Effect of Temperature and Covering Structures in Seed Dormancy and Germination Traits of Manchurian Striped Maple (Acer tegmentosum Maxim.) Native to Northeast Asia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Samara Characteristics
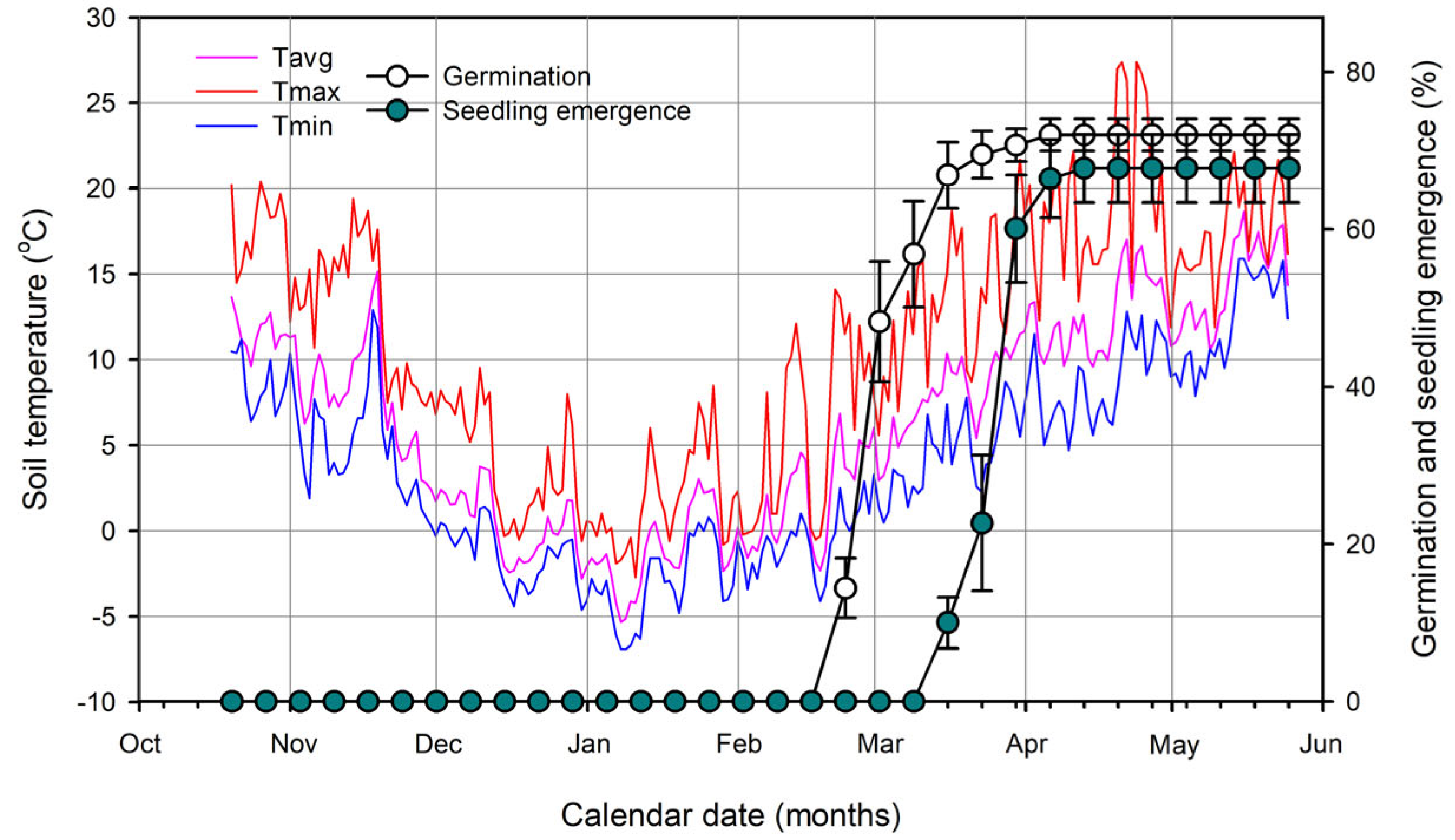
2.2. Phenology of Germination and Seedling Emergence in the Field
2.3. Move-Along Experiments
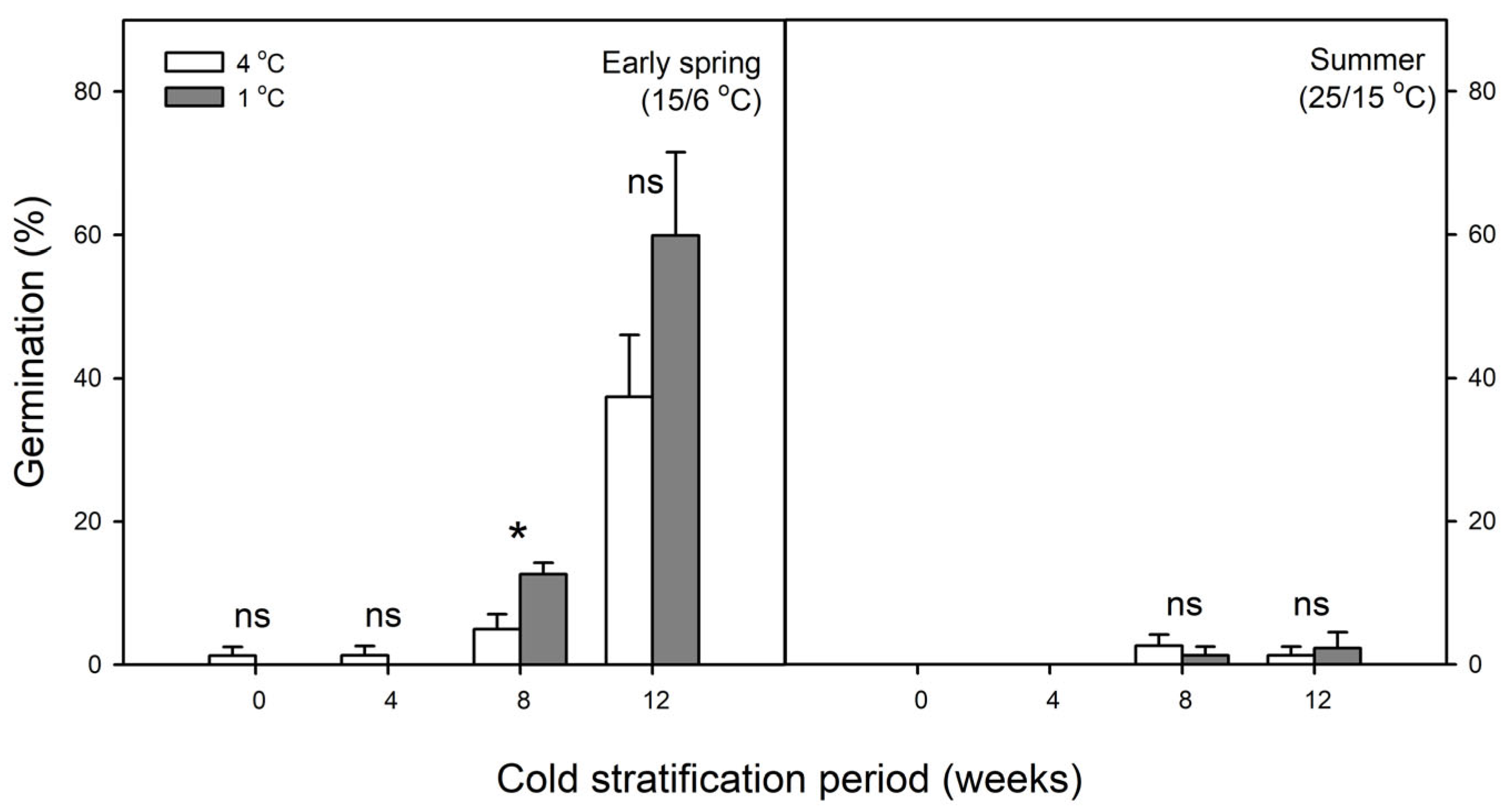
2.4. Effect of Cold Stratification on Germination
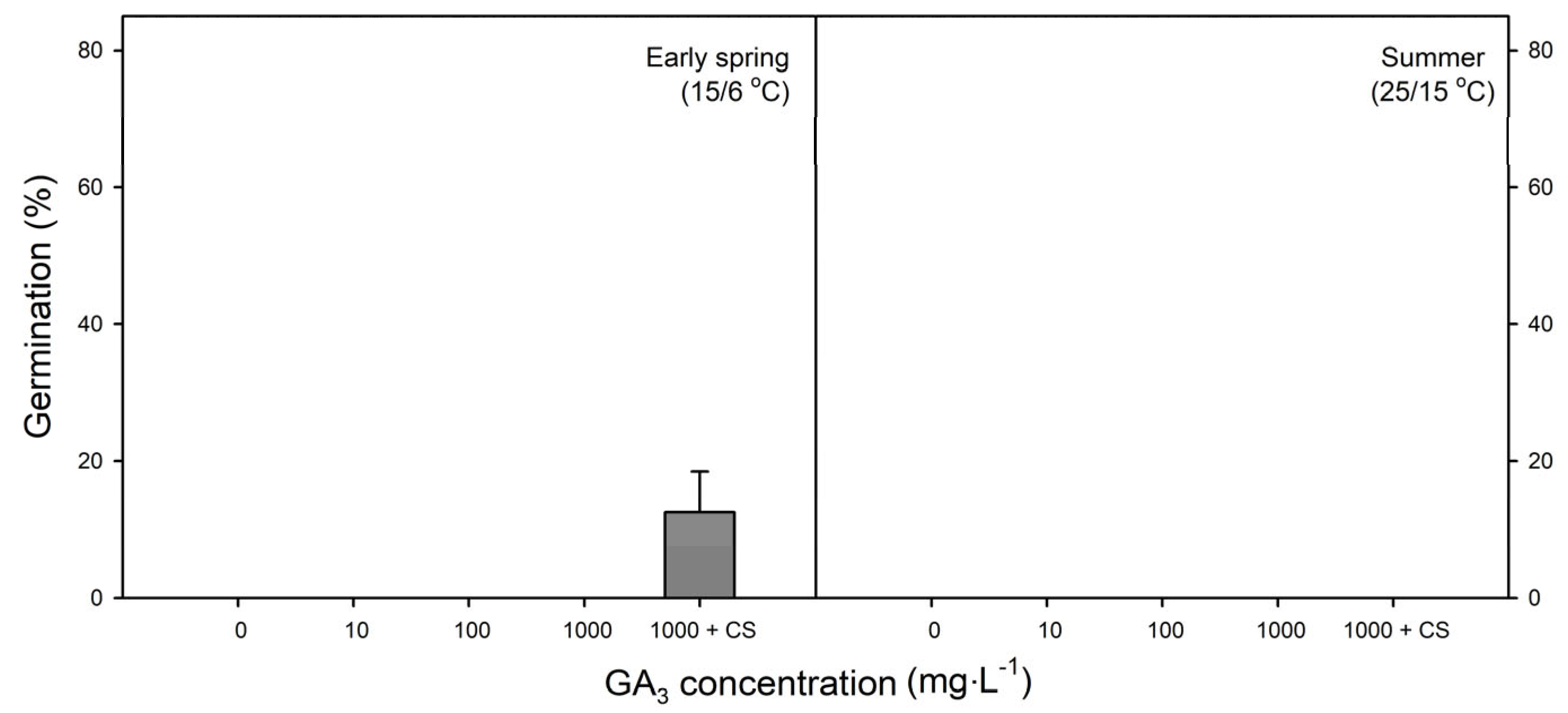
2.5. Effect of Exogenous GA3 on Germination
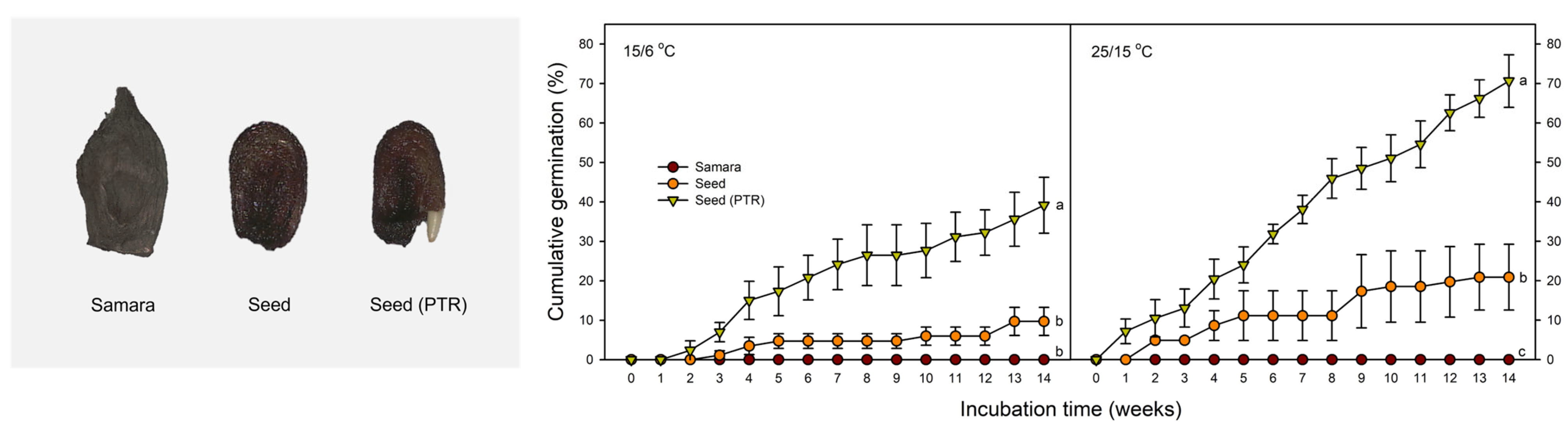
2.6. Effect of Pericarp and Testa on Germination
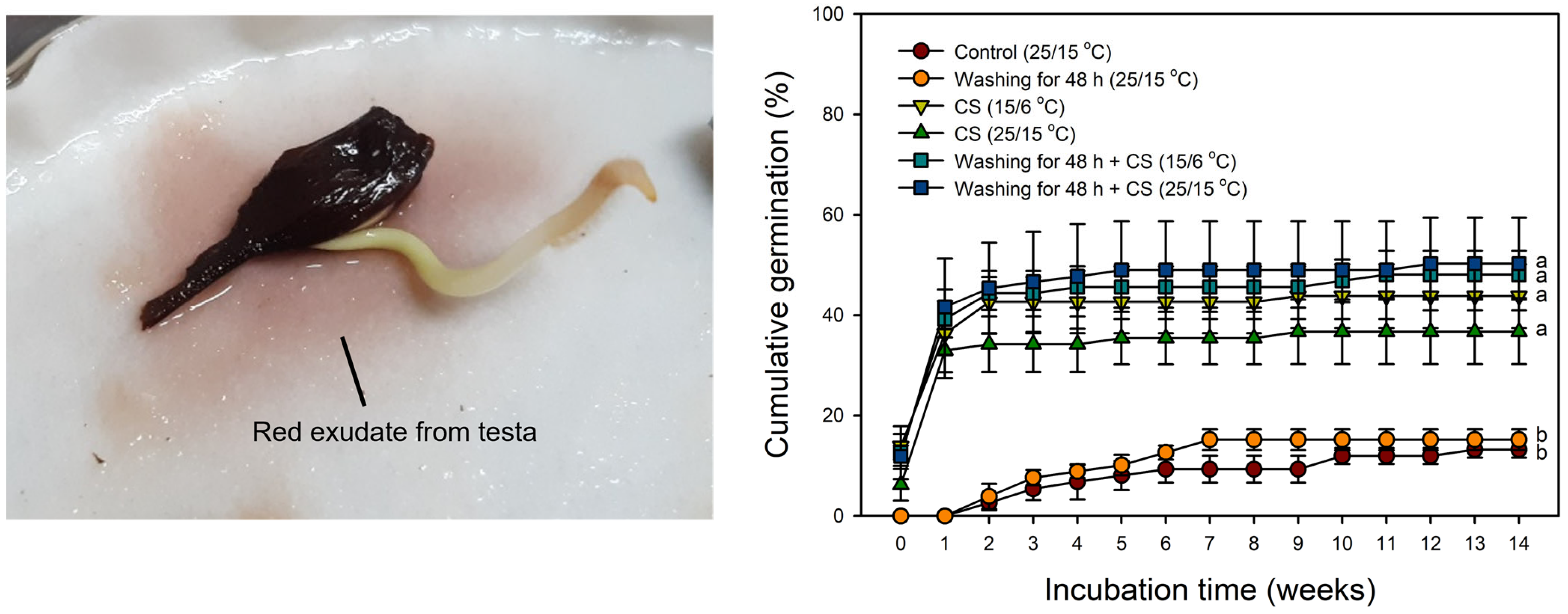
2.7. Effect of Washing on Germination
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Collection and Characteristics of Samaras
4.2. Phenology of Germination and Seedling Emergence in a Field
4.3. Germination Test in the Laboratory
4.4. Move-Along Experiments
4.5. Effect of Cold Stratification on Germination
4.6. Effect of Exogenous GA3 on Germination
4.7. Effect of Pericarp and Testa on Germination
4.8. Effect of Washing on Germination
4.9. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kozhevnikov, A.E.; Kozhevnikova, Z.V.; Kwak, M.; Lee, B.Y. Illustrated flora of the Southwest Primorye (Russian Far East); National Institute of Biological Resources: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.S.; Chung, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, W.; Lee, B.Y.; Pak, J.H. Floristic study and conservation management strategies of algific talus slopes on the Korean peninsula. Korean J. Plant Taxon. 2016, 46, 213–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.J.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, D.H.; Kwon, S.J.; Park, W.G.; Kim, Y.S. Growth environment and vegetation structure of habitats of Acer tegmentosum Maxim. J. Agric. Life Sci. 2016, 50, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea National Arboretum. Available online: http://www.nature.go.kr/kbi/plant/pilbk/selectPlantPilbkDtl.do?plantPilbkNo=36448 (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Kim, S.H.; Park, H.J.; Choi, J.W. Hepatoprotective activity of salidroside isolated from Acer termentosum Max on D-galactosamine induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Korean J. Orient. Physiol. Pathol. 2008, 22, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.M.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kong, K.S.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, H.J. Ethinobotany in Korea: The Traditional Knowledge and Use of Indigenous Plants, 2nd ed.; Korea National Arboretum: Pocheon, Republic of Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, Y.R.; Kim, Y.D.; Park, D.J.; Song, H.J.; Kim, H.G.; Yang, W.H.; Jeong, M.J.; Im, H.J.; Choi, M.S. Micropropagation of Acer tegmentosum Max. through induction of multiple shoots from axillary bud cultures. J. Agric. Life Sci. 2016, 50, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN Red List. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/193883/2288647 (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Wang, S.; Xie, Y. China Species Red List; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2004; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.I.; Min, W.G.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, S.G.; Jung, B.H.; Cho, Y.B. Red Data Book of Endangered Insects in Korea II; National Institute of Biological Resources: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kuprin, A.V. The longicorn beetles (Insecta, Coleoptera: Cerambycoidae) of the Ussuri Nature Reserve and adjacent territories. Far East. Entomol. 2016, 309, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Amarsanaa, G.; Jung, S.Y.; Cho, W.B.; Han, E.K.; So, S.; Lee, J.H. Definition and species list of northern lineage plants on the Korean Peninsula. Korean Herb. Med. Inf. 2020, 8, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.S.; Lee, S.; Yoon, K.; Park, H. Environmental characteristics of wind-hole and phytogeographical values. J. Environ. Impact Assess. 2011, 20, 381–395. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, M.S.; Seo, C.; Lee, M.; Kim, J.Y.; Jeon, J.Y.; Adhikari, P.; Hong, S.B. Prediction of potential species richness of plants adaptable to climate change in the Korean Peninsula. J. Environ. Impact Assess. 2018, 27, 562–581. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, M.; Cross, R.; Dixon, K.; Huynh, T.; Lawrie, A.; Nesbitt, L.; Pritchard, A.; Swarts, N.; Thomson, R. Propagation and reintroduction of Caladenia. Aust. J. Bot. 2009, 57, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, A.; Kelly, A.; Brown, K.; Cunneen, S. Relationships between seed germination requirements and ecophysiological characteristics aid the recovery of threatened native plant species in Western Australia. Ecol. Manage. Restor. 2002, 3, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kildisheva, O.A.; Dixon, K.W.; Silveira, F.A.O.; Chapman, T.; Di Sacco, A.; Mondoni, A.; Turner, S.R.; Cross, A.T. Dormancy and germination: Making every seed count in restoration. Restor. Ecol. 2020, 28, S256–S265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtasun, M.M.; Giamminola, E.M.; Baskin, C.C.; de Viana, M.L.; Morandini, M.N.; Lamas, C.Y.; Rojas, M.F. Dormancy release, germination and ex situ conservation of the southern highland papaya (Vasconcellea quercifolia, Caricaceae), a wild crop relative. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 263, 109134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskin, J.M.; Baskin, C.C. A classification system for seed dormancy. Seed Sci. Res. 2004, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskin, C.C.; Baskin, J.M. Seeds: Ecology, Biogeography and Evolution of Dormancy and Germination, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein, R.; Reeves, W.; Ariizumi, T.; Steber, C. Molecular aspects of seed dormancy. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 387–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Smith, M.W.; Brown, R.G.S.; Kamiya, Y.; Sun, T.P. Phytochrome regulation and differential expression of gibberellin 3b-hydroxylase genes in germinating Arabidopsis seeds. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jensen, M. Temperature relations of germination in Acer platanoides L. seeds. Scand. J. For. Res. 2001, 16, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, P. Raising Trees and Shrubs from Seed; Forestry Commission: Edinburgh, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zasada, J.C.; Strong, T.F. Acer L. In The Woody Plant Seed Manual; Bonner, F.T., Karrfalt, R.P., Eds.; Agriculture Handbook 727; USDA Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 204–216. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, D.P.; Staden, J.V.; Wareing, P.F. Seed dormancy in Acer: Changes in endogenous cytokinins, gibberellins and germination inhibitors during the breaking of dormancy in Acer saccharum Marsh. J. Exp. Bot. 1973, 24, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-Y.; Chou, S.-H.; Tsai, C.-C.; Hsu, W.-Y.; Baskin, C.C.; Baskin, J.M.; Chien, C.-T.; Kuo-Huang, L.-L. Effects of moist cold stratification on germination, plant growth regulators, metabolites and embryo ultrastructure in seeds of Acer morrisonense (Sapindaceae). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 94, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staszak, A.M.; Guzicka, M.; Pawlowski, T.M. Signalling regulators of abscisic and gibberellic acid pathways are involved in dormancy breaking of Norway maple (Acer platanoides L.) seeds. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2017, 14, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.F.; Hibbs, D.E.; Fischer, B.C. Seed dormancy in striped maple. Can. J. For. Res. 1979, 9, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, M. Seed Dormancy Breaking of Temperate Region Deciduous Tree Species. Master’s Thesis, Lancaster University, Lancaster, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Baskin, J.M.; Baskin, C.C. Ecological life cycle and physiological ecology of seed germination of Arabidopsis thaliana. Can. J. Bot. 1972, 50, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldaña-Acosta, A.; Zuloaga, S.; Jardel, E.J. Germinación de Acer skutchii Rehder y Magnolia iltisiana Vázquez en la reserva de la Biosfera Sierra de Manantlán, Jalisco, México. For. Veracruzana 2001, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Carl, C.M. Stratification of sugar maple seeds. Tree Plant. Notes 1983, 34, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Godman, R.M.; Yawney, H.W.; Tubbs, C.H. Acer saccharum Marsh. Sugar Maple. In Silvics of North America; Burns, R.M., Honkala, B.H., Eds.; Agriculture Handbook 654; USDA Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; Volume 2, pp. 78–91. [Google Scholar]
- Vandelook, F.; Van de Moer, D.; Van Assche, J.A. Environmental signals for seed germination reflect habitat adaptations in four temperate Caryophyllaceae. Funct. Ecol. 2008, 22, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.H. A Study on Habitat and Propagation of Acer tegmentosum Max. Master’s Thesis, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Republic of Korea, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.C. Study on the Growth Characteristics and Utilization Plan of Acer tegmentosum Maxim. Ph.D. Thesis, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Republic of Korea, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Baskin, C.C.; Baskin, J.M. When breaking seed dormancy is a problem: Try a move-along experiment. Nativ. Plants J. 2003, 4, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Footitt, S.; Douterelo-Soler, I.; Clay, H.; Finch-Savage, W.E. Dormancy cycling in Arabidopsis seeds is controlled by seasonally distinct hormone-signaling pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20236–20241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.P.; Koizuka, N.; Martin, R.C.; Nonogaki, H. The BME3 (Blue Micropylar End. 3) GATA zinc finger transcription factor is a positive regulator of Arabidopsis seed germination. Plant J. 2005, 44, 960–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phartyal, S.S.; Thapliyal, R.C.; Nayal, J.S.; Joshi, G. Seed dormancy in Himalayan maple (Acer caesium) I: Effect of stratification and phyto-hormones. Seed Sci. Technol. 2003, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, B.; Tabari, M.; Phartyal, S.S.; Abedi, M. Deep physiological dormancy in seeds of Balkan maple (Acer hyrcanum): A rare tree in the Hyrcanian Mountain forests of Iran. Seed Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiseleva, O.A.; Loretts, O.G.; Veselkin, D.V.; Joshi, G. Seed size and cold stratification affect Acer negundo and Acer ginnala seeds germination. Agron. Res. 2020, 18, 461–471. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, D.P.; Wareing, P.F. Seed dormancy in Acer pseudoplatanus L.; the role of covering structures. J. Exp. Bot. 1972, 23, 813–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleiser, G.; Picher, M.C.; Veintimilla, P.; Martinez, J.; Verdu, M. Seed dormancy in relation to seed storage behaviour in Acer. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2004, 145, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vordtriede, S.A.; Vordtriede, P.B.; Schulz, K.E.; Kulfinski, F.B.; Bolyard, M.G. Embryo germination in Acer ginnala Maxim. and the activity of an endogenous exudate. Trans. Ill. State Acad. Sci. 1999, 92, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Honduvilla, C.J.; Santos-Ruiz, A. Germination inhibitors in the pine seed coat. Planta 1978, 141, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Hanada, A.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kuwahara, A.; Kamiya, Y.; Yamaguchi, S. Gibberellin biosynthesis and response during Arabidopsis seed germination. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1591–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch-Savage, W.E.; Leubner-Metzger, G. Seed dormancy and the control of germination. New Phytol. 2006, 171, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, J.; Garrett, P.W. Optimum temperatures for stratification of several maple species. Tree Plant. Notes 1989, 40, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, P. Temperature and seed dormancy. In Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology; Ruhland, W., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1965; Volume 15/2, pp. 746–803. [Google Scholar]
- Geneve, R.L. Impact of temperature on seed dormancy. HortScience 2003, 38, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhu, J.; Yan, Q. Effects of light quality on the seed germination of main tree species in a secondary forest ecosystem of Northeast China. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2012, 23, 2625–2631. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, K.M.; Van Staden, J.; Bell, W.E. Seed coat structure and dormancy. Plant Growth Regul. 1992, 11, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morpeth, D.R.; Hall, A.M. Microbial enhancement of seed germination in Rosa corymbifera ‘Laxa’. Seed Sci. Res. 2000, 4, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Sánchez, P.; Ortega-Amaro, M.A.; Jiménez-Bremont, J.F.; Flores, J. Are fungi important for breaking seed dormancy in desert species? Experimental evidence in Opuntia streptacantha (Cactaceae). Plant Biol. 2011, 13, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Sánchez, P.; Jiménez-Bremont, J.F.; Guerrero-González, M.L.; Flores, J. Effect of fungi and light on seed germination of three Opuntia species from semiarid lands of central Mexico. J. Plant Res. 2013, 126, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperber, K.; Steinbrecher, T.; Graeber, K.; Scherer, G.; Clausing, S.; Wiegand, N.; Hourston, J.E.; Kurre, R.; Leubner-Metzger, G.; Mummenhoff, K. Fruit fracture biomechanics and the release of Lepidium didymum pericarp-imposed mechanical dormancy by fungi. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch-Savage, W.E.; Footitt, S. Seed dormancy cycling and the regulation of dormancy mechanisms to time germination in variable field environments. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, T.; Sakai, E.; Shimomura, K. Effect of rapid freezing and thawing on hard-seed breaking in Astragalus mongholicus Bunge (Leguminosae). J. Plant Physiol. 1995, 147, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, D.P.; Wareing, P.F. Seed dormancy in Acer: Endogenous germination inhibitors and dormancy in Acer pseudoplatanus L. Planta 1972, 104, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, J.; Loescher, W. Germination requirements for Acer macrophyllum, big leaf maple. Ornam. Northwest Arch. 1981, 5, 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Pipinis, E.; Milios, E.; Georgiou, M.; Smiris, P. Effects of gibberellic acid and cold stratification on seed germination of two Sorbus species. For. Ideas 2015, 21, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Rosner, L.S.; Harrington, J.T.; Dreesen, D.R.; Murray, L. Effect of gibberellic acid and standard seed treatments on mountain snowberry germination. Nativ. Plants J. 2001, 3, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Rathcke, B.; Lacey, E.P. Phenological patterns of terrestrial plants. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1985, 16, 124–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, R.E.; Cunningham, M. Seed dormancy of red maple in east Tennessee. For. Sci. 1981, 27, 446–448. [Google Scholar]
- Farmer, R.E.; Goelz, J.C. Germination characteristics of red maple in northwestern Ontario. For. Sci. 1984, 30, 670–672. [Google Scholar]
- Bourgoin, A.; Simpson, J.D. Soaking, moist-chilling, and temperature effects on germination of Acer pensylvanicum seeds. Can. J. For. Res. 2004, 34, 2181–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphey, M.; Kovach, K.; Elnacash, T.; He, H.; Bentsink, L.; Donohue, K. DOG1-imposed dormancy mediates germination responses to temperature cues. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2015, 112, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganuma, N.; Ohno, H. Role of pericarp in reducing spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) seed germination at supra-optimal temperatures. J. Japan Soc. Hort. Sci. 1984, 53, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, C.; Corbineau, F.; Côme, D. Effects of temperature and oxygen on seed germination and seedling growth in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 1991, 31, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiwa, K. Advantages of early germination for growth and survival of seedlings of Acer mono under different overstorey phenologies in deciduous broad-leaved forests. J. Ecol. 1998, 86, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdú, M.; Traveset, A. Early emergence enhances plant fitness: A phylogenetically controlled meta-analysis. Ecology 2005, 86, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, E.; Bungmann, H.; Bigler, C. Early emergence increases survival of tree seedlings in Central European temperate forests despite severe late frost. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 8238–8252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necajeva, J.; Probert, R.J. Effect of cold stratification and germination temperature on seed germination of two ecologically distinct species, Linaria loeselii and L. vulgaris (Scrophulariaceae). Pol. Bot. J. 2011, 56, 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Kanazashi, A.; Nagamitsu, T.; Suzuki, W. Seed dormancy and germination characteristics in relation to the regeneration of Acer pycnanthum, a vulnerable tree species in Japan. J. For. Res. 2015, 20, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Li, J. Conflicting phylogenies of section Macrantha (Acer, Aceroideae, Sapindaceae) based on chloroplast and nuclear DNA. Syst. Bot. 2010, 35, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Rhie, Y.H.; Kim, K.S. Non-deep simple morphophysiological dormancy in seeds of Thalictrum rochebrunianum, an endemic perennial herb in the Korean Peninsula. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2015, 56, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Collection Location | Collection Date | Length (mm) | Width (mm) | Thickness (mm) | 100 Seed Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hantaek Botanical Garden (37°05′40.4″ N, 127°24′19.3″ E) | 3–19 October 2020 | 10.4 ± 0.12 z | 5.2 ± 0.08 | 2.1 ± 0.04 | 3.9 ± 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.; Ko, C.H.; Kwon, H.C.; Rhie, Y.H.; Lee, S.Y. Effect of Temperature and Covering Structures in Seed Dormancy and Germination Traits of Manchurian Striped Maple (Acer tegmentosum Maxim.) Native to Northeast Asia. Plants 2025, 14, 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050767
Kim S, Ko CH, Kwon HC, Rhie YH, Lee SY. Effect of Temperature and Covering Structures in Seed Dormancy and Germination Traits of Manchurian Striped Maple (Acer tegmentosum Maxim.) Native to Northeast Asia. Plants. 2025; 14(5):767. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050767
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sieun, Chung Ho Ko, Hak Cheol Kwon, Yong Ha Rhie, and Seung Youn Lee. 2025. "Effect of Temperature and Covering Structures in Seed Dormancy and Germination Traits of Manchurian Striped Maple (Acer tegmentosum Maxim.) Native to Northeast Asia" Plants 14, no. 5: 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050767
APA StyleKim, S., Ko, C. H., Kwon, H. C., Rhie, Y. H., & Lee, S. Y. (2025). Effect of Temperature and Covering Structures in Seed Dormancy and Germination Traits of Manchurian Striped Maple (Acer tegmentosum Maxim.) Native to Northeast Asia. Plants, 14(5), 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050767








