Medication Use and Storage, and Their Potential Risks in US Households
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
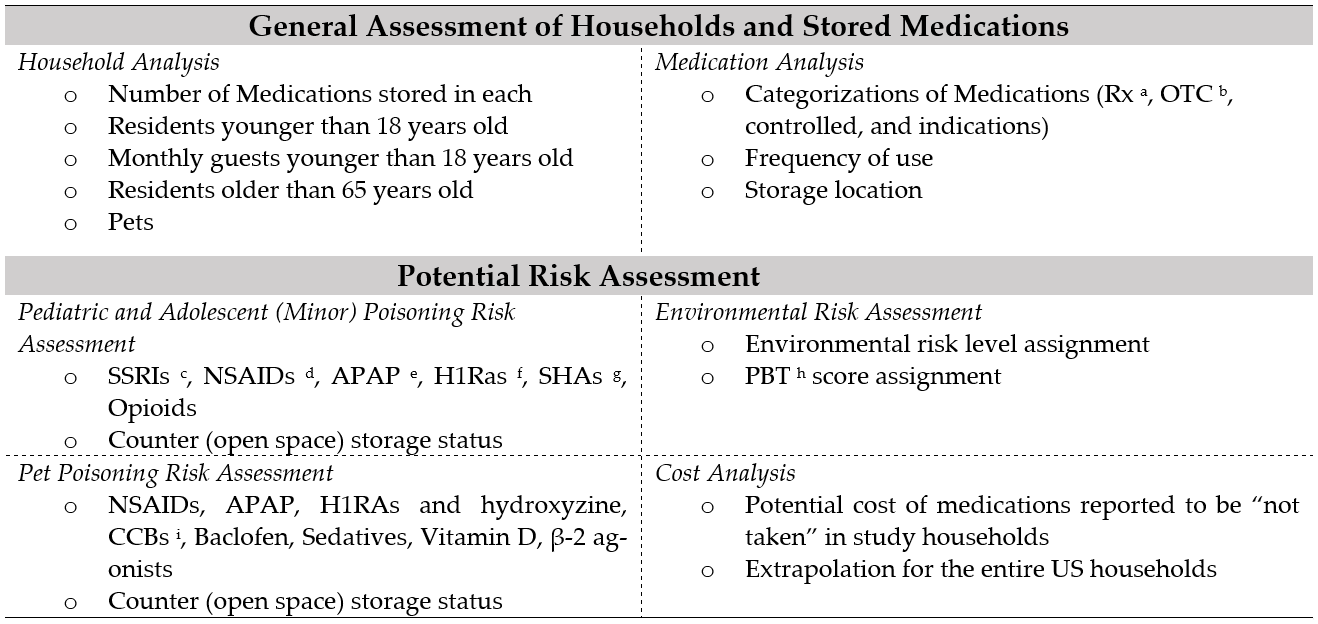
2.1. General Assessment of Households and Stored Medications
2.1.1. Household Analysis
2.1.2. Medication Analysis
- (a)
- Categorization of medications
- (b) Medication frequency of use and storage locations
2.2. Potential Risk of Poisoning Analysis
2.3. Potential Environmental Risk Analysis
2.4. Cost Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Assessment of Households and Stored Medications
3.1.1. Household Analysis
3.1.2. Medication Analysis
- (a)
- Categorization of medications
- (b) Medication frequency of use and storage locations
3.2. Potential Risk of Poisoning Analysis
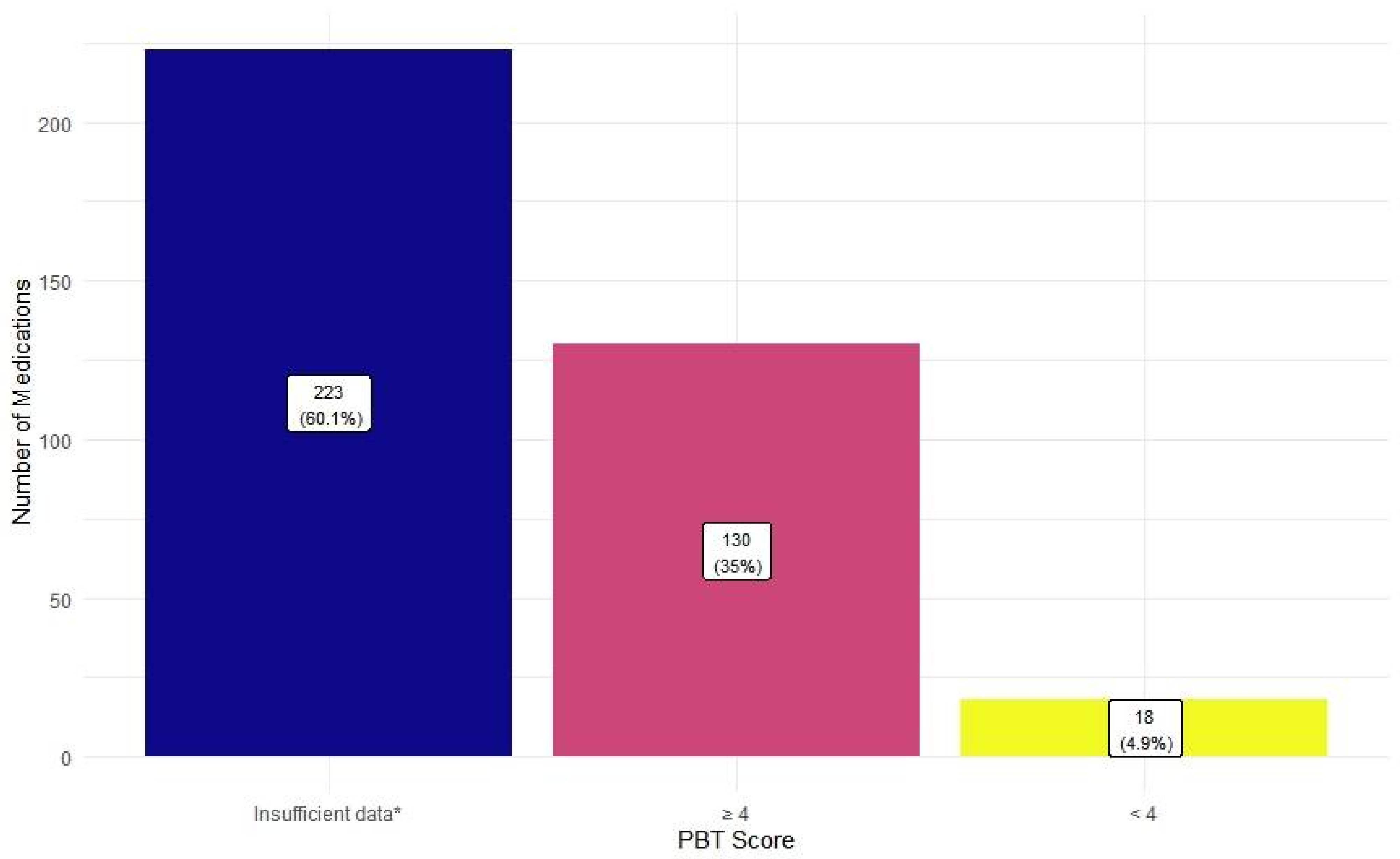
3.3. Potential Environmental Risk Analysis
3.4. Cost Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Objective #1: To Assess the US Household Members and the Number, Indications, Frequency of Use and Storage Locations of Their Medications Stored at Home
4.2. Objective #2: To Evaluate the Potential Risk for Poisoning of Minors and Pets and for the Environment Posed by the Medications Stored in the Study Households
4.2.1. Poisoning Risk
4.2.2. Environmental Risk
4.3. Objective #3: To Calculate the Potential Cost of the Unused Medications or Medications Reported to Be “Not Taken” and Stored in the US Households
4.4. Potential Solutions for Risk Mitigation
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Process of Assigning Medication Indications
Appendix B. Crude Responses (Prescription-only Non-Controlled Medications)
| Indications | Entries |
| Cardiovascular therapy | lipitor, lipitor, Simvastatin, provastatin, AMLODIPINE, lisinopril, atenolol, lisinopril, lisinopril, linsinopril, Simvistatin, simvastatin, Benazapril, elanapril, Benezipril, lisinopril, rosuvastatin calcium, carvedilol, hydrocholotyide, lisinopril, Olmesartan Medoxomil, Lisinoprill, Diltiazem, Verapamil, Pravastatin, amlodipine, Spironolactone, metoprolol tarrate, metoprolol l tartrate, amlodopin, atorvastatin, losartan, diltiazem, lisinopril, Nifedipine, simvastatin, Lisinopril, atenolol, pravostatin, carvedilol, fenofibrate, Propranolol, Trilipix, warfarin, eliquis, hydrochlothazide, Losartan Potassium, simvastatin, Lovastatin, finofibrate, lisinopril, Simvastatin, Isosorbide Mononitrate, ATORVASTATIN, Atorvastatin, Brillintal, losartan, lisinopril, pravastatin, propranolol, clopidogrel, LOSARTAN, Diltiazem, lisinopril, Astrovastatin, Losartan, sotalol, Metoprolol Tartrate, Metroprolol Tartrate, metoprolol, spironalactone, clopidogrel, pravastatin, isosorbide mononitrate, niacin, metoprolol succ er, metoprolol, lovastatin, lisinopril |
| Mental health | CYMBALTA, Zoloft, Duloxetine, Paxel, lexapor, zoloft, lexapro, Fluoxetine, abilify, paroxetine, Paxil, Prozac, Paxil, ESCITALOPRAM, Sertraline, Paxil, celexa, Risperidone, Geodone, citaopram, paxil, Prozac, duloxetine, Lithium, Risperidone, Lamotrigine, Zoloft, Wellbutrin, Wellbutrin, cymbalta, aripiprazole, Buspirone, cymbolta, effexor, prozac, duloxetine, Atomoxetine HCL, duloxetine, escitalopram oxalate, venaflaxine, Buspirone, buspar, QUETIAPINE, Buspirone |
| Endocrine therapy | metformin, Metformin, Levothyroxin, levothyroxine, MEDFORMIN, Fosamax, Glimepride, levoxyl, Levoxylthrine, metformin, Starlix, levothyroxine sodium, allopernol, levothyroxine, Levothyroxine, Alendronate, Tradjenta, synthroid, Metformin, Finesteride, metformin, Calcitriol, levthyroine, Glimepiride, Onglyza, metformin, glimeperide, glipizide, glipizide, prednisone, Lantus, lantus, humalog, apidra, Victoza, Estrofem, vivelle dot patch, estarylla, Microgestin |
| Antibiotics | Amoxicillin, zythromician, amoxicillin, CLINDAMYCIN, ciprofloxacin, metronidazole, Peniclin, penacillian, doxycycline |
| Muscle spasm | tizanadine, tizanidine, cyclobednzaprine, cyclobenzaprine hcl, cyclobenzaprine, Tizanidine, cyclobenzapran, tizanidine |
| Insomnia | trazadone, Trazadone, Mirtazapine, Mirtazapine, trazodone, remeron, mirtazapine |
| Inhalers (COPD, Asthma) | Ventolin inhaler, flovent 220, proair inhaler, ventolin, proair albuterol, advair |
| Neuropathic pain | gabapentin, gabapentin, Gabapentin, gabapentin, gabapentin, GABAPENTIN |
| Specialty injections | humira, humira, Remicade, humira, humira, enbrel |
| Anticonvulsant | dilantin, zonegran, zonisamide, CARBAMAZEPINE, carbamazepine |
| Gastrointestinal therapy | bentyl, librax, dexilant, dicyclomine |
| Fluid retention | furosemide, furosemide, furosamide |
| Pain | meloxicam, meloxicam, Meloxicam |
| Asthma (oral) | singular, singular |
| Cardiovascular therapy and mental health | Clonidine HCl, Clonidine |
| Incontinence | Vesicare, oxybutynin |
| Immunosuppressants | methotrexate, ARAVIA |
| Mental health and allergies | hydroyoxyzine |
| Anticonvulsant and antiglaucoma | acetazolamide |
| Cough | BENZONATATE |
| Cardiovascular therapy and gastrointestinal therapy | yosorala |
| Hair loss (topical) | vaniqa |
| Antiviral (HIV) | atripla |
| Migraine | immetrex |
| Steroid (topical) | Triamcinalone |
| Electrolyte supplementation | klor con |
Appendix C. Crude Responses (Controlled Substances)
| Indications | Entries |
| Mental health | Phenobarbiyol, Concerta, ritalin, Adderall, Focalin Benzodiazepines clonazepam, Xanax, ativan, Xanax, Klonopin, Xanax, xnax, lorazepam, alprazolam benzodiazepine-like non-benzodiazepines Ambean |
| Pain/controlled | tramadol, Tramadol, Tramadol, tramadol hcl Opioids oxycodone, vicodin, Norco, Norco Neuropathic pain lyrica |
| Weight loss/controlled | phentermine |
Appendix D. Crude Responses (OTC Medications)
| Indications | Entries |
| Pain | Tylenol, alieve, advil, tylenol, advil, ibuprofen, advil, ADVIL, aleeve, Acetametophin, advil, Ibuprofen, advil, Acetaminophen, advil, aleve, Advil, ibprofen, Advil, ibupfrofen, Tylenol, tylenol, advil, tylenol, tylenol, aleve, acetaminophen, tynol, motrin, tylanol, tylenol, Ibrfrophen, advil, Tylenol, advil, Tylenol, ibuprofen, IBUPROFEN, tylenol, Ibiprogen, ibuprofen, advil, Ibuprofen, NAPROXEN, tylenol, Extra Strength Tylenol, IBUPROFEN, TYLENOL, acetaminophen, Ibruprofen pm, Naproxen, ibuprofen, ibuprofen |
| Supplements | pnv, vitamins, multivitamins, b12, Flintstone Vitamins, folic acid, oneaday, cinnamon, iron, cholecalciferol vd3, calcium with D, Vitamin C, Biotin, vitamin d, multi-vitamin, b12, B12, cinnamon, ONE DAY WOME;S MULTIVITAMINS, vitamin d, IRON, coq10, vitamin d3, glucosamine, magnesium, hydrangea root |
| Gastrointestinal therapy | omezaprole, omeprezole, omeprosole, SENNA-LAX, Zantac, Omeprazole, Equate antacid, omeprazole, meta-mucil, omeprazol, Omeprazole, OMEPRAZOLE, nexium, omeprazole, Pepto Bismal, Omeprazole, senexon, polyethylene glycol, simethicone |
| Cardiovascular therapy and pain | aspirin, ASPHRAN, aspirin, aspirin, ASPIRIN, Aspirin, aspirin, aspirin, aspirin, aspirin, aspirine |
| Allergies | zyrtec, Loratadin, claritin, Fexofenadine, allegra, wal-zyr, loratadine, Xyzal |
| Cold | NyQuil, Advil PM, dimatep, Tylenol PM, nyquil, acetaminophen phenylephrine dextromethorphan, dextromethorphan doxylamine succinate |
| Nasal sprays (decongestants) | nasacort, Flonase, flonase, flonase, flournase, luticasone |
| Allergies and insomnia | Benadryl, Simply Sleep, benadryl |
| Cardiovascular therapy | fish oil, fish oil |
| Migraine | excedrin, Excedrin |
| Pain (topical) | arnicare, Therapain |
| Eye drops | Refresh |
| Insomnia | Melatonin |
| Sore throat (topical) | Chloraseptic |
| Antiseptic (topical) | hydrogen peroxide |
Appendix E. “Duplicate” and “Invalid” Responses
| Duplicate | advil, ibuprophen, levoxyl, advil, atorvastatin, advil, Lipitor, VITAMINS |
| Invalid | good, ahn, one, yes, one, one, Nore, hgygu, borg, medizel, Fevers, gius, metrolmsop, gtreth, one, as, sustatin, unknown, dol, idk, CAPSULES, Jetson, BANDAGE, Fevers, oxy, metrokoloious, Unsure, Muscle Relax, birth control, trats, Nite Time, ear drops, Sleep Aid, Exelium, Bayer, tyroid, after sun lotion, Avien, callous liquid, mucus relief, Anti Allergy, birth control, Sinus Relief, hydrochloride, allergy relief |
Appendix F. Complete Counts of Indications of Medications Stored in the Households (N = 404)
| Prescription Medications | OTC Medications | ||||
| Non-Controlled | Controlled Substances | ||||
| Indications | N = 236 | Indications | N = 25 | Indications | N = 143 |
| Cardiovascular therapy | 79 (33.5%) | Mental health | 15 (60%) | Pain | 53 (37.1%) |
| Mental health | 44 (18.6%) | Pain | 9 (36%) | Supplements | 26 (18.2%) |
| Endocrine therapy | 39 (16.5%) | Weight loss | 1 (4%) | Gastrointestinal therapy | 19 (13.3%) |
| Antibiotics | 9 (3.8%) | Cardiovascular therapy and pain | 11 (7.7%) | ||
| Muscle spasm | 8 (3.4%) | Allergies | 8 (5.6%) | ||
| Insomnia | 7 (3.0%) | Cold | 7 (4.9%) | ||
| Inhalers (COPD, Asthma) | 6 (2.5%) | Nasal sprays (decongestants) | 6 (4.2%) | ||
| Neuropathic pain | 6 (2.5%) | Allergies and insomnia | 3 (2.1%) | ||
| Specialty injections | 6 (2.5%) | Cardiovascular therapy | 2 (1.4%) | ||
| Anticonvulsant | 5 (2.1%) | Migraine | 2 (1.4%) | ||
| Gastrointestinal therapy | 4 (1.7%) | Pain (topical) | 2 (1.4%) | ||
| Muscle spasm | 8 (3.4%) | Eye drops | 1 (0.7%) | ||
| Insomnia | 7 (3.0%) | Insomnia | 1 (0.7%) | ||
| Inhalers (COPD, Asthma) | 6 (2.5%) | Sore throat (topical) | 1 (0.7%) | ||
| Neuropathic pain | 6 (2.5%) | Antiseptic (topical) | 1 (0.7%) | ||
| Specialty injections | 6 (2.5%) | ||||
| Anticonvulsant | 5 (2.1%) | ||||
| Gastrointestinal therapy | 4 (1.7%) | ||||
| Fluid retention | 3 (1.3%) | ||||
| Pain | 3 (1.3%) | ||||
| Asthma (oral) | 2 (0.9%) | ||||
| Cardiovascular therapy and mental health | 2 (0.9%) | ||||
| Incontinence | 2 (0.9%) | ||||
| Immunosuppressants | 2 (0.9%) | ||||
| Mental health and allergies | 1 (0.4%) | ||||
| Anticonvulsant and antiglaucoma | 1 (0.4%) | ||||
| Cough | 1 (0.4%) | ||||
| Cardiovascular therapy and gastrointestinal therapy | 1 (0.4%) | ||||
| Hair loss (topical) | 1 (0.4%) | ||||
| Antiviral (HIV) | 1 (0.4%) | ||||
| Migraine | 1 (0.4%) | ||||
| Steroid (topical) | 1 (0.4%) | ||||
| Electrolyte supplementation | 1 (0.4%) | ||||
References
- Mikulic, M. Drug Prescription Volume U.S. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/238702/us-total-medical-prescriptions-issued/ (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Schumock, G.T.; Li, E.C.; Suda, K.J.; Matusiak, L.M.; Hunkler, R.J.; Vermeulen, L.C.; Hoffman, J.M. National Trends in Prescription Drug Expenditures and Projections for 2014. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2014, 71, 482–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumock, G.T.; Li, E.C.; Suda, K.J.; Wiest, M.D.; Stubbings, J.; Matusiak, L.M.; Hunkler, R.J.; Vermeulen, L.C. National Trends in Prescription Drug Expenditures and Projections for 2015. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2015, 72, 717–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumock, G.T.; Li, E.C.; Suda, K.J.; Wiest, M.D.; Stubbings, J.; Matusiak, L.M.; Hunkler, R.J.; Vermeulen, L.C. National Trends in Prescription Drug Expenditures and Projections for 2016. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2016, 73, 1058–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumock, G.T.; Li, E.C.; Wiest, M.D.; Suda, K.J.; Stubbings, J.; Matusiak, L.M.; Hunkler, R.J.; Vermeulen, L.C. National Trends in Prescription Drug Expenditures and Projections for 2017. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2017, 74, 1158–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schumock, G.T.; Stubbings, J.; Wiest, M.D.; Li, E.C.; Suda, K.J.; Matusiak, L.M.; Hunkler, R.J.; Vermeulen, L.C. National Trends in Prescription Drug Expenditures and Projections for 2018. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2018, 75, 1023–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumock, G.T.; Stubbings, J.; Hoffman, J.M.; Wiest, M.D.; Suda, K.J.; Rim, M.H.; Tadrous, M.; Tichy, E.M.; Cuellar, S.; Clark, J.S.; et al. National Trends in Prescription Drug Expenditures and Projections for 2019. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2019, 76, 1105–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichy, E.M.; Schumock, G.T.; Hoffman, J.M.; Suda, K.J.; Rim, M.H.; Tadrous, M.; Stubbings, J.; Cuellar, S.; Clark, J.S.; Wiest, M.D.; et al. National Trends in Prescription Drug Expenditures and Projections for 2020. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2020, 77, 1213–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OTC Use Statistics—Consumer Healthcare Products Association. Available online: https://www.chpa.org/about-consumer-healthcare/research-data/otc-use-statistics (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Mikulic, M. Prescription Drug Spending in U.S. 1960–2020. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/184914/prescription-drug-expenditures-in-the-us-since-1960/ (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Wieczorkiewicz, S.M.; Kassamali, Z.; Danziger, L.H. Behind Closed Doors: Medication Storage and Disposal in the Home. Ann. Pharmacother. 2013, 47, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhoy, I.S.; Daughton, C.G. Beyond the Medicine Cabinet: An Analysis of Where and Why Medications Accumulate. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, A.V.; Sakharkar, P.; Zargarzadeh, A.; Tai, B.W.B.; Hess, K.; Hata, M.; Mireles, R.; Ha, C.; Park, T.J. Taking Stock of Medication Wastage: Unused Medications in US Households. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. 2015, 11, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeng, D.D.; Tom, L.A.; Wright, E.A. Patient Characteristics and Healthcare Utilization Patterns Associated with Unused Medications among Medicare Patients. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. 2017, 13, 1090–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekker, C.L.; Gardarsdottir, H.; Egberts, A.C.G.; Molenaar, H.A.; Bouvy, M.L.; van den Bemt, B.J.F.; Hövels, A.M. What Does It Cost to Redispense Unused Medications in the Pharmacy? A Micro-Costing Study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2019, 19, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, M.R.; Chew, L. Turning Waste Medicines to Cost Savings: A Pilot Study on the Feasibility of Medication Recycling as a Solution to Drug Wastage. Palliat. Med. 2017, 31, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, P.A.; Jibilian, A.; Herasme, O.; Valencia, J.; Hernandez, E.C.; Jurado, S.; Aguais, J. The Efficacy of a US-Based Medicine Recycling Program Delivering Antiretroviral Drugs Worldwide. J. Int. Assoc. Physicians AIDS Care 2009, 8, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briones, N. Current State of Drug Recycling Programs in the United States. Available online: https://chicagounbound.uchicago.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1121&context=international_immersion_program_papers (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- HIV Medicine Recycling Program. Available online: https://aidforaids.org/hiv-recycling-program/ (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- About RAMP—RAMP—Recycled AIDS Medicine Program. Available online: http://rampusa.org/about-ramp/ (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- Nicoli, F.; Paudel, D.; Bresciani, G.; Rodi, D.; Siniscalchi, A. Donation Programme of Returned Medicines: Role of Donors and Point of View of Beneficiaries. Int. Health 2018, 10, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughton, C.G.; Ruhoy, I.S. PharmEcovigilance: Aligning Pharmacovigilance with Environmental Protection. In An Introduction to Environmental Pharmacology; Rahman, S.Z., Shahid, M., Gupta, V., Eds.; Ibn Sina Academy: Aligarh, India, 2008; pp. 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Bekker, C.; van den Bemt, B.; Egberts, T.C.; Bouvy, M.; Gardarsdottir, H. Willingness of Patients to Use Unused Medication Returned to the Pharmacy by Another Patient: A Cross-Sectional Survey. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e024767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker, C.L.; Gardarsdottir, H.; Egberts, T.C.G.; Bouvy, M.L.; van den Bemt, B.J.F. Redispensing of Medicines Unused by Patients: A Qualitative Study among Stakeholders. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2017, 39, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshemari, A.; Breen, L.; Quinn, G.; Sivarajah, U. Can We Create a Circular Pharmaceutical Supply Chain (CPSC) to Reduce Medicines Waste? Pharmacy 2020, 8, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donyai, P.; McCrindle, R.; Hui, T.K.L.; Sherratt, R.S. Stakeholder Views on the Idea of Medicines Reuse in the UK. Pharmacy 2021, 9, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhoy, I.S.; Daughton, C.G. Types and Quantities of Leftover Drugs Entering the Environment via Disposal to Sewage—Revealed by Coroner Records. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 388, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, L.; Stokes, J.A.; Purdie, D.M.; Woodward, M.; Roberts, M.S. Medication Management at Home: Medication-Related Risk Factors Associated with Poor Health Outcomes. Age Ageing 2005, 34, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gummin, D.D.; Mowry, J.B.; Beuhler, M.C.; Spyker, D.A.; Brooks, D.E.; Dibert, K.W.; Rivers, L.J.; Pham, N.P.T.; Ryan, M.L. 2019 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 37th Annual Report. Clin. Toxicol. 2020, 58, 1360–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gummin, D.D.; Mowry, J.B.; Spyker, D.A.; Brooks, D.E.; Beuhler, M.C.; Rivers, L.J.; Hashem, H.A.; Ryan, M.L. 2018 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 36th Annual Report. Clin. Toxicol. 2019, 57, 1220–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gummin, D.D.; Mowry, J.B.; Spyker, D.A.; Brooks, D.E.; Osterthaler, K.M.; Banner, W. 2017 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 35th Annual Report. Clin. Toxicol. 2018, 56, 1213–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gummin, D.D.; Mowry, J.B.; Spyker, D.A.; Brooks, D.E.; Fraser, M.O.; Banner, W. 2016 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 34th Annual Report. Clin. Toxicol. 2017, 55, 1072–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mowry, J.B.; Spyker, D.A.; Brooks, D.E.; Zimmerman, A.; Schauben, J.L. 2015 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 33rd Annual Report. Clin. Toxicol. 2016, 54, 924–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFee, R.B.; Caraccio, T.R. “Hang Up Your Pocketbook”—An Easy Intervention for the Granny Syndrome: Grandparents as a Risk Factor in Unintentional Pediatric Exposures to Pharmaceuticals. J. Am. Osteopath Assoc. 2006, 106, 405–411. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, G.R.; Woodward, R.W.; Ho, M. The Growing Impact of Pediatric Pharmaceutical Poisoning. J. Pediatrics 2012, 160, 265270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovegrove, M.C.; Weidle, N.J.; Budnitz, D.S. Trends in Emergency Department Visits for Unsupervised Pediatric Medication Exposures, 2004-2013. Pediatrics 2015, 136, e821–e829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gregorian, R.; Marrett, E.; Sivathanu, V.; Torgal, M.; Shah, S.; Kwong, W.J.; Gudin, J. Safe Opioid Storage and Disposal: A Survey of Patient Beliefs and Practices. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, J.; Reddy, A.; de la Cruz, M.; Wu, J.; Liu, D.; Bruera, E.; Todd, K.H. Frequency of Unsafe Storage, Use, and Disposal Practices of Opioids among Cancer Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department. Palliat. Support Care 2017, 15, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy-Hendricks, A.; Gielen, A.; McDonald, E.; McGinty, E.E.; Shields, W.; Barry, C.L. Medication Sharing, Storage, and Disposal Practices for Opioid Medications Among US Adults. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 1027–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maughan, B.C.; Hersh, E.V.; Shofer, F.S.; Wanner, K.J.; Archer, E.; Carrasco, L.R.; Rhodes, K.V. Unused Opioid Analgesics and Drug Disposal Following Outpatient Dental Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2016, 168, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neill, L.A.; Kim, H.S.; Cameron, K.A.; Lank, P.M.; Patel, D.A.; Hur, S.I.; Opsasnick, L.A.; Curtis, L.M.; Eifler, M.R.; Courtney, D.M.; et al. Who Is Keeping Their Unused Opioids and Why? Pain Med. 2020, 21, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.; de la Cruz, M.; Rodriguez, E.M.; Thames, J.; Wu, J.; Chisholm, G.; Liu, D.; Frisbee-Hume, S.; Yennurajalingam, S.; Hui, D.; et al. Patterns of Storage, Use, and Disposal of Opioids Among Cancer Outpatients. Oncologist 2014, 19, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCauley, J.L.; Back, S.E.; Brady, K.T. Pilot of a Brief, Web-Based Educational Intervention Targeting Safe Storage and Disposal of Prescription Opioids. Addict. Behav. 2013, 38, 2230–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, J.E.; Campagna, E.; Dart, R.C. RADARS System Poison Center Investigators The Underrecognized Toll of Prescription Opioid Abuse on Young Children. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2009, 53, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, M.; Lovegrove, M.C.; Geller, R.J.; Pomerleau, A.C.; Sapiano, M.R.P.; Weidle, N.J.; Morgan, B.W.; Budnitz, D.S. Circumstances Involved in Unsupervised Solid Dose Medication Exposures among Young Children. J. Pediatr. 2020, 219, 188195.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortinovis, C.; Pizzo, F.; Caloni, F. Poisoning of Dogs and Cats by Drugs Intended for Human Use. Vet. J. 2015, 203, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, D.M.; Granzin, K.L. Consumer Logistics: The Inventory Subsystem. In Proceedings of the 1984 Academy of Marketing Science (AMS) Annual Conference; Lindquist, J.D., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Stiff, R.; Johnson, K.; Tourk, K.A. Scarcity and Hoarding: Economic and Social Explanations and Marketing Implications. ACR N. Am. Adv. 1975, 2, 203–216. [Google Scholar]
- Center for Drug Evaluation and Disposal of Unused Medicines: What You Should Know. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/safe-disposal-medicines/disposal-unused-medicines-what-you-should-know (accessed on 12 June 2021).
- Batt, A.L.; Bruce, I.B.; Aga, D.S. Evaluating the Vulnerability of Surface Waters to Antibiotic Contamination from Varying Wastewater Treatment Plant Discharges. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 142, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, R.; Ternes, T.; Haberer, K.; Kratz, K.-L. Occurrence of Antibiotics in the Aquatic Environment. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 225, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassmeyer, S.T.; Hinchey, E.K.; Boehme, S.E.; Daughton, C.G.; Ruhoy, I.S.; Conerly, O.; Daniels, R.L.; Lauer, L.; McCarthy, M.; Nettesheim, T.G.; et al. Disposal Practices for Unwanted Residential Medications in the United States. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockholms Lans Landsting 2014–2015 Enviornmentally Classified Pharmaceuticals. Available online: https://noharm-global.org/sites/default/files/documents-files/2633/Environmental%20classified%20pharmaceuticals%202014-2015%20booklet.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Masnoon, N.; Shakib, S.; Kalisch-Ellett, L.; Caughey, G.E. What Is Polypharmacy? A Systematic Review of Definitions. BMC Geriatr. 2017, 17, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zia, A.; Kamaruzzaman, S.B.; Tan, M.P. Polypharmacy and Falls in Older People: Balancing Evidence-Based Medicine against Falls Risk. Postgrad. Med. 2015, 127, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prithviraj, G.K.; Koroukian, S.; Margevicius, S.; Berger, N.A.; Bagai, R.; Owusu, C. Patient Characteristics Associated with Polypharmacy and Inappropriate Prescribing of Medications among Older Adults with Cancer. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2012, 3, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, J.P.; Shakib, S.; Singhal, N.; Hogan-Doran, J.; Prowse, R.; Johns, S.; Bell, J.S. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Polypharmacy in Older People with Cancer. Support. Care Cancer 2014, 22, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, O.; Gnjidic, D.; Hilmer, S.N.; Naganathan, V.; McLachlan, A.J. Investigating Polypharmacy and Drug Burden Index in Hospitalised Older People. Intern. Med. J. 2013, 43, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcum, Z.A.; Gellad, W.F. Medication Adherence to Multi-Drug Regimens. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2012, 28, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saljoughian, M. Polypharmacy and Drug Adherence in Elderly Patients. Available online: https://www.uspharmacist.com/article/polypharmacy-and-drug-adherence-in-elderly-patients (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- Franchi, C.; Ardoino, I.; Ludergnani, M.; Cukay, G.; Merlino, L.; Nobili, A. Medication Adherence in Community-Dwelling Older People Exposed to Chronic Polypharmacy. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2021, 75, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RED BOOK Online. IBM Micromedex [Database Online]. Truven Health Analytics/IBM Watson Health. 2021. Available online: https://www.micromedexsolutions.com (accessed on 16 July 2021).
- US Census Bureau, C.H.S. Statistical Abstracts—History—U.S. Census Bureau. Available online: https://www.census.gov/history/www/reference/publications/statistical_abstracts.html (accessed on 19 July 2021).
- Chronic Diseases in America | CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/chronicdisease/resources/infographic/chronic-diseases.htm (accessed on 12 June 2021).
- Michas, F. Leading Diagnoses for Primary Care Physicians U.S. 2019. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1029294/leading-diagnoses-for-primary-care-physicians-us/ (accessed on 12 June 2021).
- Mental Health By the Numbers | NAMI: National Alliance on Mental Illness. Available online: https://www.nami.org/mhstats (accessed on 12 June 2021).
- National Health Index. Available online: https://www.bcbs.com/the-health-of-america/health-index/national-health-index (accessed on 12 June 2021).
- Funk, O.G.; Yung, R.; Arrighi, S.; Lee, S. Medication Storage Appropriateness in US Households. Innov. Pharm. 2021, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tips to Prevent Poisonings | Home and Recreational Safety | CDC Injury Center. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/homeandrecreationalsafety/poisoning/preventiontips.htm (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Maton, B.L.; Simmonds, E.E.; Lee, J.A.; Alwood, A.J. The Use of High-Dose Insulin Therapy and Intravenous Lipid Emulsion to Treat Severe, Refractory Diltiazem Toxicosis in a Dog. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2013, 23, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, E.T.; Cucciare, M.A.; Trafton, J.A. What Do Patients Do with Unused Opioid Medications? Clin. J. Pain 2014, 30, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) Overview. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/rcra/resource-conservation-and-recovery-act-rcra-overview (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Veolia Medical Waste Disposal, Now and in the Future. Available online: http://blog.veolianorthamerica.com/medical-waste-disposal-now-and-future (accessed on 2 August 2021).
- National Conference of State Legislatures State Prescription Drug Return, Reuse and Recycling Laws. Available online: https://www.ncsl.org/research/health/state-prescription-drug-return-reuse-and-recycling.aspx (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- American Society of Clinical Oncology 2020 Drug Repository Position Statement. Available online: https://www.asco.org/sites/new-www.asco.org/files/content-files/advocacy-and-policy/documents/2020-DrugRepositoryPositionStatement.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- Alhamad, H.; Patel, N.; Donyai, P. How Do People Conceptualise the Reuse of Medicines? An Interview Study. Int. J. Pharm. Pract. 2018, 26, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, T.K.L.; Donyai, P.; McCrindle, R.; Sherratt, R.S. Enabling Medicine Reuse Using a Digital Time Temperature Humidity Sensor in an Internet of Pharmaceutical Things Concept. Sensors 2020, 20, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, T.K.L.; Mohammed, B.; Donyai, P.; McCrindle, R.; Sherratt, R.S. Enhancing Pharmaceutical Packaging through a Technology Ecosystem to Facilitate the Reuse of Medicines and Reduce Medicinal Waste. Pharmacy 2020, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SIRUM Saving Medicine: Saving Lives. Available online: https://www.sirum.org/ (accessed on 3 October 2021).
- Kaldy, J. Program Turns Discarded Drugs Into Lifesavers for Needy. Caring Ages 2015, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Number of Medications Stored in Households | Number of Househods Storing at Least One Medication (n = 154) | p-Value a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| With at Least One Resident Older than 65 Years (n = 46) | Without a Resident Older than 65 Years (n = 108) | ||
| 1–4 medication(s) | 102 (66.2%) | 0.10 | |
| 27 (58.7%) | 75 (69.4%) | ||
| 5–10 medications | 42 (27.3%) | ||
| 13 (28.3%) | 29 (26.9%) | ||
| >10 medications | 10 (6.5%) | ||
| 6 (13%) | 4 (3.7%) | ||
| Prescription Medications | OTC Medications | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Controlled | Controlled Substances | ||||
| Indications | n = 236 | Indications | n = 25 | Indications | n = 143 |
| Cardiovascular therapy | 79 (33.5%) | Mental health c | 15 (60%) | Pain | 53 (37.1%) |
| Mental health | 44 (18.6%) | Pain d | 9 (36%) | Supplements | 26 (18.2%) |
| Endocrine therapy | 39 (16.5%) | Weight loss | 1 (4%) | Gastrointestinal therapy | 19 (13.3%) |
| Antibiotics | 9 (3.8%) | Cardiovascular therapy and pain | 11 (7.7%) | ||
| Others b | 57 (24.1%) | Others e | 34 (23.8%) | ||
| Frequency of Use (n = 465) | |
|---|---|
| Taken daily | 306 (65.8%) |
| Taken as needed | 130 (28%) |
| Not taken, saving for future | 12 (2.6%) |
| Not taken, would like to discard | 7 (1.5%) |
| Other | 10 (2.2%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Schommer, J.C. Medication Use and Storage, and Their Potential Risks in US Households. Pharmacy 2022, 10, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy10010027
Lee S, Schommer JC. Medication Use and Storage, and Their Potential Risks in US Households. Pharmacy. 2022; 10(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy10010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, SuHak, and Jon C. Schommer. 2022. "Medication Use and Storage, and Their Potential Risks in US Households" Pharmacy 10, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy10010027
APA StyleLee, S., & Schommer, J. C. (2022). Medication Use and Storage, and Their Potential Risks in US Households. Pharmacy, 10(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy10010027







