Constrained Parameterized Differential Dynamic Programming for Waypoint-Trajectory Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries and Problem Formulation
2.1. Modeling of the Spatial–Temporal Trajectory Optimization Problem with Multiple Waypoints
2.2. Parameterized Differential Dynamic Programming (PDDP)
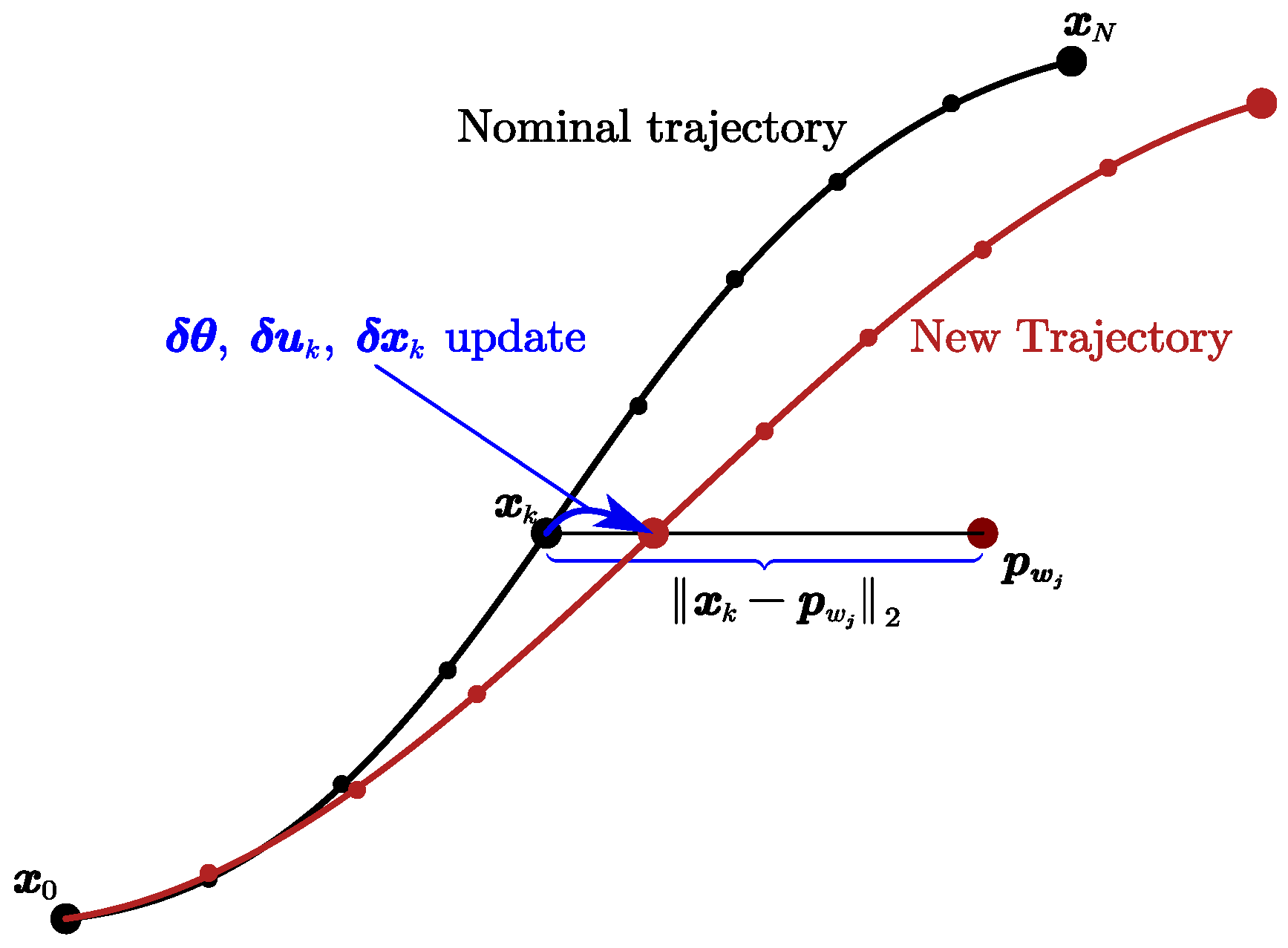
3. Constrained Parameterized Differential Dynamic Programming for Spatial–Temporal Optimization
3.1. Constrained Parameterized Differential Dynamic Programming
3.2. Constrained Parameterized Differential Dynamic Programming for Spatial–Temporal Optimization
3.3. Scaling the Flight Time of Trajectory Segments
| Algorithm 1 Constrained parameterized differential dynamic programming |
|
4. Application Example
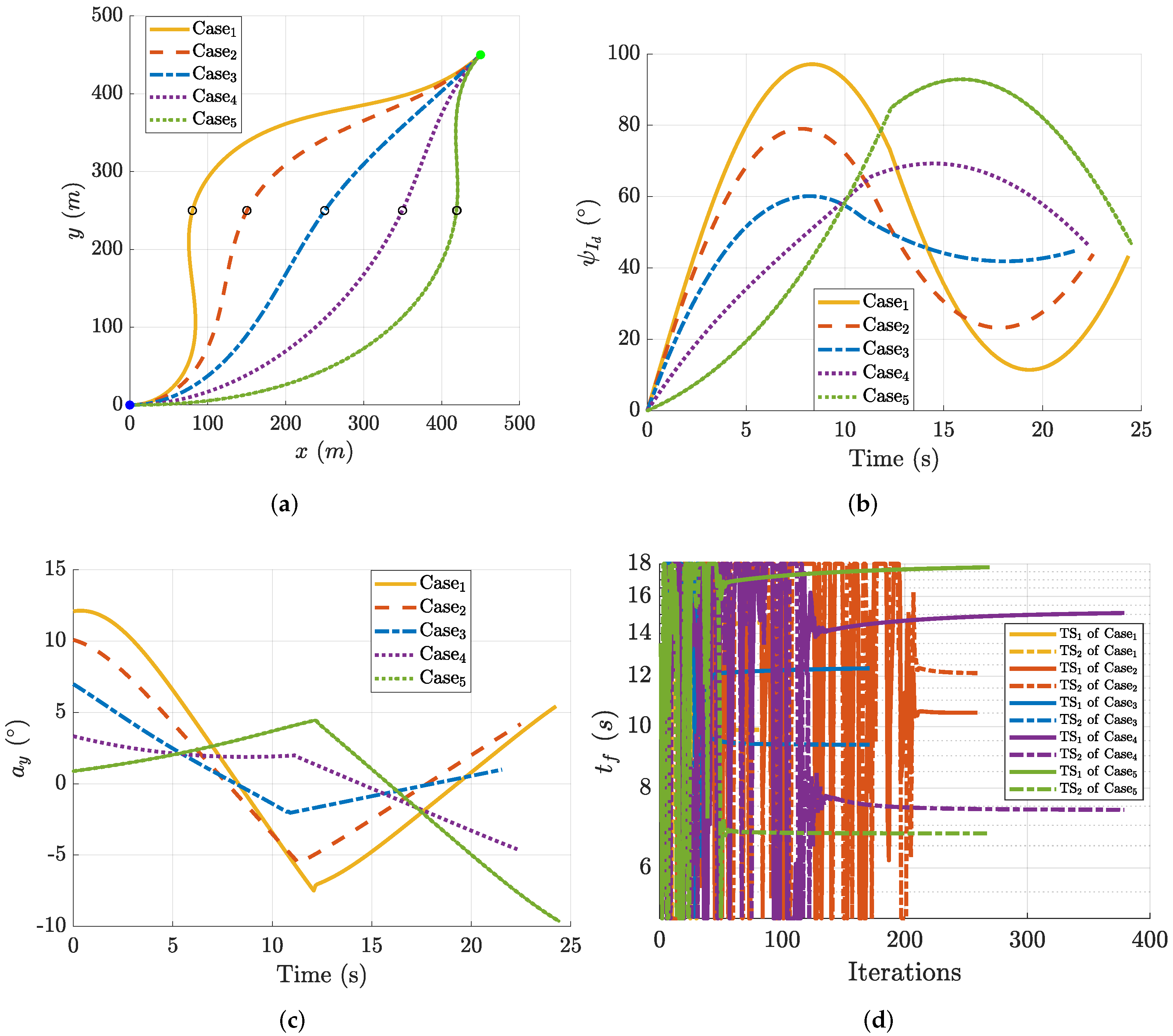
4.1. Mission Scenario and Simulation Setup
4.2. Performance of the C-PDDP Algorithm
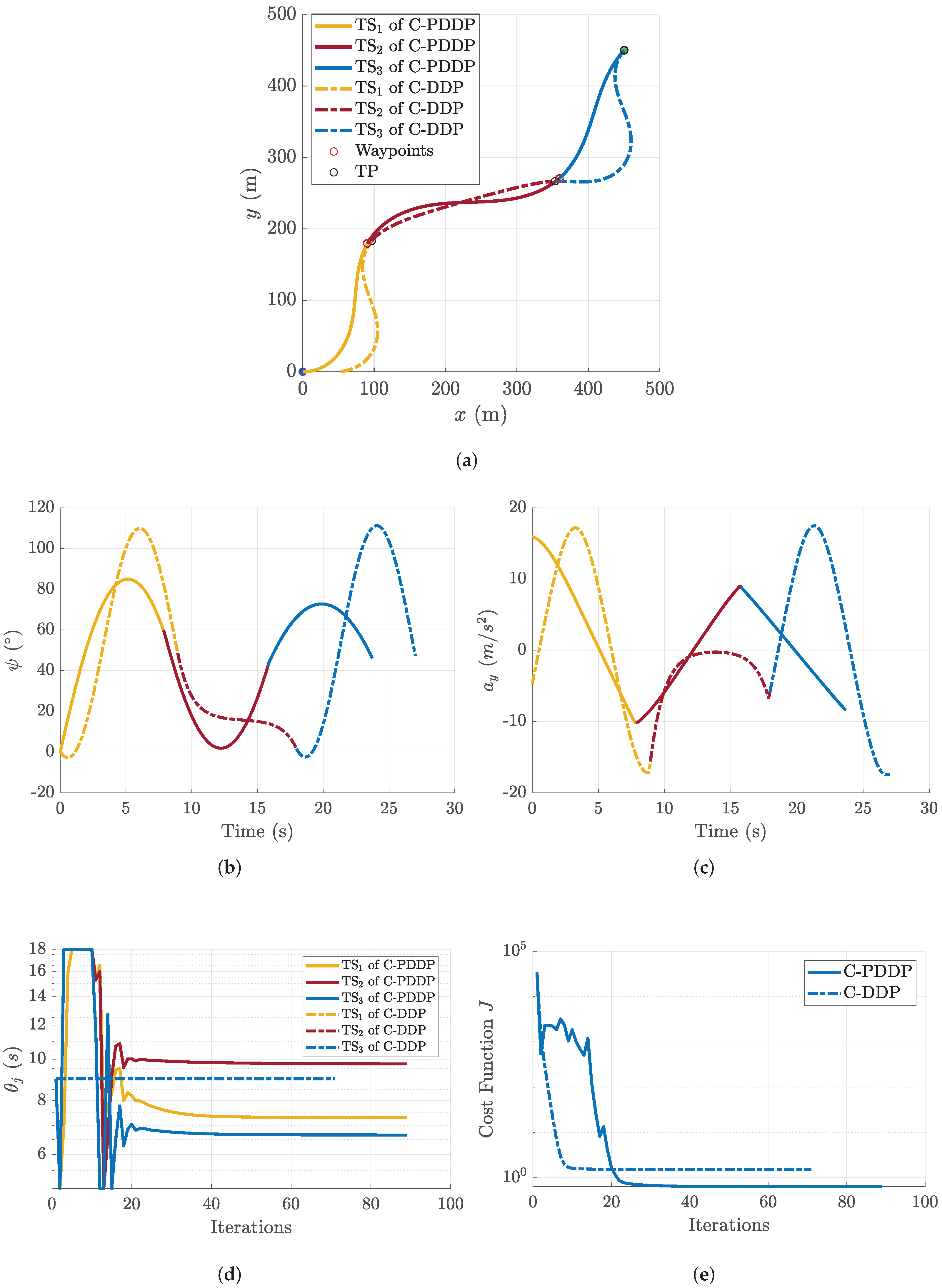
4.3. Comparison with C-DDP
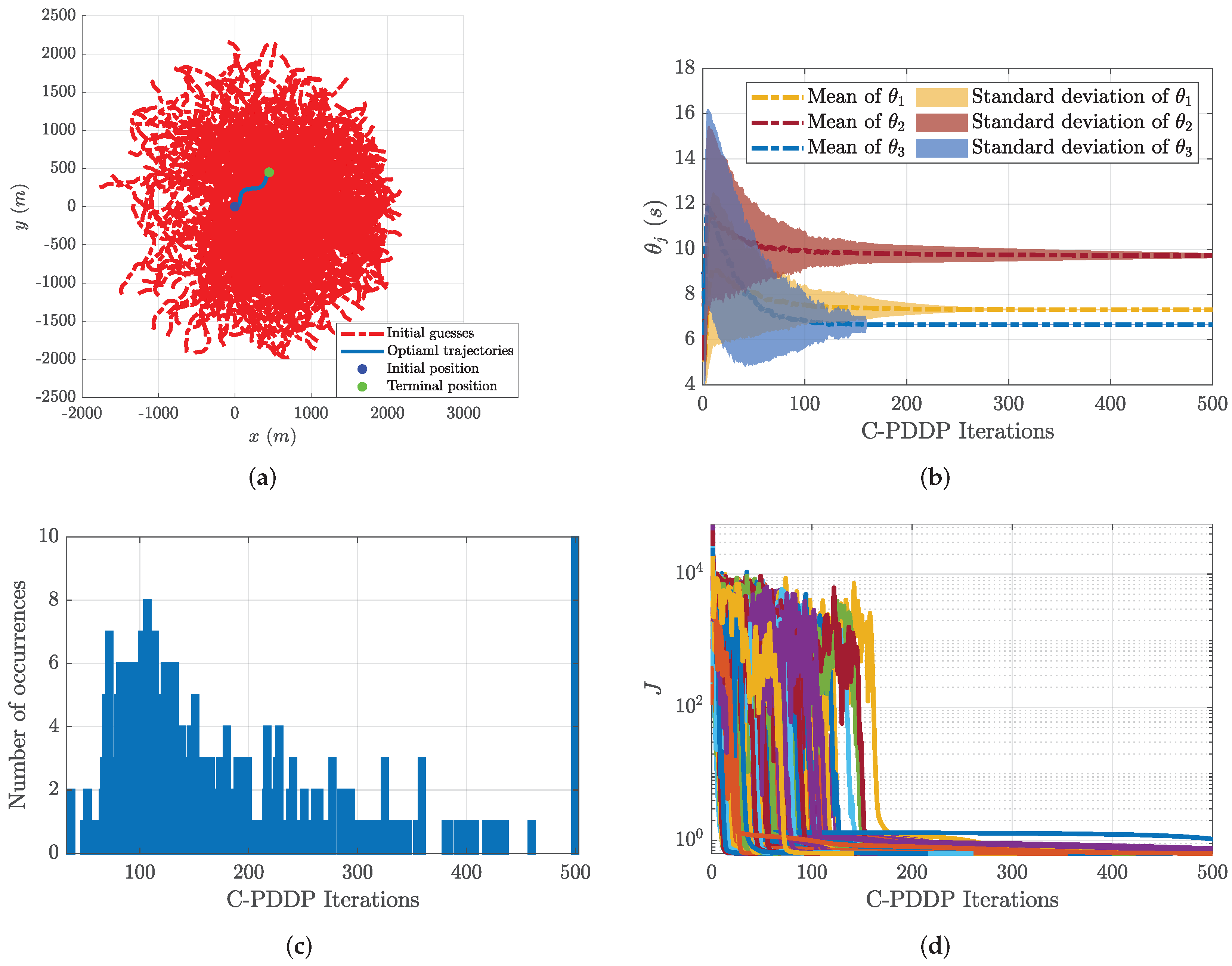
4.4. Monte Carlo Simulation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mulumba, T.; Diabat, A. Optimization of the drone-assisted pickup and delivery problem. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2024, 181, 103377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Han, Q.; Hu, Y. Sharing instant delivery UAVs for crowdsensing: A data-driven performance study. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 191, 110100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Sun, C.S.; Chen, Y.H. Optimal routing and scheduling of unmanned aerial vehicles for delivery services. Transp. Lett. 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, H.; Su, H. Analysis of the Development of Foreign Small Loitering Munitions and Their Early Warning System Response Strategy. Air Space Def. 2023, 6, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Kunze, O. A Comparative Review of Air Drones (UAVs) and Delivery Bots (SUGVs) for Automated Last Mile Home Delivery. Logistics 2023, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Lee, C.H.; Shin, H.S.; Tsourdos, A. Minimum-effort waypoint-following guidance. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2019, 42, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Shin, H.S.; Tsourdos, A.; Lee, C.H. Energy-optimal waypoint-following guidance considering autopilot dynamics. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 56, 2701–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.; Rahman, S.U.; Ullah, I.; Khan, I.; Alghadhban, A.J.; Al-Adhaileh, M.H.; Ali, G.; ElAffendi, M. A UAV-Swarm-Communication Model Using a Machine-Learning Approach for Search-and-Rescue Applications. Drones 2022, 6, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, R.; Savvaris, A.; Tsourdos, A.; Chai, S.; Xia, Y. A review of optimization techniques in spacecraft flight trajectory design. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2019, 109, 100543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Grant, M.J. Constrained trajectory optimization for planetary entry via sequential convex programming. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2017, 40, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Maity, A.; Holzapfel, F.; Tang, S. Adaptive trajectory generation based on real-time estimated parameters for impaired aircraft landing. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2019, 50, 2733–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Shin, H.S.; Tsourdos, A. Optimal Guidance for Integrated Waypoint Following and Obstacle Avoidance. In Proceedings of the 2019 Workshop on Research, Education and Development of Unmanned Aerial Systems (RED UAS), Cranfield, UK, 25–27 November 2019; pp. 325–334. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, R.; Savvaris, A.; Tsourdos, A. Violation Learning Differential Evolution-Based hp-Adaptive Pseudospectral Method for Trajectory Optimization of Space Maneuver Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 53, 2031–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Jiang, F.; Li, J. Fuel-optimal low-thrust trajectory optimization using indirect method and successive convex programming. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 2053–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laad, D.; Elango, P.; Mohan, R. Fourier Pseudospectral Method for Trajectory Optimization with Stability Requirements. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2020, 43, 2073–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Maity, A.; Holzapfel, F. Free Final-Time Constrained Sequential Quadratic Programming Based Flight Vehicle Guidance. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2021, 44, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, K.; Meng, G.; Tian, S. Spacecraft maneuvers via singularity-avoidance of control moment gyros based on dual-mode model predictive control. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2015, 51, 2546–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y. Entry Trajectory Optimization With Virtual Motion Camouflage Principle. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 56, 2527–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.; Chung, S.J.; Hadaegh, F.Y. Model predictive control of swarms of spacecraft using sequential convex programming. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2014, 37, 1725–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augugliaro, F.; Schoellig, A.P.; D’Andrea, R. Generation of collision-free trajectories for a quadrocopter fleet: A sequential convex programming approach. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura-Algarve, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; pp. 1917–1922. [Google Scholar]
- Deligiannis, A.; Amin, M.; Lambotharan, S.; Fabrizio, G. Optimum Sparse Subarray Design for Multitask Receivers. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 55, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, J.D.; Scheeres, D.J.; Lantoine, G. Hybrid Differential Dynamic Programming in the Circular Restricted Three-Body Problem. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2019, 42, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Pan, Y.; Lim, J.; Theodorou, E.A.; Tsiotras, P. Min-Max Differential Dynamic Programming: Continuous and Discrete Time Formulations. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2018, 41, 2568–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, N.; Campagnola, S.; Funase, R.; Yam, C.H. Stochastic Differential Dynamic Programming with Unscented Transform for Low-Thrust Trajectory Design. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2018, 41, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, J.; Atkeson, C.G. Minimax differential dynamic programming: An application to robust biped walking. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2002, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Todorov, E. Iterative Linear Quadratic Regulator Design for Nonlinear Biological Movement Systems. In Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics; SciTePress: Setubal, Portugal, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 222–229. [Google Scholar]
- Tassa, Y.; Erez, T.; Smart, W.D. Receding Horizon Differential Dynamic Programming. In Proceedings of the NIPS, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–6 December 2007; pp. 1465–1472. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Shin, H.S.; Tsourdos, A. Computational guidance using sparse Gauss–Hermite quadrature differential dynamic programming. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wen, C.; Han, H.; Qiao, D. Aerocapture Trajectory Planning Using Hierarchical Differential Dynamic Programming. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 2022, 59, 1647–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayne, D. A Second-order Gradient Method for Determining Optimal Trajectories of Non-linear Discrete-time Systems. Int. J. Control 1966, 3, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhao, X.; Xu, X.; Mei, C.; Xing, W.; Wang, X. Trajectory tracking control for underactuated autonomous vehicles via adaptive dynamic programming. J. Frankl. Inst. 2024, 361, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsekas, D.P. Reinforcement Learning and Optimal Control; Athena Scientific: Belmont, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Manchester, Z.; Kuindersma, S. Derivative-free trajectory optimization with unscented dynamic programming. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 55th Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 12–14 December 2016; pp. 3642–3647. [Google Scholar]
- Giftthaler, M.; Neunert, M.; Stäuble, M.; Buchli, J.; Diehl, M. A Family of Iterative Gauss–Newton Shooting Methods for Nonlinear Optimal Control. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini, E.; Russell, R.P. A multiple-shooting differential dynamic programming algorithm. Part 1: Theory. Acta Astronaut. 2020, 170, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yu, W.; Zhang, T.; Wensing, P.M. A Unified Perspective on Multiple Shooting In Differential Dynamic Programming. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Detroit, MI, USA, 1–5 October 2023; pp. 9978–9985. [Google Scholar]
- Mastalli, C.; Budhiraja, R.; Merkt, W.; Saurel, G.; Hammoud, B.; Naveau, M.; Carpentier, J.; Righetti, L.; Vijayakumar, S.; Mansard, N. Crocoddyl: An Efficient and Versatile Framework for Multi-Contact Optimal Control. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 2536–2542. [Google Scholar]
- Foehn, P.; Romero, A.; Scaramuzza, D. Time-optimal planning for quadrotor waypoint flight. Sci. Robot. 2021, 6, eabh1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, A.; Padhi, R.; Mallaram, S.; Rao, G.M.; Manickavasagam, M. A robust and high precision optimal explicit guidance scheme for solid motor propelled launch vehicles with thrust and drag uncertainty. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2016, 47, 3078–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; He, S.; Lin, D. Constrained Trajectory Optimization With Flexible Final Time for Autonomous Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 58, 1818–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chai, R.; Chai, S.; Zhang, B.; Tsourdos, A. Flexible Final-Time Stochastic Differential Dynamic Programming for Autonomous Vehicle Trajectory Optimization. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2023, 59, 6658–6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshin, A.; Houghton, M.D.; Acheson, M.J.; Gregory, I.M.; Theodorou, E.A. Parameterized Differential Dynamic Programming. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.03727. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, S.; Griffin, R.; Mastalli, C. Multi-Contact Inertial Estimation and Localization in Legged Robots. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.17161. [Google Scholar]
- Nocedal, J.; Wright, S. Numerical Optimization; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Plancher, B.; Manchester, Z.; Kuindersma, S. Constrained unscented dynamic programming. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 5674–5680. [Google Scholar]
- Farshidian, F.; Neunert, M.; Winkler, A.W.; Rey, G.; Buchli, J. An efficient optimal planning and control framework for quadrupedal locomotion. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Tassa, Y.; Mansard, N.; Todorov, E. Control-limited differential dynamic programming. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 1168–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, D.M.; Yakowitz, S.J. Differential dynamic programming and Newton’s method for discrete optimal control problems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1984, 43, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassa, Y.; Erez, T.; Todorov, E. Synthesis and stabilization of complex behaviors through online trajectory optimization. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura-Algarve, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; pp. 4906–4913. [Google Scholar]
- AeroVironment, Inc. Available online: https://www.avinc.com/lms/switchblade (accessed on 17 May 2024).
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Terminal weighting matrix | |
| Control weighting matrix | 1 |
| State weighting matrix | |
| LM parameter | |
| LM parameter | |
| Damping coefficient | 0.4 |
| Penalty factor | 50 |
| Number of discrete nodes N | 270 |
| Penalty factor growth rate | |
| Stopping threshold |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| UAV initial parameters | |
| Target point parameters | |
| UAV flight speed V | |
| Lateral acceleration limitation | |
| Waypoint 1 position | |
| Waypoint 2 position | |
| Waypoint 3 position | |
| Waypoint 4 position | |
| Waypoint 5 position | |
| Flight time initial guess for each segment | |
| Segment flight time limitations |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Waypoint 1 position | |
| Waypoint 2 position | |
| Initial flight time guess for each segment |
| Algorithm | Error at the Waypoint | Total Flight Time | Energy Consumption |
|---|---|---|---|
| C-PDDP | 1.06 m | 23.67 s | 2099.0 |
| C-DDP | 7.34 m | 27.00 s | 4901.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, X.; Xia, F.; Lin, D.; Jin, T.; Su, W.; He, S. Constrained Parameterized Differential Dynamic Programming for Waypoint-Trajectory Optimization. Aerospace 2024, 11, 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11060420
Zheng X, Xia F, Lin D, Jin T, Su W, He S. Constrained Parameterized Differential Dynamic Programming for Waypoint-Trajectory Optimization. Aerospace. 2024; 11(6):420. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11060420
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Xiaobo, Feiran Xia, Defu Lin, Tianyu Jin, Wenshan Su, and Shaoming He. 2024. "Constrained Parameterized Differential Dynamic Programming for Waypoint-Trajectory Optimization" Aerospace 11, no. 6: 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11060420
APA StyleZheng, X., Xia, F., Lin, D., Jin, T., Su, W., & He, S. (2024). Constrained Parameterized Differential Dynamic Programming for Waypoint-Trajectory Optimization. Aerospace, 11(6), 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11060420







