Leaf Morpho-Anatomy of Twelve Cymbidium (Orchidaceae) Species from China and Their Taxonomic Significance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Leaf Morphology
2.2. Leaf Section
3. Discussion
3.1. Taxonomic Significance of Leaf Morpho-Anatomy in Cymbidium
3.1.1. Leaf Epidermal Cell
3.1.2. Stomata
3.1.3. Vascular Bundles
3.1.4. Cuticle
3.1.5. Mesophyll
3.1.6. Fiber Bundle
3.1.7. Stegmata
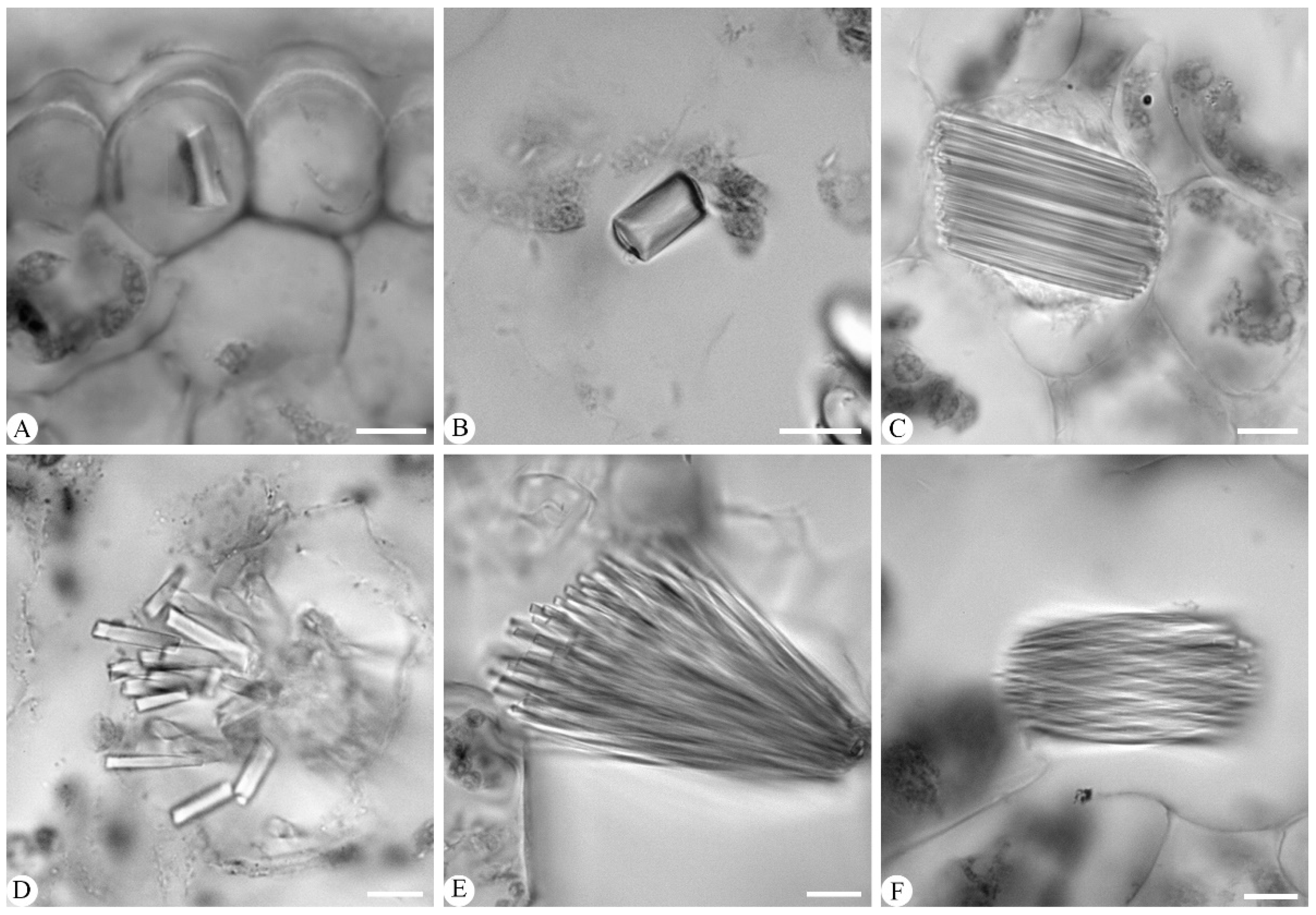
3.1.8. Crystals
3.1.9. Stigmata
3.2. Implications for Infrageneric Taxonomy for Cymbidium
3.2.1. Delimitation of Species in subgen. Cyperorchis
3.2.2. Species Delimitation in subgen. Jensoa
3.2.3. Species Delimitation in subgen. Cymbidium
3.2.4. Species Delimitation of Cymbidium Based on Leaf Morpho-Anatomic Features
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. A Key to Twelve Cymbidium Species Based on Leaf Morpho-Anatomic Features
| 1. Leaf shape oblanceolate to oblong | C. lancifolium |
| 1. Leaf lorate | (2) |
| 2. Leaf margin toothed | (3) |
| 2. Leaf margin entire | (6) |
| 3. Leaf with petiole | C. qiubeiense |
| 3. Leaf without petiole | (4) |
| 4. Leaf base with articulate | C. kanran |
| 4. Leaf base without articulate | (5) |
| 5. Stomata sunken | C. faberi |
| 5. Stomata flat | C. serratum |
| 6. Leaf apex with slightly two-lobed tip | (7) |
| 6. Leaf apex without two-lobed tip | (8) |
| 7. Stomata amphistomatic; stomatal index largest | C. eburneum |
| 7. Stomata hypostomatous | C. mastersii |
| 8. The leaf midrib with shallow V-shape | (9) |
| 8. The leaf midrib with V-shape | (10) |
| 9. Polygonal ad-abaxial epidermal cells | C. hookerianum |
| 9. Polygonal ad-abaxial epidermal cells | C. defoliatum |
| 10. Flat leaf mid-rib adaxial side cross-section outline; the cuticle thickest | C. tracyanum |
| 10. Semicircular leaf mid-rib adaxial side cross-section outline | (11) |
| 11. Lacked fiber bundles; without stegmata | C. floribundum |
| 11. With fiber bundles and stegmata | C. wenshanense |
References
- Cribb, P.J.; Du Puy, D.J. The Genus Cymbidium; Royal Botanic Garden: Kew, UK, 2007; 359p. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.J.; Chen, X.Q.; Cribb, J.P. Cymbidium Swartz. In Flora of China: Orchidaceae; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009; Volume 25, pp. 260–280. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.Q.; Liu, Z.J.; Zhu, G.H.; Lang, K.Y.; Ji, Z.H.; Luo, Y.B.; Jin, X.H.; Cribb, P.J.; Wood, J.J.; Gale, S.W.; et al. Flora of China (Orchidaceae); Science Press: Beijing, China, 1999; Volume 18, pp. 191–194. [Google Scholar]
- Hinsley, A.; De Boer, H.J.; Fay, M.F.; Gale, S.W.; Gardiner, L.M.; Gunasekara, R.S.; Kumar, P.; Masters, S.; Metusala, D.; Roberts, D.L.; et al. A review of the trade in orchids and its implications for conservation. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2018, 186, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Jin, X.; Gao, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, D.-Y. Assessing conservation efforts against threats to wild orchids in China. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 243, 108484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Forestry and Grassland Administration. List of National Key Protected Wild Plants in China. 2021. Available online: https://www.forestry.gov.cn/c/www/lczc/10746.jhtml (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Balilashaki, K.; Vahedi, M.; Ho, T.-T.; Niu, S.-C.; Cardoso, J.C.; Zotz, G.; Khodamzadeh, A.A. Biochemical, cellular and molecular aspects of Cymbidium orchids: An ecological and economic overview. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2022, 44, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Puy, D.; Cribb, P. The Classification of Cymbidium; Kew Publishing, Royal Botanic Garden: Kew, UK, 1988; pp. 50–194. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.J.; Chen, S.C.; Ru, Z.Z. The Genus Cymbidium in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006; 237p. [Google Scholar]
- Averyanov, L.V.; Nguyen Van, C.; Nguyen, K.; Maisak, T.; Truong, V. New Orchids (Orchidaceae) in the Flora of Vietnam I Epidendroideae. Taiwania 2019, 64, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, C.J.; Cribb, P.J. A reassessment of the sectional limits in the genus Cymbidium Swartz. In Orchid Biology: Reviews and Perspectives; Arditti, J., Ed.; Cornell University Press: London, UK, 1984; pp. 283–322. [Google Scholar]
- Trias-Blasi, A.; Vorontsova, M. Plant identification is key to conservation. Nature 2015, 521, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-B.; Dai, Y.; Hao, G.-Y.; Li, J.-W.; Fu, X.-W.; Zhang, J.-L. Differentiation of water-related traits in terrestrial and epiphytic Cymbidium species. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Shi, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, X.; Jin, X. Orchid conservation in China from 2000 to 2020: Achievements and perspectives. Plant Divers. 2021, 43, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, C.; Ryan, A.; Cribb, P.J.; Chase, M.W. Molecular phylogenetics of Cymbidium (Orchidaceae: Maxillarieae): Sequence data from internal transcribed spacers (ITS) of nuclear ribosomal DNA and plastid matK. Lindleyana 2002, 17, 102–111. [Google Scholar]
- Yukawa, T.; Miyoshi, K.; Yokoyama, J. Molecular Phylogeny and Character Evolution of Cymbidium (Orchidaceae). Bull. Natl. Sci. Mus. Tokyo Ser. B 2002, 28, 129–139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.-W.; Huang, J.-L.; Ya, J.-D.; Zhe, M.-Q.; Zeng, C.-X.; Zhang, Z.-R.; Zhang, S.-B.; Li, D.-Z.; Li, H.-T. DNA barcoding of Cymbidium by genome skimming: Call for next-generation nuclear barcodes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2023, 23, 424–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidt, E.C.; Gallo, L.W.; Scatena, V.L. Leaf anatomical and molecular studies in Bulbophyllum section Micranthae (Orchidaceae) and their implications for systematics. Braz. J. Bot. 2013, 36, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.X.; Wang, Y.; Tao, L.; Liu, W.; Luo, Y.; Li, L. Leaf morpho-anatomy and taxonomic significance in five Dendrobium sect. Stachyobium species from China. Flora 2024, 317, 152560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Y.; Luo, T.; Zhang, N. Leaf structure characteristics of five species of Cymbidium. Plant Sci. J. 2019, 37, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.C. Investigations on leaves of Cymbidium, Paphiopedilum, Dendrobium under scanning electron microscope. J. Wuhan Bot. Res. 1995, 13, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Yukawa, T.; Stern, W.L. Comparative vegetative anatomy and systematics of Cymbidium (Cymbidieae: Orchidaceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2002, 138, 383–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, W.L.; Whitten, W.M. Comparative vegetative anatomy of Stanhopeinae (Orchidaceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1999, 129, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stern, W.L.; Judd, W.S. Systematic and comparative anatomy of Cymbidieae (Orchidaceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2002, 139, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathapattayanon, A. Taxonomic Revision of Orchids in the Genus Dendrobium Sw. Section Formosae (Benth. & Hook. f.) Hook. f. Thailand and Adjacent Areas. Ph.D. Thesis, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand, 2008; pp. 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Vimala, Y.; Lavania, S.; Verma, D. Leaf epidermal features in relation to taxonomy of some species of Bulbophyllum (Orchidaceae) from Northeast India. Rheedea 2020, 30, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saensouk, S.; Saensouk, P. Comparative leaf surfaces of Orchidaceae species from Thailand. Suranaree J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 27, 030032. [Google Scholar]
- Yukawa, T.; Ando, T.; Karasawa, K.; Hashimoto, K. Existence of two stomatal shapes in the genus Dendrobium (Orchidaceae) and its systematic significance. Am. J. Bot. 1992, 79, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, V.P. Die oherirflischen Vegetationsorgane der Orchideen in ihren Beziehungen zu Klima und Standort. Flora 1883, 66, 435–523. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Q.; Duan, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, L. Leaf morphology and taxonomic significance of five species in Hypoxidaceae from China. Guihaia 2022, 42, 1661–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindyastuti, R.; Nurfadilah, S.; Rahadiantoro, A.; Hapsari, L.; Abywijaya, I.K. Leaf anatomical characters of four epiphytic orchids of Sempu Island, East Java, Indonesia: The importance in identification and ecological adaptation. Biodivers. J. Biol. Divers. 2018, 19, 1906–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, E.; Cuartero, J.; Heredia, A. An overview on plant cuticle biomechanics. Plant Sci. 2011, 181, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, W.L.; Carlsward, B.S. Comparative vegetative anatomy and systematics of Oncidiinae (Maxillarieae, Orchidaceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2006, 152, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, J.D.; Rasmussen, H. Stegmata in Orchidales: Character state distribution and polarity. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1984, 89, 53–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prychid, C.J.; Rudall, P.J.; Gregory, M. Systematics and biology of silica bodies in monocotyledons. Bot. Rev. 2003, 69, 377–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riverón-Giró, F.B.; Damon, A.; García-González, A.; Solís-Montero, L.; Aguilar-Romero, O.; Ramírez-Marcial, N.; Nieto, G. Anatomy of the invasive orchid Oeceoclades maculata: Ecological implications. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2017, 184, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, W.L.; Morris, M.W.; Judd, W.S. Anatomy of the thick leaves in Dendrobium section Rhizobium (Orchidaceae). Int. J. Plant Sci. 1994, 155, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xie, Y.; Zou, L.; Luo, Y.; Li, L. Leaf morpho-anatomy and taxonomic significance in six Phalaenopsis s.l. (Orchidaceae) species from China. Flora 2025, 326, 152710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, D.A. Plant Microtechnique; McGraw Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.X.; Jiang, X.S. H2O2-CH2COOH maceration, a simple and perfect method for leaf epidermis. Guihaia 2009, 29, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, J.D. A new morphological classification of stomatal complexes. Phytomorphology 1981, 29, 218–229. [Google Scholar]
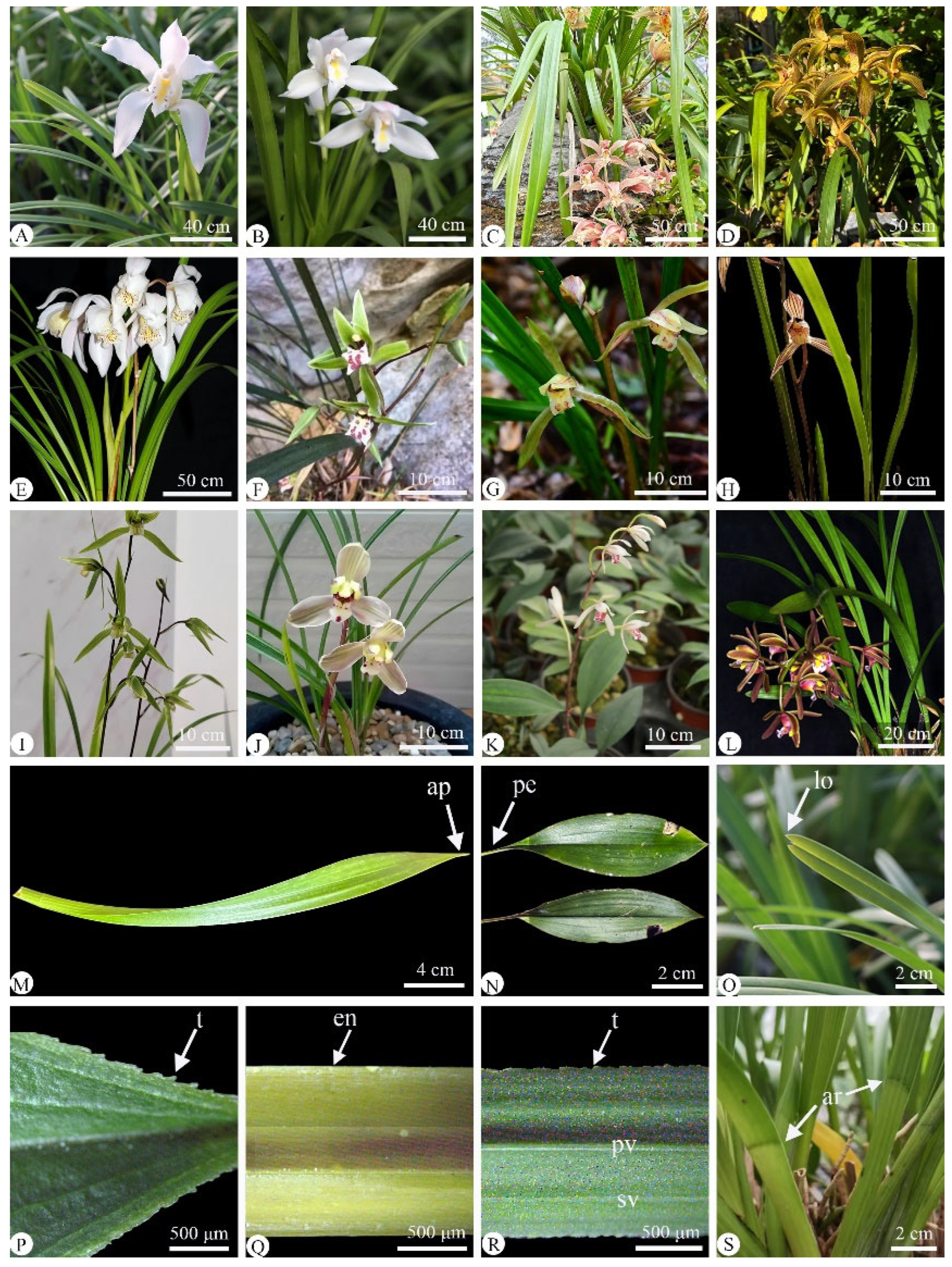
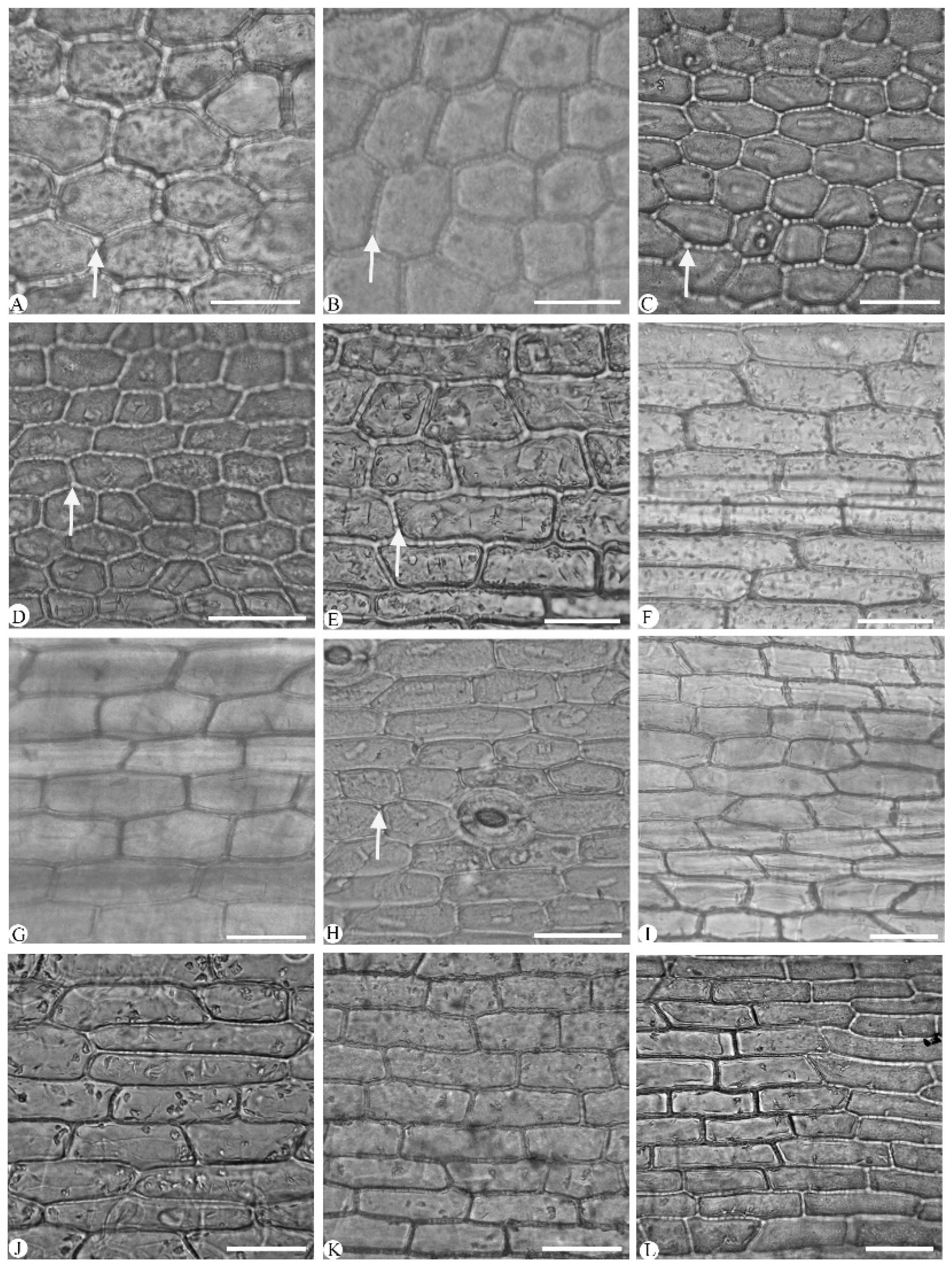


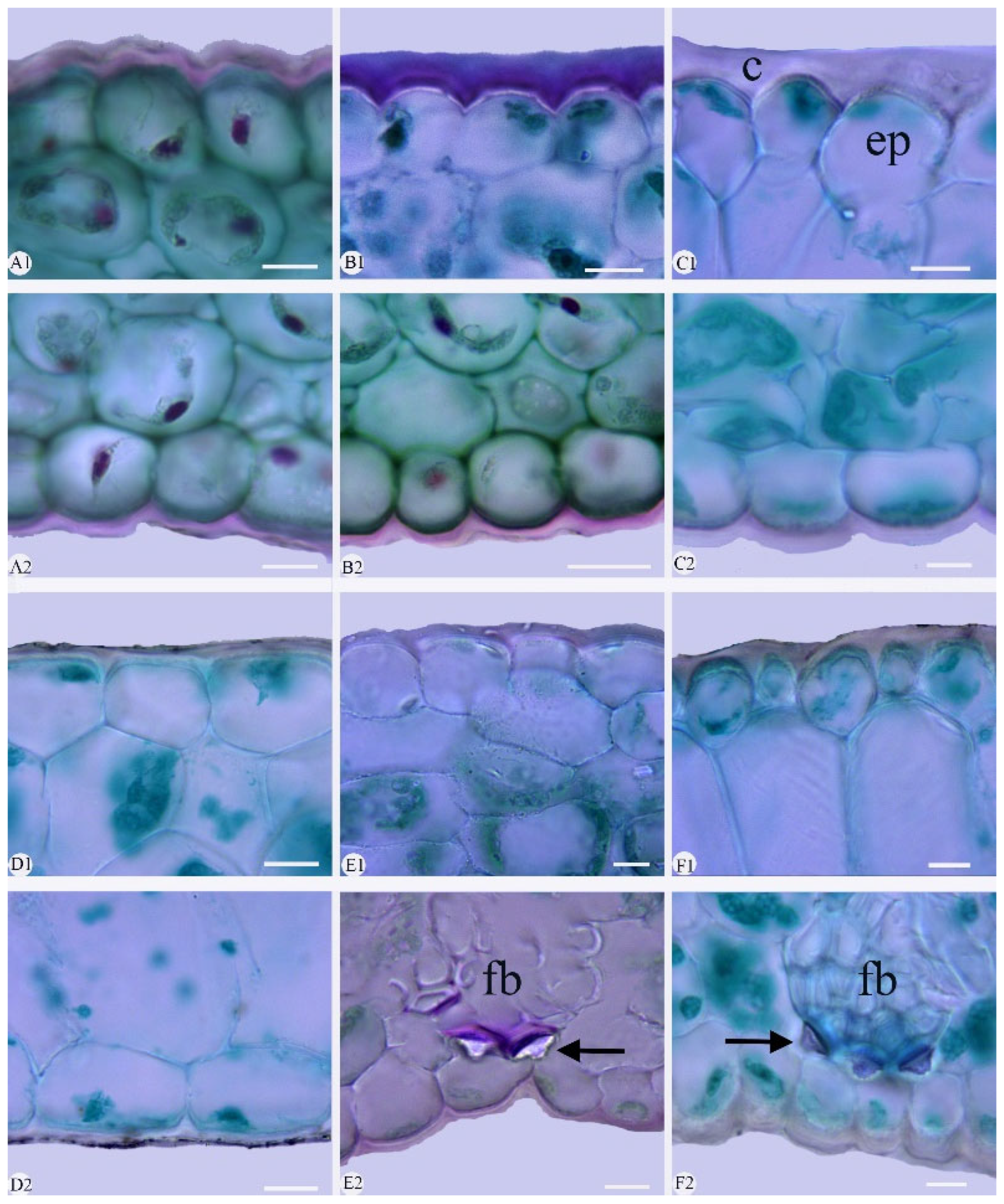
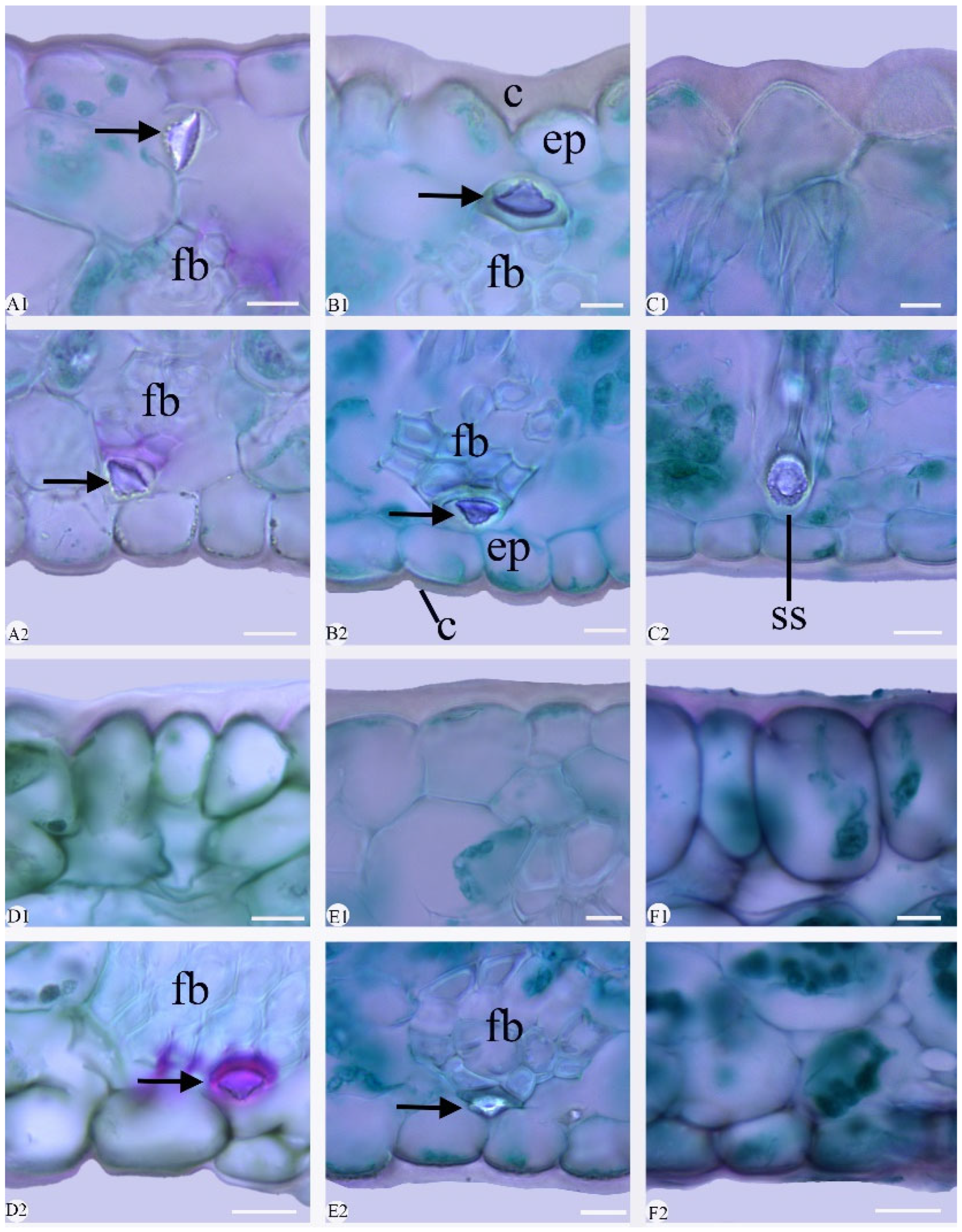
| Species | Chen et al., (1999) [3] | Liu et al., (2006) [9] | Distribution | Voucher |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| —— | Subgen. Cyperorchis | Subgen. Cyperorchis | —— | —— |
| C. eburneum | Sect. Eburnea | Sect. Eburnea | China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, Vietnam | Lilu20190228 |
| C. mastersii | Sect. Eburnea | Sect. Eburnea | Asia | Lilu20220725 |
| C. hookerianum | Sect. Iridorchis | Sect. Iridorchis | China, India, Nepal, Vietnam | Lilu20200526 |
| C. tracyanum | Sect. Iridorchis | Sect. Iridorchis | China, Myanmar, Thailand | Lilu20181218 |
| C. wenshanense | Sect. Iridorchis | Sect. Annamaea | China, Vietnam | Lilu20200324 |
| —— | Subgen. Jensoa | Subgen. Jensoa | —— | —— |
| C. defoliatum * | Sect. Jensoa | Sect. Jensoa | China | Lilu20201112 |
| C. kanran | Sect. Jensoa | Sect. Jensoa | China, Japan, Korea | Lilu20201111 |
| C. qiubeiense * | Sect. Jensoa | Sect. Jensoa | China | Lilu20220114 |
| C. faberi | Sect. Jensoa | Sect. Nanula | China, India, Nepal | Lilu20170725 |
| C. serratum * | Sect. Jensoa | Sect. Nanula | China | Lilu20220715 |
| C. lancifolium | Sect. Geocymbidium | Sect. Geocymbidium | Asia, Oceania | Lilu20180728 |
| —— | Subgen. Cymbidium | Subgen. Cymbidium | —— | —— |
| C. floribundum | Sect. Floribunda | Sect. Floribunda | China, Vietnam | Lilu20180730 |
| Species | Shapes | Size (L × W), cm | Margin | Apex | Base | Petiole |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. defoliatum | lorate | 10–40 × 0.5–1 | entire | acute | articulate | absent |
| C. eburneum | lorate | 57–65 × 1.4–2.1 | entire | acute, slightly two lobed | articulate | absent |
| C. faberi | lorate | 25–80 × 0.4–1.2 | toothed | acute | absent | absent |
| C. floribundum | lorate | 22–50 × 0.8–1.8 | entire | acute, slightly oblique | articulate | absent |
| C. hookerianum | lorate | 35–60 × 1.4–2.3 | entire | acute | articulate | absent |
| C. kanran | lorate | 40–70 × 0.9–1.7 | toothed | acute | articulate | absent |
| C. lancifolium | oblanceolate oblong | 6–17 × 4–7 | toothed | acute | articulate | petiole |
| C. mastersii | lorate | 24–75 × 1.1–2.5 | entire | acute, slightly two lobed | articulate | absent |
| C. qiubeiense | lorate | 30–80 × 5–10 | toothed | acute | articulate | petiole |
| C. serratum | lorate | 20–40 × 0.5–0.9 | toothed | acute | absent | absent |
| C. tracyanum | lorate | 55–80 × 1.5–3.4 | entire | acute | articulate | absent |
| C. wenshanense | lorate | 60–90 × 1.3–1.7 | entire | acute | articulate | absent |
| Species | Adaxial Epidermis | Abaxial Epidermis | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELad | EWad | L/W | ELab | EWab | L/W | SL | SW | SL/SW | SI | SD | |
| C. defoliatum | 45.48 ± 2.11 e | 17.35 ± 0.40 e | 2.62 | 42.85 ± 1.71 bc | 18.17 ± 0.54 bc | 2.36 | 32.49 ± 0.63 a | 27.70 ± 0.37 ab | 1.17 | 5.21 ± 0.23 d | 1.37 ± 0.10 bcd |
| C. eburneum | 56.32 ± 3.42 abc | 19.49 ± 0.47 d | 2.89 | 25.91 ± 1.25 f | 16.13 ± 0.24 cdef | 1.60 | 31.71 ± 0.56 bcd | 25.99 ± 0.60 a | 1.22 | 8.01 ± 0.20 a | 1.67 ± 0.13 ab |
| C. faberi | 58.54 ± 2.06 ab | 13.26 ± 0.59 f | 4.41 | 45.61 ± 2.10 ab | 16.80 ± 0.72 cde | 2.71 | 30.65 ± 0.55 cd | 24.41 ± 0.37 a | 1.25 | 6.87 ± 0.29 bc | 1.27 ± 0.82 cd |
| C. floribundum | 23.69 ± 1.11 g | 13.15 ± 0.48 f | 1.80 | 20.81 ± 0.73 g | 17.14 ± 0.50 cde | 1.21 | 24.68 ± 0.67 f | 20.18 ± 0.39 d | 1.22 | 6.37 ± 0.21 c | 1.47 ± 0.10 bcd |
| C. hookerianum | 54.02 ± 1.80 bc | 15.00 ± 1.10 f | 3.60 | 31.72 ± 1.10 e | 13.67 ± 0.60 de | 2.32 | 32.33 ± 0.63 bc | 27.54 ± 0.62 a | 1.18 | 6.60 ± 0.24 bc | 1.36 ± 0.10 bcd |
| C. kanran | 52.30 ± 2.14 bcd | 17.92 ± 0.33 de | 2.92 | 36.64 ± 1.40 d | 16.71 ± 0.67 cde | 2.19 | 30.19 ± 0.61 cd | 26.22 ± 0.42 ab | 1.15 | 6.79 ± 0.30 bc | 1.80 ± 0.15 a |
| C. lancifolium | 62.10 ± 0.87 a | 59.34 ± 0.90 a | 1.05 | 38.59 ± 2.06 cd | 26.65 ± 0.68 a | 1.45 | 39.37 ± 0.63 f | 29.68 ± 0.56 d | 1.33 | 4.19 ± 0.21 e | 1.10 ± 0.56 d |
| C. mastersii | 50.73 ± 2.50 cde | 22.91 ± 0.45 c | 2.21 | 40.81 ± 2.34 cd | 16.93 ± 0.56 cde | 2.41 | 33.34 ± 0.48 ab | 27.24 ± 0.69 a | 1.25 | 4.00 ± 0.20 e | 1.36 ± 0.10 bcd |
| C. qiubeiense | 47.54 ± 1.80 de | 14.12 ± 0.46 f | 3.36 | 30.10 ± 0.73 f | 15.87 ± 0.38 e | 1.89 | 29.50 ± 0.53 d | 25.19 ± 0.65 c | 1.17 | 6.38 ± 0.20 c | 1.37 ± 0.10 bcd |
| C. serratum | 56.08 ± 2.92 abc | 13.43 ± 0.50 f | 4.17 | 48.17 ± 2.34 a | 14.59 ± 0.33 fg | 3.30 | 30.33 ± 0.47 d | 24.14 ± 0.45 c | 1.27 | 3.98 ± 0.11 e | 1.30 ± 0.98 cd |
| C. tracyanum | 27.98 ± 1.40 g | 14.10 ± 0.49 f | 1.98 | 25.65 ± 0.43 f | 13.68 ± 0.54 b | 1.89 | 26.60 ± 0.53 e | 24.53 ± 0.52 c | 1.08 | 6.45 ± 0.21 c | 1.50 ± 0.12 abc |
| C. wenshanense | 34.38 ± 1.04 f | 26.30 ± 0.75 b | 1.31 | 22.40 ± 2.08 cd | 17.78 ± 0.63 cd | 1.25 | 30.15 ± 0.36 d | 27.61 ± 0.48 a | 1.09 | 7.23 ± 0.21 b | 1.50 ± 0.10 abc |
| Species | LT | TM | MT | VBT | ETad | ETab | ETad/ETab | Cad | Cab |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C.lancifolium | 317.71 ± 6.73 c | 371.92 ± 3.32 d | 268.93 ± 4.09 de | 141.47 ± 3.66 ef | 27.56 ± 0.61 a | 17.68 ± 0.37c | 1.58 | 5.65 ± 0.31 cde | 3.99 ± 0.21 bc |
| C. serratum | 217.16 ± 4.69 f | 211.83 ± 3.41 fg | 185.63 ± 7.60 h | 88.98 ± 7.12 g | 44.70 ± 2.00 bc | 11.10 ± 0.79 b | 4.02 | 4.14 ± 0.29 fg | 1.85 ± 0.09 g |
| C. mastersii | 215.24 ± 2.67 f | 273.61 ± 1.43 f | 183.55 ± 2.23 h | 92.88 ± 3.61 g | 13.77 ± 1.06 bcd | 11.45 ± 0.33 b | 1.07 | 3.39 ± 0.14 g | 2.19 ± 0.08 fg |
| C. kanran | 203.90 ± 1.23 g | 239.62 ± 10.58 g | 177.27 ± 1.10 h | 119.83 ± 4.86 fg | 18.01 ± 0.62 f | 10.13 ± 0.40 b | 1.79 | 3.54 ± 0.13 g | 1.88 ± 0.07 g |
| C. Wenshanense | 344.64 ± 7.47 b | 423.01 ± 12.86 bc | 277.75 ± 3.74 cd | 158.16 ± 10.79 de | 23.75 ± 0.85 b | 10.89 ± 0.20 a | 2.18 | 7.61 ± 0.35 b | 4.31 ± 0.21 a |
| C. hookerianum | 293.52 ± 3.29 d | 325.29 ± 13.44 f | 254.94 ± 1.86 f | 180.50 ± 2.23 g | 16.57 ± 0.52 h | 9.13 ± 0.60 de | 1.81 | 7.48 ± 0.41 b | 3.75 ± 0.19 c |
| C. tracyanum | 245.87 ± 2.66 e | 454.14 ± 16.41 b | 207.54 ± 2.21 g | 126.77 ± 4.90 ef | 22.14 ± 1.21 cdef | 10.82 ± 0.91 c | 2.05 | 9.03 ± 0.60 a | 2.34 ± 0.12 ef |
| C. faberi | 347.06 ± 3.14 b | 449.16 ± 10.23 b | 287.52 ± 2.34 c | 250.86 ± 15.87 b | 21.00 ± 0.63 b cde | 14.04 ± 0.39 c | 1.54 | 4.93 ± 0.17 ef | 3.64 ± 0.10 c |
| C. eburneum | 293.45 ± 4.68 d | 312.34 ± 4.56 e | 253.19 ± 3.53 f | 150.82 ± 4.91 ef | 23.43 ± 0.89 b | 10.26 ± 0.29 a | 2.28 | 5.21 ± 0.29 cde | 2.65 ± 0.12 de |
| C. defoliatum | 344.26 ± 2.26 b | 410.61 ± 14.31 c | 313.80 ± 3.07 b | 214.75 ± 15.32 c | 15.00 ± 0.33 g | 9.76 ± 0.41 c | 1.58 | 5.94 ± 0.19 cd | 4.31 ± 0.16 ab |
| C. qiubeiense | 490.81 ± 3.60 a | 697.75 ± 18.88 a | 440.36 ± 3.47 a | 293.73 ± 22.40 a | 28.18 ± 0.68 ef | 12.65 ± 0.32 cd | 2.23 | 6.18 ± 0.35 c | 4.51 ± 0.26 ab |
| C. floribundum | 302.90 ± 5.14 d | 421.45 ± 6.10 bc | 262.67 ± 4.39 ef | 174.31 ± 6.50 d | 20.26 ± 0.36 def | 16.33 ± 0.50 e | 1.22 | 4.84 ± 0.18 ef | 2.87 ± 0.12 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Tao, L.; Huang, J.; Tao, K.; Ma, D.; Li, L. Leaf Morpho-Anatomy of Twelve Cymbidium (Orchidaceae) Species from China and Their Taxonomic Significance. Plants 2025, 14, 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091396
Hu X, Tao L, Huang J, Tao K, Ma D, Li L. Leaf Morpho-Anatomy of Twelve Cymbidium (Orchidaceae) Species from China and Their Taxonomic Significance. Plants. 2025; 14(9):1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091396
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xiangke, Lei Tao, Jialin Huang, Kaifeng Tao, Dong Ma, and Lu Li. 2025. "Leaf Morpho-Anatomy of Twelve Cymbidium (Orchidaceae) Species from China and Their Taxonomic Significance" Plants 14, no. 9: 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091396
APA StyleHu, X., Tao, L., Huang, J., Tao, K., Ma, D., & Li, L. (2025). Leaf Morpho-Anatomy of Twelve Cymbidium (Orchidaceae) Species from China and Their Taxonomic Significance. Plants, 14(9), 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091396






