Qualitative Exploration of Barriers to Medication Adherence Among Patients with Uncontrolled Diabetes in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
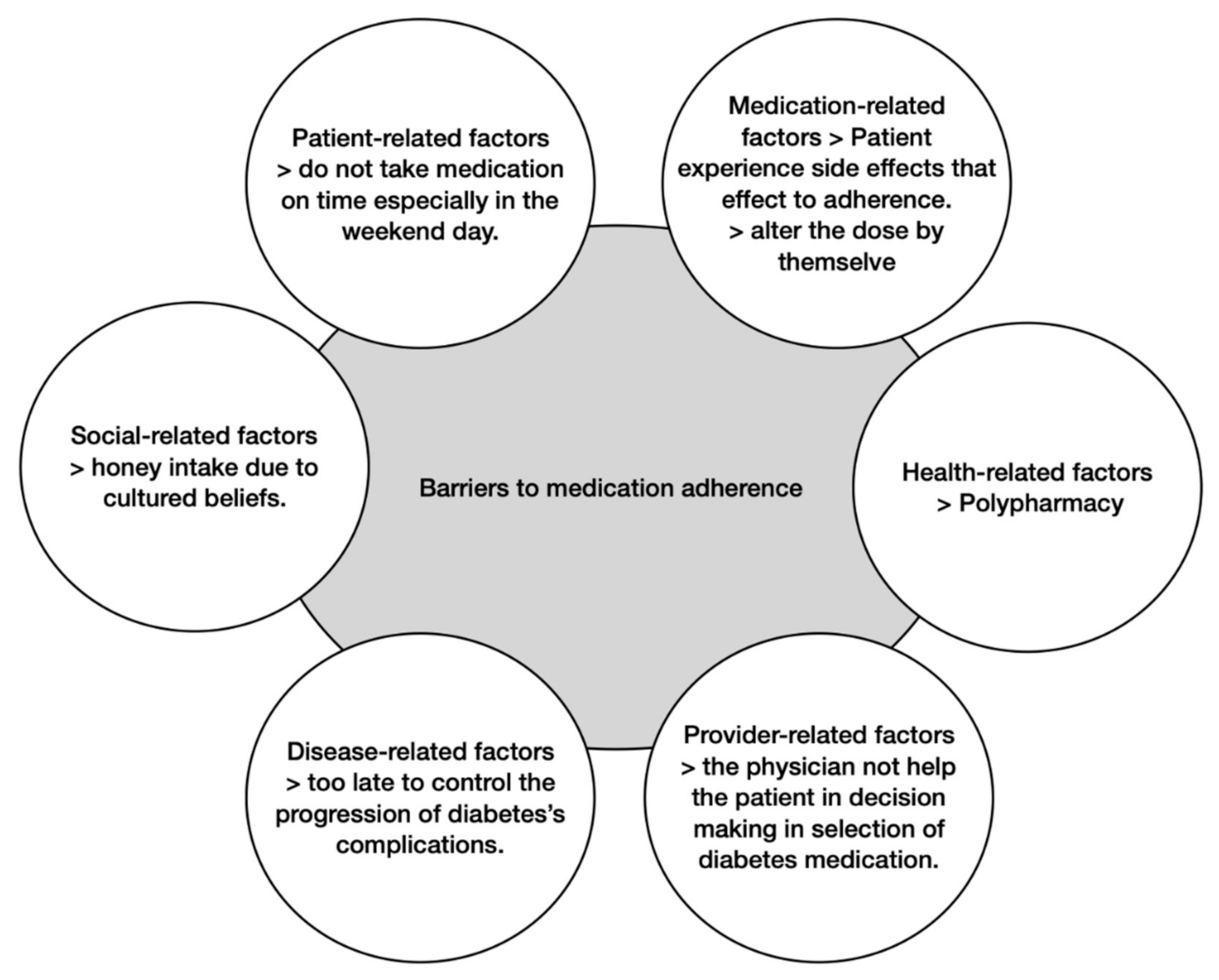
3.1. Barriers to Medication Adherence
3.1.1. Patient-Related Factors
3.1.2. Medication-Related Factors
3.1.3. Social-Related Factors
3.1.4. Healthcare-Related Factors
3.1.5. Provider-Related Factors
3.1.6. Disease-Related Factors
4. Discussion
5. Strengths and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jennifer, D.G.; Dhiren, K.P.; David, S. Diabetes mellitus. In Applied Therapeutics: The Clinical Use of Drugs, 11th ed.; Carolina, S.Z., Michael, G.C., Eds.; Wlters Kluwen: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 1071–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Danaei, G.; Finucane, M.; Lu, Y.; Singh, G.M.; Cowan, M.J.; Paciorek, C.J.; Lin, J.K.; Farzadfar, F.; Khang, Y.H.; Stevens, G.A.; et al. National, regional, and global trends in fasting plasma glucose and diabetes prevalence since 1980: Systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 370 country-years and 2.7 million participants. Lancet 2011, 378, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Expert Committee. International Expert Committee report on the role of the A1C assay in the diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumvoll, M.; Goldstein, B.; van Haeften, T. Type 2 diabetes: Principles of pathogenesis and therapy. Lancet 2005, 365, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rubeaan, K.; Abu El-Asrar, A.M.; Youssef, A.M.; Subhani, S.N.; Ahmad, N.A.; Al-Sharqawi, A.H.; Alguwaihes, A.; Alotaibi, M.S.; Al-Ghamdi, A.; Ibrahim, H.M. Diabetic retinopathy and its risk factors in a society with a type 2 diabetes epidemic: A Saudi National Diabetes Registry-based study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015, 93, e140–e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alwakeel, J.S.; Al-Suwaida, A.; Isnani, A.C.; Al-Harbi, A.; Alam, A. Concomitant macro and microvascular complications in diabetic nephropathy. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2009, 20, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vanstone, M.; Rewegan, A.; Brundisini, F.; Dejean, D.; Giacomini, M. Patient perspectives on quality of life with uncontrolled type 1 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and qualitative meta-synthesis. Ont. Health Technol. Assess. Ser. 2015, 15, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wabe, N.T.; Angamo, M.T.; Hussein, S. Medication adherence in diabetes mellitus and self-management practices among type-2 diabetics in Ethiopia. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 3, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polonsky, W.H.; Fisher, L.; Guzman, S.; Villa-Caballero, L.; Edelman, S.V. Psychological insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes: The scope of the problem. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 2543–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabaté, E.; WHO Adherence to Long Term Therapies Project, Global Adherence Interdisciplinary Network, World Health Organization. Dept. of Management of Noncommunicable Diseases. Adherence to Long-Term Therapies: Evidence for Action. World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; Available online: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publica-tions/2003/9241545992.pdf (accessed on 6 October 2018).
- Jaam, M.; Hadi, M.A.; Kheir, N.; Ibrahim, M.I.M.; Diab, M.I.; Al-Abdulla, S.A.; Awaisu, A. A qualitative exploration of barriers to medication adherence among patients with uncontrolled diabetes in Qatar: Integrating perspectives of patients and health care providers. Patient Prefer. Adher. 2018, 12, 2205–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaam, M.; Ibrahim, M.I.M.; Kheir, N.; Awaisu, A. Factors associated with medication adherence among patients with diabetes in the Middle East and North Africa region: A systematic mixed studies review. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2017, 129, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saudi Arabian Ministry of Health. The Kingdom Successfully Make Another Haj Season. 2006. Available online: http://www.moh.gov.sa/ar/modules/news/print.php?storyid=383 (accessed on 21 November 2020).
- Krass, I.; Schieback, P.; Dhippayom, T. Adherence to diabetes medication: A systematic review. Diabet Med. 2015, 32, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunghi, C.; Zongo, A.; Moisan, J.; Grégoire, J.P.; Guénette, L. Factors associated with antidiabetic medication non-adherence in patients with incident comorbid depression. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2017, 31, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, H.T.T.; Bonner, A.; Clark, R.; Ramsbotham, J.; Hines, S. The effectiveness of the teach-back method on adherence and self-management in health education for people with chronic disease: A systematic review. JBI Database Syst. Rev. Implement. Rep. 2016, 14, 210–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levesque, C. Therapeutic lifestyle changes for diabetes mellitus. Nurs. Clin. North. Am. 2017, 52, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignon Zomahoun, H.T.; de Bruin, M.; Guillaumie, L.; Moisan, J.; Grégoire, J.P.; Pérez, N.; Vézina-Im, L.A.; Guénette, L. Effectiveness and content analysis of interventions to enhance oral antidiabetic drug adherence in adults with type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Value Health 2015, 18, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeire, E.; Wens, J.; van Royen, P.; Biot, Y.; Hearnshaw, H.; Lindenmeyer, A. Interventions for improving adherence to treatment recommendations in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005, CD003638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarab, A.S.; Alqudah, S.G.; Mukattash, T.L.; Shattat, G.; Al-Qirim, T. Randomized controlled trial of clinical pharmacy management of patients with type 2 diabetes in an outpatient diabetes clinic in Jordan. J. Manag. Care Pharm. 2012, 18, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoine, S.L.; Pieper, D.; Mathes, T.; Eikermann, M. Improving the adherence of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with pharmacy care: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2014, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alotaibi, M.M.; Istepanian, R.; Philip, N. A mobile diabetes management and educational system for type-2 diabetics in Saudi Arabia (SAED). Mhealth 2016, 2, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | Number of Patients (n = 68) |
|---|---|
| Age (years); mean ± SD | 54.8 (±12.2) |
| Gender | |
| Male, n (%) | 24 (35.29) |
| Female, n (%) | 44 (64.71) |
| Nationality | |
| Saudis, n (%) | 67 (98.53) |
| Non-Saudis, n (%) | 1 (1.47) |
| Education | |
| Illiterate | 22 (32.35) |
| Primary school | 13 (19.12) |
| High school | 13 (19.12) |
| Secondary school | 7 (10.29) |
| Diploma degree | 3 (4.41) |
| Bachelor’s degree | 10 (14.71) |
| Income | |
| Low | 13 (19.12) |
| Medium | 44 (64.71) |
| High | 11 (16.18) |
| Type of diabetes Type 1 Type 2 | 1 (1.47) 67 (98.53) |
| Number of medications | |
| One medication | 11 (16.18) |
| Two medications | 17 (25.00) |
| Three medications | 35 (51.47) |
| Four medications | 5 (7.35) |
| Type of medications | |
| Oral antidiabetics | 35 (51.5) |
| Insulin | 6 (8.8) |
| Combination of oral antidiabetics and insulin | 27 (39.7) |
| Number of diabetes complications | |
| No complications | 16 (23.53) |
| One complication | 29 (42.65) |
| Two complications | 18 (26.47) |
| Three complications | 5 (7.35) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alodhaib, G.; Alhusaynan, I.; Mirza, A.; Almogbel, Y. Qualitative Exploration of Barriers to Medication Adherence Among Patients with Uncontrolled Diabetes in Saudi Arabia. Pharmacy 2021, 9, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy9010016
Alodhaib G, Alhusaynan I, Mirza A, Almogbel Y. Qualitative Exploration of Barriers to Medication Adherence Among Patients with Uncontrolled Diabetes in Saudi Arabia. Pharmacy. 2021; 9(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy9010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlodhaib, Ghaida, Imtinan Alhusaynan, Ahmer Mirza, and Yasser Almogbel. 2021. "Qualitative Exploration of Barriers to Medication Adherence Among Patients with Uncontrolled Diabetes in Saudi Arabia" Pharmacy 9, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy9010016
APA StyleAlodhaib, G., Alhusaynan, I., Mirza, A., & Almogbel, Y. (2021). Qualitative Exploration of Barriers to Medication Adherence Among Patients with Uncontrolled Diabetes in Saudi Arabia. Pharmacy, 9(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy9010016





