An EMR-Based Approach to Determine Frequency, Prescribing Pattern, and Characteristics of Patients Receiving Drugs with Pharmacogenomic Guidelines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Demographics for Patients with Encounters, Medication Orders, and CPIC Drug Orders 2015–2019
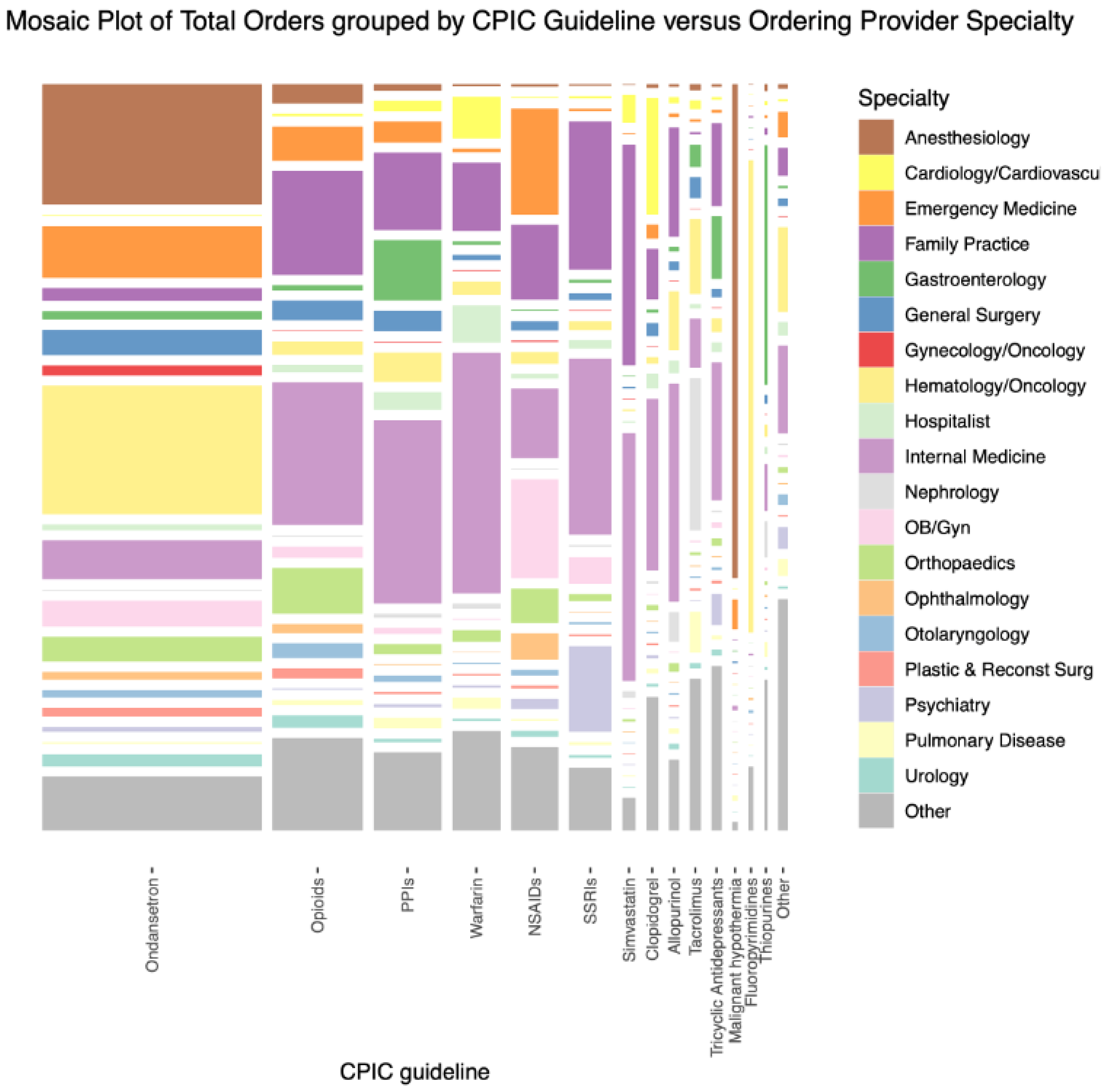
3.2. Comparison of CPIC Drug Ordering Characteristics in 2015–2019
3.3. Combinations of CPIC Drugs Ordered in 2015–2019
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; McLeod, H.L.; Weinshilboum, R.M. Genomics and drug response. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hawke, R.L. Chapter 1. Developing Perspectives on Pharmacogenomics. In Pharmacogenomics: An Introduction and Clinical Perspective; Bertino, J.S., Jr., DeVane, C., Fuhr, U., Kashuba, A.D., Ma, J.D., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Relling, M.V.; Evans, W.E. Pharmacogenomics in the clinic. Nature 2015, 526, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefaivre, A.; Litinski, V.; Vandenhurk, M. Pharmacogenetic Testing May Improve Drug Treatments and Shorten Disability Leaves. Benefits Q. 2017, 33, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC). [Database]. Available online: https://www.cpicpgx.org (accessed on 6 April 2023).
- Dunnenberger, H.M.; Crews, K.R.; Hoffman, J.M.; Caudle, K.E.; Broeckel, U.; Howard, S.C.; Hunkler, R.J.; Klein, T.E.; Evans, W.E.; Relling, M.V. Preemptive clinical pharmacogenetics implementation: Current programs in US medical centers. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 55, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Skierka, J.M.; Blommel, J.H.; Moore, B.E.; VanCuyk, D.L.; Bruflat, J.K.; Peterson, L.M.; Veldhuizen, T.L.; Fadra, N.; Peterson, S.E.; et al. Preemptive Pharmacogenomic Testing for Precision Medicine. J. Mol. Diagn. 2016, 18, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzi SPGx Experience at Boston Children’s Hospital [Webinar]; Boston Children’s Hospital: Boston, MA, USA, 2019.
- Pharmacogenomics Testing: Harnessing the Power of Genetic Data for Personalized Medicine. Translational Software: [Whitepaper]. 2019, pp. 3–7. Available online: https://www.translationalsoftware.com/whitepaper-pharmacogenomics-testing (accessed on 8 November 2019).
- “Pharmacogenomics”. National Institute of General Medical Sciences, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Available online: https://www.nigms.nih.gov/education/fact-sheets/Pages/pharmacogenomics.aspx (accessed on 6 April 2023).
- Center for Drug Evaluation Research. Table of Pharmacogenomic Biomarkers. U.S. Food and Drug Administration; Published 2019. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/science-and-research-drugs/table-pharmacogenomic-biomarkers-drug-labeling (accessed on 6 April 2023).
- What Is PharmGKB. [Database]. Available online: https://www.pharmgkb.org/whatIsPharmgkb/prescribing (accessed on 6 April 2023).
- Keeling, N.J.; Rosenthal, M.M.; West-Strum, D.; Patel, A.S.; Haidar, C.E.; Hoffman, J.M. Preemptive pharmacogenetic testing: Exploring the knowledge and perspectives of US payers. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbeurgt, P.; Mamiya, T.; Oesterheld, J. How common are drug and gene interactions? Prevalence in a sample of 1143 patients with CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 genotyping. Pharmacogenomics 2014, 15, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caudle, K.E.; Gammal, R.S.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Hoffman, J.M.; Relling, M.V.; Klein, T.E. Evidence and resources to implement pharmacogenetic knowledge for precision medicine. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2016, 73, 1977–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Roden, D.M.; McLeod, H.L.; Relling, M.V.; Williams, M.S.; Mensah, G.A.; Peterson, J.F.; Van Driest, S.L. Pharmacogenomics. Lancet 2019, 394, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AMA/ASHP Pharmacogenomics Virtual Summit Series: Summit #1: Pharmacogenomics Landscape. Knowledge Connection. Published 15 March 2022. Available online: https://elearning.ashp.org/products/8783/ama-ashp-pharmacogenomics-virtual-summit-series-summit-1-pharmacogenomics-landscape (accessed on 6 April 2023).
- Relling, M.V.; Klein, T.E. CPIC: Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium of the Pharmacogenomics Research Network. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 89, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, J.K.; Dunnenberger, H.M.; Gumpper, K.F.; Haidar, C.E.; Hoffman, J.M. Integrating pharmacogenomics into electronic health records with clinical decision support. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2016, 73, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing FAQ for Healthcare Professionals. Genome.gov. Available online: https://www.genome.gov/For-Health-Professionals/Provider-Genomics-Education-Resources/Healthcare-Provider-Direct-to-Consumer-Genetic-Testing-FAQ#:~:text=Direct%2Dto%2Dconsumer%20genetic%20tests (accessed on 6 April 2023).
- Pharmacogenetics: Genetic Testing for Drug Processing—23andMe. Available online: https://www.23andme.com/topics/pharmacogenetics/ (accessed on 6 April 2023).
- Jorde, L.B.; Bamshad, M.J. Genetic Ancestry Testing: What Is It and Why Is It Important? JAMA 2020, 323, 1089–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIH’s All of Us Research Program Returns Genetic Health-Related Results to Participants All of Us Research Program|, N.I.H. Published 28 November 2022. Available online: https://allofus.nih.gov/news-events/announcements/nihs-all-us-research-program-returns-genetic-health-related-results-participants (accessed on 6 April 2023).
- About Our System. Froedtert & the Medical College of Wisconsin. Available online: https://www.froedtert.com/about (accessed on 6 April 2023).
| With Encounters | With Medication Orders | With CPIC Drug Orders | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Patients | Median Age | IQR | Patients | Median Age | IQR | Patients | Median Age | IQR |
| Female | 463,929 | 47 | (30–64) | 327,698 | 46 | (29–64) | 190,375 | 50 | (33–64) |
| Male | 381,165 | 48 | (29–64) | 262,800 | 48 | (29–64) | 145,474 | 54 | (36–64) |
| Other/ Unknown | 424 | 40 | (22–59) | 28 | 34 | (24–45) | BT | BT | BT |
| Days in Ordering Episode 1 | Orders in Ordering Episode | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Orders | Unique Patients | Median | IQR | 99th Percentile | Median | IQR | 99th Percentile | |
| Ondansetron | ||||||||
| ondansetron | 1,302,015 | 202,113 | 1 | (1–57) | 1245 | 1 | (1–3) | 28 |
| Opioids | ||||||||
| all for guideline | 508,685 | 137,982 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| hydrocodone | 280,351 | 83,785 | 1 | (1–9) | 1656 | 1 | (1–2) | 32 |
| tramadol | 144,365 | 45,852 | 1 | (1–41) | 1615 | 1 | (1–3) | 23 |
| codeine | 83,969 | 43,934 | 1 | (1–1) | 1152 | 1 | (1–2) | 12 |
| NSAIDs | ||||||||
| all for guideline | 268,377 | 122,817 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| ibuprofen | 186,829 | 95,582 | 1 | (1–2) | 956 | 1 | (1–2) | 7 |
| meloxicam | 46,007 | 21,696 | 1 | (1–78) | 1544 | 1 | (1–2) | 11 |
| celecoxib | 22,708 | 8431 | 1 | (1–32) | 1608 | 1 | (1–2) | 11 |
| flurbiprofen | 12,342 | 5680 | 1 | (1–14) | 385 | 1 | (1–2) | 3 |
| piroxicam | 491 | 172 | 1 | (1–326) | 1691 | 1 | (1–4) | 14 |
| PPIs | ||||||||
| all for guideline | 375,230 | 92,183 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| pantoprazole | 246,842 | 66,882 | 2 | (1–170) | 1628 | 2 | (1–4) | 18 |
| omeprazole | 117,466 | 39,656 | 10 | (1–500) | 1704 | 2 | (1–4) | 11 |
| lansoprazole | 7557 | 2955 | 1 | (1–284) | 1682 | 1 | (1–3) | 11 |
| dexlansoprazole | 3365 | 1109 | 2 | (1–430) | 1679 | 2 | (1–4) | 12 |
| SSRIs | ||||||||
| all for guideline | 232,950 | 53,723 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| sertraline | 100,702 | 25,105 | 56 | (1–432) | 1708 | 2 | (1–5) | 17 |
| escitalopram | 67,838 | 18,752 | 56 | (1–396) | 1693 | 2 | (1–4) | 16 |
| citalopram | 41,129 | 10,338 | 83 | (1–602) | 1727 | 2 | (1–5) | 16 |
| paroxetine | 21,904 | 5045 | 91 | (1–669) | 1733 | 3 | (1–6) | 18 |
| fluvoxamine | 1377 | 275 | 70 | (1–429) | 1764 | 3 | (1–6) | 20 |
| Malignant hypothermia | ||||||||
| succinylcholine | 36,058 | 23,895 | 1 | (1–1) | 413 | 1 | (1–1) | 4 |
| Warfarin | ||||||||
| warfarin | 264,046 | 16,036 | 103 | (3–729) | 1779 | 7 | (3–18) | 78 |
| Simvastatin | ||||||||
| simvastatin | 70,444 | 15,736 | 619 | (1–1373) | 1757 | 4 | (2–6) | 12 |
| Clopidogrel | ||||||||
| clopidogrel | 65,658 | 15,097 | 23 | (1–416) | 1701 | 2 | (1–5) | 16 |
| Interval Days 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Number of CPIC Drugs | Unique Patients | Distinct Drug Combinations | Median | IQR | 99th Percentile |
| 1 | 133,380 | 47 2 | NA | NA | NA |
| 2 | 84,334 | 593 | 4 | (0–254) | 1530 |
| 3 | 51,357 | 2090 | 172 | (2–661) | 1647 |
| 4 | 29,628 | 3819 | 457 | (86–976) | 1709 |
| 5 | 17,560 | 4678 | 694 | (250–1159) | 1746 |
| 6 | 9772 | 4479 | 875 | (433–1299) | 1765 |
| 7 | 5197 | 3457 | 1035 | (617–1398) | 1769 |
| 8 | 2600 | 2095 | 1153 | (762–1473) | 1779 |
| 9 | 1233 | 1133 | 1272 | (902–1529) | 1791 |
| 10+ | 792 | 776 | 1317 | (985–1563) | 1792 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
MacKinnon, G.E., III; Mills, M.; Stoddard, A.; Urrutia, R.A.; Broeckel, U. An EMR-Based Approach to Determine Frequency, Prescribing Pattern, and Characteristics of Patients Receiving Drugs with Pharmacogenomic Guidelines. Pharmacy 2023, 11, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy11060178
MacKinnon GE III, Mills M, Stoddard A, Urrutia RA, Broeckel U. An EMR-Based Approach to Determine Frequency, Prescribing Pattern, and Characteristics of Patients Receiving Drugs with Pharmacogenomic Guidelines. Pharmacy. 2023; 11(6):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy11060178
Chicago/Turabian StyleMacKinnon, George E., III, Megan Mills, Alexander Stoddard, Raul A. Urrutia, and Ulrich Broeckel. 2023. "An EMR-Based Approach to Determine Frequency, Prescribing Pattern, and Characteristics of Patients Receiving Drugs with Pharmacogenomic Guidelines" Pharmacy 11, no. 6: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy11060178
APA StyleMacKinnon, G. E., III, Mills, M., Stoddard, A., Urrutia, R. A., & Broeckel, U. (2023). An EMR-Based Approach to Determine Frequency, Prescribing Pattern, and Characteristics of Patients Receiving Drugs with Pharmacogenomic Guidelines. Pharmacy, 11(6), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy11060178






