A Stepwise Pharmacist-Led Medication Review Service in Interdisciplinary Teams in Rural Nursing Homes
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Aim of the Study
1.2. Ethics
2. Methods
2.1. Setting and Study Population
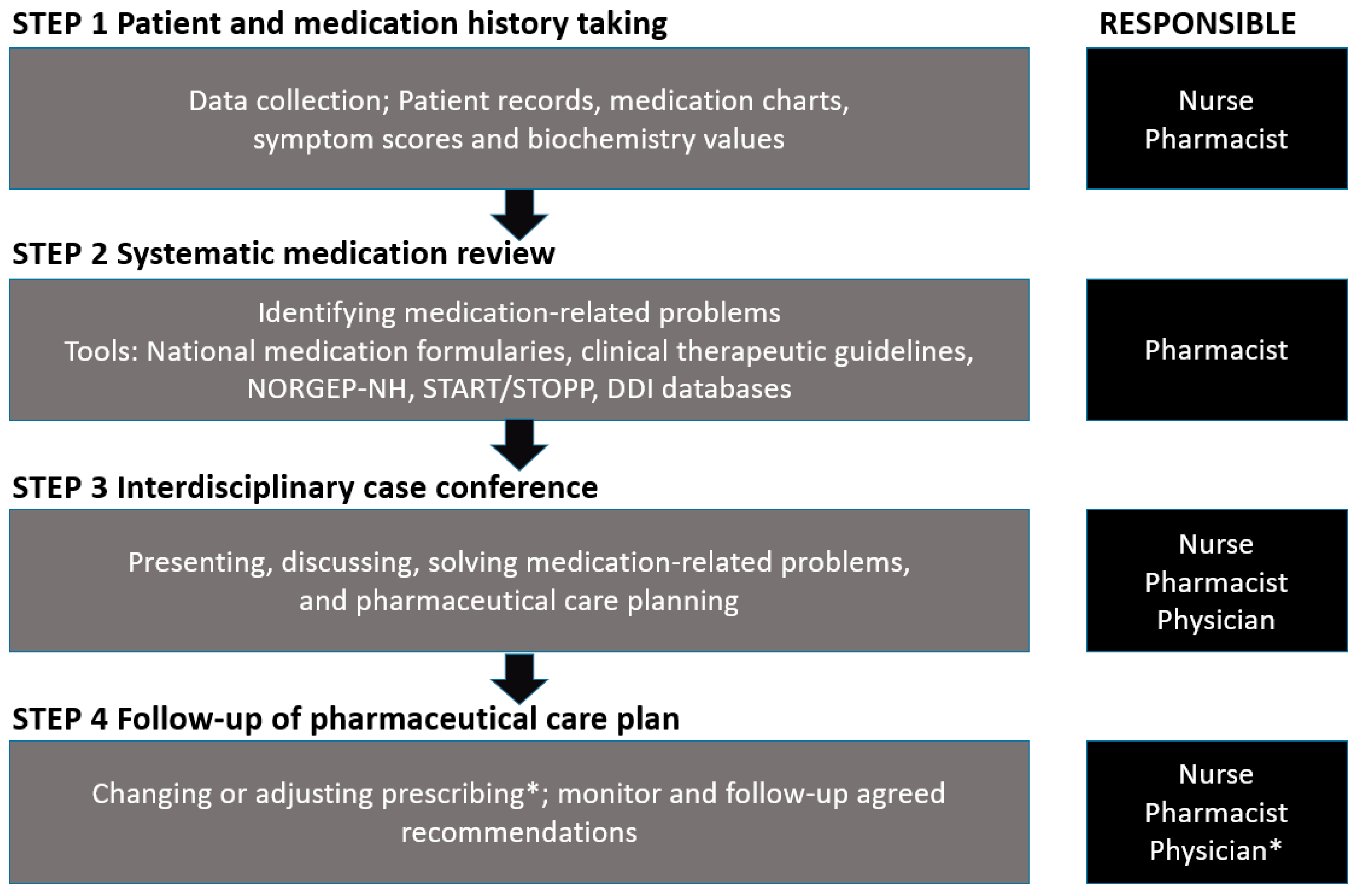
2.2. Interdisciplinary Stepwise Approach
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Medication Use and Medication Related Problems
4.2. The Interdisciplinary Team Collaboration
4.3. Factors Associated with MRPs
4.4. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barber, A. Maintaining Medical Independence in Advanced Age. Care Manag. J. 2009, 10, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halvorsen, K.H.; Granas, A.G.; Engeland, A.; Ruths, S. Prescribing quality for older people in Norwegian nursing homes and home nursing services using multidose dispensed drugs. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2012, 21, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selbæk, G.; Kirkevold, Ø.; Engedal, K. The prevalence of psychiatric symptoms and behavioural disturbances and the use of psychotropic drugs in Norwegian nursing homes. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2007, 22, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blytt, K.M.; Selbaek, G.; Drageset, J.; Natvig, G.K.; Husebo, B.S. Comorbid Dementia and Cancer in Residents of Nursing Homes: Secondary Analyses of a Cross-Sectional Study. Cancer Nurs. 2018, 2, E13–E20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, M.; Sjölander, M.; Pfister, B.; Jonsson, J.; Schneede, J.; Lövheim, H. Drug-related hospital admissions among old people with dementia. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 72, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alldred, D.P.; Kennedy, M.-C.; Hughes, C.; Chen, T.F.; Miller, P. Interventions to optimise prescribing for older people in care homes. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2, CD009095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnheim, K. When drug therapy gets old: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in the elderly. Exp. Gerontol. 2003, 38, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, A.B.; McLachlan, A.J.; E Brien, J.-A. Effectiveness of pharmacist-led medication reconciliation programmes on clinical outcomes at hospital transitions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devik, S.A.; Olsen, R.M.; Fiskvik, I.L.; Halbostad, T.; Lassen, T.; Kuzina, N.; Enmarker, I. Variations in drug-related problems detected by multidisciplinary teams in Norwegian nursing homes and home nursing care. Scand. J. Prim. Heal. Care 2018, 36, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvorsen, K.H.; Ruths, S.; Granas, A.G.; Viktil, K.K. Multidisciplinary intervention to identify and resolve drug-related problems in Norwegian nursing homes. Scand. J. Prim. Heal. Care 2010, 28, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PCNE Working Group on Medication Review: PCNE. 2017. Available online: http://www.pcne.org/working-groups/1/medication-review (accessed on 22 December 2017).
- Legemiddelgjennomgang. Medication reviews: Statens legemiddelverket, Norwegian Medicines Agency. 2016. Available online: https://legemiddelverket.no/bivirkninger-og-sikkerhet/rad-til-helsepersonell/legemiddelgjennomgang#sjekkliste-for-legemiddelgjennomgang (accessed on 20 December 2016).
- Forslag til Prosedyre for samstemming av legemiddellisten og legemiddelgjennomgang (LMG) i sykehjem for pasienter med langtidsopphold [Guidelines for medication reconciliation and medication review for long-term patients in nursing homes]: Utviklingssenter for sykehjem og hjemmetjenester, Sandefjord kommune [Municipality of Sandefjord]. Available online: https://www.pasientsikkerhetsprogrammet.no/s%c3%b8k/_attachment/1312?_ts=13a6a035268 (accessed on 04 November 2019).
- Ruths, S.; Straand, J.; Nygaard, H. Multidisciplinary medication review in nursing home residents: What are the most significant drug-related problems? The Bergen District Nursing Home (BEDNURS) study. Qual. Saf. Health Care 2003, 12, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersten, H.R.S.; Wyller, T.B. Farmakoterapi i sykehjem. Tidsskrift for den Norske Laegeforening 2009, 129, 1732–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidsson, M.; Vibe, O.E.; Ruths, S.; Blix, H.S. A multidisciplinary approach to improve drug therapy in nursing homes. J. Multidiscip. Health 2011, 4, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fog, A.F.; Kvalvaag, G.; Engedal, K.; Straand, J. Drug-related problems and changes in drug utilization after medication reviews in nursing homes in Oslo, Norway. Scand. J. Prim. Health Care 2017, 35, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. ATC/DDD Index 2018. Available online: https://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/ (accessed on 05 May 2019).
- O’Mahony, D.; O’Sullivan, D.; Byrne, S.; O’Connor, M.N.; Ryan, C.; Gallagher, P. STOPP/START criteria for potentially inappropriate prescribing in older people: Version 2. Age Ageing 2015, 44, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyborg, G.; Straand, J.; Klovning, A.; Brekke, M. The Norwegian General Practice—Nursing Home criteria (NORGEP-NH) for potentially inappropriate medication use: A web-based Delphi study. Scand. J. Prim. Health Care 2015, 33, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Interaction database for Norwegian clinicians. Interaksjoner.no [Internet]. Legemiddelverket [Norwegian Medicines Agency]. Available online: http://interaksjoner.azurewebsites.net/ (accessed on 05 May 2019).
- Stockley’s Drug Interaction Database [Internet]. Medicines Complete. Available online: https://www.medicinescomplete.com/mc/stockley/2010/ (accessed on 05 May 2019).
- Helsebiblioteket [The Norwegian Electronic Health Library]. Folkehelseinstituttet [Norwegian Institute of Public Health]. Available online: www.helsebiblioteket.no (accessed on 05 May 2019).
- Norsk legemiddelhåndbok [Norwegian Drug and Therapeutic Formulary for Health Personnel]. Available online: https://www.legemiddelhandboka.no/ (accessed on 05 May 2019).
- Felleskatalogen [The Norwegian Pharmaceutical Product Compendium]. Available online: https://www.felleskatalogen.no/medisin (accessed on 05 May 2019).
- National Kidney Foundation®. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Available online: https://www.kidney.org/professionals/KDOQI/gfr (accessed on 05 May 2019).
- Ruths, S.; Viktil, K.K.; Blix, H.S. Classification of drug-related problems. Tidsskrift for den Norske Laegeforening 2007, 127, 3073–3076. [Google Scholar]
- Modig, S.; Holmdahl, L.; Bondesson, A. Medication reviews in primary care in Sweden: Importance of clinical pharmacists’ recommendations on drug-related problems. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2016, 38, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milos, V.; Rekman, E.; Bondesson, Å.; Eriksson, T.; Jakobsson, U.; Westerlund, T.; Midlöv, P. Improving the Quality of Pharmacotherapy in Elderly Primary Care Patients Through Medication Reviews: A Randomised Controlled Study. Drugs Aging 2013, 30, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brulhart, M.I.; Wermeille, J.P. Multidisciplinary medication review: Evaluation of a pharmaceutical care model for nursing homes. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2011, 33, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, M.B.; Chang, F.; Tocco, A.; Mills, M.E.; Hwang, J.M.; Garwood, C.L.; Khreizat, H.S.; Gupta, N.S. Drug-Related-Problem Outcomes and Program Satisfaction from a Comprehensive Brown Bag Medication Review. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2015, 63, 1900–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheewala, P.A.; Peterson, G.M.; Curtain, C.M.; Nishtala, P.S.; Hannan, P.J.; Castelino, R.L. Impact of the Pharmacist Medication Review Services on Drug-Related Problems and Potentially Inappropriate Prescribing of Renally Cleared Medications in Residents of Aged Care Facilities. Drugs Aging 2014, 31, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, J. A national program for patient safety in Norway: Johan Lund. Eur. J. Public Health 2016, 26 (Suppl. 1), ckw168.064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tommelein, E. Deprescribing in nursing homes is safe and should be pursued. Évid. Based Nurs. 2018, 21, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Service (NHS) England. Clinical Pharmacists in General Practice. 2019. Available online: https://www.england.nhs.uk/gp/gpfv/workforce/building-the-general-practice-workforce/cp-gp/ (accessed on 31 October 2019).
- Kjeldsen, L.J.; Nielsen, T.R.; Olesen, C. The challenges of outcome research. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2016, 38, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blix, H.S.; Viktil, K.K.; Moger, T.A.; Hjemaas, B.J.; Pretsch, P.; Vraalsen, T.F.; Walseth, E.K. The majority of hospitalised patients have drug-related problems: Results from a prospective study in general hospitals. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 60, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, J.; Boyd, M.; Cumin, D. Teams, tribes and patient safety: Overcoming barriers to effective teamwork in healthcare. Postgrad. Med. J. 2014, 90, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Nursing Home | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | SD (%) | n | SD (%) | n | SD (%) | n | SD (%) | n | SD (%) | ||
| Participants | 35 | 43 | 31 | 42 | 151 | ||||||
| Female | 23 | (65.7) | 31 | (72.0) | 20 | (64.5) | 28 | (66.7) | 102 | (67.5) | |
| Male | 12 | (34.3) | 12 | (28.0) | 11 | (35.5) | 14 | (33.3) | 49 | (32.5) | |
| Age, years | |||||||||||
| Mean | 83.1 | 10.1 | 86.4 | 6.9 | 84.4 | 8.8 | 86.4 | 8.4 | 85.2 | 8.6 | |
| Mean months in nursing home | 28.9 | 26.1 | 36 | 32.3 | 20.4 | 25.3 | 40.8 | 70.5 | 32.5 | 44.5 | |
| Mean number of medications | |||||||||||
| Total | 11.1 | 3.3 | 13.1 | 4.5 | 12.9 | 5.5 | 10.6 | 4.0 | 11.9 | 4.4 | |
| Used regularly | 8.2 | 2.8 | 8.9 | 3.1 | 9.3 | 3.6 | 6 | 3.2 | 8.0 | 3.4 | |
| Used as needed | 2.8 | 1.4 | 3.8 | 2.1 | 3.5 | 2.6 | 4.5 | 2.4 | 3.7 | 2.2 | |
| Short course | 0.03 | 0.2 | 0.37 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.19 | 0.5 | 0.19 | 0.5 | |
| Mean number of MRPs | 2.7 | 1.9 | 5.2 | 2.6 | 5.6 | 2.4 | 4.2 | 2.6 | 4.4 | 2.6 | |
| Mean weight, kg | 71.2 | 15.2 | 66.7 | 15.8 | 65.6 | 13.9 | 66.9 | 12.7 | 67.6 | 14.5 | |
| Mean systolic blood pressure, mmHg | 134.3 | 19.6 | 134 | 24.9 | 136.3 | 20.7 | 134.7 | 17.9 | 134.7 | 20.9 | |
| Mean diastolic blood pressure, mmHg | 75.4 | 10.1 | 73.2 | 14.2 | 79.9 | 17.8 | 73.5 | 10.3 | 75.2 | 13.4 | |
| Mean eGFR, CKD-EPI mL/min | 70.1 | 38.5 | 60.2 | 17.2 | 65.4 | 22.3 | 64.6 | 20.1 | 64.9 | 25.4 | |
| Mean eGFR, Cockcroft Gault mL/min | 66.6 | 58.5 | 50.0 | 21.1 | 50.5 | 18.3 | 53.7 | 23.6 | 55 | 34.2 | |
| Polypharmacy categories | |||||||||||
| 0–4 medicines, no polypharmacy | 1 | (3) | 1 | (2) | 4 | (13) | 15 | (36) | 21 | (14) | |
| 5–9 medicines, polypharmacy | 21 | (60) | 24 | (56) | 12 | (39) | 21 | (50) | 78 | (52) | |
| 10+ medicines, hyperpolypharmacy | 13 | (37) | 18 | (42) | 15 | (48) | 6 | (14) | 52 | (34) | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Halvorsen, K.H.; Stadeløkken, T.; Garcia, B.H. A Stepwise Pharmacist-Led Medication Review Service in Interdisciplinary Teams in Rural Nursing Homes. Pharmacy 2019, 7, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy7040148
Halvorsen KH, Stadeløkken T, Garcia BH. A Stepwise Pharmacist-Led Medication Review Service in Interdisciplinary Teams in Rural Nursing Homes. Pharmacy. 2019; 7(4):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy7040148
Chicago/Turabian StyleHalvorsen, Kjell H., Torunn Stadeløkken, and Beate H. Garcia. 2019. "A Stepwise Pharmacist-Led Medication Review Service in Interdisciplinary Teams in Rural Nursing Homes" Pharmacy 7, no. 4: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy7040148
APA StyleHalvorsen, K. H., Stadeløkken, T., & Garcia, B. H. (2019). A Stepwise Pharmacist-Led Medication Review Service in Interdisciplinary Teams in Rural Nursing Homes. Pharmacy, 7(4), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy7040148





