Comparative Plastomics of Ashwagandha (Withania, Solanaceae) and Identification of Mutational Hotspots for Barcoding Medicinal Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genome Assembly and Annotation
2.2. Comparative Chloroplast Genome Analysis
2.3. Phylogenomic Analysis
3. Results
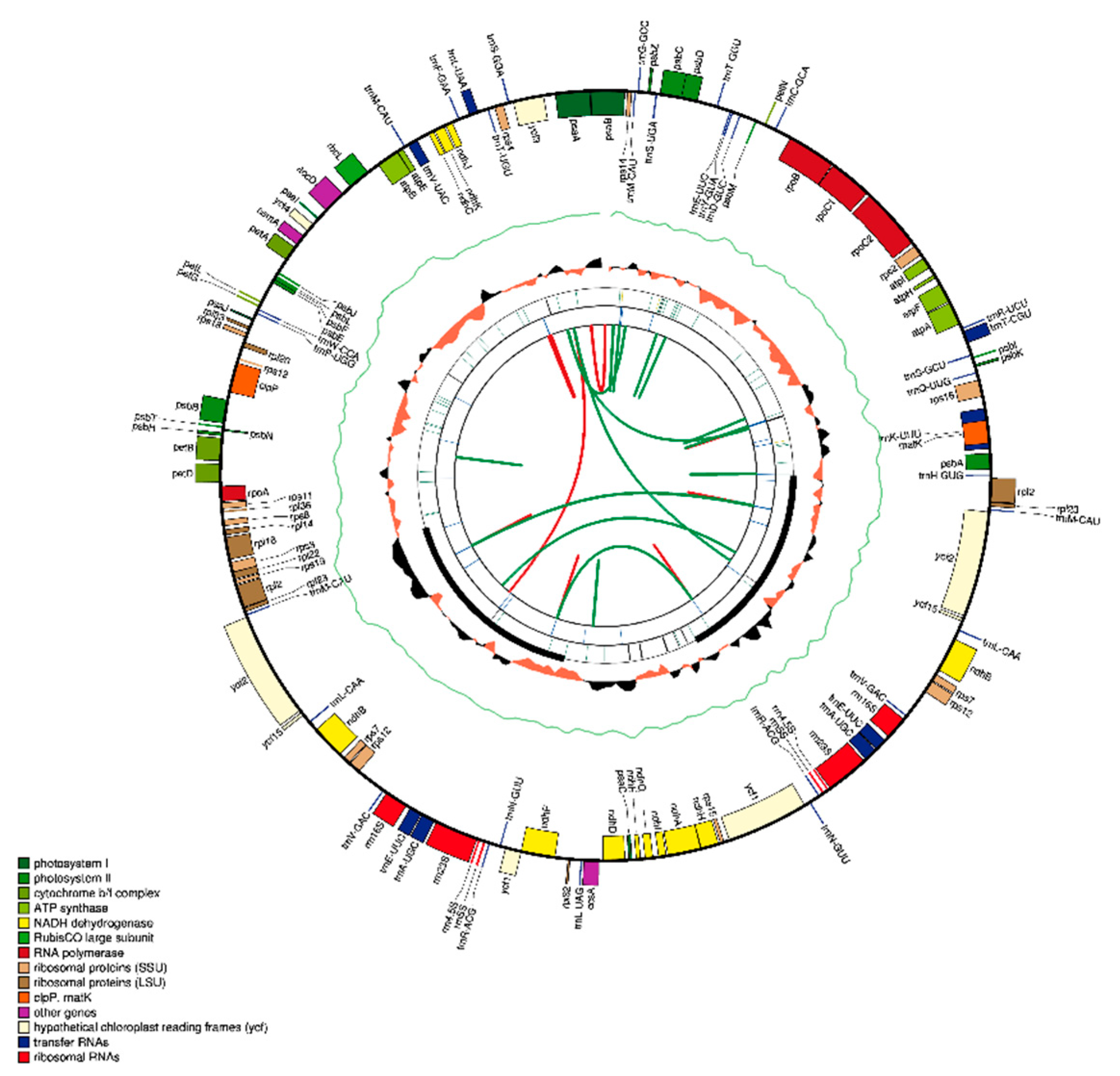
3.1. Organization and Characteristics of Withania Plastomes
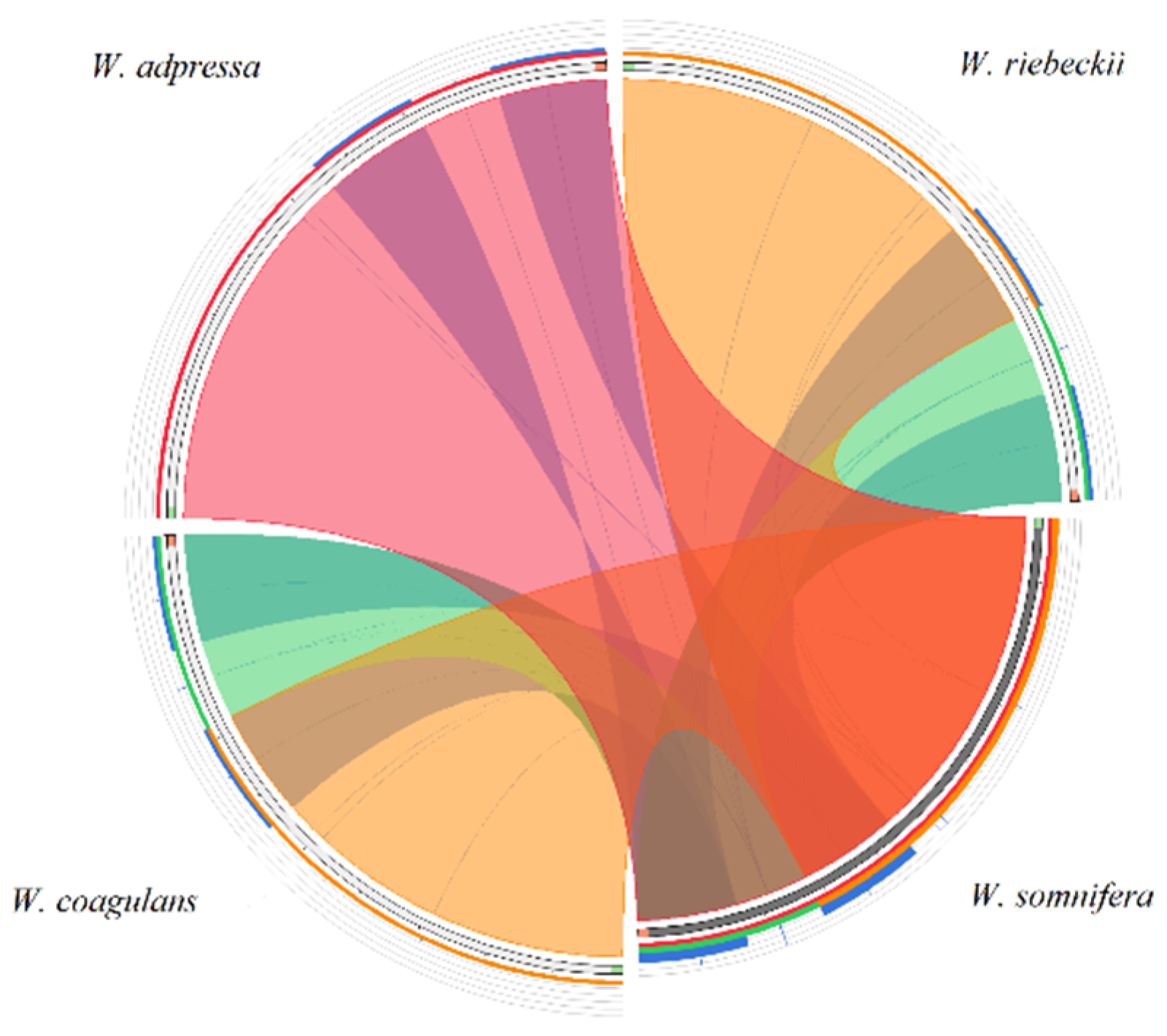
3.2. Divergence Hotspots in Withania
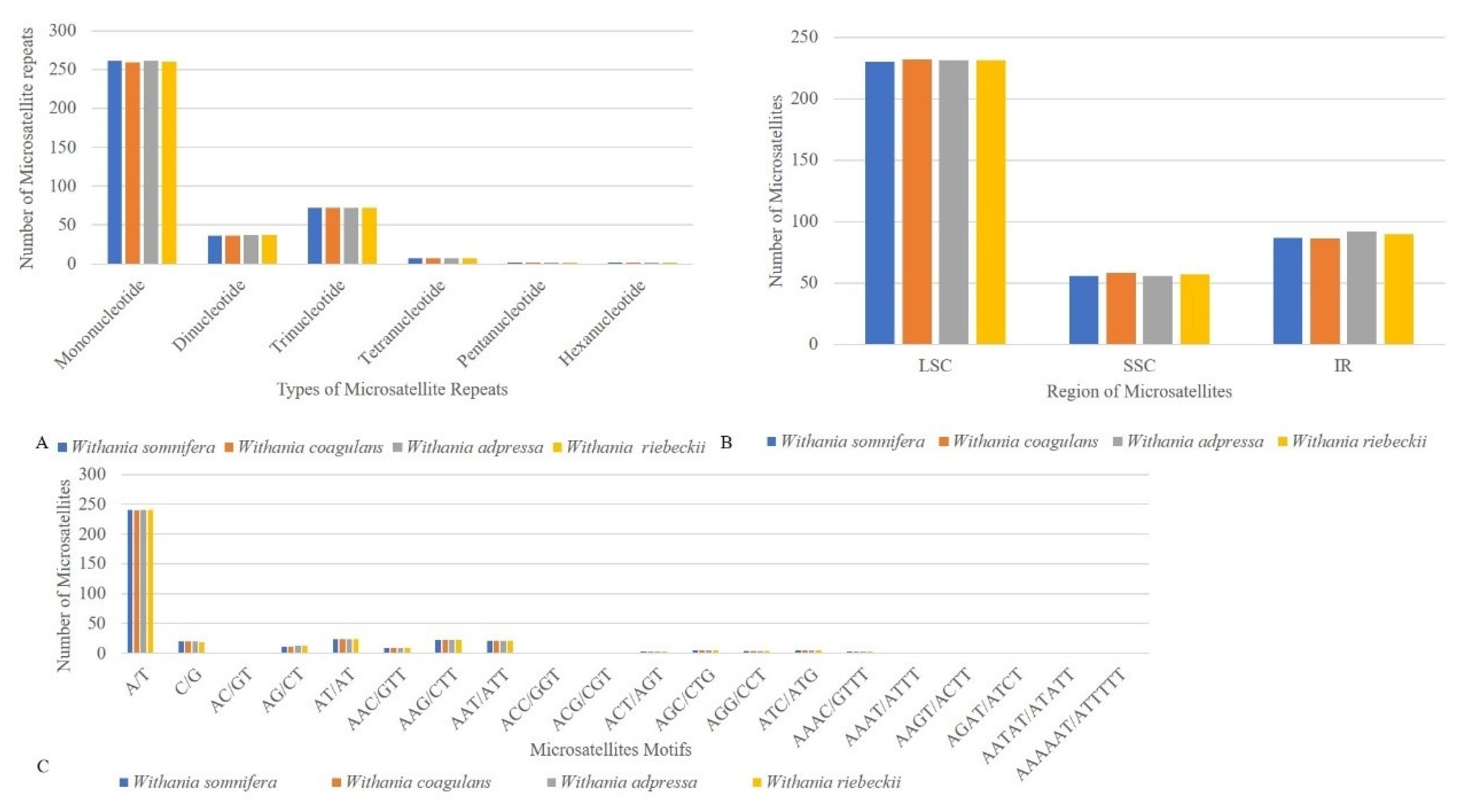
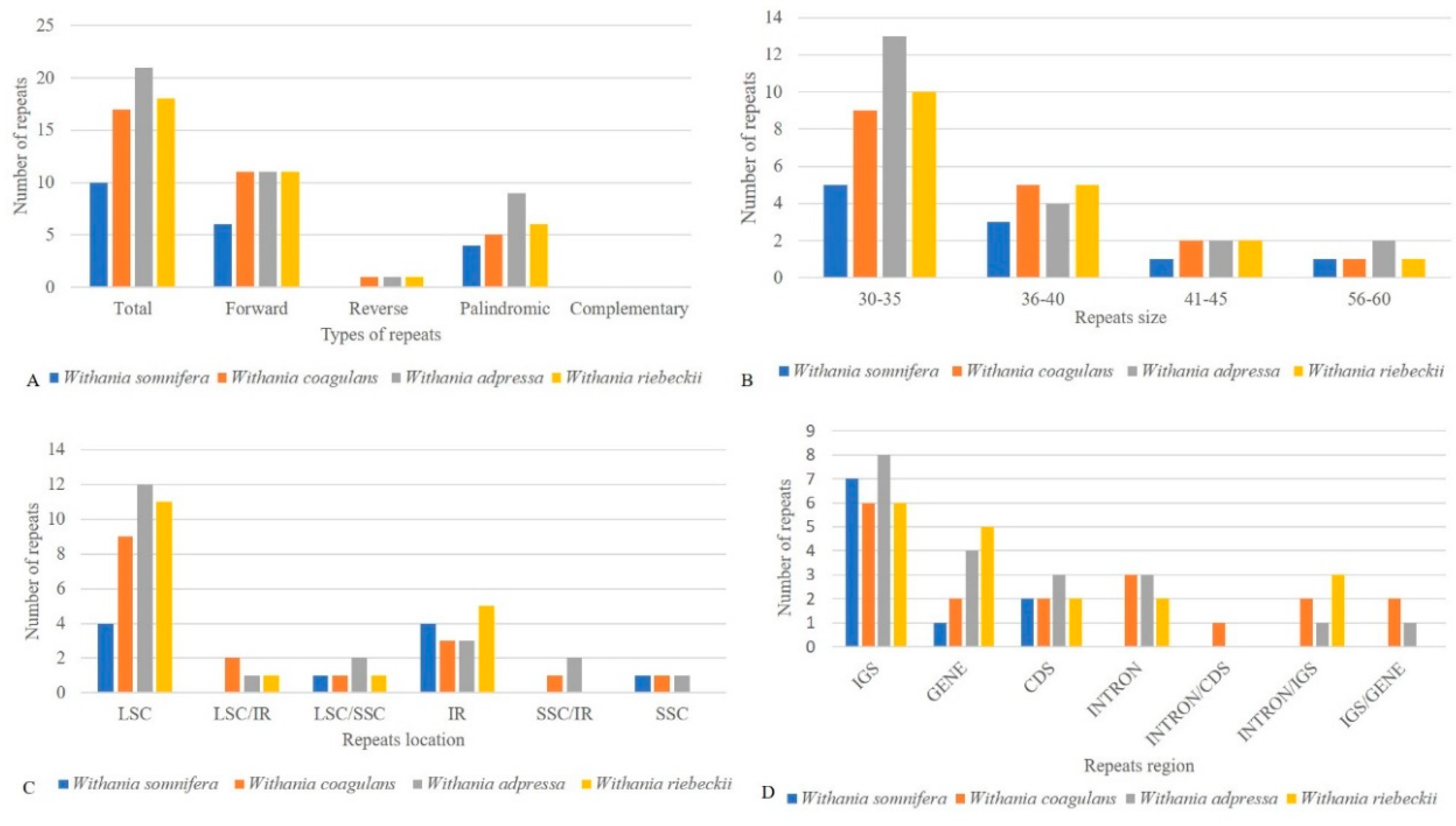
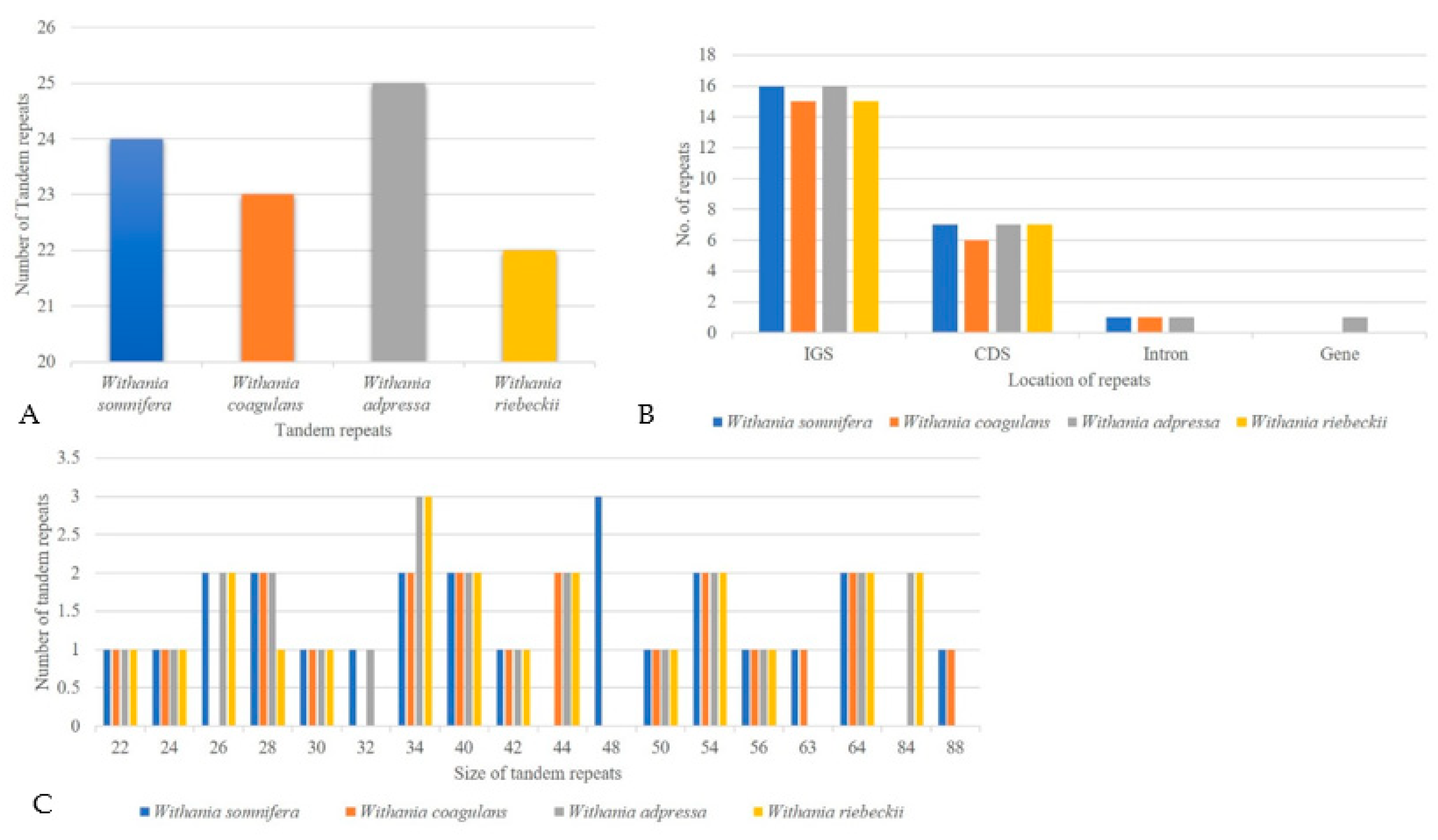
3.3. Repeat Structure and Analyses
3.4. Comparative Plastomics and Inverted Repeat Boundaries
3.5. Putative RNA-Editing Sites
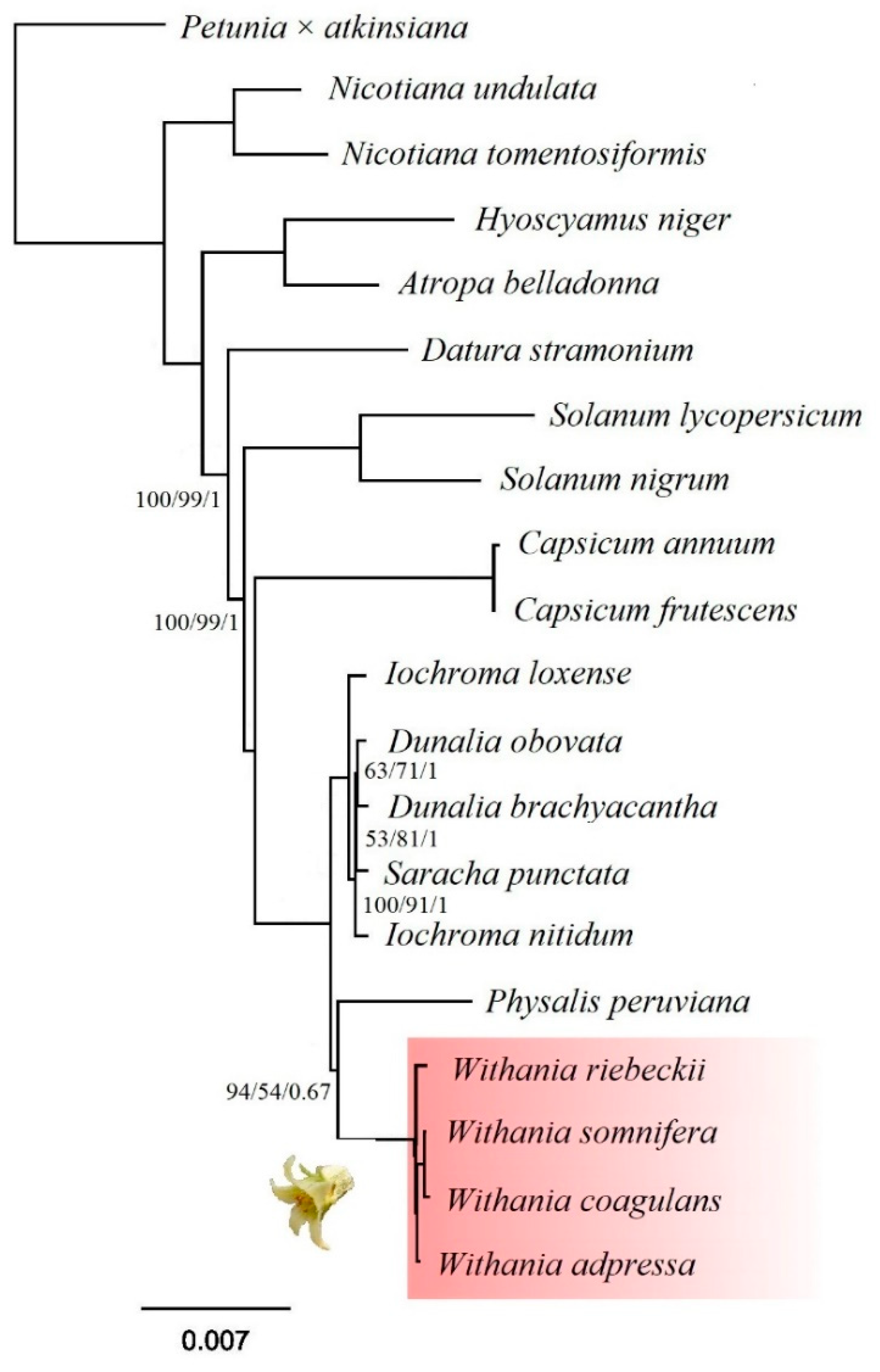
3.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olmstead, R.G.; Bohs, L.; Migid, H.A.; Santiago-Valentin, E.; Garcia, V.F.; Collier, S.M. A molecular phylogeny of the Solanaceae. Taxon 2008, 57, 1159–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmstead, R.G.; Bohs, L. A summary of molecular systematic research in Solanaceae: 1982–2006. Solanaceae IV: Genomics meets biodiversity. In Proceedings of the VIth International Solanaceae Conference, Madison, WI, USA, 23–27 July 2006; pp. 255–268. [Google Scholar]
- Knapp, S.; Bohs, L.; Nee, M.; Spooner, D.M. Solanaceae—A model for linking genomics with biodiversity. Comp. Funct. Genom. 2004, 5, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, M.H.; Moyano, E.; Bonfill, M.; Cusido, R.M.; Palazón, J. Steroidal lactones from Withania somnifera, an ancient plant for novel medicine. Molecules 2009, 14, 2373–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Guleri, R.; Singh, V.; Kaur, G.; Kataria, H.; Singh, B.; Kaur, G.; Kaul, S.C.; Wadhwa, R.; Pati, P.K. Biotechnological interventions in Withania somnifera (L.) dunal. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2015, 31, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, Q.; Samiulla, L.; Singh, V.K.; Jamil, S.S. Phytochemical and pharmacological profile of Withania somnifera dunal: A review. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 170–175. [Google Scholar]
- Maurya, R. Chemistry and pharmacology of Withania coagulans: An ayurvedic remedy. J. Pharm. Pharm. 2010, 62, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ul-Haq, I.; Youn, U.J.; Chai, X.; Park, E.-J.; Kondratyuk, T.P.; Simmons, C.J.; Borris, R.P.; Mirza, B.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Chang, L.C. Biologically active withanolides from Withania coagulans. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, S.; Keefover-Ring, K.; Haq, I.U.L.; Dilshad, E.; Khan, M.I.; Akhtar, N.; Mirza, B. Drier climatic conditions increase withanolide content of Withania coagulans enhancing its inhibitory potential against human prostate cancer cells. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 188, 460–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinwari, Z.K. Medicinal plants research in Pakistan. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 161–176. [Google Scholar]
- Raclariu, A.C.; Heinrich, M.; Ichim, M.C.; de Boer, H. Benefits and limitations of DNA barcoding and metabarcoding in herbal product authentication. Phytochem. Anal. 2018, 29, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cao, H.; But, P.P.H.; Shaw, P.C. Identification of herbal medicinal materials using DNA barcodes. J. Syst. Evol. 2011, 49, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Daniell, H. The engineered chloroplast genome just got smarter. Trends Plant. Sci. 2015, 20, 622–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, G. Chloroplasts and Other Plastids in the Cell: A Molecular Approach, 2nd ed.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, J.D. Comparative organization of chloroplast genomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1985, 19, 325–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniell, H.; Lin, C.-S.; Yu, M.; Chang, W.-J. Chloroplast genomes: Diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldenburg, D.J.; Bendich, A.J. DNA maintenance in plastids and mitochondria of plants. Front. Plant. Sci. 2015, 6, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiryousefi, A.; Hyvönen, J.; Poczai, P. The chloroplast genome sequence of bittersweet (Solanum dulcamara): Plastid genome structure evolution in Solanaceae. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah; Shahzadi, I.; Mehmood, F.; Ali, Z.; Malik, M.S.; Waseem, S.; Mirza, B.; Ahmed, I.; Waheed, M.T. Comparative analyses of chloroplast genomes among three Firmiana species: Identification of mutational hotspots and phylogenetic relationship with other species of Malvaceae. Plant. Gene 2019, 19, 100199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriquez, C.L.; Abdullah; Ahmed, I.; Carlsen, M.M.; Zuluaga, A.; Croat, T.B.; Mckain, M.R. Evolutionary dynamics of chloroplast genomes in subfamily Aroideae (Araceae). Genomics 2020, 112, 2349–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-H.; Liu, Q.; Hu, W.; Wang, T.; Xue, Q.; Messing, J. Dynamics of chloroplast genomes in green plants. Genomics 2015, 106, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.J.; Bell, C.D.; Soltis, P.S.; Soltis, D.E. Using plastid genome-scale data to resolve enigmatic relationships among basal angiosperms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19363–19368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, V.; Khurana, J.P.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, P. An update on chloroplast genomes. Plant. Syst. Evol. 2008, 271, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, F.; Abdullah; Shahzadi, I.; Ahmed, I.; Waheed, M.T.; Mirza, B. Characterization of Withania somnifera chloroplast genome and its comparison with other selected species of Solanaceae. Genomics 2020, 112, 1522–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iram, S.; Hayat, M.Q.; Tahir, M.; Gul, A.; Abdullah; Ahmed, I. Chloroplast genome sequence of Artemisia scoparia: Comparative analyses and screening of mutational hotspots. Plants 2019, 8, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, K.C.; Saha, D. Chloroplast genomics and genetic engineering for crop improvement. Agric. Res. 2012, 1, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, M.T.; Thönes, N.; Müller, M.; Hassan, S.W.; Razavi, N.M.; Lössl, E.; Kaul, H.P.; Lössl, A.G. Transplastomic expression of a modified human papillomavirus L1 protein leading to the assembly of capsomeres in tobacco: A step towards cost-effective second-generation vaccines. Transgenic Res. 2011, 20, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waheed, M.T.; Ismail, H.; Gottschamel, J.; Mirza, B.; Lössl, A.G. Plastids: The green frontiers for vaccine production. Front. Plant. Sci. 2015, 6, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I. Evolutionary Dynamics in Taro. Ph.D. Thesis, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wambugu, P.W.; Brozynska, M.; Furtado, A.; Waters, D.L.; Henry, R.J. Relationships of wild and domesticated rices (Oryza AA genome species) based upon whole chloroplast genome sequences. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, M.G.; Thompson, W.F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8, 4321–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FASTQC. A Quality Control Tool for High throughput Sequence Data. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 14 February 2020).
- Zerbino, D.R.; Birney, E. Velvet: Algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq-versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Chen, H.; Jiang, M.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, C. CPGAVAS2, an integrated plastome sequence annotator and analyzer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W65–W73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, T.M.; Chan, P.P. tRNAscan-SE On-line: Integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W54–W57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laslett, D.; Canback, B. ARAGORN, a program to detect tRNA genes and tmRNA genes in nucleotide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, W.-H.; Tan, Y.-C.; Yap, S.-J.; Ng, K.-P. Clico FS: An interactive web-based service of Circos. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3685–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with burrows-wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, I.; Bayer, M.; Cardle, L.; Shaw, P.; Stephen, G.; Wright, F.; Marshall, D. Tablet-next generation sequence assembly visualization. Bioinformatics 2009, 26, 401–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Xiao, J.; Bao, Y.; He, S.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Zhao, G.; Chen, R.; Gao, Y.; et al. Database resources of the national genomics data center in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D24–D33. [Google Scholar]
- Katoh, K.; Kuma, K.I.; Toh, H.; Miyata, T. MAFFT version 5: Improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sanchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sanchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiryousefi, A.; Hyvönen, J.; Poczai, P. IRscope: An online program to visualize the junction sites of chloroplast genomes. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3030–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darzentas, N. Circoletto: Visualizing sequence similarity with Circos. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2620–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mower, J.P. The PREP suite: Predictive RNA editors for plant mitochondrial genes, chloroplast genes and user-defined alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W253–W259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereeper, A.; Guignon, V.; Blanc, G.; Audic, S.; Buffet, S.; Chevenet, F.; Dufayard, J.-F.; Guindon, S.; Lefort, V.; Lescot, M.; et al. Phylogeny.fr: Robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W465–W469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, F.; Correia, D.; Lefort, V.; Doppelt-Azeroual, O.; Mareuil, F.; Cohen-Boulakia, S.; Gascuel, O. NGPhylogeny.fr: New generation phylogenetic services for non-specialists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W260–W265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanfear, R.; Calcott, B.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Guindon, S. PartitionFinder: Combined selection of partitioning schemes and substitution models for phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Song, J.; Gao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, J.; Pang, X.; Yao, H.; Sun, C.; Li, X.; Li, C.; et al. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of the medicinal plant Salvia miltiorrhiza. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah; Mehmood, F.; Shahzadi, I.; Ali, Z.; Islam, M.; Naeem, M.; Mirza, B.; Lockhart, P.; Ahmed, I.; Waheed, M.T. Correlations among oligonucleotide repeats, nucleotide substitutions and insertion-deletion mutations in chloroplast genomes of plant family Malvaceae. J. Syst. Evol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzadi, I.; Abdullah; Mehmood, F.; Ali, Z.; Ahmed, I.; Mirza, B. Chloroplast genome sequences of Artemisia maritima and Artemisia absinthium: Comparative analyses, mutational hotspots in genus Artemisia and phylogeny in family Asteraceae. Genomics 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lv, J.; Xu, J.; Zhu, S.; Li, M. Comparative chloroplast genomes of Sorghum species: Sequence divergence and phylogenetic relationships. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, M.; Yujiang; Zhao, D.; Tao, J. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genomes of sequences of two diploid species: Paeonia lactiflora ‘Da Fugui’ and Paeonia ostii ‘Fengdan’ in the Paeoniaceae Family. J. Hortic. 2018, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Biggs, P.J.; Matthews, P.J.; Collins, L.J.; Hendy, M.D.; Lockhart, P.J. Mutational dynamics of aroid chloroplast genomes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2012, 4, 1316–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.; Lickey, E.B.; Schilling, E.E.; Small, R.L. Comparison of whole chloroplast genome sequences to choose noncoding regions for phylogenetic studies in angiosperms: The tortoise and the hare III. Am. J. Bot. 2007, 94, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollingsworth, P.M.; Graham, S.W.; Little, D.P. Choosing and using a plant DNA barcode. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worberg, A.; Quandt, D.; Barniske, A.M.; Löhne, C.; Hilu, K.W.; Borsch, T. Phylogeny of basal eudicots: Insights from non-coding and rapidly evolving DNA. Org. Divers. Evol. 2007, 7, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, W.; Morgante, M.; McDevitt, R.; Vendramin, G.G.; Rafalski, J.A. Polymorphic simple sequence repeats regions in chloroplast genomes: Applications to the population genetics of pines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7759–7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, S.L. Polymorphic chloroplast microsatellite loci in Nelumbo (Nelumbonaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2012, 99, e240–e244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, L.; Liu, A.; Chen, J.; Wu, L.; Hu, W.; Zhang, W.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.-C.; Yang, T.-J.; et al. The Complete chloroplast genome sequences of five Epimedium species: Lights into phylogenetic and taxonomic analyses. Front. Plant. Sci. 2016, 7, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.J.; Cheng, C.L.; Chang, C.C.; Wu, C.L.; Su, T.M.; Chaw, S.M. Dynamics and evolution of the inverted repeat-large single copy junctions in the chloroplast genomes of monocots. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D.; Jansen, R.K.; Michaels, H.J.; Chase, M.W.; Manhart, J.R. Chloroplast DNA variation and plant phylogeny. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1988, 75, 1180–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; He, J.; Ding, C.; Lyu, R.; Pei, L.; Cheng, J.; Xie, L. Comparative analysis of complete chloroplast genomes of Anemoclema, Anemone, Pulsatilla, and Hepatica revealing structural variations among genera in tribe Anemoneae (Ranunculaceae). Front. Plant. Sci. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundschuh, R.; Altmüller, J.; Becker, C.; Nürnberg, P.; Gott, J.M. Complete characterization of the edited transcriptome of the mitochondrion of Physarum polycephalum using deep sequencing of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 6044–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.H.; Liao, S.C.; Chang, C.C. Identification of RNA editing sites in chloroplast transcripts of Phalaenopsis aphrodite and comparative analysis with those of other seed plants. Plant. Cell Physiol. 2007, 48, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kool, A.; Oxelman, B.; Thulin, M. Phylogeny of Withania (Solanaceae). In Proceedings of the Abstracts XVII International Botanical Congress, Vienna, Austria, 17–23 July 2005; p. 360. [Google Scholar]
- Jamil, I.; Qamarunnisa, S.; Azhar, A.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Ali, S.I.; Qaiser, M.; Jamil, I.; Al, E.T. Subfamilial relationships within Solanaceae as inferred from atpB-rbcL intergenic spacer. Pak. J. Bot. 2014, 46, 585–590. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, R.K.; Cai, Z.; Raubeson, L.A.; Daniell, H.; de Pamphilis, C.W.; Leebens-Mack, J.; Muller, K.F.; Guisinger-Bellian, M.; Haberle, R.C.; Hansen, A.K.; et al. Analysis of 81 genes from 64 plastomes resolves relationships in angiosperms and identifies genome-scale evolutionary patterns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19369–19374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmstead, R.G.; Sweere, J.A.; Spangler, R.E.; Bohs, L.; Palmer, J.D. Phylogeny and provisional classification of the Solanaceae based on chloroplast DNA. In Solanaceae IV: Advances in Biology and Utilization; Nee, M., Symon, D.E., Lester, R.N., Jessop, J.P., Eds.; Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew: Richmond, UK, 1999; pp. 111–137. [Google Scholar]
- D’Arcy, W.G. The Solanaceae since 1976, with a review of its biogeography. In Solanaceae III: Taxonomy, Chemistry, Evolution; Hawkes, J.G., Lester, R.N., Nee, M., Estrada, N., Eds.; Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew: Richmond, UK, 1991; pp. 75–138. [Google Scholar]
- Symon, D.E. Gondwanan elements of the Solanaceae. In Solanaceae III: Taxonomy, Chemistry, Evolution; Hawkes, J.G., Lester, R.N., Nee, M., Estrada, N., Eds.; Royal Botanical Gardens, Kew: Richmond, UK, 1991; pp. 139–150. [Google Scholar]
- Deanna, R.; Smith, S.D.; Särkinen, T.; Chiarini, F. Patterns of chromosomal evolution in the florally diverse Andean clade Iochrominae (Solanaceae). Perspect. Plant. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2018, 35, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepper, F.N. Old world Withania (Solanaceae): A taxonomic review and key to the species. In Solanaceae III: Taxonomy, Chemistry, Evolution; Hakes, J.G., Lester, R.N., Nee, M., Estrada, N., Eds.; Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew: Richmond, UK, 1991; pp. 211–228. [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker, A.T. Genera Solanacearum: The Genera of Solanaceae Illustrated, Arranged According to a New System; ARG Gantner Verlag: Ruggell, Liechtenstein, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, K.S.; Chung, M.G.; Park, S. The complete chloroplast genome sequences of three veroniceae species (Plantaginaceae): Comparative analysis and highly divergent regions. Front. Plant. Sci. 2016, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah; Waseem, S.; Mirza, B.; Ahmed, I.; Waheed, M.T. Comparative analyses of chloroplast genome in Theobroma cacao and Theobroma grandiflorum. Biologia 2020, 75, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriquez, C.L.; Abdullah; Ahmed, I.A.; Carlsen, M.M.; Zuluaga, A.; Croat, T.B.; Mckain, M.R. Molecular evolution of chloroplast genomes in Monsteroideae (Araceae). Planta 2020, 251, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Matthews, P.J.; Biggs, P.J.; Naeem, M.; Mclenachan, P.A.; Lockhart, P.J. Identification of chloroplast genome loci suitable for high-resolution phylogeographic studies of Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott (Araceae) and closely related taxa. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Liu, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S. Highly variable chloroplast markers for evaluating plant phylogeny at low taxonomic levels and for DNA barcoding. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Park, H.-S.; Lee, S.-C.; Lee, J.; Park, J.Y.; Yang, T.-J. Authentication markers for five major Panax species developed via comparative analysis of complete chloroplast genome sequences. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6298–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. Model of effectively neutral mutations in which selective constraint is incorporated. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 3440–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrie, D.S.; Messer, P.W.; Hershberg, R.; Petrov, D.A. Strong purifying selection at synonymous sites in D. melanogaster. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poczai, P.; Hyvönen, J. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of the CAM epiphyte Spanish moss (Tillandsia usneoides, Bromeliaceae) and its comparative analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, F.; Abdullah; Ubaid, Z.; Shahzadi, I.; Ahmed, I.; Waheed, M.T.; Poczai, P.; Mirza, B. Plastid genomics of Nicotiana (Solanaceae): Insights into molecular evolution, positive selection and the origin of the maternal genome of Aztec tobacco (Nicotiana rustica). BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah; Mehmood, F.; Shahzadi, I.; Waseem, S.; Mirza, B.; Ahmed, I.; Waheed, M.T. Chloroplast genome of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis (Malvaceae): Comparative analyses and identification of mutational hotspots. Genomics 2020, 112, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooner, D.M. DNA barcoding will frequently fail in complicated groups: An example in wild potatotes. Am. J. Bot. 2009, 96, 1177–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.T.; Spooner, D.M. Collapse of species boundaries in the wild potato Solanum brevicaule complex (Solanaceae, S. sect. Petota): Molecular data. Plant. Syst. Evol. 1999, 214, 103–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubriot, X.; Knapp, S.; Syfert, M.M.; Poczai, P.; Buerki, S. Shedding new light on the origin and spread of the brinjal eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) and its wild relatives. Am. J. Bot. 2018, 105, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulcheski, F.R.; Muschner, V.C.; Lorenz-Lemke, A.P.; Stehmann, J.R.; Bonatto, S.L.; Salzano, F.M.; Freitas, L.B. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of Petunia Juss. (Solanaceae). Genetica 2006, 126, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, J.R. Systematics of the Physalis viscosa complex (Solanaceae). Syst. Bot. 1985, 10, 426–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
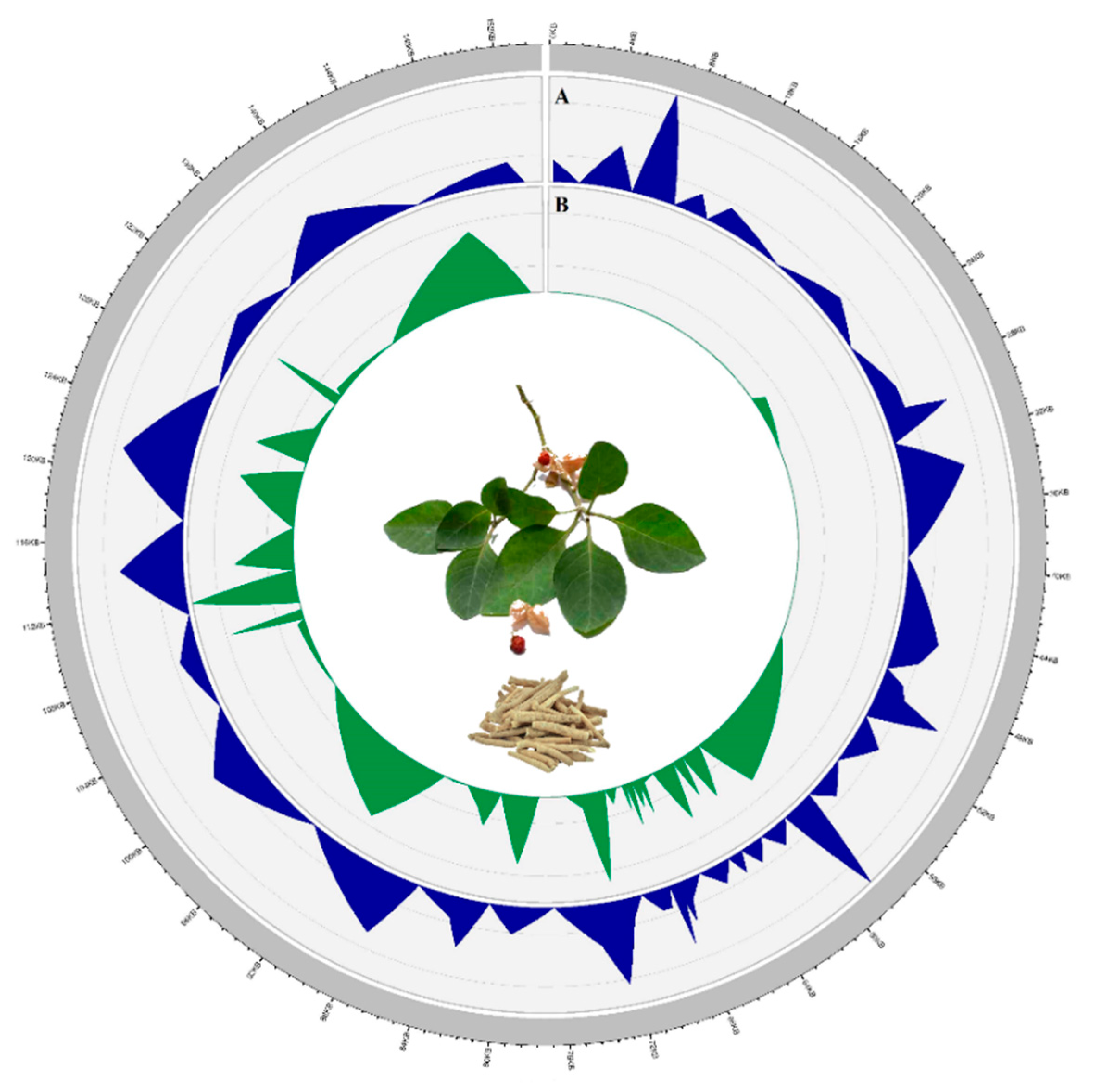
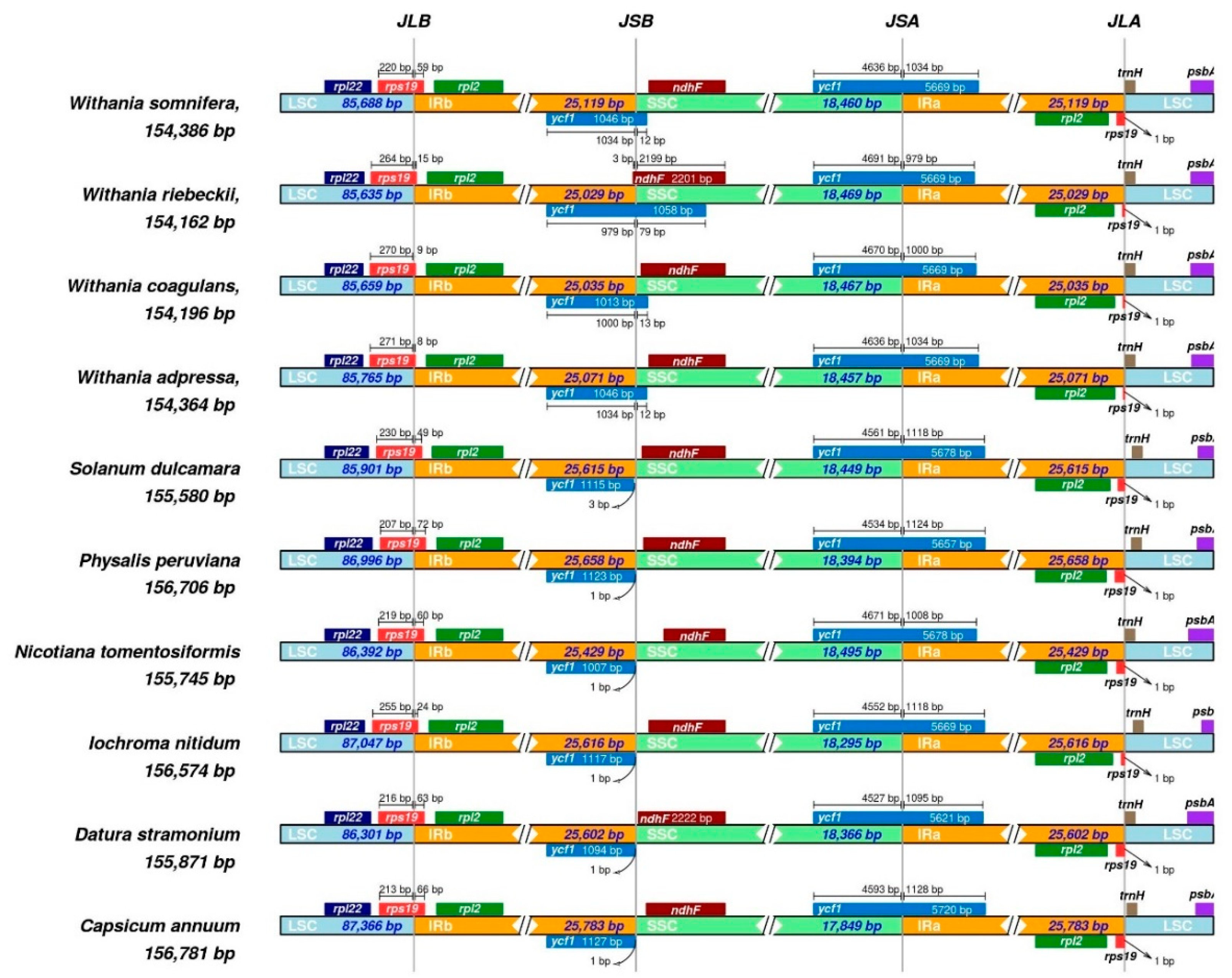



| Characteristics | W. somnifera | W. coagulans | W. adpressa | W. riebeckii | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (base pair; bp) | 154,386 | 154,196 | 154,364 | 154,162 | |
| LSC length (bp) | 85,688 | 85,659 | 85,765 | 85,635 | |
| SSC length (bp) | 18,464 | 18,467 | 18,457 | 18,469 | |
| IR length (bp) | 25,117 | 25,035 | 25,071 | 25,029 | |
| Number of genes | 132 | 132 | 132 | 132 | |
| Protein-coding genes | 86 | 86 | 86 | 86 | |
| tRNA genes | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | |
| rRNA genes | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | |
| Duplicate genes | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 | |
| GC content | Total (%) | 37.7% | 37.7% | 37.7% | 37.7% |
| LSC (%) | 35.7% | 35.7% | 35.7% | 35.7% | |
| SSC (%) | 31.8% | 31.8% | 31.8% | 31.8% | |
| IR (%) | 43.2% | 43.2% | 43.2% | 43.2% | |
| CDS (%) | 38.2% | 38.2% | 38.2% | 38.2% | |
| rRNA (%) | 55.3% | 55.3% | 55.3% | 55.3% | |
| tRNA (%) | 53% | 52.9% | 53% | 53% | |
| All gene (%) | 40% | 39.8% | 39.8% | 39.8% | |
| Protein coding part (CDS) (%bp) | 50.9% | 51.0% | 51.0% | 51.0% | |
| All gene (%bp) | 72.06% | 72.11% | 72.07% | 72.13% | |
| Non-coding region (%bp) | 27.94% | 27.89% | 27.93% | 27.87% | |
| Category for Gene | Group of Gene | Name of Gene | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photosynthesis-Related Genes | Photosystem I | psaA | psaB | psaC | psaI | psaJ |
| Photosystem II | psbA | PsbB | psbC | psbD | psbE | |
| psbF | psbH | psbI | psbJ | psbK | ||
| psbL | psbM | psbN | ||||
| Cytochrome b/f complex | psbT | psbZ | petN | petA | petL | |
| petG | petD * | petB * | ||||
| ATP synthase | atpI | atpH | atpA | atpF * | atpE | |
| atpB | ||||||
| Assembly/stability of photosystem I | ycf3 ** | ycf4 | ||||
| NADPH dehydrogenase | ndhB *,a | ndhH | ndhA * | ndhI | ndhG | |
| ndhJ | ndhE | ndhF | ndhC | ndhK | ||
| ndhD | ||||||
| Rubisco | rbcL | |||||
| Transcription and Translation Related Genes RNA Genes | Transcription Small subunit of ribosome | rpoA | rpoC2 | rpoC1 * | rpoB | rps16 * |
| rps7 a | rps15 | rps19 | rps3 | rps8 | ||
| rps14 | rps11 | rps12 a,* | rps18 | rps4 | ||
| rps2 | ||||||
| Large subunit of ribosome | rpl2 a,* | rpl23 a, | rpl32 | rpl22 | rpl14 | |
| rpl33 | rpl36 | rpl20 | rpl16 * | |||
| Ribosomal RNA | rrn16 a | rrn4.5 a | rrn5 a | rrn23 a | ||
| Transfer RNA | trnV-GAC a | trnI-CAU * | trnA-UGC a,* | trnN-GUU a | trnP-UGG | |
| trnW-CCA | trnV-UAC * | trnL-UAA * | trnF-GAA | trnR-ACG a | ||
| trnT-UGU | trnG-UCC a,* | trnT-GGU | trnR-UCU | trnE-UUC | ||
| trnY-GUA | trnD-GUC | trnC-GCA | trnS-GCU | trnH-GUG | ||
| trnK-UUU | trnQ-UUG | trnfM-CAU | trnG-GCC | trnS-UGA | ||
| trnS-GGA | trnF-GAA | trnM-CAU | trnL-CAA * | |||
| trnI-GAU *,a | trnL-UAG | |||||
| Other Genes | RNA processing | matK | ||||
| Carbon metabolism | cemA | |||||
| Fatty acid synthesis | accD | |||||
| Proteolysis | clpP ** | |||||
| Component of TIC complex | ycf1 a | |||||
| Hypothetical proteins | ycf2 a | Ycf15 | ||||
| Types | W. coagulans | W. adpressa | W. riebeckii |
|---|---|---|---|
| A/G | 4 | 19 | 28 |
| C/T | 10 | 15 | 30 |
| A/C | 3 | 11 | 18 |
| C/G | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| G/T | 4 | 14 | 25 |
| A/T | 2 | 5 | 12 |
| Total | 25 | 66 | 116 |
| LSC | 20 | 43 | 79 |
| SSC | 5 | 20 | 30 |
| IR | 0 | 3 | 7 |
| W. coagulans | Indel Length (bp) | Indel Average Length | |
| LSC | 27 | 133 | 4.926 |
| SSC | 3 | 61 | 20.33 |
| IR | 2 | 82 | 41.00 |
| W. adpressa | Indel Length (bp) | Indel Average Length | |
| LSC | 27 | 143 | 5.296 |
| SSC | 6 | 11 | 1.833 |
| IR | 5 | 68 | 13.60 |
| W. riebeckii | Indel Length (bp) | Indel Average Length | |
| LSC | 34 | 213 | 5.917 |
| SSC | 6 | 103 | 17.16 |
| IR | 4 | 106 | 26.50 |
| S. No | Region | Nucleotide Diversity | T. No’s of Mutation | Region Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ndhI-ndhA | 0.0119 | 2 | 84 |
| 2 | trnY-GUA-trnE-UUC | 0.0085 | 1 | 59 |
| 3 | rpl14-rpl16 | 0.0080 | 2 | 125 |
| 4 | rps19-rpl2 | 0.0071 | 1 | 70 |
| 5 | rps15 | 0.0064 | 3 | 261 |
| 6 | trnM-CAU-atpE | 0.0053 | 2 | 221 |
| 7 | rps4-trnT-UGU | 0.0051 | 3 | 364 |
| 8 | trnQ-UUG-psbK | 0.0048 | 3 | 346 |
| 9 | ndhH-rps15 | 0.0045 | 1 | 111 |
| 10 | trnG-GCC-trnR-UCU | 0.0041 | 1 | 164 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mehmood, F.; Abdullah; Ubaid, Z.; Bao, Y.; Poczai, P.; Mirza, B. Comparative Plastomics of Ashwagandha (Withania, Solanaceae) and Identification of Mutational Hotspots for Barcoding Medicinal Plants. Plants 2020, 9, 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9060752
Mehmood F, Abdullah, Ubaid Z, Bao Y, Poczai P, Mirza B. Comparative Plastomics of Ashwagandha (Withania, Solanaceae) and Identification of Mutational Hotspots for Barcoding Medicinal Plants. Plants. 2020; 9(6):752. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9060752
Chicago/Turabian StyleMehmood, Furrukh, Abdullah, Zartasha Ubaid, Yiming Bao, Peter Poczai, and Bushra Mirza. 2020. "Comparative Plastomics of Ashwagandha (Withania, Solanaceae) and Identification of Mutational Hotspots for Barcoding Medicinal Plants" Plants 9, no. 6: 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9060752
APA StyleMehmood, F., Abdullah, Ubaid, Z., Bao, Y., Poczai, P., & Mirza, B. (2020). Comparative Plastomics of Ashwagandha (Withania, Solanaceae) and Identification of Mutational Hotspots for Barcoding Medicinal Plants. Plants, 9(6), 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9060752








