Morphological Traits and Water–Nutrient Utilization Efficiency of Hippophae rhamnoides Fine Roots Under Different Stubble Heights in Arsenic Sandstone Area, Inner Mongolia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
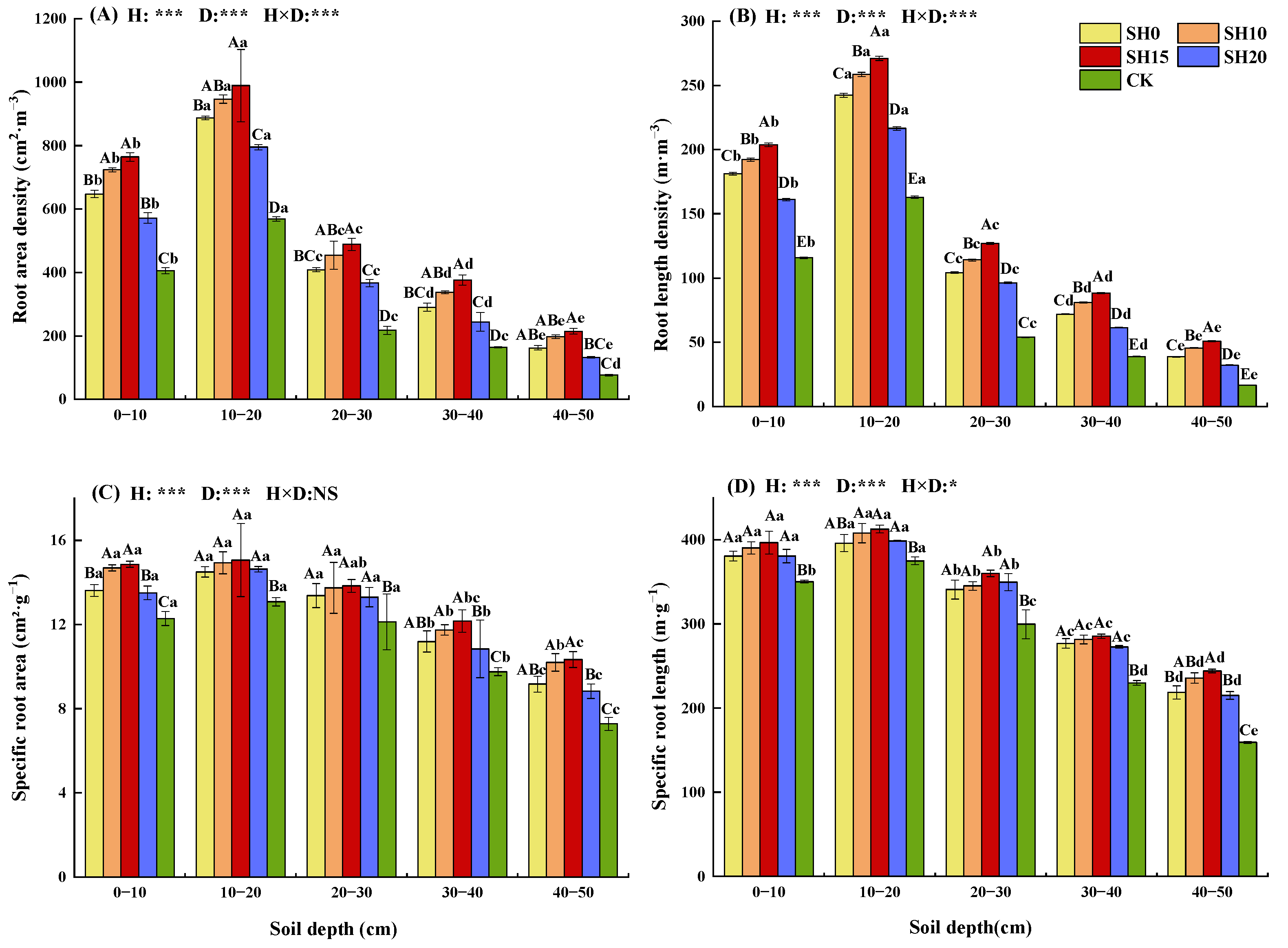
2.1. Effects of Stubble Treatment on the Fine Root Morphological Traits of H. rhamnoides
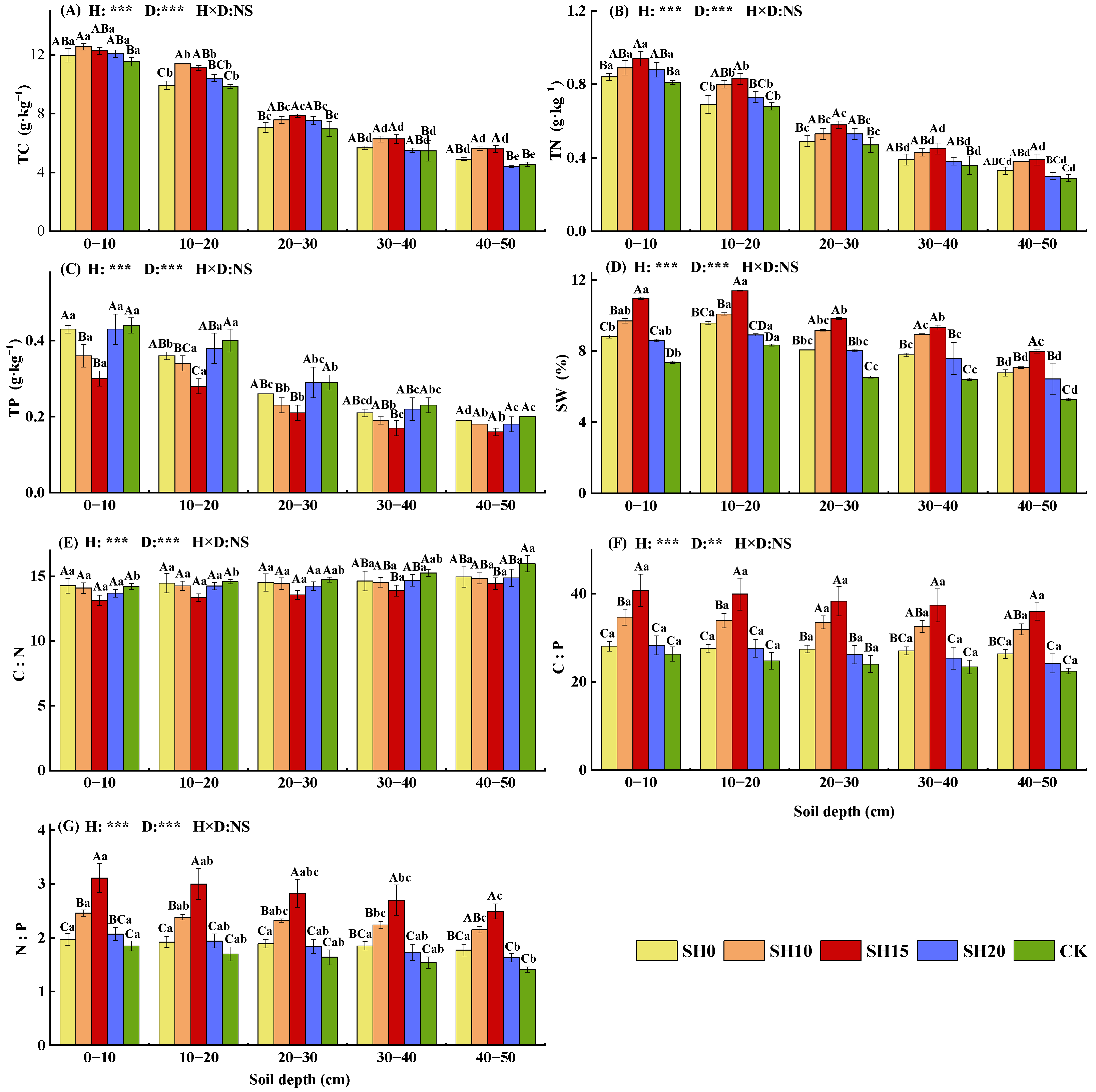
2.2. Effects of Stubble Treatments on Soil Properties
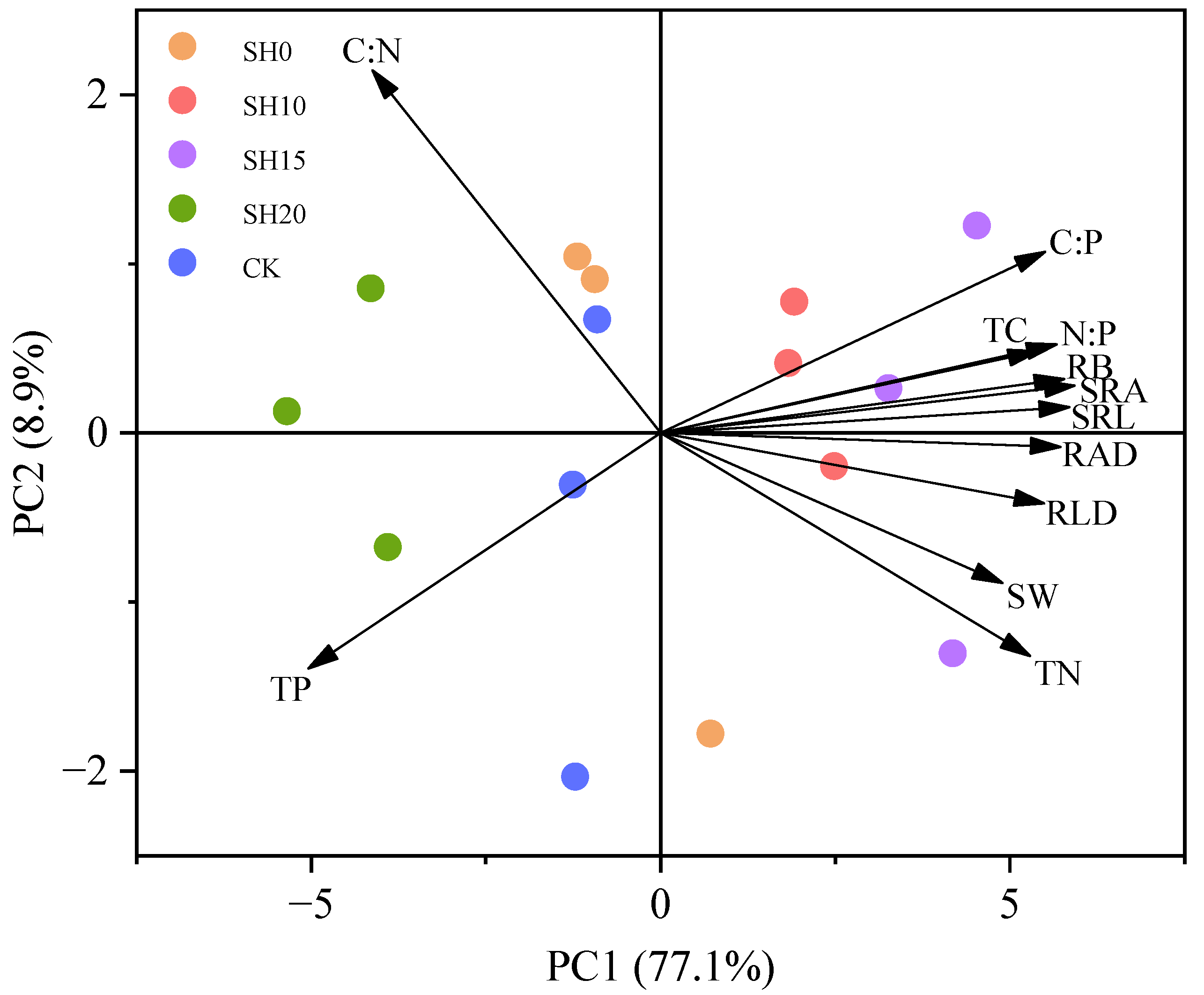
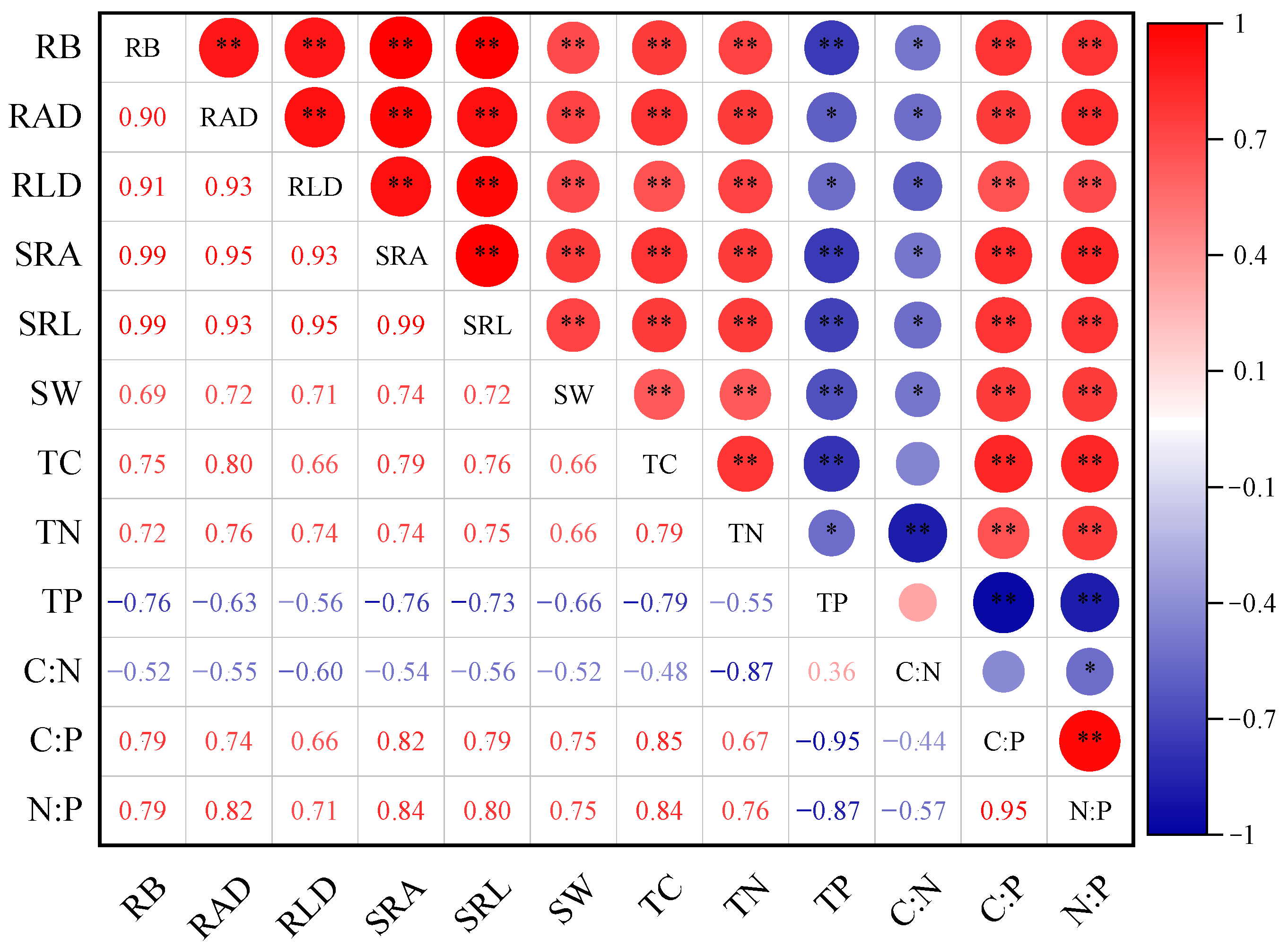
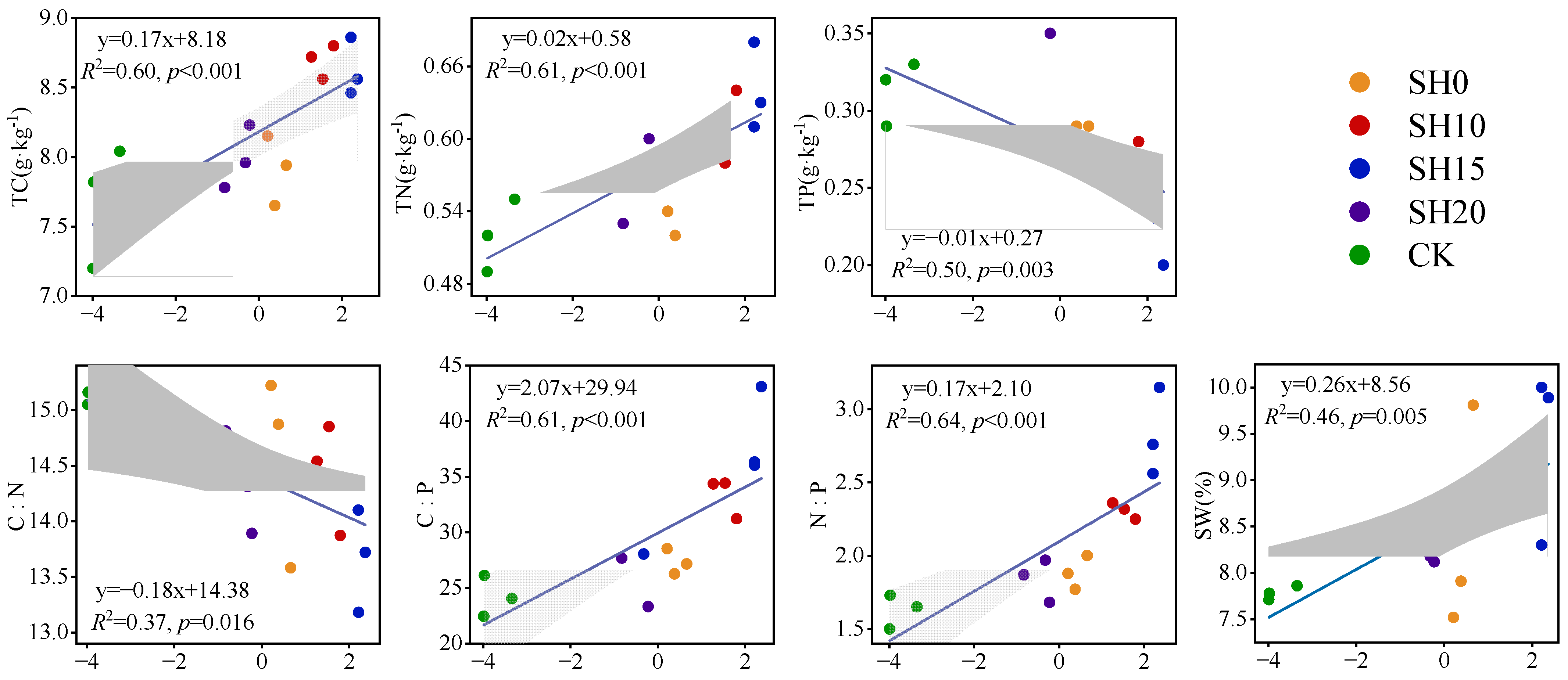
2.3. Correlations Between Fine Roots and Soil Properties
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Overview of the Study Area
3.2. Site Selection
3.3. Sample Collection
3.4. Data Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Stubble Treatment on Fine Root Morphological Traits
4.2. Effects of Stubble Treatment on Soil Characteristics in Forest Plantations
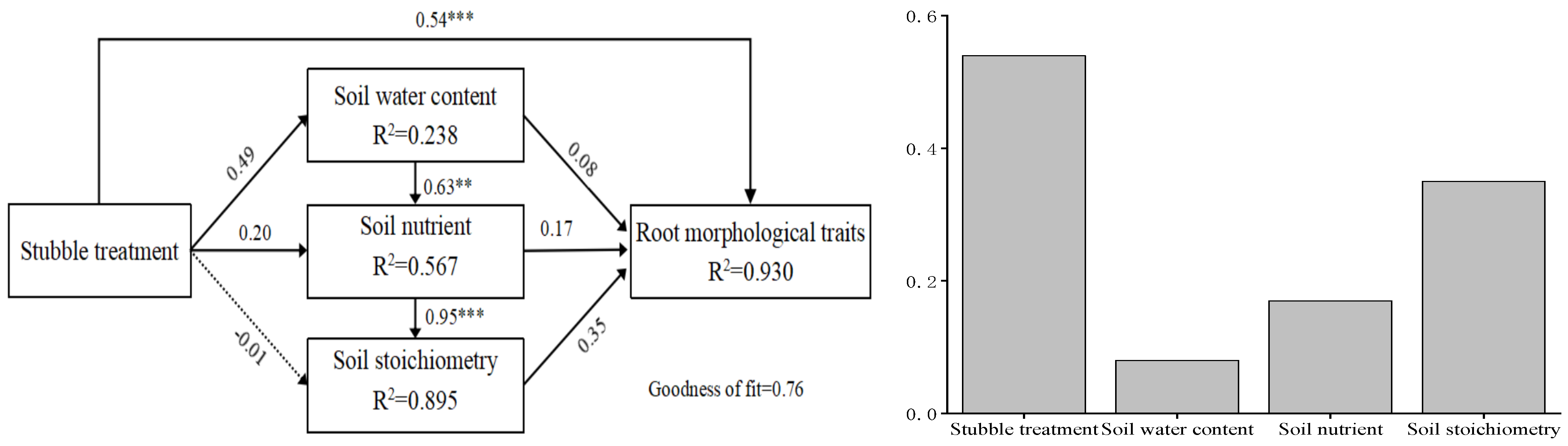
4.3. Stubble Treatment Drives the Coevolution of Fine Roots and Soil
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, Y.N.; Zhang, H.D.; Bao, Y.Y.; Tan, H.Z.; Liu, X.H. Distribution Characteristics of Soil AM Fungi Community in Soft Sandstone Area. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, D.Q.; Yang, Z.Q.; Guo, J.Y.; Qin, F.C.; He, H.F.; Han, W.J. Study on Plant Diversity and Soil Properties of Different Forest Types in Pisha Sandstone Area and Their Correlation. Forests 2025, 16, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Liu, L.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; An, L. Effects of Climate Change and Human Activities on Vegetation Coverage in the Arsenic Sandstone Area of the Yellow River Basin. Soil Water Conserv. Bull. 2023, 43, 412–420. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, S.; Qin, F.; Che, Z.; Sheng, Y. Geochemical Characteristics and Their Indication to Weathering and Provenance of Pisha Sandstone from Lower Jurassic Yan’an Formation in Jungar Banner, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. Soil Water Conserv. Bull. 2024, 44, 196–204. [Google Scholar]
- Han, F.P.; Ren, L.L.; Zhang, X.C.; Li, Z.B. The WEPP Model Application in a Small Watershed in the Loess Plateau. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguin, H.; Mathaux, C.; Guibal, F.; Prin, Y.; Mandin, J.; Gauquelin, T.; Duponnois, R. Ecology of vertical life in harsh environments: The case of mycorrhizal symbiosis with secular cliff climbing trees (Juniperus phoenicea L.). J. Arid. Environ. 2016, 134, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, S.X.; Zhang, P.; Ren, Y.N.; Zhang, Y. Dynamic Simulation Study of Soil Erosion Intensity on Slopes with Different Vegetation Patterns in Pisha Sandstone Area. Ecol. Model. 2024, 491, 110665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Yu, K.X.; Li, Z.B.; Ren, Z.P.; Li, H.T.; Peng, L. Identification of Vegetation Coverage Variation and Quantitative the Impact of Environmental Factors on Its Spatial Distribution in the Pisha Sandstone Area. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ma, M.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, C.; Li, B. Correlation Analysis of Twig and Leaf Characteristics and Leaf Thermal Dissipation of Hippophae rhamnoides in the Riparian Zone of the Taohe River in Gansu Province, China. Plants 2025, 14, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.B.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, J.; Yang, Q.H. Pullout Properties of Hippophae rhamnoides L. Roots in the Loess Area. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2023, 69, 2170–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.L.; Li, T.J.; Li, G.Q.; Liu, C.H.; Gao, H.Y.; Dai, G.H.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Li, S.L. Modular Growth and Clonal Propagation of Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. sinensis in Response to Irrigation Intensity. J. For. Res. 2016, 27, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.S.; Bi, C.F.; Cao, M.M.; Li, H.E.; Wang, X.H.; Wu, W. Simulation of Sediment Retention Effects of the Double Seabuckthorn Plant Flexible Dams in the Pisha Sandstone Area of China. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.P.; Minggagud, H.; Baoyin, T.G.T.; Li, F.Y.H. Plant Production Decreases Whereas Nutrients Concentration Increases in Response to the Decrease of Mowing Stubble Height. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 253, 109745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.B.; Zhou, Y.C.; Bai, Y.X.; Han, Z.G. Available Nitrogen and Enzyme Activity in Rhizosphere Soil Dominate the Changes in Fine-Root Nutrient Foraging Strategies During Plantation Development. Geoderma 2024, 446, 116901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basílio, J.J.N.; Campoe, O.C.; Queiroz, T.B.; de Souza, C.R.; Carneiro, R.L.; Alvares, C.A.; Figura, M.A. Fine Root Density Dynamics and Carbon Stock of Eucalyptus spp.: Interplay of Age, Genotype, and Edaphoclimatic Conditions. Plants 2024, 13, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, D.B.; Meir, P.; Aragão, L.E.O.C.; da Costa, A.C.L.; Braga, A.P.; Gonçalves, P.H.L.; Silva Junior, J.A.; de Almeida, S.S.; Dawson, L.A.; Malhi, Y.; et al. The Effects of Water Availability on Root Growth and Morphology in an Amazon Rainforest. Plant Soil 2008, 311, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampela, M.; Minkkinen, K.; Straková, P.; Bhuiyan, R.; He, W.; Mäkiranta, P.; Ojanen, P.; Penttilä, T.; Laiho, R. Responses of Fine-Root Biomass and Production to Drying Depend on Wetness and Site Nutrient Regime in Boreal Forested Peatland. Front. For. Glob. Change 2023, 6, 1190893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, J.; Weigelt, A.; van Der Plas, F.; Laughlin, D.C.; Kuyper, T.W.; Guerrero-Ramirez, N.; Valverde-Barrantes, O.J.; Bruelheide, H.; Freschet, G.T.; Iversen, C.M.; et al. The Fungal Collaboration Gradient Dominates the Root Economics Space in Plants. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Liu, F.; Xue, S. Nitrogen Addition Enhanced Water Uptake by Affecting Fine Root Morphology and Coarse Root Anatomy of Chinese Pine Seedlings. Plant Soil 2017, 418, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, C.P.; Bueno, C.G.; Toussaint, A.; Träger, S.; Díaz, S.; Moora, M.; Munson, A.D.; Pärtel, M.; Zobel, M.; Tamme, R. Fine-Root Traits in the Global Spectrum of Plant Form and Function. Nature 2021, 597, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, M.L.; Guo, D.; Iversen, C.M.; Chen, W.; Eissenstat, D.M.; Fernandez, C.W.; Li, L.; Ma, C.; Ma, Z.; Poorter, H.; et al. Building a Better Foundation: Improving Root-Trait Measurements to Understand and Model Plant and Ecosystem Processes. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, J.; Bai, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.-H.; Weiser, M. The Response of Root Traits to Precipitation Change of Herbaceous Species in Temperate Steppes. Funct. Ecol. 2019, 33, 2030–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Guan, F.; Li, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X. Effects of Tree Species on Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis (Carriere) J. Houzeau) Fine Root Morphology, Biomass, and Soil Properties in Bamboo–Broadleaf Mixed Forests. Forests 2022, 13, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Yu, W.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, N.; Fu, H.; Di, N.; Duan, J.; Li, X.; Xi, B. Response of Fine-Root Traits of Populus tomentosa to Drought in Shallow and Deep Soil. Forests 2023, 14, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, X. Assessment of Crop Residues and Corresponding Nutrients Return to Fields via Root, Stubble, and Straw in Southwest China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yu, L.; Man, Y.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, J. Application of Stubble and Root Cutting in Artificial Cultivation of Non-Timber Forest Products (NTFPs): A Study Case of Aralia elata (Miq.) Seem. Forests 2022, 13, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.G.; Jia, L.M.; Pang, Q.; Li, R. Stumping Effects on Number and Distribution of Roots of Caragana microphylla Lam. Plantations. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2010, 32, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Nie, K.; Lu, S.; Yao, Z.; Li, G. Effects of Stubble Height on Stump Sprouting and Nutrient Accumulation and Allocation of Hippophae rhamnoides ssp. sinensis. J. Plant Ecol. 2024, 17, rtae031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Yao, Y.; Qi, W. Coordinated Variation in Root and Leaf Functional Traits of Hippophae rhamnoides Treated at Different Stump Heights in Feldspathic Sandstone Areas of Inner Mongolia. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1104632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Zhang, L.; Cao, C.; Zhang, P.; Yang, W.; Han, J. Topographic Gradient Effect of Land Use Change at Arsenic Sandstone Area in the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2023. Soil Water Conserv. Bull. 2025, 45, 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.; Yang, Z.; Qin, F.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X. Influence of Afforestation Density on Plant Diversity and Soil Physicochemical Properties of Pinus tabulaeformis in Arsenic Sandstone Area. Soil Water Conserv. Bull. 2024, 44, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.J. Effects of Different Stubble Height on Fine Root Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Hippophae rhamnoides in Arsenic Sandstone Area. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Freschet, G.T.; Pagès, L.; Iversen, C.M.; Comas, L.H.; Rewald, B.; Roumet, C.; Klimešová, J.; Zadworny, M.; Poorter, H.; Postma, J.A.; et al. A Starting Guide to Root Ecology: Strengthening Ecological Concepts and Standardising Root Classification, Sampling, Processing and Trait Measurements. New Phytol. 2021, 232, 973–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epson Corporation. Expression 12000XL (Models J331B and EU-234); Epson Corporation: Suwa, Nagano, Japan, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Regent Instruments Inc. WinRHIZO Pro 2019a; Regent Instruments Inc.: Quebec City, QC, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.D.; Du, Z.X.; Yang, Y.S.; Li, X.B.; Zhang, Y.C.; Yang, Z.F. Effects of Land Cover Change on Soil Organic Carbon and Light Fraction Organic Carbon at River Banks of Fuzhou Urban Area. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 2010, 21, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tighe, M.; Edwards, M.M.; Cluley, G. Colorimetrically Determining Total Antimony in Contaminated Waters and Screening for Antimony Speciation. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Huang, Z.; Luo, J.; Qiu, K.; López-Vicente, M.; Wu, G.-L. Litter Cover Breaks Soil Water Repellency of Biocrusts, Enhancing Initial Soil Water Infiltration and Content in a Semi-Arid Sandy Land. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 107009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Li, M.K.; Yao, J.J.; Zhou, Y.M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Li, W.; Wu, T.; Han, Z.H.; Xu, X.F.; et al. Root Architecture Characteristics of Differing Size-Controlling Rootstocks and the Influence on the Growth of ‘Red Fuji’ Apple Trees. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 281, 109959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Hao, L.; Bai, S. Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry and Microbial Nutrient Limitation in Response to Shrub Planting Patterns and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Inoculation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 200, 105449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Qi, W.; Zhen, L.; Yao, Y.; Qin, F. Compensatory Growth and Understory Soil Stoichiometric Features of Hippophae rhamnoides at Different Stubble Heights. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambalvo, D.; Amato, G.; Stringi, L. Effects of Stubble Height and Cutting Frequency on Regrowth of Berseem Clover in a Mediterranean Semiarid Environment. Crop Sci. 2011, 51, 1808–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.X.; Peng, T.T.; Liu, N.; Wang, D.; Min, J.G.; Guan, Q.W. Response of Carbon Storage, Fine Root Biomass and Morphology to Thinning in Platycladus orientalis Plantation. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2013, 41, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, J.L.; Giannini-Kurina, F.; Eriksen, J. Similar Root and Stubble Biomass Carbon in Grass–Clover Leys Irrespective of Yield, Species Composition, Sward Age, and Fertilization. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2024, 187, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Han, Y.Z.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wu, X.G. Effects of Cutting Disturbance on Spatial Heterogeneity of Fine Root Biomass of Larix principis-rupprechtii. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, W.J.; Midgley, J.J. Ecology of Sprouting in Woody Plants: The Persistence Niche. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2001, 16, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Wang, X.; Cui, M.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y. Mowing Increases Fine Root Production and Root Turnover in an Artificially Restored Songnen Grassland. Plant Soil 2021, 465, 549–561. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, X.; Liu, F.; Chen, W.; Lan, J.H. Effects of Harvesting Intensity on Fine Root Biomass and Morphological Characteristics of Mixed Plantations of Cunninghamia lanceolata and Broadleaved Trees. For. Res. 2021, 34, 128. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, M.K.; Horner, L.M.; Kubota, T.; Keller, N.A.; Abrahamson, W.G. Extensive Clonal Spread and Extreme Longevity in Saw Palmetto, a Foundation Clonal Plant. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 3730–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.J.; Zhang, W.H.; Deng, L.; Yu, B.Y.; Li, G.; He, T.; Fan, R.R. Effects of Thinning Intensity on Fine Root Biomass and Morphological Characteristics of Middle-Aged Pinus tabulaeformis Plantations in the Huanglong Mountains. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 3065–3073. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Zhu, J.; Wei, X.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, J.; Jiang, L.; Xu, D.; Shen, C.; Liu, J.; He, Z. Adaptation Strategies of Seedling Root Response to Nitrogen and Phosphorus Addition. Plants 2024, 13, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.H.; Chu, P.F.; Chen, D.M.; Bai, Y.F. Functional Correlations Between Specific Leaf Area and Specific Root Length Along a Regional Environmental Gradient in Inner Mongolia Grasslands. Funct. Ecol. 2016, 30, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Hu, Y.; Li, W.; Cui, L. Specific root length regulated the rhizosphere effect on denitrification across distinct macrophytes. Geoderma 2024, 449, 117002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. Effects of Stumping on the Habitat of Caragana korshinskii Forest and Identification of Macro-Dominant Fungi. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Bu, C.; Gao, G. Effect of Pruning Measure on Physiology Character and Soil Waters of Caragana korshinskii. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.-S.; Shen, Y.; Ma, H.-B.; Fang, P.; Cao, Y. Effects of Caragana intermedia stubble on soil water characteristics and water balance on the desert steppe. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2024, 33, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.J.; Liu, M.Y.; Zuo, X.F.; Guo, J.; Xie, Y.H.; Wu, H.; Yue, P.Q. Effects of Prune Measure on Vegetation Characteristics and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties of Hedysarum scoparium Protection Forest in Jilantai Salt Lake. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 37, 250–257. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.M.; Hou, X.L.; Liu, W.Z. Soil and Water Conservation Function and Ecology Benefits of Different Types Vegetation in Semi-arid Loess Hilly Region. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 14, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; He, C.; Zhou, Y.M.; Zhang, Q.D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Jin, N.; Zhao, L.X.; Li, D.; Dong, C.Y. Study on Coppicing and Rejuvenation Techniques of Caragana spp. Shelterbelts in Minqin Desert Area. J. Soil Water Conserv. China 2021, 5, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna Murthy, R.; Nagaraju, B.; Govinda, K.; Uday Kumar, S.N.; Basavaraja, P.K.; Saqeebulla, H.M.; Gangamrutha, G.V.; Srivastava, S.; Dey, P. Soil Test Crop Response Nutrient Prescription Equations for Improving Soil Health and Yield Sustainability—A Long-Term Study under Alfisols of Southern India. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1439523. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, G.; Wang, Y.; Kong, Y.; Zhou, J. Hillside Topographic Pattern of Tree Species Diversity and Soil Nutrients in Mount Tai, China. Plant Soil 2024, 504, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Effects of Soil Nutrients on Plant Nutrient Traits in Natural Pinus tabuliformis Forests. Plants 2023, 12, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.G. The Impacts of Shrub Branch Covering on Soil Respiration in a Desert Steppe of Ningxia. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Y.Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.M.; Liu, B.W.; Wang, J.R. Effects of Prune Measure on Soil Properties of Artificial Caragana intermedia Forest in Desert Steppe. J. Grassl. Sci. 2018, 26, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.G.; Li, H.H.; Yu, Y.S.; Li, H. Effects of Shrub Encroachment in Grasslands on Soil Fungal Communities in Inner Mongolia, China. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2024, 30, 271–281. [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge, C.A.; Rameau, C.; Wijerathna-Yapa, A. Lessons from a century of apical dominance research. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 3903–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Liang, X.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X. Depletion of Stem Non-Structural Carbohydrates Supports Release of Lateral Branches from Apical Control in Quercus mongolica Seedlings. Trees-Struct. Funct. 2022, 36, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Geng, X.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Z. Drought Decreases Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation and Nitrogen Transfer in a Populus tomentosa-Hippophae rhamnoides Mixed Plantation on the Semiarid Loess Plateau, China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 558, 121815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lin, Y.; Fang, L.; Li, J.; Han, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. Sex-Related Ecophysiological Responses of Hippophae rhamnoides Saplings to Simulated Sand Burial Treatment in Desertification Areas. Forests 2023, 14, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.B.; He, F.K.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Xiao, H.X.; Hoang, D.T.T.; Pu, S.Y.; Razavi, B.S. Nutrients in the Rhizosphere: A Meta-Analysis of Content, Availability, and Influencing Factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 153908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Gao, C.; Zhang, H.; Mouazen, A.M.; Shao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jiao, H. Stoichiometry of Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus in Soil: Impacts of Soil Development and Land Use Across the Catchment Scale. Catena 2025, 252, 108862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, X.; Wen, Y.; Cheng, M.; Wang, X. The Critical Role of Soil Ecological Stoichiometric Ratios: How Does Reforestation Improve Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorus Availability? Plants 2024, 13, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Yao, Y.F.; QI, W. Stump Height after Regenerative Cutting of Sea-Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) Affects Fine Root Architecture and Rhizosphere Soil Stoichiometric Properties. Rhizosphere 2022, 24, 100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noutcheu, R.; Oliveira, F.M.P.; Wirth, R.; Tabarelli, M.; Leal, I.R. Coppicing as a Driver of Plant Resprouting and the Regeneration of a Caatinga Dry Forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 529, 120736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, A.; Bosch-Serra, A.D.; Lidon, A.; Ginestar, D.; Boixadera, J. Soil Mineral Nitrogen Dynamics in Fallow Periods in a Rainfed Semiarid Mediterranean Agricultural System. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 622–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wan, B.; Jiang, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Lan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, X. Interactions of Organic Phosphorus with Soil Minerals and the Associated Environmental Impacts: A Review. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 74–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; He, Y.; Liu, T.; Hao, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z. Characteristics of Rhizosphere Soil Microecological Environment of Different Ecological Restoration Vegetation in Arsenic Sandstone Areas. Bull. Bot. Res. 2023, 43, 531–539. [Google Scholar]


| Stubble Treatment | Soil Layer (cm) | Total Biomass (g·m−2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 | 10–20 | 20–30 | 30–40 | 40–50 | ||
| SH0 | 74.74 ± 0.70 Bb | 96.11 ± 2.13 Ba | 47.98 ± 1.32 Bc | 40.76 ± 0.61 Cd | 27.82 ± 0.85 Ce | 287.41 ± 4.39 C |
| SH10 | 77.38 ± 0.94 ABb | 99.60 ± 2.26 ABa | 51.88 ± 0.52 Ac | 45.14 ± 0.66 Bd | 30.39 ± 0.60 Be | 304.39 ± 4.32 B |
| SH15 | 80.73 ± 2.24 Ab | 103.13 ± 1.17 Aa | 55.43 ± 0.92 Ac | 48.57 ± 0.49 Ad | 32.60 ± 0.41 Ae | 320.46 ± 0.63 A |
| SH20 | 66.44 ± 1.02 Cb | 85.32 ± 0.41 Ca | 43.28 ± 1.14 Cc | 35.36 ± 0.26 Dd | 23.52 ± 0.46 De | 253.92 ± 2.36 D |
| CK | 51.86 ± 0.19 Db | 68.24 ± 0.44 Da | 28.30 ± 1.50 Dc | 26.45 ± 0.18 Ec | 16.30 ± 0.20 Ed | 191.16 ± 2.01 E |
| Stubble heights (H): *** Soil depth (D): *** H × D: *** | ||||||
| Traits | Traits | Sample Size | Minimum Value | Maximum Value | Mean Value | Coefficient of Variation Among Stubble Treatments | Coefficient of Variation Among Soil Layers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root biomass (g·m2) | RB | 75 | 16.05 | 104.75 | 54.29 | 16.92% | 42.52% |
| Root area density (cm2·m−3) | RAD | 75 | 71.38 | 1138.09 | 457.10 | 21.64% | 53.44% |
| Root length density (m2·m−3) | RLD | 75 | 16.40 | 272.41 | 121.052 | 20.33% | 58.17% |
| Specific root area (cm2·g−1) | SRA | 75 | 6.87 | 17.41 | 12.36 | 7.16% | 15.98% |
| Specific root length (m·g−1) | SRL | 75 | 157.60 | 419.65 | 320.20 | 6.36% | 21.56% |
| Traits | Traits | Sample Size | Minimum Value | Maximum Value | Mean Value | Coefficient of Variation Among Stubble Treatments | Coefficient of Variation Among Soil Layers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil water (%) | SM | 75 | 6.09 | 11.24 | 8.56 | 12.66% | 12.09% |
| Total carbon (g·kg−1) | TC | 75 | 4.31 | 12.83 | 8.18 | 5.61% | 33.29% |
| Total nitrogen (g·kg−1) | TN | 75 | 0.27 | 0.99 | 0.58 | 8.66% | 35.75% |
| Total phosphorus (g·kg−1) | TP | 75 | 0.14 | 0.49 | 0.28 | 13.57% | 30.20% |
| Carbon-to-nitrogen ratio | C:N | 75 | 12.61 | 16.64 | 14.38 | 4.24% | 3.92% |
| Carbon-to-phosphorus ratio | C:P | 75 | 29.94 | 45.96 | 29.94 | 18.76% | 6.55% |
| Nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratio | N:P | 75 | 1.35 | 3.48 | 2.10 | 21.36% | 7.97% |
| Stubble Treatment | Sample Information | Stand Factor | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | Size of Plots (m × m) | Slope (°) | Slope Position | Average Plant Height (cm) | Average Crown Width (cm) EW/SN | Current Year Branch Length (cm) | Current Year Basal Diameter (cm) | |
| SH0 | 11 | 50 × 50 | 4 | Upper slope | 59.37 | 43.75/41.54 | 103.54 | 1.71 |
| SH10 | 11 | 50 × 50 | 4 | Upper slope | 65.53 | 51.93/48.77 | 116.24 | 1.83 |
| SH15 | 11 | 50 × 50 | 4 | Upper slope | 72.46 | 54.72/52.77 | 127.42 | 1.90 |
| SH20 | 11 | 50 × 50 | 4 | Upper slope | 62.35 | 46.77/43.74 | 99.87 | 1.65 |
| CK | 11 | 50 × 50 | 4 | Upper slope | 103.54 | 89.85/81.78 | 64.93 | 1.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yue, Y.; Hao, L.; Qi, W.; Gao, R.; Dong, X. Morphological Traits and Water–Nutrient Utilization Efficiency of Hippophae rhamnoides Fine Roots Under Different Stubble Heights in Arsenic Sandstone Area, Inner Mongolia. Plants 2025, 14, 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091329
Xu Y, Guo Y, Yue Y, Hao L, Qi W, Gao R, Dong X. Morphological Traits and Water–Nutrient Utilization Efficiency of Hippophae rhamnoides Fine Roots Under Different Stubble Heights in Arsenic Sandstone Area, Inner Mongolia. Plants. 2025; 14(9):1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091329
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yajie, Yuefeng Guo, Yongjie Yue, Longfei Hao, Wei Qi, Runhong Gao, and Xiaoyu Dong. 2025. "Morphological Traits and Water–Nutrient Utilization Efficiency of Hippophae rhamnoides Fine Roots Under Different Stubble Heights in Arsenic Sandstone Area, Inner Mongolia" Plants 14, no. 9: 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091329
APA StyleXu, Y., Guo, Y., Yue, Y., Hao, L., Qi, W., Gao, R., & Dong, X. (2025). Morphological Traits and Water–Nutrient Utilization Efficiency of Hippophae rhamnoides Fine Roots Under Different Stubble Heights in Arsenic Sandstone Area, Inner Mongolia. Plants, 14(9), 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14091329





