Abstract
This article considers the identification and classification of salient Aktionsart properties in Anindilyakwa (Gunwinyguan, Australia). Through examining the grammatically permissible (and impermissible) distribution and co-occurrence of various temporal adverbials and morpho-syntactic structures, I identify key Aktionsart properties exhibited in Anindilyakwa. I demonstrate that the properties of dynamism and atomicity are particularly important to consider in this language, while telicity is less prominent. The detailed description and analysis of Aktionsart properties in this article contributes towards a more nuanced understanding of the aspectuo-temporal system of Anindilyakwa. In addition, it provides novel perspectives with which to consider cross-linguistic aspectuo-temporal research, particularly with a focus on smaller-scale, under-described languages.
1. Introduction
This article provides an in-depth examination of Aktionsart properties in Anindilyakwa (Gunwinyguan), the language of the Groote Eylandt archipelago, in the Gulf of Carpentaria, Australia.
Research into Aktionsart1 has a long and rich history in the philosophic and linguistic literature, however the vast majority of this research has been heavily biased towards a handful of widely-spoken, global languages. Over the last few decades efforts to investigate this topic cross-linguistically have increased (cf. Smith 1996; Tatevosov 2002), however there remains almost no comprehensive research in this domain considering Australian Indigenous languages.2 This article seeks to bridge this gap, providing a detailed account of Aktionsart in an Australian language.
The intersection between lexical properties of the verbal complex (i.e., Aktionsart) and the system of inflectional marking of the verb is integral to TAM expression in Anindilyakwa. Anindilyakwa demonstrates a high degree of aspectuo-temporal underspecification in its inflectional system, and therefore Aktionsart properties (as well as discourse and contextual factors) are particularly salient in distinguishing between different aspectuo-temporal readings. A detailed understanding of Aktionsart is therefore essential.
The article is organised as follows. Section 2 provides a typological background of Anindilyakwa, in addition to an overview of the data and methods used in this study. In Section 3, I provide an overview and a brief history of research within the domain of Aktionsart, highlighting in particular the influential work of Vendler (1957) in Section 3.1, along with the key Aktionsart parameters that I consider in this study in Section 3.2 and Section 3.3. I consider cross-linguistic perspectives relating to Aktionsart in Section 3.4 before focusing on language-specific Aktionsart features and how they are established in Anindilyakwa in Section 4. Section 5 provides concluding remarks and avenues for future research.
2. Anindilyakwa
Anindilyakwa is a Gunwinyguan language spoken on the Groote Eylandt archipelago, east Arnhem Land, Northern Territory (see Figure 1). It is a vibrant language, spoken by over 1400 people and is one of the few Australian languages still being acquired by children.3
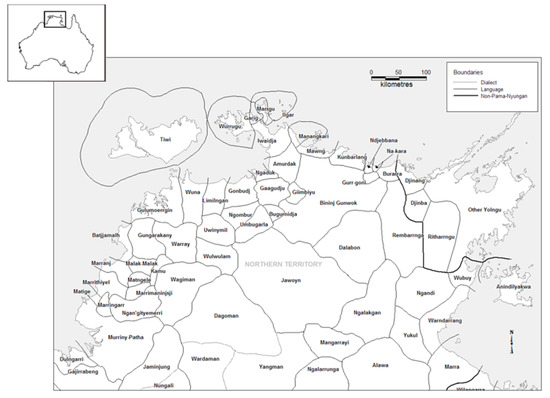
Figure 1.
Languages of norther Australia (Harvey 2008).
2.1. Typological Overview
Typologically, Anindilyakwa has been noted for its polysynthetic structure and morphological complexity. It is a head-marking language, marking core arguments on the verb. It has a productive system of nominal incorporation, and employs various argument-changing affixes within the verbal template (Bednall 2020, p. 7). The verbal complex is the most elaborate word class in the language, comprising verb stems that historically consist of an uninflecting verb root plus an inflecting element, and involve multiple (2+) discontinuous morphs to express different temporal, aspectual and modal categories. Compare, for instance, example (1) expressing a past temporal reading with realis-V-past verbal marking, to example (2) expressing a future temporal reading with irrealis-V-npst marking.
| 1. | James n-angaba ni-yedha-ngə=ma James 3m.that.over.there real.3m-arrive-pst=mut Numbulwar arakba place.name compl.act ‘James already arrived in Numbulwar’ (JL, JRB1-018-01, 00.04.07) |
| 2. | nganyangwa nabə-rraka kəni-yedhe-na=ma 1.pro.poss 3m.son-1kin irr.3m-arrive-npst=mut adhənuba in.short.time ‘My son will arrive soon’ (JL, JRB1-044-01, 00:11:37–00:11:44) |
2.2. Data for This Study
Data for this study are drawn primarily from a corpus collected by the author in 2016–2019.4 Data were documented through a variety of methods in order to produce results that are as robust as possible, including (i) semi-structured elicitation using visual video stimuli,5 (ii) tense-aspect questionnaires, and (iii) grammaticality judgment tasks. These all targeted different kinds of aspectuo-temporal categories, Aktionsart parameters and complex event structures. These elicited and semi-elicited tasks were complemented by a collection of audio-recorded and text-based narratives.
Aktionsart tests involved asking Anindilyakwa language consultants for judgements of acceptability, truth, and felicity of sentences in Anindilyakwa. Data involving less complex situations were first examined (considering, for instance, situations involving no change (e.g., n-akəna nenəngkwarba n-ambilya yelakwa (3m-that 3m.man real.3m-stay.pst here) ‘the man stayed here’; stative, durative, non-atomic) or a clear change of state (e.g., n-akəna nenəngkwarba ni-jungə-na (3m-that 3m.man real.3m-die-pst) ‘the man died’; dynamic, instantaneous, atomic), before then turning to more complex event structures.
In addition to data collected via careful elicitation, natural narrative corpus data were examined to confirm hypotheses based on Aktionsart tests. For example, the distribution and collocations of adverbials that were examined in the Aktionsart tests were investigated in the corpus data, in order to confirm the results that emerged from the elicited tests and activities. The combination of careful elicitation, speakers’ grammaticality judgements and naturalistic data (comprised of oral narratives and texts) means that we can be more confident of the properties discussed and the claims made in this article. Of course, the variables examined are not necessarily exhaustive, and further research in this area could further uncover other variables of relevance.
3. Aktionsart
Aktionsart refers to the intrinsic aspectual properties of the verbal complex, determined by the disambiguated, contextualised semantics of the verbal complex (Caudal 2012, p. 272). I assume a two-component theory of aspect (à la Smith 1997), where Aktionsart is distinguished from viewpoint aspect. Viewpoint aspect, in contrast, refers to the grammatical marking of the speaker’s perspective of the event, denoting how much of the event is made visible (e.g., the whole event, or only a subpart of an event), and is generally expressed through inflectional tense-aspect marking.
In examining Aktionsart, it is the aspectual properties of the verbal complex (i.e., the verb and its arguments; the verb as interpreted in combination with complements, adjuncts and modifiers) that we are concerned with. While it has sometimes been assumed that the domain under examination is the verb (thus Aktionsart being a classification of verbs themselves), Verkuyl (1972) and Dowty (1972, 1979) (and much subsequent literature) have made clear that Aktionsart should be understood not as a lexical parameter, but a structural one, involving sentence meaning: the verbal complex/constellation (comprising of the verb, its arguments, adjuncts and modifiers) all of which play a role in determining Aktionsart properties (Moens 1987, pp. 59–60).
While these intrinsic properties are fundamental to aspectual expression across the world’s languages, the salience of Aktionsart properties and how they interact with other aspectuo-temporal elements (in particular, with viewpoint aspect, tense and (aspectuo-temporal) adverbials) differ substantially cross-linguistically (cf. Tatevosov 2002).
3.1. Vendler Classes
The place of Aktionsart in the modern semantics literature is couched in research on Indo-European languages (particularly English), and draws principally on the work of philosopher Zeno Vendler. Vendler’s (1957) seminal article proposed that clusters of syntactic properties can be used to characterise different situation types (i.e., general semantic categories that represent classes of idealised situations, that are organised according to their semantic temporal properties) (Smith 1996, p. 228). Vendler proposed four such Aktionsart ‘classes’, used to classify situations: States, Activities, Achievements and Accomplishments. These four classes, along with a subsequent fifth class, Semelfactives (cf. Comrie 1976), have consequently proven very influential in Aktionsart research. Table 1 lists these five classes, along with the intrinsic temporal properties by which they are frequently differentiated.

Table 1.
Properties distinguishing Aktionsart classes (Smith 1997, p. 20).
As shown in Table 1, the temporal properties of dynamism (i.e., whether a situation is perceived as being static or dynamic), telicity (i.e., whether or not there is an inherent endpoint to a situation), and durativity (i.e., the duration of a situation) have traditionally been acknowledged as central domains involved in Aktionsart (discussed further in Section 3.2). In more recent work, however, further proposals for distinguishing Aktionsart parameters have been made, taking into account situations that don’t neatly fit the Vendler system. In particular, these include events involving scalarity (including e.g., gradual changes of state (i.e., degree achievements à la Dowty 1979)) (cf. Caudal 2005; Kennedy and McNally 1999, 2005). This is considered in relation to Anindilyakwa in Section 4.
While Vendler’s Aktionsart classes have been very influential in research on Aktionsart, the diagnostics used to isolate and differentiate these temporal distinctions are heavily based on English data. It is clearly problematic to make cross-linguistic assumptions based on just a small subset of languages, thus it is imperative that Aktionsart parameters are established separately for individual languages, using language-specific means (Smith 1996, p. 228). This is explored further in Section 3.4 and Section 4.
3.2. Aktionsart Properties
As demonstrated in Table 1, dynamism, telicity, and durativity have traditionally been considered central temporal properties associated with Aktionsart. I acknowledge these three properties. However, the core temporal properties I assume are dynamism and telicity, along with atomicity (i.e., whether an event can be split up into intermediary subparts, or involves only a one-step change of state). The property of durativity is also discussed in relation to telicity and atomicity. I outline these properties in Section 3.2.1, Section 3.2.2, Section 3.2.3 and Section 3.2.4.
In this section I also briefly consider how these properties are related to stage structure (i.e., how situations are decomposed into distinct stages).
3.2.1. Dynamism
Dynamism is the quality determining whether a situation is static or dynamic. Statives consist of a single, undifferentiated period (i.e., which entails no change). Statives differ from atelic dynamic events (i.e., activities), in that dynamic events like activities involve some agent or controller of the event (including implicit controllers, such as natural force), while statives do not. Unless there is some disturbance, statives have the capacity to continue indefinitely, without effort (Comrie 1976). Examples of statives in English are ‘the teacher is at school’ and ‘the student knows the answer’, while examples of dynamic events in English are ‘the athlete runs’, ‘the choir sings’ and ‘the train leaves the station’.
Stative situations can be further classified into stage-level and individual-level statives. Stage-level statives are associated with expressing temporary or accidental properties (such as ‘the child is thirsty’ or ‘the customer is angry’), while individual-level statives are associated with permanent or inherent properties (such as ‘John is short’ or ‘Mary is a doctor’) (Carlson 1977, 1980).
3.2.2. Telicity
Telicity is concerned with the presence or absence of some endpoint or limit. Telic situations possess a ‘natural finishing point beyond which the same event cannot continue, because it is finished’ (Kearns 2000, p. 202). Thus, telic situations include sentences that encompass the final endpoint in their inherent meaning, such as English sentences involving ‘to finish’, ‘to arrive’ and ‘to fill up’. Example (3) provides an example of a telic (dynamic, non-atomic, durative) situation in English.
| 3. | ‘Mary walked to school in an hour’ (Smith 1997, p. 43) |
In contrast, atelic situations do not have an intrinsic endpoint or termination point specified. Their endpoints are arbitrary, with the situation able to continue indefinitely (Kearns 2000, p. 202) (such as stative situations like ‘John believes Mary’ and ‘Joan knows Spanish’, and dynamic events like ‘Jill swims’ or ‘Patrick sits on the beach’). Example (4) provides an example of an atelic (dynamic, non-atomic, durative) situation in English.
| 4. | ‘Mary walked in the park for an hour’ (Smith 1997, p. 43) |
3.2.3. Atomicity
Atomic events involve a holistic, one-step change-of-state which cannot be interrupted and then resumed. They are devoid of proper subparts (i.e., they are comprised of only two points in time (a minimal and a maximal one) needed for the change of state to occur), e.g., ‘the man died’, ‘the bomb exploded’. Non-atomic situations, on the other hand, involve a complex change-of-state, and its development can be measured along intermediary subparts (which follow a complex development scale) (Caudal 2005, p. 104). (Non-)atomicity interacts closely with the notion of incrementality (i.e., a property of verbs whose development can be mapped onto the internal structure of one of their arguments, as in (Dowty 1991)) (Caudal 1999, p. 3). Tests for atomicity in English include the ability to occur with ‘finish’, the perfect progressive, and degree adverbials (such as ‘completely’), as shown in examples (5) and (6) (Caudal 2005, p. 104).
| 5. | a. ‘The boy finished eating his porridge’ (non-atomic) b. ‘The boy has been eating his porridge’ c. ‘The boy ate his porridge completely’ (Caudal 2005, p. 104) |
| 6. | a. *‘The boy finished leaving’6 (atomic) b. #‘The boy has been leaving’ (ok with iterative reading) c. #‘The boy left completely’ (ok with frequentative) |
While atomic events are generally non-durative, and non-atomic situations generally durative, this is not always necessarily the case: atomic events can be durative (as in example (7)), and non-atomic events can be instantaneous (as in example (8)). Atomicity should not be confused with punctuality, which is a combination of both atomicity plus non-durativity (Caudal 2005, p. 105).
| 7. | ‘The supernova exploded’ (atomic, durative) a. ?‘The supernova finished exploding’ b. *‘The supernova has been exploding’ c. *‘The supernova exploded completely’ |
| 8. | ‘John crushed the seed’ (non-atomic, instantaneous) a. ‘John finished crushing the seed’ b. ‘John has been crushing the seed’ c. ‘John crushed the seed completely’ |
3.2.4. Durativity
Durativity is a temporal concept, concerned with the temporal extent or duration of a situation. Durative situations occur (or have the potential to occur) with some temporal extent (such as ‘she talks’, ‘he eats’, ‘the mechanic fixes the car’ or ‘the explorer climbs a mountain’ in English), while non-durative situations are momentary transitions from one state of affairs to another (such as ‘the visitors arrive’, ‘he finds the key’ or ‘the dog dies’ in English). Durative events are generally non-atomic, although as mentioned above, this is not always the case.
3.3. Stage Structure
In discussing Aktionsart properties, it is also helpful to consider stage structure. Stage structure is topological, involving situation ‘chunks’: preparatory, inner, and result stages (cf. Moens and Steedman 1988).
Following Caudal and Roussarie (2000) and Caudal (2005, 2006), I assume that aspectual properties of each (disambiguated, contextualised) verbal complex occur in a stage structure, in which situations are decomposed into distinct stages (or subevents):
- (i)
- Preparatory stages: causal event stages involved in some types of atomic telic events. Preparatory stages are selected (e.g., in English) under prospective readings of the past progressive (e.g., ‘Mona was reaching the summit’). These stages are peripheral to the stage structure (i.e., ‘detachable’ from the stage structure (cf. Smith 1997), having a presuppositional status (they remain valid under negation and modals—e.g., John did not win the race nevertheless entails that John took part in the race);
- (ii)
- Inner stages: ‘core’ stages of all situations (what Smith (1997) calls ‘developments’). If a situation is telic then the inner stages include its culmination. Inner stages of telic situations are selected (e.g., in English) by unmarked uses of the past progressive or simple past (e.g., ‘Mona reached the summit’), and if non-atomic, by ‘begin’ and ‘start’;
- (iii)
- Result stages: stative result stages, applicable to all situations (although with major differences apparent between telic and atelic situations). They can be selected (e.g., in English) by the perfect (e.g., ‘Mona has reached the summit’) (Caudal and Roussarie 2000, p. 362).
These three stages are demonstrated in Figure 2, for the atomic event ‘Mona reach the summit’.
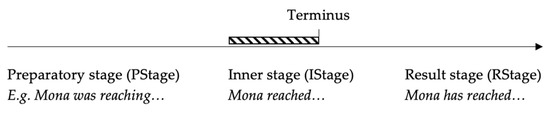
Figure 2.
Stage structure for verbal complex ‘Mona reach the summit’ (Caudal and Roussarie 2000, p. 362).
3.4. Typological Perspective
As has been established in Section 3.1, Section 3.2 and Section 3.3, Vendler’s classes and the diagnostic tests used to establish Aktionsart properties of different situations are heavily biased to Indo-European (particularly English) data. As such, they are not necessarily transferable for use with other languages cross-linguistically. Despite this, a widespread (often tacit) assumption is that the parameters and notions on which Vendler’s classes are established are universal (i.e., are not subject to cross-linguistic variation). A consequence of this, as pointed out by Tatevosov (2002, p. 322), has been that many linguists have worked under the assumption that situations in every language can be classified into Vendlerian classes as established for English (perhaps with minor modifications), as has been displayed by dozens of language-specific studies of aspect (e.g., cf. language-specific chapters in Bache et al. 1994).
While it is not a trivial task to identify language-specific Aktionsart parameters in a given language (Filip 2012, p. 724), clearly it is imperative for these parameters to be established separately for individual languages, using language-specific means (Smith 1996, p. 228), and that the cross-linguistic application of such diagnostic tests is not taken for granted (Filip 2012; Sasse 2002).
Despite the English and more broadly Indo-European bias in Aktionsart research, acknowledgement and examination of cross-linguistic variation with respect to Aktionsart has been the subject of various studies. Notable works include that of Smith (1997), which considers Aktionsart in Mandarin Chinese and Navajo (in addition to the more widely studied English, French and Russian), with Navajo examined in particular detail also in Smith (1996). Tatevosov (2002) provides probably the most extensive investigation to date examining cross-linguistic variation relating to Aktionsart and provides an in-depth discussion about methods for cross-linguistic approaches to examining Aktionsart.
4. Aktionsart in Anindilyakwa
Intrinsic temporal properties of the verbal complex are integral to the system of aspectual expression in Anindilyakwa. Examining and understanding Aktionsart in this language is particularly relevant given that its inflectional system demonstrates a high degree of aspectuo-temporal underspecification.
In Anindilyakwa TAM expression is realised inflectionally through combining (at least) two obligatory, discontinuous morphological slots of the verbal template. One of three series of portmanteau prefixes (realis; irrealis; deontic) combines with one of four TAM suffixes (non-past; past; underspecified (Ø); potential), resulting in different possible TAM readings, including the aspectually underspecified realis-V-past and aspectuo-temporally underspecified realis-V-usp. Table 2 shows the different possible inflectional combinations, and some of their core TAM readings (for further information see Bednall 2020, chp. 6 and 9).

Table 2.
Combinations of prenominal prefix and TAM suffix paradigms (positive polarity).7
Given the aspectuo-temporally underspecified nature of the inflectional system, Aktionsart properties (as well as discourse and contextual factors) often play an important role in distinguishing between different aspectuo-temporal readings. Thus, understanding Aktionsart properties and the intersection between lexical properties of the verbal complex and the system of inflectional verbal marking is key to understanding the overall aspectual system.
In this section I identify salient Aktionsart properties in Anindilyakwa by examining the grammatically permissible (and impermissible) distribution and co-occurrence of various temporal adverbials (primarily measure adverbials and indirect duration adverbials), as well as through examining morpho-syntactic properties of reduplication patterns and inflectional TAM marking. Through the examination of these Aktionsart properties and the variables with which they can be identified, I demonstrate that the properties of dynamism and atomicity are particularly salient in Anindilyakwa, while telicity is less prominent.
4.1. Dynamism
Dynamism (i.e., contrasting dynamic vs. stative situations) is a salient semantic feature in Anindilyakwa. Cross-linguistically, statives are stable, on-going situations that entail that no change takes place, and are often less-associated with the expression of agentivity and volition than dynamic situations (Smith 1996, p. 234). Consequently, certain grammatical structures involving statives tend to be semantically ill-formed (or at least dispreferred by speakers). In English, for example, many stative imperatives and statives in combination with certain adverbs are semantically ill-formed, as in examples (9) and (10) (Smith 1996, p. 234).
| 9. | #‘Be tall!’ (Smith 1996, p. 234) |
| 10. | *‘She carefully owned the farm’ (Smith 1996, p. 234) |
This imperative ill-formedness is apparent in Anindilyakwa, where dynamic imperatives are semantically well-formed (as in example 11), whereas many stative imperatives are not (as in example 12).
| 11. | yi-rrəngka-Ø ngayuwə=wa deon.2>1-look.at-usp 1.pro=all ‘Look at me!’ (Stokes n.d.-b: 72) |
| 12. | *Ø-məreya-na deon.2-be.hungry-npst ‘Be hungry!’ (JL, fieldnotes, 22/11/2018) |
Grammatical distinctions that can be used to identify statives in English typically involve imperfective (progressive) viewpoint aspect and pseudo-cleft do clauses. These structures are grammatical for dynamic events, while for statives they are more restricted (e.g., *I am knowing the answer; *What she did was know the answer) (Smith 1996, p. 235).
In Anindilyakwa a key grammatical distinction that can be used as a diagnostic of dynamism involves the interaction of Aktionsart with the inflectional TAM system. Verbs inflected with the realis prefix paradigm and the bare stem suffixal paradigm (i.e., a phonologically Ø suffixal slot of the verbal template) can express both past (perfective) and present temporal reference, however these are not available with all situation types. The temporal reference available is dependent on the Aktionsart properties of the verbal complex (along with the contextual interpretation of the verb). For dynamic events, verbs marked with realis-V-usp inflectional marking have the ability to express a past temporal reference point (atomic events, as in example (13), only have a past temporal reading available, while non-atomic events, as in examples (14) and (15), can express both present and past temporal readings), while for stative verbs past temporal reference is disallowed, with present temporal reference being the only option available, as in example (16). See Bednall (2020, chp. 6) for a detailed analysis of the aspectual semantics of realis-V-usp inflectional marking, and a discussion of cross-linguistic research into languages without overt inflectional tense marking in their grammatical systems (i.e., so-called ‘tenseless’ languages, cf. Mucha 2015; Tonhauser 2015).
| 13. | yarrungkwa n-akəna nenəngkwarba nə-lyumadhu-Ø=ma yesterday 3m-that 3m.man real.3m-disappear-usp=mut ‘He disappeared’ (past) *’He disappears’ (present) (JL, JRB1-050-01, 00.27.52–00.27.59) |
| 14. | yarrungkwa n-akəna nenəngkwarba nə-lhəkəraka-Ø yesterday 3m-that 3m.man real.3m-build-usp alhəkəra neut.house ‘Yesterday that man built a house’ (past) (JL, JRB1-060-02, 00.01.33–00.01.38) |
| 15. | enenuwiya n-aka nenəngkwarba nə-lhəkəraka-Ø now 3m-that 3m.man real.3m-build-usp alhəkəra neut.house ‘That man builds a house’ (present) (JL, JRB1-060-02, 00.00.22–00.00.31) |
| 16. | ngayuwa ngu-məreya-Ø anhəngu=wa 1.pro real.1-be.hungry-usp neut.food=all ‘I’m hungry for food’ (present) *I was hungry for food (past) (JL, JRB1-050-01, 00.15.27–00.15.32) |
A summary of the effects of Aktionsart on the aspectuo-temporal properties of verbs inflected with realis-V-usp marking (particularly highlighting the unavailability of past temporal reference for statives) is shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Aktionsart and temporal effects.
4.2. Telicity
Telicity refers to the presence or absence of some endpoint or limit. While there are grammatical correlates for telicity in Anindilyakwa, they are not as salient as other temporal parameters such as atomicity, for instance (which appears to play a much more important role in the acceptable distribution of various grammatical properties of the language; see Section 4.3).
There are distributional correlates for telicity distinctions in many languages, such as in English, where telic verbs are compatible with verbs and adverbials of completion (e.g., ‘finish’; ‘in an hour’), but are ill-formed with verbs and adverbials of simple duration (e.g., ‘stop’, ‘for an hour’). In such languages, the inverse is true of atelic verbs (i.e., compatible with verbs and adverbials of simple duration (e.g., ‘stop’; ‘for an hour’), ill-formed with verbs and adverbials of completion (e.g., ‘finish’; ‘in an hour’)) (Smith 1996, p. 236). Anindilyakwa shows some similar restrictions in its distribution of measure adverbials with different situation types, however while in English these restrictions are based on telicity distinctions, in Anindilyakwa they are dependent upon atomicity properties of the verbal complex (i.e., both telic and atelic events are grammatical and well-formed in combination with measure adverbials; see Section 4.3).
One area in which telicity does appear to play a role in determining acceptable distributional correlates in Anindilyakwa, however, involves reduplication. Verbal reduplication acts as an Aktionsart/stage-aspect modifier with atelic situations, centring on the ‘core’ inner stages in order to focus on the progression of the situation. Reduplicated verb roots of atelic situations can express these prolonged/extended/continuous aspectual readings, in addition to pluractional aspectual readings. With telic situations, however, only pluractional readings may be expressed. Compare, for instance, the atelic situation in (17) to the telic one in (18). Additionally, while reduplicated verb roots of telic situations in positive polarity contexts can be inflected with the bare stem paradigm (i.e., with a phonologically Ø suffixal TAM slot), as in (18), this is not permissible with atelic ones, as in (19).
| 17. | nə-lharrma-lharrma-na=mərra real.3m>neut-redup-chase-npst=mut ‘He keeps on chasing it’ (Leeding 1989, p. 358) |
| 18. | na-lhawu-lhawurradh-Ø, nuw-angkarra-Ø real.neut-redup-return-usp real.neut-run-usp ‘It [the mother cat] kept going back [i.e., repeatedly going and returning], it ran off’ (GL, A3369a Side 1 a3.4, Bujikeda ‘Mother cat’, 00.07.28–00.07.32) |
| 19. | *n-akəna nə-lharrma-lharrma-Ø 3m-that real 3m>neut-redup-chase-usp ‘He keeps on chasing [it]’ (JL, fieldnotes, 19 November 2018) |
Other tests for telicity involving scalarity (such as examining proportionate degree modifiers such as ‘partially’/’completely’) are not productive in Anindilyakwa, given that these adverbials (e.g., enəngangkawura ‘thoroughly, completely’) are multifunctional, being able to express readings associated with both proportionate degree modification (‘thoroughly’/‘completely’), as well as habituality/durational extent (‘always’/’forever’).
4.3. Atomicity
The property of atomicity is a salient semantic feature in Anindilyakwa, key to distinguishing between different kinds of situations. Non-atomic events are those that involve a complex change-of-state whose development can be measured along its sub-parts, and which can be resumed if interrupted (Caudal 2005, p. 104) (e.g., nakəna nenəngkwarba nəmebina emeba ‘the man sings’, dhakəna dhədharrəngka yingilhəkəna mijiyelyuwa ‘the woman goes to the beach’), while atomic events involve a holistic one-step change-of-state (i.e., only two points in time, a minimal and maximal one) (e.g., nijungəna ‘he dies’, yingilyumadhəna ‘she disappears’, narrəngawardena ‘she kills them’, narrenangajina ‘he kills them’).
There are various grammatical distinctions in Anindilyakwa that correlate with properties of atomicity. Durational adverbials (measure adverbials and implied durational adverbials) are particularly useful diagnostics for these parameters in Anindilyakwa. The inflectional T/A system (specifically the combination of the realis pronominal prefix paradigm with the bare stem paradigm (i.e., the phonologically Ø suffixal TAM slot)), is also sensitive to properties of atomicity, observable through the available temporal interpretation of the verbal complex.
4.3.1. Measure Adverbials
In English, measure adverbials (e.g., ‘for an hour’) are compatible with atelic situations, but incompatible with telic ones. Telic situations are either ungrammatical with these adverbials, or they are coerced to behave differently, taking either an ingressive interpretation (relating to the interval before the event takes place), or triggering the interpretation of a durative event with internal stages (e.g., cough for an hour) (Smith 1996, p. 235).
In Anindilyakwa there are two measure adverbials,8 adhuwaya ‘for short [duration of] time’ and amiyerra ‘for long [duration of] time’, used to express the duration of time of a situation. Unlike the examples of English provided above, these are not used as diagnostics of telicity in Anindilyakwa, but rather of atomicity. Both telic and atelic events are grammatical and well-formed in combination with these adverbials. Atomic events, however, are disallowed in combination with these adhuwaya and amiyerra measure adverbials.
Examples (20) and (21) demonstrate the compatibility of adhuwaya and amiyerra with atelic, non-atomic, durative events (including statives (20) and dynamic, non-atomic events (21)), and examples (22)–(25) demonstrate their compatibility with non-atomic, durative, telic events. As demonstrated by examples (24) and (25), culmination does not affect the compatibility of adhuwaya and amiyerra (i.e., these measure adverbials are equally compatible with culminating and non-culminating readings).9
| 20. | kembirra Aburema-mərriya narrə-lhalhəka-Ø wurr-akəna then Abram-the.rest real.3a-leave-pst 3a-that Kenina akwa na-mərndakə-lhəke-na angerriba Yijibu=wa, Canaan and real.3a-many-go-pst to.over.there Egypt=all kajungwa kuw-ambilyi=yedha yakwujina adhuwaya, so.that irr.3a-stay.pst=purp there for.short.time nara+wiya ebina anhənga ambaka neg+quant neut.this.same neut.food later Kenina=manja Canaan=loc ‘There was so little food that Abram and his family left Canaan and went down to Egypt to live there for a while’ (Bible Society in Australia 1992, p. 83) |
| 21. | amiyerraambak mema kəmə-dhadhə-na=ma long.time later veg.this irr.veg-become.cooked-npst=mut ‘It’ll take a while to cook these yams’ (JL, JRB1-049-01, 00:54:11.494–00:54:14.069) |
| 22. | n-akəna nə-mərəkwarrkə-nə=ma arəngbərrə=lhangwiya 3m-that real.3m-cross-pst=mut neut.wide=perl angalya a-warnk-amiyerra10 neut.place neut-dim-long.time ‘He [that man] crossed that big plain [for a long time]’ (JL, JRB1-082-02, 00:10:27.484–00:11:07.409) |
| 23. | n-akəna nenəngkwarba nen-eniba-ka-Ø=ma n-akəna 3m-that 3m.man real.3m>3m-alive-fact-pst=mut 3m-that nenjarrngalya adhuwaya 3m.boy for.short.time ‘That man saved [the] little boy for a little while’ [i.e., ‘maybe when he was having this heart attack, or something like that, then he [the man] was trying his best [to save him]… maybe he got better for a little while… [but afterwards, maybe the boy got better, maybe he didn’t], we don’t know’ (JL, JRB1-089-01, 00:24:49.735–00:25:09.915) |
| 24. | n-akəna nenəngkwarba nen-eniba-ka-Ø=ma n-akəna 3m-that 3m.man real.3m>3m-alive-fact-pst=mut 3m-that nenjarrngalya amiyerra yandhə+lhangwa n-enib=dha 3m.boy for.long.time nothing+abl [until] 3m-alive=trm ‘That man brought the life of that boy, young man, for a while, until [he] was back to life’ (JL, JRB1-089-02, 00:19:04.875–00:20:40.145) |
| 25. | n-akəna nenəngkwarba nen-eniba-ka-Ø=ma n-akəna 3m-that 3m.man real.3m>3m-alive-fact-pst=mut 3m-that nenjarrngalya amiyerra akena nara kən-enibə-dha-Ø 3m.boy for.long.time but neg irr.3m-alive-inch-usp ‘That man, he brought the boy’s life [back, for a] little while, but he never brought him back, just for a little while, then he was gone, he never came back to life’ (JL, JRB1-089-02, 00:20:53.200–00:23:27.270) |
For telic situations, as in (22)–(25), the adverbial modifies the inner stages of the situation, leading up to (but not including) its culmination. Figure 3 demonstrates this modification of the inner stages of the event ‘he crossed that big plain’ (example (22)), by the measure adverbial amiyerra ‘for short time’.
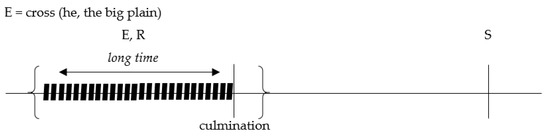
Figure 3.
’He crossed that big plain [for a long time]’.
Adhuwaya and amiyerra can only occur grammatically with atomic verbal complexes if they coerce an iterative reading, as in examples (26) and (27).
| 26. | dh-akəna dhədharrəngka yingənə-warda-ngə=ma n-akəna 3f-that 3f.woman real.3f>3m-hit-pst=mut 3m-that nenəngkwarba a-warnk-amiyerra 3m.man neut-dim-long.time ‘The woman hit the man for a long time’ *The woman hit the man [one hit] for a long time (JL, JRB1-082-02, 00:19:18.279–00:19:25.929) |
| 27. | n-angaba nenəngkwarba nə-mədhilyakbə-rna=ma 3m-that.over.there 3m.man real.3m-cough-npst=mut a-warnk-amiyerra neut-dim-long.time ‘When you cough, when you say about, you coughing a lot, for a long time’ ‘That man coughs for a long time’ *The man coughs [one cough] for a long time (JL, JRB1-083-01, 00:09:31.510–00:09:38.050) |
Anindilyakwa speakers accept that these clauses are grammatical and well-formed (with an iterative reading), but still generally disfavour these adverbials in such circumstances, preferring other temporal adverbials that can express both temporal duration and temporal deictic readings (e.g., adhənuba ‘in a short time (before/after), soon’; adhəna[k]ba ‘first, already’; ar[ə]ngkədharrba ‘in a short time (before/after), for a short time (before/after), soon’), as shown by speakers’ intuitions about these adverbials in such contexts in examples (28) and (29).
| 28. | ‘Adhuwaya doesn’t suit in coughing’ (JL, JRB1-083-01, 00:05:14.555–00:06:28.365) |
| 29. | ‘The language doesn’t seem to be connected to each other when you mention adhuwaya’ [talking about ‘coughing’] (JL, JRB1-083-01, 00:08:30.365–00:08:40.545) |
Atomic verbal complexes that are unable to coerce an iterative reading cannot occur in any semantically well-formed manner with the measure adverbials adhuwaya and amiyerra. This is demonstrated in examples (30) and (31).
| 30. | *dh-akəna dhədharrəngka yingi-jerrukwa-Ø akəna 3f-that 3f.woman real.3f-finish-pst neut.that sandwich adhuwaya neut.sandwich for.short.time ‘The woman finished [eating] the sandwich for a short time’ [‘this amiyerra and adhuwaya make you muddle up that sandwich sentence’ (JL)] (JL, JRB1-089-01, 00:30:07.265–00:30:21.240) |
| 31. | *n-akəna nenəngkwarba ni-jerrukwa-Ø 3m-that 3m.man real.3m-finish-pst nə-ngekburaka-Ø=ma akəna enungkwa adhuwaya real.3m-make-pst=mut neut.that neut.spear for.short.time ‘The man finished making the spear for a short time’ (JL, JRB1-089-01, 00:31:49.550–00:32:01.890) |
4.3.2. Implied Durational Adverbials
In addition to measure adverbials (i.e., direct durational adverbs), adverbials that imply (rather than make explicit) temporal duration (such as the adverbs ‘slowly’ and ‘quickly’ in English) can be used as diagnostics for different Aktionsart properties in some languages (Smith 1996, p. 238).
In Anindilyakwa, the indirect durational adverbials wəranja ‘quickly, soon’ and ambaka=lhangwa ‘slowly, carefully’ are compatible with all dynamic situation types, however with non-atomic ones (as in example (32)), the adverbial modifies the inner stage(s) of the situation, while for atomic events, the adverbial modifies an interval of time preliminary to the event (the preparatory stage(s)), rather than referring to any core inner stage of the situation (as in (33)). The interpretation of such implied durational adverbials can therefore be used as a diagnostic criterion relating to atomicity.
| 32. | n-akəna nenəngkwarba nə-rədha-ngə=ma 3m-that 3m.man real.3m>neut-cut.up-pst=mut akəna ayika wəranjəbə+wiya angkw-ababərn=lhangwa neut.that neut.tree quickly+quant time-many=abl alyarrəngwalya mena nu-wərrk-awərriya-dhə-nə=ma at.night because real.3m-chest-upset-inch-pst=mut n-akəna wərr-akəna rangers kenə-rrəngka-Ø=maka 3m-that 3a-that 3a.rangers irr.3a>3m-see-pst=evit kembirra adhuwayə+wiya nə-rədha-ngə=ma then in.short.time+quant real.3m> neut-cut.up-pst=mut ena ayika neut.this neut.tree ‘That man cut the trees down [every night, quickly, because] but he didn’t want the rangers to see him, so he cut the trees [quickly, in a] short time, without rangers seeing him’ (JL, JRB1-082-01, 00:08:32–00:09:03) |
| 33. | ni-yedha-Ø yakwujina wərənjabə=wiya real.3m-arrive-usp there quickly=quant ‘He got there quick’ (JL, JRB1-082-02, 00:16:21.559–00:16:26.409) |
4.3.3. Interaction with Inflectional T/A Marking
As discussed in Section 4.1, the interaction of Aktionsart with the inflectional TAM system can be used as a diagnostic for the features of both dynamism and atomicity in Anindilyakwa. While non-atomic situations inflected with the realis prefix paradigm and the bare stem paradigm (i.e., realis-V-usp inflectional marking) are compatible with a present temporal reference point, atomic events that take realis-V-usp inflectional marking are compatible only with past temporal expression, as in example (34). Table 3 provides a summary of the effects of Aktionsart on the aspectuo-temporal properties of verbs inflected with realis-V-usp marking.
| 34. | n-akəna nenəngkwarba ni-jungə-Ø=ma, n-akəna 3m-that 3m.man real.3m-die-usp=mut 3m-that nenəngkwarb ni-jungə-Ø=ma 3m.man real.3m-die-usp=mut ‘He passed away’ *He passes away/is passing away [now] (JL, JRB1-049-01, 00.47.04–00.47.16) |
4.4. Summary
The key lexical and morpho-syntactic variables that can be used to identify distinctions regarding the inherent temporal properties of different situations in Anindilyakwa, as discussed in Section 4.1, Section 4.2 and Section 4.3, are summarised in Table 4.

Table 4.
Aktionsart properties in Anindilyakwa and variables with which to identify them.
5. Conclusions
In this article we have seen that intrinsic temporal properties of the verbal complex are integral to the system of aspectual expression in Anindilyakwa, particularly given the underspecified nature of the inflectional aspectuo-temporal system.
Salient Aktionsart properties were identified in Anindilyakwa by examining the grammatically permissible (and impermissible) distribution and co-occurrence of various temporal adverbials (primarily measure adverbials and indirect duration adverbials), as well as through examining morpho-syntactic properties of reduplication patterns and inflectional TAM marking. Through this examination, it was observed that some of the most salient variables that can be used to identify distinctions with respect to the inherent temporal properties of different Anindilyakwa verbal complexes relate to the properties of dynamism and atomicity. Telicity was observed as less salient than other parameters in distinguishing between different kinds of situations in Anindilyakwa.
This article, through its language-specific means of identifying and classifying Aktionsart properties, offers new perspectives with which to consider cross-linguistic aspectuo-temporal research, in addition to providing a more detailed and nuanced understanding of aspectuo-temporal semantics in Anindilyakwa.
Funding
This research was funded by the ARC Centre of Excellence for the Dynamics of Language (Project ID: CE140100041), an Australian Government Research Training Program Scholarship, the School of Literature, Languages and Linguistics at the Australian National University, and the Laboratoire de Linguistique Formelle (LLF) UMR7110 at Université de Paris (formerly Université Paris Diderot).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data collection for this study was approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee at the Australian National University (Protocol 2015/143) and the Anindilyakwa Services Aboriginal Corporation.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Recordings cited here are archived with the Pacific and Regional Archive for Digital Sources in Endangered Cultures (PARADISEC) (https://catalog.paradisec.org.au/collections/JRB1 accessed on 24 September 2021) and the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies (Groote_E01 Collection, Waddy_J01 Collection, Waddy_J02 Collection).
Acknowledgments
I am indebted to the Warnumamalya people of the Groote Eylandt archipelago, who have generously and patiently taught me about their Anindilyakwa language. In particular I thank Judy Lalara, Sylvia Tkac and Carol Wurramara. I thank Patrick Caudal and Jane Simpson, whose mentorship and supervision was crucial for the larger project on which this study is based. I thank two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments. Any errors or oversights are, of course, my own.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest. The funding bodies had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
| 1 | first person (exclusive) | m | masculine gender |
| 2 | second person | mut | marker of symmetrical information access from speaker perspective |
| 3 | third person | ||
| a | augmented | neg | negative |
| abl | ablative | neut | neuter nominal class |
| all | allative | npst | non-past |
| coll | collective noun class | perl | perlative |
| compl.act | completed action | poss | possessive |
| deon | deontic | pro | pronoun |
| dim | diminutive | pst | past |
| evit | evitative | purp | purposive |
| f | feminine gender | quant | quantitative |
| fact | factitive | real | realis |
| inch | inchoative | redup | reduplication |
| irr | irrealis | trm | terminative |
| kin | possessed kin | usp | underspecified, phonologically null TAM |
| loc | locative |
Notes
| 1 | Various terms have been employed in the literature to refer to this domain, including ‘Aktionsart’, ‘action’, ‘actionality’, ‘aspectual character’, ‘aspectual class’, ‘situation type’ and ‘event structure aspect’ (amongst others). Throughout this article I use the term ‘Aktionsart’. | ||||
| 2 | Although for detailed studies considering various other topics within the temporal/aspectual domain in a number of Australian languages, see the special issue of the Australian Journal of Linguistics 32(1) (2012), along with Bednall (2020, forthcoming), Collins (2015), Phillips (2021) and Ritz and Schultze-Berndt (2015). | ||||
| 3 | The 2016 Australian Bureau of Statistics Census recorded 1478 people reporting to speak Anindilyakwa, including 377 children under 14 years old, however this is likely an underestimate (cited in Department of Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development and Communications et al. 2020, pp. 48–49). | ||||
| 4 | This data was collected predominantly with three language consultants (all female, born in the 1950s–70s, and from the community of Angurugu). This data is available at https://catalog.paradisec.org.au/collections/JRB1 (accessed on 9 April 2021). | ||||
| 5 | Staged video stimuli were used as the primary semi-elicited data collection method. The video stimuli used came from the Event Description Elicitation Database (EDED) (Caudal et al. 2016). | ||||
| 6 | I use the following conventions: * marks unacceptability; # indicates that the sentence is acceptable but cannot be given the interpretation in question. | ||||
| 7 | Rows shaded in grey indicates that this combination of prenominal prefix + TAM suffix is not possible. | ||||
| 8 | Most temporal adverbials associated with duration in Anindilyakwa are multifunctional, being able to express readings associated with both duration as well as temporal deixis, however adhuwaya ‘for short [duration of] time’ and amiyerra ‘for long [duration of] time’ are not, expressing only a durative meaning. | ||||
| 9 | More generally in Anindilyakwa, for telic events involving a verbal predicate inflected for realis-V-past or irrealis-V-past marking, both culminating and non-culminating readings are possible—there is an implicature of culmination, however this can be cancelled (generally through a following clause that specifies the non-culmination). On the other hand, telic events involving verbal predicates inflected for realis-V-usp or irrealis-V-usp entail that culmination occurred (i.e., a non-culminating reading is disallowed). Compare examples (a) and (b), and see Bednall (2020, chp. 4) for further details.
| ||||
| 10 | In some of these examples amiyerra occurs with the diminutive prefix -warnk-, which indicates the time span referred to is smaller than amiyerra (often translated as ‘a little bit long time’; i.e., ‘a fairly long time’). | ||||
| 11 | No examples of reduplicated verbal roots of atomic events have been identified in the existing corpora. |
References
- Bache, Carl, Hans Basbøll, and Carl-Erik Lindberg, eds. 1994. Tense, Aspect and Action: Empirical and Theoretical Contributions to Language Typology. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter. [Google Scholar]
- Bednall, James. 2020. Temporal, Aspectual and Modal Expression in Anindilyakwa, the Language of the Groote Eylandt Archipelago, Australia. Ph.D. thesis, 2020, Australian National University, Canberra, Australia, Université de Paris, Paris, France. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednall, James. Forthcoming. Tense and aspect. In The Oxford Guide to Australian Languages. Edited by Claire Bowern. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Bible Society in Australia. 1992. Neningikarrawara-Langwa Ayakwa [=Anindilyakwa Bible]. Canberra: Bible Society in Australia. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, Gregory. 1977. A unified analysis of the English bare plural. Linguistics and Philosophy 1: 413–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, Gregory. 1980. Reference to kinds of English. New York: Garland Publishing Company. [Google Scholar]
- Caudal, Patrick. 1999. Computational lexical semantics incrementality and the so-called punctuality of events. In Proceedings of the 37th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics on Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudal, Patrick. 2005. Degree Scales and Aspect. In Cross-Linguistic Views on Tense, Aspect and Modality. Edited by Bart Hollebrandse, Angeliek van Hout and Co Vet. Amsterdam and New York: Rodopi, pp. 103–18. [Google Scholar]
- Caudal, Patrick. 2006. The Aspectual Contribution of Tenses and the Semantics/Pragmatics Interface. Paper presented at UT Discourse Workshop, Austin, TX, USA, March 3–5; Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.584.9051&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Caudal, Patrick. 2012. Pragmatics. In The Oxford Handbook of Tense and Aspect. Edited by Robert Binnick. Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 269–305. [Google Scholar]
- Caudal, Patrick, and Laurent Roussarie. 2000. Event structure vs. stage structure and abstract aspectual relations. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual Meeting of the Berkeley Linguistics Society: General Session and Parasession on Aspect. Edited by Andrew K. Simpson. Berkeley: Berkeley Linguistics Society, pp. 361–72. Available online: https://halshs.archives-ouvertes.fr/halshs-01450454 (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Caudal, Patrick, Robert Mailhammer, and James Bednall. 2016. The Event Description Elicitation Database (EDED). Paris: U. Paris-Diderot, Sydney: U. Western Sydney. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, Brighde. 2015. Aspectual Expression in Ngandi: Past and Present. Master’s thesis, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11343/56545 (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Comrie, Bernard. 1976. Aspect. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development and Communications, Jacqueline Battin, Jason Lee, Douglas Marmion, Rhonda Smith, Tandee Wang, Yonatan Dinku, Janet Hunt, Francis Markham, Denise Angelo, and et al. 2020. National Indigenous Languages Report; Canberra: Australian Government Department of Infrastructure, Transport, Regional Development and Communications, formerly the Department of Communications and the Arts. Available online: https://www.arts.gov.au/what-we-do/indigenous-arts-and-languages/national-indigenous-languages-report (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Dowty, David R. 1972. Studies in the Logic of Verb Aspect and Time Reference in English. Ph.D. thesis, Univsity of Texas, Austin, TX, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Dowty, David R. 1979. Word Meaning and Montague Grammar. Dordrecht: Reidel. [Google Scholar]
- Dowty, David R. 1991. Thematic proto-roles and argument selection. Languages 67: 547–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, Hana. 2012. Lexical aspect. In The Oxford Handbook of Tense and Aspect. Edited by Robert Binnick. Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 721–51. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, Mark. 2008. Non-Pama-Nyungan Languages: Mapping Database and Maps [Online]. ASEDA. Available online: http://www1.aiatsis.gov.au/aseda/802_Harvey/MH_top_end.png (accessed on 15 December 2015).
- Kearns, Kate. 2000. Semantics. Basingstoke: Macmillan. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, Christopher, and Louise McNally. 1999. Degree modification and the scalar structure of gradable adjectives. In Description des Adjectifs pour les Traitements Informatiques (Proceedings of TALN 1999). Edited by Pierrette Bouillon and Evelyne Viegas. Cargèse: Association pour le Traitement Automatique des Langues, pp. 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, Christopher, and Louis McNally. 2005. The Syntax and Semantics of Multiple Degree Modification in English. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Head-Driven Phrase Structure Grammar. Edited by Stefan Müller. Stanford: CA CSLI Publications, pp. 178–91. Available online: https://semantics.uchicago.edu/kennedy/docs/kennedy-mcnally05.pdf (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Leeding, Velma. 1989. Anindilyakwa Phonology and Morphology. Ph.D. thesis, University of Sydney. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2123/1558 (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Moens, Marc. 1987. Tense, Aspect, and Temporal Reference. Ph.D. thesis, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1842/5369 (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Moens, Marc, and Mark Steedman. 1988. Temporal ontology and temporal reference. Computational Linguistics 14: 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Mucha, Anne. 2015. Temporal Interpretation and Cross-Linguistic Variation. Ph.D. thesis, University of Potsdam, Potsdam, Germany. Available online: https://publishup.uni-potsdam.de/opus4-ubp/frontdoor/deliver/index/docld/8593/file/mucha_diss.pdf (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Phillips, Joshua. 2021. At the Intersection of Temporal and Modal Interpretation: Essays on Irreality. Ph.D. thesis, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Ritz, Marie-Eve, and Eva Schultze-Berndt. 2015. The semantics and pragmatics of marking temporal progression in an Australian language. Lingua 166: 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasse, Hans-Jürgen. 2002. Recent activity in the theory of aspect: Accomplishments, achievements, or just non-progressive state? Linguistic Typology 6: 199–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, Carlota. 1996. Aspectual categories in Navajo. International Journal of American Linguistics 62: 227–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Carlota. 1997. The Parameter of Aspect, 2nd ed. Dordrecht: Kluwer. [Google Scholar]
- Tatevosov, Sergej. 2002. The parameter of actionality. Linguistic Typology 6: 317–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonhauser, Judith. 2015. Cross-linguistic temporal reference. Annual Review of Linguistics 1: 129–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendler, Zeno. 1957. Verbs and Times. The Philosophical Review 66: 143–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verkuyl, Henk J. 1972. On the Compositional Nature of the Aspects. Dordrecht: Reidel. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).