 1441–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiglitz, J. (2002). Information and the change in paradigm in economics. American Economic Review, 92, 406–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoiljković, A., Tomić, S., Leković, B., & Matić, M. (2022). Determinants of capital structure: Empirical evidence of manufacturing companies in the Republic of Serbia. Sustainability, 15(1), 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucuahi, W., & Cambarihan, J. (2016). Influence of profitability to the firm value of diversified companies in the Philippines. Journal of Accounting and Finance Research, 2, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudiyatno, B., Puspitasari, E., Suwarti, T., & Asyif, M. M. (2020). Determinants of firm value and profitability: Evidence from Indonesia. Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 7, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suffah, R., & Riduwan, A. (2016). Effect of profitability, leverage, company size and dividend policy on firm value. Ilmudan Journal of Accounting Research, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Sunarto, P., & Agus, B. (2009). Effect of leverage, size and growth of companies on profitability. TEMA Journal, 6(1), 86–103. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S., Syarif, A., & Ariza, D. (2014). Analysis of factors that affecting the stock price of industry transportation services which is listed on the Indonesian stock exchange years of 2009 to 2012. Journal of Management Dynamics, 2, 116–129. [Google Scholar]
- Tarigan, J., Hervindra, C., & Hatane, S. E. (2018). Does board diversity influence financial performance? International Research Journal of Business, 11(3), 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, S., Pedersen, T., & Kvist, H. (2006). Blockholder ownership: Effects on firm value in market and control based governance systems. Journal of Corporate Finance, 12(2), 246–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiska, S. (2015). Effect of profitability and investment opportunity on firm value. Bakrie University Scientific Journal, 3(1), 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Titman, S., & Wessels, R. (1988). The determinants of capital structure choice. The Journal of Finance, 43(1), 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursel, N., & Zhong, L. (2018). Why do firms pay high underwriting fees? SEO withdrawal, underwriter certification and CEO turnover. Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money, 54, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. F., & Huang, Y. T. (2014). How do auditors increase substantially firm value. International Journal of Economics and Finance, 6(10), 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, N. (2017). The throne vs. the kingdom: Founder control and value creation in startups. Strategic Management Journal, 38(2), 255–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, A. L. (2020). The effect of audit quality on firm value: A case in Indonesian manufacturing firm. Journal of Accounting, Finance and Auditing Studies, 6(1), 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yammeesri, J., Lodh, S. C., & Herath, S. K. (2006). Influence of ownership structure and corporate performance precrisis: Evidence from Thailand. International Journal of Electronic Finance, 1(2), 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yermack, D. (1996). Higher market valuation of companies with a small board of directors. Journal of Financial Economics, 40(2), 185–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulsiati, H. (2016). Influence of earning per share, return on equity and debt to equity ratio against stock price on jakarta islamic index (JII) listed in Indonesia stock exchange (BEI) period 2010–2014. Journal of Administration, 2(1), 104–127. [Google Scholar]
| Variables | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Dependent Variable | |
| Tobin’s Q | (Total assets − book value of equity + market value of equity)/total assets |
| Control Variables | |
| Firm size | Natural logarithm of total assets of the firm |
| Listing history | Years listed on the stock exchange |
| Independent Variables | |
| Financial performance | |
| ROE | Net income/Total equity |
| ROA | Profit before interest and taxes/Book value of total assets |
| CR | Current assets/Current liabilities |
| DER | Total liabilities/Shareholders’ equity |
| Leverage | Total liabilities relative to total assets |
| TATO | Net sales/Total assets |
| Solvency | Total equity/Total debt |
| Corporate Governance | |
| Cross-listing | Equals 1 when the firm is cross-listed internationally; otherwise, it equals 0 |
| Auditing firm | Equals 1 if firms appointing one of the Big Four auditing firms. Equals 0 otherwise |
| Controlling shareholder | Percentage of the largest shareholder (%) |
| Second-largest shareholder | Percentage of the second-largest shareholder (%) |
| Board size | Number of directors on the board |
| Independent directors | Percentage of independent directors on the board (%) |
| Chairperson and CEO duality | A value of 1 indicates that the CEO also serves as the chairperson of the board; 0 indicates otherwise |
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | Observation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control Variables | |||||
| Firm size | 17.0322 | 2.1427 | 8.0290 | 21.2646 | 361 |
| Listing history | 0.7852 | 0.6703 | 0.0000 | 2.1972 | 227 |
| Independent Variables | |||||
| ROE | −2.7404 | 1.6890 | −7.4217 | 2.6327 | 198 |
| ROA | −3.6264 | 1.4868 | −8.3958 | 1.6572 | 192 |
| CR | 5.3975 | 12.389 | 0.0000 | 126.959 | 355 |
| DER | 0.5496 | 6.7427 | 0.0000 | 108.600 | 327 |
| Leverage | 0.47 | 0.4068 | 0.001 | 5.99 | 359 |
| TATO | 0.2046 | 0.4200 | 0.0000 | 5.2600 | 320 |
| Solvency | 0.5852 | 1.9966 | −4.6877 | 8.3964 | 351 |
| Corporate Governance | |||||
| Cross-listing | 0.0083 | 0.0909 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 361 |
| Auditing firm | 0.5900 | 0.4925 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 361 |
| Controlling shareholder | 0.5133 | 0.3395 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 361 |
| Second-largest shareholder | 0.1137 | 0.1085 | 0.0000 | 0.4638 | 361 |
| Board size | 6.2709 | 2.9391 | 1.0000 | 14.0000 | 361 |
| Independent directors | 0.7637 | 0.3215 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 360 |
| Chairperson and CEO duality | 0.3158 | 0.4655 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 361 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | (11) | (12) | (13) | (14) | (15) | (16) | (17) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tobin’s Q | Leverage | ROE | ROA | Firm Size | CR | DER | TATO | Solvency | Listing History | Controlling Shareholder | Second-Largest Shareholder | Board Size | Independent Directors | Cross-Listing | Auditing Firm | Chairperson–CEO Duality | ||
| (1) | Tobin’s Q | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| (2) | Leverage | −0.0582 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| (3) | ROE | 0.0073 | 0.2404 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| (4) | ROA | 0.0226 | 0.0152 | 0.9389 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| (5) | Firm size | −0.6513 | 0.0697 | −0.0682 | −0.1717 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| (6) | CR | −0.0390 | −0.1922 | −0.0490 | −0.0064 | 0.0046 | 1 | |||||||||||
| (7) | DER | −0.0364 | 0.6750 | 0.2293 | 0.0004 | −0.0284 | −0.4114 | 1 | ||||||||||
| (8) | TATO | −0.1196 | 0.4562 | 0.3982 | 0.2787 | −0.2225 | −0.1295 | 0.7297 | 1 | |||||||||
| (9) | Solvency | 0.0575 | −0.9674 | −0.2772 | 0.0075 | −0.1458 | 0.1854 | −0.7273 | −0.4687 | 1 | ||||||||
| (10) | Listing history | −0.0782 | 0.2804 | 0.1184 | 0.013 | 0.0157 | −0.3771 | 0.4856 | 0.4389 | −0.3127 | 1 | |||||||
| (11) | Controlling shareholder | 0.0084 | −0.1209 | 0.0567 | −0.0021 | 0.1313 | 0.1278 | 0.1514 | 0.1485 | 0.0334 | 0.0255 | 1 | ||||||
| (12) | Second-largest shareholder | 0.2234 | 0.3584 | 0.0269 | −0.1046 | −0.2192 | −0.0472 | 0.2914 | 0.1667 | −0.3916 | 0.0760 | −0.1700 | 1 | |||||
| (13) | Board size | 0.1008 | 0.1116 | 0.0238 | −0.0114 | −0.0705 | 0.1344 | 0.0669 | 0.1233 | −0.1172 | 0.1269 | −0.0863 | 0.1245 | 1 | ||||
| (14) | Independent directors | −0.1489 | −0.1183 | 0.0925 | 0.0854 | 0.2043 | −0.0692 | −0.0411 | 0.0072 | 0.0782 | 0.0552 | 0.0976 | −0.2287 | 0.5692 | 1 | |||
| (15) | Cross-listing | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| (16) | Auditing firm | 0.0072 | −0.2389 | 0.0759 | 0.0734 | 0.1523 | 0.1917 | −0.2664 | −0.3011 | 0.1733 | 0.0186 | 0.0862 | −0.1864 | 0.0262 | 0.1201 | 0 | 1 | |
| (17) | Chairperson–CEO duality | 0.1421 | 0.1995 | 0.0541 | 0.0559 | −0.1565 | 0.0157 | −0.0105 | 0.1021 | −0.1497 | −0.0493 | −0.1006 | 0.3535 | 0.0804 | −0.2069 | 0 | −0.0677 | 1 |
| Dependent Variable: Tobin’s Q | FEM 1 | FEM 2 | FEM 3 | FEM 4 | FEM 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 12.885 *** | 13.727 *** | 13.050 *** | 12.029 *** | 12.572 *** |
| (11.44) | (10.68) | (11.26) | (8.30) | (7.28) | |
| Control variable (firm-specific variable) | |||||
| Firm size | −0.072 *** | −0.769 *** | −0.768 *** | −0.766 *** | −0.734 *** |
| (−10.90) | (−10.17) | (−10.66) | (−9.09) | (−7.86) | |
| Listing history | −0.697 | −0.065 | 0.090 | 0.060 | 0.069 |
| (−0.79) | (−0.58) | (0.76) | (0.55) | (0.57) | |
| Independent variables | |||||
| Financial variables | |||||
| ROE | 0.497 ** | 0.072 * | 0 | 0.089 * | |
| (2.12) | (1.53) | 0 | (1.59) | ||
| ROA | −0.501 ** | 0 | 0.766 | ||
| (−2.17) | 0 | (1.46) | |||
| CR | −0.018 | −0.095 * | −0.077 | ||
| (−0.35) | (−1.60) | (−1.25) | |||
| DER | −0.098 | −0.0620698 | −0.009199 | ||
| (−1.15) | (−0.66) | (−0.10) | |||
| Leverage | −0.594 ** | −1.070 *** | −0.151 * | ||
| (−2.43) | (−4.41) | (1.60) | |||
| TATO | −0.296 *** | −0.461 *** | −0.483 *** | ||
| (−3.27) | (−4.01) | (−4.15) | |||
| Solvency | −0.605 *** | −1.059 *** | |||
| (−2.63) | (−4.93) | ||||
| Governance variables | |||||
| Cross-listing | 0 | ||||
| 0 | |||||
| Auditing firm | −0.105 | 0.102 | |||
| (0.74) | (0.16) | ||||
| Controlling shareholder | 0.232 ** | 0.274 ** | |||
| (1.93) | (2.14) | ||||
| Second-largest shareholder | −0.067 | −0.0009 | |||
| (−0.61) | (−0.01) | ||||
| Board size | 0.287 | 0.187 | |||
| (1.30) | (0.78) | ||||
| Independent directors | −0.102 | −0.002 | |||
| (−0.76) | (−0.01) | ||||
| Chairperson and CEO duality | 0.136 | 0.033 | |||
| (0.74) | (0.16) | ||||
| No. of firms | 86 | 54 | 54 | 44 | 44 |
| No. of observations | 227 | 127 | 126 | 108 | 108 |
| Hausman test | 41.86 | 49.34 | 33.97 | 28.17 | 50.35 |
| R-sq | 0.618 | 0.696 | 0.718 | 0.713 | 0.676 |
| Wald (Chi-sq) | 123.62 | 112.44 | 137.06 | 95.59 | 72.78 |
| Variable | Model FEM 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tobin’s Q | Coef | P | SE |
| Listing history | 0.0691 | 0.566 | 0.120438 |
| Firm size | −0.7345 | 0.000 | 0.0934592 |
| ROE | 0.0895 | 0.111 | 0.0562399 |
| CR | −0.0770 | 0.2111 | 0.0615767 |
| DER | −0.0091 | 0.922 | 0.0935102 |
| Leverage | −0.1516 | 0.109 | 0.0946662 |
| TATO | −0.4834 | 0.000 | 0.1164236 |
| Controlling shareholder | 0.2748 | 0.033 | 0.1286467 |
| Second-largest shareholder | −0.00094 | 0.994 | 0.1178343 |
| Board size | 0.1872 | 0.438 | 0.2412099 |
| Independent directors | −0.0022 | 0.988 | 0.1484875 |
| Auditing firm | 0.1020 | 0.625 | 0.2087649 |
| Chairperson and CEO duality | 0.0330 | 0.876 | 0.2120663 |
| Constant | 12.5729 | 0.000 | 1.728036 |
| Hausman test | 50.35 | 0.000 | Prob > Chi2 |
| R-sq | 0.6766 | ||
| Wald (Chi-sq) | 72.78 | 0.000 | |
| No. of observations | 108 | ||
| P = Standard Error | |||
| Fixed effects | |||
| Autocorrelation and heteroscedasticity problem corrected with regression of | |||
| Prais–Winsten | |||
| Variables in natural logarithm | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez Valencia, L. Financial Performance and Corporate Governance on Firm Value: Evidence from Spain. Int. J. Financial Stud. 2025, 13, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13030123
Rodríguez Valencia L. Financial Performance and Corporate Governance on Firm Value: Evidence from Spain. International Journal of Financial Studies. 2025; 13(3):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13030123
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez Valencia, Leslie. 2025. "Financial Performance and Corporate Governance on Firm Value: Evidence from Spain" International Journal of Financial Studies 13, no. 3: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13030123
APA StyleRodríguez Valencia, L. (2025). Financial Performance and Corporate Governance on Firm Value: Evidence from Spain. International Journal of Financial Studies, 13(3), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijfs13030123







