Integrated Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Reveal Key Genes and Metabolic Pathway in Flower and Fruit Color Formation of Cerasus humilis (Bge.) Sok
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
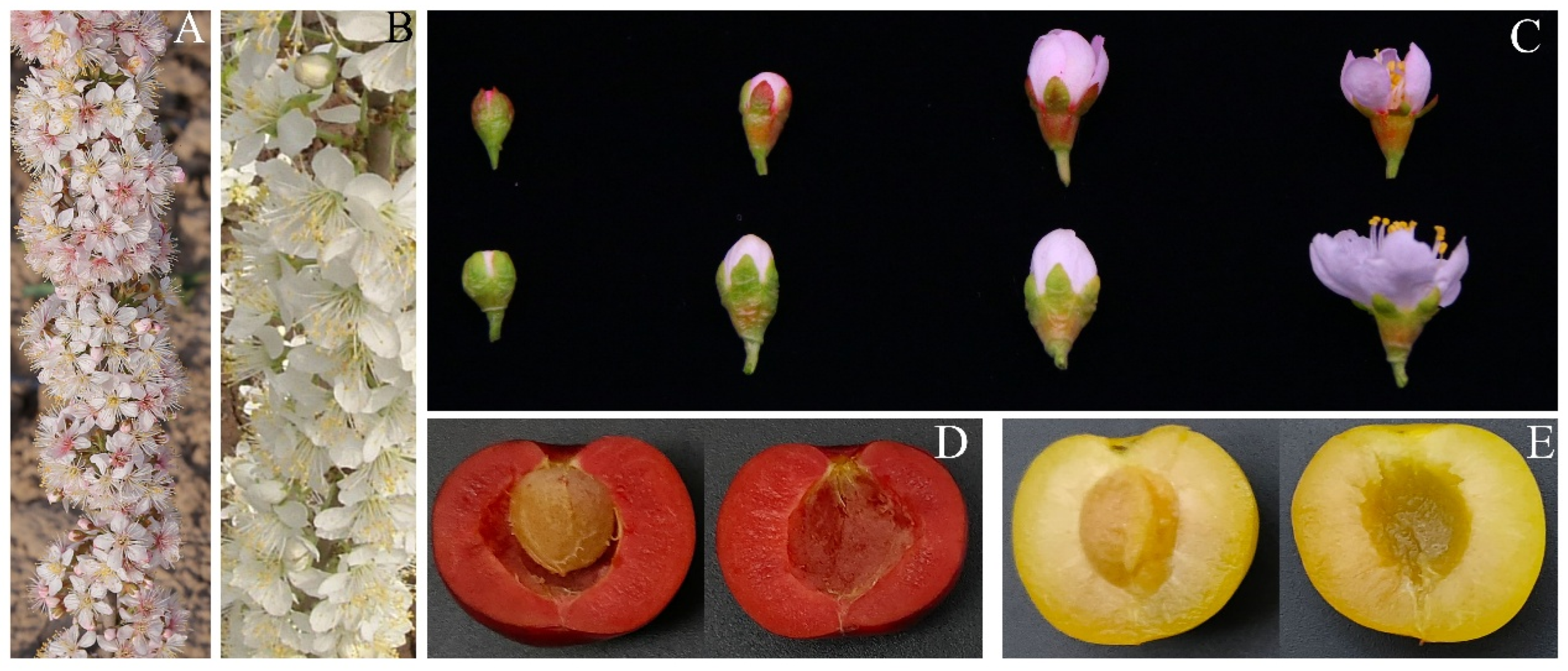
2.1. Phenotypic Differences in Flowers and Fruits of ‘Jinou 1’ and ‘Nongda 5’
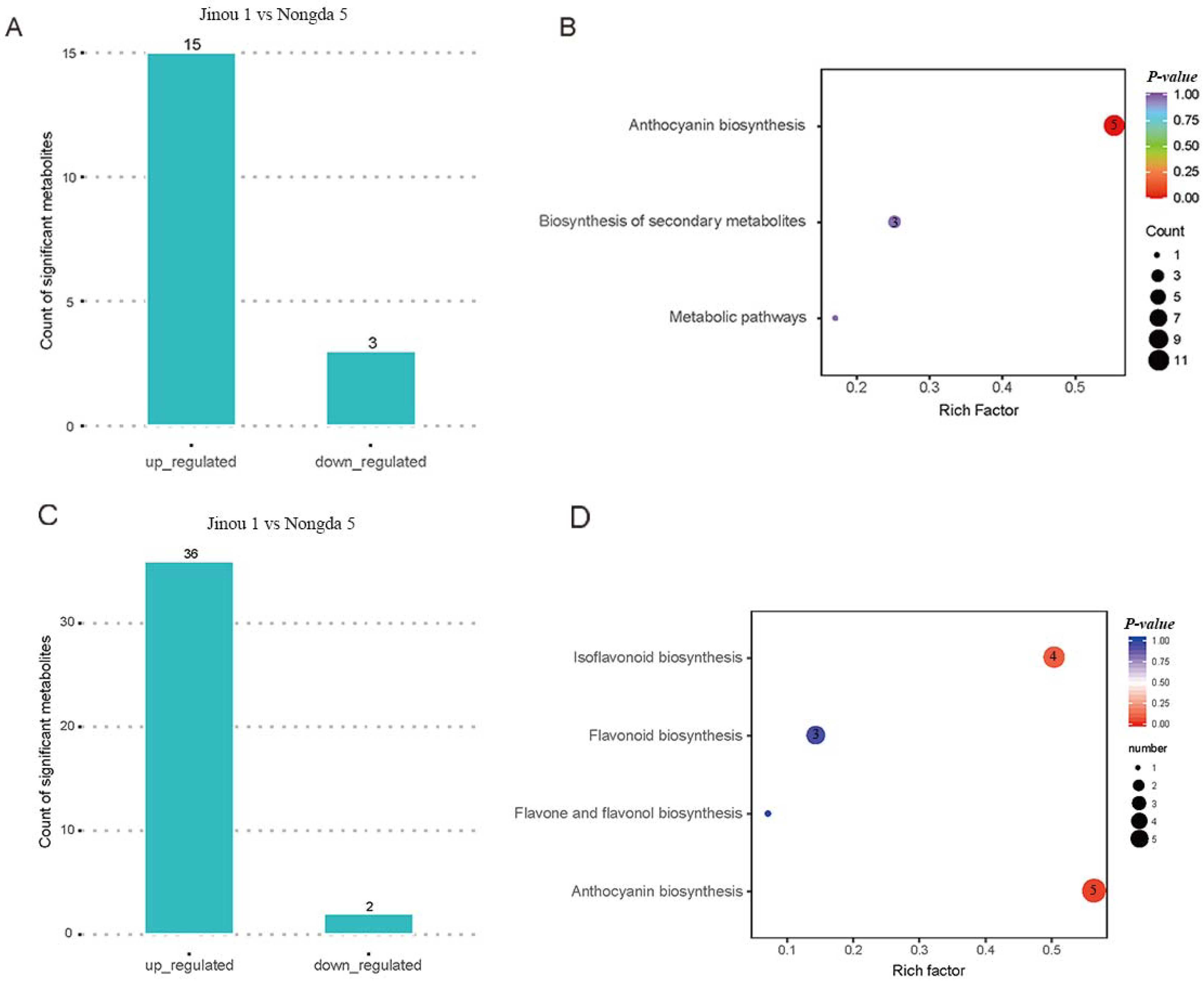
2.2. Metabolomic Analysis of Flowers and Fruits of ‘Jinou 1’ and ‘Nongda 5’
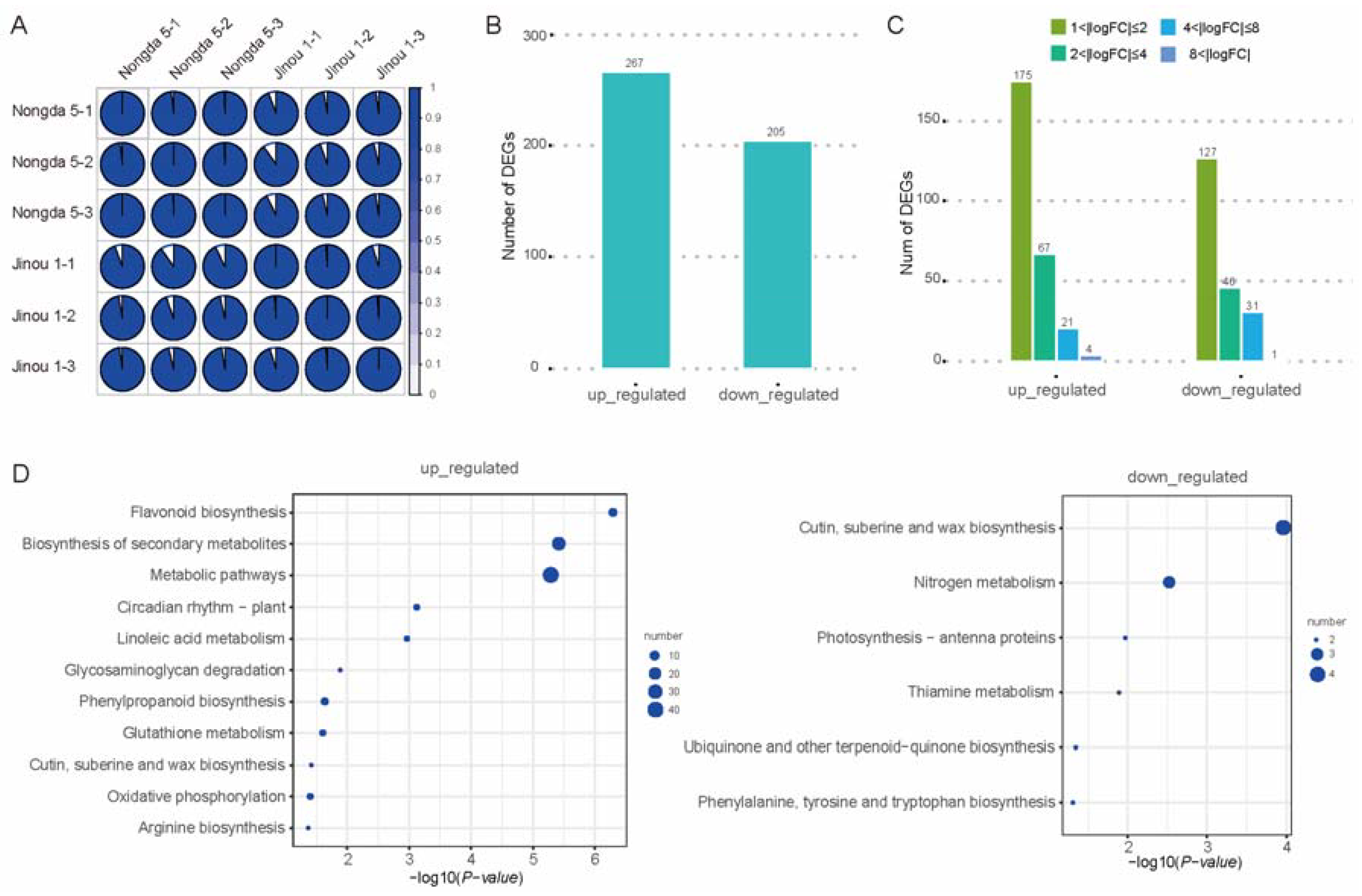
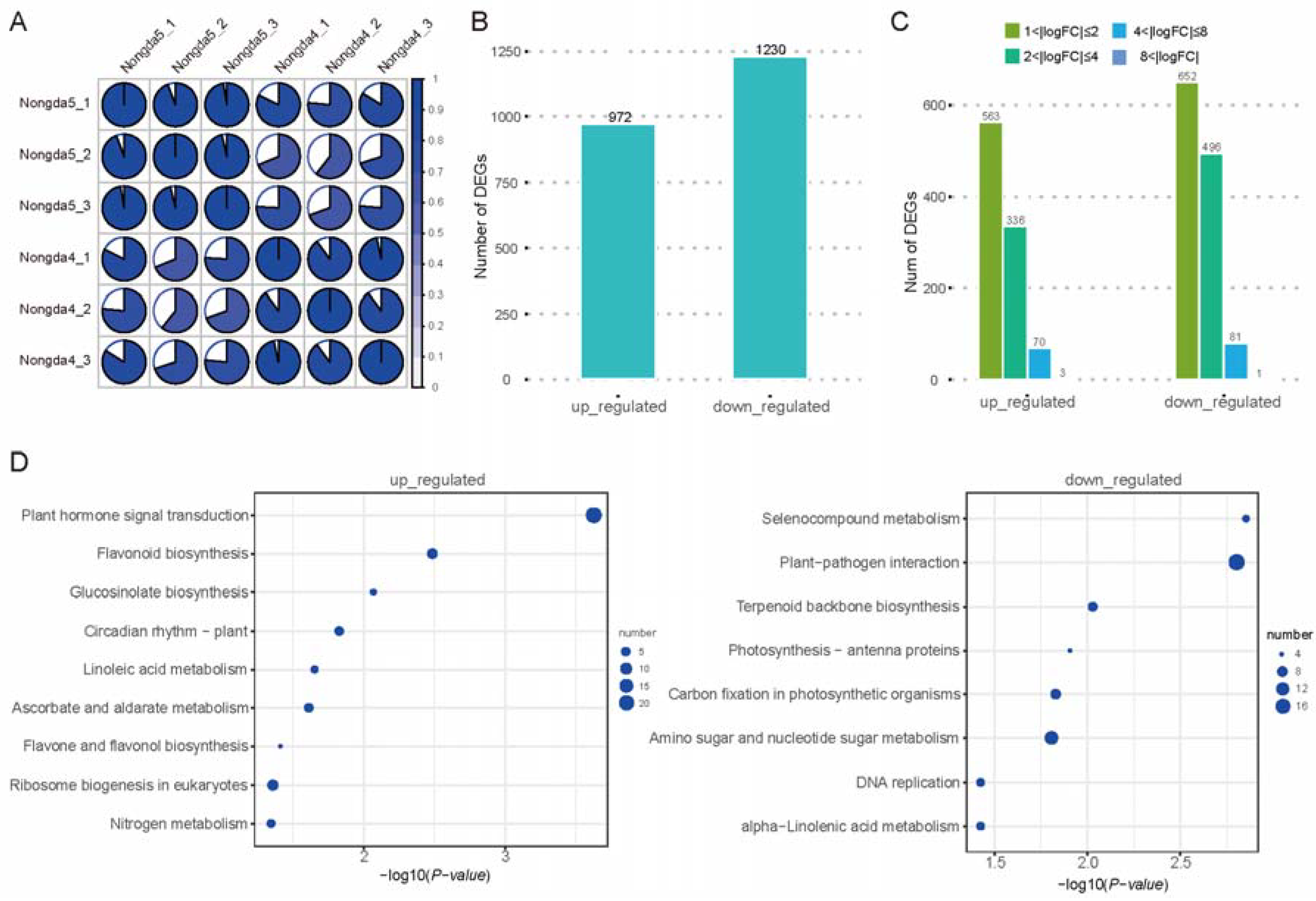
2.3. Transcriptomic Analysis of Flowers and Fruits of ‘Jinou 1’ and ‘Nongda 5’
2.4. Analysis of Anthocyanin Pathway Genes in Flowers and Fruits
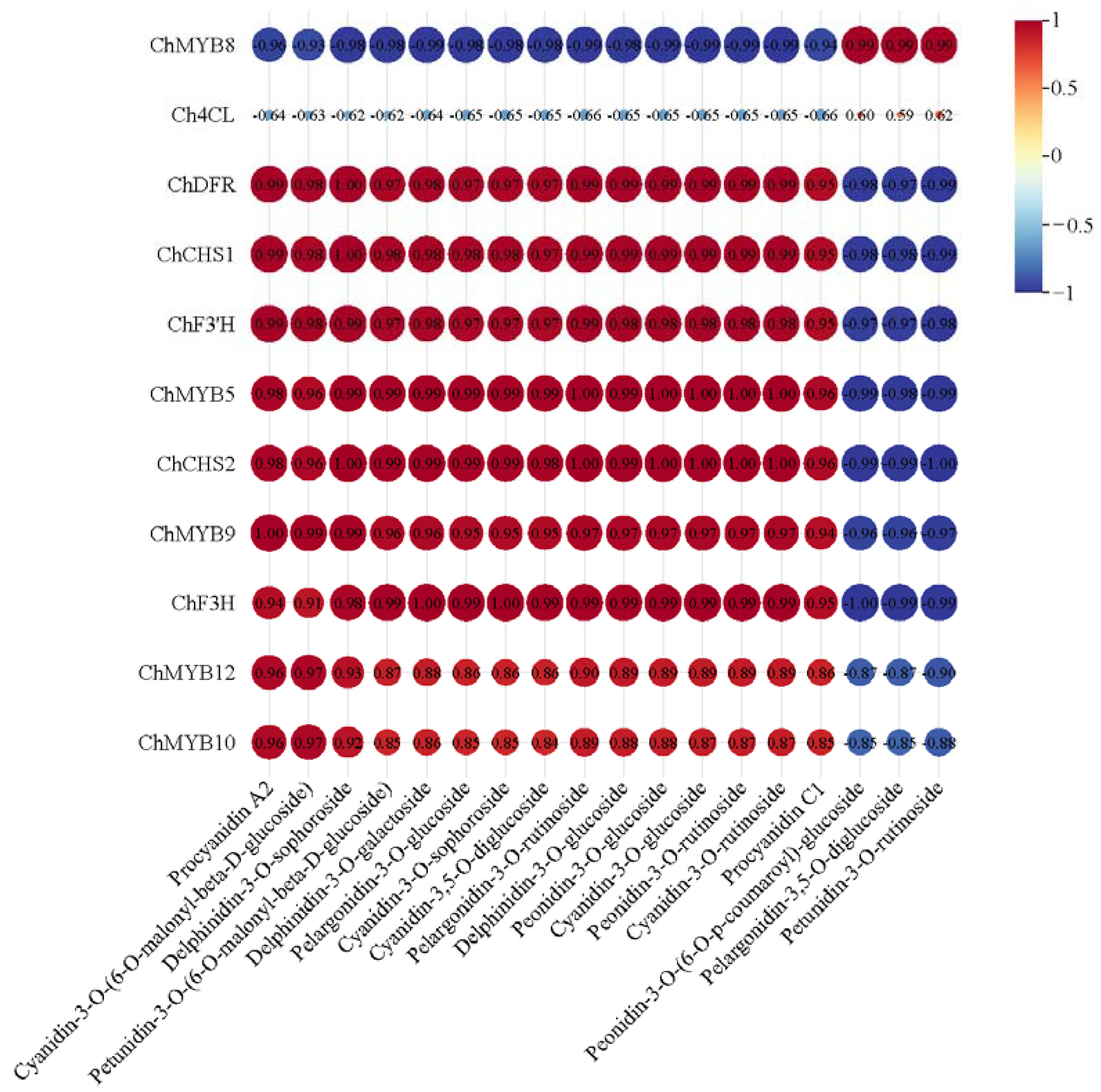
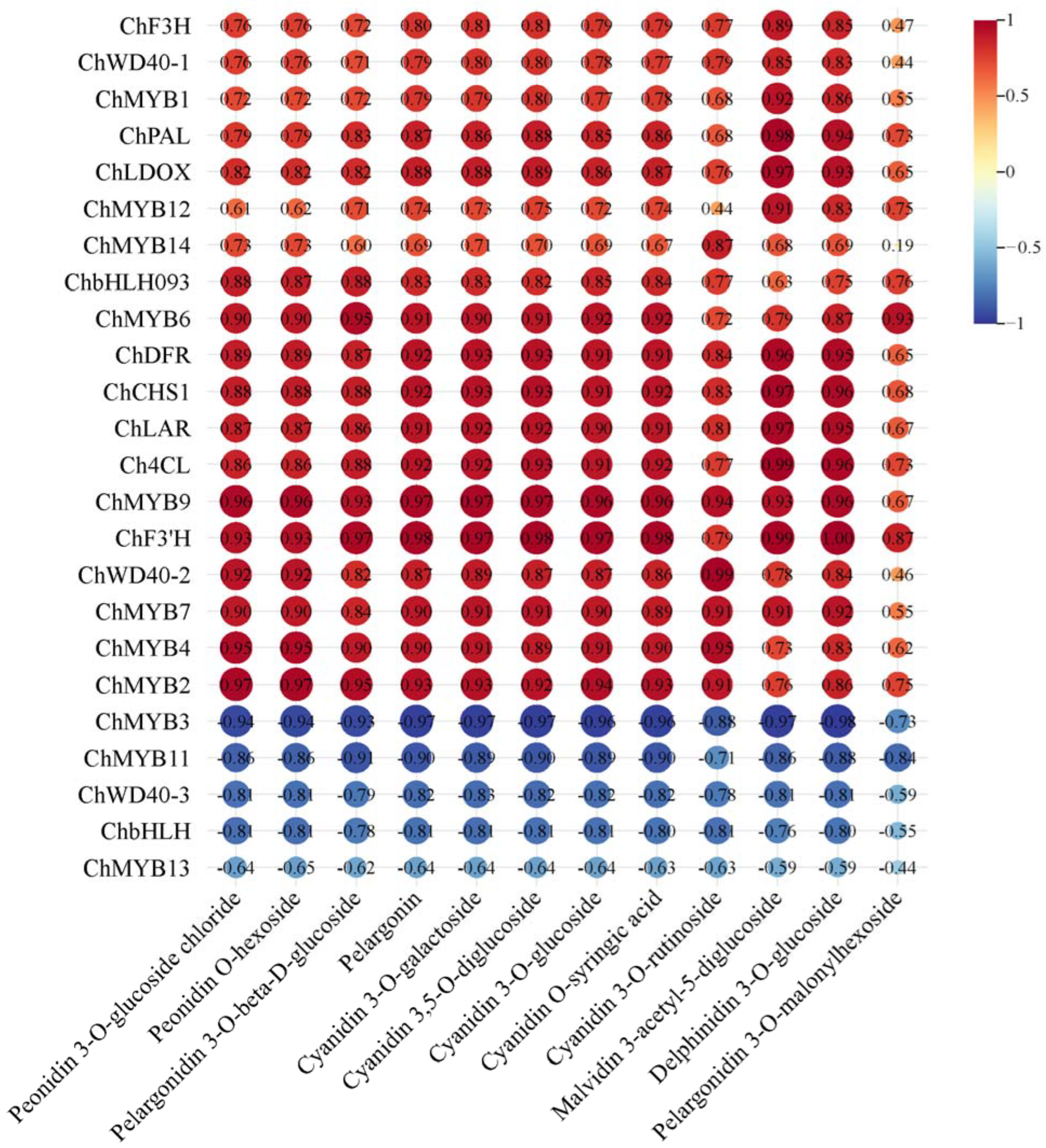
2.5. Correlation Analysis of Transcriptome and Metabolome of ‘Jinou 1’ and ‘Nongda 5’ Flowers and Fruits
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Metabolomic Analysis
4.3. Transcriptome Analysis
4.4. Differential Expression Analysis and Gene Annotation
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, P.; Mu, X.; Du, J.; Gao, Y.; Bai, D.; Jia, L.; Zhang, J.; Ren, H.; Xue, X. Flavonoid content and radical scavenging activity in fruits of Chinese dwarf cherry (Cerasus humilis) genotypes. J. For. Res. 2018, 29, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.J. Prunus Humilis (Ouli), a Unique Forest Fruit Species Endemic to China; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Koes, R.; Verweij, W.; Quattrocchio, F. Flavonoids: A colorful model for the regulation and evolution of biochemical pathways. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 236–242. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Park, T.K.; Kim, Y.P.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, T.W. Transcription factors BZR1 and PAP1 cooperate to promote anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis shoots. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 3654–3673. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.; Du, J.; Zhu, D.; Li, X.; Li, X. Metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses of anthocyanin biosynthesis mechanisms in the color mutant Ziziphus jujuba cv. Tailihong. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 15186–15198. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, D.; Zhang, H.; Lai, B.; Liu, L.; Pan, X.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Shi, S.; Wei, Y. Integrative analysis of the coloring mechanism of red Longan pericarp through metabolome and transcriptome analyses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1806–1815. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, R.A.; Liu, C.; Jun, J.H. Metabolic engineering of anthocyanins and condensed tannins in plants. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Qiu, J.; Yang, G.; Huang, S.; Yin, J. Isolation and characterization of a R2R3-MYB transcription factor gene related to anthocyanin biosynthesis in the spathes of Anthurium andraeanum (Hort.). Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 2151–2165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Liu, H.; Lou, Q.; Liu, Y. Ectopic expression of the grape hyacinth (Muscari armeniacum) R2R3-MYB transcription factor gene, MaAN2, induces anthocyanin accumulation in tobacco. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1722–1723. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Fang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, F.; Chen, X.; Wang, N. MdMYB305-MdbHLH33-MdMYB10 regulates sugar and anthocyanin balance in red-fleshed apple fruits. Plant J. 2023, 113, 1062–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wei, B.; Li, Y.; Fang, X.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, L. Transcription factor MdNAC33 is involved in ALA-induced anthocyanin accumulation in apples. Plant Sci. 2024, 339, 111949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepiniec, L.; Debeaujon, I.; Routaboul, J.M.; Baudry, A.; Pourcel, L.; Nesi, N.; Caboche, M. Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Dubos, C.; Lepiniec, L. Transcriptional control of flavonoid biosynthesis by MYB-bHLH-WDR complexes. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, A.; Zhao, M.; Leavitt, J.M.; Lloyd, A.M. Regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway by the TTG1/b HLH/Myb transcriptional complex in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J. 2008, 53, 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Peng, Q.; Zhao, J.; Owiti, A.; Ren, F.; Liao, L.; Wang, L.; Deng, X.; Jiang, Q.; Han, Y. Multiple R2R3-MYB transcription factors involved in the regulation of anthocyanin accumulation in peach flower. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wu, J.; Hu, K.D.; Wei, S.W.; Sun, H.Y.; Hu, L.Y.; Han, Z.; Yao, G.F.; Zhang, H. PyWRKY26 and PybHLH3 cotargeted the PyMYB114 promoter to regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis and transport in red-skinned pears. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, S.; Wang, H.; Ming, F. The MYB transcription factor RcMYB1 plays a central role in rose anthocyanin biosynthesis. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yin, L.; Qu, P.; Wang, P.; Mu, X.; Zhang, S.; Xie, P.; Cheng, C.; et al. Comparison of bioactive compounds and antioxidant activities in differentially pigmented Cerasus humilis fruits. Molecules 2023, 28, 6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Gong, Z.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shao, A.; Li, H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, J. ChBBX6 and ChBBX18 are positive regulators of anthocyanins biosynthesis and carotenoids degradation in Cerasus humilis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 137195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Tao, J. Recent advances on the development and regulation of flower color in ornamental plants. Front Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Liao, L.; Li, L.; Xu, Q. A novel histone methyltransferase gene CsSDG40 positively regulates carotenoid biosynthesis during citrus fruit ripening. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, 2633–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipollini, M.; Levey, D.J. Antifungal activity of Solanum fruit glycoalkaloids: Implications for frugivory and seed dispersal. Ecology 1997, 78, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Ni, N.; Sun, S.; Nie, M.; Du, W.; Irfan, M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L. Transcription factors LvBBX24 and LvbZIP44 coordinated anthocyanin accumulation in response to light in lily. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhae211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.J.; Peng, J.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, A.; Jiang, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, F. CmBBX28-CmMYB9a module regulates petal anthocyanin accumulation in response to light in Chrysanthemum. Plant Cell Environ. 2025, early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Tao, J.; Zhao, D. Tree peony R2R3-MYB transcription factor PsMYB30 promotes petal blotch formation by activating the transcription of anthocyanin synthase gene. Plant Cell Physiol. 2022, 63, 1101–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.Q.; Zhou, X.L.; Lyu, Z.Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, L.; Shen, S.K. Anthocyanin accumulation underlies petal blotch coloration in Rhododendron rex and its medicinal potential. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 224, 120335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Yang, R.; Wang, Q.; Gao, L.; Li, S.; Li, L.; Chen, M.; Jiang, S.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.; et al. Multi-omics analysis uncovers novel gene regulatory networks of flower coloration in Lagerstroemia indica. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 216, 118710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, K.; Cooney, J.M.; Wang, T.; Espley, R.V.; Allan, A.C. Differential regulation of the anthocyanin profile in purple kiwifruit (Actinidia species). Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; He, W.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Tang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Comparative metabolomics profiling highlights unique color variation and bitter taste formation of Chinese cherry fruits. Food Chem. 2024, 439, 138072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, H.; Wu, Y.; Lyu, L.; Wu, W.; Li, W. Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics analysis unveil flavonoid and anthocyanin metabolism in pink and blue blueberry cultivars. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 327, 112798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Tao, R.; Tang, Y.; Yin, L.; Ma, Y.; Ni, J.; Yan, X.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zeng, Y.; et al. BBX16, a B-box protein, positively regulates light-induced anthocyanin accumulation by activating MYB10 in red pear. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1985–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubos, C.; Stracke, R.; Grotewold, E.; Weisshaar, B.; Martin, C.; Lepiniec, L. MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia, A.; Heredia-Guerrero, J.; Domínguez, E. CHS silencing suggests a negative cross-talk between wax and flavonoid pathways in tomato fruit cuticle. Plant Signal Behav. 2015, 10, e1019979. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Shen, W.; Mohtar, C.A.E.; Zhao, X.; Gmitter, F.G., Jr. Functional study of CHS gene family members in citrus revealed a novel CHS gene affecting the production of flavonoids. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 189. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.; Tian, M.; An, G.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Yan, C. Rapid identification of the purple stem (Ps) gene of Chinese kale (Brassica oleracea var. alboglabra) in a segregation distortion population by bulked segregant analysis and RNA sequencing. Mol. Breed. 2017, 37, 153. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Liu, C.; Zhao, A.; Yu, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Y. A MITE insertion in the promoter region of anthocyanidin synthase from Morus alba L. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 36, 188–194. [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.; Tao, R.; Liu, W.; Yu, C.; Yue, Z.; He, S.; Lavelle, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; An, G.; et al. Characterization of four polymorphic genes controlling red leaf colour in lettuce that have undergone disruptive selection since domestication. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Osbourn, A.; Ma, P. MYB transcription factors as regulators of phenylpropanoid metabolism in plants. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 689–708. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shan, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Gao, R.; Zhou, L.; Bao, T.; Han, T.; Wang, S.; Gao, X.; Wang, L. A functional homologue of Arabidopsis TTG1 from Freesia interacts with bHLH proteins to regulate anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynjournal in both Freesia hybrida and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 141, 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Tang, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Guo, X.; Lu, H.; Yang, Y.; Fang, C.; Niu, X.; et al. A MYB/bHLH complex regulates tissue specific anthocyanin biosynjournal in the inner pericarp of red-centered kiwifruit Actinidia chinensis cv. Hongyang. Plant J. 2019, 99, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, S. GLABRA2, a common regulator for epidermal cell fate determination and anthocyanin biosynjournal in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4997. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, S.; Zhao, D.; Peng, C.; Tan, C.; Wang, Q.; Gong, J. Effects of theabrownin on serum metabolites and gut microbiome in rats with a high-sugar diet. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 7063–7080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X.; Mu, X.; Du, J. Organic acid metabolism in Chinese dwarf cherry [Cerasus humilis (Bge.) Sok.] is controlled by a complex gene regulatory network. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 982112. [Google Scholar]
- Verde, I.; Jenkins, J.; Dondini, L.; Micali, S.; Pagliarani, G.; Vendramin, E.; Paris, R.; Aramini, V.; Gazza, L.; Rossini, L.; et al. The Peach v2.0 release: High-resolution linkage mapping and deep resequencing improve chromosome-scale assembly and contiguity. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 225. [Google Scholar]
- Pertea, M.; Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Leek, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, I.L.; Wolfgang, H.; Simon, A. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Li, T.; Liu, S.; Qi, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jia, L.; Wang, P.; Mu, X. Integrated Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Reveal Key Genes and Metabolic Pathway in Flower and Fruit Color Formation of Cerasus humilis (Bge.) Sok. Plants 2025, 14, 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071103
Zhang S, Li T, Liu S, Qi X, Yang Y, Zhang J, Jia L, Wang P, Mu X. Integrated Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Reveal Key Genes and Metabolic Pathway in Flower and Fruit Color Formation of Cerasus humilis (Bge.) Sok. Plants. 2025; 14(7):1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071103
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shuai, Tianyuan Li, Shan Liu, Xinliang Qi, Yu Yang, Jiancheng Zhang, Luting Jia, Pengfei Wang, and Xiaopeng Mu. 2025. "Integrated Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Reveal Key Genes and Metabolic Pathway in Flower and Fruit Color Formation of Cerasus humilis (Bge.) Sok" Plants 14, no. 7: 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071103
APA StyleZhang, S., Li, T., Liu, S., Qi, X., Yang, Y., Zhang, J., Jia, L., Wang, P., & Mu, X. (2025). Integrated Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Reveal Key Genes and Metabolic Pathway in Flower and Fruit Color Formation of Cerasus humilis (Bge.) Sok. Plants, 14(7), 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14071103





