Performance Enhancement by Wing Sweep for High-Speed Dynamic Soaring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
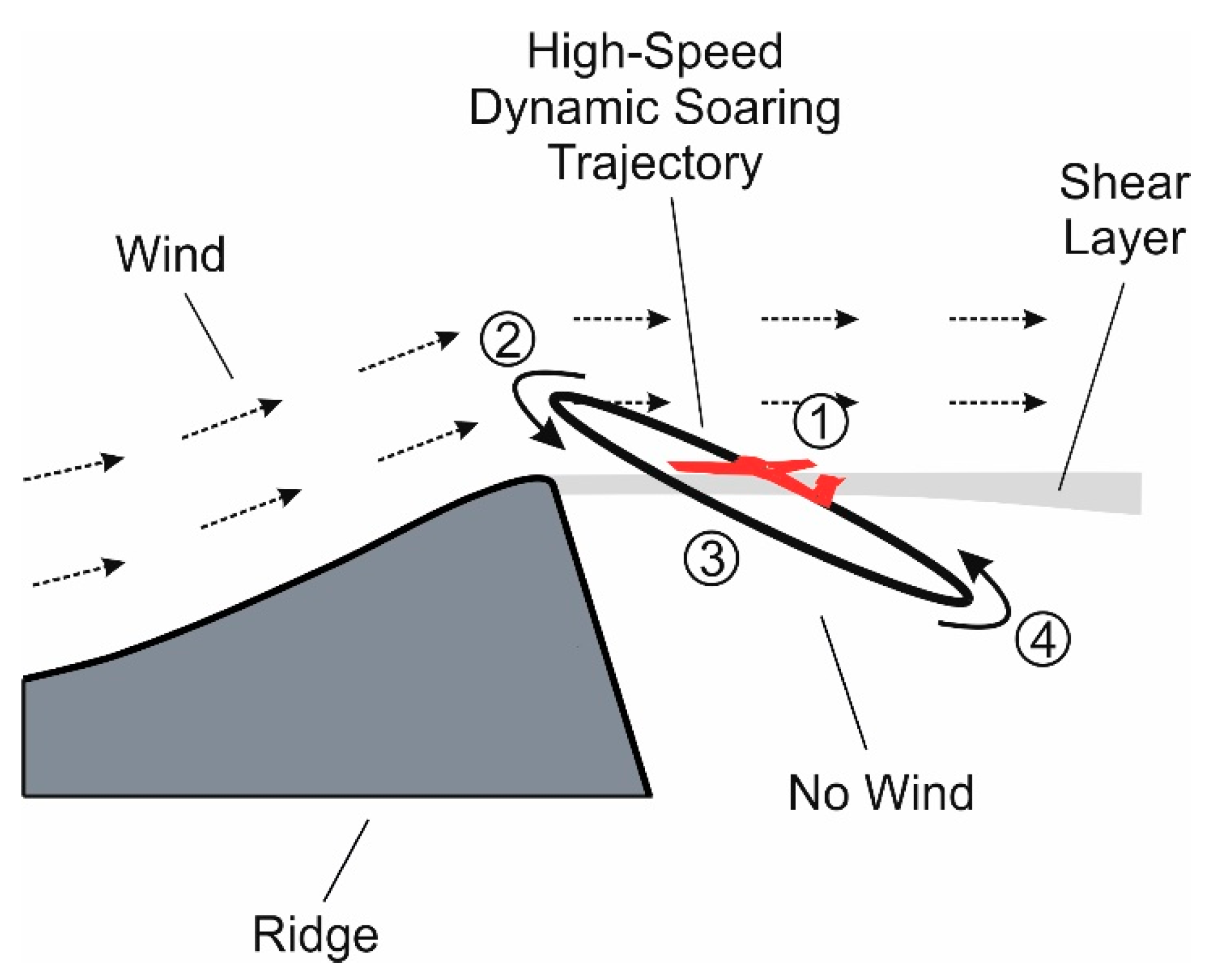
2. Flight Mechanics Modellings of High-Speed Dynamic Soaring
- (1)
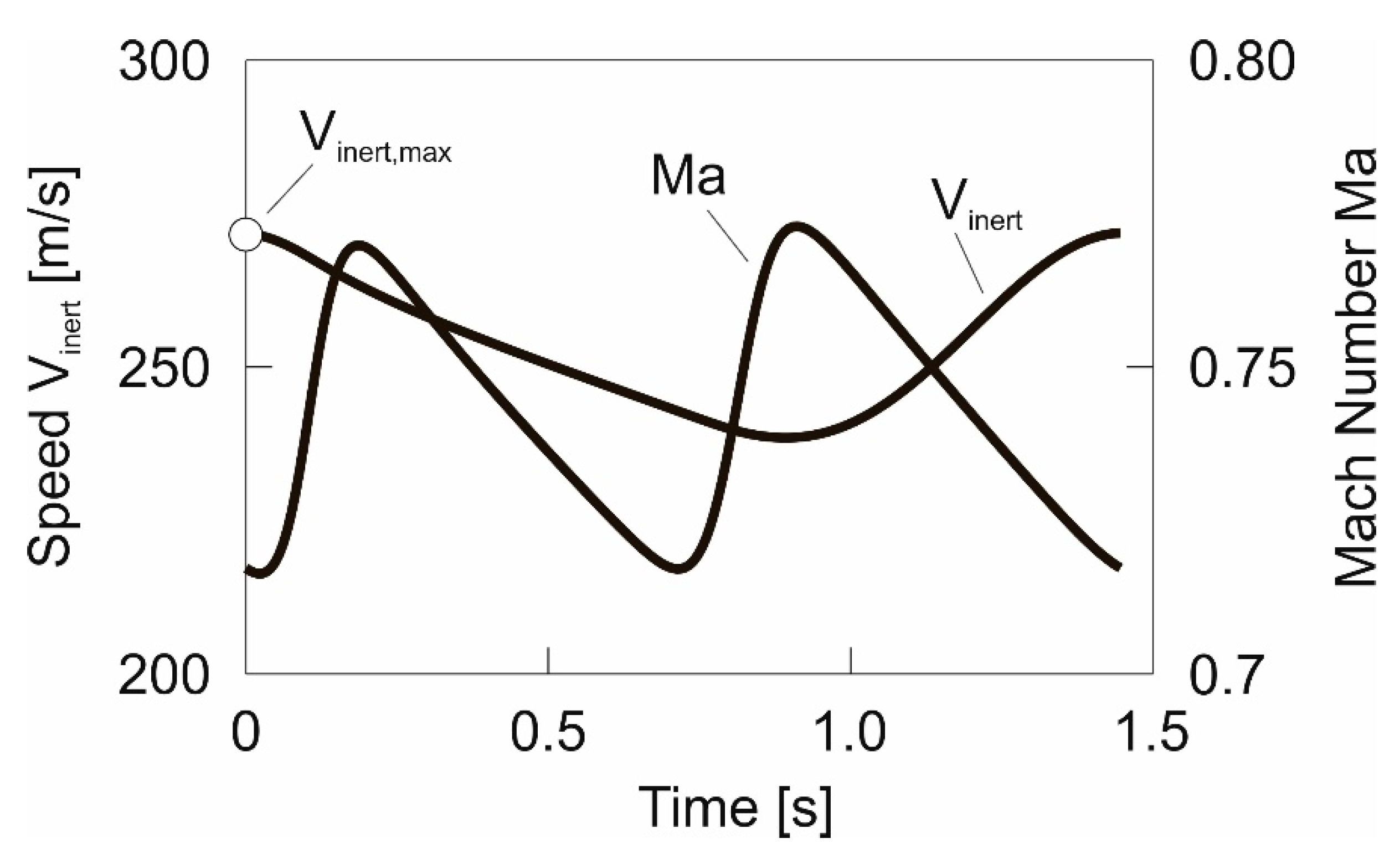
- Windward climb where the wind shear layer is traversed upwards.
- (2)
- Upper curve in the region of high wind speed, with a flight direction change from windward to leeward.
- (3)
- Leeward descent where the wind shear layer is traversed downwards.
- (4)
- Lower curve in the no wind region, with a flight direction change from leeward to windward.
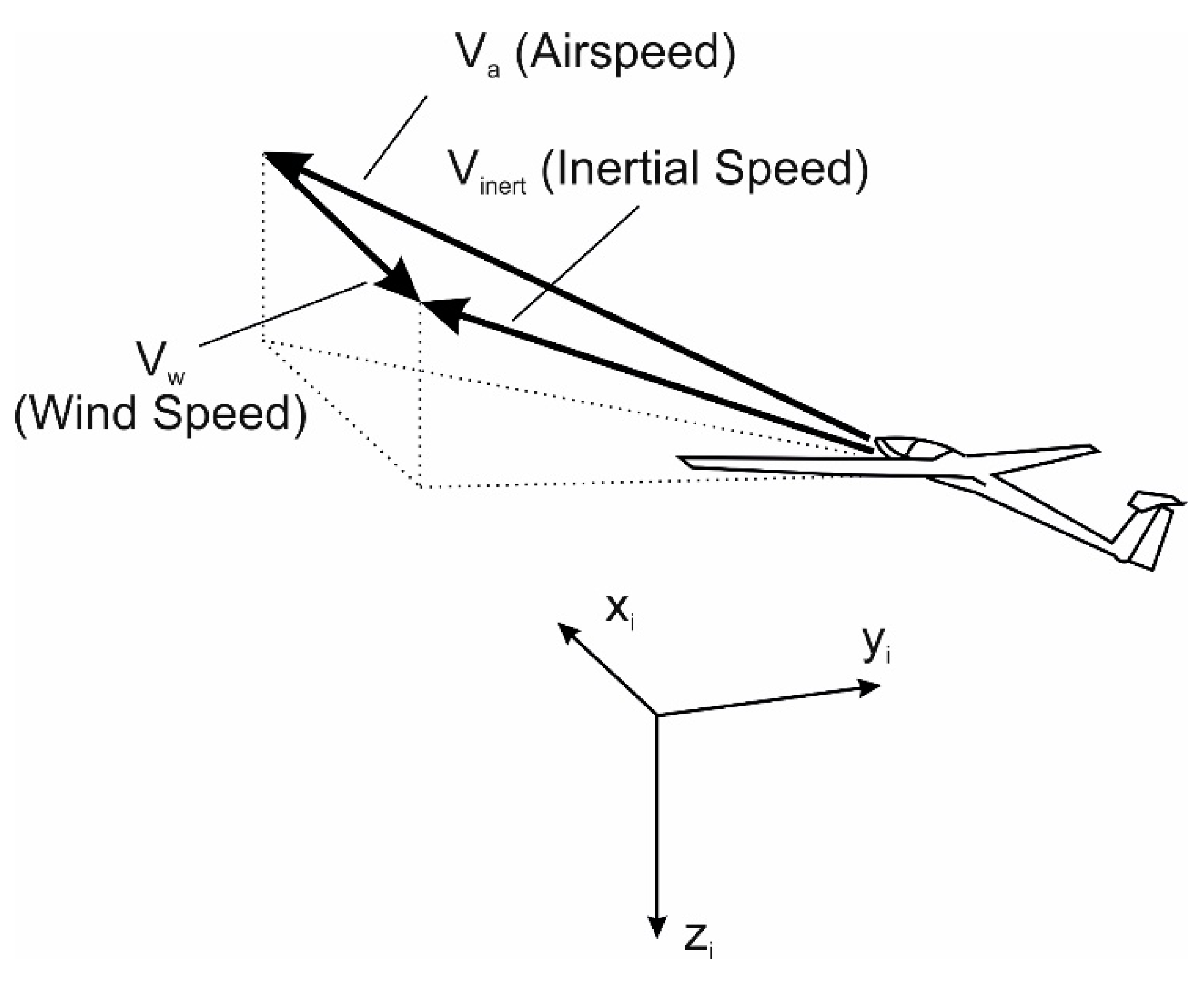
2.1. 3-DOF Dynamics Model
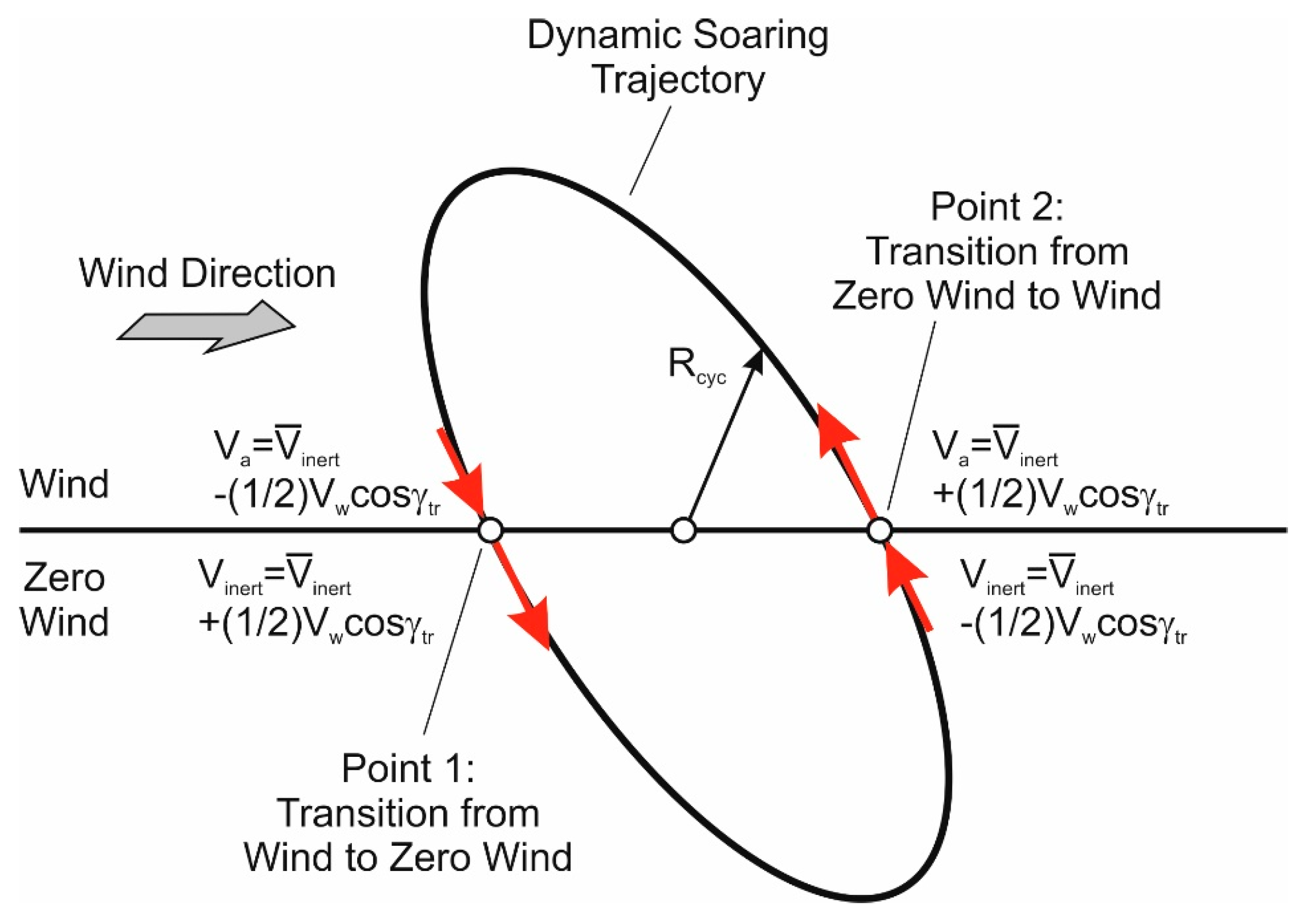
2.2. Energy Model
- (1)
- wind speed,
- (2)
- maximum lift-to-drag ratio,
2.3. Straight Wing Reference Configuration (Aerodynamics, Size and Mass Properties)
3. Maximum Speed Achievable with Straight-Wing Configuration
3.1. Maximum-Speed Performance of Straight Wing Reference Configuration
3.2. Maximum-Speed Performance and Related Key Factors
4. Increase of Maximum-Speed Performance by Wing Sweep
4.1. Aerodynamic Characteristics of Swept Wing Glider Configurations
- (1)
- Energy based model
- (2)
- Critical Mach number,
- (3)
- Maximum lift-to-drag ratio,
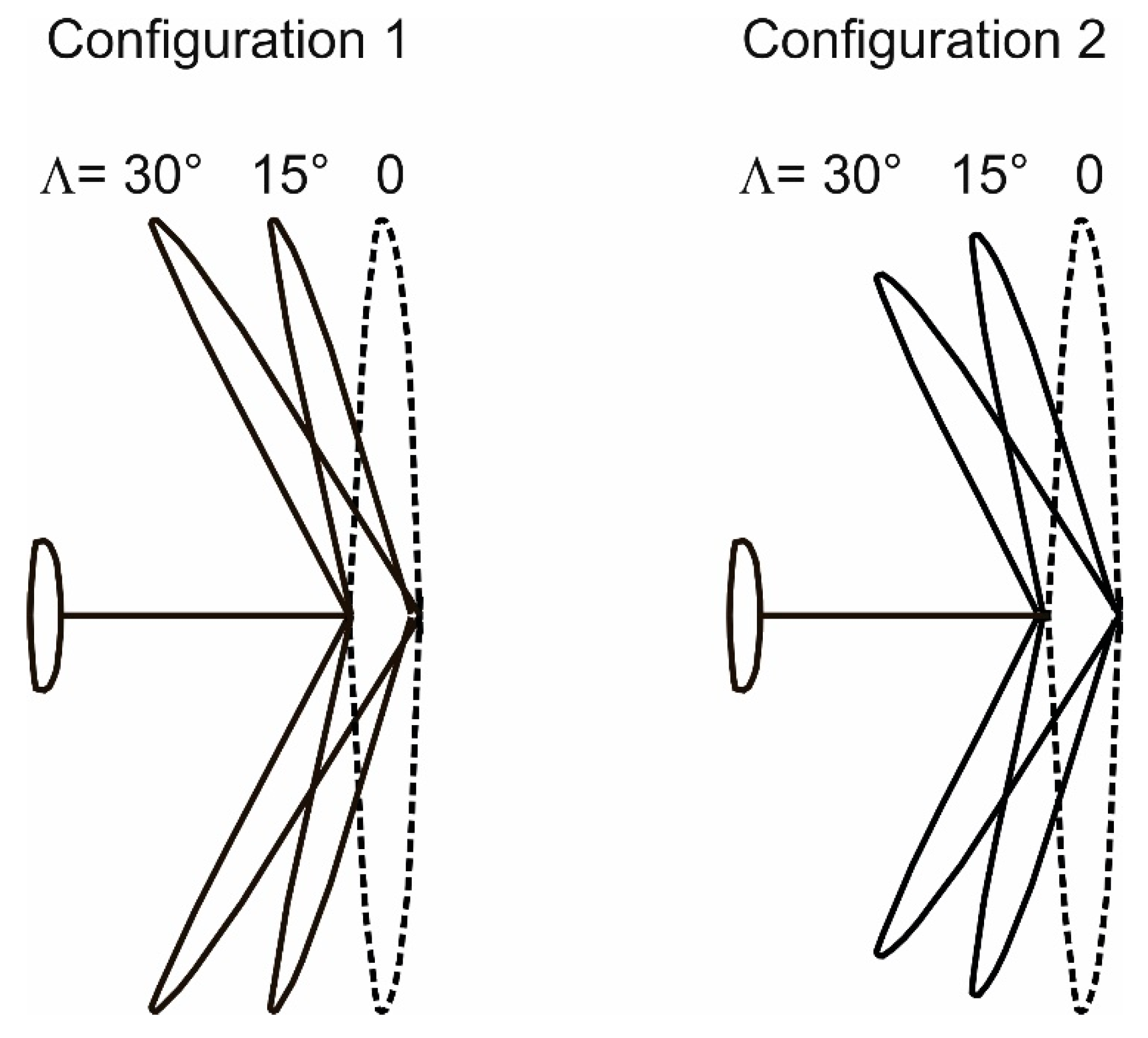
4.2. Swept Wing Configurations
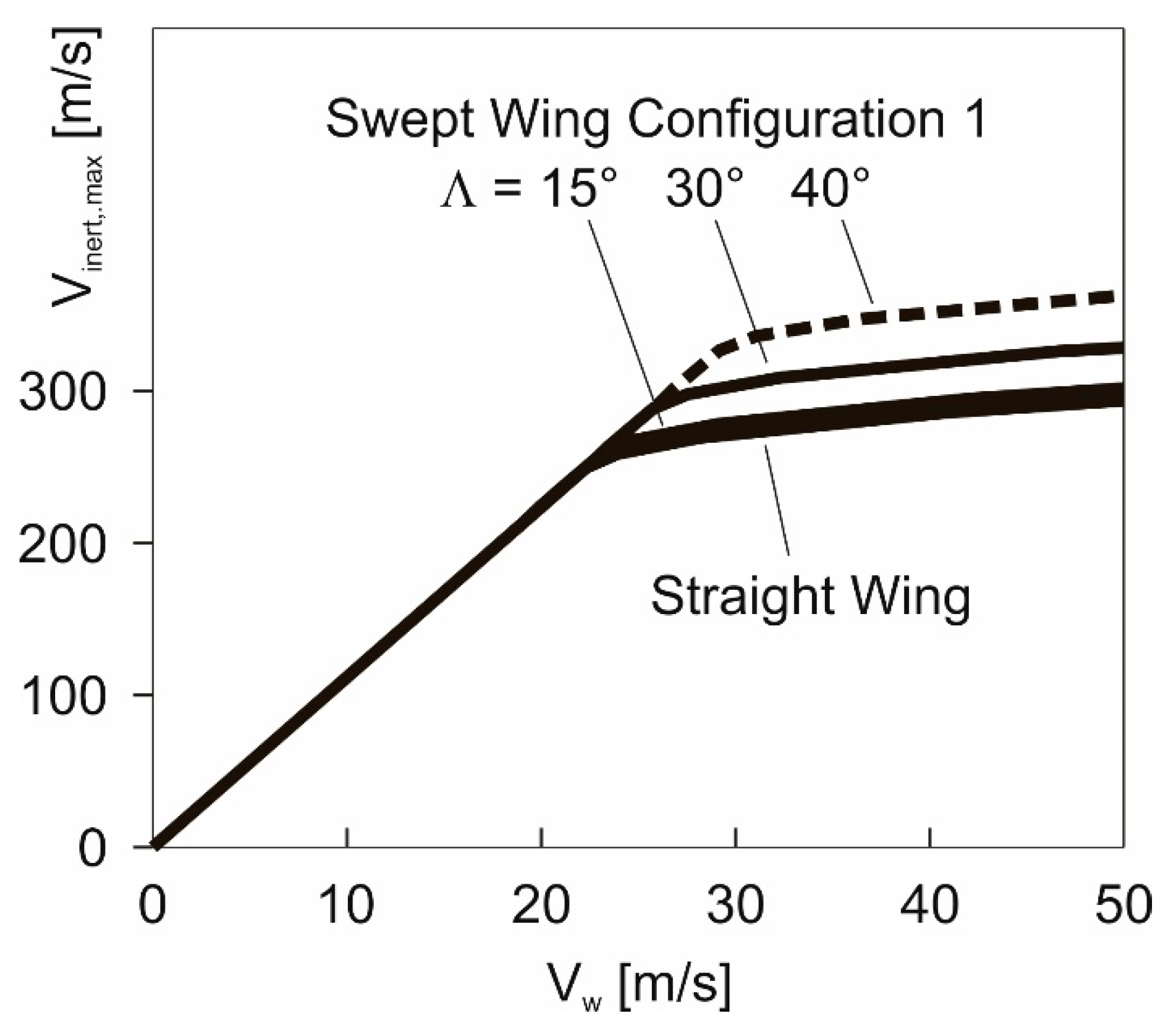
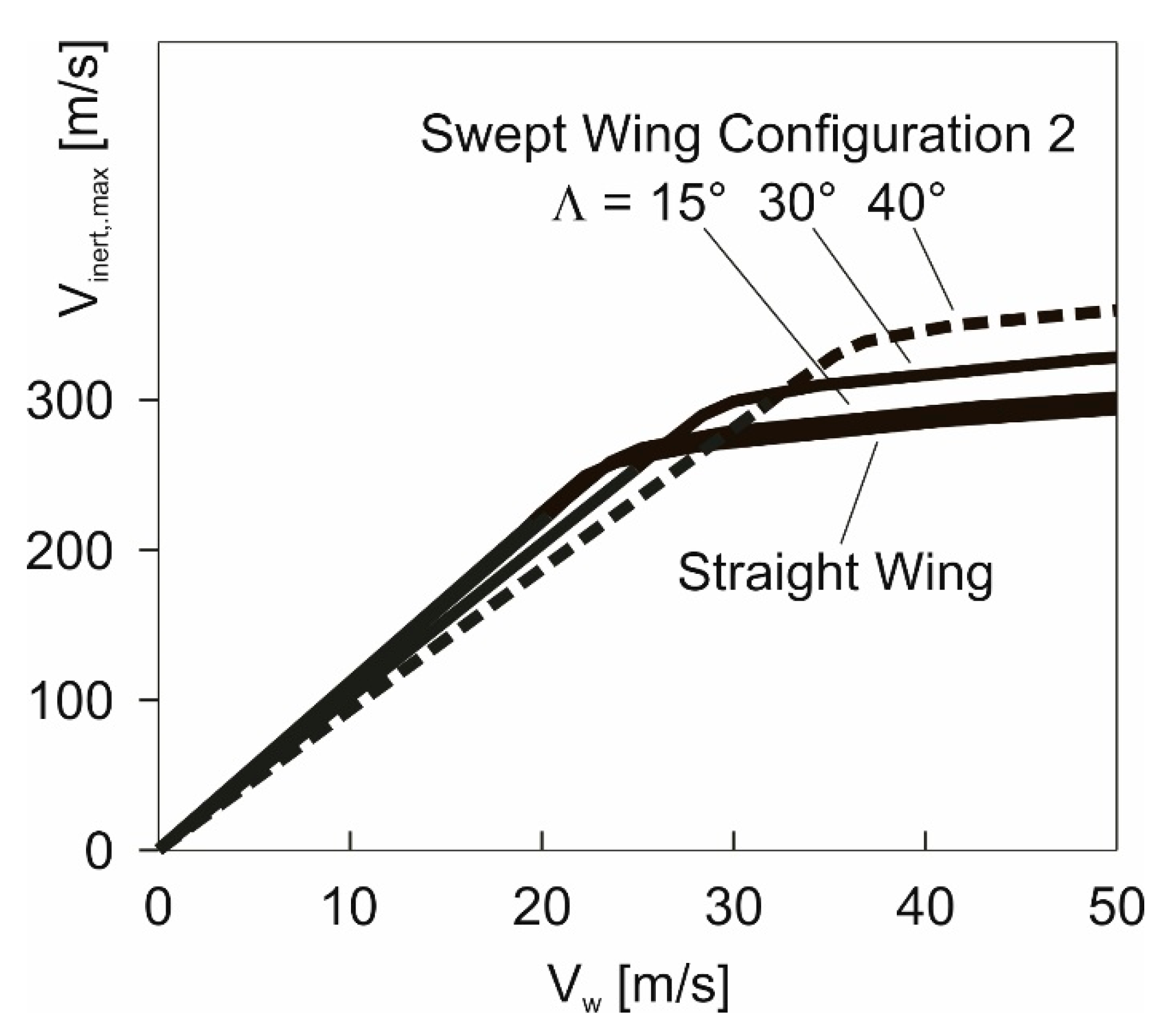
4.3. Potential of Wing Sweep for Enhancing the Maximum-Speed Performance
- −
- Sweep angles up to around 15° yield only a very small improvement.
- −
- The area between the curve for and the curve for shows that there are efficient possibilities for enhancing the maximum-speed performance by wing sweep. The area between the curve for and the curve for can serve as an indication for the performance potential of larger sweep angles.
5. Further Effects of Wing Sweep Important for High-Speed Dynamic Soaring
- −
- cycle time
- −
- load factor
- −
- trajectory radius
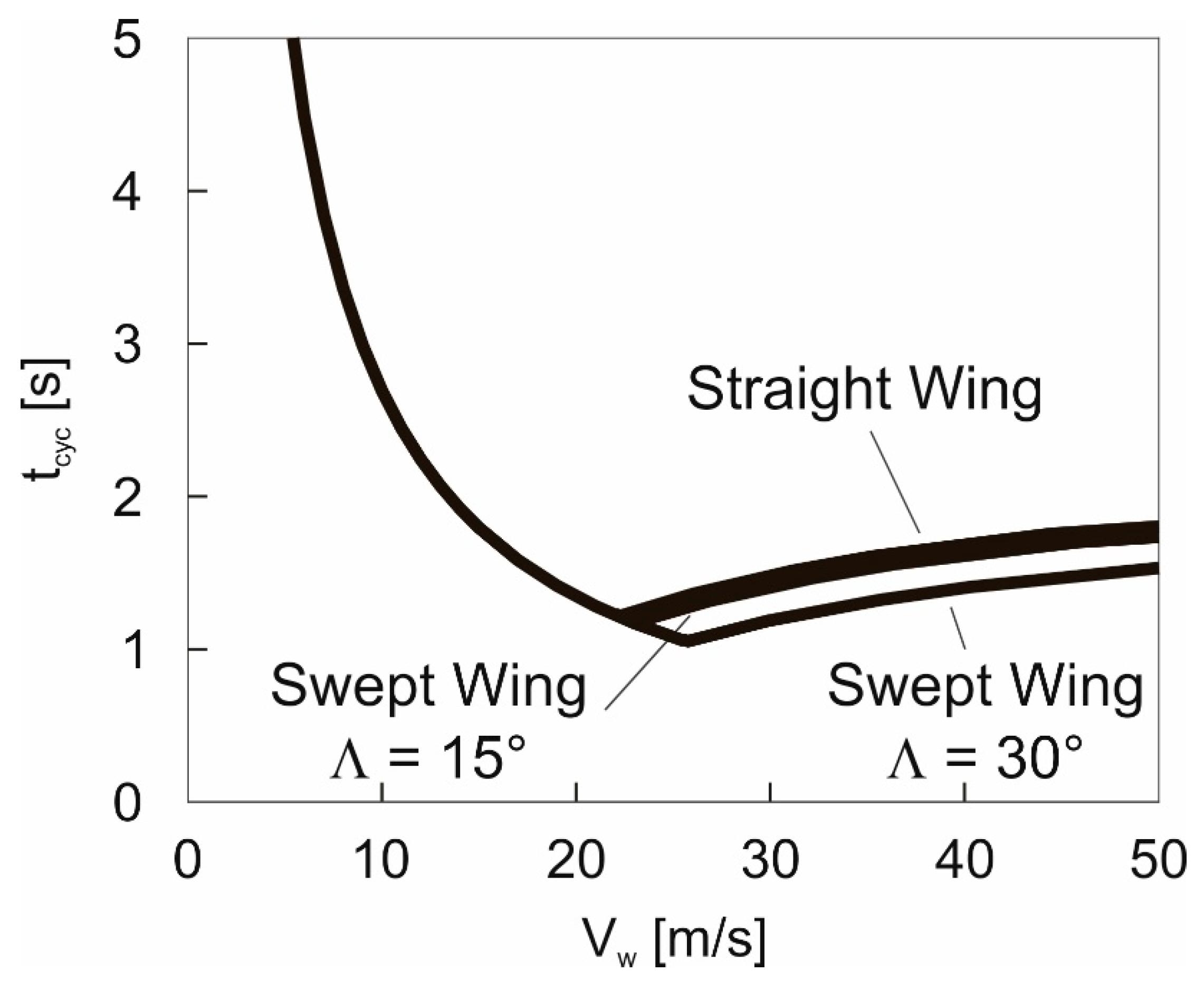
5.1. Optimal Cycle Time
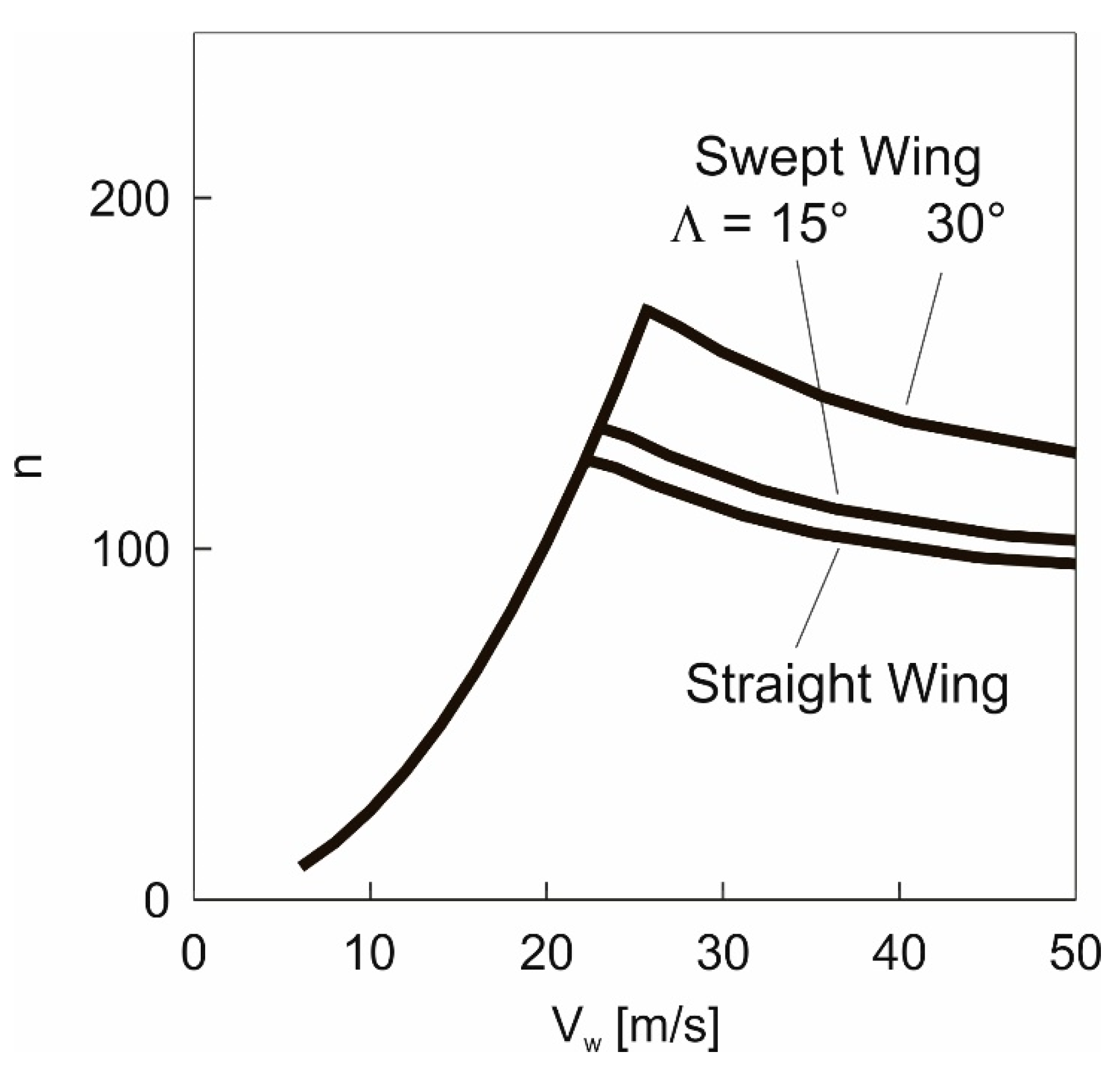
5.2. Load Factor
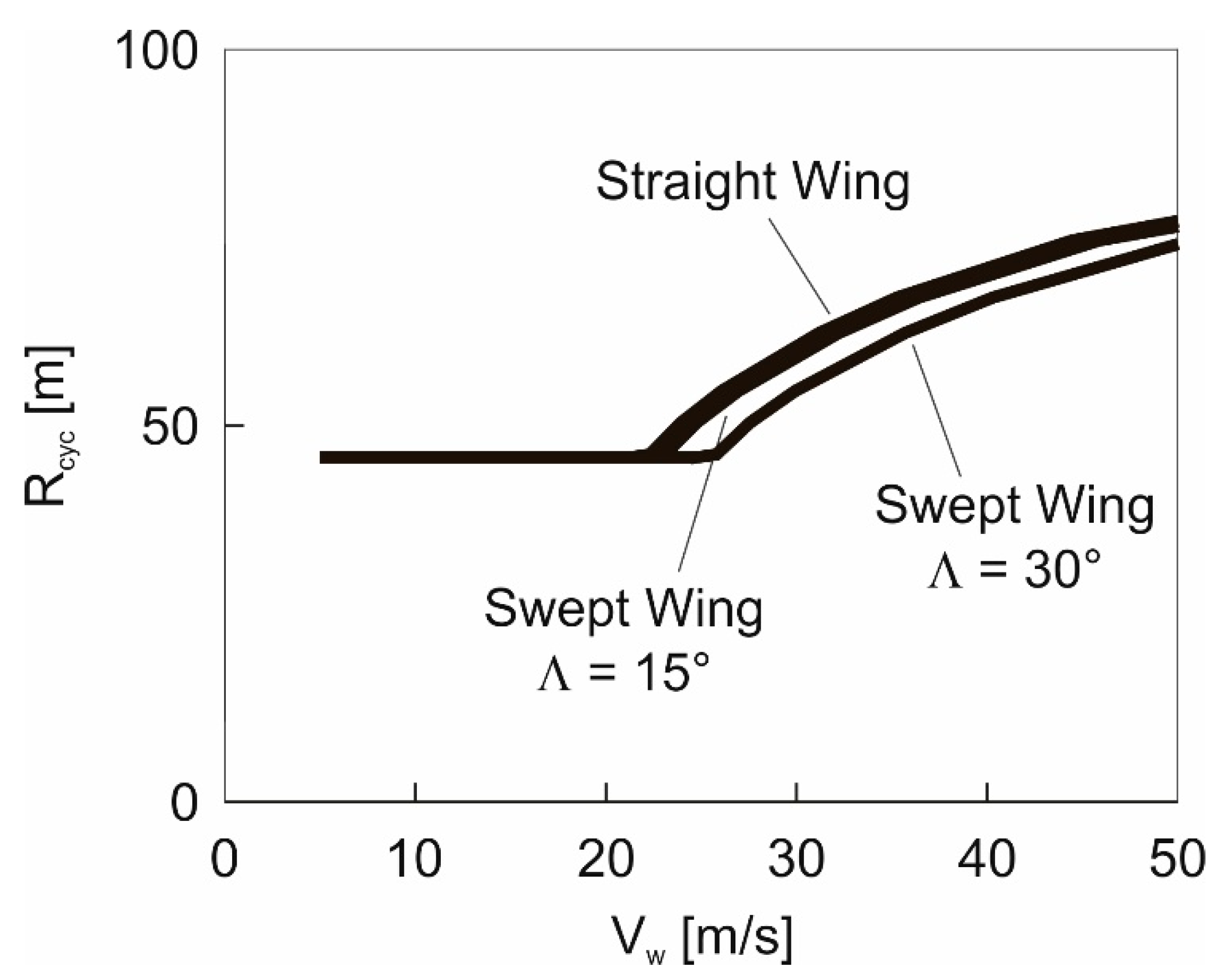
5.3. Trajectory Radius of Maximum-Speed Cycle
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| aij | coefficients |
| b | wing span |
| CD | drag coefficient |
| CL | lift coefficient |
| D | drag |
| E | energy |
| g | acceleration due to gravity |
| h | altitude |
| J | performance criterion |
| L | lift |
| Ma | Mach number |
| m | mass |
| n | load factor |
| Rcyc | loop radius |
| S | wing reference area |
| s | length |
| t | time |
| u, v, wi | speed components |
| u | control vector |
| Va | airspeed |
| Vinert | inertial speed |
| Vw | wind speed |
| x | longitudinal coordinate |
| x | state vector |
| W | work |
| y | lateral coordinate |
| z | vertical coordinate |
| A | aspect ratio |
| χ | azimuth angle |
| γ | flight path angle |
| sweep angle | |
| μ | bank angle |
| ρ | air density |
Appendix A. Formulation of Optimal Control Problem
References
- Idrac, P. Experimentelle Untersuchungen über den Segelflug Mitten im Fluggebiet Großer Segelnder Vögel (Geier, Albatros Usw.)—Ihre Anwendung auf den Segelflug des Menschen; Verlag von R. Oldenbourg: München, Germany; Berlin, Germany, 1932. [Google Scholar]
- Cone, C.D., Jr. A mathematical analysis of the dynamic soaring flight of the albatross with ecological interpretations. In Special Scientific Report No. 50; Virginia Institute of Marine Science: Gloucester Point, VA, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Sachs, G. Minimum shear wind strength required for dynamic soaring of albatrosses. Ibis 2005, 147, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurts, J. Dynamic soaring. SE Modeler Mag. 1998, 5, 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, P.L. High-speed dynamic soaring. R/C Soar. Dig. 2012, 29, 36–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lisenby, S. Dynamic soaring. In Proceedings of the Big Techday 10 Conference, München, Germany, 2 June 2017; TNG Technology Consulting GmbH: Unterföhring, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sachs, G.; Grüter, B. Trajectory optimization and analytic solutions for high-speed dynamic soaring. Aerospace 2020, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, P.L. High-speed robotic albatross: Unmanned aerial vehicle powered by dynamic soaring. R/C Soar. Dig. 2012, 29, 4–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sachs, G.; Grüter, B. Dynamic soaring at 600 mph. In Proceedings of the AIAA SciTech 2019 Forum, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–11 January 2019; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- DSKinetic. Available online: www.DSKinetic.com (accessed on 11 August 2021).
- Deittert, M.; Richards, A.; Toomer, C.A.; Pipe, A. Engineless unmanned aerial vehicle propulsion by dynamic soaring. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2009, 32, 1446–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langelaan, J.W.; Roy, N. Enabling new missions for small robotic aircraft. Science 2009, 326, 1642–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrance, N.R.J.; Acevedo, J.J.; Chung, J.J.; Nguyen, J.L.; Wilson, D.; Sukkarieh, S. Long endurance autonomous flight for unmanned aerial vehicles. AerospaceLab 2014, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA. Available online: http://www.max3dmodels.com/vdo/NASA-Albatross-Dynamic-Soaring-Open-Ocean-Persistent-Platform-UAV-Concept/F4zEaYl01Uw.html (accessed on 8 April 2020).
- Bonnin, V.; Benard, E.; Moschetta, J.M.; Toomer, C.A. Energy-harvesting mechanisms for UAV flight by dynamic soaring. Int. J. Micro Air Veh. 2015, 7, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, G.; Grüter, B. Maximum travel speed performance of albatrosses and UAVs using dynamic soaring. In Proceedings of the AIAA Scitech 2019 Forum, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–11 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mir, I.; Maqsood, A.; Taha, H.E.; Eisa, S.A. Soaring energetics for a nature inspired unmanned aerial vehicle. In Proceedings of the AIAA SciTech Forum 2019-1622, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–11 January 2019; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilović, N.; Bronz, M.; Moschetta, J.-M. Bioinspired energy harvesting from atmospheric phenomena for small unmanned aerial vehicles. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2020, 43, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskam, J.; Lan, C.-T.E. Airplane Aerodynamics and Performance; DARcorporation: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Sachs, G.; Grüter, B. High-speed flight without an engine: A unique performance capability enabled by dynamic soaring. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2021, 44, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.D., Jr. Fundamentals of Aerodynamics; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- RCSpeeds. Available online: http://rcspeeds.com (accessed on 12 August 2021).
- Schygulla, M. Aerodynamische Auslegung Eines Transsonischen Flugkonzeptes für Dynamic Soaring. Bachelor’s Thesis, Institute of Aerodynamics and Gas Dynamics, University of Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolai, L.M.; Carichner, G.E. Fundamentals of Aircraft and Airship Design, Volume I—Aircraft Design; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Inc.: Reston, VA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rossow, C.-C. Aerodynamik. In Handbuch der Luftfahrzeugtechnik; Carl Hanser Verlag: München, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tomas, F. Fundamentals of Sailplane Design; Milgram, J., Ed.; College Park Press: College Park, MD, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rieck, M.; Bittner, M.; Grüter, B.; Diepolder, J. FALCON.m—User Guide; Institute of Flight System Dynamics, Technische Universität München: München, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wächter, A.; Biegler, L.T. On the implementation of an interior-point filter line-search algorithm for large-scale nonlinear programming. Math. Program. 2006, 106, 25–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



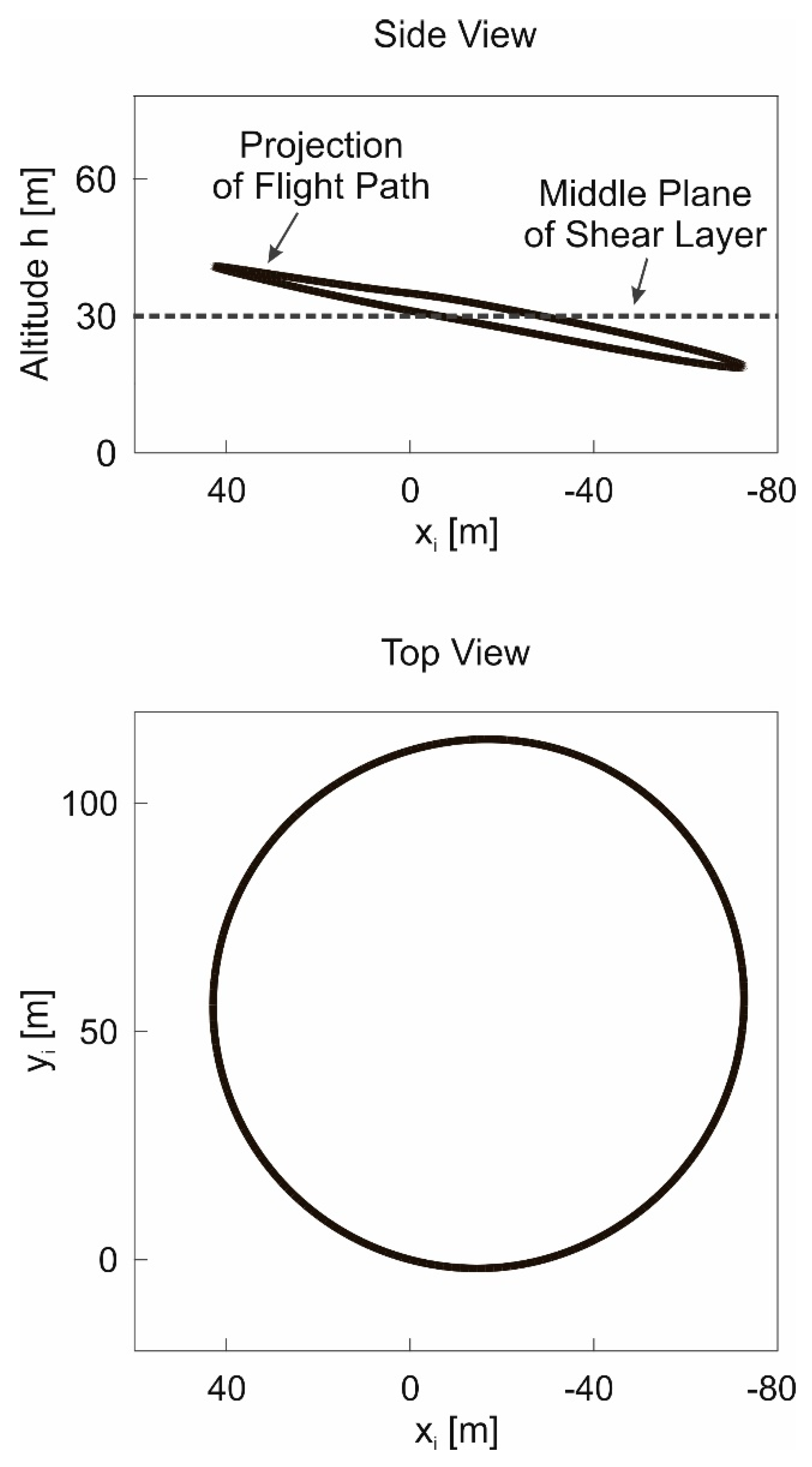
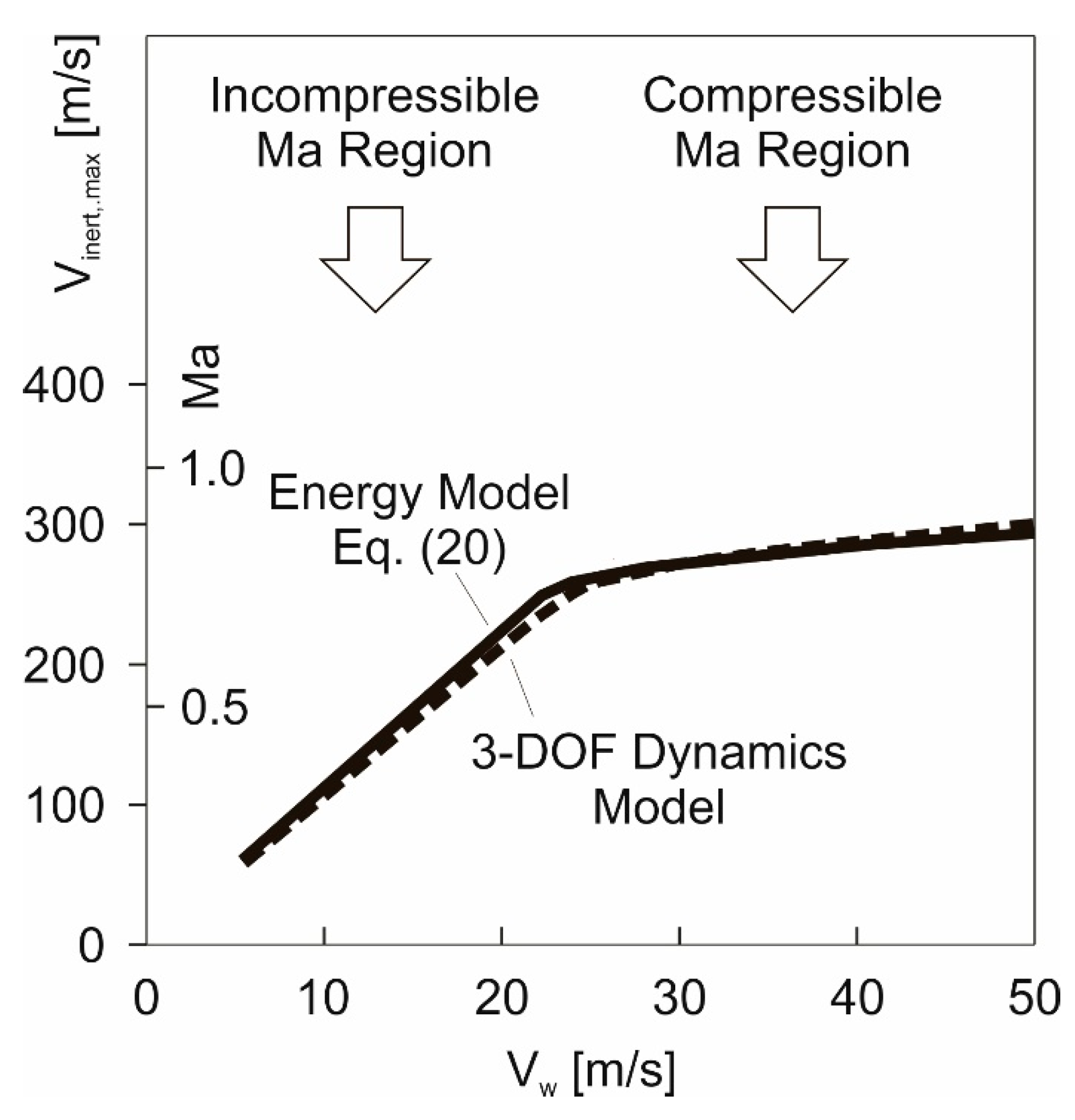
 Results obtained using the energy model, Equation (20).
Results obtained using the energy model, Equation (20).  Results obtained using the 3-DOF dynamics model.
Results obtained using the 3-DOF dynamics model.
 Results obtained using the energy model, Equation (20).
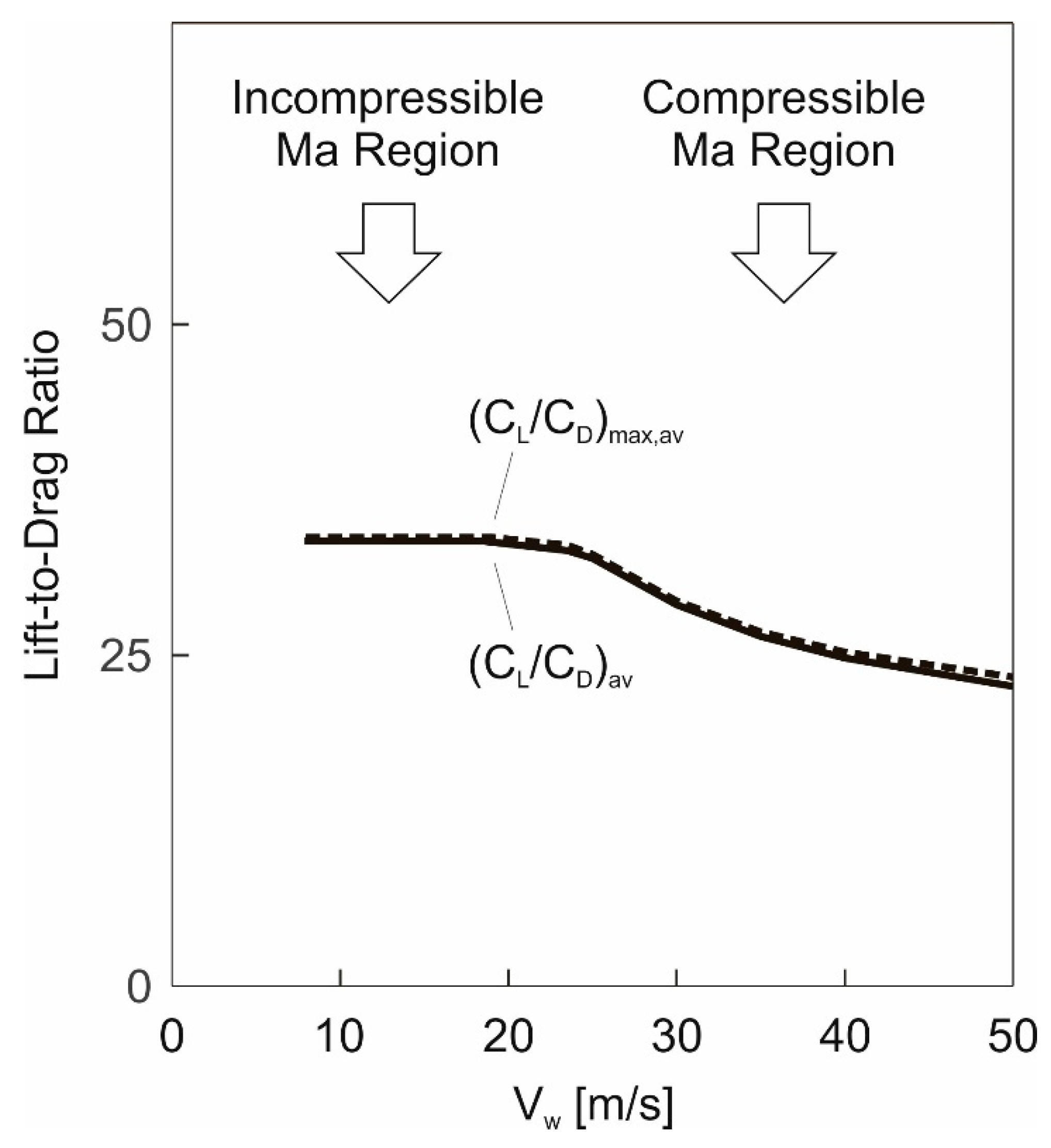
Results obtained using the energy model, Equation (20).  Results obtained using the 3-DOF dynamics model.
Results obtained using the 3-DOF dynamics model.

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sachs, G.; Grüter, B.; Hong, H. Performance Enhancement by Wing Sweep for High-Speed Dynamic Soaring. Aerospace 2021, 8, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace8080229
Sachs G, Grüter B, Hong H. Performance Enhancement by Wing Sweep for High-Speed Dynamic Soaring. Aerospace. 2021; 8(8):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace8080229
Chicago/Turabian StyleSachs, Gottfried, Benedikt Grüter, and Haichao Hong. 2021. "Performance Enhancement by Wing Sweep for High-Speed Dynamic Soaring" Aerospace 8, no. 8: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace8080229
APA StyleSachs, G., Grüter, B., & Hong, H. (2021). Performance Enhancement by Wing Sweep for High-Speed Dynamic Soaring. Aerospace, 8(8), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace8080229







