Abstract
The ethylene-insensitive3-like/ethylene-insensitive3 (EIL/EIN3) protein family can serve as a crucial factor for plant growth and development under diverse environmental conditions. EIL/EIN3 protein is a form of a localized nuclear protein with DNA-binding activity that potentially contributes to the intricate network of primary and secondary metabolic pathways of plants. In light of recent research advances, next-generation sequencing (NGS) and novel bioinformatics tools have provided significant breakthroughs in the study of the EIL/EIN3 protein family in cotton. In turn, this paved the way to identifying and characterizing the EIL/EIN3 protein family. Hence, the high-throughput, rapid, and cost-effective meta sequence analyses have led to a remarkable understanding of protein families in addition to the discovery of novel genes, enzymes, metabolites, and other biomolecules of the higher plants. Therefore, this work highlights the recent advance in the genomic-sequencing analysis of higher plants, which has provided a plethora of function profiles of the EIL/EIN3 protein family. The regulatory role and crosstalk of different metabolic pathways, which are apparently affected by these transcription factor proteins in one way or another, are also discussed. The ethylene hormone plays an important role in the regulation of reactive oxygen species in plants under various environmental stress circumstances. EIL/EIN3 proteins are the key ethylene-signaling regulators and play important roles in promoting cotton fiber developmental stages. However, the function of EIL/EIN3 during initiation and early elongation stages of cotton fiber development has not yet been fully understood. The results provided valuable information on cotton EIL/EIN3 proteins, as well as a new vision into the evolutionary relationships of this gene family in cotton species.
1. Introduction
The gaseous ethylene phytohormone plays an important role in the regulation of different biological processes such as plant growth, plant development, and stress responses [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. A large number of molecular studies have associated the ethylene pathway with signal transduction by triggering downstream ethylene response genes [8]. Furthermore, the EIL/EIN3 genes also act as a foundation for ethylene connections with other signals, such as the crosstalk between ethylene and other hormones, light signaling, as well as various abiotic and biotic stress responses [9,10]. In cotton, two pathways of ethylene related genes were found to be associated with fiber yield [11]. Ethylene-insensitive3 pathways such as (EIN3) and EIN3-like (EIL) proteins are one of the main transcription factors [12,13,14]. The EIL/EIN3 proteins were indicated to be involved in the expression of the GCC-box-binding domain of Arabidopsis ethylene-response factors [15]. The EIN3/EIL protein family is a small group of transcription factors in higher plants. Several transcription factor genes of EIL/EIN3 proteins have been investigated in Arabidopsis [16,17], tobacco [18], tomato [19], cucumber [20,21,22], and rice [23]. Plant specific EIL/EIN3 proteins have highly conserved amino acid sequences at the N-termini, and are located in the nuclei compartment [16]. Some important structural forms were shown in the first half of the EIL/EIN3 protein sequences, such as highly acidic N-terminus amino acid regions, 5-basic amino acid groups, and proline-rich regions [17]. It is known that the EIN3/EIL protein family has multiple functions in plant growth and development. In Arabidopsis, EIL3 acts as the central transcriptional regulator of plant sulfur response and metabolism process [24]. Overexpression of EIL3 restores the sulfur limitation responseless morphologies of Arabidopsis mutants (slim1 mutants) [24]. In addition, it was found that EIN3 significantly associates with the expression of chlorophyll biosynthesis genes [25]. Transcriptome analysis of Arabidopsis mutants found several EIN3-regulated genes that were coregulated by the other transcription factors such as PIFs (light signaling) and RHD6 (root hair development) [26], which indicates co-regulation of EIL/EIN3-activated transcription by certain developmental processes and environmental conditions. In tomato, overexpression of EIN3-binding F-box protein2 gene prompted elongated fruit shape and delayed fruit development and ripening [27]. In cotton, ethylene plays a vital role in enhancing the fiber cell elongation stage by regulating the expression of tubulin, sucrose synthase, and expansin genes [28]. The gene encoding ethylene insensitive 3-like protein was differentially expressed between TM-1 and ZMS12 [11]. Recently, investigations on the application of the relative genome in the analysis of function and evolution of the EIL/EIN3 gene family have been reported [18,29,30]. However, there is still a lack of specific evolutionary relationships of the EIL/EIN3 gene family in cotton. Fiber mutants are powerful tools for investigating the molecular mechanism and physiological process of fiber cell developmental stages. Mutant cotton analysis has accelerated the identification and characterization of interest genes or molecular elements associated with various stages of cotton fiber development [31,32,33,34]. To fill this gap, the evolutionary relationships of EIL/EIN3 genes from cotton species, including Gossypium hirsutum, Gossypium arboreum, and Gossypium raimondii were analyzed, according to their tree topology and sequence similarity. Moreover, the expression levels of upland cotton EIL/EIN3 genes were studied on a variety of fiber-cell developmental stages including 0, 3, 5, 8, and 10 days post anthesis (DPA). The results of this study provide fundamental evidence into the role of EIL/EIN3 genes in cotton fiber development and will support future functional examination of this vital gene family. In cotton, the EIL/EIN3 transcription factor plays an important role in the ethylene signaling pathway, which is involved in regulating the posttranscriptional level, whereas transcriptional regulations of EIL/EIN3 are not yet fully known.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gene Identification Procedures
The identification of the EIL/EIN3 transcription factor family in three cotton genome protein sequences (G. hirsutum, G. arboreum and G. raimondii) were downloaded from cottongen database resources (https://www.cottongen.org/). To identify EIL/EIN3 transcription factors in the cotton genome a BLASTP search was conducted using Arabidopsis, P. trichocarpa, maize, sorghum, and rice. EIL/EIN3 protein sequences were identified in the Phytozome database (https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html). The Hidden Markov Model profile of the EIL/EIN3 protein domain (PF04873) was downloaded from the Pfam database resources (http://pfam.xfam.org) and used as query sequences to identify EIL/EIN3 genes with an E-value < 10−10. To confirm the presence of the EIL/EIN3 protein domain in the three cotton genome protein sequences, all putative protein sequences were scanned by the InterPro online tool (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/) and SMART database (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/) to validate the EIL/EIN3 domain. Additionally, only the protein sequences with the EIN3/EIL domain were kept for further investigation. The physiochemical features (isoelectric point and molecular mass) of all the identified EIL/EIN3 protein domains were examined by the ExPASy Server tool. Moreover, the prediction of subcellular location was done by WoLF PSORT (https://wolfpsort.hgc.jp/) and confirmed by Protein Prowler Subcellular Localization Predictor version 1.2 (http://bioinf.scmb.uq.edu.au:8080/pprowler_webapp_1-2/) and TargetP1.1 Server11 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TargetP/). The physical locations of EIN3/EIL genes were determined through blastN queries against the three cotton genomes. The MapChart tool (https://mapchart.net/) was used to locate EIN3/EIL genes on the specific chromosome.
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the EIL/EIN3 Protein Family
The ClustalW method was used to align full amino acid sequences of EIL/EIN3 genes from G. hirsutum, G. arboreum, G. raimondii, Arabidopsis thaliana, P. trichocarpa, maize, sorghum, and rice. Moreover, a neighbor-joining (NJ) phylogeny method was conducted using MEGA 6.0 software (https://www.megasoftware.net/) with the following parameters: A Poisson model and 1000 bootstraps. The EIL/EIN3 gene organizations (exon/intron) were created by Gene Structure Displayer Server 2.0 (http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/) according to their genomic DNA sequences [31]. The 10 conserved motifs of EIN3/EIL proteins were examined by the MEME program (http://meme-suite.org/).
2.3. Analysis of Cis-Acting Regulatory Elements and miRNA Targets
The cis-acting regulatory elements in each promoter sequence of EIN3/EIL genes (2 kb upstream of the translation starting site) were investigated using the PlantCARE database (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/). The plant small RNA target analysis server (http://plantgrn.noble.org/psRNATarget/) [35] was used to predict the miRNAs target G. hirsutum EIL/EIN3 genes.
2.4. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Pathway Analysis of EIL/EIN3 Genes
Gene Ontology (GO) was used to get information about the EIL/EIN3 genes involvement in three ways: biological processes, cellular components, and molecular function. GO annotation analysis of cotton EIN3/EIL genes was done based on an OmicsBox/Blast2Go (https://www.biobam.com/omicsbox/). The KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) pathway was also used for a bioinformatics investigation that sought to examine the organismal and cellular functions of the EIL/EIN3 genes. To visualize the KEGG-pathway-enrichment of cotton EIL/EIN3 genes, Arabidopsis gene homologs for the identified EIL/EIN3 proteins in cotton were utilized as input data for the David database (http://david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov/).
2.5. Protein Interaction Networks of EIL/EIN3 Genes
The investigation of protein–protein interactions simplifies the understanding of plant gene functions [36]. Consequently, to gain more insight into the role of EIN3/EIL genes in biological involvement through protein–protein interaction, the STRING online database (https://string-db.org/) was used to conduct the protein interaction networks.
2.6. Plant Material, RNA-seq, and Data Analysis
Upland cotton, Ligonlintless-1 mutant, and wild-type genotypes were planted in the experimental field at the ICR, Institute of Cotton Research, CAAS (Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences) under normal conditions. For self-pollination, cotton flowers before the anthesis day were tied and labeled. All cotton samples were collected with biological triplicates for each sample from both the Ligonlintless-1 mutant and wild-type at the following stages of cotton fiber development: 0, 3, 5, 8, and 10 DPA and cotton leaf. The collected cotton samples were quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen and kept at −80 °C until further analysis. RNA-seq data for upland cotton, Ligonlintless-1, and wild-type from cotton fiber developmental stages at 0, 3, and 8 DPA, and cotton leaf were used to identify the spatio-temporal expression levels of G. hirsutum EIN3/EIL genes. The raw reads were mapped to the upland reference genome [37]. The transcriptome assembly and expression counts were gained using STRINGTIE [38]. The FPKM value (fragments per kilo-base of exon per million fragments mapped) was used to calculate the gene expression pattern. The RT-qPCR analysis was also used to calculate the expression pattern of G. hirsutum EIL/EIN3 genes associated with cotton fiber developmental stages, 0, 3, 5, 8, and 10 DPA. The SYBER premix ExTaq kit (TaKaRa, Osaka, Japan) and Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) were used to conduct RT-qPCR experiments. The G. hirsutum constitutive β-actin gene was applied as a reference gene and special EIL/EIN3 gene primers were employed for RT-qPCR. The following thermal cycle circumstances were applied: 95 °C for 2 min, 40 cycles of 95 °C for 5 s, and 60 °C for 34 s. The expression profiles for each gene were measured as the mean signal intensity across the three biological replicates. The Ct was used for the relative calculation of the input target number.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Gene Identification Procedures
To identify the EIL/EIN3 transcription factor family in G. hirsutum, G. raimondii, and G. arboreum, two methods of the blast (local blast and HMM research) were used to search against the tree cotton genomes for E-values ≤ 10−10. Multiple sequence alignment was implemented to remove the redundant sequences of EIL/EIN3 genes. Pfam (http://pfam.xfam.org/) and SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/) databases were used to confirm the presence of the EIL/EIN3 domain in cotton protein sequences. Finally, the redundant protein sequences were removed, resulting in 37 genes, including, 18, 10, and 9 EIL/EIN3 genes in G. hirsutum, G. raimondii, and G. arboreum, respectively. The results of this study revealed that the EIN3/EIL transcription factor family is significantly smaller than other transcription factor families [39]. The same conclusion was reached in earlier reports in different plants [29,30,39]. Based on bioinformatics analyses of the studied species, an EIN3 protein domain in each protein sequence of the EIL/EIN3 gene members was found and localized in the nucleus, and various EIL/EIN3 genes were found in higher plant genomes [15,29,39]. This indicated that the EIL/EIN3 gene family may be involved in regulating various functions in different species. Additionally, the predicted nuclear positions may prove that the EIL/EIN3 genes act as transcription factors. To obtain more insight into the possible role of the proteins encoded by the EIL/EIN3 gene under examination, it is necessary to understand their physiochemical properties, for instance, the proteins can be divided based on their molecular weight and isoelectric point properties [40]. Through the enzyme association on the carrier, the bumper must have a pH value supporting electrostatic interactions with the surface of the carrier [40]. Additionally, in calculating any given protein family in plants, diverse physiological properties are investigated, for instance, in the sucrose synthase protein family in cotton, molecular weights and isoelectric points, among others were factored into the investigations [41]. The variations of an amino acid sequence of the cotton EIL/EIN3 genes significantly varied in size and were divergent in physicochemical characteristics (Table 1). For example, the cotton EIL/EIN3 proteins varied in length from 109 to 690 amino acids. Cotton EIL/EIN3 proteins had a huge divergence in the isoelectric point (pI), ranging from 4.78 to 9.35. The molecular weight of the cotton EIN3/EIL proteins ranged from 13052.13 kDa to 77907.98 kDa (Table 1). WoLF PSORT, Protein Prowler Subcellular Localization Predictor, and TargetP1.1 Server analyses found that all of these cotton EIL/EIN3 proteins, including soybean, P. trichocarpa, and Arabidopsis EIL/EIN3 family proteins, were found to be localized in the nucleus compartment, which is in-line with their role in transcriptional regulation [39,42]. These results suggest that the EIL/EIN3 protein family may be involved in the regulation of various aspects of plant growth and development.

Table 1.
Information about the EIL/EIN3 gene family in cotton.
To analyze the distribution of the EIL/EIN3 genes on chromosomes on G. hisurtum, G. raimondii, and G. arboreum, a chromosome map was constructed based on three cotton genome sequences. In G. hirsutum, 17 genes were distributed across 13 of the 26 chromosomes while 1 gene was mapped to an unknown chromosome (scaffold). Two EIL/EIN3 genes were mapped to chromosomes Ah05, Ah13, Dh03, and Dh13, and one EIL/EIN3 gene was localized on chromosomes Ah02, Ah03, Ah06, Ah08, Dh05, Dh06, Dh07, Dh08, and Dh12 (Table 1 and Figure S1). The distribution of EIL/EIN3 genes within the At and Dt sub-genomes were consistent, with 8 and 9 EIL/EIN3 genes located in the sub-genomes, respectively. Nevertheless, there is a strong indication of gene loss between the two loci sets of homologous chromosomes. For instance, chrAh03 has a single EIN3/EIL gene, but its homolog, chromosome Dh03 has 2 EIL/EIN3 genes. Likewise, chromosome Ah05 has 2 EI EIL/EIN3 N3/EIL genes, whereas chromosome Dh05 only has one gene. Almost similar numbers of putative EIN3/EIL were located on the At and Dt sub-genomes with 8 and 9 genes, respectively. In G. raimondii, two genes were mapped to chromosomes Chr D503, Chr D509, and Chr D513 while one gene was localized on chromosomes Chr D501, Chr D504, Chr D507, and Chr D510. In G. arboreum, two genes were distributed on chromosomes ChrA205 and Chr A213, and one gene was mapped to chromosomes Chr A201, Chr A202, Chr A206, and Chr A208, with the remaining one gene localized on a scaffold region. Genome chromosomal position analyses revealed that the supposed 37 EIL/EIN3 genes were not consistently distributed throughout all cotton chromosomes (Table 1 and Figure S1).
3.2. Gene Structure Analysis and Conserved Motif Analysis of EIL/EIN3 Genes
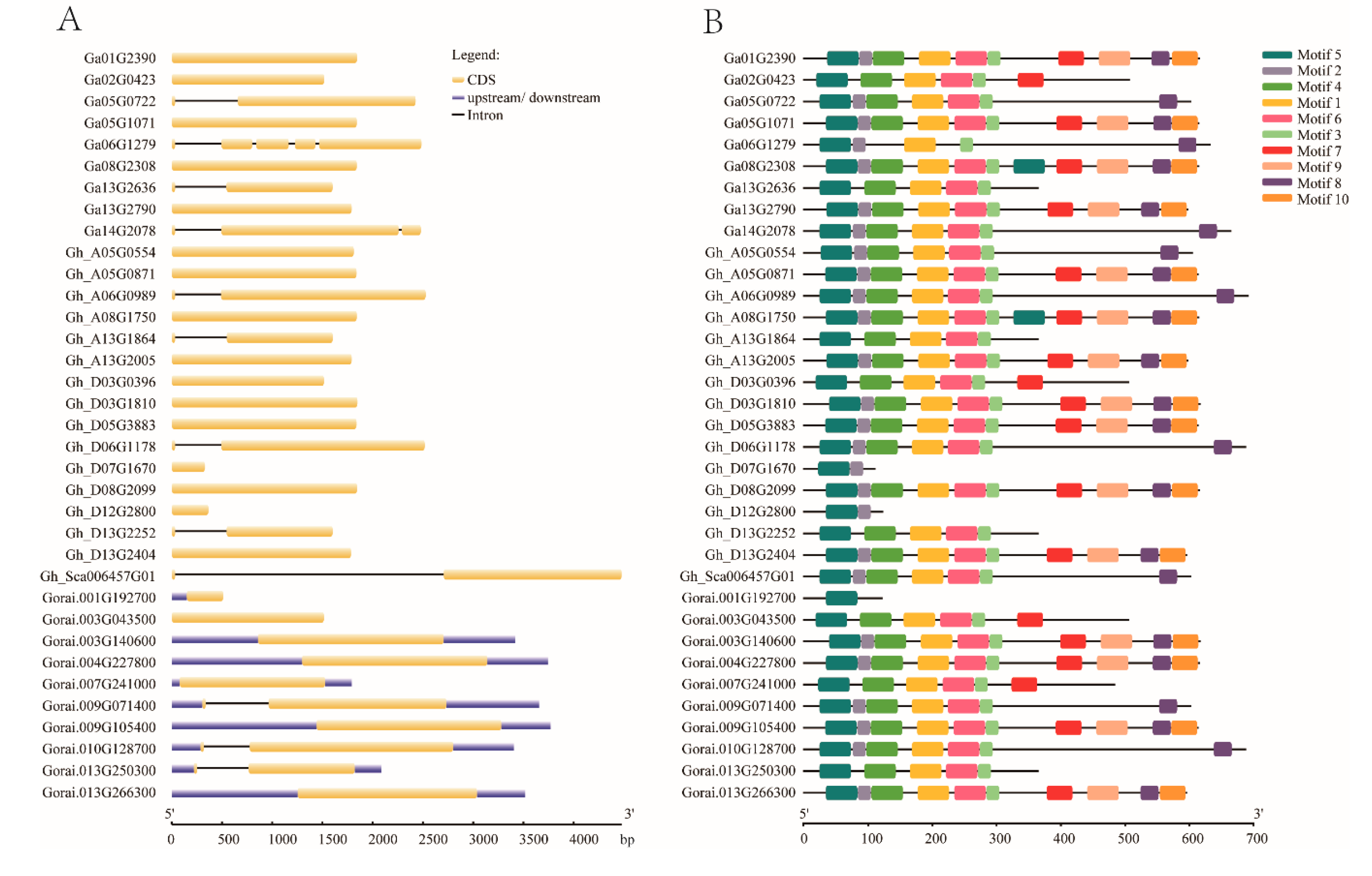
The variation in gene arrangement is the key factor involved in the evolution of multigene families [43,44,45]. To elucidate the organizational diversities of cotton EIL/EIN3 genes, the exon/intron arrangements of these cotton genes were investigated. The result of the gene structure analysis found that most cotton EIL/EIN3 genes (24) did not have introns, while 12 genes contained an intron. Of the 12 EIL/EIN3 genes with introns, ten genes had one intron, one contained two introns, and the other contained four introns (Figure 1A). These last two genes were from G. arboreum, and it was speculated that some members of the EIL/EIN3 genes lost extra introns during the course of hybridization. However, in the majority of G. raimondii genes with upstream and downstream fragments, it was noticed that gene members of G. raimondii reformed during the process of hybridization.
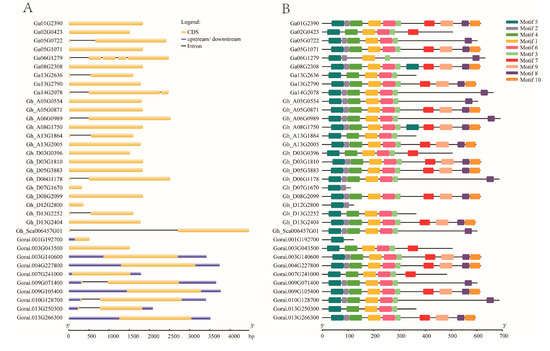
Figure 1.
Structural features of EIL/EIN3 transcription factor in cotton. (A) The exon–intron arrangement of EIL/EIN3 genes. The blue shapes represent upstream/downstream, yellow shapes indicate CDS (exons), and black lines represent introns. (B) Ten motifs identified by the MEME tool are represented by colored boxes, and their consensus sequences are shown in Figure S2.
In order to obtain further insight into the conserved motifs, 10 motifs in cotton EIL/EIN3 proteins were conducted using the MEME program (Figure 1B and Figure S2). A set of 37 EIL/EIN3 protein sequences resulted in three common motif sequences: 1, 3, and 5 motifs were associated with the EIN3 (PF04873) domain, which was found to be located in the first half of the amino acid sequences (starting from 33 to 208 residues, approximately). In previous identification of conserved motifs in higher plants, it was found that motifs 1, 3, 4, 5, and 6 were related to the domain of EIN3/EILs [12,14,29,30]. Earlier studies reported that the first part of the EIL/EIN3 gene was found to contain highly homologous sequences, which were associated with the domain of EIN3 [15]. This was similarly confirmed in several recent works [29,42]. Additionally, some changes in the motif numbers and sequences were also mentioned in the first half of the N-terminus, except in the first ~80 residues for activity [17]. Moreover, the existence of two long conserved motif residues related to the EIN3 domain also implicated the significantly conserved motif organizations of cotton EIL/EIN3.
3.3. Phylogeny of EIL/EIN3 Members
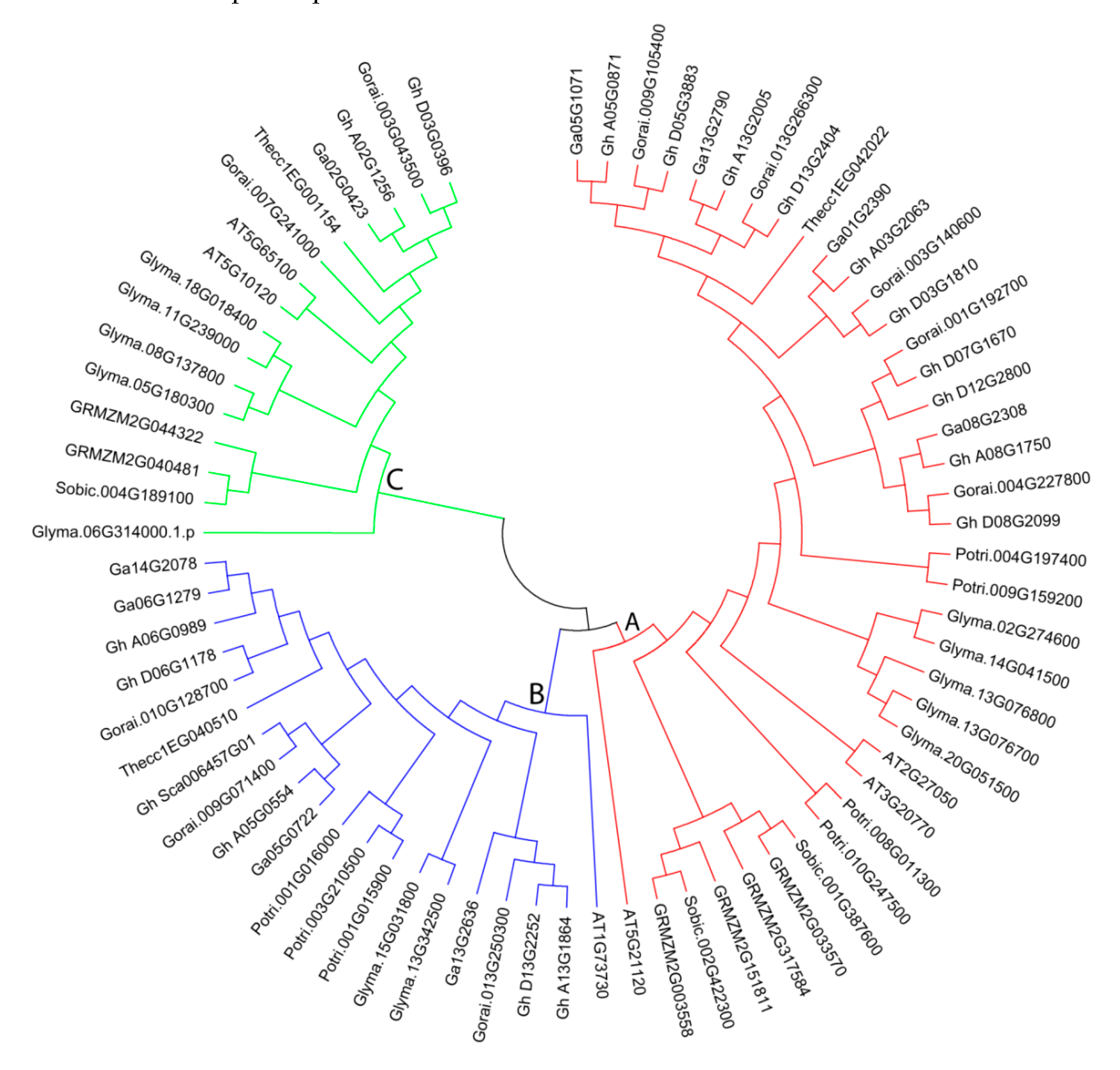
Phylogenetic tree analysis was generated by MEGA6 software with the NJ method for 1000 bootstraps using 74 EIL/EIN3 protein sequences from 18 G. hirsutum, 9 G. arboreum, 10 G. raimondii, 6 Arabidopsis, 7 P. trichocarpa, 6 maize, 3 sorghum, 3 T. cacao, and 12 soybean EIL/EIN3 proteins (Figure 2). Phylogeny was applied to gather functional relationships for the supposed 74 EIL/EIN3 genes. Phylogenetic tree analysis of the 74 EIL/EIN3 protein sequences was divided into three main groups, labeled as groups A, B, and C, which varied in number from 16 to 38 EIL/EIN3 genes (Figure 2). Group A had the largest number with 38 EIL/EIN3 genes, followed by group B with 20, and group C with 16. The results of this study are in agreement with previous reports in other plants on classifications of these EIL/EIN3 gene groupings [30,39,42]. The EIL/EIN3 protein families in dicots and monocots were grouped in different sub-groups in our phylogenetic tree compared to previous findings. The current findings revealed that nine plant species presented into the three main groups of EIL/EIN3 gene members, which provided a strong sign that the variance of these plants arose after the extension of the EIL/EIN3 transcription factor gene family. The distribution of EIL/EIN3 genes was much greater in the three Gossypium genomes than in other plant species. Furthermore, a unique observation was made, in which several clades only contained members of EIL/EIN3 genes derived from a particular plant species. Some EIL/EIN3 gene homologs were clustered by plant species within a sub-group, which referred to that plant species.
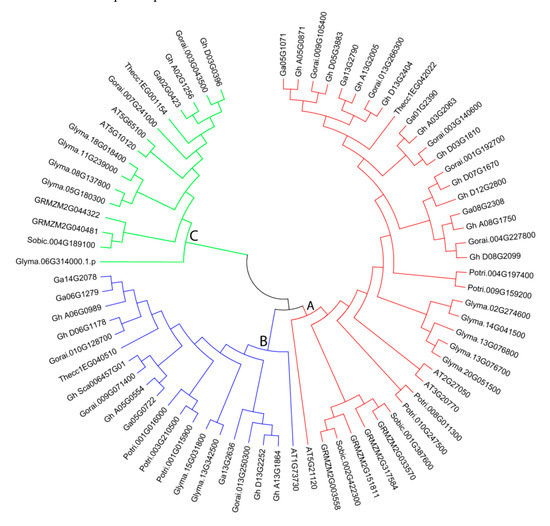
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree relationships between 18 G. hirsutum, 9 G. arboreum, 10 G. raimondii, 6 Arabidopsis, 7 P. trichocarpa, 6 maize, 3 sorghum, 3 T. cacao, and 12 soybean EIL/EIN3 proteins. The phylogenetic tree was created by the MEGA 6.0 program using the NJ (neighbor-joining) method. The bootstrap test was done with 1000 iterations. The three groups (A, B, and C) are shown in colors.
3.4. Cis-Regulatory Element Analysis
The presence of various cis-regulatory elements in promoter regions of EIL/EIN3 genes may indicate that the functions of these genes are diverse. In order to explore cis-regulatory elements in the promoter regions of cotton EIL/EIN3 genes, a 1500 bp upstream region of the transcription start site in each gene was identified and then searched for in the PlantCARE database. Various types of cis-regulatory elements were found in the promoter regions of cotton EIL/EIN3 genes (Table S1). Particularly, regulatory sequences such as CAATs, TATA boxes, TGACG-motifs, MYB recognition sites, and STREs (rapid stress response elements) were detected in all upland cotton EIL/EIN3 genes. CAAT and TATA boxes are the main cis-acting elements found in the promoter sequences of transcriptional eukaryotic genes. In addition, the CAAT-box forms a binding position for RNA transcription factors and is involved in modulating the expression of genes [46,47,48]. The CAAT-box element plays an important role in regulating the nopaline synthase promoter [49]. Recently, the TATA-box was reported to harbor a binding site for histones or transcription factors, which supported its role in the transcriptional process [50,51]. STREs are involved in the primary transcriptional stress response to abiotic and biotic stresses in vivo [52]. Furthermore, several identified cis-regulatory elements were associated with hormone responses such as the CGTCA- and TGACG-motifs (cis-acting regulatory elements involved in MeJA-responsiveness), GARE-motif (cis-acting regulatory element involved in the gibberellin-responsive element), TGA-element (cis-acting regulatory element involved in auxin responsiveness), TCA-element (cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness), and ABRE (cis-acting regulatory element involved in abscisic acid responsiveness) (Table S1). In cotton ovules, it was noticed that abscisic acid is involved in the regulation of the cotton fiber developmental stages, along with auxins, ethylene, and gibberellins [53]. In general, plant hormones play an important role in the cotton fiber developmental stages such as initiation, elongation, and secondary cell wall development [54]. The result of this study also showed other cis-regulatory elements with diverse functions, such as improving the ability of the plant’s responses to drought and light, among others. Analysis of the identified cis-regulatory elements revealed that EIL/EIN3 genes are related to various functions during cotton plant growth and development. The majority of EIL/EIN3 gene promoters had a combination of various hormones related to cis-elements. These findings support that EIL/EIN3 genes play a vital role in regulating diverse hormone signaling pathways, and suggest that these EIL/EIN3 genes are transcriptionally controlled by a multicomplex network of hormones. The outcome of this investigation indicated that some cis-regulatory elements associated with EIL/EIN3 genes might be involved in the regulation of cotton fiber developmental stages.
3.5. GO and KEGG Pathway Analysis of EIL/EIN3 Genes
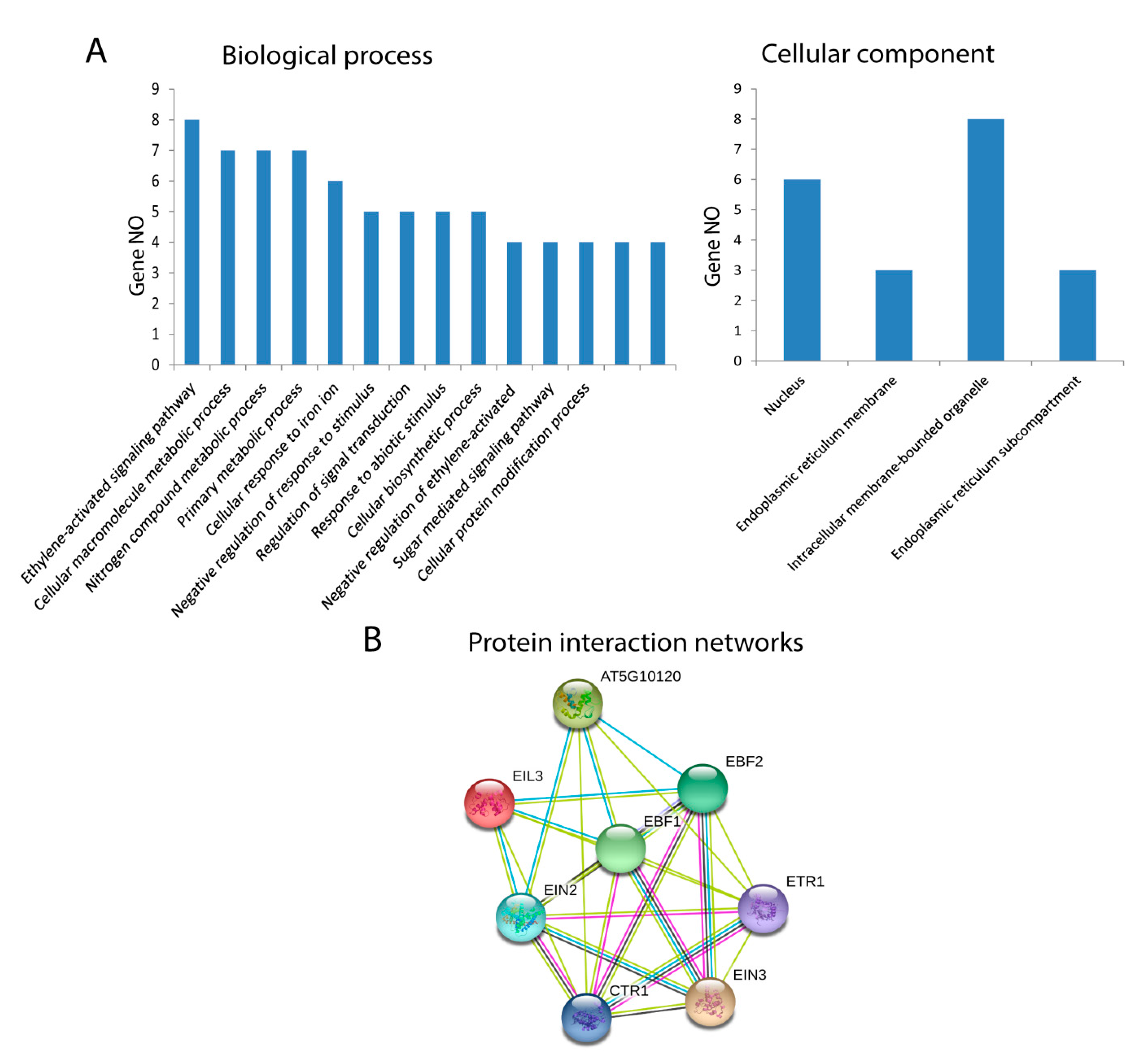
The GO annotations and KEGG pathway analyses were conducted using the OmicsBox/Blast2Go tool and KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) pathway, and they presented the possible functions of EIL/EIN3 proteins. Cotton EIL/EIN3 genes were classified into two groups by GO annotation analysis according to their categories: biological processes and cellular components. The GO annotation results assigned the EIL/EIN3 genes into 14 clusters of biological processes; a great number of EIL/EIN3 genes were involved in the ethylene-activated signaling pathway, cellular macromolecule metabolic process, nitrogen compound metabolic process, primary metabolic process, and cellular response to iron ions (Figure 3A). In terms of the cellular component prediction of EIL/EIN3 genes, they were significantly enriched in the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum membrane, intracellular membrane-bounded organelles, and endoplasmic reticulum sub-compartment. The KEGG pathway analysis showed that these EIL/EIN3 genes play roles in ethylene regulatory networks of plant hormone signal transduction (ath04075). Ethylene plays a key role in promoting cotton fiber elongation by increasing the expression of tubulin, sucrose synthase, and expansin genes [55]. The ethylene pathway is one of the most important biosynthetic pathways related to cotton fiber development during the elongation stage [56].
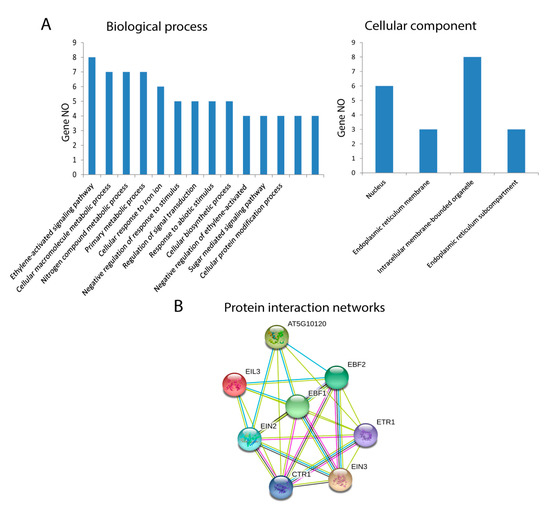
Figure 3.
Functional analysis of EIL/EIN3 proteins in upland cotton. (A) Gene ontology (GO) annotation results of the EIL/EIN3 proteins. GO analysis of EIL/EIN3 proteins tested for their function in biological processes, molecular functions, and cellular components. (B) Protein–protein interaction networks of EIL/EIN3 transcription factors. Each node represents a protein and each edge represents an interaction between two proteins.
3.6. Protein–Protein Interaction Networks of EIL/EIN3 Genes
Protein interaction networks are significantly involved in regulation of various cellular functions, including metabolic pathways, signal transduction, and cell cycle development [57]. In animals, protein interaction networks regulate signal transduction, which affects developmental patterns, global homeostasis, normal physiology, and disease [58]. In plants, protein interaction networks associate with molecular mechanisms of biological processes such as signal transduction, cell cycle regulation, pattern formation, organ formation, and plant defense [59,60]. To understand the roles of the EIL/EIN3 genes in regulating cotton fiber developmental processes, the STRING database was used to generate the protein–protein interaction networks (Figure 3B and Table S2). The result of protein–protein interactions of the EIL/EIN3 genes showed that the EIN3 protein domains physically interact with the serine/threonine-protein kinase CTR1, signal transduction histidine kinase/ethylene sensor (ETR), and E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes (EBF1 and EBF2). Serine/threonine protein kinase plays an important role in a multiplicity of developmental pathways including cell migration, cell proliferation, and cytoskeleton regulation [61,62]. Activation by diverse effectors containing growth factor receptors results in a conformational change and consequent autophosphorylation on several serine/threonine residues [63]. CTR1 associates with the endoplasmic reticulum membranes in Arabidopsis as a result of its connections with ethylene receptors [64]. The function E3 ubiquitin ligase is more complicated in several cellular processes because of the E3 action based on the existence of different subunits [65]. Many E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes are key players in the regulation of physiological and developmental processes in plant biology [66,67,68]. The ubiquitin-proteasomal system regulates the degradation of various proteins in plant cells and disturbs a wide-range of cellular processes such as cell division, signal transduction, and immune responses [69]. The results showed that a member of the EIL/EIN3 protein family might form functional transcriptional factor complexes, mediating the expression of ethylene-insensitive3-like/ethylene-insensitive3 (EIL/EIN3) protein genes in cotton fiber developmental stages.
3.7. Expression Level Analysis of Cotton EIL/EIN3 Genes
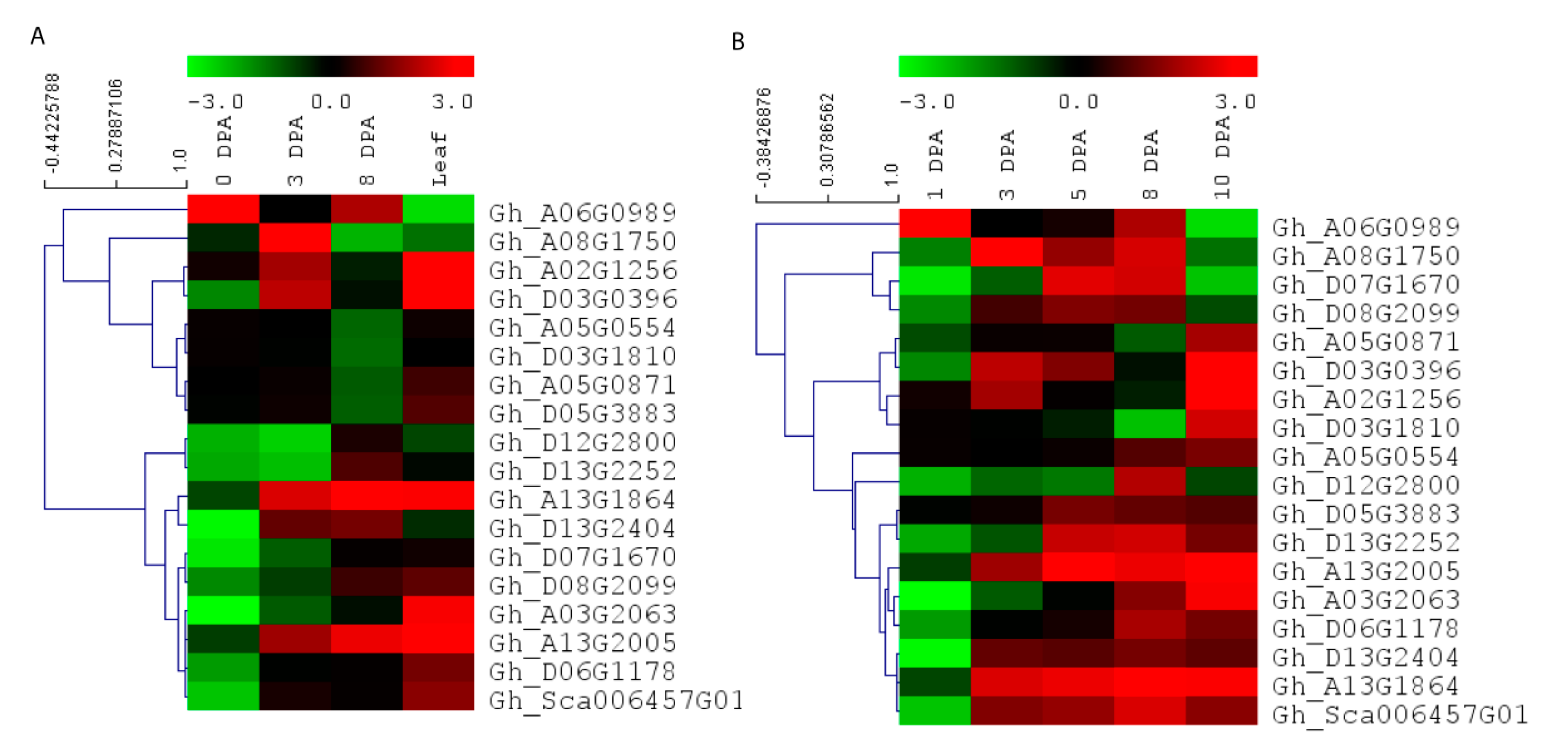
To further understand the expression pattern of EIL/EIN3 genes in cotton fiber developmental stages and their potential functions in the early termination of the fiber elongation process, RNA-seq data, including three stages of fiber cell development (0, 3, and 8 DPA) and cotton leaf, from Ligonlintless-1 and its wild-type were generated by Illumina sequencing. It was shown that all EIL/EIN3 genes were expressed at three stages (0, 3, and 8 DPA) of cotton fiber development and leaf using the FPKM value (Figure 4A). In addition, most EIL/EIN3 genes showed a variation in expression levels in different cotton tissues. The results showed that the EIL/EIN3 genes were differentially expressed in the initiation and elongation stages of fiber development and cotton leaf. To investigate whether the expression pattern of the EIL/EIN3 genes had a function in fiber developmental stages, we estimated the expression patterns of EIL/EIN3 genes from each transcript between Ligonlintless-1 and wild-type. A total of 4, 11, and 10 genes were up-regulated, and 14, 7, and 8 genes were down-regulated in fiber developmental stages at 0, 3, and 8 DPA, respectively (Figure 4), which provides evidence of being directly or indirectly associated with a Ligonlintless-1 mutant and the wild-type during the cotton fiber developmental stages. In addition, at 3 and 8 DPA, more up-regulated EIL/EIN3 genes than down-regulated EIL/EIN3 genes in Ligonlintless-1 with comparison to wild-type implies that they could be playing a key role in regulating fiber development in mutation. Overall, the results of the RNA-seq data are consistent with the qRT-PCR analysis (Figure 4B). Data from this study show that some EIL/EIN3 transcription factors involved in regulating fiber cell initiation and elongation stages at 0, 3, 5, 8, and 10 DPA may be the possible reason for the early termination of fiber development in the mutant cotton fiber. This transcriptome analysis revealed differential expression levels of some EIL/EIN3 genes at various developmental stages of fibers, an indication that EIL/EIN3 genes may play an important role in regulating the metabolic pathways of cotton fiber development. This result is consistent with earlier reports showing that several genes encoding for ethylene production of cotton fibers were up-regulated in the Ligonlintless-1 mutant compared to wild-type at 5 and 7 DPA [70]. In this research, we found higher levels of ethylene produced during fiber development at 8 DPA in the Ligonlintless-1 mutant, possibly leading to early termination of cotton fiber development. Ethylene metabolism-associated genes are differentially expressed in cotton species during fiber developmental stages [71]. The expression patterns of EIL/EIN3 genes are an indicator of their involvement in various physiological and biochemical functions, which are directly associated with fiber development during initiation and elongation stages. The accumulation of ethylene in G. raimondii results in the reduction of cotton fiber cells [72]. The findings suggest that ethylene may play a critical role in fiber cell development during the initiation and elongation stages.
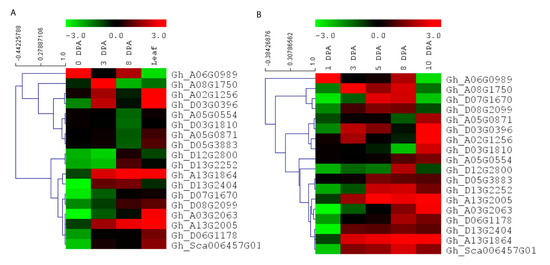
Figure 4.
Expression patterns of EIL/EIN3 genes in different stages of cotton fiber development and leaf. (A) Hierarchical clustering of expression profiles of the EIL/EIN3 genes in cotton leaf and fiber development at 0, 3, and 8 days post anthesis (DPA) based on RNAseq data. (B) Hierarchical clustering of expression profiles of the EIL/EIN3 genes in cotton fiber development at 0, 3, 5, 8, and 10 DPA using qRT-PCR analysis. The fold change values were log2 transformed. The standardized expression data were used to create heatmap with hierarchical clustering according to the Manhattan correlation with average linkage using the MeV software package. The color scale above the heatmap shows the expression levels: red indicates up-regulated while green indicates down-regulated genes.
3.8. Prediction of miRNA Targets in Cotton EIL/EIN3 Genes during Cotton Fiber Development
Fiber developmental stages rely on the multicomplex regulation networks of numerous genes. The miRNAs play an important role in the regulation of cotton fiber development. The miRNAs are defined as part of the noncoding RNAs, which broadly play an important role in regulating various aspects of plant growth and development [73]. In cotton, miRNAs are involved in different features of growth such as fiber developmental stages and response to various abiotic stresses [74,75,76]. Previously, it was mentioned that several miRNAs were extremely expressed in the elongation stage of cotton fiber in Ligonlitless-1 (Li1) and Ligonlintless-2 (Li2) mutants, and their wild-type (WT) [77]. In order to determine the additional roles of EIL/EIN3 genes, we submitted whole genes to the psRNATarget [78] for investigating if some EIL/EIN3 genes were targeted by miRNAs. A total of 9 miRNAs (ghr-miR156a, ghr-miR156d, ghr-miR159a, ghr-miR394b, ghr-miR7491, ghr-miR7495a, ghr-miR7497, ghr-miR7502, and ghr-miR7504b) were differentially expressed in cotton fiber development during initiation and elongation stages (Table 2). These nine miRNAs targeted 11 EIL/EIN3 genes (Gh_A05G0871, Gh_A06G0989, Gh_A08G1750, Gh_A13G1864, Gh_A13G2005, Gh_D05G3883, Gh_D06G1178, Gh_D08G2099, Gh_D13G2252, Gh_D13G2404, and Gh_Sca006457G01) and the great number of them are linked to cotton fiber developmental stages [75]. Several EIL/EIN3 genes were targeted by more than one microRNA; for example, Gh_A05G0871, Gh_D05G3883, and Gh_D08G2099 genes were targeted by 4 microRNAs, and the Gh_A08G1750 gene was targeted by 2 microRNAs (Table S3). In cotton, a number of miRNAs were differentially expressed at 8 DPA of cotton development, such as ghr-miR156a, ghr-miR156c, ghr-mi-R159, and ghr-mi-miR2949 [77]. In earlier reports, it was found that miR156 is involved in reducing fiber length in cotton [79]. In this study, we found five genes were repressed by ghr-mi-miR156, ghr-mi-miR159, and ghr-mi-miR2949, this could explain the early termination of fiber elongation in the Ligonlintless-1 mutant. Additionally, ghr-miR156a could play a crucial role in cotton fiber initiation [80]. Previously, it noted that miR166, miR167, miR172, and miR2949 were highly expressed in ovules [76]. In cotton, ghr-miR7496a was down-regulated, but ghr-miR7497 was up-regulated during fiber development in Ligonlintless-1 [33]. These results shows that some EIL/EIN3 genes may directly play a crucial role in regulating fiber developmental stages (initiation and elongation stages). The interactions between EIL/EIN3 genes and microRNAs provide fundamental information on the regulation of gene expression.

Table 2.
Expression levels of miRNAs targeting EIL/EIN3 genes in Ligonlintless-1 and wild-type.
4. Conclusions
The results of this work revealed insights into the EIL/EIN3 transcription factor family in cotton, a representative cash crop. These results show that some EIL/EIN3 genes were directly targeted by miRNAs related to cotton fiber developmental stages. Further examination with functional studies of EIL/EIN3 transcription factors is needed to understand the regulation and interaction of various molecular pathways in enhancing cotton fiber development during the initiation and elongation stages. The findings of this study provided fundamental evidence into the role of EIL/EIN3 genes, which will support future functional examination of various important biological molecular mechanisms of this vital gene family in cotton.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2223-7747/9/1/128/s1, Table S1: Cis-element analysis of putative EIL/EIN3 promoter regions. Table S2: Results of the protein–protein interaction networks of EIL/EIN3 genes. Table S3: The miRNAs predicted to be targeted by EIL/EIN3 genes in cotton. Figure S1: Distribution of EIL/EIN3 genes on cotton chromosomes. (A) The chromosomal position of EIL/EIN3 genes mapped to the G. hirsutum genome. (B) and (C) The chromosomal position of EIL/EIN3 genes mapped to the G. raimondii and G. arboretum genomes, respectively. Figure S2: Conserved motif sequences of the EIL/EIN3 genes in cotton.
Author Contributions
H.S., S.H., and X.D. designed the experiment. H.L. and Z.P. grew the cotton seedlings and performed the experiments. H.S. analyzed the results and prepared the manuscript. X.D. revised the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31601353) and the National Key Project of Research and Development Plan (No. 2016YFD0100203).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Science and Technology of China and China Scholarship Council (CSC) as both contributed with funding towards the research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Availability of Materials and Data
All related data are available within the manuscript and its additional files.
References
- Lata, C.; Prasad, M. Role of DREBs in regulation of abiotic stress responses in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 4731–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbineau, F.; Xia, Q.; Bailly, C.; El-Maarouf-Bouteau, H. Ethylene, a key factor in the regulation of seed dormancy. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Ruyter-Spira, C.; Bouwmeester, H. The interaction between strigolactones and other plant hormones in the regulation of plant development. Front. Plant Sci. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahad, S.; Hussain, S.; Matloob, A.; Khan, F.A.; Khaliq, A.; Saud, S.; Hassan, S.; Shan, D.; Khan, F.; Ullah, N.; et al. Phytohormones and plant responses to salinity stress: A review. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 75, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-F.; Etheridge, N.; Schaller, G.E. Ethylene Signal Transduction. Ann. Bot. 2005, 95, 901–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, S.C.; Kieber, J.J. Eto Brute? Role of ACS turnover in regulating ethylene biosynthesis. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Cara, B.; Giovannoni, J.J. Molecular biology of ethylene during tomato fruit development and maturation. Plant Sci. 2008, 175, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Ji, Y.; He, W.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M.; Guo, H. Coordinated regulation of apical hook development by gibberellins and ethylene in etiolated Arabidopsis seedlings. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, C.; Chang, C. Mechanistic Insights in Ethylene Perception and Signal Transduction. Plant Physiol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, B.P.; Shakeel, S.N.; Schaller, G.E. Ethylene receptors: Ethylene perception and signal transduction. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2007, 26, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, X.; Chen, S.; Zhou, B.; et al. Genomic analyses in cotton identify signatures of selection and loci associated with fiber quality and yield traits. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, F.; Zhao, Q.; Ji, Y.; Li, W.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhang, C.; Han, Y.; He, W.; Liu, Y.; et al. Ethylene-Induced Stabilization of ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3 and EIN3-LIKE1 Is Mediated by Proteasomal Degradation of EIN3 Binding F-Box 1 and 2 That Requires EIN2 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Online 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinshi, H. Ethylene-regulated transcription and crosstalk with jasmonic acid. Plant Sci. 2008, 175, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; An, F.; Feng, Y.; Li, P.; Xue, L.; Mu, A.; Jiang, Z.; Kim, J.-M.; To, T.K.; Li, W.; et al. Derepression of ethylene-stabilized transcription factors (EIN3/EIL1) mediates jasmonate and ethylene signaling synergy in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12539–12544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, K.; Kigawa, T.; Inoue, M.; Yamasaki, T.; Yabuki, T.; Aoki, M.; Seki, E.; Matsuda, T.; Tomo, Y.; Terada, T.; et al. Solution structure of the major DNA-binding domain of Arabidopsis thaliana ethylene-insensitive3-like3. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 348, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, Q.; Rothenberg, M.; Solano, R.; Roman, G.; Terzaghi, W.; Ecker, J.R. Activation of the ethylene gas response pathway in arabidopsis by the nuclear protein ETHYLENE-INSENSITIVE3 and related proteins. Cell 1997, 89, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano, R.; Stepanova, A.; Chao, Q.; Ecker, J.R. Nuclear events in ethylene signaling: A transcriptional cascade mediated by ETHYLENE-INSENSITIVE3 and ETHYLENE-RESPONSE-FACTOR1. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 3703–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzyńska, A.; Lewandowska, M.; Sirko, A. Nicotiana tabacum EIL2 directly regulates expression of at least one tobacco gene induced by sulphur starvation. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Tang, L.; Yang, Y.; Zouine, M.; Bouzayen, M. A conserved phosphorylation site regulates the transcriptional function of ETHYLENE-INSENSITIVE3-like1 in tomato. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Xu, L.; Jia, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Fei, Z.; Lu, X.; Chen, H.; Huang, S. Genetic association of ETHYLENE-INSENSITIVE3-like sequence with the sex-determining M locus in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Appl. Genet. 2008, 117, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, B.B.; Pan, J.S.; He, H.L.; Yang, X.Q.; Zhao, J.L.; Cai, R. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of the ethylene insensitive3 (EIN3) gene in cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Genet. Mol. Res. 2013, 12, 4179–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Qin, Z.; Wu, T.; Zhou, X. Identification of Ethylene-Responsive Genes in Ethrel-Treated Shoot Apices of Cucumber by Suppression Subtractive Hybridization. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 29, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ma, B.; He, S.-J.; Xiong, Q.; Duan, K.-X.; Yin, C.-C.; Chen, H.; Lu, X.; Chen, S.-Y.; Zhang, J.-S. MAOHUZI6/ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3-LIKE1 and ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3-LIKE2 Regulate Ethylene Response of Roots and Coleoptiles and Negatively Affect Salt Tolerance in Rice. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama-Nakashita, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Tohge, T.; Saito, K.; Takahashi, H. Arabidopsis SLIM1 is a central transcriptional regulator of plant sulfur response and metabolism. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 3235–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Zhao, M.; Shi, T.; Shi, H.; An, F.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, H. EIN3/EIL1 cooperate with PIF1 to prevent photo-oxidation and to promote greening of Arabidopsis seedlings. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21431–21436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Lyu, M.; Luo, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; He, H.; Wei, N.; Deng, X.W.; Zhong, S. Genome-wide regulation of light-controlled seedling morphogenesis by three families of transcription factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6482–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, W.; Yang, Y. Overexpression of an EIN3-binding F-box protein2-like gene caused elongated fruit shape and delayed fruit development and ripening in tomato. Plant Sci. 2018, 272, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.H.; Zhu, S.W.; Mao, X.Z.; Feng, J.X.; Qin, Y.M.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, J.; Wei, L.P.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhu, Y.X. Transcriptome profiling, molecular biological, and physiological studies reveal a major role for ethylene in cotton fiber cell elongation. Plant Cell 2006, 8, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Han, Y.; Meng, D.; Li, D.; Jin, Q.; Lin, Y.; Cai, Y. Genome-wide analysis suggests high level of microsynteny and purifying selection affect the evolution of EIN3/EIL family in Rosaceae. PEER J. 2017, 5, e3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, R.; Liang, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, J. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the EIN3/EIL gene family in allotetraploid Brassica napus reveal its potential advantages during polyploidization. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyssen, G.N.; Fang, D.D.; Turley, R.B.; Florane, C.; Li, P.; Naoumkina, M. Next generation genetic mapping of the Ligon-lintless-2 (Li₂) locus in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 2183–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoumkina, M.; Thyssen, G.N.; Fang, D.D. RNA-seq analysis of short fiber mutants Ligon-lintless-1 (Li 1) and-2 (Li 2) revealed important role of aquaporins in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) fiber elongation. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salih, H.; Gong, W.; He, S.; Xia, W.; Odongo, M.R.; Du, X. Long non-coding RNAs and their potential functions in Ligon-lintless-1 mutant cotton during fiber development. BMC Genom. 2019, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, H.; Gong, W.; He, S.; Mustafa, N.S.; Du, X. Comparative transcriptome analysis of TUCPs in Gossypium hirsutum Ligon-lintless-1 mutant and their proposed functions in cotton fiber development. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2018, 294, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhao, P.X. PsRNATarget: A plant small RNA target analysis server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W155–W159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Wyder, S.; Forslund, K.; Heller, D.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Santos, A.; Tsafou, K.P.; et al. STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D447–D452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Fang, L.; Guan, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Saski, C.A.; Scheffler, B.E.; Stelly, D.M.; et al. Sequencing of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1) provides a resource for fiber improvement. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, H.; Gong, W.; He, S.; Sun, G.; Sun, J.; Du, X. Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of MYB transcription factors in Gossypium hirsutum. BMC Genet. 2016, 17, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiz, E.; Vatansever, R.; Ozyigit, I.I.; Uras, M.E.; Sen, U.; Anjum, N.A.; Pereira, E. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of EIL gene family in woody plant representative poplar (Populus trichocarpa). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 627, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanagi, M.M.; Salleh, S.; Ibrahim, W.A.W.; Naim, A.A.; Hermawan, D.; Miskam, M.; Hussain, I.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Molecularly imprinted polymer solid-phase extraction for the analysis of organophosphorus pesticides in fruit samples. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2013, 32, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; He, S.; Li, F.; Li, Z.; Ding, M.; Liu, Q.; Rong, J. Analyses of the sucrose synthase gene family in cotton: Structure, phylogeny and expression patterns. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Shen, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, C.; Zheng, Y. The EIL transcription factor family in soybean: Genome-wide identification, expression profiling and genetic diversity analysis. Febs Open Bio 2019, 9, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Gracia, A.; Vieira, F.G.; Almeida, F.C.; Rozas, J. Comparative Genomics of the Major Chemosensory Gene Families in Arthropods. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, K.T.J.; Tsagkogeorga, G.; Bennett, N.C.; Dávalos, L.M.; Faulkes, C.G.; Rossiter, S.J. Molecular evolution of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors in long-lived, small-bodied mammals. Gene 2014, 549, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, C.E.; Palmer, G.H.; Hötzel, I.; McElwain, T.F. Structure, sequence, and transcriptional analysis of the Babesia bovis rap-1 multigene locus. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1998, 93, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laloum, T.; De Mita, S.; Gamas, P.; Baudin, M.; Niebel, A. CCAAT-box binding transcription factors in plants: Y so many? Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shore, P.; Sharrocks, A.D. The MADS-Box Family of Transcription Factors. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 229, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramji, D.P.; Foka, P. CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins: Structure, function and regulation. Biochem. J. 2002, 365 Pt 3, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; An, K.; Edward, G.E.; An, G. Functional role of CAAT box element of the nopaline synthase (nos) promoter. J. Plant Biol. 1999, 42, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isogai, Y.; Keles, S.; Prestel, M.; Hochheimer, A.; Tjian, R. Transcription of histone gene cluster by differential core-promoter factors. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2936–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.H.; Han, H.W.; Moon, J. Functional analysis of the molecular interactions of TATA box-containing genes and essential genes. PLoS ONE 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walley, J.W.; Coughlan, S.; Hudson, M.E.; Covington, M.F.; Kaspi, R.; Banu, G.; Harmer, S.L.; Dehesh, K. Mechanical stress induces biotic and abiotic stress responses via a novel cis-element. PLoS Genet. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasani, S.H.; Thaker, V.S. Role of abscisic acid in cotton fiber development. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2006, 53, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.L. Goldacre paper: Rapid cell expansion and cellulose synthesis regulated by plasmodesmata and sugar: Insights from the single-celled cotton fibre. Funct. Plant Biol. 2007, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Y. A pivotal role of hormones in regulating cotton fiber development. Front. Plant Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Sun, J.; Yao, L.; Yuan, Y. Transcriptome analysis reveals critical genes and key pathways for early cotton fiber elongation in Ligon lintless-1 mutant. Genomics 2012, 100, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, S.J. Notch signalling: A simple pathway becomes complex. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, C.R.; Lingappa, V.R.; Hansen, W.J. The Emergence of Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Capsid Assembly as Potential Antiviral Therapeutics. In Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry; Elsvier: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dreze, M.; Carvunis, A.-R.; Charloteaux, B.; Galli, M.; Pevzner, S.J.; Tasan, M.; Ahn, Y.-Y.; Balumuri, P.; Barabasi, A.-L.; Bautista, V.; et al. Evidence for Network Evolution in an Arabidopsis Interactome Map. Science 2011, 33, 601–607. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, P.; Yuan, J. Plant Protein-Protein Interaction Network and Interactome. Curr. Genom. 2009, 11, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Hutchison, C.E.; Laskey, J.; Kieber, J.J. Biochemical and functional analysis of CTR1, a protein kinase that negatively regulates ethylene signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2003, 33, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Li, B.; Lu, D.; Chen, S.; Zhu, N.; He, P.; Shan, L. Tyrosine phosphorylation of protein kinase complex BAK1/BIK1 mediates Arabidopsis innate immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3632–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S.K.; Dagenais, N.; Chory, J.; Weigel, D. Regulation of auxin response by the protein kinase PINOID. Cell 2000, 100, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Chen, Y.F.; Randlett, M.D.; Zhao, X.C.; Findell, J.L.; Kieber, J.J.; Schaller, G.E. Localization of the Raf-like Kinase CTR1 to the Endoplasmic Reticulum of Arabidopsis through Participation in Ethylene Receptor Signaling Complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 34725–34732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzucotelli, E.; Belloni, S.; Marone, D.; De Leonardis, A.; Guerra, D.; Di Fonzo, N.; Cattivelli, L.; Mastrangelo, A. The E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Gene Family in Plants: Regulation by Degradation. Curr. Genom. 2006, 7, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Joshi, D.; Yadav, P.K.; Gupta, A.K.; Bhatt, T.K. Role of ubiquitin-mediated degradation system in plant biology. Front. Plant Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, D.R.; Estelle, M. Ubiquitin-mediated control of plant hormone signaling. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santner, A.; Estelle, M. The ubiquitin-proteasome system regulates plant hormone signaling. Plant J. 2010, 61, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuring, D.; Künzl, F.; Viotti, C.; Yan, M.S.W.; Jiang, L.; Schellmann, S.; Robinson, D.G.; Pimpl, P. Ubiquitin initiates sorting of Golgi and plasma membrane proteins into the vacuolar degradation pathway. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, H.; Leng, X.; He, S.P.; Jia, Y.H.; Gong, W.F.; Du, X.M. Characterization of the early fiber development gene, Ligon-lintless 1 (Li1), using microarray. Plant Gene 2016, 6, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.M.; Hu, C.Y.; Pang, Y.; Kastaniotis, A.J.; Hiltunen, J.K.; Zhu, Y.X. Saturated very-long-chain fatty acids promote cotton fiber and Arabidopsis cell elongation by activating ethylene biosynthesis. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 3692–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Fan, G.; Lu, C.; Xiao, G.; Zou, C.; Kohel, R.J.; Ma, Z.; Shang, H.; Ma, X.; Wu, J.; et al. Genome sequence of cultivated Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum TM-1) provides insights into genome evolution. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. Plant MicroRNAs and Development. J. Genet. Genom. 2013, 40, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, P.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Qiu, C.; Yang, Z. Enrichment of a set of microRNAs during the cotton fiber development. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Wang, Q.; Sun, R.; Zhang, B. Deep sequencing reveals important roles of microRNAs in response to drought and salinity stress in cotton. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Jones, D.C.; Wang, Q.; Sun, R.; Zhang, B. Small RNA sequencing identifies miRNA roles in ovule and fibre development. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoumkina, M.; Thyssen, G.N.; Fang, D.D.; Hinchliffe, D.J.; Florane, C.B. Small RNA sequencing and degradome analysis of developing fibers of short fiber revealed a role for miRNAs and their targets in cotton fiber elongation. BMC Genom. 2016, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.J.; Ma, Y.K.; Chen, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.J. PsRobot: A web-based plant small RNA meta-analysis toolbox. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Tu, L.; Tang, W.; Gao, W.; Lindsey, K.; Zhang, X. Small RNA and degradome profiling reveals a role for miRNAs and their targets in the developing fibers of Gossypium barbadense. Plant J. 2014, 80, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Xu, X.; Wang, M.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Zhao, R.; Zhu, S.; He, Q.; Chen, J. Identification and profiling of upland cotton microRNAs at fiber initiation stage under exogenous IAA application. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).