Leveling Up: Evaluation of IV v. PO Linezolid Utilization and Cost after an Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Revision of IV to PO Conversion Criteria within a Healthcare System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
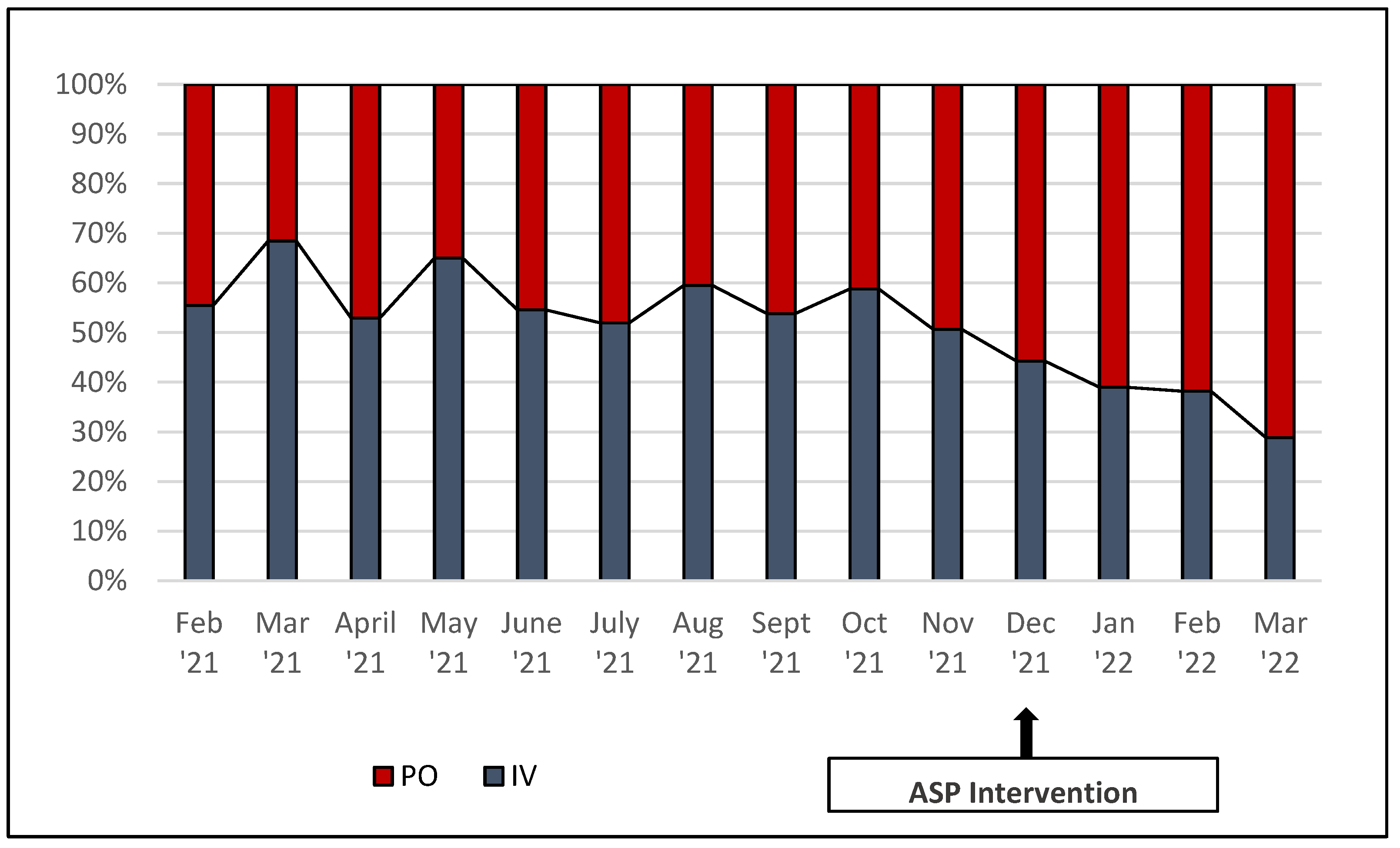
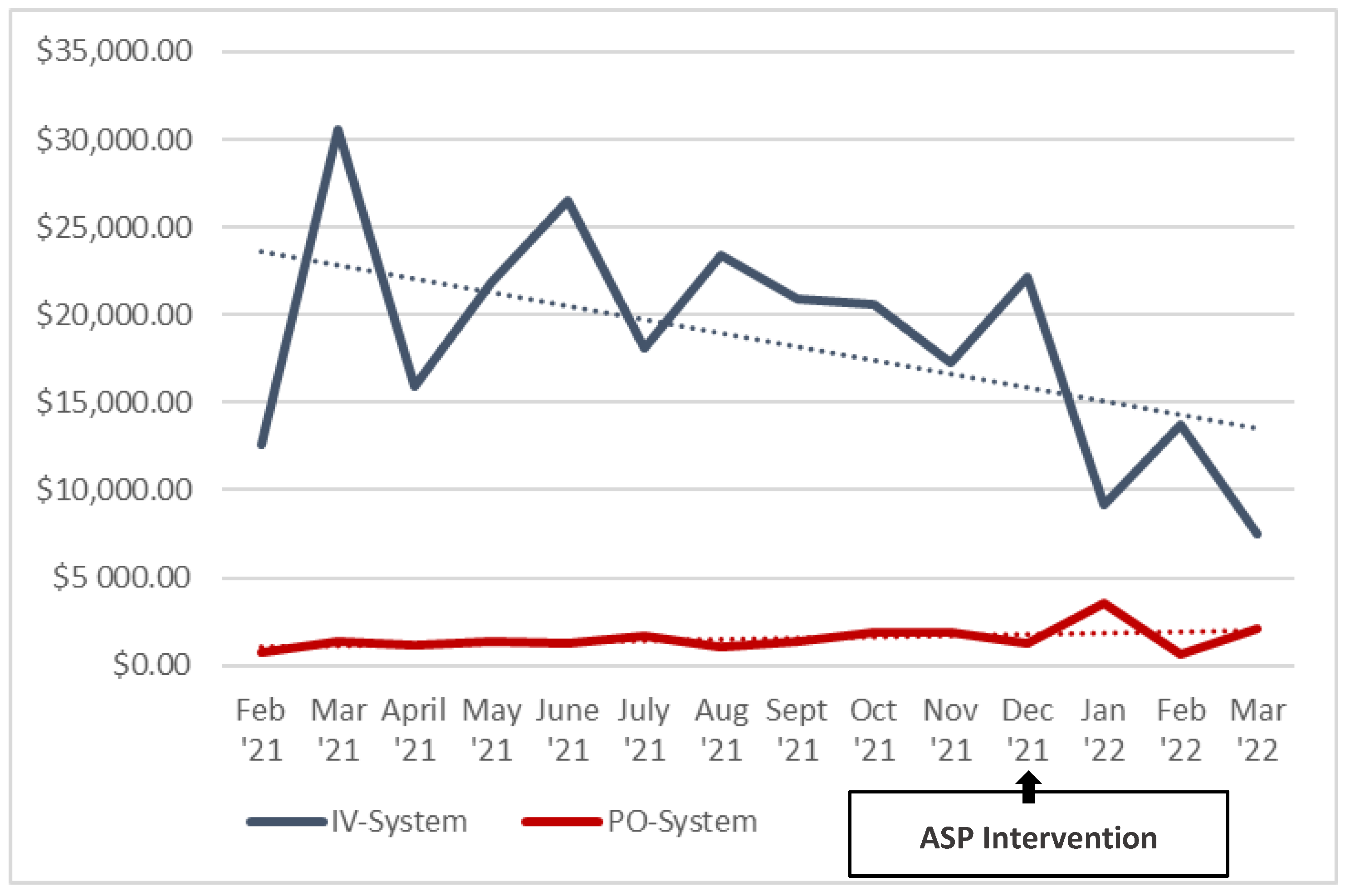
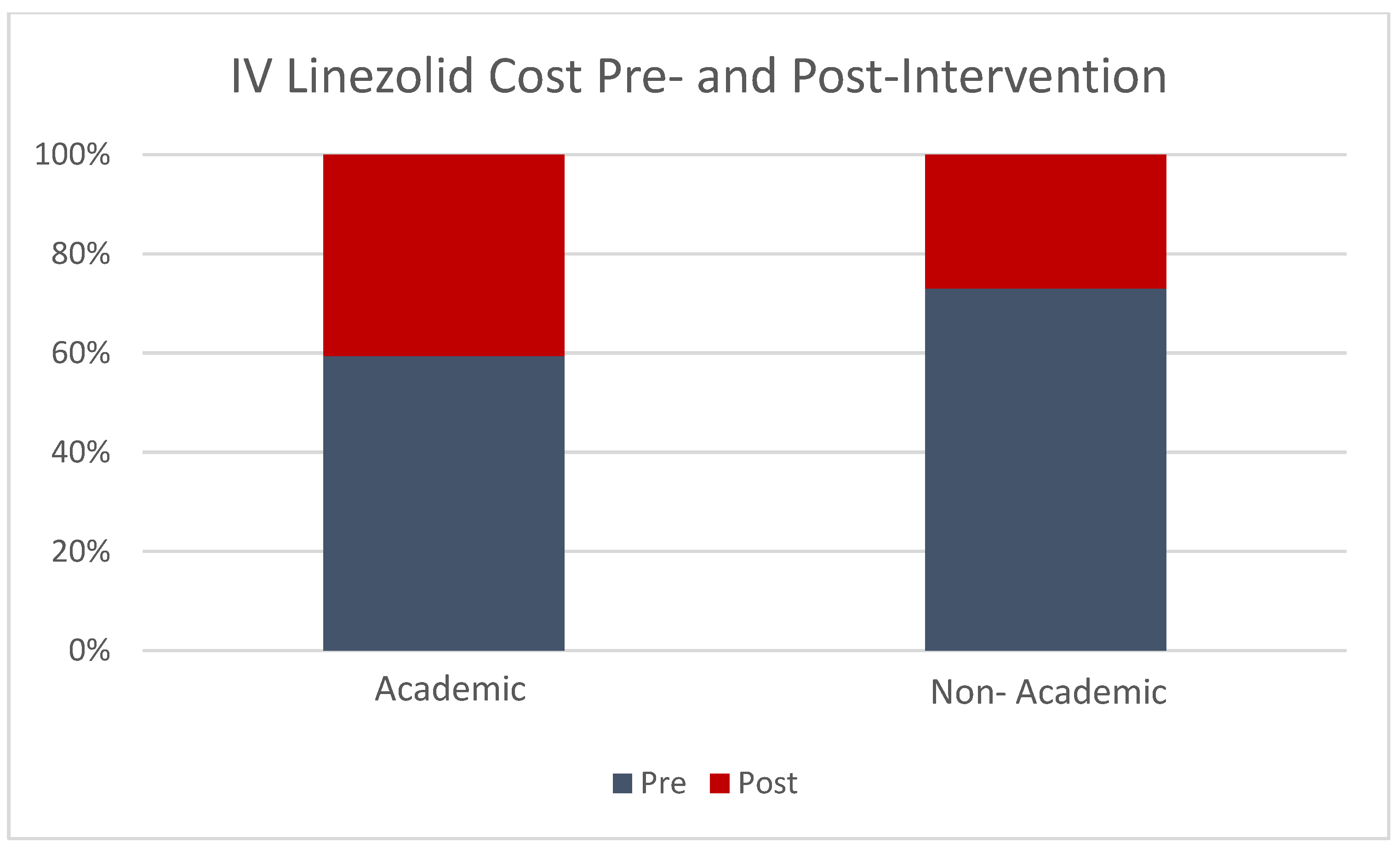
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CDC. Core Elements of Hospital Antibiotic Stewardship Programs; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019.
- Iversen, K.; Ihlemann, N.; Gill, S.U.; Madsen, T.; Elming, H.; Jensen, K.T.; Bruun, N.E.; Høfsten, D.E.; Fursted, K.; Christensen, J.J.; et al. Partial Oral versus Intravenous Antibiotic Treatment of Endocarditis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-K.; Rombach, I.; Zambellas, R.; Walker, A.S.; McNally, M.A.; Atkins, B.L.; Lipsky, B.A.; Hughes, H.C.; Bose, D.; Kümin, M.; et al. Oral versus Intravenous Antibiotics for Bone and Joint Infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlam, T.F.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Abbo, L.M.; MacDougall, C.; Schuetz, A.N.; Septimus, E.J.; Srinivasan, A.; Dellit, T.H.; Falck-Ytter, Y.T.; Fishman, N.O.; et al. Implementing an Antibiotic Stewardship Program: Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, 51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Mang, N.; Ortwine, J.; Alvarez, K.; Prokesch, B. IV to PO Conversion of Antimicrobials: Small Intervention, Big Impact. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downen, J.; Jaeger, C. Quality improvement of intravenous to oral medication conversion using Lean Six Sigma methodologies. BMJ Open Qual. 2020, 9, e000804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, B.P.; Lau, T.T.; Balen, R.M.; Naumann, T.L.; Jewesson, P.J. The impact of a pharmacist-managed dosage form conversion service on ciprofloxacin usage at a major Canadian teaching hospital: A pre- and post-intervention study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2005, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohlfelder, B.; Stashek, C.; Anger, K.; Szumita, P. Improvements in a program to convert i.v. to oral medications at an academic medical center. Am. J. Health -Syst. Pharm. 2015, 72, S145–S149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carver, K.H.; Burgess, L.H.; Cooper, M.; Elders, T.; Kramer, J. Use of clinical decision support to identify i.v.-to-oral conversion opportunities and cost savings. Am. J. Health -Syst. Pharm. 2018, 75 (Suppl. S4), S82–S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, B.D.; Pinto, B.L.; Thiemann, D.R.; Lehmann, C.U. Budget impact analysis of conversion from intravenous to oral medication when clinically eligible for oral intake. Clin Ther. 2011, 33, 1792–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtzhalts, K.E.; Sellick, J.A., Jr.; Ruh, C.A.; Carbo, J.F.; Ott, M.C.; Mergenhagen, K.A. Impact of Antimicrobial Stewardship on Outcomes in Hospitalized Veterans with Pneumonia. Clin Ther. 2016, 38, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, T.; Kwan, D.; Chan, T.; Das, P.; Raybardhan, S. Implementation of a Clinical Decision Support Tool to Improve Antibiotic IV-to-Oral Conversion Rates at a Community Academic Hospital. Can. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2019, 72, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertz, M.; Koller, M.; Haller, P.; Lampert, M.L.; Plagge, H.; Hug, B.; Koch, G.; Battegay, M.; Flückiger, U.; Bassetti, S. Outcomes of early switching from intravenous to oral antibiotics on medical wards. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, C.M.; Bodasing, N.; Boyter, A.C.; Fenelon, C.; Fox, J.G.; Seaton, R.A. Pharmacy-implemented guidelines on switching from intravenous to oral antibiotics: An intervention study. Q. J. Med. 2005, 98, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Criteria for IV to PO Conversion of Antimicrobials | |
|---|---|
| Pre-intervention | The patient must:
|
| Post-intervention | The patient must:
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaggar, J.; Cleveland, K.O.; Twilla, J.D.; Patterson, S.; Hobbs, A.L.V. Leveling Up: Evaluation of IV v. PO Linezolid Utilization and Cost after an Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Revision of IV to PO Conversion Criteria within a Healthcare System. Pharmacy 2023, 11, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy11020070
Jaggar J, Cleveland KO, Twilla JD, Patterson S, Hobbs ALV. Leveling Up: Evaluation of IV v. PO Linezolid Utilization and Cost after an Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Revision of IV to PO Conversion Criteria within a Healthcare System. Pharmacy. 2023; 11(2):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy11020070
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaggar, Jessica, Kerry O. Cleveland, Jennifer D. Twilla, Shanise Patterson, and Athena L. V. Hobbs. 2023. "Leveling Up: Evaluation of IV v. PO Linezolid Utilization and Cost after an Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Revision of IV to PO Conversion Criteria within a Healthcare System" Pharmacy 11, no. 2: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy11020070
APA StyleJaggar, J., Cleveland, K. O., Twilla, J. D., Patterson, S., & Hobbs, A. L. V. (2023). Leveling Up: Evaluation of IV v. PO Linezolid Utilization and Cost after an Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Revision of IV to PO Conversion Criteria within a Healthcare System. Pharmacy, 11(2), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy11020070





