Seasonal Shifts in Water Utilization Strategies of Typical Desert Plants in a Desert Oasis Revealed by Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopes and Leaf δ13C
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
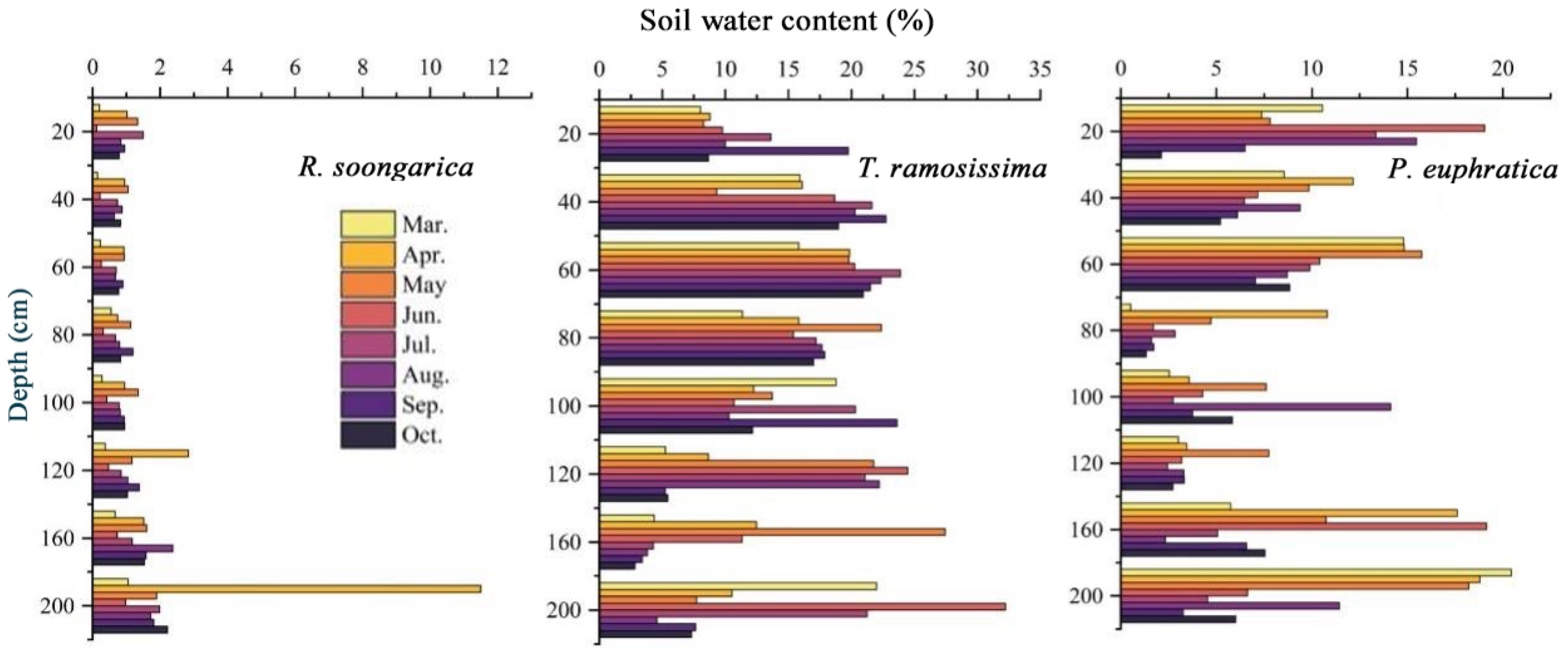
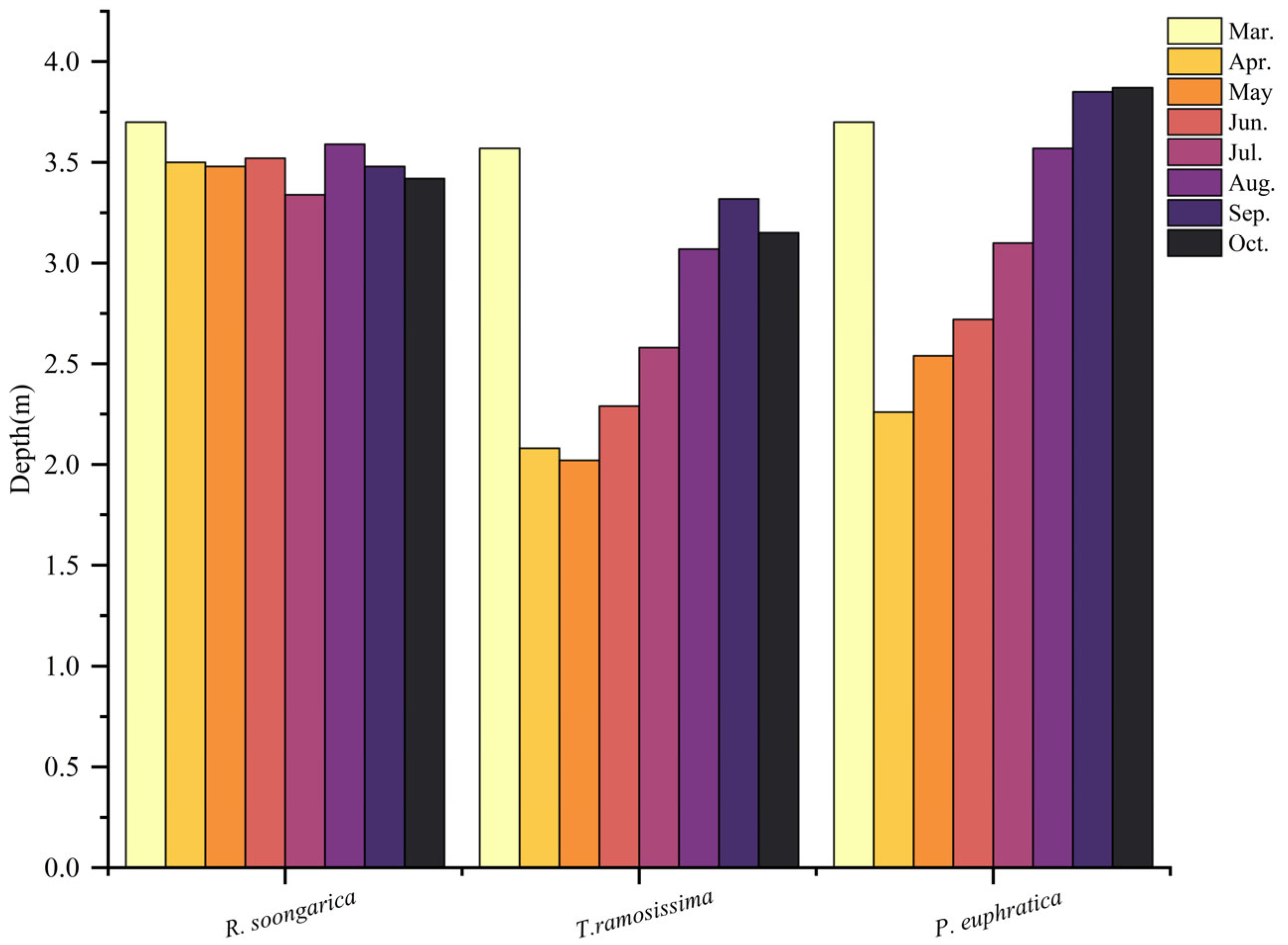
2.1. Seasonal Dynamics of Soil Moisture and Groundwater Depth
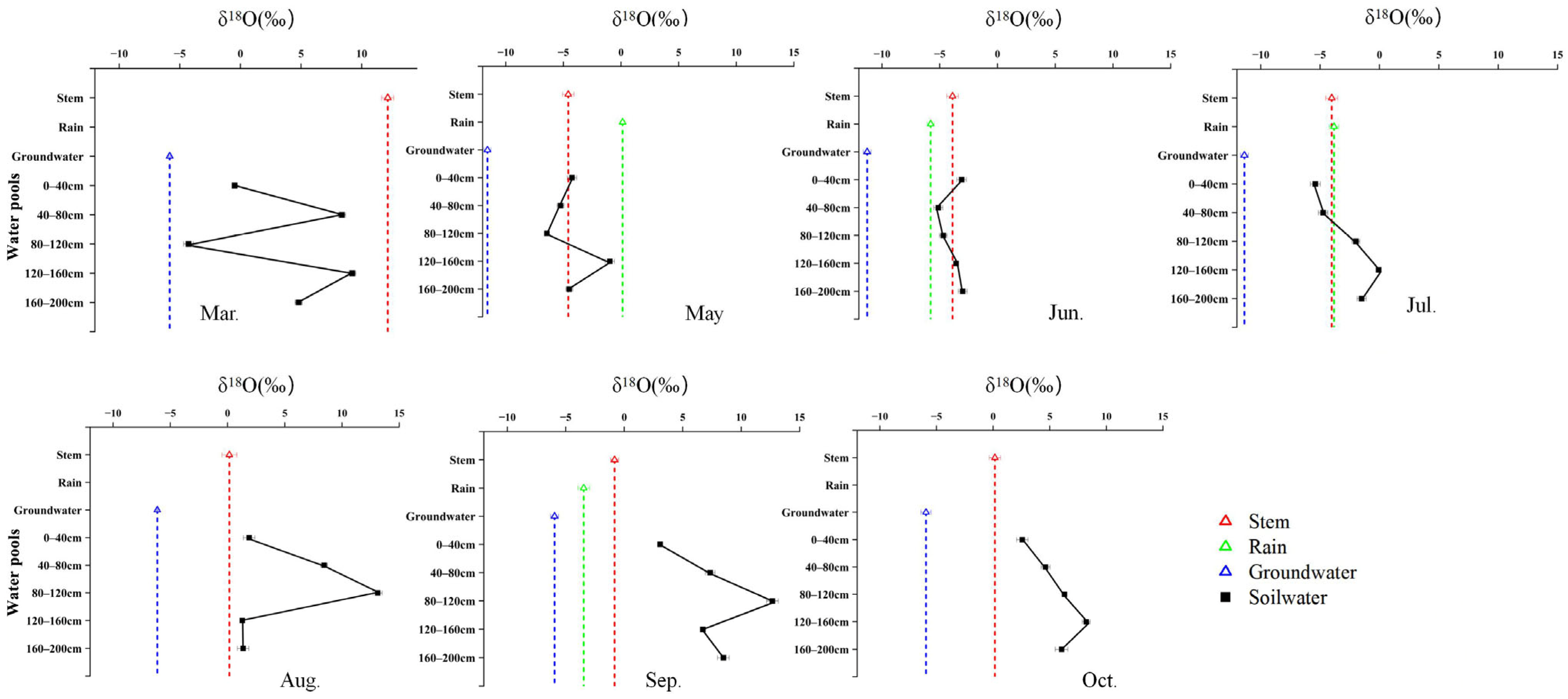
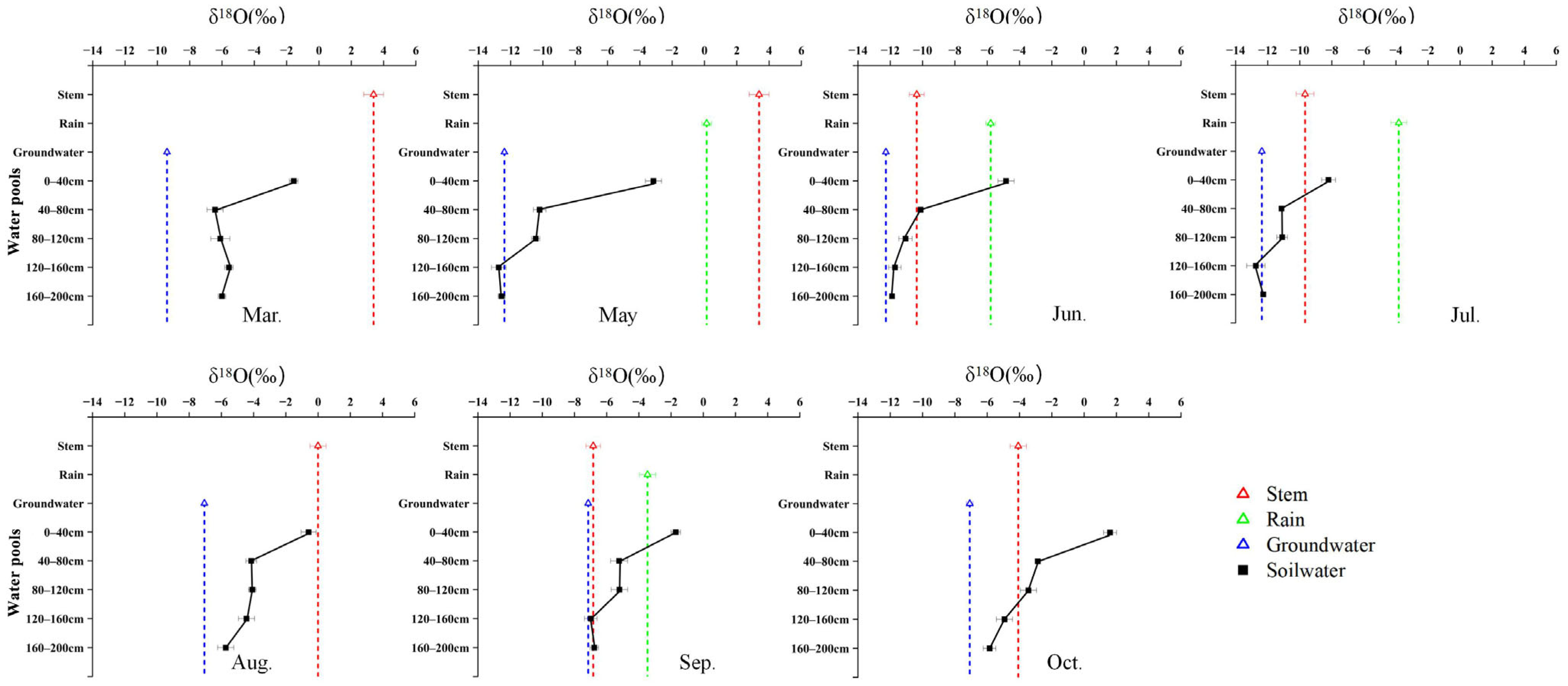
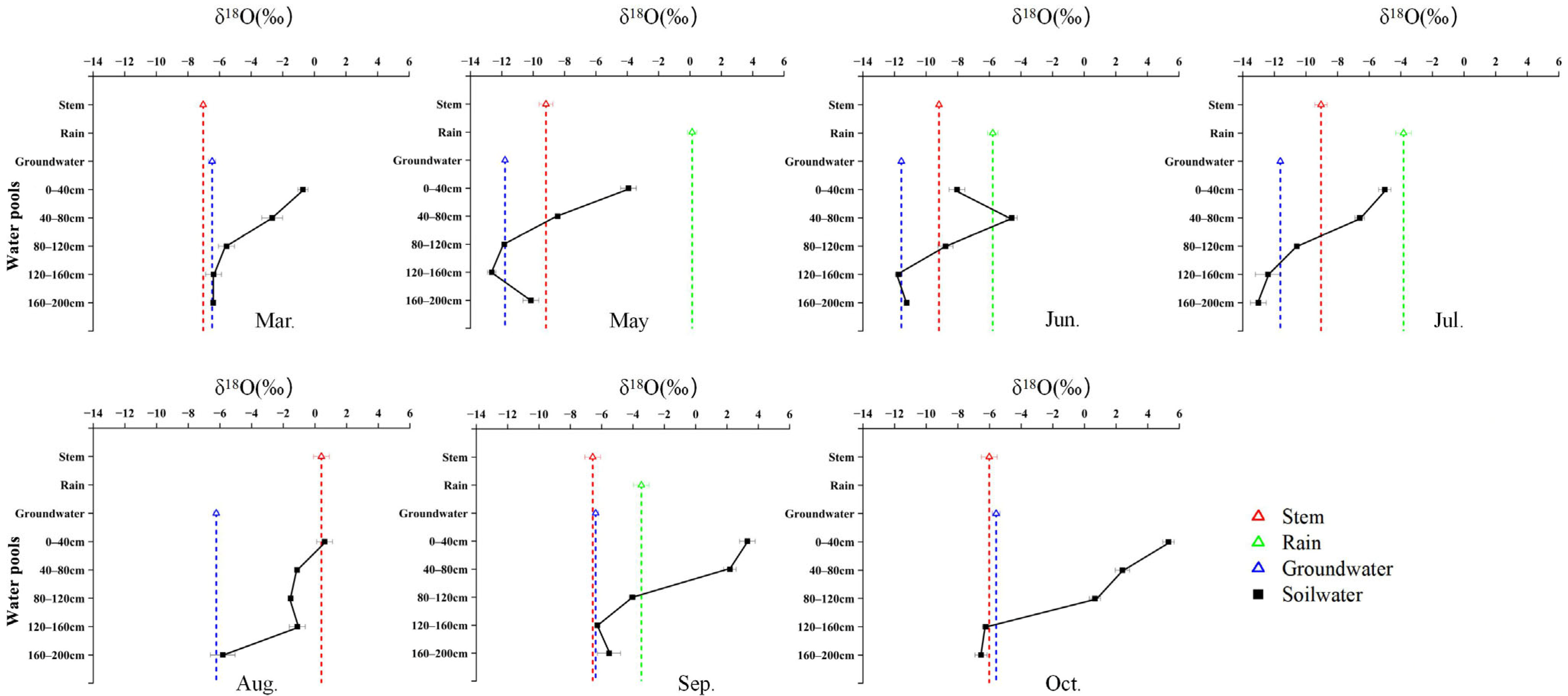
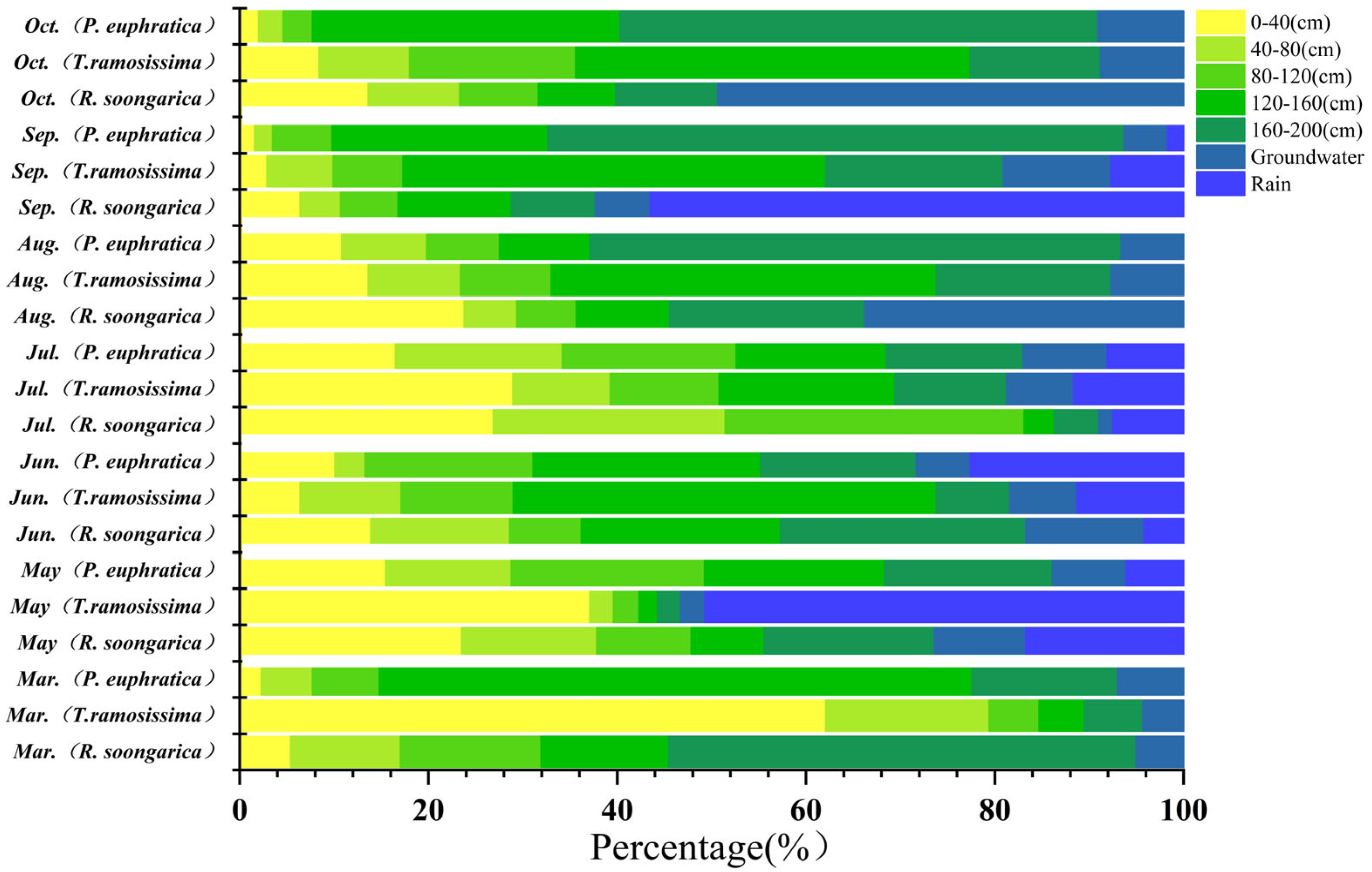
2.2. Seasonal Variation in δ18O Signatures and Water-Source Contributions Among Species
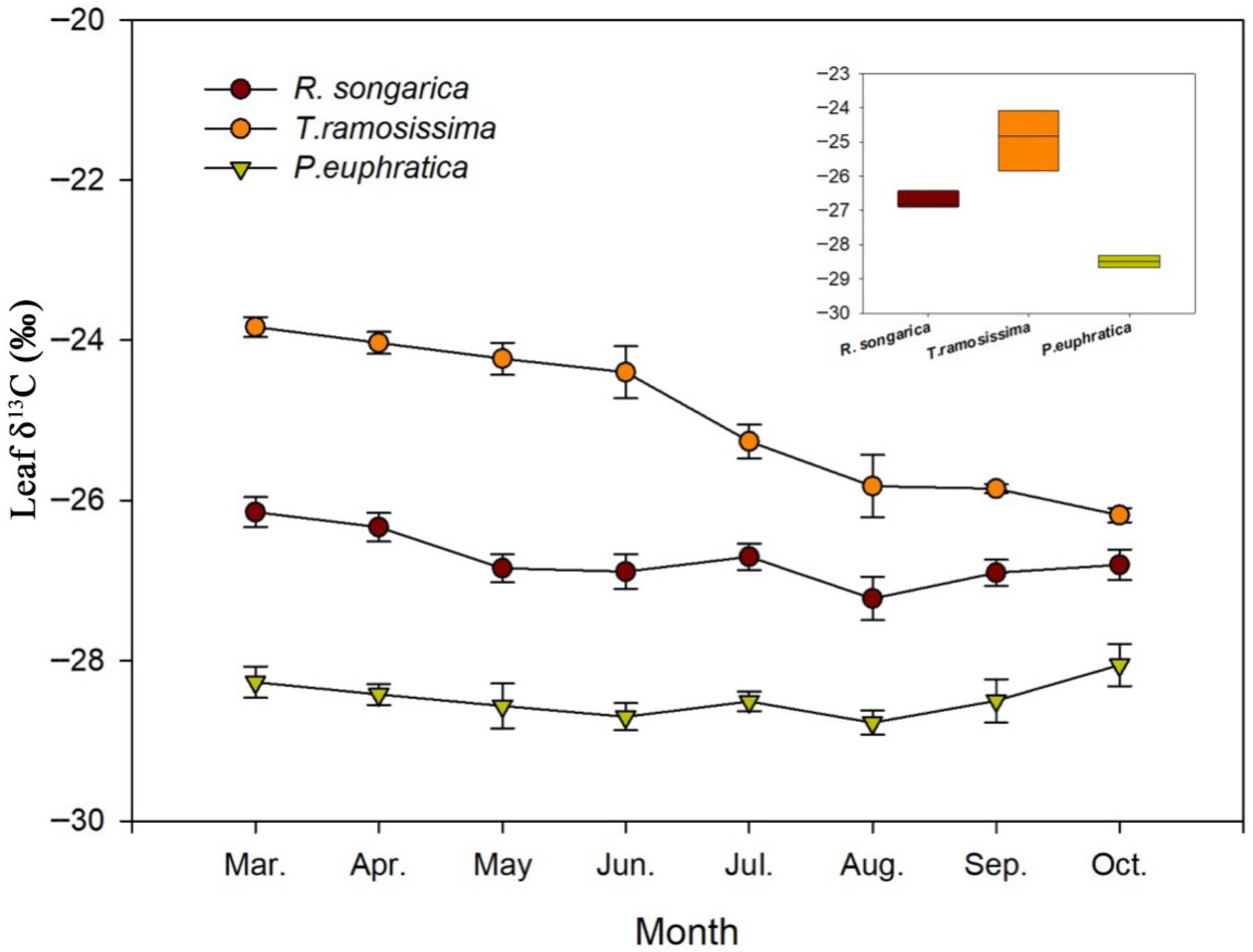
2.3. Seasonal Patterns of Leaf δ13C and Inferred Water-Use Efficiency
3. Discussion
3.1. Ecohydrological Niche Differentiation and Vertical Water-Source Partitioning
3.2. Deep Soil Water as a Major Hydrological Reservoir in Hyper-Arid Inland Basins
3.3. Water-Use Efficiency, Physiological Adaptation and Implications for Vegetation Resilience
4. Materials and Methods
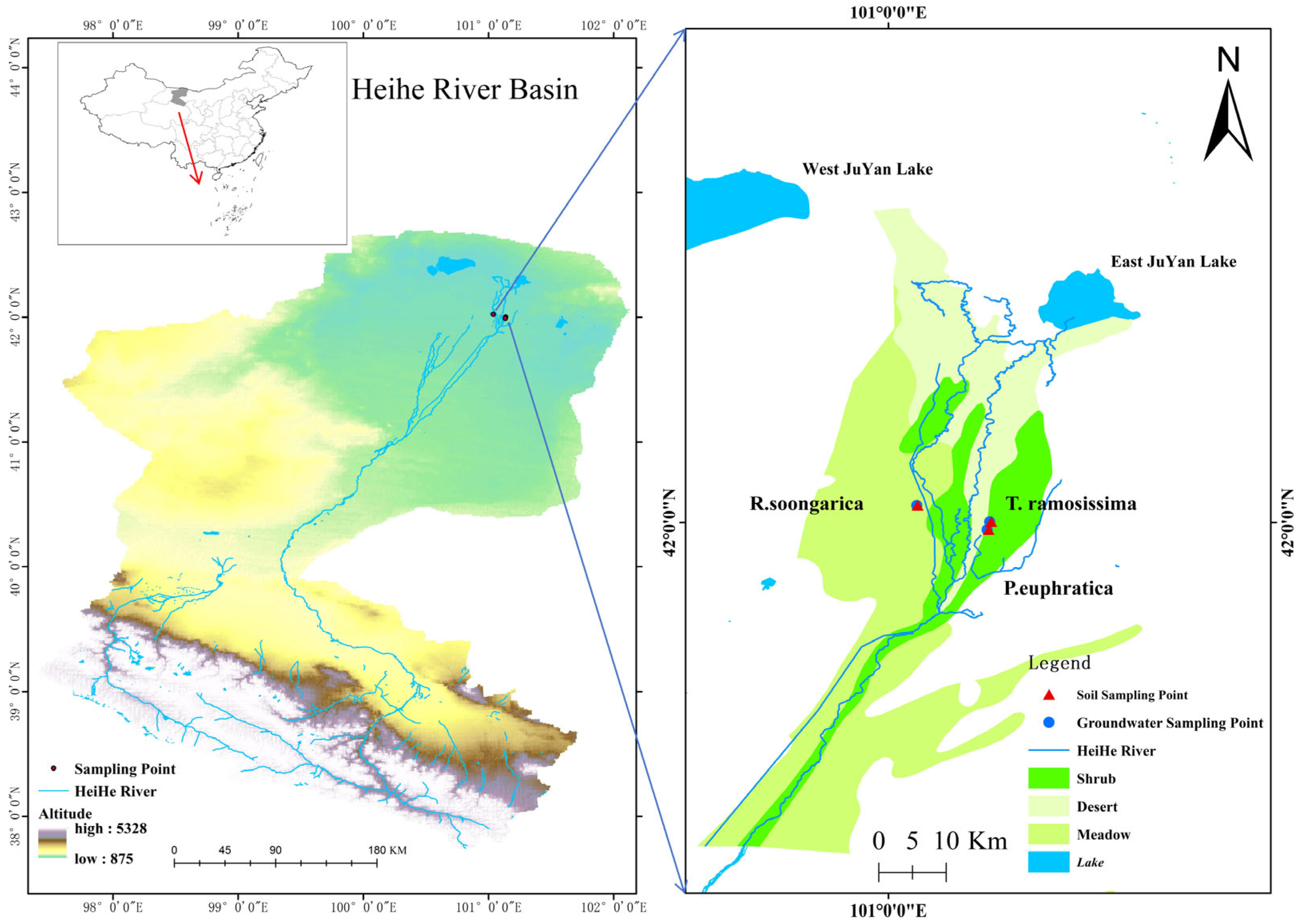
4.1. Study Site
4.2. Experiment Design
4.3. Soil Moisture and Plant and Groundwater Sampling
4.4. Water Extraction and Isotope Measurement
4.5. Water-Source Modeling Using MixSIAR
4.6. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodríguez-Iturbe, I.; Porporato, A. Ecohydrology of Water-Controlled Ecosystems: Soil Moisture and Plant Dynamics; Cambridge Univ. Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Good, S.P.; Noone, D.; Bowen, G. Hydrologic connectivity constrains partitioning of global terrestrial water fluxes. Science 2015, 349, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Niu, J.; Luo, Y.; Li, C.; Xiao, J.; Cao, Z. Seasonal water sources of xerophytic shrubs in arid China. Plant Soil 2018, 426, 273–287. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; An, J.; Shao, Y.; Gao, G. Responses of leaf-level physiological traits and water use characteristics to drought of a xerophytic shrub in northern China. J. Hydrol. 2025, 658, 133204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, C.; Ye, Z.; Chen, Y. Desert riparian vegetation and groundwater in the lower reaches of the Tarim River Basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, J.; Monk, W.A.; Zhang, L.; Hannah, D.M. Ecohydrological interactions during drought. Ecohydrology 2022, 15, e2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.R.; Barnard, H.R.; Coulombe, R.; McDonnell, J.J. Ecohydrological separation of water between trees and streams in a Mediterranean climate. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, J.J. The two water worlds hypothesis: Ecohydrological separation of water between streams and trees? WIREs Water 2014, 1, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.X.; Hu, C.C.; Lei, Y.B.; Tan, Y.H.; Liu, X.Y. Carbon isotope constraints on plant water use efficiency in a tropical invaded ecosystem. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2025, 130, e2025JG008997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benettin, P.; Volkmann, T.H.M.; von Freyberg, J.; Frentress, J.; Penna, D.; Dawson, T.E.; Kirchner, J.W. Effects of climatic seasonality on the isotopic composition of evaporating soil waters. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 2881–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowling, D.R.; Schulze, E.S.; Hall, S.J. Revisiting streamside trees that do not use stream water: Can the two water worlds hypothesis and snowpack isotopic effects explain a missing water source? Ecohydrology 2017, 10, e1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.C.; Li, X.Y.; Wu, H.W.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.C.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.M. Differences in water-use strategies along an aridity gradient between two coexisting desert shrubs (Reaumuria soongorica and Nitraria sphaerocarpa): Isotopic approaches with physiological evidence. Plant Soil 2017, 419, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Tong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Yang, C. Responses of two desert riparian species to fluctuating groundwater depths in hyperarid areas of Northwest China. Ecohydrology 2019, 12, e2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.L.; Newsome, S.D.; Gregg, J.W. Combining sources in stable isotope mixing models: Alternative methods. Oecologia 2005, 144, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, M.; Hamutoko, J.T.; Wanke, H.; Gaj, M.; Koeniger, P. Examination of deep root water uptake using anomalies of soil water stable isotopes, depth-controlled isotopic labeling and mixing models. J. Hydrol. 2018, 566, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, X.J.; Li, Y.; Tang, L.S. Seasonal changes in the water use strategies of three co-occurring desert shrubs. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 6265–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehleringer, J.R.; Phillips, S.L.; Comstock, J.P. Seasonal variation in the carbon isotopic composition of desert plants. Funct. Ecol. 1992, 6, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.T.; Kirchner, J.W.; Braun, S.; Siegwolf, R.T.W.; Goldsmith, G.R. Seasonal origins of soil water used by trees. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araguás-Araguás, L.; Froehlich, K.; Rozanski, K. Deuterium and oxygen-18 isotope composition of precipitation and atmospheric moisture. Hydrol. Process. 2000, 14, 1341–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, N.; Eugster, W.; Buchmann, N.; Kahmen, A. Species-specific differences in water uptake depth of mature temperate trees vary with water availability in the soil. Plant Biol. 2019, 21, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ji, X.; Jin, B.; Zhang, J. Root distribution of three dominant desert shrubs and their water uptake dynamics. J. Plant Ecol. 2017, 10, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Cieraad, E. Variation of water use efficiency across seasons and years: Different role of herbaceous plants in desert ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzlaff, D.; Buttle, J.; Carey, S.K.; Kohn, M.J.; Laudon, H.; McNamara, J.P.; Smith, A.; Sprenger, M.; Soulsby, C. Stable isotopes of water reveal differences in plant–soil water relationships across northern environments. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannenberg, S.A.; Anderegg, W.R.L.; Knapp, A.K. Dominant role of soil moisture in mediating carbon and water fluxes in dryland ecosystems. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, A.T.; Yahdjian, L.; Stark, J.M.; Belnap, J.; Porporato, A.; Norton, U.; Ravetta, D.A.; Schaeffer, S.M. Water pulses and biogeochemical cycles in arid and semiarid ecosystems. Oecologia 2004, 141, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Hu, H.; Tian, F.; Dong, Z.; Khan, M.Y.A. Ecohydrological separation hypothesis: Review and prospect. Water 2020, 12, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasechko, S.; Sharp, Z.D.; Gibson, J.J.; Birks, S.J.; Yi, Y.; Fawcett, P.J. Terrestrial water fluxes dominated by transpiration. Nature 2013, 496, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, L.; Wu, L. Soil properties regulating water constraint by dominating ecosystem water demand in water-limited ecosystems. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 124078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, D.; Wang, J.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; Jin, B.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J. River–groundwater interactions in the arid and semiarid areas of northwestern China. Hydrogeol. J. 2024, 32, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, E.J.; Fu, H.; Si, B. A process-based water stable isotope mixing model for plant water sourcing. Ecohydrology 2024, 17, e2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Murillo, R.; Durán-Quesada, A.M. Preface to stable isotopes in hydrological studies in the tropics: Ecohydrological perspectives in a changing climate. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 33, 2160–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Si, J.; Yu, T.; Li, X. Response of Populus euphratica Oliv. sap flow to environmental variables for a desert riparian forest in the Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. J. Arid Land 2016, 8, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuecco, G.; Amin, A.; Frentress, J.; Engel, M.; Marchina, C.; Anfodillo, T.; Borga, M.; Carraro, V.; Scandellari, F.; Tagliavini, M.; et al. A comparative study of plant water extraction methods for isotopic analyses: Scholander-type pressure chamber vs. cryogenic vacuum distillation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fu, B.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z. Soil moisture–plant interactions: An ecohydrological review. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Guan, T.Y.; Zhou, J.H.; Cai, W.T.; Gao, N.N.; Du, H.; Jiang, L.H.; Lai, L.M.; Zheng, Y.R. Groundwater depth and soil properties are associated with variation in vegetation of a desert riparian ecosystem in an arid area of China. Forests 2018, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.L.; Niu, G.Y.; Yu, J.J.; Ma, N.; Wu, Z.N.; Pozdniakov, S.P.; Yan, D.H. Drought adaptability of phreatophytes: Insight from vertical root distribution in drylands of China. J. Plant Ecol. 2021, 14, 1128–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z. Soil hydrology process and rational use of soil water in desert regions. Water 2021, 13, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Shi, Q.; Dai, Y.; Marhaba, N.; Peng, L.; Shi, H. Water use characteristics of Populus euphratica Oliv. and Tamarix chinensis Lour. at different growth stages in a desert oasis. Forests 2022, 13, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, A.; Xu, H.; Waheed, A.; Lin, T.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, X. Drought resistance of desert riparian forests: Vegetation growth index and leaf physiological index approach. Sustainability 2024, 16, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Cai, W.; Bai, N.; Wang, J.; Hong, Y. Seasonal Shifts in Water Utilization Strategies of Typical Desert Plants in a Desert Oasis Revealed by Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopes and Leaf δ13C. Plants 2026, 15, 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants15020340
Wang Y, Li W, Cai W, Bai N, Wang J, Hong Y. Seasonal Shifts in Water Utilization Strategies of Typical Desert Plants in a Desert Oasis Revealed by Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopes and Leaf δ13C. Plants. 2026; 15(2):340. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants15020340
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yang, Wenze Li, Wei Cai, Nan Bai, Jiaqi Wang, and Yu Hong. 2026. "Seasonal Shifts in Water Utilization Strategies of Typical Desert Plants in a Desert Oasis Revealed by Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopes and Leaf δ13C" Plants 15, no. 2: 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants15020340
APA StyleWang, Y., Li, W., Cai, W., Bai, N., Wang, J., & Hong, Y. (2026). Seasonal Shifts in Water Utilization Strategies of Typical Desert Plants in a Desert Oasis Revealed by Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopes and Leaf δ13C. Plants, 15(2), 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants15020340





