Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.): A Potential Candidate for Phytoremediation? Biological and Economical Points of View
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Growth, Morphology, and Habitat
3. Plant Selection Considerations
4. Studies Related to Phytoremediation of the Flax Plant
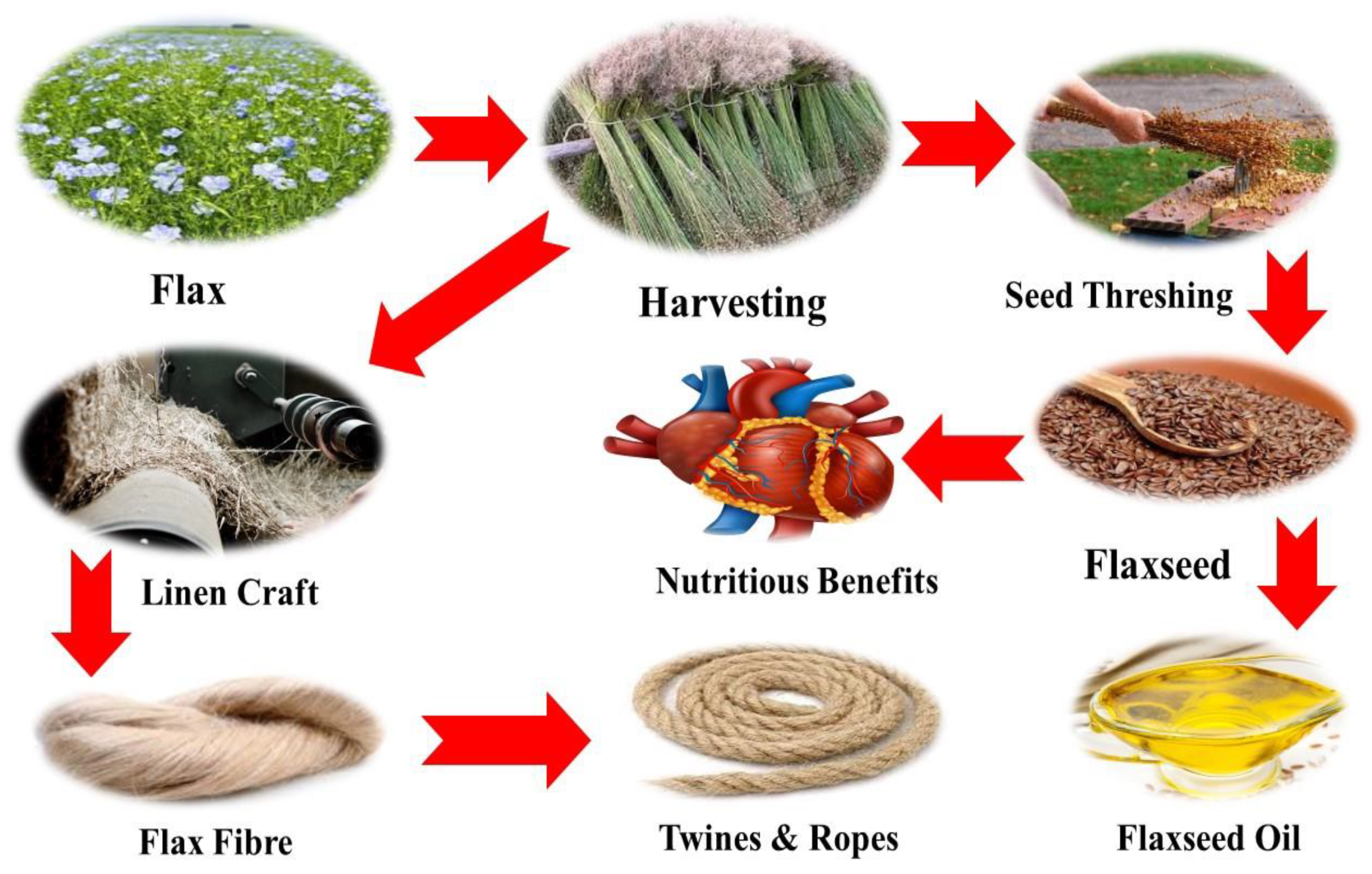
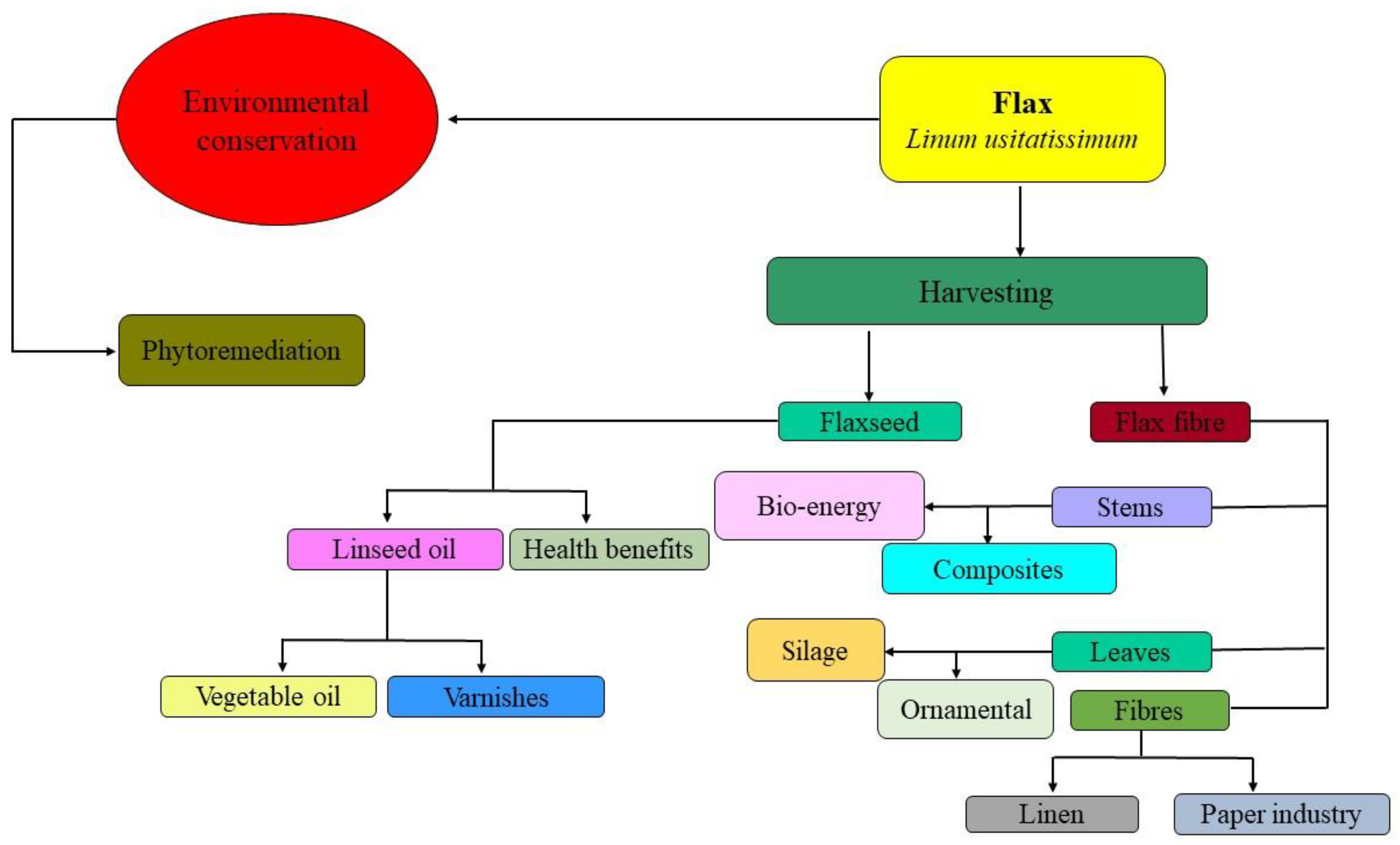
5. Value-Added Products
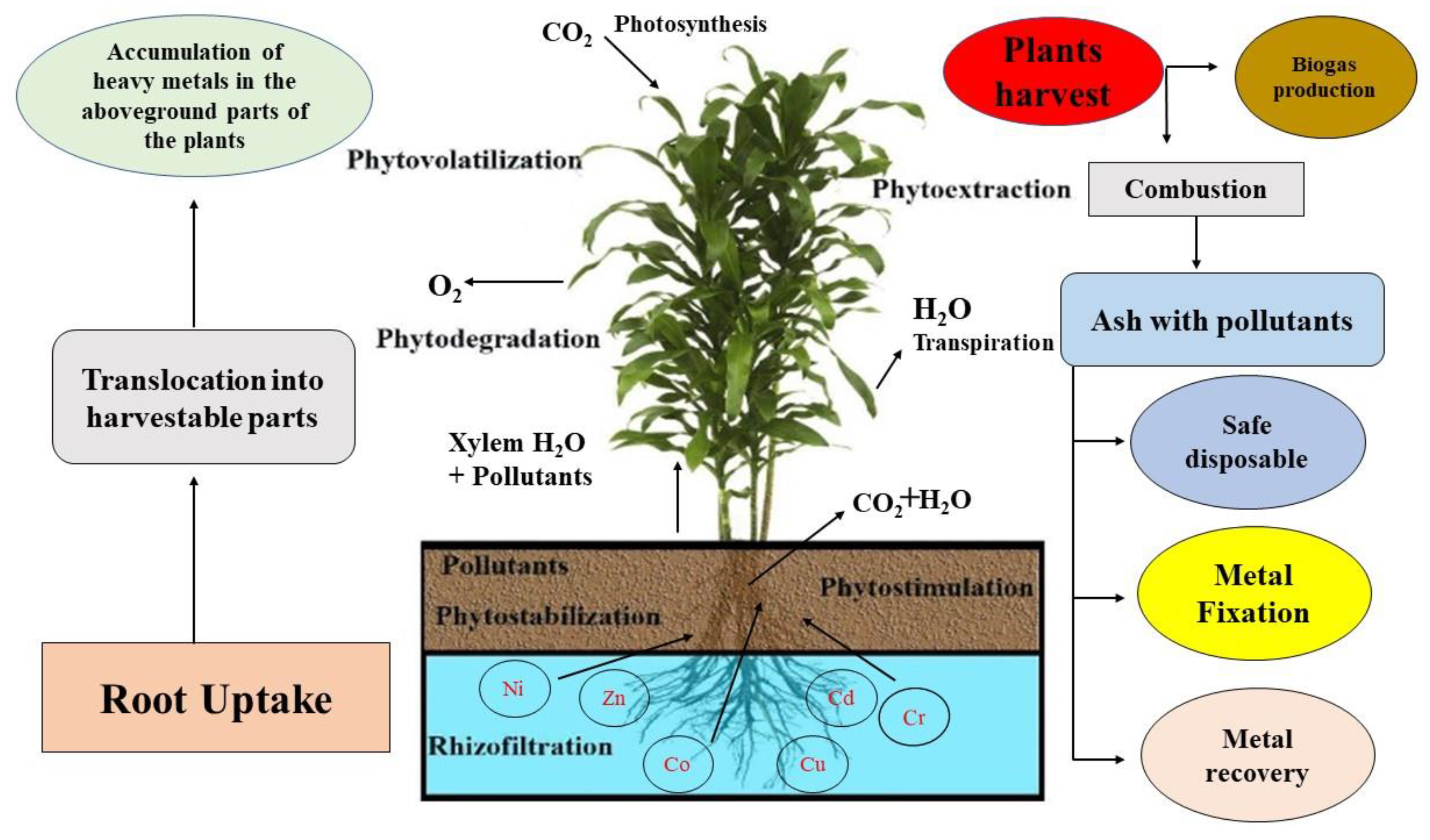
6. Enhancement of Phytoremediation Potential Using Flax Plants
7. Conclusions and Future Prospects
- Many studies showed that flax is a hyper accumulator (able to accumulate a larger amount of heavy metals in the aboveground parts then the belowground parts of the plants) species for different heavy metals;
- A few studies show that flax can also remove petroleum hydrocarbons from contaminated soil. For this property it is very popular in Middle-Eastern countries;
- Among the different heavy metals, flax can remove Cd the best, and most studies are related to the phytoremediation of Cd, as discussed in detail by Griga and Bjelková [47];
- Phytoremediation potential and biomass of flax can be improved by using chelating agents or metallothioneins;
- After phytoremediation, the biomass of flax can be used for the production of value-added by-products such as flaxseed oil or fibers.
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eissa, M.A.; Almaroai, Y.A. Phytoremediation Capacity of Some Forage Plants Grown on a Metals-Contaminated Soil. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2019, 28, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, A.; Wang, P.; Ali, A.; Awasthi, M.K.; Lahori, A.H.; Wang, Q.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z. Challenges and opportunities in the phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated soils: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagajyoti, P.C.; Lee, K.D.; Sreekanth, T. Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2010, 8, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Ali, S.; Rehman, M.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Rizwan, M.; Irshad, S.; Shafiq, F.; Iqbal, M.; Alharbi, B.M.; Alnusaire, T.S. Jute: A Potential Candidate for Phytoremediation of Metals—A Review. Plants 2020, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Hou, M.; Cao, L.; Xia, Y.; Shen, Z.; Hu, Z. Glutathione S-transferases modulate Cu tolerance in Oryza sativa. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 155, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q.; Saleem, M.H.; Bashir, S.; Ullah, S.; Peng, D. Copper environmental toxicology, recent advances, and future outlook: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 18003–18016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, Z.; Song, H.; Chen, Q. EDTA-facilitated toxic tolerance, absorption and translocation and phytoremediation of lead by dwarf bamboos. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, D.; Zeng, C.; Long, C. Improving Cobalt Phytoextraction by Astragalus Sinicus L. Grown in Co-Contaminated Soils Using Biodegradable Chelators. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2019, 28, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, K.; Gill, R.A.; Islam, F.; Farooq, M.A.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W. Ecotoxicological and Interactive Effects of Copper and Chromium on Physiochemical, Ultrastructural, and Molecular Profiling in Brassica napus L. BioMed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9248123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amna; Masood, S.; Syed, J.H.; Munis, M.F.H.; Chaudhary, H.J. Phyto-extraction of Nickel by Linum usitatissimum in Association with Glomus intraradices. Int. J. Phytoremed. 2015, 17, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ul Hassan, Z.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Hussain, A.; Akbar, Z.; Rasool, N.; Abbas, F. Role of zinc in alleviating heavy metal stress. In Essential Plant Nutrients; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 351–366. [Google Scholar]
- Feller, U.; Anders, I.; Wei, S. Distribution and Redistribution of 109Cd and 65Zn in the Heavy Metal Hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L.: Influence of Cadmium and Zinc Concentrations in the Root Medium. Plants 2019, 8, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbricino, M.; Ferraro, A.; Luongo, V.; Pontoni, L.; Race, M. Soil washing optimization, recycling of the solution, and ecotoxicity assessment for the remediation of Pb-contaminated sites using EDDS. Sustainability 2018, 10, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrees, M.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Abbas, F.; Farid, M.; Qayyum, M.F.; Irshad, M.K. Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 119, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; He, S.; Yan, S.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, L.; Li, L. Exogenous EDDS modifies copper-induced various toxic responses in rice. Protoplasma 2014, 251, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, T.; Mi, M.; Wang, C.; Qian, M.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Z.; Shen, Z.; Xia, Y. A methionine-R-sulfoxide reductase, OsMSRB5, is required for rice defense against copper toxicity. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 153, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrees, M.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Abbas, F.; Farid, M.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Irshad, M.K.; Bharwana, S.A. The effect of excess copper on growth and physiology of important food crops: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 8148–8162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Naggar, Y.; Khalil, M.S.; Ghorab, M.A. Environmental pollution by heavy metals in the aquatic ecosystems of Egypt. Open Acc. J. Toxicol. 2018, 3, 555603. [Google Scholar]
- Zaheer, I.E.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Farid, M.; Shakoor, M.B.; Gill, R.A.; Najeeb, U.; Iqbal, N.; Ahmad, R. Citric acid assisted phytoremediation of copper by Brassica napus L. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 120, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuana, R.A.; Okieimen, F.E. Heavy metals in contaminated soils: A review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. ISRN Ecol. 2011, 2011, 402647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Malik, Z.; Parveen, A.; Huang, L.; Riaz, M.; Bashir, S.; Mustafa, A.; Abbasi, G.H.; Xue, B.; Ali, U. Ameliorative Effects of Biochar on Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) Growth and Heavy Metal Immobilization in Soil Irrigated with Untreated Wastewater. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, X. Contamination characteristics and source apportionment of heavy metals in topsoil from an area in Xi’an city, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 151, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shafi, M.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Ye, Z.; Peng, D.; Yan, W.; Liu, D. Copper induced oxidative stresses, antioxidant responses and phytoremediation potential of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens). Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, R.; Khan, M.A.; Asaf, S.; Lee, I.-J.; Kim, K.M. Metal Resistant Endophytic Bacteria Reduces Cadmium, Nickel Toxicity, and Enhances Expression of Metal Stress Related Genes with Improved Growth of Oryza Sativa, via Regulating Its Antioxidant Machinery and Endogenous Hormones. Plants 2019, 8, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrington, G. The good, the bad and the ugly: Copper and arsenic in soils. In Soil Health: The Foundation of Sustainable Agriculture; Wollongbar Agricultural Institute: Wollongbar, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, M.H.; Fahad, S.; Rehman, M.; Saud, S.; Jamal, Y.; Khan, S.; Liu, L. Morpho-physiological traits, biochemical response and phytoextraction potential of short-term copper stress on kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) seedlings. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazy Abdou, M.; Wahdan, M. Citric Acid-Enhanced Phytoremediation of Lead Using Corchorus capsularis L. and Eucalyptus Camaldulensis; ResearchGate: Berlin, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Wang, W.; Guo, J.; Qin, J.; Shi, D.; Li, Y.; Xu, J. Zinc improves salt tolerance by increasing reactive oxygen species scavenging and reducing Na+ accumulation in wheat seedlings. Biol. Plant. 2014, 58, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M. Phytoremediation on the brink of commercialization. 1997. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vareda, J.P.; Durães, L. Efficient adsorption of multiple heavy metals with tailored silica aerogel-like materials. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszynska, E.; Hanus-Fajerska, E. Why are heavy metal hyperaccumulating plants so amazing? Biotechnol. J. Biotechnol. Comput. Biol. Bionanotechnol. 2015, 96, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, B.; Xia, J.; Miao, Y. SRO1 regulates heavy metal mercury stress response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 3134–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.; Ali, Q.; Zahir, Z.A.; Ashraf, S.; Asghar, H.N. Phytoremediation: Environmentally sustainable way for reclamation of heavy metal polluted soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Hussain, I.; Rasheed, R.; Iqbal, M.; Riaz, M.; Arif, M.S. Advances in microbe-assisted reclamation of heavy metal contaminated soils over the last decade: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 198, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kołaciński, Z.; Rincón, J.; Szymański, T.; Sobiecka, E. Thermal plasma vitrification process as the effective technology for hospital incineration fly ash immobilization. In Vitrification and Geopolimerization of Wastes for Immobilization or Recycling; Universidad Miguel Hernandez: Alicante, Spain, 2017; Volume 51. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, M.; Ali, S.; Rehman, M.; Rana, M.; Rizwan, M.; Kamran, M.; Imran, M.; Riaz, M.; Hussein, M.; Elkelish, A.; et al. Influence of phosphorus on copper phytoextraction via modulating cellular organelles in two jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) varieties grown in a copper mining soil of Hubei Province, China. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zheng, J.; Sharp, R. Phytoremediation in engineered wetlands: Mechanisms and applications. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 1315–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Ali, S.; Irshad, S.; Hussaan, M.; Rizwan, M.; Rana, M.S.; Hashem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Ahmad, P. Copper Uptake and Accumulation, Ultra-Structural Alteration, and Bast Fibre Yield and Quality of Fibrous Jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) Plants Grown Under Two Different Soils of China. Plants 2020, 9, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, S.; Singh, V. Phytoremediation approaches for heavy metal pollution: A review. J. Plant Sci. Res. 2015, 2, 135. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, R.; Arora, P.; Kumar, S.; Chaudhury, A. Perspectives for genetic engineering of poplars for enhanced phytoremediation abilities. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 1574–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeeta, M.; Maiti, S.K. Phytoremediation of metal enriched mine waste: A review. Am. Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2010, 9, 560–575. [Google Scholar]
- Wiszniewska, A.; Hanus-Fajerska, E.; MUSZYŃSKA, E.; Ciarkowska, K. Natural organic amendments for improved phytoremediation of polluted soils: A review of recent progress. Pedosphere 2016, 26, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Chali, B.; Azam, T. Bioremediation of arsenic and lead by plants and microbes from contaminated soil. Res. Plant Sci. 2013, 1, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, M.H.; Fahad, S.; Khan, S.U.; Din, M.; Ullah, A.; Sabagh, A.E.; Hossain, A.; Llanes, A.; Liu, L. Copper-induced oxidative stress, initiation of antioxidants and phytoremediation potential of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) seedlings grown under the mixing of two different soils of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Kamran, M.; Zhou, Y.; Parveen, A.; Rehman, M.; Ahmar, S.; Malik, Z.; Mustafa, A.; Anjum, R.M.A.; Wang, B. Appraising growth, oxidative stress and copper phytoextraction potential of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) grown in soil differentially spiked with copper. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 257, 109994. [Google Scholar]
- Imran, M.; Sun, X.; Hussain, S.; Ali, U.; Rana, M.S.; Rasul, F.; Saleem, M.H.; Moussa, M.G.; Bhantana, P.; Afzal, J. Molybdenum-Induced Effects on Nitrogen Metabolism Enzymes and Elemental Profile of Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Under Different Nitrogen Sources. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3009. [Google Scholar]
- Griga, M.; Bjelková, M. Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) and Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) as fibre crops for phytoextraction of heavy metals: Biological, agro-technological and economical point of view. In Plant-Based Remediation Processes; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 199–237. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, M.H.; Fahad, S.; Khan, S.U.; Ahmar, S.; Khan, M.H.U.; Rehman, M.; Maqbool, Z.; Liu, L. Morpho-physiological traits, gaseous exchange attributes, and phytoremediation potential of jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) grown in different concentrations of copper-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 109915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, K.; Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Abu-Dieyeh, M.H. Phytoremediation: Halophytes as Promising Heavy Metal Hyperaccumulators. Heavy Met. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Liu, L.; Bashir, S.; Saleem, M.H.; Chen, C.; Peng, D.; Siddique, K.H. Influence of rice straw biochar on growth, antioxidant capacity and copper uptake in ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.) grown as forage in aged copper-contaminated soil. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 138, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najeeb, U.; Xu, L.; Ali, S.; Jilani, G.; Gong, H.; Shen, W.; Zhou, W. Citric acid enhances the phytoextraction of manganese and plant growth by alleviating the ultrastructural damages in Juncus effusus L. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, U.; Ali, S.; Shakoor, M.B.; Farid, M.; Hussain, S.; Yasmeen, T.; Adrees, M.; Bharwana, S.A.; Abbas, F. EDTA ameliorates phytoextraction of lead and plant growth by reducing morphological and biochemical injuries in Brassica napus L. under lead stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 9899–9910. [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu, G.P.S.; Bali, A.S.; Singh, H.P.; Batish, D.R.; Kohli, R.K. Ethylenediamine disuccinic acid enhanced phytoextraction of nickel from contaminated soils using Coronopus didymus (L.) Sm. Chemosphere 2018, 205, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Yang, X.; He, Z. Growth response and phytoextraction of copper at different levels in soils by Elsholtzia splendens. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, M.H.; Ali, S.; Seleiman, M.F.; Rizwan, M.; Rehman, M.; Akram, N.A.; Liu, L.; Alotaibi, M.; Al-Ashkar, I.; Mubushar, M. Assessing the Correlations between Different Traits in Copper-Sensitive and Copper-Resistant Varieties of Jute (Corchorus capsularis L.). Plants 2019, 8, 545. [Google Scholar]
- Ogunkunle, C.O.; Ziyath, A.M.; Adewumi, F.E.; Fatoba, P.O. Bioaccumulation and associated dietary risks of Pb, Cd, and Zn in amaranth (Amaranthus cruentus) and jute mallow (Corchorus olitorius) grown on soil irrigated using polluted water from Asa River, Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin Nizam, M.; Mokhlesur Rahman, M.; Kim, J.E. Phytoremediation Potential of Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.), Mesta (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.), and Jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) in Arsenic-contaminated Soil. Korean J. Environ. Agric. 2016, 35, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakari, M.; Moomin, A.; Nyarko, G.; Dawuda, M. Heavy metals concentrations and risk assessment of roselle and jute mallow cultivated with three compost types. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2017, 62, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.N.; Wahid-Uz-Zaman, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.S.; Islam, M.S. Phytoremediation Potentiality of Lead from Contaminated Soils by Fibrous Crop Varieties. Am. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2016, 2, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, D.A.; Slima, D.F. Heavy metal accumulation by Corchorus olitorius L. irrigated with wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14996–15005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, O.; Bledzki, A.K.; Fink, H.-P.; Sain, M. Biocomposites reinforced with natural fibers: 2000–2010. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1552–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S.B.; Sharma, H.K.; Karmakar, P.G.; Kumar, A.; Saha, A.R.; Hazra, P.; Mahapatra, B.S. Nutritional profile of cultivated and wild jute (‘Corchorus’) species. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2013, 7, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Thiruchitrambalam, M.; Athijayamani, A.; Sathiyamurthy, S.; Thaheer, A.S.A. A review on the natural fiber-reinforced polymer composites for the development of roselle fiber-reinforced polyester composite. J. Nat. Fibers 2010, 7, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Rehman, M.; Zahid, M.; Imran, M.; Xiang, W.; Liu, L. Morphological changes and antioxidative capacity of jute (Corchorus capsularis, Malvaceae) under different color light-emitting diodes. Braz. J. Bot. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, R.; Mieleniak, B.; Helwig, M.; Przepiera, A. Flame resistant lignocellulosic-mineral composite particleboards. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1999, 64, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Guha, G.; Gupta, K.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, U.C. Trend of arsenic pollution and subsequent bioaccumulation in Oryza sativa and Corchorus capsularis in Bengal Delta. Int. Lett. Nat. Sci. 2014, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osundiya, M.; Ayejuyo, O.; Olowu, R.; Bamgboye, O.; Ogunlola, A. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in frequently consumed leafy vegetable grown along Nigeria-Benin Seme Border, West Africa. Pelagia Res. Libr. 2014, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mahapatra, B.; Mitra, S.; Ramasubramanian, T.; Sinha, M. Research on jute (Corchorus olitorius and C. capsularis) and kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus and H. sabdariffa): Present status and future perspective. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 79, 951–967. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, A.; Misra, M. Studies on jute composites—A literature review. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 1995, 34, 729–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdan, S.; Smith, G.D. Natural fiber reinforced polyester composites: A literature review. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2015, 34, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndlovu, J.; Afolayan, A. Nutritional analysis of the South African wild vegetable Corchorus olitorius L. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2008, 7, 615–618. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, H.; Singh, J.I.P.; Singh, S.; Dhawan, V.; Tiwari, S.K. A Brief Review of Jute Fibre and Its Composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 28427–28437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Rahman, M. Hand book on agricultural technologies of Jute, Kenaf and Mesta crops. Bangladesh Jute Res. Inst. Dhaka 2008, 2, 92. [Google Scholar]
- Sarwar, N.; Imran, M.; Shaheen, M.R.; Ishaque, W.; Kamran, M.A.; Matloob, A.; Rehim, A.; Hussain, S. Phytoremediation strategies for soils contaminated with heavy metals: Modifications and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Zhang, J.; Luo, T.; Liu, J.; Ni, F.; Rizwan, M.; Fahad, S.; Hu, L. Morpho-physiological and biochemical responses of tolerant and sensitive rapeseed cultivars to drought stress during early seedling growth stage. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2019, 41, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Parveen, A.; Ahmar, S.; Malik, Z.; Hussain, S.; Chattha, M.S.; Saleem, M.H.; Adil, M.; Heidari, P.; Chen, J.T. An Overview of Hazardous Impacts of Soil Salinity in Crops, Tolerance Mechanisms, and Amelioration through Selenium Supplementation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, A.R.; Lee, S.S.; Awad, Y.M.; Lim, K.J.; Yang, J.E.; Ok, Y.S. Soil pollution assessment and identification of hyperaccumulating plants in chromated copper arsenate (CCA) contaminated sites, Korea. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadir, M.; Oster, J. Vegetative bioremediation of calcareous sodic soils: History, mechanisms, and evaluation. Irrig. Sci. 2002, 21, 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, H.D.; Reddy, K.R. Geoenvironmental Engineering: Site Remediation, Waste Containment, and Emerging Waste Management Technologies; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Laghlimi, M.; Baghdad, B.; El Hadi, H.; Bouabdli, A. Phytoremediation mechanisms of heavy metal contaminated soils: A review. Open J. Ecol. 2015, 5, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.N.; Husain, S.Z.; Nazir, I. Heavy metal contamination and accumulation in soil and wild plant species from industrial area of Islamabad, Pakistan. Pak. J. Bot. 2010, 42, 291–301. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, S.; Mishra, R.; Sinam, G.; Mallick, S.; Gupta, A. Comparative evaluation of metal phytoremediation potential of trees, grasses, and flowering plants from tannery-wastewater-contaminated soil in relation with physicochemical properties. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2013, 22, 958–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.; Ferdous, A.S.; Sarker, S.; Islam, M.; Hossain, K.; Khan, H. Identification and expression profiling of microRNAs and their corresponding targets related to phytoremediation of heavy metals in jute (Corchorus olitorius var. O-9897). Biores. Commun. 2016, 2, 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Nwaichi, E.O.; Dhankher, O.P. Heavy metals contaminated environments and the road map with phytoremediation. J. Environ. Prot. 2016, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyedele, D.; Asonugho, C.; Awotoye, O. Heavy metals in soil and accumulation by edible vegetables after phosphate fertilizer application. Electron. J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 5, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Anwer, S.; Ashraf, M.Y.; Hussain, M.; Ashraf, M.; Jamil, A. Citric acid mediated phytoextraction of cadmium by maize (Zea mays L.). Pak. J. Bot. 2012, 44, 1831–1836. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, M.; Bhantana, P.; Sun, X.-C.; Imran, M.; Shaaban, M.; Moussa, M.; Saleem, M.H.; Elyamine, A.; Binyamin, R.; Alam, M.; et al. Molybdenum as an Essential Element for Crops: An Overview. Int. J. Scien. Res. Growth 2020, 24, 18535. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, M.; Yang, M.; Fahad, S.; Saleem, M.H.; Liu, L.; Liu, F.; Deng, G. Morpho-physiological traits, antioxidant capacity and nitrogen metabolism in Boehmeria nivea L. under nitrogen fertilizer. Agron. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Dagari, M.; Babayo, A. Effect of citric acid on cadmium ion uptake and stress response of hydroponically grown jute mallow (Corchorus olitorius). J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2016, 6, 375. [Google Scholar]
- Oguntade, O.A.; Olagbenro, T.S.; Odusanya, O.A.; Olagunju, S.O.; Adewusi, K.M.; Adegoke, A.T. Assessment of composted kitchen waste and poultry manure amendments on growth, yield and heavy metal uptake by Jute mallow Corchorus olitorius Linn. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2019, 8, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogoko, E. Accumulation of heavy metal in soil and their transfer to leafy vegetables with phytoremediation potential. Am. J. Chem. 2015, 5, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Idirs, S.; Yisa, J.; Ndamitso, M. Nutritional composition of Corchorus olitorius leaves. Anim. Prod. Res. Adv. 2009, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nörtemann, B. Biodegradation of chelating agents: EDTA, DTPA, PDTA, NTA, and EDDS. Biogeochem. Chelating Agents 2005, 910, 150–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiba, U.; Ali, S.; Farid, M.; Shakoor, M.B.; Rizwan, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Abbasi, G.H.; Hayat, T.; Ali, B. EDTA enhanced plant growth, antioxidant defense system, and phytoextraction of copper by Brassica napus L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 1534–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshan, S.; Ali, S.; Bharwana, S.A.; Rizwan, M.; Farid, M.; Abbas, F.; Ibrahim, M.; Mehmood, M.A.; Abbasi, G.H. Citric acid enhances the phytoextraction of chromium, plant growth, and photosynthesis by alleviating the oxidative damages in Brassica napus L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 11679–11689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, M.; Kuittinen, S.; Salam, M.M.A.; Peräniemi, S.; Laine, S.; Pulkkinen, P.; Kaipiainen, E.; Vepsäläinen, J.; Pappinen, A. Chelate-assisted phytoextraction: Growth and ecophysiological responses by Salix schwerinii EL Wolf grown in artificially polluted soils. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 205, 106335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.H.; Park, K.; Chang, P.C.; Liu, W.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, K.W. Influence of phosphate and citric acid on the phytoextraction of as from contaminated soils. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2013, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gu, J.; Zhao, J.; Fu, J. Citric acid and EDTA on the growth, photosynthetic properties and heavy metal accumulation of Iris halophila Pall. cultivated in Pb mine tailings. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 128, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M.; Ali, S.; Shakoor, M.B.; Bharwana, S.A.; Rizvi, H.; Ehsan, S.; Tauqeer, H.M.; Iftikhar, U.; Hannan, F. EDTA assisted phytoremediation of cadmium, lead and zinc. Int. J. Agron. Plant Prod. 2013, 4, 2833–2846. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.Y.; Chaudhury, S. EDTA-enhanced phytoextraction by Tagetes sp. and effect on bioconcentration and translocation of heavy metals. Environ. Process. 2016, 3, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsan, S.; Ali, S.; Noureen, S.; Mahmood, K.; Farid, M.; Ishaque, W.; Shakoor, M.B.; Rizwan, M. Citric acid assisted phytoremediation of cadmium by Brassica napus L. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 106, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Plant Species | Major Characteristics | Phytoremediation Potential | References | Remarks | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese mustard (Brassica juncea) | It is also known as green mustard cabbage, Indian mustard, mustard green, or leaf mustard with edible leaves, stem, and seeds. The vegetative parts of this mustard are consumable, cooked or raw. | It was reported that Chinese mustard has huge biomass and can accumulate an impressive amount of Cd in their above-ground parts. | [58] | Cd is the most frequently studied element in flax plants while the presence of high Cd in soil causes chronic toxicity in humans. | [59] |
| Chinese ladder brake fern (Pteris vittata) | It is native to China and found in many counties of South America and North America. It has a very close resemblance to the swamp fern Blechnum serrulatum | The Chinese brake fern has an exceptional ability to accumulate a high amount of As from the soil. It can consist of up to 2% arsenite. | [60] | It was noted that among different heavy metals flax has potential to remove the most amount of As from contaminated soil. | [61] |
| Pennycress (Thlaspi Caerulescens) | Pennycress is a biennial herbaceous plant belonging to the family Brassicaceae. It is a flowering plant and found in Europe and Scandinavia. It also grows on gardens, forest margins, and bare places. | Pennycress can accumulate and tolerate Zn, Cd, and Ni. It frequently occurs on mineralized soils, particularly those with high Zn content. | [62] | When flax grows under different heavy metals (Cd, Zn, and Pb), a progressive decrease in heavy metal content from the soil was observed. | [53] |
| Barley (Hordeum vulgare) | Barley is a member of the grass family, is a cereal crop, and found in the temperate regions of the world. It is used as animal fodder and fermented beer. | Barley can be used as good phytoremediation material in petroleum-contaminated soils and can remove Cd, Pb, Ni, Zn, and Cu from the ground. | [63] | Like very few species (such as sorghum), flax is able to grow on highly hydrocarbon polluted soil, i.e., 40,000 ppm. | [64] |
| Fescue (Festuca arundinacea) | Fescue is a genus of flowering plants and belongs to the family Poaceae. They are evergreen, and herbaceous plants can reach a height of 200 cm. It is used as an ornamental plant and tough grasses. | Fescue has been used for the phytoremediation of Pb and Zn and many other heavy metals and is thus considered as a potential candidate for phytoremediation. | [65] | Flax has huge biomass and can remove 253 mg kg−1 Cu from 600 mg kg−1 Cu in the soil. | [12] |
| Metal Type | Metal in Soil | Metal Accumulate by Shoots | Metals Accumulated by Roots | Experiment Type | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | 1008 | 255 | - | Pot | [53] |
| Cd | 41 | 13 | - | Pot | [53] |
| Pb | 704 | 310 | - | Pot | [53] |
| Cu | 617 | 814 | 246 | Pot | [12] |
| Pb | 1100 | 332 | - | Pot | [78] |
| Zn | 800 | 116 | - | Pot | [78] |
| Cd | 6 | 49 | - | Pot | [78] |
| Zn | 100 | 26 | - | Pot | [79] |
| Cd | 100 | 190 | - | Pot | [79] |
| Pb | 200 | 104 | 15 | Pot | [80] |
| Cu | 96 | 31 | 5 | Pot | [80] |
| Zn | 536 | 213 | 33 | Pot | [80] |
| Cd | 12 | 9 | 2 | Pot | [80] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saleem, M.H.; Ali, S.; Hussain, S.; Kamran, M.; Chattha, M.S.; Ahmad, S.; Aqeel, M.; Rizwan, M.; Aljarba, N.H.; Alkahtani, S.; et al. Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.): A Potential Candidate for Phytoremediation? Biological and Economical Points of View. Plants 2020, 9, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9040496
Saleem MH, Ali S, Hussain S, Kamran M, Chattha MS, Ahmad S, Aqeel M, Rizwan M, Aljarba NH, Alkahtani S, et al. Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.): A Potential Candidate for Phytoremediation? Biological and Economical Points of View. Plants. 2020; 9(4):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9040496
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaleem, Muhammad Hamzah, Shafaqat Ali, Saddam Hussain, Muhammad Kamran, Muhammad Sohaib Chattha, Shoaib Ahmad, Muhammad Aqeel, Muhammad Rizwan, Nada H. Aljarba, Saad Alkahtani, and et al. 2020. "Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.): A Potential Candidate for Phytoremediation? Biological and Economical Points of View" Plants 9, no. 4: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9040496
APA StyleSaleem, M. H., Ali, S., Hussain, S., Kamran, M., Chattha, M. S., Ahmad, S., Aqeel, M., Rizwan, M., Aljarba, N. H., Alkahtani, S., & Abdel-Daim, M. M. (2020). Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.): A Potential Candidate for Phytoremediation? Biological and Economical Points of View. Plants, 9(4), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9040496









