Identification and Characterization of a Male Sterile Rapeseed (Brassica napus) Line for Hybrid Seed Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
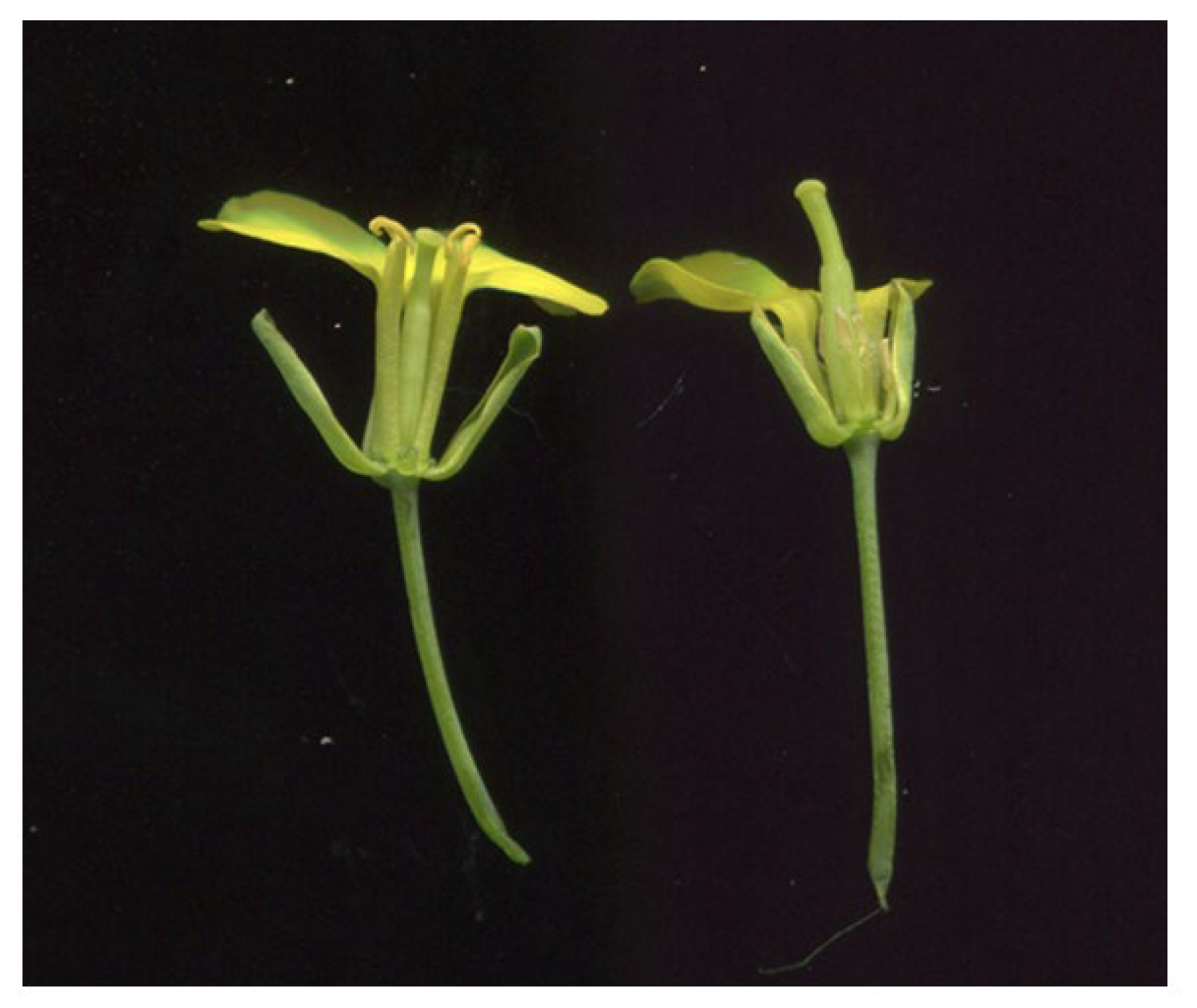
2.1. Phenotypic and Genetic Analysis of the S201 Mutant
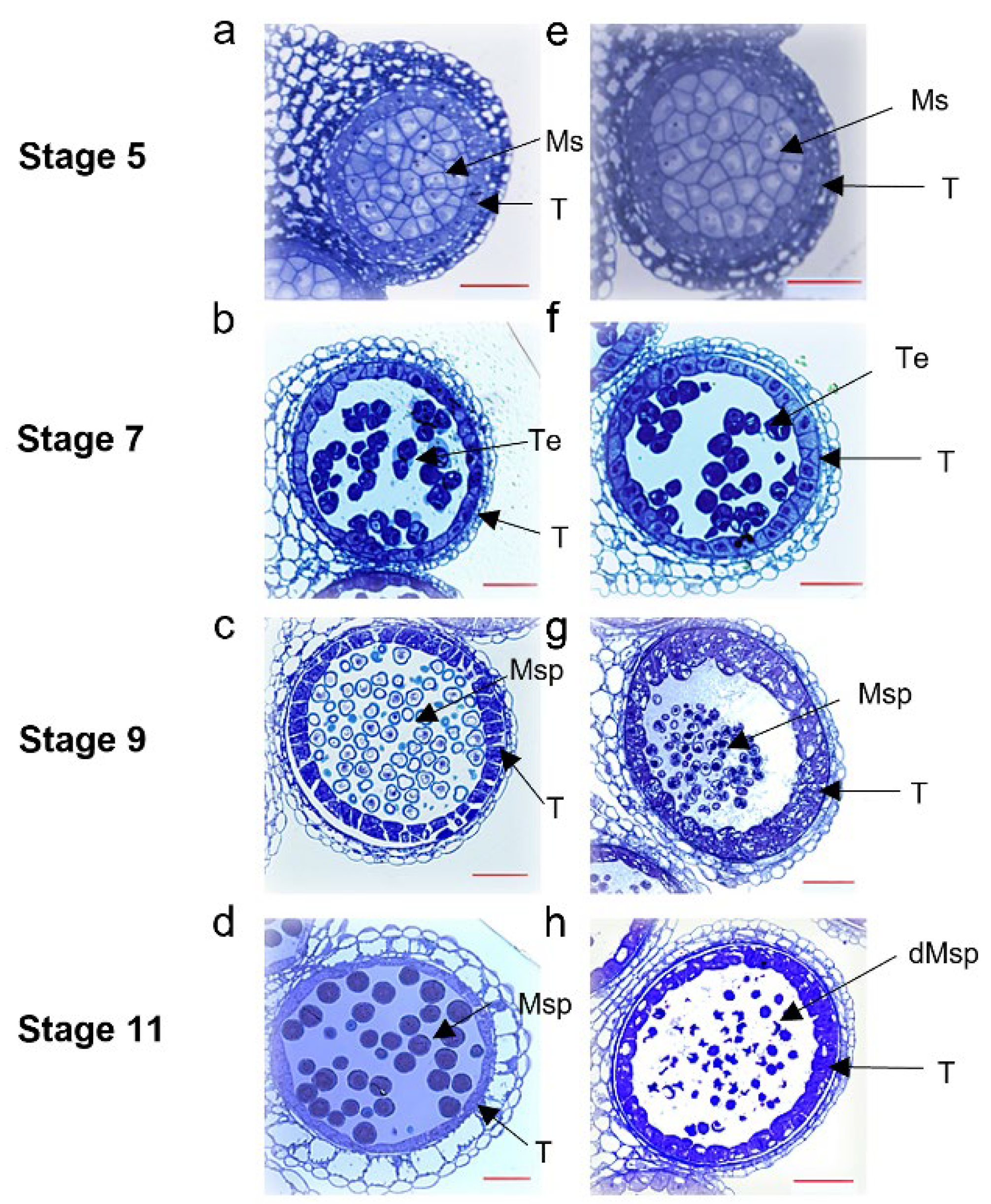
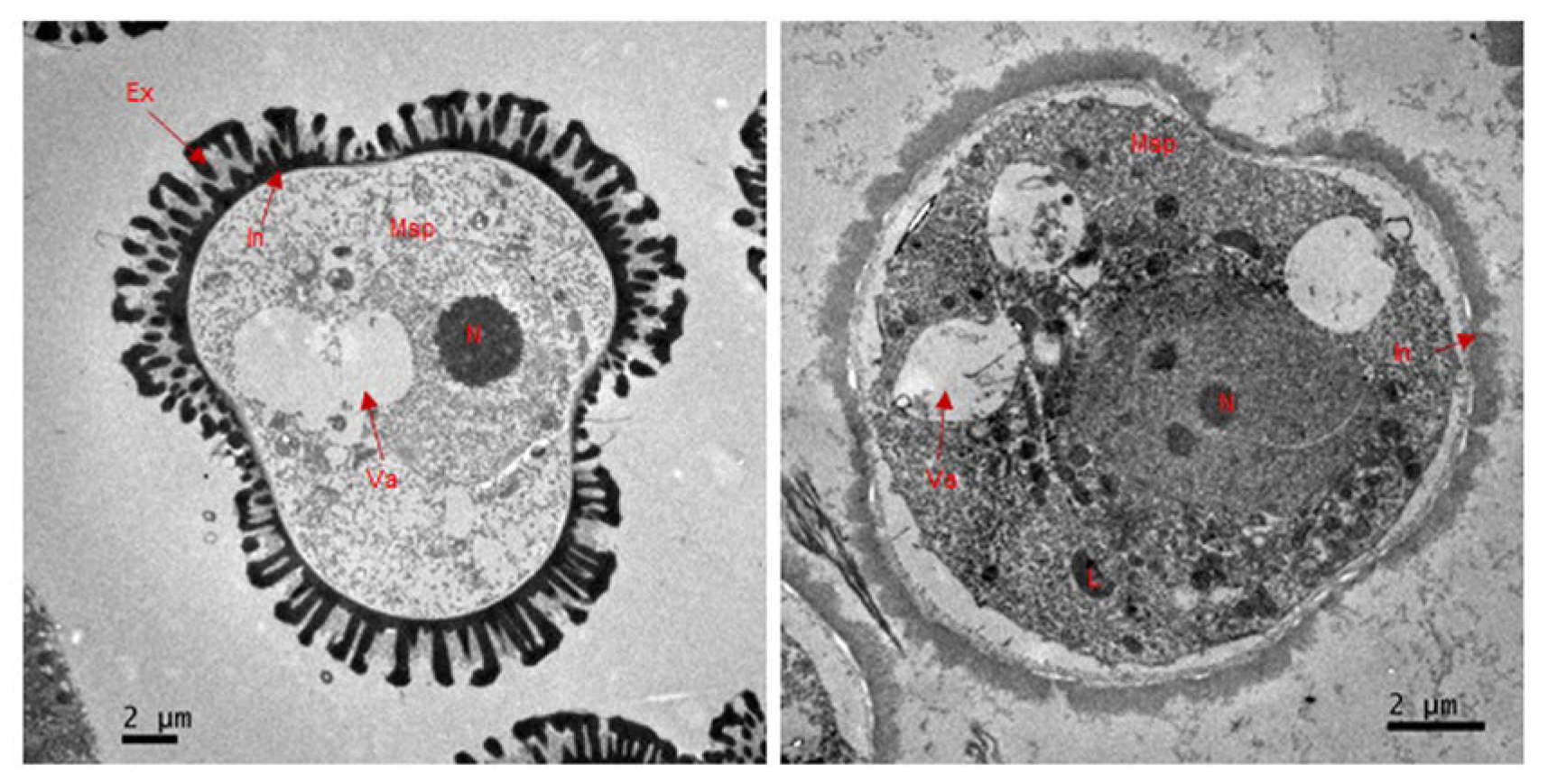
2.2. The S201 Mutant Shows a Defect in Microspore Development
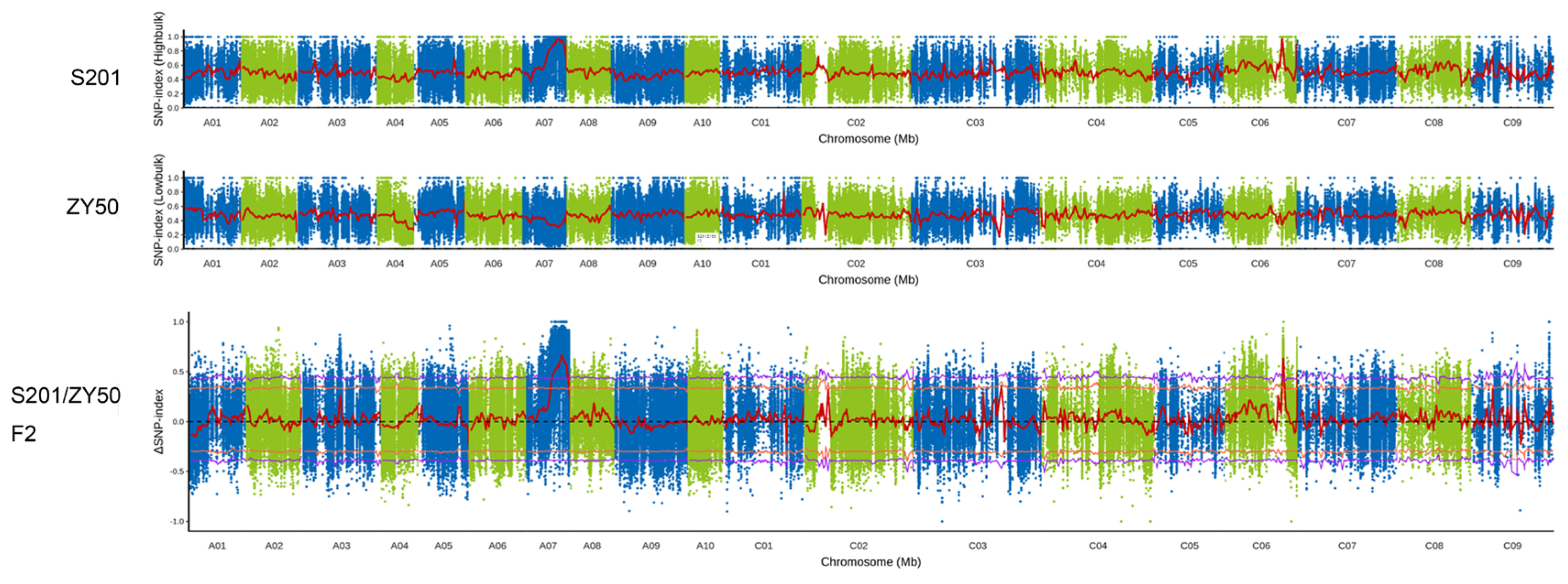
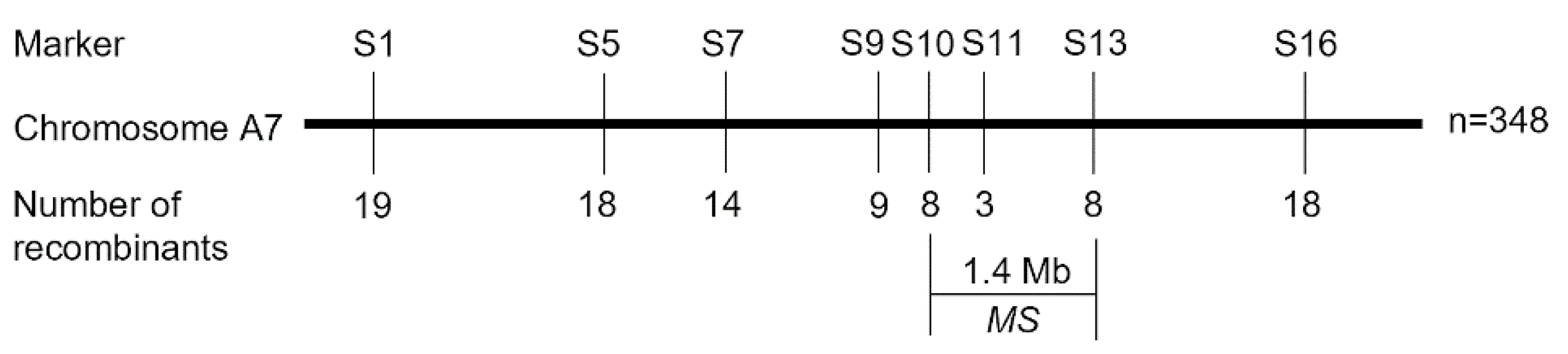
2.3. BSA and Genetic Mapping
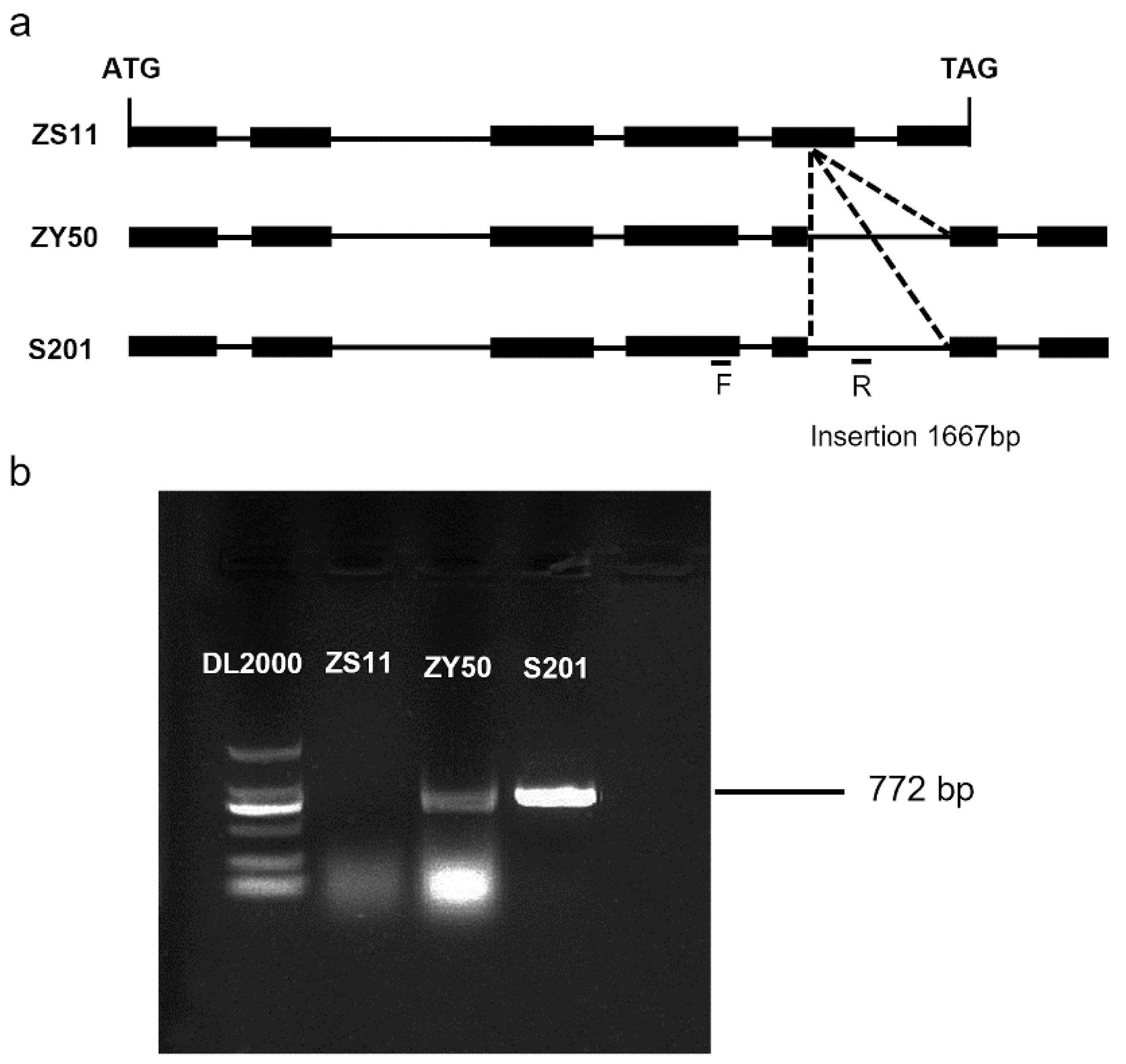
2.4. Sequence Analysis of the MS Gene
2.5. Sequence Analysis of the MS Homolog
2.6. Genic Male Sterility Lines Selection in the Breeding Populations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Inheritance Analysis
4.3. Light and Electron Microscopy
4.4. Bulked Segregant Analysis
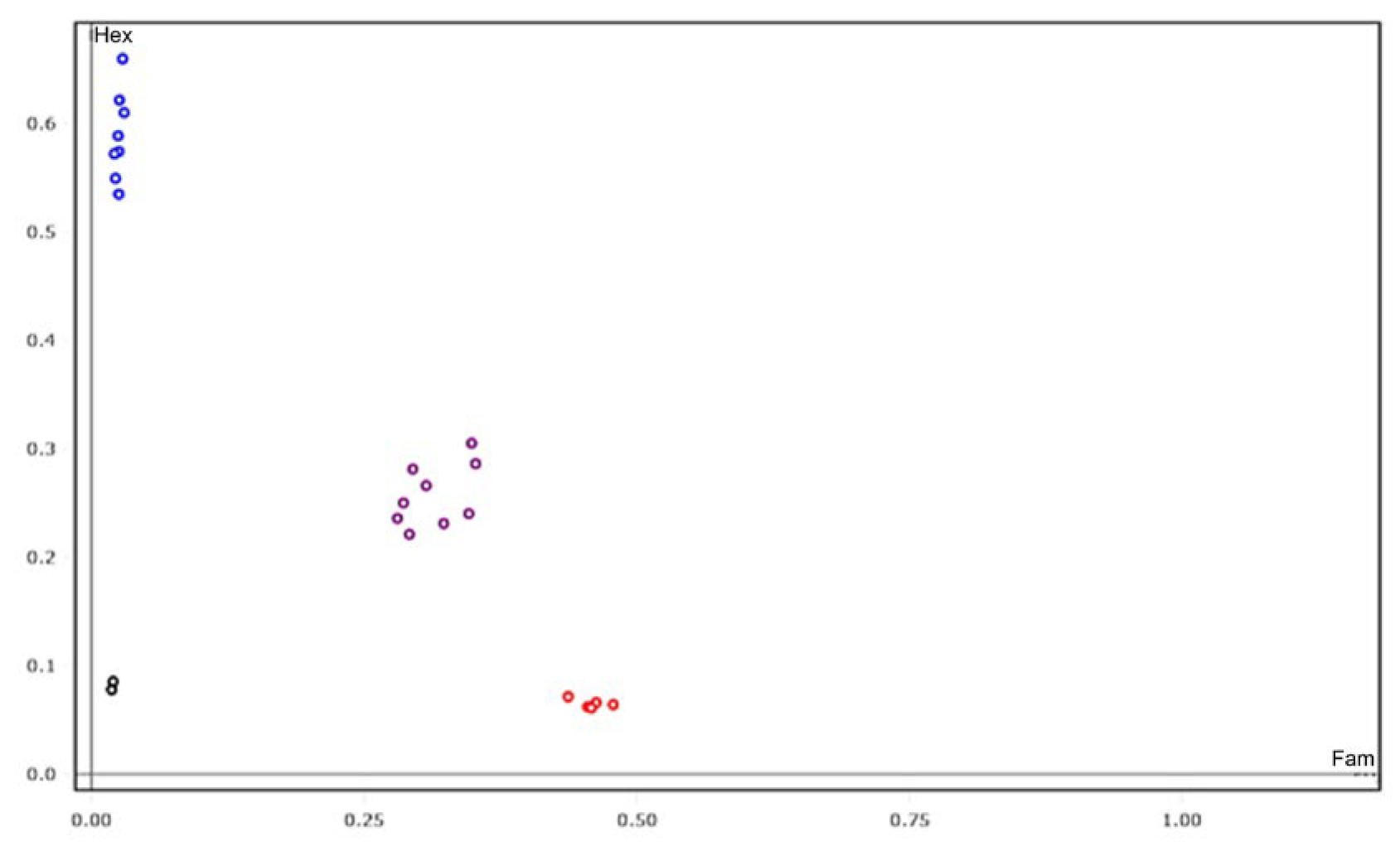
4.5. SNP Primer Design and KASP Genotyping
4.6. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of MS Alleles
4.7. RT-PCR Analysis
4.8. Screening Male Sterility Plants in Rapeseed Breeding
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MS | Male sterility |
| CMS | Cytoplasmic male sterility |
| GMS | Genic male sterility |
| B. napus | Brassica napus L. |
| BSA | Bulked segregant analysis |
| RT-PCR | Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| KASP | Kompetitive allele-specific PCR |
References
- Ohlrogge, J.B. Design of New Plant Products: Engineering of Fatty Acid Metabolism. Plant Physiol. 1994, 104, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thelen, J.J.; Ohlrogge, J.B. Metabolic engineering of fatty acid biosynthesis in plants. Metab. Eng. 2002, 4, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tester, M.; Langridge, P. Breeding technologies to increase crop production in a changing world. Science 2010, 327, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Pinot, F.; Sauveplane, V.; Werck-Reichhart, D.; Diehl, P.; Schreiber, L.; Franke, R.; Zhang, P.; Chen, L.; Gao, Y.; et al. Cytochrome P450 family member CYP704B2 catalyzes the omega-hydroxylation of fatty acids and is required for anther cutin biosynthesis and pollen exine formation in rice. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, M.; Dun, X.; Yi, B.; Wen, J.; Ma, C.; et al. Altered Transcription and Neofunctionalization of Duplicated Genes Rescue the Harmful Effects of a Chimeric Gene in Brassica napus. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 2060–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, B.; Wang, J.; Yi, L.; Liu, C.; Wu, J.; King, G.J.; Liu, K. Generation and characterization of tribenuron-methyl herbicide-resistant rapeseed (Brasscia napus) for hybrid seed production using chemically induced male sterility. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.K.; Li, Z.; Yuan, F.J.; Zhu, S.L.; Chen, P.; Yu, W.; Yang, Q.H.; Fu, X.J.; Yu, X.M.; Li, B.Q.; et al. Inheritance and fine mapping of a restorer-of-fertility (Rf) gene for the cytoplasmic male sterility in soybean. Plant Sci. 2012, 188–189, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Kan, R.; Qiu, M.; Deng, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, L.; Dong, H.; et al. A novel strategy for creating a new system of third-generation hybrid rice technology using a cytoplasmic sterility gene and a genic male-sterile gene. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budar, F.; Touzet, P.; De Paepe, R. The nucleo-mitochondrial conflict in cytoplasmic male sterilities revisited. Genetica 2003, 117, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, H.; Bhat, S.R. Cytoplasmic male sterility in Brassicaceae crops. Breed. Sci. 2014, 64, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Wen, J.; Dai, C.; Ma, C.; Tu, J.; Shen, J.; Fu, T.; et al. Molecular Analysis Uncovers the Mechanism of Fertility Restoration in Temperature-Sensitive Polima Cytoplasmic Male-Sterile Brassica napus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Zhao, F.; Gao, S.; Wang, X.; Wei, A.; Chen, Z.; Liu, N.; Tong, X.; Fu, X.; Wen, C.; et al. Fine mapping of a male sterility gene ms-3 in a novel cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) mutant. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, B.; Zeng, F.; Lei, S.; Chen, Y.; Yao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, J.; Shen, J.; Ma, C.; Tu, J.; et al. Two duplicate CYP704B1-homologous genes BnMs1 and BnMs2 are required for pollen exine formation and tapetal development in Brassica napus. Plant J. 2010, 63, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, B.; Chen, Y.; Lei, S.; Tu, J.; Fu, T. Fine mapping of the recessive genic male-sterile gene (Bnms1) in Brassica napus L. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 113, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Yao, X.; Yi, B.; Chen, W.; Ma, C.; Tu, J.; Fu, T. Towards map-based cloning: Fine mapping of a recessive genic male-sterile gene (BnMs2) in Brassica napus L. and syntenic region identification based on the Arabidopsis thaliana genome sequences. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 115, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Zhang, Y. Research advance on functional genomics in rapeseed. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2018, 40, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhmann, P.; Engstler, C.; Klopfer, K.; Gugel, I.L.; Abbadi, A.; Dreyer, F.; Leckband, G.; Bolter, B.; Hagn, F.; Soll, J.; et al. Two wrongs make a right: Heat stress reversion of a male-sterile Brassica napus line. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 3531–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, X.; Zhou, Z.; Xia, S.; Wen, J.; Yi, B.; Shen, J.; Ma, C.; Tu, J.; Fu, T. BnaC.Tic40, a plastid inner membrane translocon originating from Brassica oleracea, is essential for tapetal function and microspore development in Brassica napus. Plant J. 2011, 68, 532–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ke, L.; Hong, D.; Xie, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, P.; Yang, G. Fine mapping of a recessive genic male sterility gene (Bnms3) in rapeseed (Brassica napus) with AFLP- and Arabidopsis-derived PCR markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 117, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yi, B.; Xiao, L.; Ma, C.; Tu, J.; Fu, T. Fine mapping of the recessive genic male sterility gene (Bnms3) in Brassica napus L. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 115, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobritsa, A.A.; Shrestha, J.; Morant, M.; Pinot, F.; Matsuno, M.; Swanson, R.; Moller, B.L.; Preuss, D. CYP704B1 is a long-chain fatty acid omega-hydroxylase essential for sporopollenin synthesis in pollen of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 574–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Akita, K.; Suzuki, M.; Ohta, D.; Nagata, N. Fertile Arabidopsis cyp704b1 mutant, defective in sporopollenin biosynthesis, has a normal pollen coat and lipidic organelles in the tapetum. Plant Biotechnol. 2021, 38, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, M.; Thilges, K.; Cho, M.J.; Cigan, A.M. MS26/CYP704B is required for anther and pollen wall development in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and combining mutations in all three homeologs causes male sterility. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, Z.A.; Zhang, D.B. From Arabidopsis to rice: Pathways in pollen development. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 1479–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhao, H.; Lu, S.; Yu, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, W.; et al. Genome- and transcriptome-wide association studies provide insights into the genetic basis of natural variation of seed oil content in Brassica napus. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 470–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePristo, M.A.; Banks, E.; Poplin, R.; Garimella, K.V.; Maguire, J.R.; Hartl, C.; Philippakis, A.A.; del Angel, G.; Rivas, M.A.; Hanna, M.; et al. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, H.; Abe, A.; Yoshida, K.; Kosugi, S.; Natsume, S.; Mitsuoka, C.; Uemura, A.; Utsushi, H.; Tamiru, M.; Takuno, S.; et al. QTL-seq: Rapid mapping of quantitative trait loci in rice by whole genome resequencing of DNA from two bulked populations. Plant J. 2013, 74, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Yu, H.; Fu, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Zheng, T.; Ni, X.; Zhao, J. Development and validation of functional kompetitive allele-specific PCR markers for herbicide resistance in Brassica napus. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1213476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Pearce, M.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Basutkar, P.; Lee, J.; Edbali, O.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Kolesnikov, A.; Lopez, R. Search and sequence analysis tools services from EMBL-EBI in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W276–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Cross | Population | No. of Plants | χ2 | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fertile | Sterile | Total | ||||
| S201 X ZY50 | F1 | 45 | 0 | 45 | _ | _ |
| F2 | 89 | 26 | 115 | 0.350725 | 0.553703 | |
| S201 X ZS72 | F1 | 52 | 0 | 52 | _ | _ |
| F2 | 112 | 32 | 144 | 0.592593 | 0.441418 | |
| Genotype | BC1F2 (No. of Plants) | Phenotype | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZY50/S201//ZY50 | ZS72/S201//ZS72 | ||
| AA | 26 | 33 | Fertile |
| Aa | 52 | 50 | Fertile |
| aa | 24 | 19 | sterile |
| p value (1:2:1) | 0.995110034 | 0.143534986 | - |
| χ2 | 0.00980392 | 3.882352941 | - |
| - | 0.731600589 | 0.137194216 | p value (3:1) |
| - | 0.11764706 | 2.209150327 | χ2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, J.; Yu, H.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, T.; Ni, X.; Zheng, T.; Zhao, J. Identification and Characterization of a Male Sterile Rapeseed (Brassica napus) Line for Hybrid Seed Production. Plants 2025, 14, 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091397
Shi J, Yu H, Liu R, Zhang Y, Fu Y, Wang T, Ni X, Zheng T, Zhao J. Identification and Characterization of a Male Sterile Rapeseed (Brassica napus) Line for Hybrid Seed Production. Plants. 2025; 14(9):1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091397
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Jianghua, Huasheng Yu, Renhu Liu, Yaofeng Zhang, Ying Fu, Tanliu Wang, Xiyuan Ni, Tao Zheng, and Jianyi Zhao. 2025. "Identification and Characterization of a Male Sterile Rapeseed (Brassica napus) Line for Hybrid Seed Production" Plants 14, no. 9: 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091397
APA StyleShi, J., Yu, H., Liu, R., Zhang, Y., Fu, Y., Wang, T., Ni, X., Zheng, T., & Zhao, J. (2025). Identification and Characterization of a Male Sterile Rapeseed (Brassica napus) Line for Hybrid Seed Production. Plants, 14(9), 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091397





