Clinical Evaluation of Basal-Bolus Therapy Delivered by the V-Go® Wearable Insulin Delivery Device in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Criteria
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
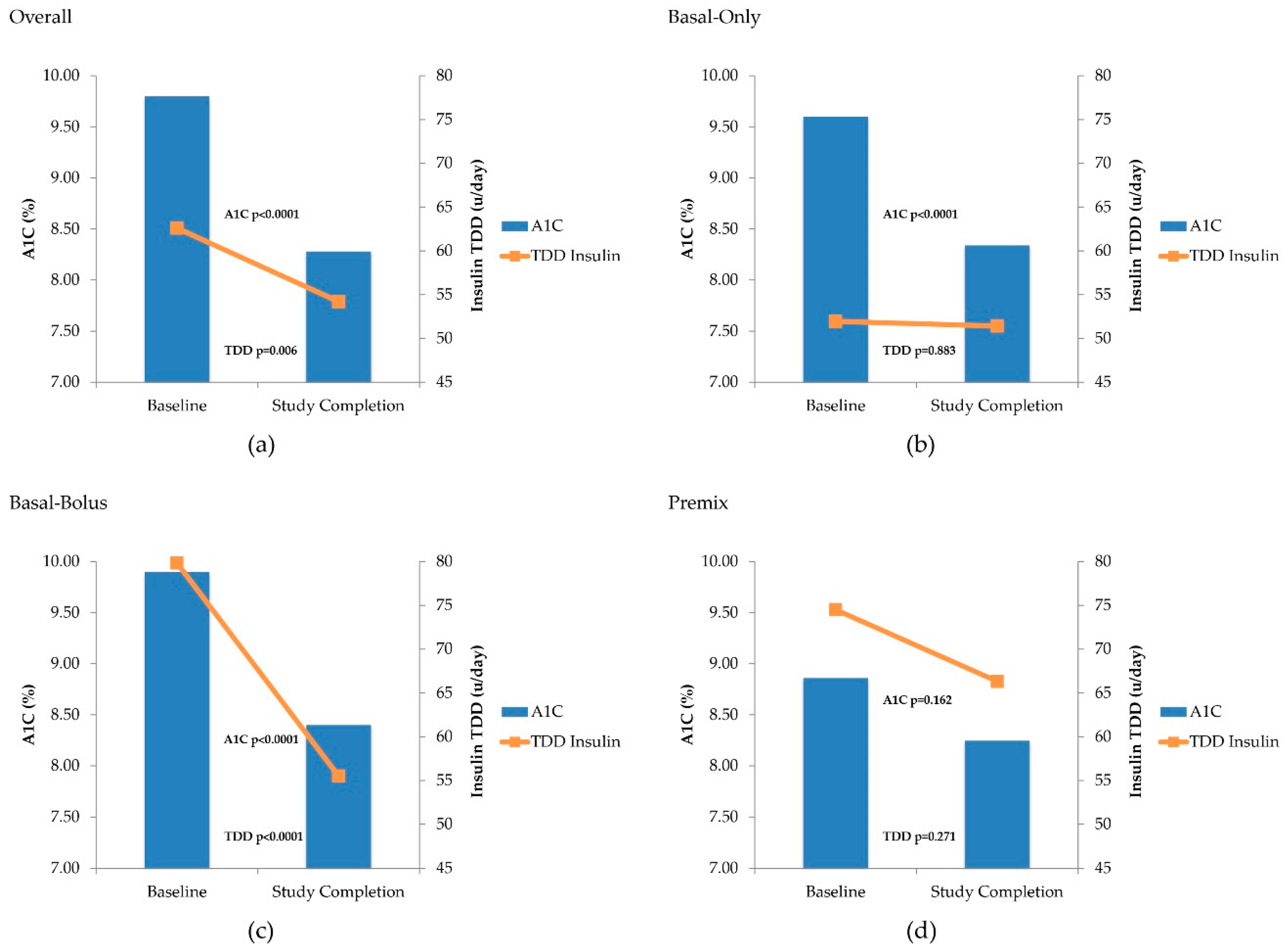
3.2. Clinical Response with V-Go
3.3. Safety Assessments
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centers for Disease Control. Type 2 Diabetes. 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/type2.html (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Stratton, I.M.; I Adler, A.; Neil, H.A.W.; Matthews, D.R.; E Manley, S.; A Cull, C.; Hadden, D.; Turner, R.C.; Holman, R.R. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): Prospective observational study. BMJ 2000, 321, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA). Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set (HEDIS). Available online: https://www.ncqa.org/hedis/measures/comprehensive-diabetes-care/ (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2020. Chapter 6: Glycemic Targets. Diabetes Care 2020, 43 (Suppl. 1), S66–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, A.J.; Abrahamson, M.J.; Barzilay, J.I.; Blonde, L.; Bloomgarden, Z.T.; Bush, M.A.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Einhorn, D.; Fonseca, V.A.; et al. Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm—2017 executive summary. Endocr. Pract. 2017, 23, 207–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2020. Chapter 9: Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment. Diabetes Care 2020, 43 (Suppl. 1), S98–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorli, C.; Heile, M.K. Identifying and meeting the challenges of insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes. J. Multidiscip. Health 2014, 7, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsaei, S.; Radfar, M.; Heydari, Z.; Abbasi, F.; Qorbani, M. Insulin adherence in patients with diabetes: Risk factors for injection omission. Prim. Care Diabetes 2014, 8, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrak, F.; Stridde, E.; Leverkus, F.; Crispin, A.A.; Forst, T.; Pfützner, A. Development and Validation of a New Measure to Evaluate Psychological Resistance to Insulin Treatment. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 2199–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peyrot, M.; Barnett, A.H.; Meneghini, L.F.; Schumm-Draeger, P.-M. Factors associated with injection omission/non-adherence in the Global Attitudes of Patients and Physicians in Insulin Therapy study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2012, 14, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2019. Chapter 7: Diabetes Technologies. Diabetes Care 2019, 41 (Suppl. 1), S71–S80. [Google Scholar]
- Valeritas. A Quick-Start Guide for Your Practice. 2020. Available online: https://www.go-vgo.com/hcp/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2020/06/ART-712_Rev-E_HCP_Start_Guide_FINAL_052820.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Grunberger, G.; Rosenfeld, C.R.; Bode, B.W.; Abbott, S.D.; Nikkel, C.C.; Shi, L.; Strange, P. Effectiveness of V-Go® for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in a Real-World Setting: A Prospective Observational Study. Drugs Real World Outcomes 2020, 7, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cziraky, M.J.; Abbott, S.; Nguyen, M.; Larholt, K.; Apgar, E.; Wasser, T.; Strange, P.; Shi, L.; Harrison, H.C.; Everitt, B.; et al. A Pragmatic Clinical Trial to Compare the Real-World Effectiveness of V-Go versus Standard Delivery of Insulin in Patients with Advanced Type 2 Diabetes. J. Health Econ. Outcomes Res. 2019, 6, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lajara, R.; Fetchick, D.A.; Morris, T.L.; Nikkel, C.C. Use of V-Go® Insulin Delivery Device in Patients with Sub-optimally Controlled Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Analysis from a Large Specialized Diabetes System. Diabetes Ther. 2015, 6, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lajara, R.; Nikkel, C.C.; Abbott, S. The Clinical and Economic Impact of the V-Go® Disposable Insulin Delivery Device for Insulin Delivery in Patients with Poorly Controlled Diabetes at High Risk. Drugs Real World Outcomes 2016, 3, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lajara, R.; Davidson, J.A.; Nikkel, C.; Morris, T.L. Clinical and cost-effectiveness of insulin delivery with V-Go disposable insulin delivery device versus multiple daily injections in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on basal insulin. Endocr. Pr. 2016, 22, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajara, R.; Nikkel, C. Practical Considerations for switching to V-Go for insulin delivery in patients with type 2 diabetes. Pract. Diabetol. 2016, 5, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld, C.R.; Bohannon, N.J.; Bode, B.W.; Kelman, A.S.; Mintz, S.N.; Schorr, A.B.; I Sandberg, M.; Nambi, S.; Agarwala, S.K.; Leichter, S.B.; et al. The V-Go Insulin Delivery Device Used in Clinical Practice: Patient Perception and Retrospective Analysis of Glycemic Control. Endocr. Pr. 2012, 18, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, B.R.; Jones, T.C.; Sink, I.J.H.; Cooke, C.E. Real-World Assessment of Glycemic Control After V-Go® Initiation in an Endocrine Practice in the Southeastern United States. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2014, 8, 1060–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, D.; Higdon, C.D.; Nikkel, C.; Hilsinger, K.A. Clinical Benefits Over Time Associated with Use of V-Go Wearable Insulin Delivery Device in Adult Patients with Diabetes: A Retrospective Analysis. Adv. Ther. 2018, 35, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, B.; Harrison, H.C.; Nikkel, C.C.; Laswell, E.; Chen, A.M.H. Clinical and economic considerations based on persistency with a novel insulin delivery device versus conventional insulin delivery in patients with type 2 diabetes: A retrospective analysis. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. 2019, 15, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, A.; Lintner, M.; Knezevich, E. V-Go Insulin Delivery System Versus Multiple Daily Insulin Injections for Patients With Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2015, 9, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, P.J.; Bodkin, N.L.; Fradkin, J.; Glasgow, R.E.; Greenfield, S.; Gregg, E.; Kerr, E.A.; Pawlson, L.G.; Selby, J.V.; Sutherland, J.E.; et al. Diabetes Performance Measures: Current Status and Future Directions. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Workgroup on Hypoglycemia. Defining and reporting hypoglycemia in diabetes: A report from the American Diabetes Association Workgroup on Hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998, 352, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
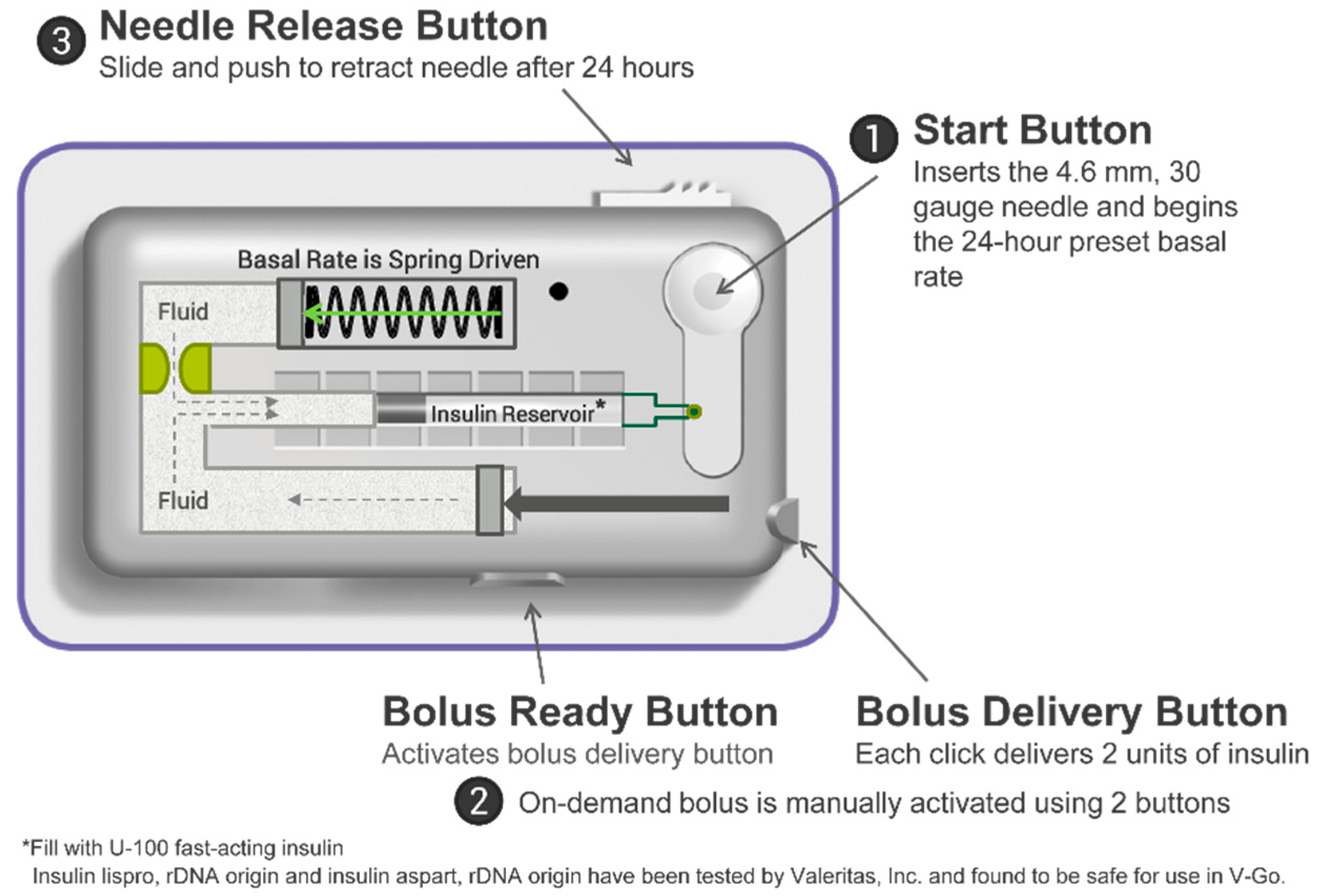
| Characteristic | N (%) or Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Age | 59.98 ± 11.60 |
| Sex | |
| Female | 81 (58) |
| Male | 58 (42) |
| Race | |
| White | 115 (83) |
| Black | 19 (14) |
| Asian | 1 (<1) |
| Biracial/multiracial | 1 (<1) |
| Not reported | 3 (2) |
| Duration of diabetes (years) | 13.82 ± 8.72 |
| A1c (%) | 9.80 ± 1.62 |
| A1c < 8% | 20 (14) |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 35.03 ± 6.10 |
| Weight, kg | 102.40 ± 18.98 |
| Insulin daily dose (u/day) | 63 ± 39 |
| Insulin regimen | |
| Basal-only | 73 (53) |
| Basal-bolus | 36 (26) |
| Premix | 13 (9) |
| Naïve | 17 (12) |
| NIGLM | Baseline (Pre V-Go) N (%) | Study Completion (On V-Go) N (%) |
|---|---|---|
| At least 1 NIGLM | 121 (87) | 115 (83) |
| Metformin | 65 (47) | 61 (44) |
| Sulfonylurea | 62 (45) | 37 (27) |
| GLP-1 agonist | 28 (20) | 35 (25) |
| DDP-4 inhibitor (DDP-4 I) | 21 (15) | 16 (12) |
| SLGT-2 inhibitor | 18 (13) | 25 (18) |
| Thiazolidinedione | 13 (9) | 15 (11) |
| DPP-4 I/metformin | 9 (6) | 8 () |
| Metformin/sulfonylurea | 2 (1) | 2 (1) |
| Other 1 | 14 (10) | 8 (6) |
| Baseline (Pre V-Go) N (%) | Study Completion (On V-Go) N (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypoglycemia < 55 mg/dL | 15 (11%) | 9 (6%) | 0.200 |
| Hypoglycemia < 70 mg/dL1 | 38 (27%) | 34 (24%) | 0.239 |
| No hypoglycemia | 98 (71%) | 103 (74%) | |
| Not reported | 3 (2%) | 2 (1%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeidan, T.; Nikkel, C.; Dziengelewski, B.; Wu, S.; Chen, A.M.H. Clinical Evaluation of Basal-Bolus Therapy Delivered by the V-Go® Wearable Insulin Delivery Device in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Analysis. Pharmacy 2020, 8, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy8040215
Zeidan T, Nikkel C, Dziengelewski B, Wu S, Chen AMH. Clinical Evaluation of Basal-Bolus Therapy Delivered by the V-Go® Wearable Insulin Delivery Device in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Analysis. Pharmacy. 2020; 8(4):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy8040215
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeidan, Trisha, Carla Nikkel, Beth Dziengelewski, Stephanie Wu, and Aleda M. H. Chen. 2020. "Clinical Evaluation of Basal-Bolus Therapy Delivered by the V-Go® Wearable Insulin Delivery Device in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Analysis" Pharmacy 8, no. 4: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy8040215
APA StyleZeidan, T., Nikkel, C., Dziengelewski, B., Wu, S., & Chen, A. M. H. (2020). Clinical Evaluation of Basal-Bolus Therapy Delivered by the V-Go® Wearable Insulin Delivery Device in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Analysis. Pharmacy, 8(4), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy8040215





