Effectiveness and Safety of Glucosamine in Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Data Analysis and Outcome Measure
2.4. Risk of Bias
3. Results
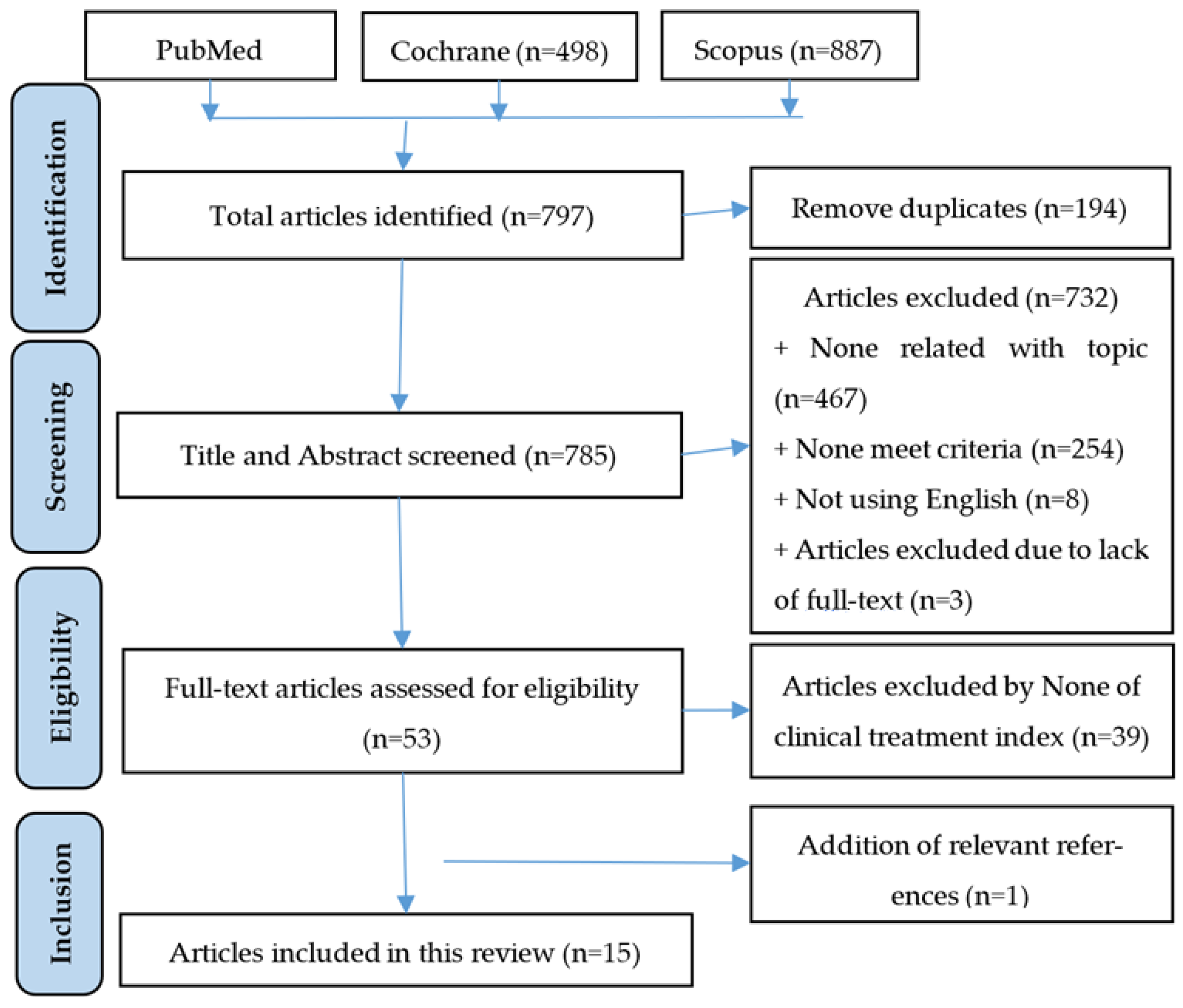
3.1. Selection of Study Process
3.2. Risk of Bias Assessment
3.3. Effectiveness of Glucosamine on Knee Osteoarthritis
3.4. Safety
3.4.1. Adverse Events
3.4.2. Drug Interactions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colletti, A.; Cicero, A.F.G. Nutraceutical Approach to Chronic Osteoarthritis: From Molecular Research to Clinical Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrozier, T.; Lohse, T. Glucosamine as a Treatment for Osteoarthritis: What If It’s True? Front. Pharm. 2022, 13, 820971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregori, D.; Giacovelli, G.; Minto, C.; Barbetta, B.; Gualtieri, F.; Azzolina, D.; Vaghi, P.; Rovati, L.C. Association of Pharmacological Treatments With Long-term Pain Control in Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis. JAMA 2018, 320, 2564–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, T.; Ideno, Y.; Akai, M.; Seichi, A.; Hagino, H.; Iwaya, T.; Doi, T.; Yamada, K.; Chen, A.-Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Effects of glucosamine in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 2479–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simental-Mendía, M.; Sánchez-García, A.; Vilchez-Cavazos, F.; Acosta-Olivo, C.A.; Peña-Martínez, V.M.; Simental-Mendía, L.E. Effect of glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Rheumatol. Int. 2018, 38, 1413–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smedslund, G.; Kjeken, I.; Musial, F.; Sexton, J.; Østeråsa, N. Interventions for osteoarthritis pain: A systematic review with network meta-analysis of existing Cochrane reviews. Osteoarthr Cart. Open 2022, 4, 100242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghouri, A.; Conaghan, P.G. Update on novel pharmacological therapies for osteoarthritis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet Dis. 2019, 11, 1759720X19864492. [Google Scholar]
- Marinho, A.; Nunes, C.; Reis, S. Hyaluronic Acid: A Key Ingredient in the Therapy of Inflammation. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Sang, L.; Wu, D.; Rong, J.; Jiang, L. Effectiveness and safety of glucosamine and chondroitin for the treatment of osteoarthritis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2018, 13, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellavato, A.; Restaino, O.F.; Vassallo, V.; Cassese, E.; Finamore, R.; Ruosi, C.; Schiraldi, C. Chondroitin Sulfate in USA Dietary Supplements in Comparison to Pharma Grade Products: Analytical Fingerprint and Potential Anti-Inflammatory Effect on Human Osteoartritic Chondrocytes and Synoviocytes. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruyère, O.; Altman, R.D.; Reginster, J.-Y. Efficacy and safety of glucosamine sulfate in the management of osteoarthritis: Evidence from real-life setting trials and surveys. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2016, 45, S12–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notes Need to Know about Glucosamine. Available online: http://bachmai.gov.vn/tin-tuc-va-su-kien/thong-tin-thuoc-menuleft-124/6734-mot-so-dieu-can-biet-ve-glucosamin.html (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- MOH. List and Rates and Payment Conditions for Pharmaceutical Drugs, Biological Products, Radioactive Drugs and Markers within the Scope of Benefits of Participants of Health Insurance; Circular No. 20/2022/TT-BYT; Ministry of Health: Ha Noi, Vietnam, 2022.
- Riddle, D.L.; Perera, R.A. The WOMAC Pain Scale and Crosstalk From Co-occurring Pain Sites in People With Knee Pain: A Causal Modeling Study. Phys. Ther. 2020, 100, 1872–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, D.A.; Lambert, B.S.; Boutris, N.; McCulloch, P.C.; Robbins, A.B.; Moreno, M.R.; Harris, J.D. Validation of Digital Visual Analog Scale Pain Scoring With a Traditional Paper-based Visual Analog Scale in Adults. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. Glob. Res. Rev. 2018, 2, e088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runhaar, J.; Rozendaal, R.M.; Middelkoop, M.V.; Bijlsma, H.J.W.; Doherty, M.; Dziedzic, K.S.; Lohmander, L.S.; McAlindon, T.; Zhang, W.; Zeinstra, S.B. Subgroup analyses of the effectiveness of oral glucosamine for knee and hip osteoarthritis: A systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis from the OA trial bank. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1862–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieman, D.C.; Shanely, R.A.; Luo, B.; Dew, D.; Meaney, M.P.; Sha, W. A commercialized dietary supplement alleviates joint pain in community adults: A double-blind, placebo-controlled community trial. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransen, M.; Agaliotis, M.; Nairn, L.; Votrubec, M.; Bridgett, L.; Su, S.; Jan, S.; March, L.; Edmonds, J.; Norton, R.; et al. Glucosamine and chondroitin for knee osteoarthritis: A double-blind randomised placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluating single and combination regimens. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwoh, C.K.; Roemer, F.W.; Hannon, M.J.; Moore, C.E.; Jakicic, J.M.; Guermazi, A.; Green, S.M.; Evans, R.W.; Boudreau, R. Effect of oral glucosamine on joint structure in individuals with chronic knee pain: A randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, K.; Chanda, K.; Saji, M.J. Safety and efficacy of Curcuma longa extract in the treatment of painful knee osteoarthritis: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Inflammopharmacology 2013, 21, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, S.G.; Beyer, N.; Hansen, M.; Holm, L.; Aagaard, P.; Mackey, A.L.; Kjaer, M. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug or glucosamine reduced pain and improved muscle strength with resistance training in a randomized controlled trial of knee osteoarthritis patients. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2011, 92, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, N.; Fioravanti, A.; Papakostas, P.; Montella, A.; Giorgi, G.; Nuti, R. The efficacy and tolerability of glucosamine sulfate in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Curr. Ther. Res. Clin. Exp. 2009, 70, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frestedt, J.L.; Walsh, M.; Kuskowski, M.A.; Zenk, J.L. A natural mineral supplement provides relief from knee osteoarthritis symptoms: A randomized controlled pilot trial. Nutr. J. 2008, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero-Beaumont, G.; Ivorra, J.A.R.; Trabado, M.D.C.; Blanco, F.J.; Benito, P.; Martín-Mola, E.; Paulino, J.; Marenco, J.L.; Porto, A.; Laffon, A.; et al. Glucosamine sulfate in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis symptoms: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study using acetaminophen as a side comparator. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clegg, D.O.; Reda, D.J.; Harris, C.L.; Klein, M.A.; O’Dell, J.R.; Hooper, M.M.; Bradley, J.D.; Bingham, C.O.B., III; Weisman, M.H.; Jackson, C.G.; et al. Glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, and the two in combination for painful knee osteoarthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cibere, J.; Kopec, J.A.; Thorne, A.; Singer, J.; Canvin, J.; Robinson, D.B.; Pope, J.; Hong, P.; Grant, E.; Esdaile, J.M. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled glucosamine discontinuation trial in knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 51, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAlindon, T.; Formica, M.; LaValley, M.; Lehmer, M.; Kabbara, K. Effectiveness of glucosamine for symptoms of knee osteoarthritis: Results from an internet-based randomized double-blind controlled trial. Am. J. Med. 2004, 117, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.; Carr, A. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of glucosamine sulphate as an analgesic in osteoarthritis of the knee. Rheumatology 2002, 41, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelká, K.; Gatterová, J.; Olejarová, M.; Machacek, S.; Giacovelli, G.; Rovati, L.C. Glucosamine sulfate use and delay of progression of knee osteoarthritis: A 3-year, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2002, 162, 2113–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reginster, J.Y.; Deroisy, R.; Rovati, L.C.; Lee, R.L.; Lejeune, E.; Bruyere, O.; Giacovelli, G.; Henrotin, Y.; Dacre, J.E.; Gossett, C. Long-term effects of glucosamine sulphate on osteoarthritis progression: A randomised, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Lancet 2001, 357, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindone, J.P.; Hiller, D.; Collacott, E.; Nordhaugen, N.; Arriola, G. Randomized, controlled trial of glucosamine for treating osteoarthritis of the knee. West J. Med. 2000, 172, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOH. Drugbank. Available online: https://drugbank.vn/ (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Williams, C.; Ampat, G. Glucosamine Sulfate; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Drug Interaction Report Glucosamine and Warfarin. Available online: https://www.drugs.com/interactions-check.php?drug_list=1182-0,2311-0 (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Dahmer, S.; Schiller, R.M. Glucosamine. Am. Fam. Physician 2008, 78, 471–476. [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen, J.F.; Sokol, G.H. Potential glucosamine-warfarin interaction resulting in increased international normalized ratio: Case report and review of the literature and MedWatch database. Pharmacotherapy 2008, 28, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, B.R.d.; Saadat, P.; Basciani, R.; Agarwal, A.; Johnston, B.C.; Jüni, P. Visual Analogue Scale has higher assay sensitivity than WOMAC pain in detecting between-group differences in treatment effects: A meta-epidemiological study. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2021, 29, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Beaumont, G.; Largo, R. Glucosamine and O-GlcNAcylation: A novel immunometabolic therapeutic target for OA and chronic, low-grade systemic inflammation? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1261–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozendaal, R.M.; Koes, B.W.; Osch, G.J.V.M.vV.; Uitterlinden, E.J.; Garling, E.H.; Willemsen, S.P.; Ginai, A.Z.; Verhaar, J.A.N.; Weinans, H.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.A. Effect of glucosamine sulfate on hip osteoarthritis: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 148, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawitzke, A.D.; Shi, H.; Finco, M.F.; Dunlop, D.D.; Harris, C.L.; Singer, N.G.; Bradley, J.D.; Silver, D.; Jackson, C.G.; Lane, N.E.; et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of glucosamine, chondroitin sulphate, their combination, celecoxib or placebo taken to treat osteoarthritis of the knee: 2-year results from GAIT. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolic, G.; Nedeljkovic, B.; Trajkovic, G.; Rasic, D.; Mirkovic, Z.; Pajovic, S.; Grbic, R.; Sipetic, S.; Vujcic, I. Pain, Physical Function, Radiographic Features, and Quality of Life in Knee Osteoarthritis Agricultural Workers Living in Rural Population. Pain Res. Manag. 2019, 2019, 7684762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Woo, J.-H.; Choi, S.J.; Ji, J.D.; Song, G.G. Effect of glucosamine or chondroitin sulfate on the osteoarthritis progression: A meta-analysis. Rheumatol. Int. 2010, 30, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noack, W.; Fischer, M.; Förster, K.K.; Rovati, L.C.; Setnikar, I. Glucosamine sulfate in osteoarthritis of the knee. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 1994, 2, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
| Author, Year, and Country | Study Design | OA Type | Intervention | N in Control Group | N in Glucosamine Group | Follow-Up (Months) | * Age | Tool to Evaluate Degree of Pain | Primary Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fransen et al., 2015, Australia [18] | Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial | Knee | GS vs. GS + CS vs. CS vs. P | 151 | 152 | 24 | 61.2 ± 7.7 60.6 ± 8.1 | WOMAC | Improvement |
| Kwoh et al., 2014, USA [19] | Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial | Knee | GS + P | 103 | 98 | 6 | 52.17 ± 6.05 52.29 ± 6.72 | WOMAC | Improvement |
| Madhu et al., 2013, India [20] |
Randomized, placebo-controlled, single-blind trial | Knee | GS vs. P vs NR-INF-02 vs. NR-INF-02 + GS | 30 | 30 | 1.5 (42 days) | 56.80 ± 7.99 56.77 ± 9.98 | WOMAC, VAS, CGIC | Improvement |
| Nieman et al., 2013, USA [17] |
Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial | Knee, Hip Ankles Shoulders Hand | GS vs. P | 51 | 101 | 2 | 57.6 ± 0.9 58.3 ± 0.8 | WOMAC, VAS, SF-36, 6-MWD | Improvement |
| Petersen et al., 2011, Denmark [21] |
Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial | Knee | GS vs ibuprofen vs. P | 12 | 12 | 3 | 62.2 ± 3.4 63.1 ± 4.7 | VAS | Improvement |
| Giordano et al., 2009, Italia [22] |
Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial | Knee | GS vs. P | 30 | 30 | 3 | 57.2 ± 7.2 58.0 ± 8.3 | WOMAC, VAS | Improvement |
| Frestedt et al., 2008, USA [23] |
Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial | Knee | GS vs. P vs Aquamin vs. GS + aquamin | 16 | 19 | 3 | 59.2 ± 8.3 58.9 ± 7.4 | WOMAC, 6-MWD | Improvement |
| Herrero-Beaumont et al., 2007, Spain [24] |
Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial | Knee | GS vs. P | 104 | 106 | 6 | 63.4 ± 6.9 64.5 ± 7.2 | WOMAC | Improvement |
| Clegg et al., 2006, USA [25] |
Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial | Knee | GH vs. CS vs GH + CS vs. P vs Celecoxib | 313 | 317 | 6 | 58.6 ± 10.2 58.2 ± 9.8 | WOMAC | Improvement |
| Cibere et al., 2004, Canada [26] |
Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial | Knee | GS vs. P | 66 | 71 | 6 | 64 (40–83) a 65 (43–88) a | WOMAC, EQ-5D | Improvement |
| McAlindon et al., 2004, USA [27] |
Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial | Knee | GH vs. P | 104 | 101 | 3 | ND ND | WOMAC | Improvement |
| Hughes et al., 2002, UK [28] |
Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial | Knee | GS vs. P | 40 | 40 | 6 | ** 62.28 ± 9.12 | WOMAC, VAS, McGill pain questionnaire | Improvement |
| Pavelka et al., 2002, Czech Republic [29] | Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial | Knee | GS vs. P | 101 | 101 | 36 | 61.2 ± 7.2 63.5 ± 6.9 | WOMAC | Improvement |
| Reginster et al., 2001, Belgium [30] |
Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial | Knee | GS vs. P | 106 | 106 | 36 | 66.0 ± 8.1 65.5 ± 7.5 | WOMAC | Improvement |
| Rindone et al., 2000, USA [31] |
Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial | Knee | GS vs. P | 49 | 49 | 2 | 63 ± 12 64 ± 11 | VAS | Improvement |
| Study and Year | Placebo | Glucosamine | Std. Mean Difference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Mean | SD | Total | Mean | SD | Weight | IV, Random, 95% CI | |
| Fransen et al., 2015 [18] | 151 | −7.2 | 33.8 | 152 | −8.6 | 24.5 | 4.1% | −1.40 |
| [−8.05, 5.25] | ||||||||
| Madhu et al., 2013 [20] | 29 | −15.5 | 18.3 | 24 | −31.7 | 19.0 | 3.5% | −16.20 |
| [−26.31, −6.09] | ||||||||
| Petersen et al., 2011 [21] | 12 | −1.9 | 10.7 | 12 | −16.8 | 17.3 | 3.3% | −14.90 |
| [−26.41, −3.39] | ||||||||
| Giodarno et al., 2009 [22] | 30 | 0.3 | 10.8 | 30 | −16.6 | 22.4 | 3.7% | −16.90 |
| [−25.80, −8.00] | ||||||||
| Clegg et al., 2006 [25] | 313 | −16.6 | 25.2 | 317 | −16.0 | 26.9 | 4.5% | 0.60 |
| [−3.47, 4.67] | ||||||||
| Rindone et al., 2000 [31] | 49 | −15.0 | 23.4 | 49 | −15.0 | 26.6 | 3.6% | 0.00 |
| [−9.92, 9.92] | ||||||||
| Study and Year | Placebo | Glucosamine | Std. Mean Difference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Mean | SD | Total | Mean | SD | Weight | IV, Random, 95% CI | |
| Kwoh et al., 2014 [19] | 103 | −19.1 | 20.1 | 98 | −15.1 | 19.3 | 9.9% | 4.00 |
| [−1.45, 9.45] | ||||||||
| Madhu et al., 2013 [20] | 29 | −9.3 | 11.4 | 24 | −23.4 | 17.1 | 7.3% | −14.10 |
| [−22.0, −6.10] | ||||||||
| Frestedt et al., 2008 [23] | 9 | −5.9 | 16.9 | 14 | −10.5 | 15 | 3.8% | −4.60 |
| [−18.15, 8.95] | ||||||||
| Herrero-Beaumont et al., 2007 [24] | 70 | −11.7 | 14.3 | 78 | −17.3 | 13.3 | 11.0% | −5.60 |
| [−10.06, −1.14] | ||||||||
| Cibere et al., 2004 [26] | 66 | 3.4 | 18.1 | 71 | 3.2 | 15.5 | 9.7% | −0.20 |
| [−5.86, 5.46] | ||||||||
| McAlindon et al., 2004 [27] | 104 | 7.8 | 13.5 | 101 | 7.8 | 13.1 | 11.9% | 0.00 |
| [−3.64, 3.64] | ||||||||
| Pavelka et al., 2002 [29] | 55 | −4.7 | 5.9 | 66 | −7.7 | 7.1 | 13.2% | −3.00 |
| [−5.32, −0.68] | ||||||||
| Regisnter et al., 2001 [30] | 71 | −0.6 | 19.6 | 68 | −0.2 | 19.2 | 8.8% | 0.40 |
| [−6.05, 6.85] | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vo, N.X.; Le, N.N.H.; Chu, T.D.P.; Pham, H.L.; Dinh, K.X.A.; Che, U.T.T.; Ngo, T.T.T.; Bui, T.T. Effectiveness and Safety of Glucosamine in Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. Pharmacy 2023, 11, 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy11040117
Vo NX, Le NNH, Chu TDP, Pham HL, Dinh KXA, Che UTT, Ngo TTT, Bui TT. Effectiveness and Safety of Glucosamine in Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. Pharmacy. 2023; 11(4):117. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy11040117
Chicago/Turabian StyleVo, Nam Xuan, Ngan Nguyen Hoang Le, Trinh Dang Phuong Chu, Huong Lai Pham, Khang Xuan An Dinh, Uyen Thi Thuc Che, Thanh Thi Thanh Ngo, and Tien Thuy Bui. 2023. "Effectiveness and Safety of Glucosamine in Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review" Pharmacy 11, no. 4: 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy11040117
APA StyleVo, N. X., Le, N. N. H., Chu, T. D. P., Pham, H. L., Dinh, K. X. A., Che, U. T. T., Ngo, T. T. T., & Bui, T. T. (2023). Effectiveness and Safety of Glucosamine in Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. Pharmacy, 11(4), 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy11040117







