Effect of Exogenous Melatonin on Corn Seed Germination and Seedling Salt Damage Mitigation Under NaCl Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
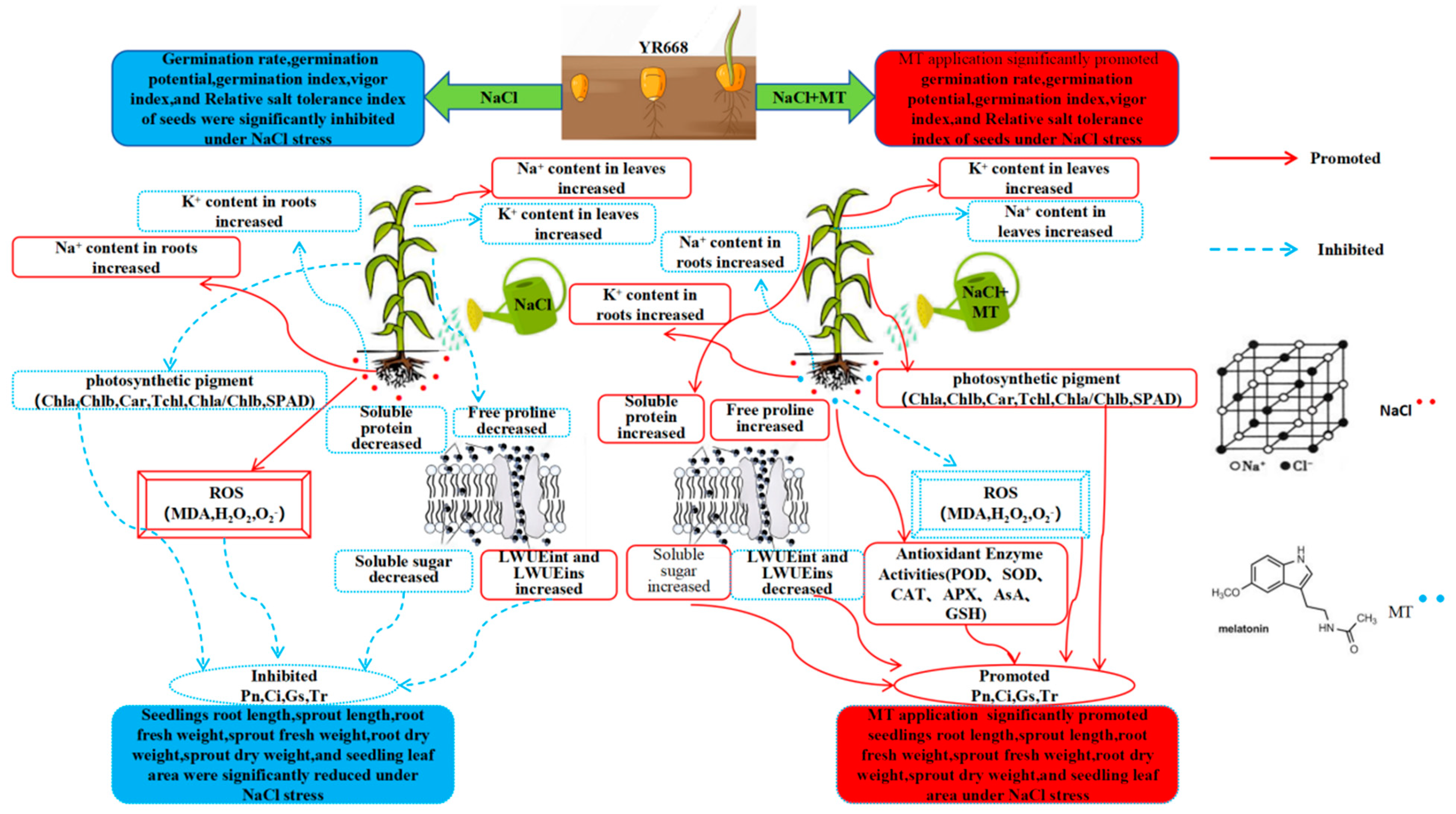
2.1. Effect of MT on Maize Seed Germination Under NaCl Stress
2.2. Effect of Exogenous MT on the Seedling Growth Indicators of Maize Under NaCl Stress
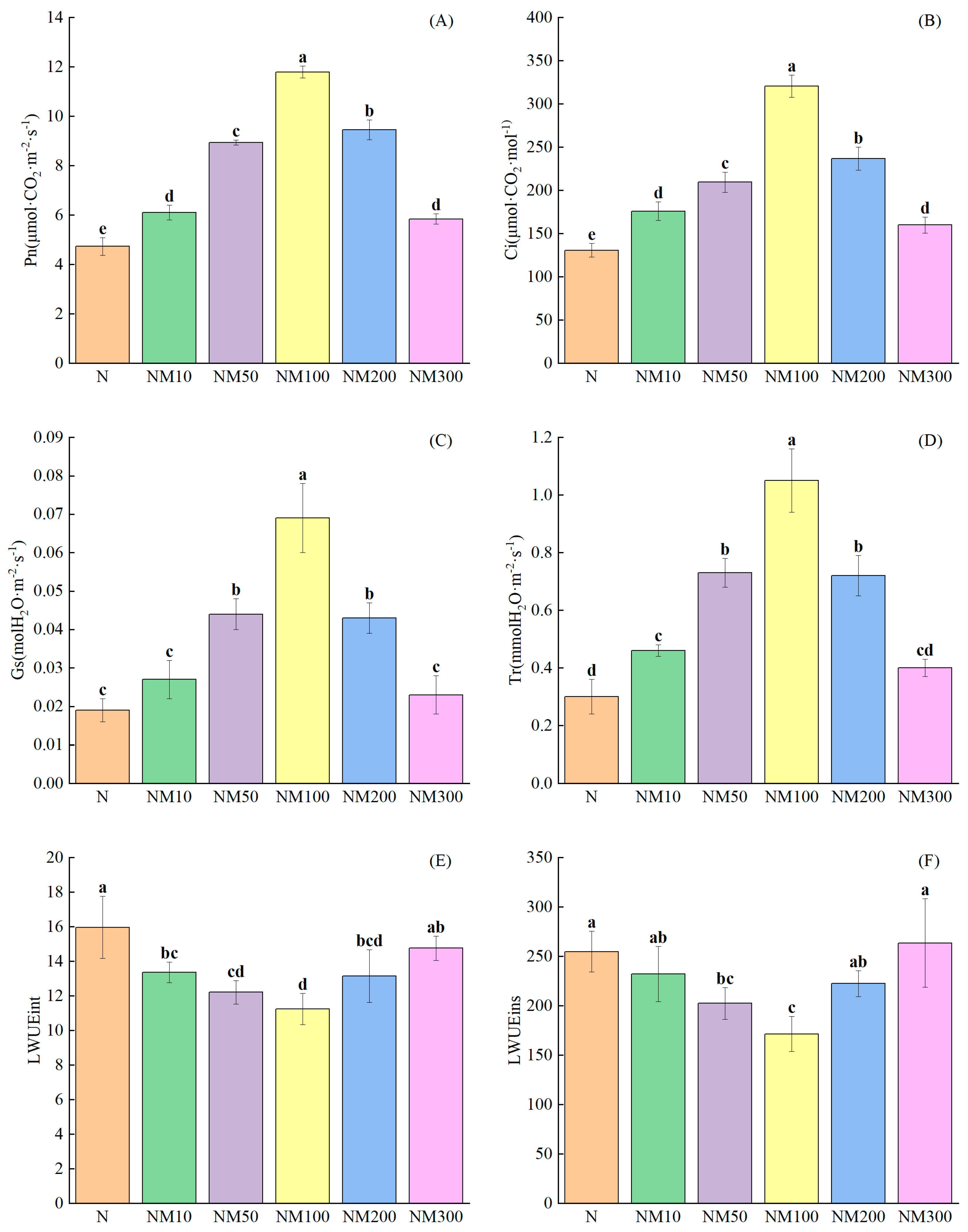
2.3. Effects of Exogenous MT on Photosynthetic Parameters of Maize Seedlings Under NaCl Stress
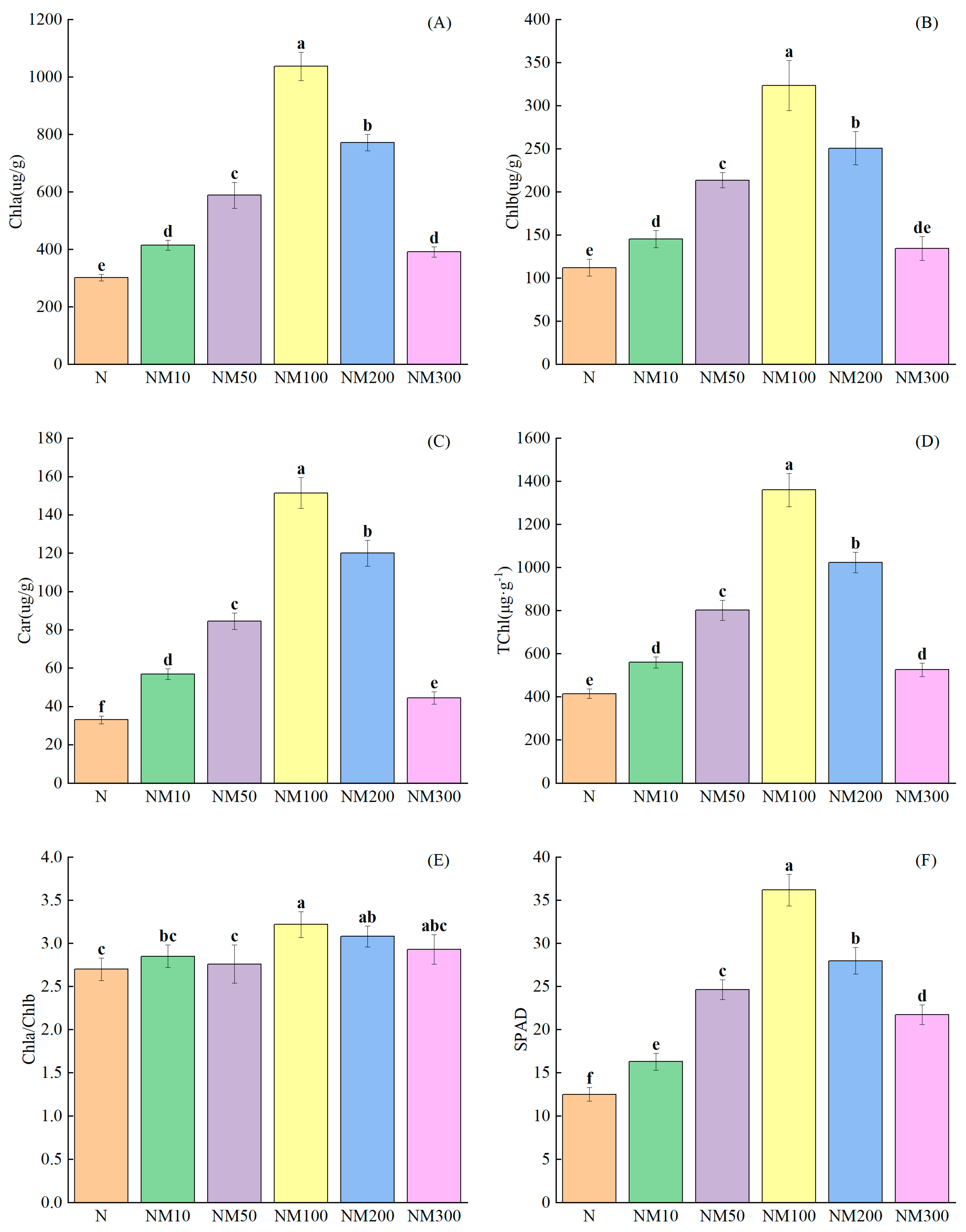
2.4. Effects of Exogenous MT on Chlorophyll Accumulation of Maize Seedlings Under NaCl Stress
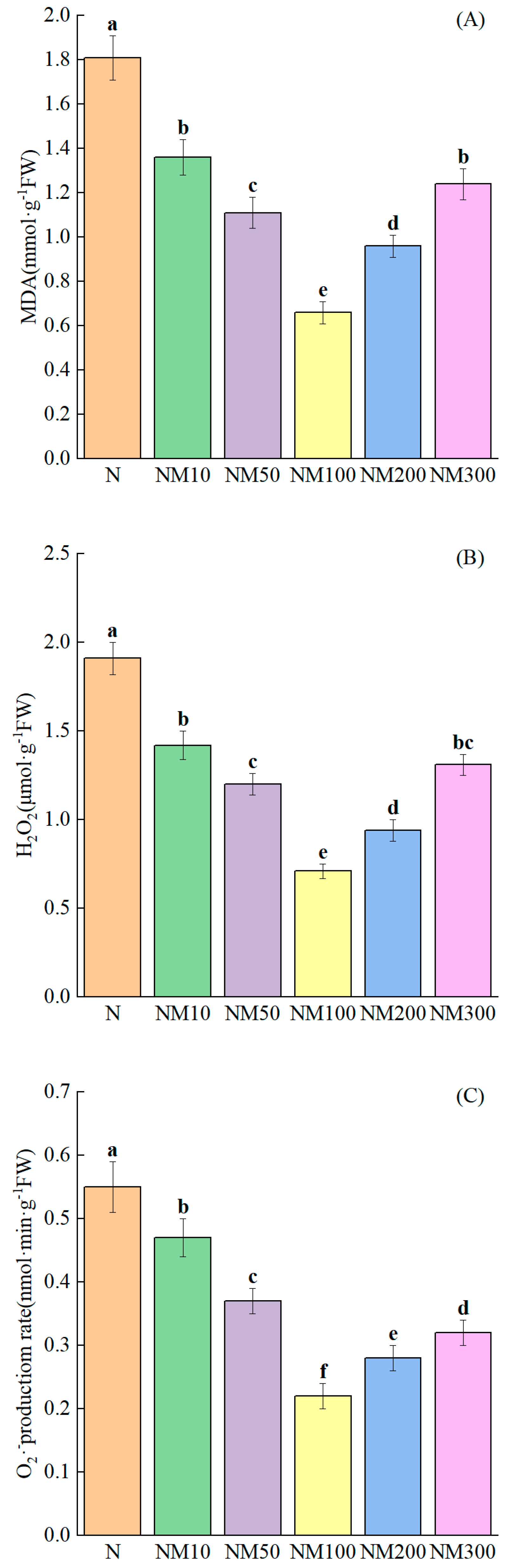
2.5. Effect of Exogenous MT on Cell Membrane Damage of Maize Seedlings Under NaCl Stress
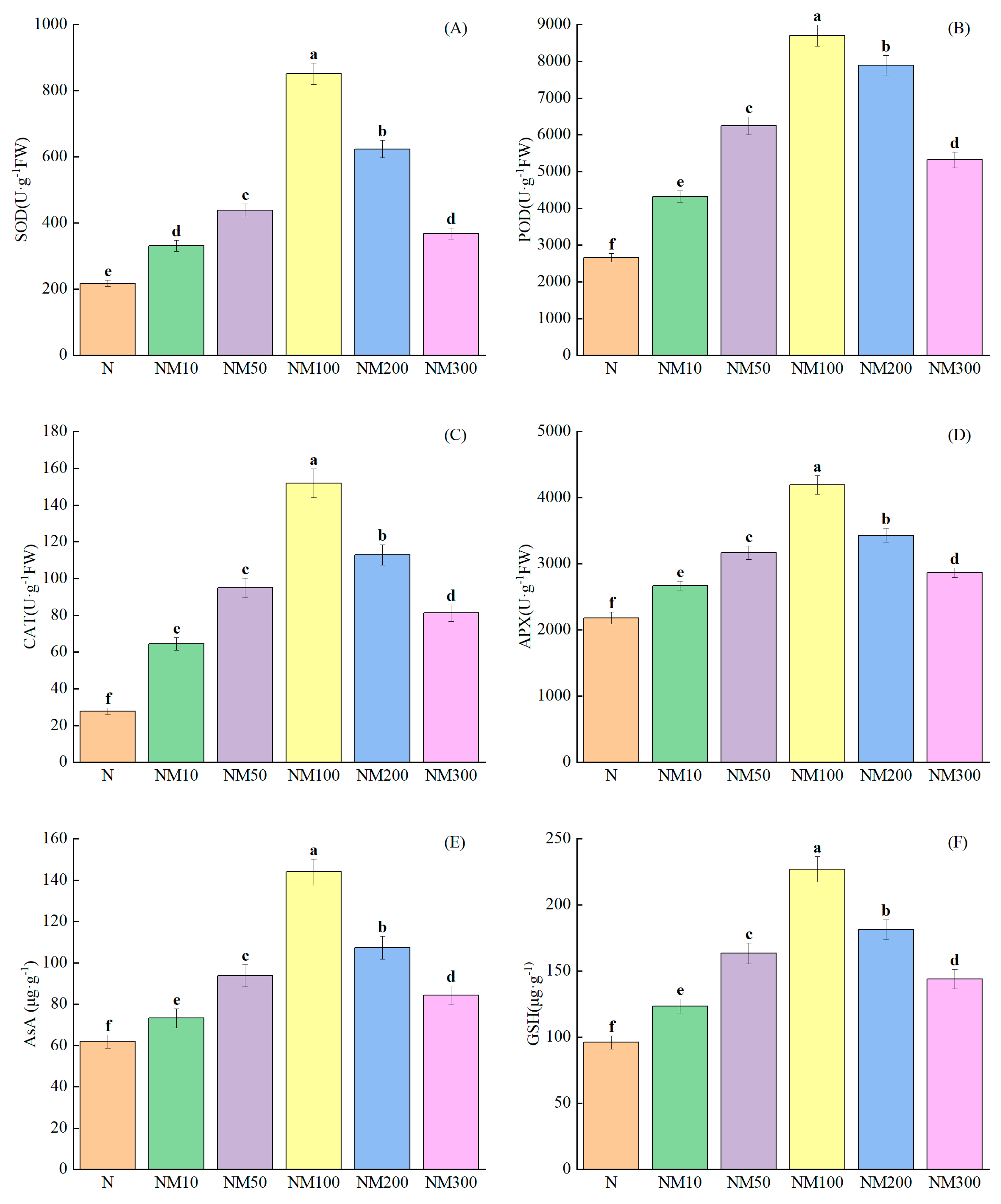
2.6. Effects of Exogenous MT on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities of Maize Seedlings Under NaCl Stress
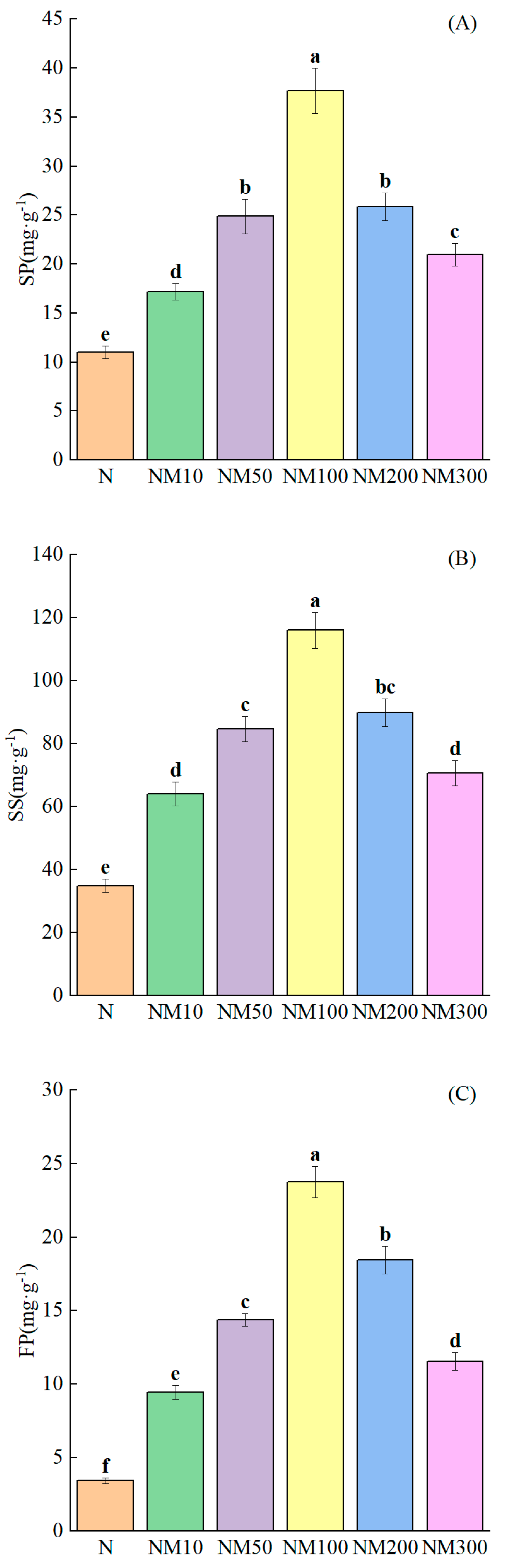
2.7. Effect of Exogenous MT on Osmoregulatory Substances in Maize Seedlings Under NaCl Stress
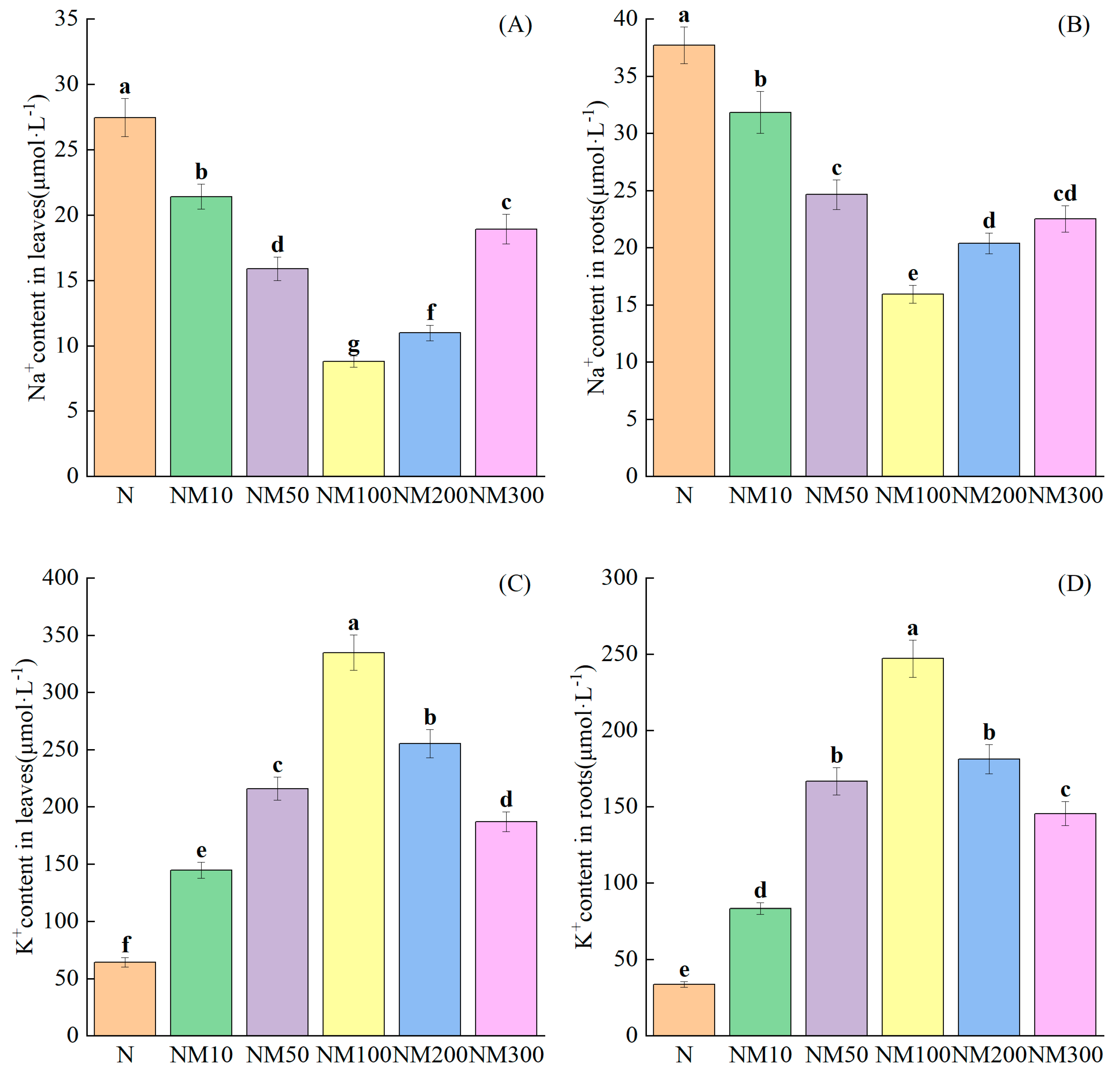
2.8. Effect of Exogenous MT on Ion Content in Maize Seedlings’ Roots and Leaves Under NaCl Stress
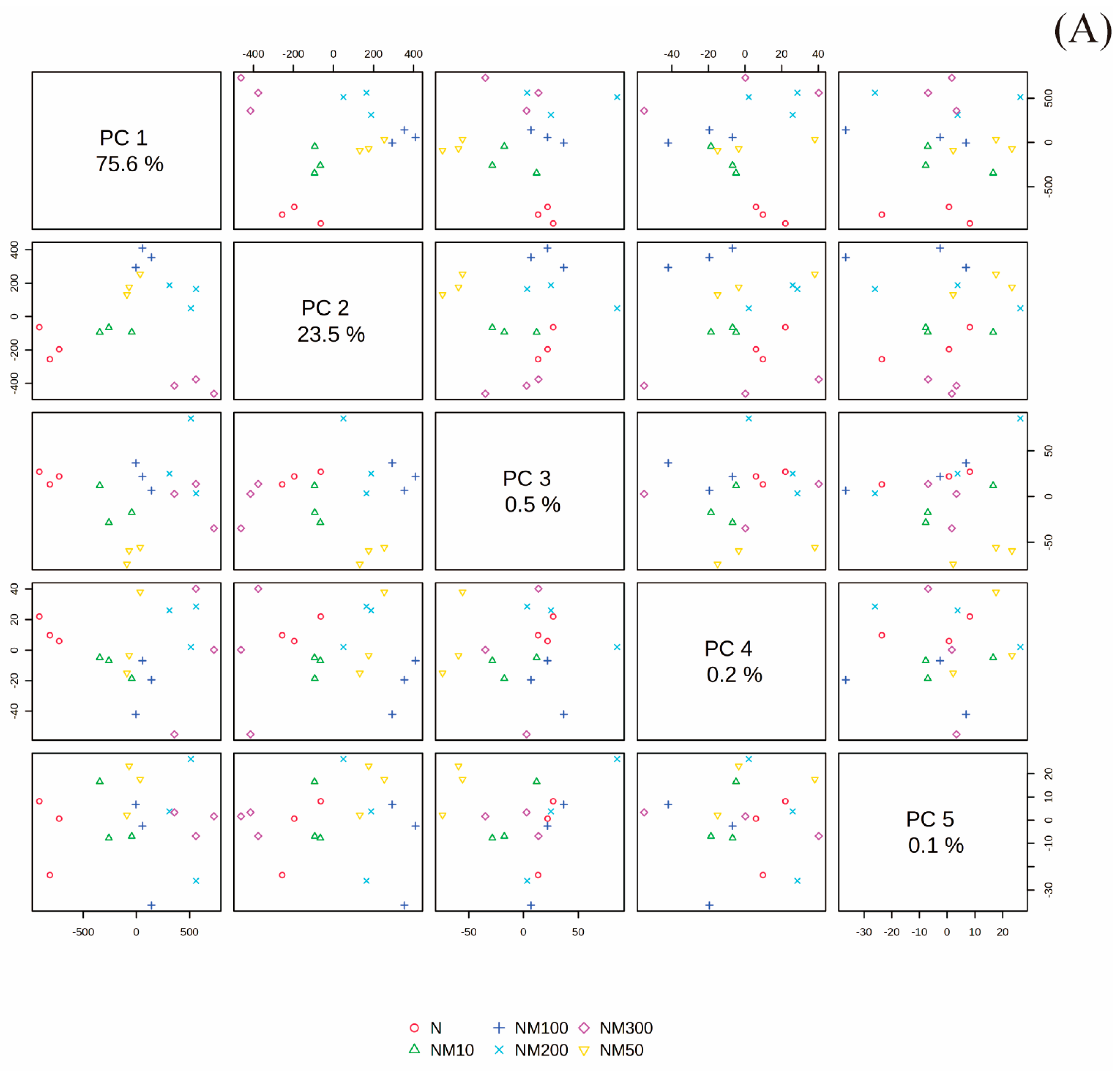
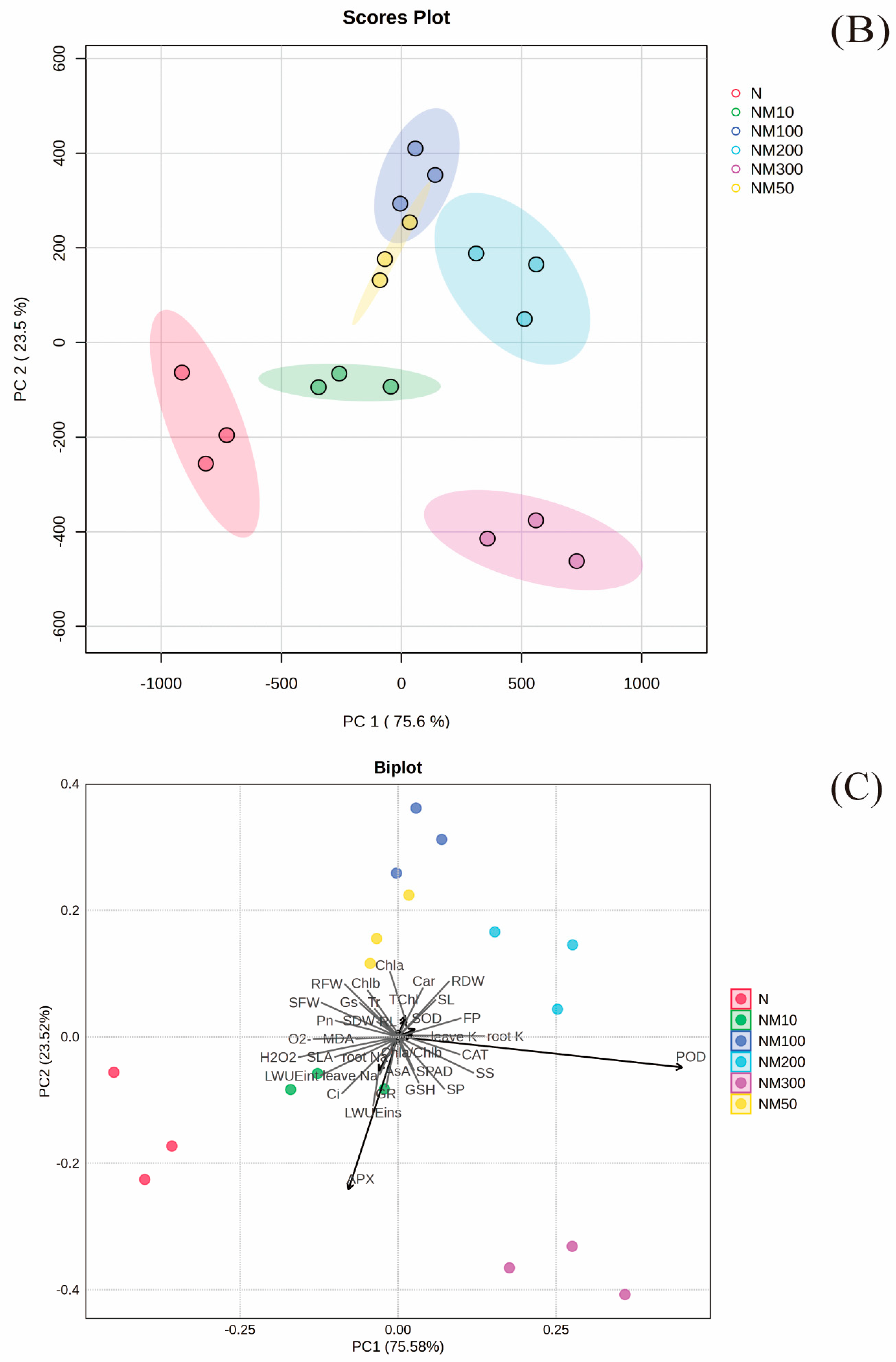
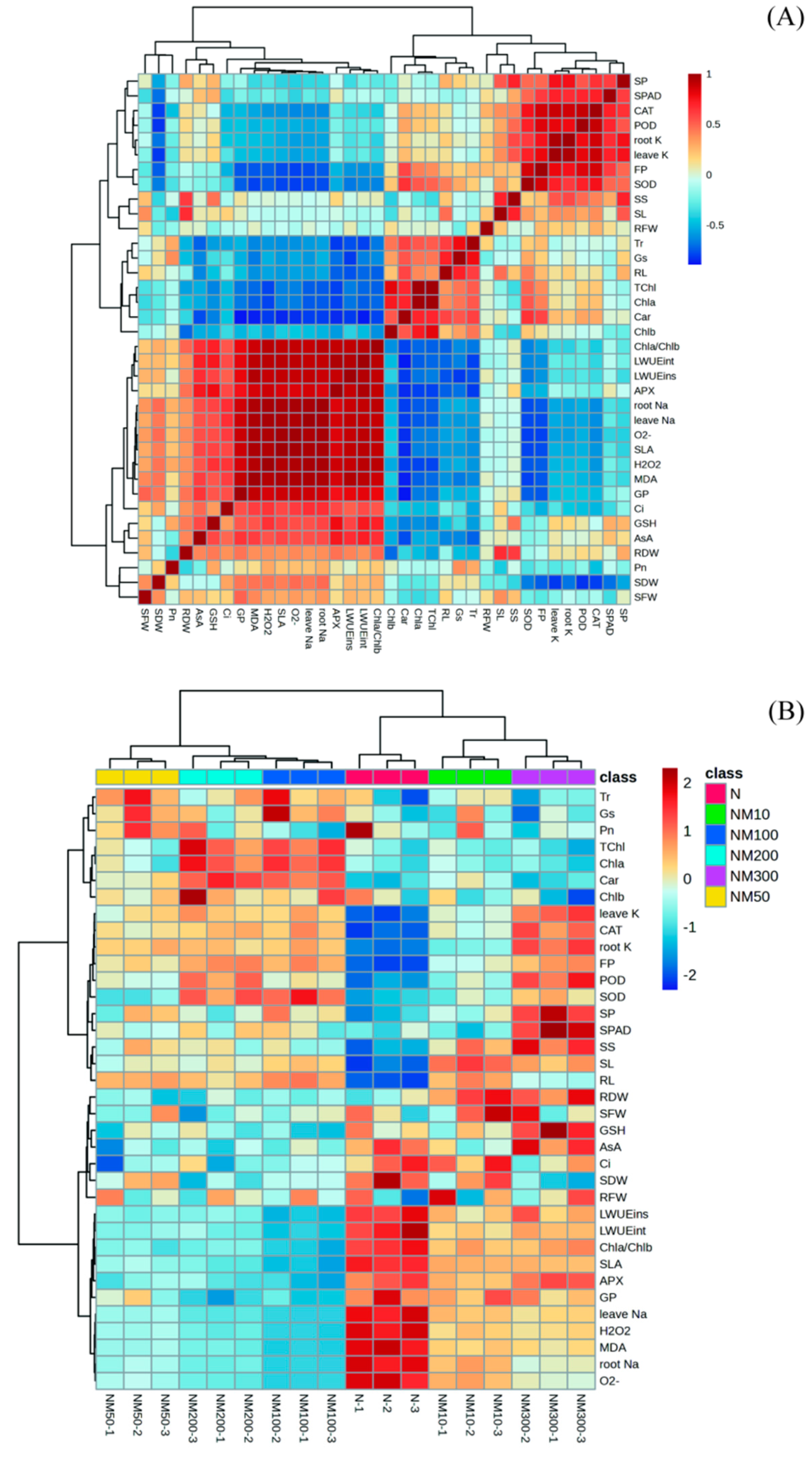
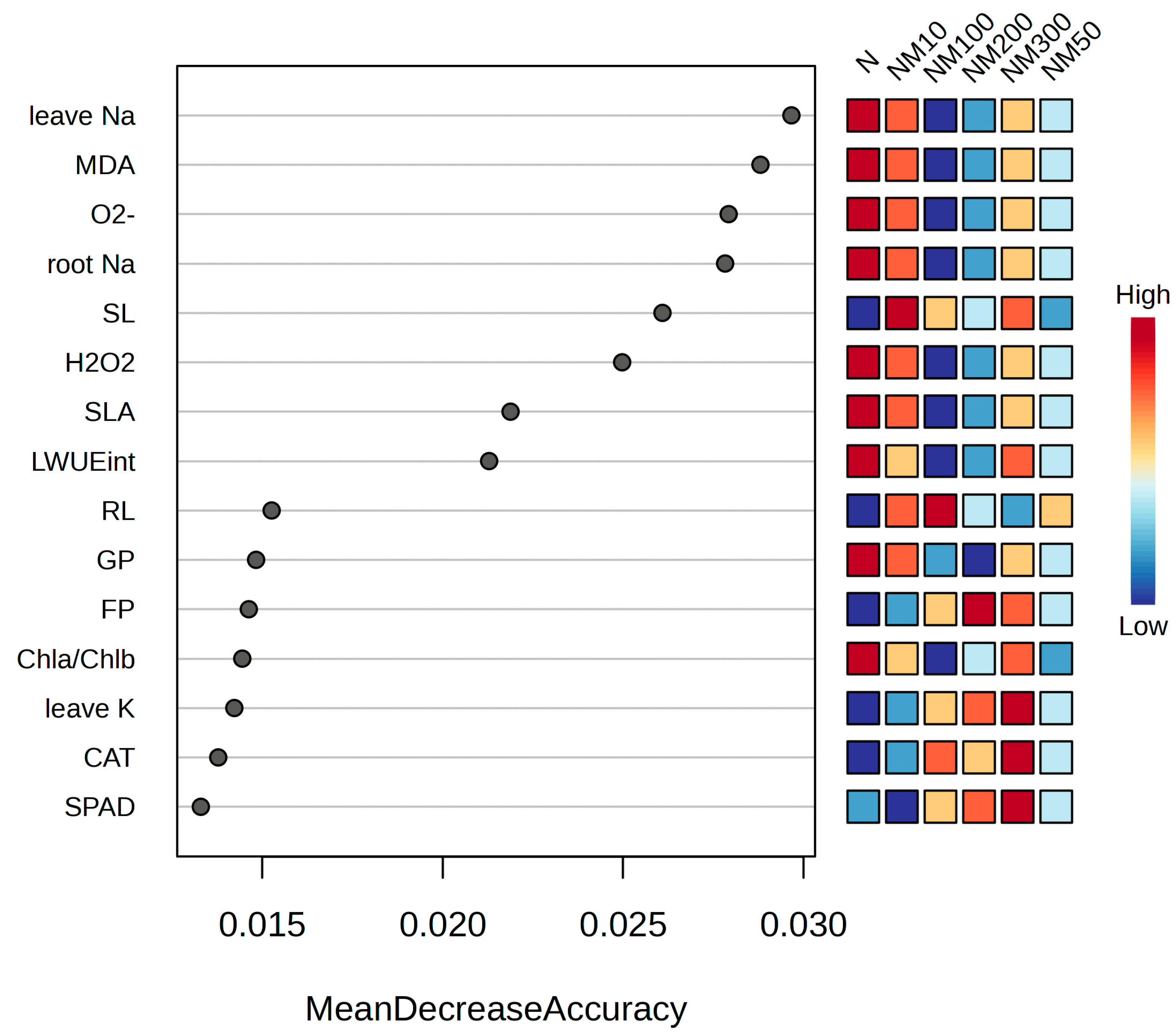
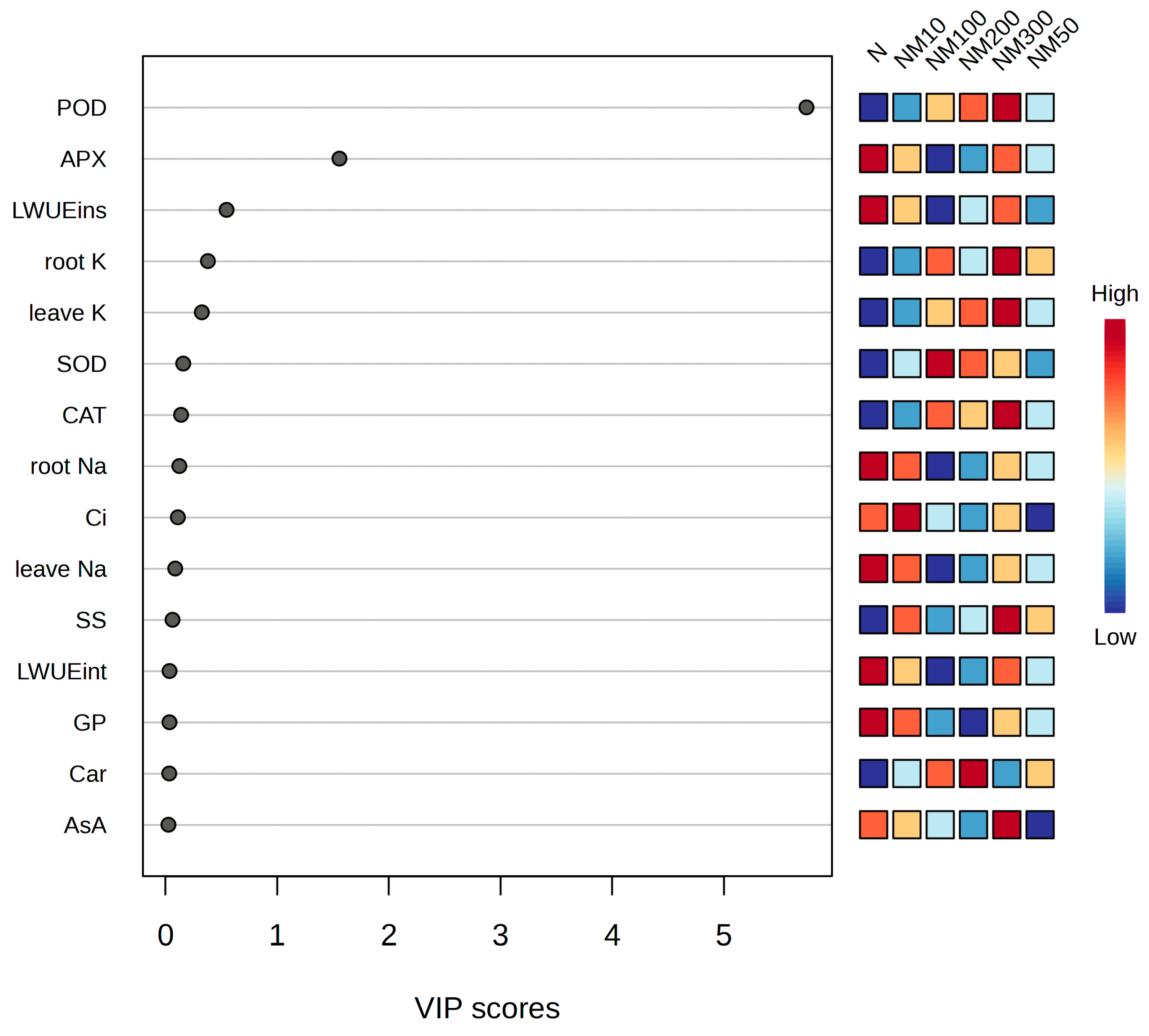
2.9. Multiple Analysis of Various Indexes Changes Induced by Exogenous MT Under NaCl Stress in Maize Seeds and Seedlings
3. Discussion
3.1. Effect of Exogenous Melatonin on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Maize Under NaCl Stress
3.2. Effect of Exogenous Melatonin on Photosynthesis in Maize Seedlings Under NaCl Stress
3.3. Effect of Exogenous Melatonin on the Antioxidant System of Maize Seedlings Under NaCl Stress
3.4. Effect of Exogenous Melatonin on the Ion Content of Roots and Leaves of Maize Seedlings Under NaCl Stress
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Seed Germination Test
4.2. Seedling Hydroponic Experiment
4.3. Determination of Germination Indicators
4.4. Determination of Physiological Indicators for Seedling Growth
4.5. Determination of Photosynthetic Parameters and Chlorophyll
4.6. Determination of Membrane Damage Index
4.7. Determination of Physiological and Biochemical Indicators
4.8. Determination of Ion Content
4.9. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Erenstein, O.; Jaleta, M.; Sonder, K.; Mottaleb, K.; Prasanna, B.M. Global maize production, consumption and trade: Trends and R&D implications. Food Secur. 2022, 14, 1295–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Liu, N.G.; Wang, X.Q.; Niu, Z.Y.; Liao, Q.; Ding, R.S.; Du, T.S.; Kang, S.Z.; Tong, L. Maintaining grain number by reducing grain abortion is the key to improve water use efficiency of maize under deficit irrigation and salt stress. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 294, 108727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Global predictions of primary soil salinization under changing climate in the 21st century. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Shi, J.; Niu, Y.N.; Lu, P.N.; Chen, X.J.; Mao, T.T. 24-epibrassinolide alleviates aluminum toxicity by improving leaf chlorophyll fluorescence and photosynthetic performance and root antioxidant-oxidant balance and ascorbate-glutathione cycle in maize. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 69, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Turk, H. Chitosan-induced enhanced expression and activation of alternative oxidase confer tolerance to salt stress in maize seedlings. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 141, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, A.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Rizwan, M.; Usman, M.; Anayatullah, S.; Areej; Alharby, H.F.; Bamagoos, A.A.; Alharbi, B.M.; Ali, S. Effects of silicon nanoparticles and conventional Si amendments on growth and nutrient accumulation by maize (Zea mays L.) grown in saline-sodic soil. Environ. Res. 2023, 227, 115740. [Google Scholar]
- Sadak, M.S.; Dawood, M.G.; El-Awadi, M.E.-S. Changes in growth, photosynthetic pigments and antioxidant system of Hordeum vulgare plant grown under salinity stress via signal molecules application. Vegetos 2024, 37, 1966–1982. [Google Scholar]
- Akhter, M.S.; Noreen, S.; Mahmood, S.; Aqeel, M.; Zafar, Z.U.; Rashid, M.; Arshad, M.N.; Owais, M.; Ahmad, J.; Shah, K.H. Silicon supplement improves growth and yield under salt stress by modulating ionic homeostasis and some physiological indices in Hordeum vulgare L. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 1694–1712. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.L.; Cao, X.S.; Yue, L.; Wang, C.X.; Tao, M.N.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xing, B.S. Foliar-applied cerium oxide nanomaterials improve maize yield under salinity stress: Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and rhizobacteria regulation. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 299, 118900. [Google Scholar]
- Sadak, M.S.; Dawood, M.G. Biofertilizer role in alleviating the deleterious effects of salinity on wheat growth and productivity. Gesunde Pflanzen. 2023, 75, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar]
- Sadak, M.S.; Hanafy, R.S.; Elkady, F.M.A.M.; Mogazy, A.M.; Abdelhamid, M.T. Exogenous calcium reinforces photosynthetic pigment content and osmolyte, enzymatic, and non-enzymatic antioxidants abundance and alleviates salt stress in bread wheat. Plants 2023, 12, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, Y.; Singh, P.; Siddiqui, H.; Bajguz, A.; Hayat, S. Salinity induced physiological and biochemical changes in plants: An omic approach towards salt stress tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 156, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.L.; Zeng, W.Z.; Ao, C.; Huang, J.S. Integrative analysis of the transcriptome and metabolome reveals Bacillus atrophaeus WZYH01-mediated salt stress mechanism in maize (Zea mays L.). J. Biotechnol. 2024, 383, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadak, M.S. Nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide as signaling molecules for better growth and yield of wheat plant exposed to water deficiency. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadak, M.S. Physiological role of Arbuscular Mycorrhizae and vitamin B1 on productivity and physio-biochemical traits of white lupine (Lupinus termis L.) under salt stress. Gesunde Pflanzen. 2023, 75, 1885–1896. [Google Scholar]
- Demidchik, V. Mechanisms of oxidative stress in plants: From classical chemistry to cell biology. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2015, 109, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadak, M.S.; Sekara, A.; Al-Ashkar, I.; Habib-ur-Rahman, M.; Skalicky, M.; Brestic, M.; Kumar, A.; Sabagh, A.E.; Abdelhamid, M.T. Exogenous aspartic acid alleviates salt stress-induced decline in growth by enhancing antioxidants and compatible solutes while reducing reactive oxygen species in wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 987641. [Google Scholar]
- Akhter, M.S.; Noreen, S.; Ummara, U.; Aqeel, M.; Saleem, N.; Ahmed, M.M.; Mahmood, S.; Athar, H.R.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Kaushik, P.; et al. Silicon-induced mitigation of NaCl stress in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.), associated with enhanced enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidant activities. Plants 2022, 11, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragaey, M.M.; Sadak, M.S.; Dawood, M.F.A.; Mousa, N.H.S.; Hanafy, R.S.; Latef, A.A.H.A. Role of signaling molecules sodium nitroprusside and arginine in alleviating salt-induced oxidative stress in wheat. Plants 2022, 11, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Kaiser, E.; Li, T.; Marcelis, L.F.M. NaCl affects photosynthetic and stomatal dynamics by osmotic effects and reduces photosynthetic capacity by ionic effects in tomato. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 3637–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hameid, A.R.; Sadak, M.S. Impact of glutathione on enhancing sunflower growth and biochemical aspects and yield to alleviate salinity stress. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 101744. [Google Scholar]
- Çam, S.; Küçük, Ç.; Almaca, A. Bacillus strains exhibit various plant growth promoting traits and their biofilm-forming capability correlates to their salt stress alleviation effect on maize. J. Biotechnol. 2023, 369, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubbels, R.; Reiter, R.J.; Klenke, E.; Goebel, A.; Schnakenberg, E.; Ehlers, C.; Schiwara, H.W.; Schloot, W. Melatonin in edible plants identifed by radioimmunoassay and by high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Pineal. Res. 1995, 18, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sardar, H.; Shafig, M.; Naz, S.; Ali, S.; Ahmad, R.; Ejaz, S. Enhancing drought tolerance in broccoli (Brassica oleracea L.) through melatonin application: Physiological and biochemical insights into growth, photosynthesis, and antioxidant defense mechanisms. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2024, 59, 103256. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.J.; Yan, D.; Lu, Z.Z.; Liu, R.; Hong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Z.; Yu, C.X.; Gao, Y.R.; Liu, Z.Y. Integration of the metabolome and transcriptome reveals diurnal variability in the effects of melatonin on salt tolerance in maize seedlings. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 43, 1672–1688. [Google Scholar]
- Santosh, K.B.; Prianka, H. Melatonin plays multifunctional role in horticultural crops against environmental stresses: A review. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 176, 104063. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, A.; Migitaka, H.; Iigo, M.; Itoh, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Ohtani-Kaneko, R.; Reiter, R.J. Identification of melatonin in plants and its effects on plasma melatonin levels and binding to melatonin receptors in vertebrates. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1995, 35, 627–634. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Chen, Y.; Kang, H. Melatonin is a potential target for improving post-harvest preservation of fruits and vegetables. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 488368. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Li, Q.T.; Chu, Y.N.; Reiter, R.J.; Yu, X.M.; Zhu, D.H.; Chen, S.Y. Melatonin enhances plant growth and abiotic stress tolerance in soybean plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 695–707. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Xie, J.; Yu, J.; Lv, J.; Zhang, J.; Ding, D.; Gao, F. Melatonin enhanced low-temperature combined with low-light tolerance of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) seedlings by regulating root growth, antioxidant defense system, and osmotic adjustment. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 998293. [Google Scholar]
- Kurt-Celebi, A.; Colak, N.; Torun, H.; Dosedělová, V.; Tarkowski, P.; Ayaz, F.A. Exogenous melatonin ameliorates ionizing radiation-induced damage by modulating growth, osmotic adjustment and photosynthetic capacity in wheat seedlings. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 187, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lou, J.; Wu, C.; Wang, H.; Cao, S.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, F. Melatonin treatment delays postharvest senescence of broccoli with regulation of carotenoid metabolism. Food Chem. 2023, 408, 135185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahcesular, B.; Yildirim, E.D.; Karaçocuk, M.; Kulak, M.; Karaman, S. Seed priming with melatonin effects on growth, essential oil compounds and antioxidant activity of basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) under salinity stress. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 146, 112165. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Lv, P.; Yan, D.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, T.; Li, R. Exogenous melatonin improves seed germination of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under salt stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamayun, M.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, A.L.; Shin, J.H.; Ahmad, B.; Shin, D.H.; Lee, I.J. Exogenous gibberellic acid reprograms soybean to higher growth and salt stress tolerance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7226–7232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Cui, W.; Kamran, M.; Ahmad, I.; Meng, X.; Wu, X.; Han, Q. Exogenous application of melatonin induces tolerance to salt stress by improving the photosynthetic efficiency and antioxidant defense system of maize seedling. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 40, 1270–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, B.; Wu, X.; Lan, R.; Huang, X.; Zheng, Q. Exogenous melatonin improves the growth of rice seedlings by regulating redox balance and ion homeostasis under salt stress. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 41, 2108–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Fu, X.; Zhai, X.; Li, D. Exogenous melatonin promotes the salt tolerance by removing active oxygen and maintaining ion balance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 787062. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, R.J.; Mayo, J.C.; Tan, D.X.; Sainz, R.M.; Alatorre-Jimenez, M.L.; Qin, L. Melatonin as an antioxidant: Under promises but over delivers. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 61, 253–278. [Google Scholar]
- Arnao, M.B.; Hernández-Ruiz, J. Melatonin: A new plant hormone and/or a plant master regulator? Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Zhang, N.A.; Yang, R.C.; Wang, L.; Sun, Q.Q.; Li, D.B.; Guo, Y.D. Melatonin promotes seed germination under high salinity by regulating antioxidant systems, ABA and GA4 interaction in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Rui, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, N.; Dai, M.; Ye, W. Melatonin improves cotton salt tolerance by regulating ROS scavenging system and Ca2+ signal transduction. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 693690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahani, A.A.; Abbas, A.; Hameed, R.; Iqbal, A.; Chen, S.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, R.; Fayyaz, A.; et al. Melatonin in plants: A pleiotropic molecule for abiotic stresses and pathogens infection. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 322, 112387. [Google Scholar]
- Talaat, N.B. Drought stress alleviator melatonin reconfigures water-stressed barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) plants’ photosynthetic efficiency, antioxidant capacity, and endogenous phytohormone profile. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Kazerooni, E.A.; Kang, S.M.; Al–Sadi, A.M.; Lee, I.J. Melatonin enhances the tolerance and recovery mechanisms in Brassica juncea (L.) Czern. under saline conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 593717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.G.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y.P.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, S. Versatile roles of melatonin in growth and stress tolerance in plants. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 41, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.; Tang, M.; Chen, H.; Yang, B.W.; Zhang, F.F.; Huang, Y.H. Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizae on photosynthesis and water status of maize plants under salt stress. Mycorrhiza 2008, 18, 287–296. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.H.; Yang, X.L.; Zou, F.; Huang, S.Q.; Zhou, W.Y.; Xu, Z.W.; Wei, Y.Q. Effects of salt and drought cross stress on germination and physiological characteristics of sweet sorghum seeds. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 23, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiab, F. Exogenous melatonin mitigates the salinity damages and improves the growth of pistachio under salinity stress. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 1468–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Q.; Ye, J.; Wang, B.; Ren, J.; Yin, L.; Deng, X. Melatonin mitigates salt stress in wheat seedlings by modulating polyamine metabolism. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 914. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Lu, B.; Liu, L.; Duan, W.; Jiang, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; et al. Melatonin promotes seed germination under salt stress by regulating ABA and GA3 in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2021, 162, 506–516. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.Y.; Liu, J.L.; Wang, W.X.; Sun, Y. Exogenous melatonin improves growth and photosynthetic capacity of cucumber under salinity-induced stress. Photosynthetica 2016, 54, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zhang, M.C.; He, S.Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Jin, X.J.; Wang, M.X.; Zhang, Y.X.; Hu, G.H. Alleviating effect of melatonin soaking on drought stress during soybean seed germination. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2020, 38, 192–198. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.H.; Chen, R.M.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X. Effects of melatonin on root growth and drought tolerance of maize seedlings. Biotechnol. Bull. 2021, 37, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Vadez, V. Root hydraulics: The forgotten side of roots in drought adaptation. Field Crops Res. 2014, 165, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.W.; Wang, X.P.; Wang, H.B.; Li, G.H.; Tang, M.S.; Cao, Z.X. Effects of salicylic acid application on the growth and physiological characteristics of cotton seedlings under salt stress. Crops 2023, 3, 188–194. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.Y.; Su, W.B.; Fan, F.Y.; Guo, X.X.; Li, Z.; Jian, C.Y.; Tian, L.; Ren, X.Y.; Gong, Q.H. Effects of NaCl stress on growth and physiological characteristics of sugar beet at different seedling stages. Acta Agric. Boreali Sin. 2019, 34, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, Y.T. Physiological Mechanism of Melatonin Regulating Seed Germination and Root Growth of Triticale Under Saline-Alkali Stress; Northeast Agricultural University: Harbin, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, O.; Min, Z.; Yao, X.M. Effects of exogenous melatonin on the growth and ion uptake and photosynthesis of Toona sinensis seedlings under salt stress. Northwest J. Bot. 2019, 39, 2226–2234. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Gai, L.Y.; Zong, H.Y. Foliage application of Chitosan alleviates the adverse effects of cadmium stress in wheat seedlings (Triticum aestivum L). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 164, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Zong, H.Y.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.E.; Chen, X.L.; Li, P.C. Protective effect of chitosan on photosynthesis and antioxidative defense system in edible rape (Brassica rapa L.) in the presence of cadmium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 138, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Li, Z.; Hassan, M.J.; Peng, Y. Chitosan regulates metabolic balance, polyamine accumulation, and Na+ transport contributing to salt tolerance in creeping bentgrass. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Li, W.W.; Ding, Y.F.; Zhong, Q.Y.; Xu, X.; Wei, H.M.; Li, G.H. Exogenous melatonin alleviates salt stress by improving leaf photosynthesis in rice seedlings. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 163, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.Y.; Zhou, G.S.; He, Q.J.; Zhou, H.L. Stomatal limitations to photosynthesis and their critical water conditions in different growth stages of maize under water stress. Agric Water Manag. 2020, 241, 106330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, I.; Kiremit, M.S.; Öztürk, E.; Subrata, B.A.G.; Osman, H.M.; Akay, H.; Arslan, H. Role of melatonin in improving leaf mineral content and growth of sweet corn seedlings under different soil salinity levels. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 288, 110376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggenhauser, M.; Aucour, A.-M.; Telouk, P.; Blommaert, H.; Sarret, G. Changes of cadmium storage forms and isotope ratios in rice during grain filling. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 645150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evelin, H.; Devi, T.S.; Gupta, S.; Kapoor, R. Mitigation of salinity stress in plants by Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Symbiosis: Current understanding and New challenges. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zelm, E.; Zhang, Y.X.; Testerink, C. Salt tolerance mechanisms of plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2020, 71, 403–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Gu, S.J.; Kang, S.Z.; Du, T.S.; Tong, L.; Wood, J.D.; Ding, R.S. Mild water and salt stress improve water use efficiency by decreasing stomatal conductance via osmotic adjustment in field maize. Sci Total Environ. 2020, 805, 150364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Y.; Wei, Z.H.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.Z.; Liu, F.L. Growth and physiological responses of cotton plants to salt stress. Agron. Crop Sci. 2021, 207, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathokleous, E.; Feng, Z.Z.; Peñuelas, J. Chlorophyll hormesis: Are chlorophylls major components of stress biology in higher plants? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.E.; Mao, J.J.; Sun, L.Q.; Huang, B.; Ding, C.B.; Gu, Y.; Liao, J.Q.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Z.W.; Yuan, S. Exogenous melatonin enhances salt stress tolerance in maize seedlings by improving antioxidant and photosynthetic capacity. Physiol. Plant. 2018, 164, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, A.; Neelofar, H.; Zainul, A.; Faisal, Z.; Anam, M.; Muhammad, N.; Ali, E.K. Exogenous melatonin application stimulates growth, photosynthetic pigments and antioxidant potential of white beans under salinity stress. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023, 160, 219–228. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, M.H.; Khan, M.N.; Mohammad, F.; Khan, M.M.A. Role of nitrogen and gibberellin (GA3) in the regulation of enzyme activities and in osmoprotectant accumulation in Brassica juncea L. under salt stress. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2008, 194, 214–224. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y. Effects of melatonin on photosynthetic performance and antioxidants in melon during cold and recovery. Biol. Plant. 2017, 61, 571–578. [Google Scholar]
- Nishihara, E.; Kondo, K.; Takahashi, K.; Parvez, M.M.; Watanabe, K.; Tanaka, K. Role of 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) on active oxygen-scavenging system in NaCl treated spinach (Spinacia oleracea). J. Plant Physiol. 2003, 160, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Van Aken, O.; Schwarzländer, M.; Belt, K.; Millar, A.H. The roles of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in cellular signaling and Stress response in plants. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 1551–1559. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, P.; Albalawi, T.H.; Altalayan, F.H.; Bakht, M.A.; Ahanger, M.A.; Raja, V.; Ashraf, M.; Ahmad, P. 24-Epibrassinolide (EBR) confers tolerance against NaCl stress in soybean plants by up-regulating antioxidant system, ascorbate-glutathione cycle, and glyoxalase system. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Shi, J.; Qi, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, T. Integrated physiological, transcriptomic, and proteomic analyses reveal the regulatory role of melatonin in tomato plants’ response to low night temperature. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchester, L.C.; Coto-Montes, A.; Boga, J.A.; Andersen, L.P.H.; Zhou, Z.; Galano, A.; Vriend, J.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin: An ancient molecule that makes oxygen metabolically tolerable. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 59, 403–419. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, M.H.; Alamri, S.; Al-Khaishany, M.Y.; Khan, M.N.; Al-Amri, A.; Ali, H.M.; Alsahli, A.A. Exogenous melatonin counteracts NaCl-induced damage by regulating the antioxidant system, proline and carbohydrates metabolism in tomato seedlings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chang, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Gu, X.; Wei, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X. Exogenous melatonin confers salt stress tolerance to watermelon by improving photosynthesis and redox homeostasis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 295. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, D.; Ni, Z.; Xia, H.; Xie, Y.; Lv, X.; Wang, J.; Lin, L.; Deng, Q.; Luo, X. Exogenous melatonin promotes biomass accumulation and photosynthesis of kiwifruit seedlings under drought stress. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 246, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.S.; Guo, S.; Baloch, A.R.; Sun, J.; Shu, S.; Wang, Y.; Ahammed, G.J.; Kabir, K.; Roy, R. Melatonin alleviates nickel phytotoxicity by improving photosynthesis, secondary metabolism and oxidative stress tolerance in tomato seedlings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, S.; Wang, J.; Mo, J. Alleviating effects of exogenous melatonin on salt stress in cucumber. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 262, 109070. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, M.A.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, C.; Shireen, F.; Zheng, Z.; Imtiaz, M.; Bie, Z.; Huang, Y. Melatonin pretreatment improves vanadium stress tolerance of watermelon seedlings by reducing vanadium concentration in the leaves and regulating melatonin biosynthesis and antioxidant-relatd gene expression. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 220, 115–127. [Google Scholar]
- Yabuta, Y.; Motoki, T.; Yoshimura, K.; Takeda, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Shigeoka, S. Thylakoid membrane-bound ascorbate peroxidase is a limiting factor of antioxidative systems under photo-oxidative stress. Plant J. 2002, 32, 915–925. [Google Scholar]
- Hojati, M.; Modarres-Sanavy, S.A.M.; Karimi, M.; Ghanati, F. Responses of growth and antioxidant systems in Carthamus tinctorius L. under water deficit stress. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2011, 33, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Selote, D.S.; Khanna-Chopra, R. Drought acclimation confers oxidative stress tolerance by inducing co-ordinated antioxidant defense at cellular and subcellular level in leaves of wheat seedlings. Physiol. Plant. 2006, 127, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, L.; Rodriguez-Concepcion, M. Open avenues for carotenoid biofortification of plant tissues. Plant Commun. 2023, 4, 100466. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, W.T.; Zheng, X.Y.; Chen, X.C.; Wang, W.J.; Liu, A.R.; Ji, J.; Wang, G.; Guan, C.F. The potential roles of carotenoids in enhancing phytoremediation of bisphenol A contaminated soil by promoting plant physiology and modulating rhizobacterial community of tobacco. Chemosphere 2020, 316, 137807. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.D.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, Z.C.; Zhang, Y.J.; Sun, H.C.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.D.; Bai, Z.Y.; Li, C.D.; Liu, L.T. Melatonin improves the germination rate of cotton seeds under drought stress by opening pores in the seed coat. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, R.Y.; Song, X.M.; Shen, J.; Jia, L.X.; Cheng, Y.A.; Ma, J.X.; Zhang, X. Effect of foliar spraying melatonin on growth and physiological characteristics of pumpkin seedlings under cold stress. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2023, 43, 805–813. [Google Scholar]
- Azevedo Neto, A.D.; Prisco, J.T.; Gomes-Filho, E. Changes in soluble amino-N, soluble proteins and free amino acids in leaves and roots of salt-stressed maize genotypes. J. Plant Interact. 2009, 4, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Bai, B. Alleviating effects of exogenous melatonin on soybeans under salt stress. North China Agric. J. 2024, 39, 116–125. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.N.; Zhang, J.; Luo, T.; Liu, J.; Rizwan, M.; Fahad, S.; Xu, Z.; Hu, L. Seed priming with melatonin coping drought stress in rapeseed by regulating reactive oxygen species detoxification: Antioxidant defense system, osmotic adjustment, stomatal traits and chloroplast ultrastructure perseveration. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 140, 111597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, L.J.; Jin, X.X. Mechanism of heavy metal tolerance stress of plants. China Biotechnol. 2015, 35, 94–104. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Jiang, X.Y.; Chen, Z.C.; Chen, R.N.; Wang, H.M.; Cao, L.; Jin, X.J.; Ren, C.Y.; Wang, M.X.; Zhang, M.C.; et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on photosynthetic fluorescence and antioxidant system of soybean V1 seedlings under low temperature. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2020, 42, 640–648. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.; Duan, M.M.; Wen, K.; Jiang, H.Q.; Liang, X.E.; Mi, Y.; Nian, H. Effects of exogenous melatonin on seedling growth and physiological characteristics of soybean under copper stress. J. South China Agric. Univ. 2023, 44, 780–786. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yu, B.; Cui, Y.; Yin, Y. Melatonin application confers enhanced salt tolerance by regulating Na+ and Cl− accumulation in rice. Plant Growth Regul. 2017, 83, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Ye, J.; Yin, L.; Li, G.; Deng, X.; Wang, S. Exogenous melatonin improves salt tolerance by mitigating osmotic, ion, and oxidative stresses in maize seedlings. Agronomy 2020, 10, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Tao, M.; Yuan, F.; Liu, L.; Wu, F.; Wu, X.; Xiang, Y.; Niu, Y.; Liu, F.; et al. Plant cell-surface GIPC sphingolipids sense salt to trigger Ca2+ influx. Nature 2019, 572, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaya, C.; Okant, M.; Ugurlar, F.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ashraf, M.; Ahmad, P. Melatonin-mediated nitric oxide improves tolerance to cadmium toxicity by reducing oxidative stress in wheat plants. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z. Study on the Regulatory Function of Water-Retaining Slow-Release Fertilizer and Melatonin on Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings; Nanjing Agricultural University: Nanjing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, L.; Sun, Z. Impact of melatonin treatment on corn seed germination under drought stress. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2019, 47, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.T.; Jiao, Q.J.; Fan, L.N.; Jiang, Y.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, P.; Chen, Y.L.; Zhu, M.; Liu, H.P.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Integrated physio-biochemical and transcriptomic analysis revealed mechanism underlying of Si-mediated alleviation to cadmium toxicity in wheat. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131366. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Zheng, D.; Feng, N.; Zhou, H.; Mu, D.; Liu, L.; Zhao, L.; Shen, X.; Rao, G.; Li, T. Effects of exogenous salicylic acid and abscisic acid on growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant system of rice. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2022, 82, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Jessup, W.; Dean, R.T.; Gebicki, J.M. Iodometric determination of hydroperoxides in lipids and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1994, 233, 289–303. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.J.; Yu, X.Z.; Li, Y.H.; Yang, L. Inhibition of the mitochondrial respiratory components (Complex I and Complex III) as stimuli to induce oxidative damage in Oryza sativa L. under thiocyanate exposure. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125472. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Principles and Techniques of Plant Physiological and Biochemical Experiments; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, Y.; Asada, K. Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol. 1981, 22, 867–880. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Zheng, D.; Feng, N.; Zhou, H.; Mu, D.; Zhao, L.; Shen, X.; Rao, G.; Meng, F.; Huang, A. Physiological mechanisms of ABA-induced salinity tolerance in leaves and roots of rice. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8228. [Google Scholar]
- Guri, A. Variation in glutathione and ascorbic acid content among selected cultivars of Phaseolus vulgaris prior to and after exposure to ozone. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1983, 63, 733–737. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, D.; Horneck, D.A. Determination of Potassium and Sodium by Flame Emission Spectrophotometry. In Handbook of Reference Methods for Plant Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
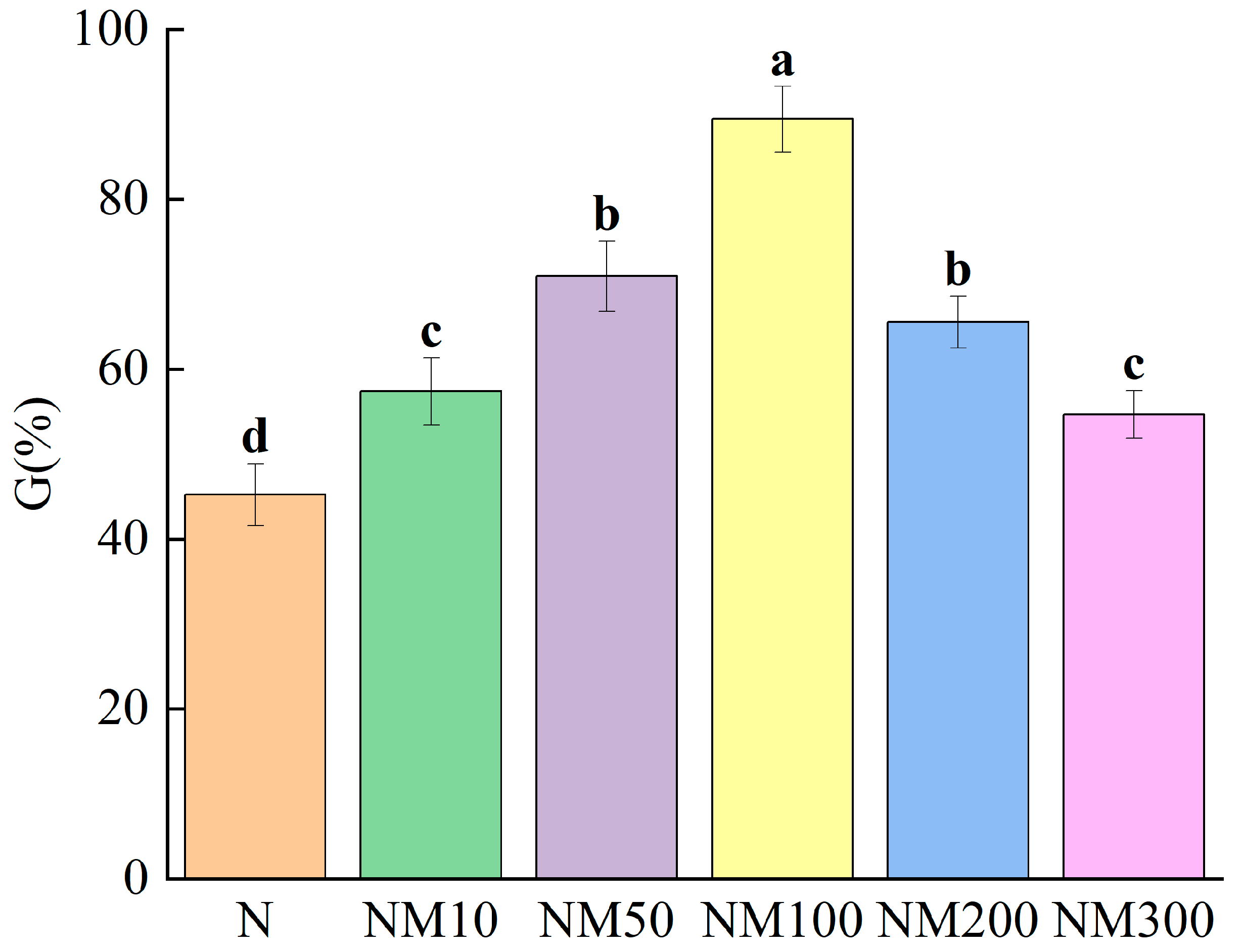
| Treatment | The Seedling Growth Indicators | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RL (cm) | SL (cm) | RFW (g) | SFW (g) | RDW (g) | SDW (g) | SLA (cm2) | |
| N | 0.70 ± 0.02 e | 0.31 ± 0.03 e | 0.24 ± 0.03 d | 0.37 ± 0.03 d | 0.024 ± 0.002 d | 0.043 ± 0.003 d | 18.53 ± 0.22 d |
| NM10 | 1.81 ± 0.06 c | 0.98 ± 0.03 c | 0.34 ± 0.05 c | 0.52 ± 0.04 c | 0.041 ± 0.003 bc | 0.053 ± 0.006 c | 20.95 ± 0.34 c |
| NM50 | 2.48 ± 0.06 b | 1.04 ± 0.03 c | 0.46 ± 0.05 b | 0.68 ± 0.04 b | 0.043 ± 0.003 bc | 0.071 ± 0.003 b | 23.73 ± 0.48 b |
| NM100 | 3.78 ± 0.04 a | 1.68 ± 0.04 a | 0.68 ± 0.04 a | 0.98 ± 0.05 a | 0.064 ± 0.004 a | 0.096 ± 0.003 a | 27.91 ± 0.43 a |
| NM200 | 2.60 ± 0.09 b | 1.16 ± 0.06 b | 0.50 ± 0.04 b | 0.71 ± 0.05 b | 0.047 ± 0.005 b | 0.066 ± 0.006 b | 24.28 ± 0.39 b |
| NM300 | 1.45 ± 0.04 d | 0.86 ± 0.04 d | 0.33 ± 0.03 c | 0.49 ± 0.04 c | 0.040 ± 0.003 c | 0.042 ± 0.003 d | 20.25 ± 0.27 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, H.; Liu, J.; Hua, J.; Xiong, M.; Song, H.; Yong, C. Effect of Exogenous Melatonin on Corn Seed Germination and Seedling Salt Damage Mitigation Under NaCl Stress. Plants 2025, 14, 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071139
Zhang Y, Li Y, Liu H, Xie H, Liu J, Hua J, Xiong M, Song H, Yong C. Effect of Exogenous Melatonin on Corn Seed Germination and Seedling Salt Damage Mitigation Under NaCl Stress. Plants. 2025; 14(7):1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071139
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuyu, Yuchuang Li, He Liu, Haili Xie, Jiani Liu, Jinzhu Hua, Mingchun Xiong, Huaifei Song, and Chengjian Yong. 2025. "Effect of Exogenous Melatonin on Corn Seed Germination and Seedling Salt Damage Mitigation Under NaCl Stress" Plants 14, no. 7: 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071139
APA StyleZhang, Y., Li, Y., Liu, H., Xie, H., Liu, J., Hua, J., Xiong, M., Song, H., & Yong, C. (2025). Effect of Exogenous Melatonin on Corn Seed Germination and Seedling Salt Damage Mitigation Under NaCl Stress. Plants, 14(7), 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071139





