Design and Structure Optimization of Arresting Gear Based on Magnetorheological Damper
Abstract
:1. Introduction
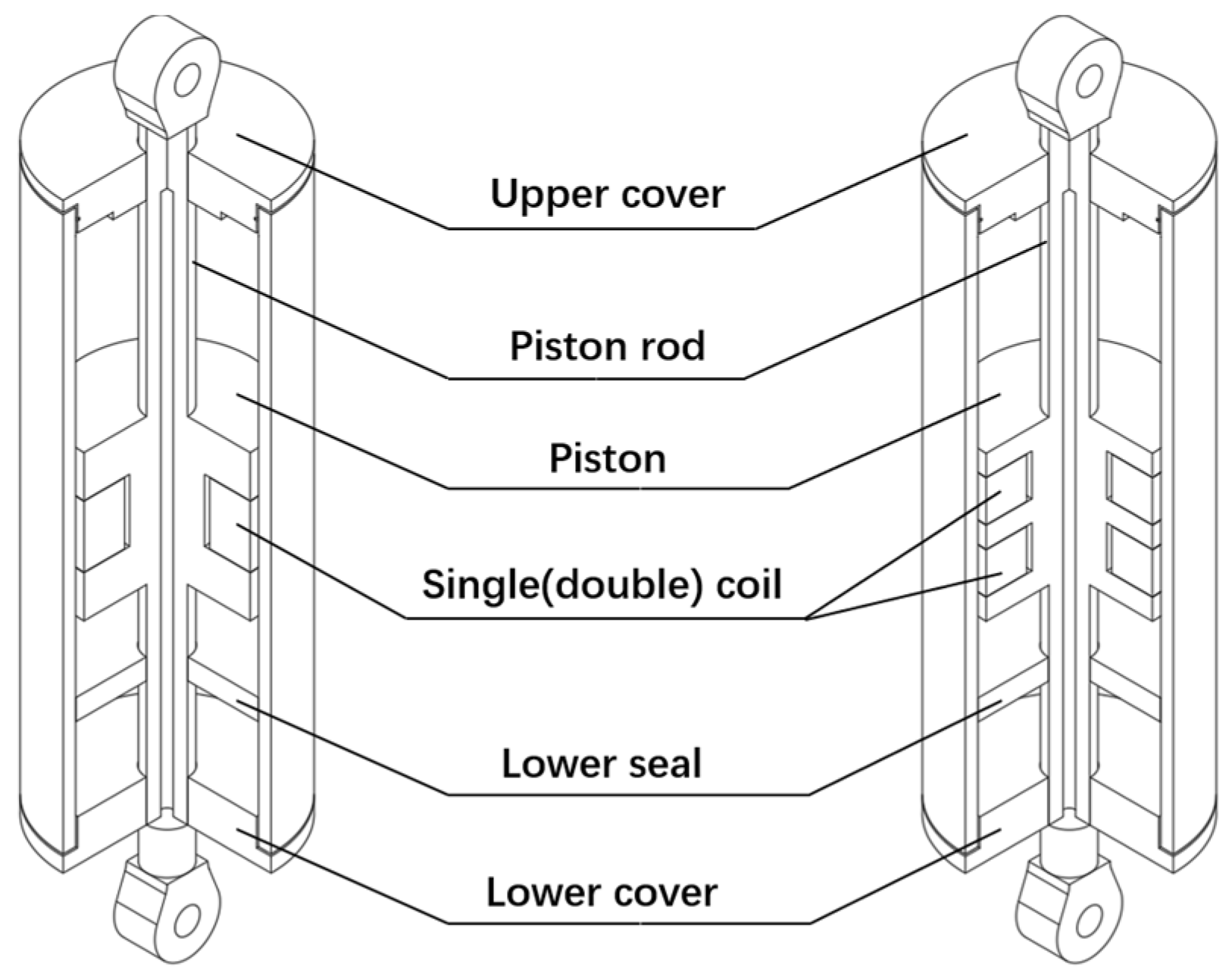
2. Structure and Numerical Modeling of MR Dampers
2.1. Parametric Modeling of MR Dampers
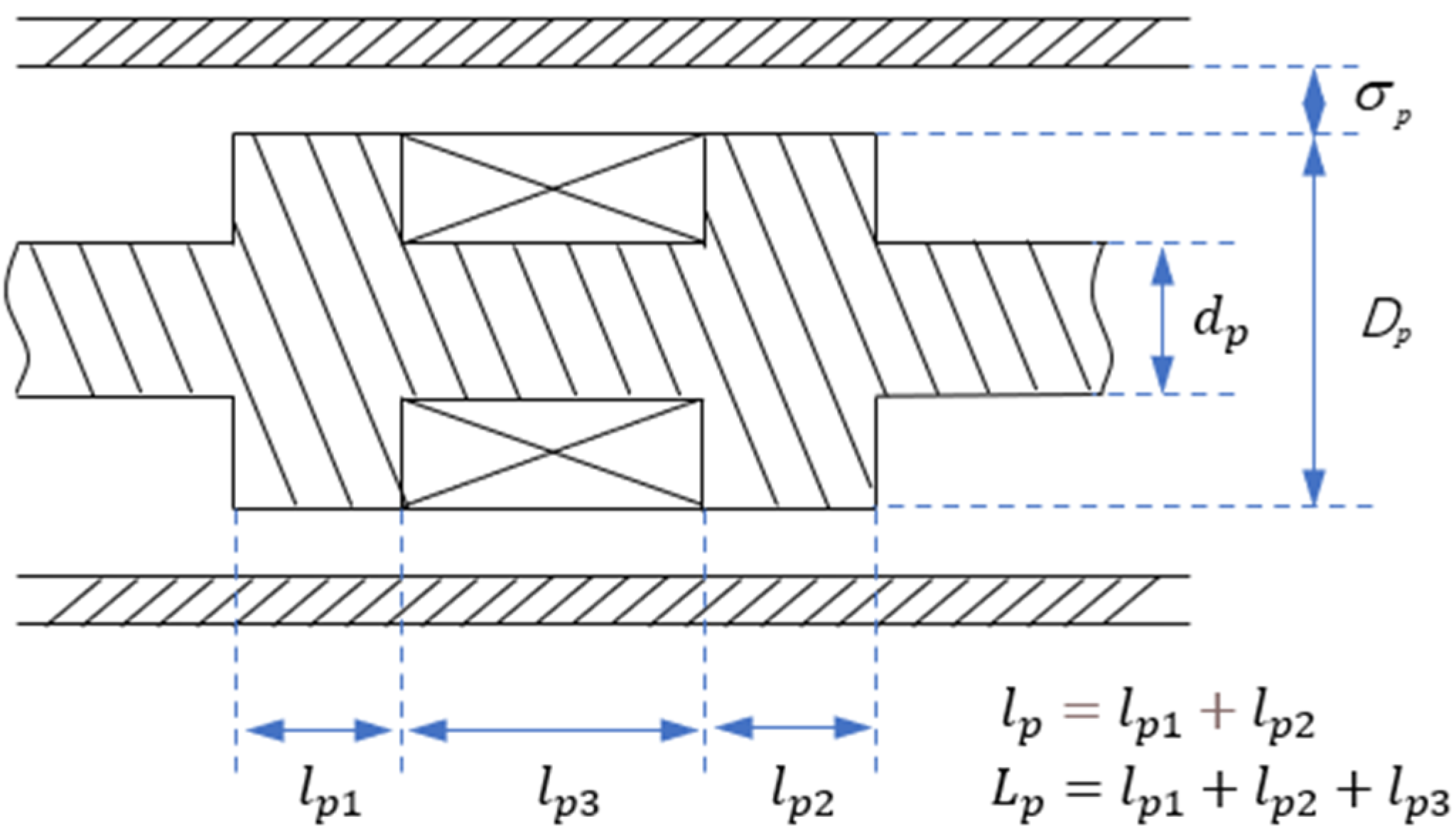
2.1.1. Parametric Modeling of Single-coil MR Damper
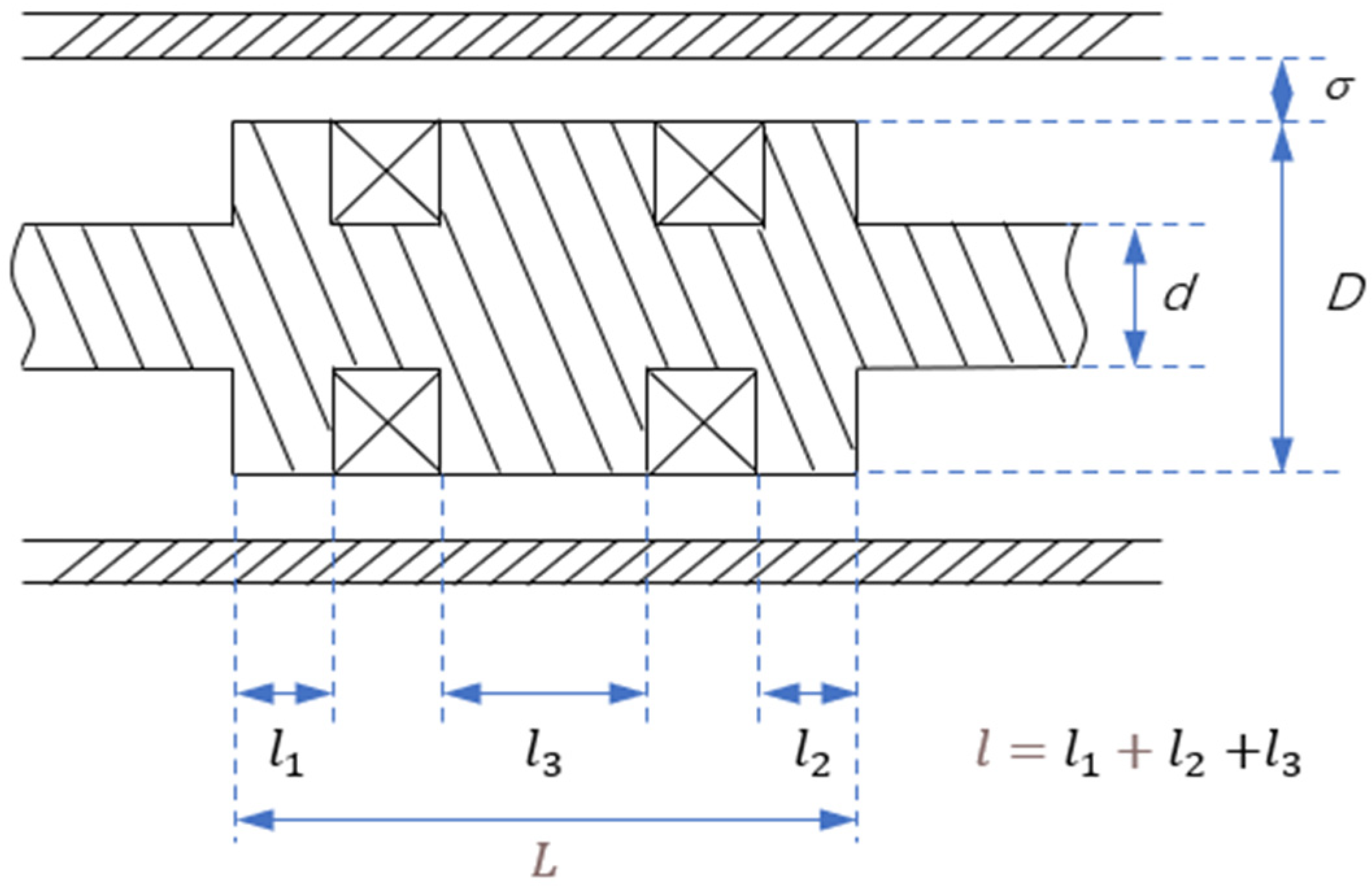
2.1.2. Parametric Modeling of Double-Coil MR Damper
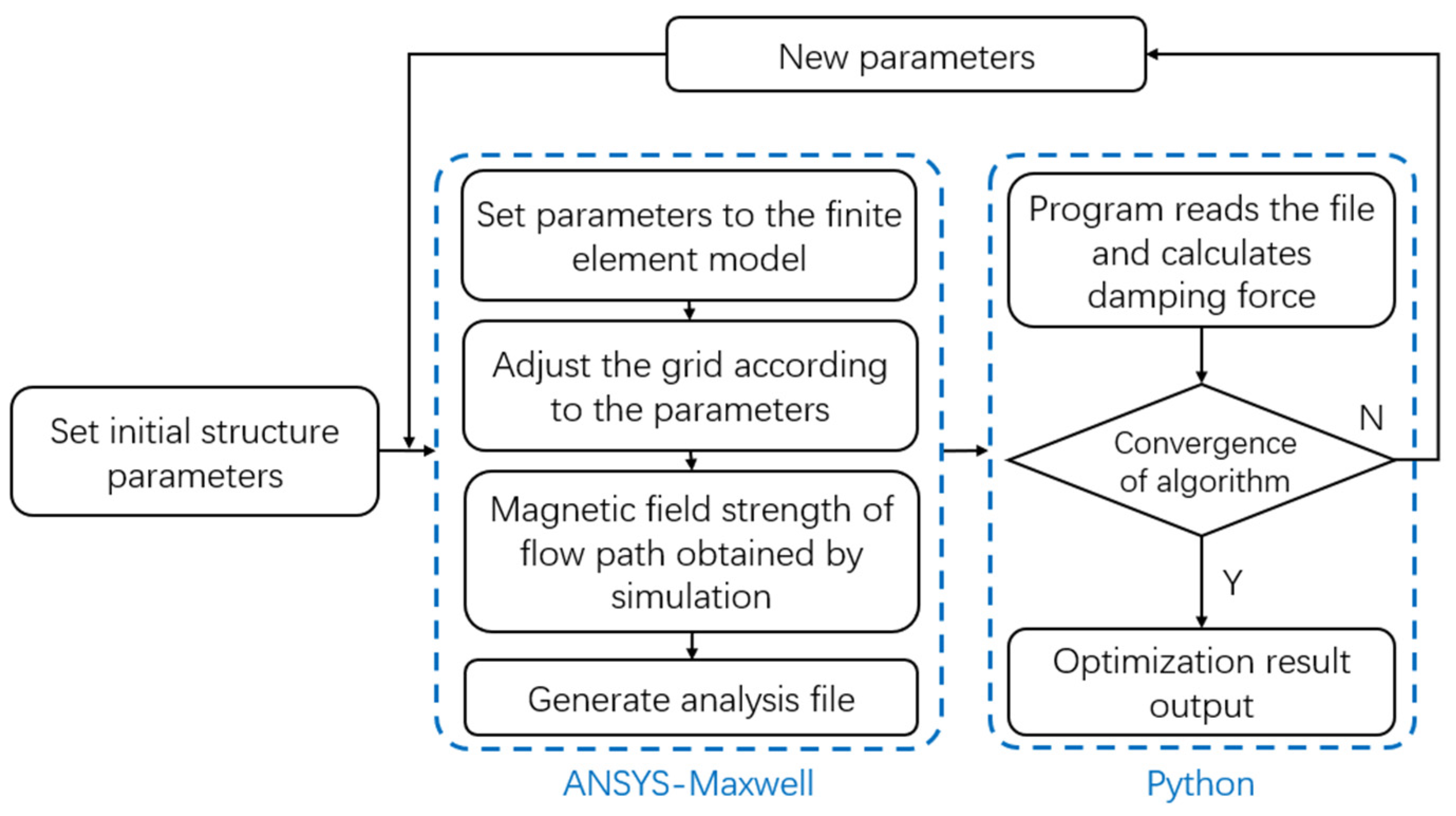
3. Optimization Process
4. Introduction of Optimization Model
4.1. Determine the Structure Parameters to Be Optimized
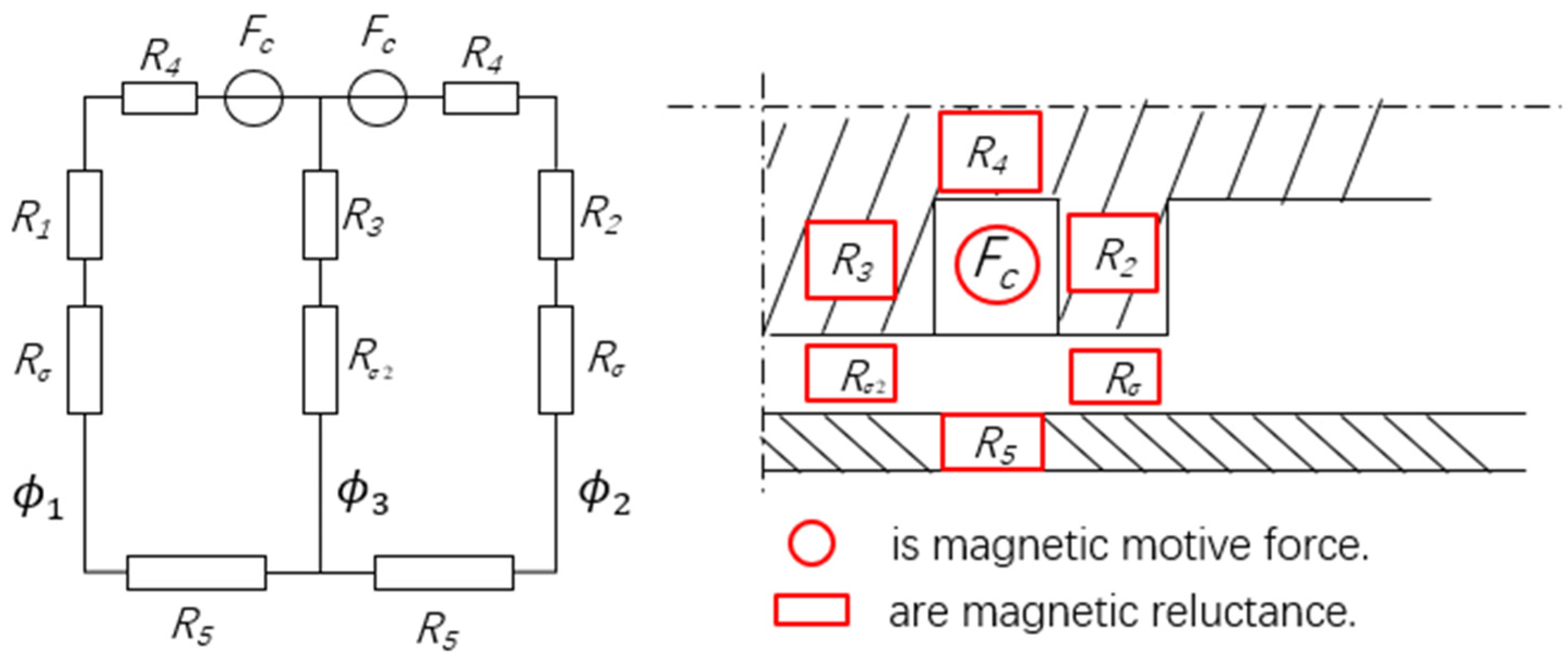
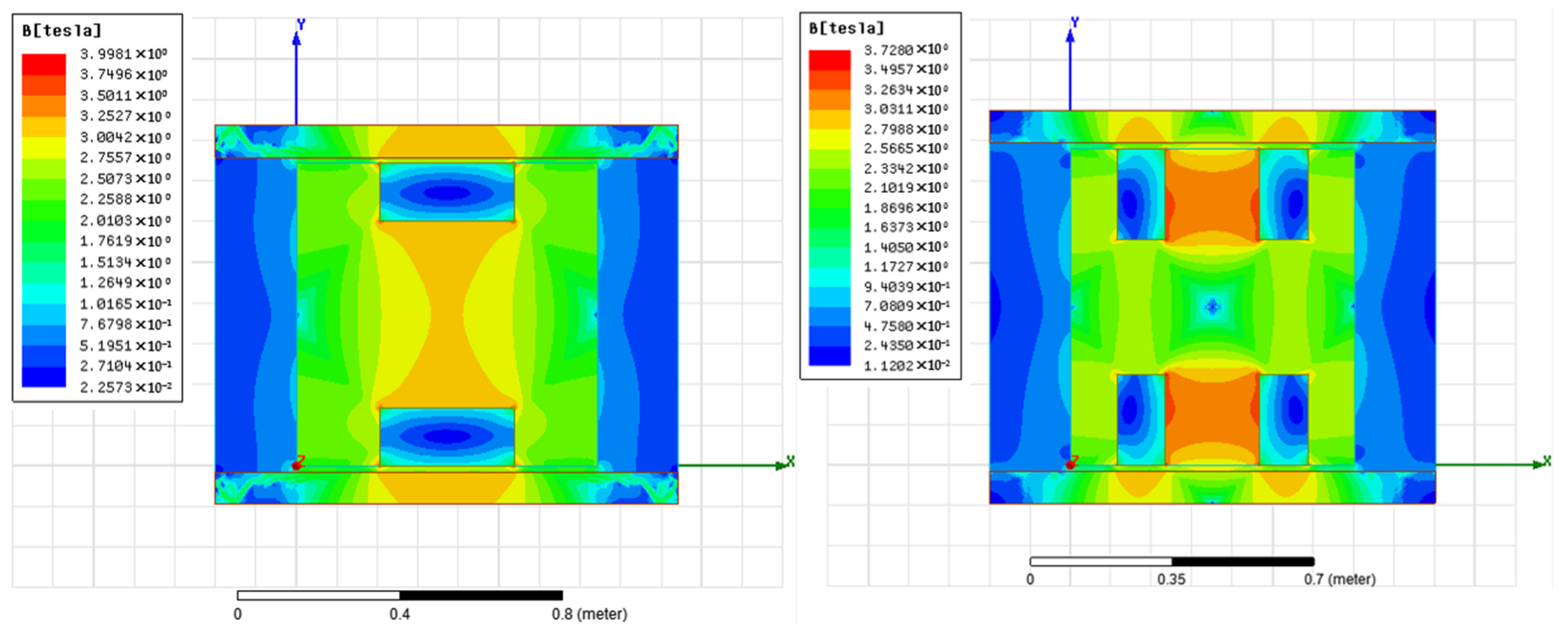
4.2. Finite Element Simulation Model of Magnetic Field of Damper
4.3. Boundary and Genetic Algorithm Optimization Model
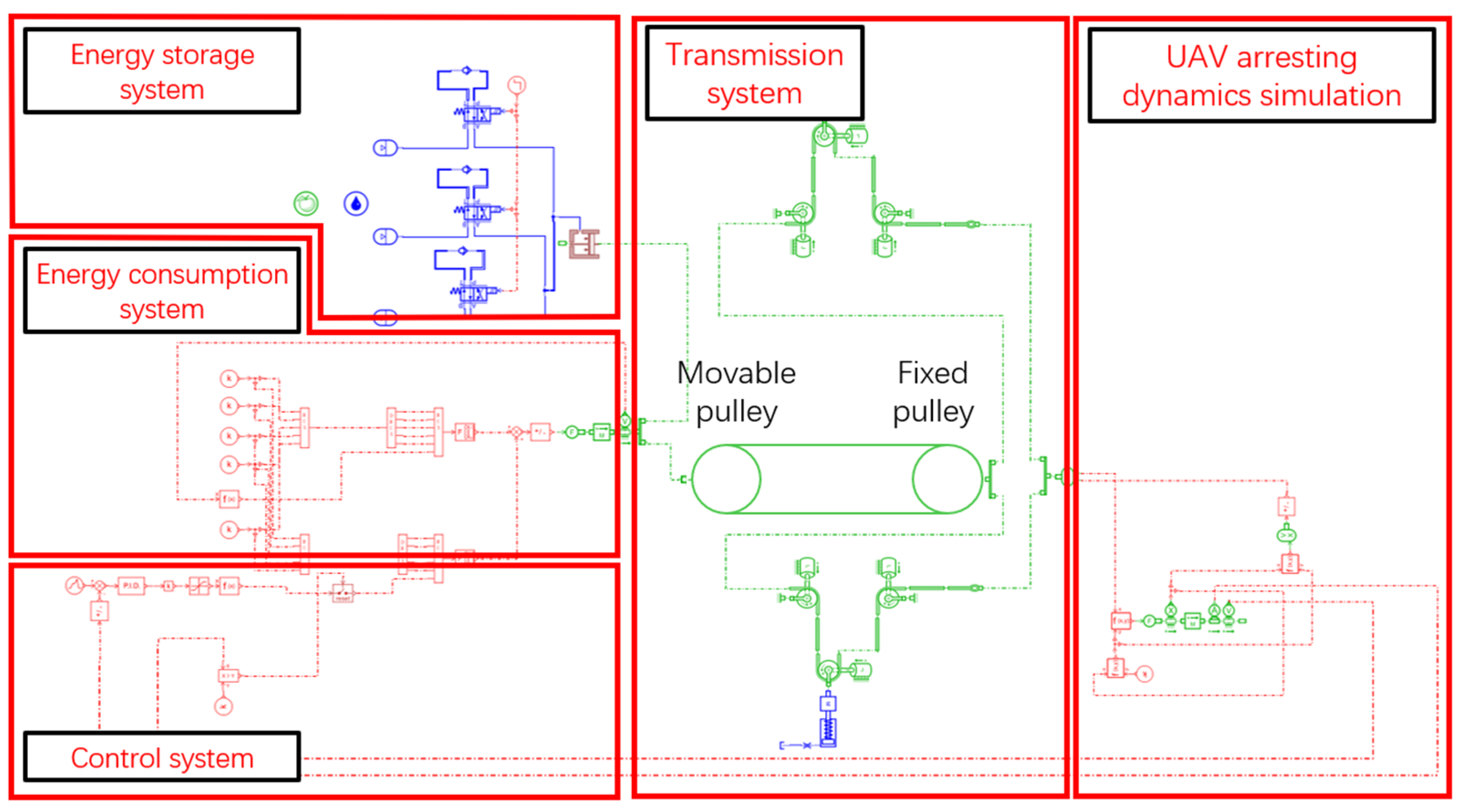
4.4. UAV Arresting Dynamics Simulation Model
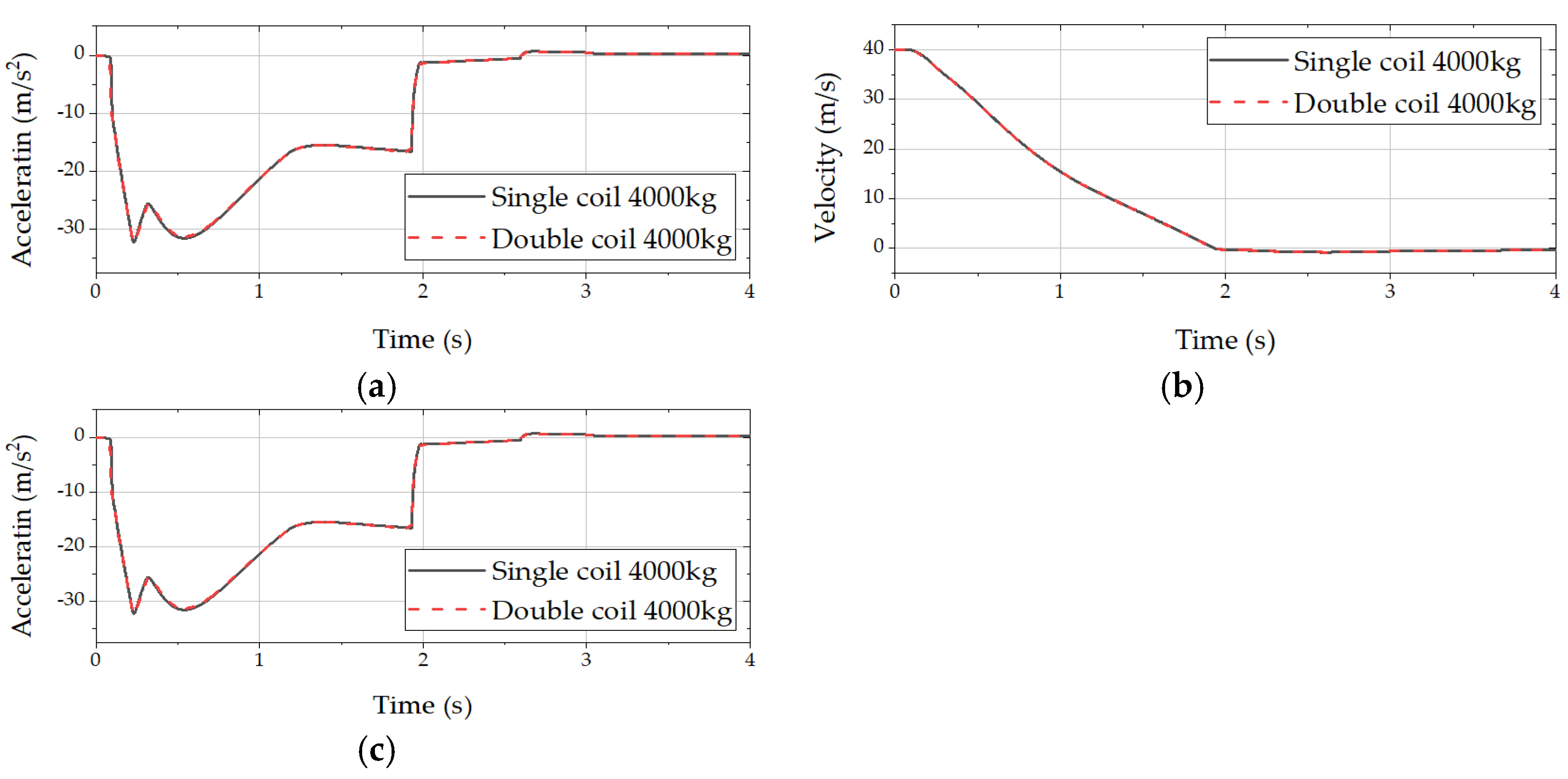
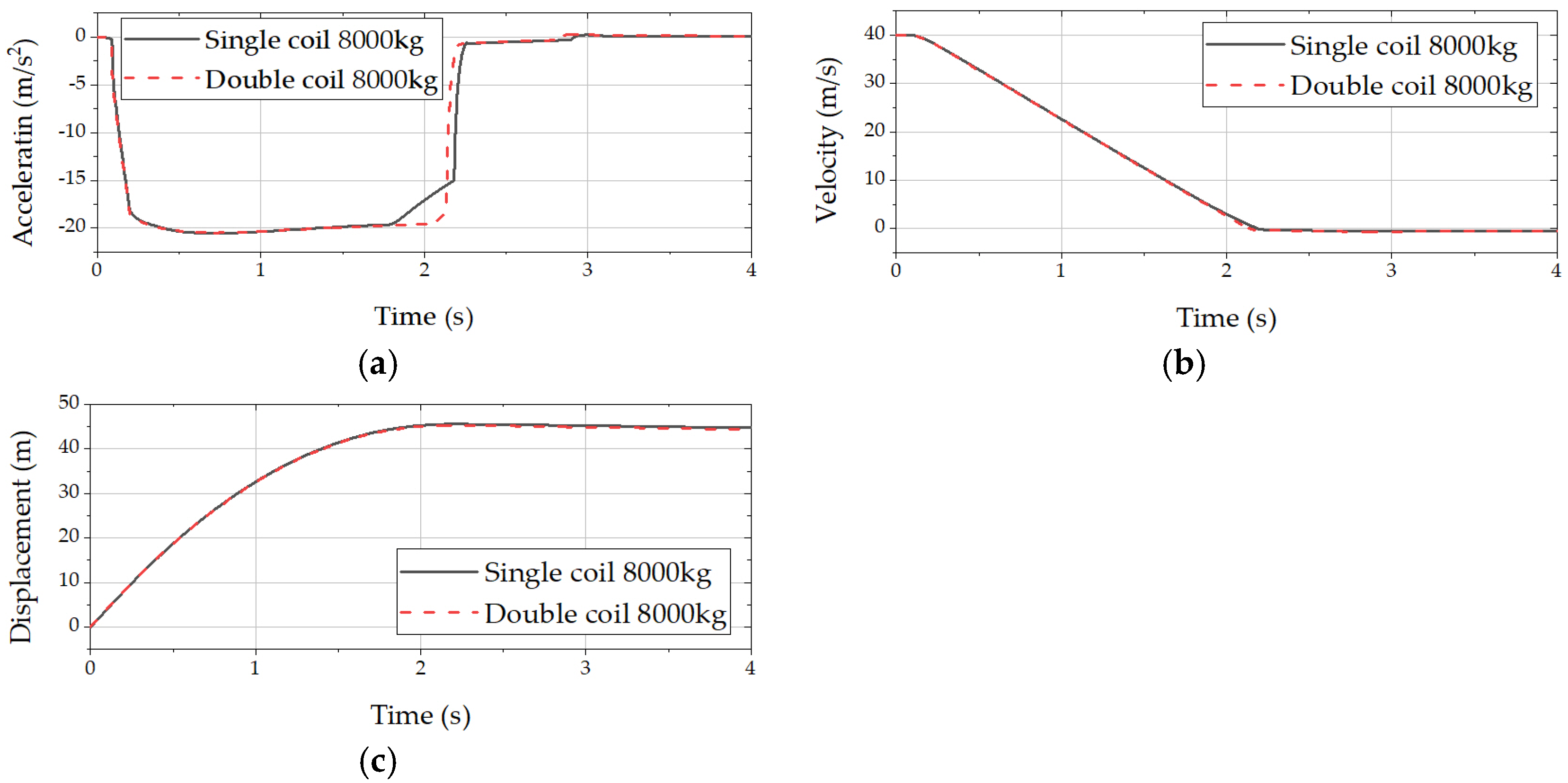
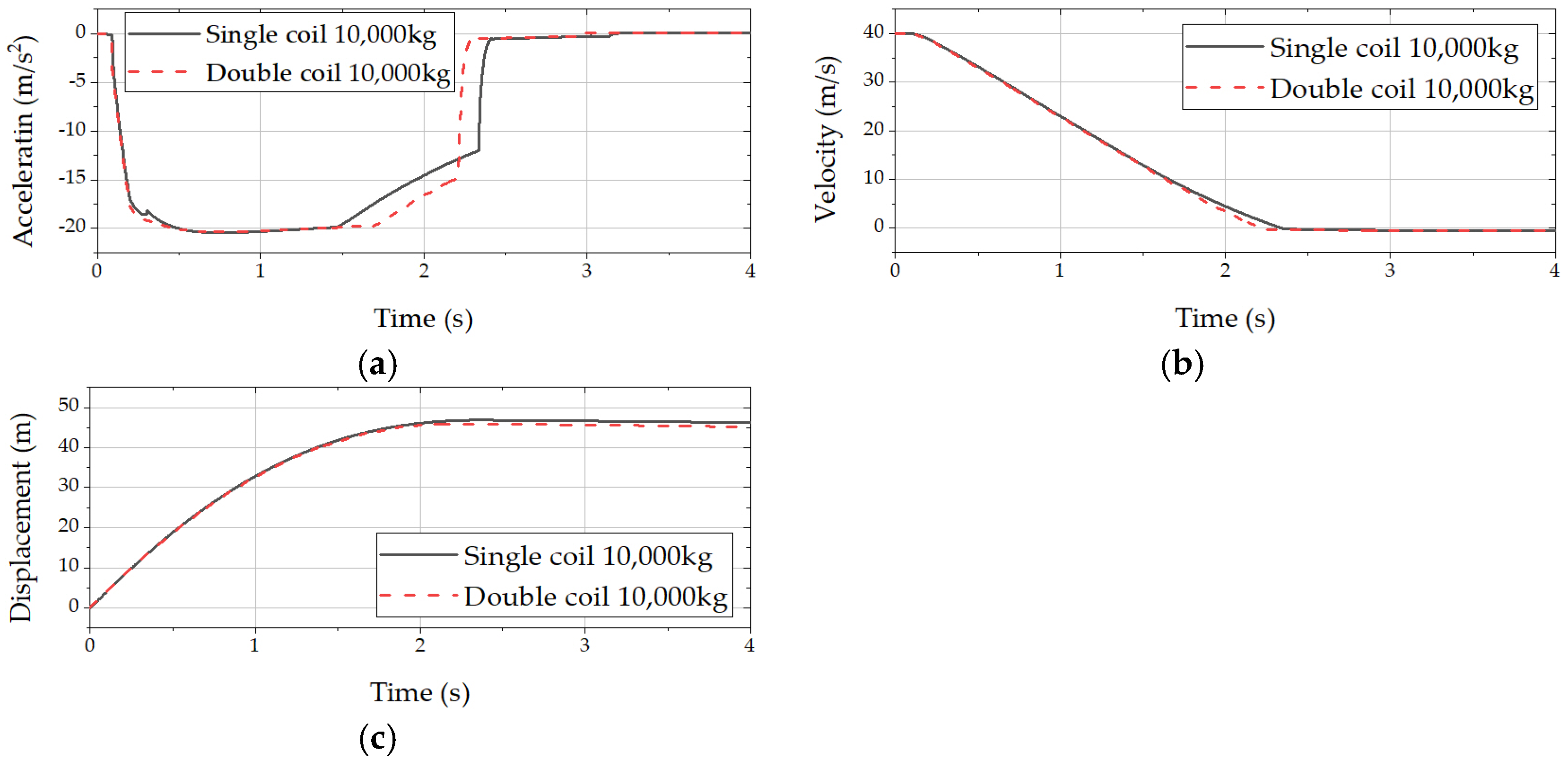
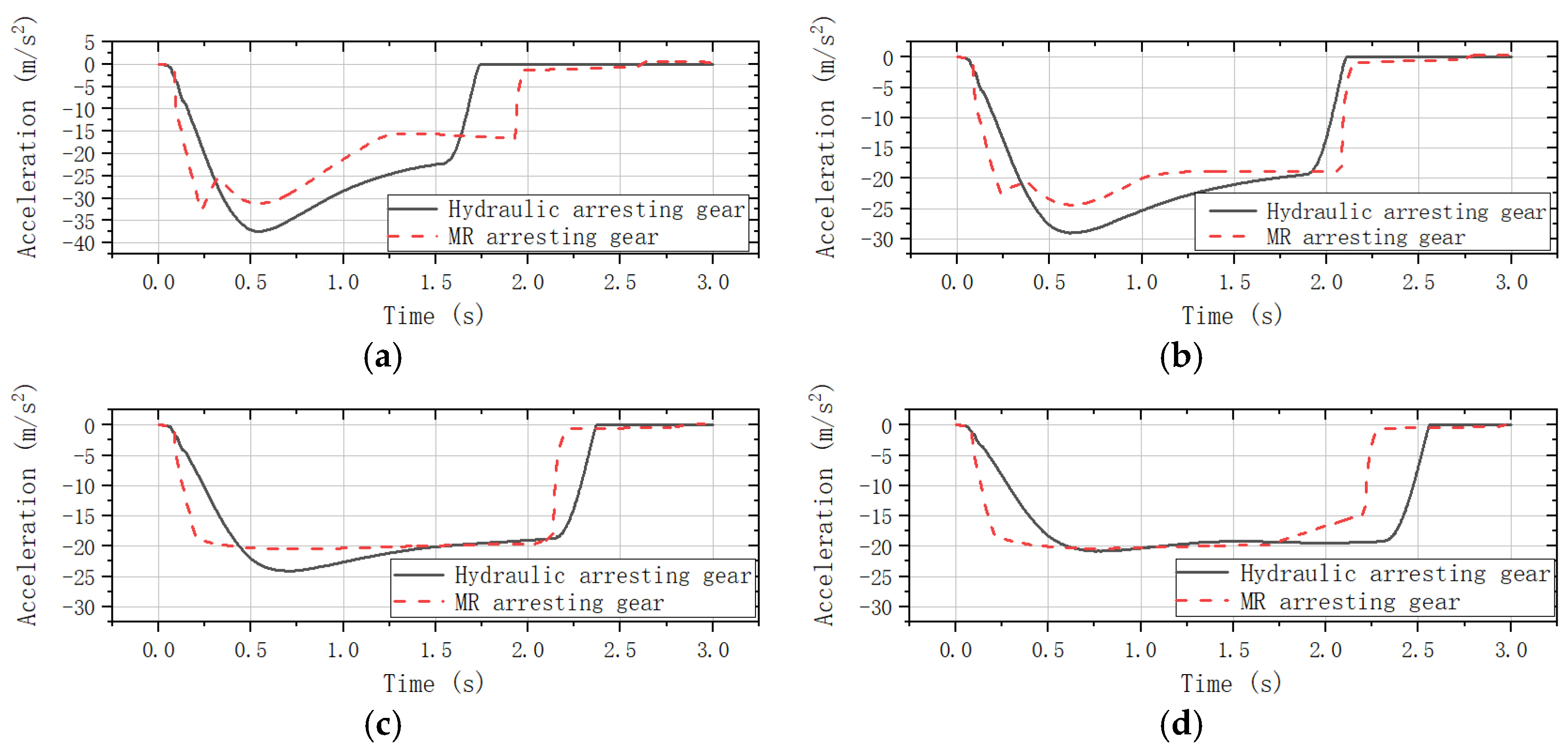
5. Optimization Results and Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Xing, J. Cooperative task assignment of multi−UAV system. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2020, 33, 2825–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Li, D.; Li, R.; Wang, Y. Analysis on MAV/UAV cooperative combat based on complex network. Def. Technol. 2020, 16, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, X. Analysis of the development status and outlook of UAV clusters and anti−UAV clusters. Acta Aeronaut. Et Astronaut. Sin. 2022, 43, 4–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J. Research on launching and recycling technology of a small marine unmanned aerial vehicle. Nanjing Nanjing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 2019, 45–61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan Raju, S.; Manjunath, H.G.; Narayan, N. Modeling of Aircraft Arresting Gear System by Multibody Dynamics Approach and Co−Simulation of Multibody Dynamics with Hydraulic System Using Adams and Easy5. In Advances in Engineering Design and Simulation: Select Proceedings of NIRC 2018; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 249–262. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Liu, F.; Xie, Z. Design, analysis, and experimental evaluation of a double coil magnetorheological fluid damper. Shock Vib. 2016, 2016, 4184726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.A.; Suresh, A.; Ramaiah, N.S. Analysis of magnetorheological fluid damper with various piston profiles. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2012, 2, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Yazid, I.M.; Mazlan, S.A.; Zamzuri, H. Parameters Consideration in Designing a Magnetorheological Damper. Key Eng. Mater. 2013, 543, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Rui, X.; Yang, F. Multi−objective optimization design for a magnetorheological damper. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2022, 33, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Feng, Z.; Chen, Y. Design and multi−objective optimization of magnetorheological damper considering the consistency of magnetic flux density. Shock Vib. 2020, 2020, 7050356. [Google Scholar]
- Olivier, M.; Sohn, J.W. Design and geometric parameter optimization of hybrid magnetorheological fluid damper. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 2953–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, Y. Modeling and control of the pulley buffer system of arresting cable for shipboard aircraft based on magneto−rheological fluid. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 2012, 17, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T. Study on Mechanical Modeling of Carrier−based Aircraft Arresting Cable on Magneto−rheological Damper. Shenyang Shenyang Aerosp. Univ. 2012, 2012, 26–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Khedkar, Y.M.; Bhat, S.; Adarsha, H. A review of magnetorheological fluid damper technology and its applications. Int. Rev. Mech. Eng. 2019, 13, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesha, A.; Patil, S.; Kumar, N.; Murthy, A. Magnetic field enhancement technique in the fluid flow gap of a single coil twin tube Magnetorheological damper using magnetic shields. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2020, 14, 6679–6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Tang, J. Application of MR Smart materials in structural vibration control. Appl. MR Smart Mater. Struct. Vib. Control 2000, 2, 15–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- MIL−STD−2066; Military Standard: Catapulting and Arresting Gear Forcing Functions for Aircraft Structural Design. Department of the Navy Air Systems Command: Patuxent, MD, USA, 1981; pp. 108–114.
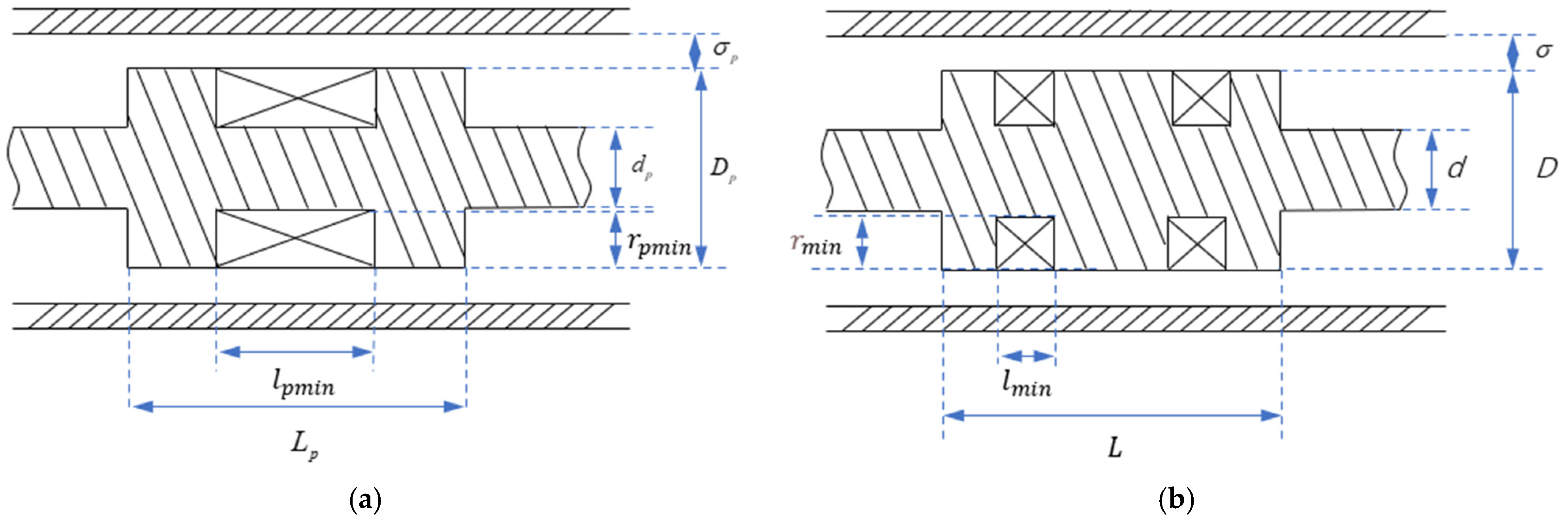



| Parameter | Symbol | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Piston diameter | Dp(D) | 0.7 | 1.0 | m |
| Depth of coil embedded in the piston | rpmin(rmin) | 0.10 | 0.20 | m |
| Width of flow path | σp(σ) | 0.006 | 0.015 | m |
| Coil length of the single-coil damper | lpmin | 0.20 | 0.40 | m |
| Coil length of the double-coil damper | lmin | 0.10 | 0.20 | m |
| Piston−length−to−diameter ratio | Lp/Dp | 0.6 | 1.0 |
| Parameter | Single Coil | Double Coil | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Unit | Value | Unit | |
| Piston radius | 0.389 | m | 0.376 | m |
| Coil depth | 0.244 | m | 0.198 | m |
| Width of flow path | 0.0149 | m | 0.0149 | m |
| Coil length | 0.200 | m | 0.100 | m |
| Ratio of piston length to diameter | 0.877 | 0.999 | ||
| Strength of magnetic field | 1.757 | T | Middle 2.405 | T |
| Sides 1.3 | ||||
| Damping force | 3,869,462 | N | 4,050,563 | N |
| Viscous damping force | 2,099,661 | N | 2,099,909 | N |
| UAV Mass | Before Optimization | After Optimization | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4000 kg (single-coil damper) | −40.5 | m/s2 | −32.5 | m/s2 |
| 6000 kg (single-coil damper) | −31.1 | m/s2 | −24.8 | m/s2 |
| 8000 kg (single-coil damper) | −28.8 | m/s2 | −21.0 | m/s2 |
| 10,000 kg (single-coil damper) | −26.8 | m/s2 | −20.0 | m/s2 |
| 4000 kg (double-coil damper) | −41.8 | m/s2 | −32.5 | m/s2 |
| 6000 kg (double-coil damper) | −32.6 | m/s2 | −24.8 | m/s2 |
| 8000 kg (double-coil damper) | −29.2 | m/s2 | −20.5 | m/s2 |
| 10,000 kg (double-coil damper) | −26.8 | m/s2 | −19.9 | m/s2 |
| UAV Mass | Displacement | Arresting Time | Acceleration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MR | Hydraulic | MR | Hydraulic | MR | Hydraulic | |
| 4000 kg | 35.1 m | 31.8 m | 1.9 s | 1.7 s | −32.5 m/s2 | −37.4 m/s2 |
| 6000 kg | 41.9 m | 39.5 m | 2.0 s | 2.1 s | −24.8 m/s2 | −29.0 m/s2 |
| 8000 kg | 44.5 m | 45.4 m | 2.1 s | 2.4 s | −20.5 m/s2 | −24.1 m/s2 |
| 10,000 kg | 46.5 m | 50.1 m | 2.2 s | 2.6 s | −19.9 m/s2 | −20.8 m/s2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, J.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Ma, H.; Wei, X. Design and Structure Optimization of Arresting Gear Based on Magnetorheological Damper. Aerospace 2023, 10, 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10121019
Hao J, Wang Y, Peng Y, Ma H, Wei X. Design and Structure Optimization of Arresting Gear Based on Magnetorheological Damper. Aerospace. 2023; 10(12):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10121019
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Jiayu, Yifeng Wang, Yiming Peng, Hui Ma, and Xiaohui Wei. 2023. "Design and Structure Optimization of Arresting Gear Based on Magnetorheological Damper" Aerospace 10, no. 12: 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10121019
APA StyleHao, J., Wang, Y., Peng, Y., Ma, H., & Wei, X. (2023). Design and Structure Optimization of Arresting Gear Based on Magnetorheological Damper. Aerospace, 10(12), 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace10121019






