Abstract
Hydrangea (Hydrangea macrophylla) is distinguished by having sepals instead of real petals, a trait that facilitates color diversity. Floral color is largely predetermined by structural genes linked to anthocyanin production, but the genetic factors determining floral hue in this non-model plant remain unclear. Anthocyanin metabolites, transcriptome, and the CIEL*a*b* hue system were employed to elucidate the biochemical and molecular mechanisms of floral color formation in three hydrangea cultivars: ‘DB’ (deep blue), ‘LB’ (light blue), and ‘GB’ (green blue). UPLC-MS/MS identified 47 metabolites, with delphinidin, cyanidin, malvidin, petunidin, pelargonidin, and peonidin being prominent. Delphinidins were 90% of the primary component in ‘DB’. The dataset identifies 51 and 31 DEGs associated with anthocyanin, flavonoid, and chlorophyll biosynthesis, with CHS, CHI, F3H, F3′5′H, DFR, ANS, BZ1, and 3AT displaying the highest expression in ‘DB’. Notably, DFR (cluster-46471.3) exhibits high expression in ‘DB’ while being down-regulated in ‘LB’ and ‘GB’, correlating with higher anthocyanin levels in floral pigmentation. Comparative analyses of ‘LB’ vs. ‘DB’, ‘DB’ vs. ‘GB’, and ‘LB’ vs. ‘GB’ revealed 460, 490, and 444 differentially expressed TFs, respectively. WRKY, ERF, bHLH, NAC, and AP2/ERF showed the highest expression in ‘DB’, aligning with the color formation and key anthocyanin biosynthesis-related gene expression. The findings reveal the molecular mechanisms behind floral pigmentation variations and lay the groundwork for future hydrangea breeding programs.
1. Introduction
Hydrangea (Linn.), commonly called ‘Ba Xian Hua’, is a genus within the Hydrangeae tribe, part of the Hydrangeaceae family. Hydrangeas come in 73 different species, 46 of which are native to China [1,2]. China is regarded as the homeland and distribution center of the hydrangea. Members of the genus Hydrangea are often categorized into five sections, with bigleaf hydrangea (H. macrophylla) being the most widely cultivated hydrangea species, originating from southern China and Japan [3,4].
H. macrophylla has a substantial inflorescence and vibrant hues, making it one of the most favored ornamental flowers globally. The species is cultivated as a cut flower and flowering potted plant, esteemed for its enormous and vividly colored inflorescences [5]. The original hue of the flower, namely the sepal, is blue. Nonetheless, diverse breeding initiatives have produced an extensive spectrum of colors, from blue to pink and purple to red, consistently or contingent upon the soil’s cultivation circumstances [6,7,8]. It is well-established that the sepal typically appears blue in acidic soil, while it assumes a crimson hue in alkaline soil. Under acidic conditions, the aluminum ion (Al3+) exhibits significant water solubility, facilitating its absorption and transit to the sepal, where it chelates anthocyanins [9,10]. Consequently, producers and researchers have consistently pursued H. macrophylla breeding in various colors to improve its aesthetic appeal.
Floral color is a crucial characteristic of ornamental plants, directly associated with the concentration and distribution of pigments [11]. Multiple studies have demonstrated that carotenoids, flavonoids, and chlorophylls are significant contributors to influencing the coloration of flowers [12]. Carotenoids contribute to flowers’ diverse coloration, producing hues ranging from vivid red to orange and yellow. Conversely, flavonoids, recognized as the predominant secondary metabolites in plants, generate hues that vary from light yellow to purple, depending upon the specific type of flavonoids present [13,14]. A single pigment, a mixture of several pigments (e.g., chlorophylls, anthocyanins, and carotenoids), or a lack of pigments altogether leads to the colors seen in the petals and sepals. The blue coloration of hydrangea sepals has been studied since the early 20th century. The main anthocyanin is 3-O-glucosyl delphinidin, with co-pigments including neochlorogenic acid, 5-O-p-coumaroylquinic acid, chlorogenic acid, and Al3+ [7,15,16].
Anthocyanins, classified as flavonoids, are significant secondary metabolites produced by plants. These widely distributed, water-soluble compounds assist several ornamental plants in developing their colors. Plants have six main anthocyanidins based on benzene ring substituents: delphinidin, petunidin, cyanidin, malvidin, pelargonidin, and peonidin [17,18]. Anthocyanins contribute to the orange, red, magenta, violet, and blue colors of flowers and enhance plants’ ability to adapt to various environmental stresses, including pathogen infection, UV radiation, drought, and low temperatures, therefore improving their aesthetic appeal [19]. Many enzymes and transcription factors regulate the intricate mechanism of anthocyanin production and accumulation, which is subsequently driven by a wide range of environmental variables, including light, water stress, and temperature [20,21]. Hydrangea cultivars show varying colors even in the same soil, highlighting intricate gene regulatory mechanisms and the association between secondary metabolites. Most studies on hydrangeas have focused on their blue pigmentation, leaving the molecular regulation of anthocyanin synthesis for H. macrophylla sepal color untouched. Consequently, further investigation is necessary to understand the mechanism governing sepal pigmentation in H. macrophylla.
Formerly, much emphasis has been placed on the influence of Al3+ and acidic soil on the process of hydrangea flower coloration; nevertheless, the molecular mechanisms and critical compounds that contribute to color development have received limited investigation. Therefore, the current research was performed to elucidate the variations in anthocyanin derivatives and the underlying molecular mechanisms in three distinct colored sepal tissues of H. macrophylla cultivars during full bloom stages. Differentially accumulation metabolites (DAMs) and differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified and analyzed. This approach is aimed at clarifying the essential genes responsible for flower color variation in hydrangeas and examining the prevalent or distinct mechanisms that contribute to this variation, ultimately providing new insights for breeding cultivars with specific sepal colors, particularly those exhibiting blends of blue, green, and multiple colors.
2. Results
2.1. Phenotypic Characterization of Hydrangea Cultivars
The coloration of flowers typically results from the large amount of carotenoids, flavonoids, and chlorophylls. Three representative-colored cultivars were selected for this study to explore the production of pigments in hydrangea. The visual examination of the three hydrangea cultivars revealed that the sepals of ‘Bo Da Lan’, ‘Qian Lan’, and ‘Lv Lan’ exhibited deep blue (‘DB’), light blue (‘LB’), and green with blue edges (‘GB’) colors, respectively (Figure 1A).
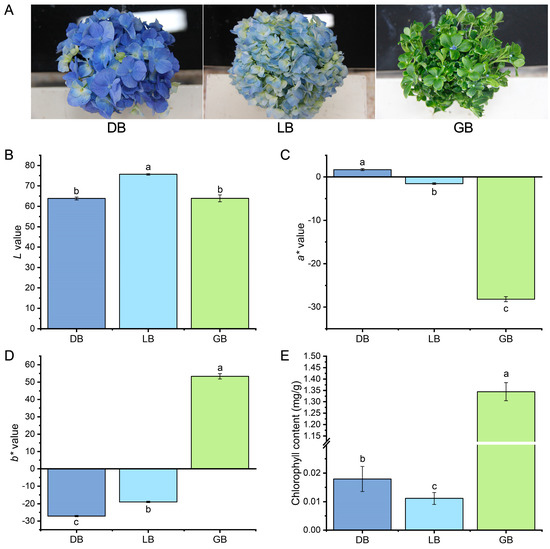
Figure 1.
Phenotypic illustration, color, and chlorophyll content of three hydrangea cultivars. (A) Pictorial view of three hydrangea cultivars. (B) L*, (C) a*, (D) b*, and (E) total chlorophyll content in hydrangea cultivars. Total chlorophyll content was obtained by summing the chlorophyll a and b concentrations. Data is denoted as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). Disparities were determined using least significant difference (LSD) at p < 0.05, with substantially different groups denoted by distinct letters (a, b, c). All measurements were performed in triplicate to ensure reproducibility and accuracy.
To assess the sepal color, we employed the CIELAB technique to specify multiple leaf color indices (L*, a*, b*) and analyze pigment concentrations. The L* (lightness) parameter ranges from 100 (white) to 0 (black); the positive a* value signifies a predominance of red over green, while the positive b* value suggests a predominance of yellow over blue. The L*a*b* three-dimensional coordinates indicated that the L*, a*, and b* values among the three cultivars were markedly distinct (Figure 1B–D). The ‘DB’ exhibits the highest value of a* and the lowest value of b*, whereas the ‘GB’ displays the highest value of b* and the lowest value of a*. The maximum L* value was observed in the ‘LB’ cultivar (Figure 1D).
We measured the chlorophyll pigment concentrations in the sepals of the three samples. Significant disparities in photosynthetic pigments were observed among the three samples. The cultivar ‘GB’ exhibited superior chlorophyll content (SPAD values) relative to the ‘DB’ and ‘LB’. The chlorophyll content was approximately 2- to 3-fold higher than the other two cultivars. Likewise, the cultivar ’DB’ exhibits significantly higher chlorophyll content than the cultivar ‘LB’ (Figure 1E).
2.2. Metabolomic Profiling of Hydrangea Cultivars
To determine the role of anthocyanin-related metabolites in the floral arrangements of hydrangea cultivars, extracts from the sepals of three hydrangea varieties were analyzed using Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). To gain insights into the broader attributes of the metabolite dataset, we initially conducted principal component analysis (PCA) (Figure 2A). Principal Component 1 and Principal Component 2 accounted for 61.72% and 34.76% of the metabolite distribution in the samples, respectively. The three sample groups were differentiated, demonstrating notable variations in anthocyanin contents across different cultivars.
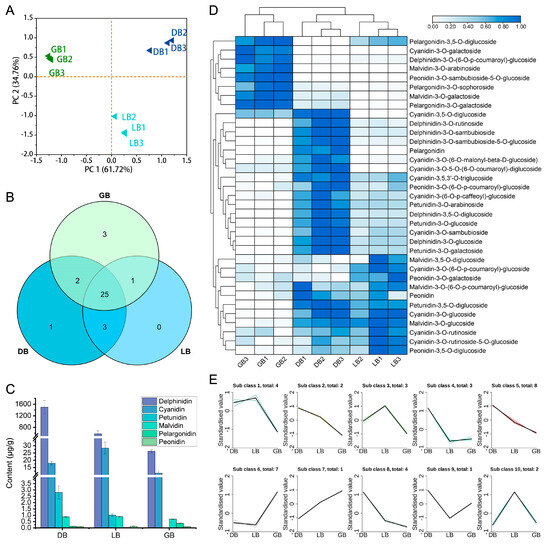
Figure 2.
Analysis of anthocyanin metabolites in three hydrangea cultivars. (A) PCA score plot, (B) Venn diagram, (C) various anthocyanin pigments, (D) Heat map, and (E) k-means cluster analysis of anthocyanin-related metabolites in hydrangea cultivars. GB1-3, DB1-3, and LB1-3 denote the biological replicates. Diverse colored lines denote cumulative patterns of distinct metabolites in each cultivar. A heatmap was generated via normalized data. Colors indicate scaled expression values, with blue for the highest expression and white for low expression levels.
The anthocyanins extracted from ‘LB,’ ‘DB,’ and ‘GB’ exhibited similar spectral properties to anthocyanin standards. By cross-referencing the mass spectrometry data from ‘DB’ samples with compound information in the database, we identified 47 anthocyanin-related metabolites. This includes 11 cyanidins, 6 delphinidins, 5 malvidins, 4 pelargonidins, 5 peonidins, 4 petunidins, 3 procyanidins, and 8 flavonoids. Of the 47 anthocyanin metabolites analyzed, 25 were identified across all cultivars (Figure 2B). The cultivars ‘GB’, ‘LB’, and ‘DB’ were associated with 4, 1, and 2 specific compounds, respectively. The total anthocyanin content enhanced progressively from ‘GB’ to ‘LB’ and then to ‘DB’, measuring 38.85, 608.89, and 1517.87 ug/g, respectively (Figure 2C; Supplementary Figure S1). Flavonoids constituted the primary components of ‘GB’, comprising 89% of the total content. In the ‘LB’ cultivar, delphinidins and flavonoids constituted the primary pigment components, accounting for 62% and 35%, respectively. Delphinidins constituted 90% of the dominant composition of ’DB’. The delphinidin concentrations were 7%, 35%, and 90% in the samples labeled ‘GB’, ‘LB’, and ‘DB’, respectively. The significant presence of delphinidin-3-O-glucoside is likely the primary factor contributing to the deeper blue hue observed in the sepals of ‘DB’ compared to ‘LB’ and ‘GB’.
Clustering by hierarchy heat map assessment of 35 differential accumulation metabolites (DAMs) revealed that certain major pigment substances with comparatively high concentrations varied with cultivar changes (Figure 2D). The data shows that cyanidin-3-O-galactoside, malvidin-3-O-arabinoside, delphinidin-3-O-(6-O-p-coumaroyl)-glucoside, peonidin-3-O-sambubioside-5-glucoside, malvidin-3-O-galactoside, and pelargonidin-3-O-galactoside were among the main compounds in ‘GB’. In ‘DB’ and ‘LB’, cyanidin, delphinidin, pelargonidin, petunidin, and peonidin-3-O-(6-O-p-coumaroyl)-glucoside were the major metabolites.
K-means clustering categorized the anthocyanin content across three cultivars into 10 distinct clusters (Figure 2E). Cluster 5 comprised 8 metabolites, cluster 6 contained 7, clusters 1 and 8 each had 4, clusters 3 and 4 featured 3, and clusters 2 and 10 possessed 2 metabolites. Meanwhile, clusters 7 and 9 comprise single anthocyanin metabolites, exhibiting distinct expression profiles across three cultivars. This signifies that a specific anthocyanin serves an essential function in sepal color development in certain hydrangea cultivars.
2.3. Analysis of the Transcriptome in the Sepals of Three Hydrangea Cultivars
To further identify the key genes responsible for the color differences observed in the sepals of three distinct hydrangea varieties, we conducted RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) and de novo assembly on the sepals of these varieties. RNA-seq data were utilized to investigate the expression profiles of the essential genes involved in anthocyanin formation among the sepals of three hydrangea cultivars. PCA, Venn diagram, and clustering heat map analysis, performed with three biological replicates, revealed minimal variation within each sample group, signifying robust data accuracy, while also demonstrating a marked distinction between groups (Figure 3). PCA indicated minimal variation within each sample, signifying strong data repeatability, whereas a substantial difference was observed between groups (Figure 3A).
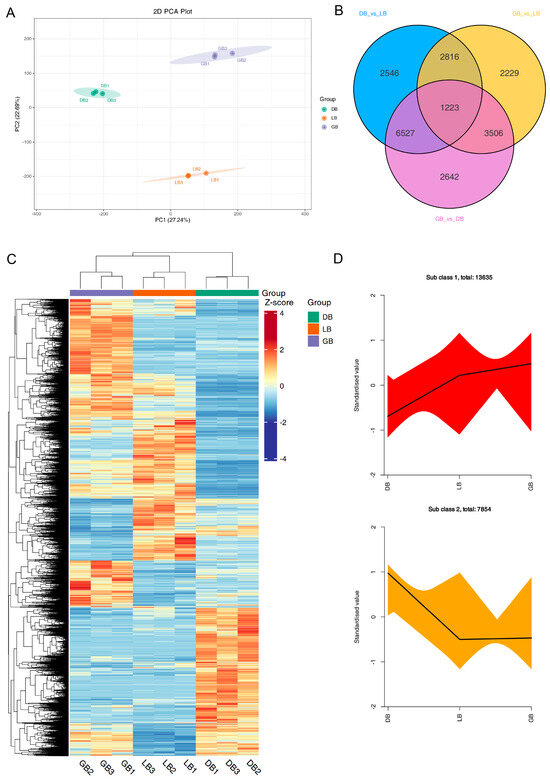
Figure 3.
RNA sequence and DEGs analysis of three hydrangea cultivars. (A) PCA score plot, (B) Venn diagram, (C) Heatmap of differentially expressed genes (DEGs), and (D) k-means cluster analysis of DEGs in hydrangea cultivars. GB1-3, DB1-3, and LB1-3 denote the biological replicates. Diverse colored lines denote cumulative patterns of distinct metabolites in each cultivar. The heat map displays DEGs relative expression values (row z-score of normalized FPKM) in three hydrangea cultivars. Colors indicate scaled expression values, with red for the highest expression and blue for low expression levels.
PCA and heatmap clustering showed little difference within each group of samples, indicating good data reproducibility, while there was a significant difference between groups (Figure 3A,C). RNA-seq data produced 6.63–7.36 GB of clean bases, with an error rate below 0.03%, a Q20 value exceeding 96.9%, a Q30 value surpassing 91.9%, and a GC content between 44.43% and 44.86% (Supplementary Table S1). Supplementary Table S2 details the length and quantity of assembled transcripts and genes. A total of 201,506 transcripts and 105,743 unigenes were identified, with mean lengths of 1030 and 1317, respectively. The results of gene annotation reveal that the KEGG, NR, Swiss-Prot, Trembl, KOG, GO, and Pfam databases annotated 45,473, 59,231, 43,012, 59,267, 35,055, 51,107, and 39,956 genes, respectively, culminating in a total of 105,743 annotated genes (Supplementary Figure S2A; Supplementary Table S3). To acquire detailed gene function information, 56.01% (59,231) of the unigenes were annotated with their putative functions in the Nr database. The four species with the highest BLASTx hits were Nyssa sinensis (19,279 hits, 32.55%), Camellia sinensis (5759 hits, 9.72%), Camellia lanceoleosa (3104 hits, 5.24%), and Actinidia chinensis var. chinensis (2972 hits, 5.02%) (Supplementary Figure S2B).
Differential expression analysis was conducted using DESeq, comparing samples from three biological replicates of ‘DB’, ‘LB’, and ‘GB’ hydrangeas. A total of 36,784 unigenes exhibiting significantly altered expression levels (DESeq2 padj < 0.05 | log2 (fold change) > 1) were identified. A Venn diagram illustrates the distribution of these DEGs across the three comparison groups: ‘DB’ versus ‘LB’, ‘GB’ versus ‘DB’, and ‘GB’ versus ‘LB’. The Venn diagram revealed that 1223 DEGs were shared among the comparisons of ‘GB’ versus ‘LB’, ‘GB’ versus ‘DB’, and ‘LB’ versus ‘DB’ (Figure 3B). A total of 13,112, 13,898, and 9774 DEGs were identified for the comparisons of ‘DB’ versus ‘LB’, ‘GB’ versus ‘DB’, and ‘GB’ versus ‘LB’, respectively (Supplementary Figure S3). Subsequently, we analyzed the DEGs among the three samples exhibiting distinct colors in a heat map (Figure 3C). To analyze the expression patterns of DEGs, we used R to standardize the FPKM expression levels. Subsequently, k-means clustering was employed to group genes exhibiting analogous expression patterns across three varieties, suggesting potential functional similarities (Figure 3D). This indicates that the expression of numerous genes varied significantly across the different cultivars.
2.4. GO Annotation and KEGG Pathway Analysis of Hydrangea Cultivars
Gene Ontology classification analysis indicated that numerous genes associated with ‘biological process’, ‘cellular component’, and ‘molecular function’ were present among the differentially expressed genes (Figure 4). In the comparison of the blue-type color cultivars ‘DB’ and ‘LB’, the most significantly enriched biological process was identified as the ‘phosphorelay signal transduction system’ (GO:0000160), the cellular process as the ‘intrinsic component of plasma membrane’ (GO:0031226), and the molecular function as ‘enzyme inhibitor activity’ (GO:0004857) (Figure 4A,C). In a comparative analysis of the green-type colored cultivar ‘GB’ with ‘DB’ and ‘LB’, the GO classification revealed that the DEGs were grouped within the same GO terms for ‘biological process’, ‘cellular component’, and ‘molecular function’ (Figure 4E). These terms included ‘photosynthesis, light reaction’ (GO:0019684), ‘photosystem’ (GO:0009521), and ‘glucosyltransferase activity’ (GO:0046527), respectively. The results indicated that the difference between ‘GB’ and both ‘LB’ and ‘DB’ is similar.
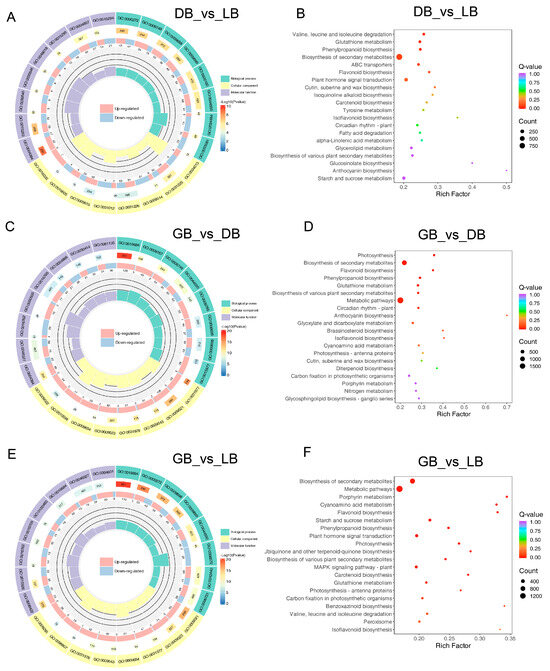
Figure 4.
GO enriched and KEGG pathway of DEGs in three hydrangea cultivars. The size of the dots indicates the number of DEGs in the corresponding pathways. Gene ontology classification among (A) DB vs. LB, (C) GB vs. DB, and (E) GB vs. LB comparisons. KEGG analysis of DEGs among the (B) DB vs. LB, (D) GB vs. DB, and (F) GB vs. LB comparisons. KEGG category enrichment was determined by employing the R programming language along with the Cluster, Biobase, and Q-value packages (p ≤ 0.01).
We performed a KEGG pathway analysis to explore the biological function of DEGs, which includes a thorough assessment of intracellular metabolic pathways and the activities of unigenes. The 20 most significantly enriched route categories were identified and presented in Figure 4B,D,F after comparing ‘LB’ and ‘GB’ with ‘DB’. The pathways with the most representative unigenes in these three comparisons were ‘Glutathione metabolism’, ‘Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites’, ’Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis’, ‘Flavonoid biosynthesis’, ‘Plant hormone signal transduction’, and ‘Anthocyanin biosynthesis’. Notably, ‘Metabolic processes’ and ‘Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites’ were the two most enriched pathways in the comparisons of ‘GB’ with ‘LB’ and ‘GB’ versus ‘DB’, with 1594 and 929, and 1901 and 1076 DEGs, respectively. The paths convey that the color creation of ‘GB’ significantly differs from that of ‘LB’ and ‘LB’, offering vital insights for examining the specific processes and pathways involved in the color distinction of hydrangea sepals.
2.5. Transcription Factors Involved in Color Formation in Hydrangea
Transcription factors serve as key regulators in the growth and development of plants. Transcription factors, including MYBs and bHLHs in Arabidopsis, significantly influence flavonoid production [22,23]. We identified 460, 490, and 444 differentially expressed transcription factors (DETFs) in the comparisons of ‘LB’ vs. ‘DB’, ‘DB’ vs. ‘GB’, and ‘LB’ vs. ‘GB’ (Table 1). Additionally, 204 TFs were upregulated in ‘LB’ compared to ‘DB’, while 256 were downregulated. Likewise, 298 TFs were upregulated in ‘DB’ compared to ‘GB’, while 192 were downregulated. In the comparison of ‘LB’ and ‘GB’, 243 TFs were upregulated while 201 TFs were downregulated. Overall, the following transcription factors were identified as having a significant impact: WRKY (4.78%), MYB (4.68%), C3H (4.38%), AP2/ERF (4.16%), bHLH (3.73%), C2H2 (3.63%), NAC (3.4%), FAR1 (3.4%), and SET (3.4%). In addition, the remaining TFs account for approximately 63.48% (Supplementary Figure S4). Among them, ERF, NAC, WRKY, MYB, bHLH, and bZIP transcription factors were paramount, indicating their significant function in modulating color biosynthesis genes and their essential contribution to hydrangea color creation.

Table 1.
List of TFs found in the DEGs of the hydrangea cultivars transcriptome dataset.
2.6. Differential Expression of Structural Genes Associated with Anthocyanin Biosynthesis Pathway
Gene expression in the anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway was compared across the three cultivars, identifying 51 DEGs associated with anthocyanin biosynthesis, as illustrated in Figure 5. Anthocyanins are a subset of flavonoids that share an identical synthetic pathway with other flavonoids and are produced by branched production processes originating from dihydrokaempferol. Figure 5 illustrates that, upstream of the synthesis pathway elements, the majority of the CHI, CHS, and DFR genes had elevated expression levels in ‘DB’ and ‘LB’, while demonstrating reduced expression in ‘GB’, thereby supplying substrates for the production of downstream anthocyanin compounds. Following the synthesis pathway, the expression levels of CHS (cluster-26710.2), CHI (cluster-47889.0), F3H (cluster-28792.0), F3′5′H (cluster-39474.0), DFR (cluster-46471.3), ANS (cluster-51681.0), BZ1 (cluster-57331.0), and 3AT (cluster-38007.2) progressively diminished from ‘DB’ to ‘GB’, correlating with the delphinidin content. Furthermore, CHS (cluster-26710.2) and DFR (cluster-46471.8) exhibit expression alone in ‘DB’, which was not detected in ‘LB’ and ‘GB’. In the anthocyanin biosynthesis process, the enzyme DFR (Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase) plays a crucial regulatory role by converting different dihydroflavonols (including dihydrokaempferol, dihydroquercetin, and dihydromyricetin) into colorless anthocyanidins (like leucodelphinidin). This is a vital stage in the production of anthocyanins, which are responsible for the vibrant hue of plants and contribute to how plants adapt to adverse conditions in their surroundings. The results demonstrated that variations in the expression of structural genes in hydrangea sepals may result in differing biosynthesis and accumulation of anthocyanins, especially delphinidins, leading to diverse sepal colors.
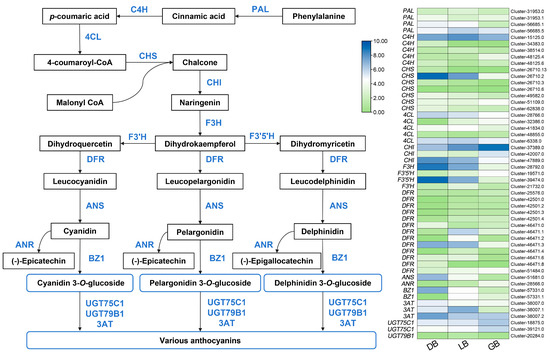
Figure 5.
Key structural genes related to the anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway. The expression profiles of these genes in three hydrangea cultivars are illustrated on the right side of the figure. The green color signifies minimal expression, whereas blue represents maximal gene expression.
2.7. Differential Expression of Structural Genes Linked to Chlorophyll Biosynthesis Pathway
The macromolecules (tetrapyrroles and magnesium) that give plants their green hue are called chlorophylls (Chls). Chlorophylls, a type of vital photosynthetic pigment, are present in nearly all plants and primarily contribute to the green coloration of flowers [24,25]. The number of genes (31 DEGs) linked to chlorophyll synthesis has been significantly elevated in the hydrangea cultivar ‘GB’, characterized by its green flower sepals (Figure 6). DEGs associated with chlorophyll biosynthesis were HemA, HemB, HemL, HemC, HemD, HemE, HemF, HemY, chlD, chlH, chlM, chll, CRD1, DVR, PORA, CAO, NOL, and HCAR. HemA (cluster-497229.2 and cluster-51775.0), HemE (cluster-27864.0 and cluster-33216.0), HemF (cluster-24014.0), HemY (cluster-54852.0), chlD (cluster-50382.0), chll (cluster-35667.0), chlM (cluster-18472.0), CRD1 (cluster-46309.0), PORA (cluster-31306.0 and cluster-31306.1), and HCAR (cluster-30576.0) exhibited a progressive increase in expression from cultivar ‘DB’ to ‘LB’, peaking in ‘GB’. Curiously, NOL (cluster-42095.3) showed higher expression in ‘DB’ and ‘LB’ compared to ‘GB’. Likewise, NOL (cluster-42095.0 and cluster-42095.1) showed maximal expression in ‘LB’ compared to ‘DB’ or ‘GB’. NOL converts chlorophyll b into 7-hydroxymethyl chlorophyll a, which is subsequently transformed into chlorophyll a by HCAR enzyme genes. Notably, PORA (cluster-31306.0 and cluster-31306.1) and CRD1 (cluster-46309.0) showed maximal expression in the green blue hydrangea cultivar (‘GB’) compared to other chlorophyll biosynthesis genes, implying their putative key role in green color formation in the sepals. Furthermore, a significant number of chlorophyll biosynthesis genes had the highest expression in ’GB’ relative to the other cultivars.
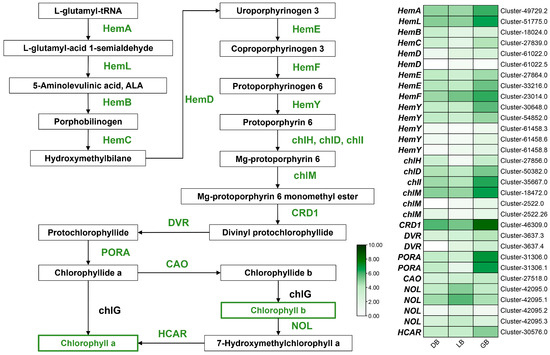
Figure 6.
Key structural genes related to the chlorophyll biosynthesis pathway. The expression profiles of these genes in three hydrangea cultivars are illustrated on the right side of the figure. The green signifies the highest expression, whereas the white denotes the lowest gene expression.
2.8. Validation of DEG Profiling via qRT-PCR
To validate the RNA-seq, ten differentially expressed genes linked to anthocyanin synthesis were chosen randomly for qRT-PCR analysis (Table S4). The genes include DFR, CHI, UGFT, P450, and CYP73A, as well as the transcription factors MYB, NAC, WRKY, and AP2/ERF (Figure 7). The expression profile of genes measured by qPCR closely aligned with the RNA-seq data values. The expression levels of NAC/P450/MYB/CYP73A were highest in the cultivar ‘LB’ compared to the other cultivars. The expression levels of WRKY/AP2/ERF were highest in ‘GB’, while UTG75C/CHI/DFR exhibited maximal mRNA transcript levels in ‘DB’. The qRT-PCR experiments confirmed the reliability of the RNA-seq-derived gene expression profiles.
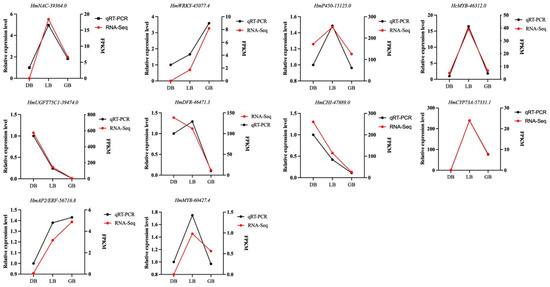
Figure 7.
Validation of the expression profiles of ten randomly selected genes using qRT-PCR in together with RNA-seq data. Actin was used as an endogenous control. The black line signifies the qRT-PCR values, whereas the red line displays the RNA-seq results. Data is denoted as the mean ± SEM (n = 3).
3. Discussion
The coloration of flowers is predominantly influenced by the chemical composition of flavonoids, particularly the subclass known as anthocyanins. Flavonoids, anthocyanins, betalains, carotenoids, and chlorophylls are recognized for their significant role in influencing plant color pigmentation [18,26,27,28]. The color of flowers is a significant characteristic of horticultural crops, exemplified by H. macrophylla [1]. It impacts economic value, visual appeal, aesthetics, and quality. There are over 400 cultivars of H. macrophylla exhibiting a variety of flower color phenotypes [29,30], yet the modulatory mechanism behind color formation among cultivars is less known. A novel mutation with green flowers has been found, offering an unprecedented chance to examine sepal coloration in H. macrophylla.
This study employed a colorimeter to analyze the coloration of three distinct H. macrophylla sepals labeled ‘LB’, ‘GB’, and ‘DB’. The ‘DB’ exhibits the highest value of a* alongside the lowest value of b*, while the ‘GB’ shows the highest value of b* and the lowest value of a* (Figure 1B–D). The * value correlated with increased anthocyanin levels in the ‘DB’ cultivar. In previous investigations, a colorimeter was utilized to measure and analyze gerbera and caladium petals, effectively classifying them into distinct color groups. The analysis revealed significant variations in the total carotenoids and total anthocyanins among different color series [31,32]. Analysis showed that ‘GB’ sepals had significantly higher chlorophyll content than ‘DB’ and ‘LB’, approximately 2–3 times greater (Figure 1E). Studies showed that chlorophyll content causes green pigmentation, playing a key role in the coloration of ‘GB’ sepals. These studies suggest that colorimetric detection effectively analyses flower color phenotypes.
Metabolomics facilitates an in-depth exploration of the intricate biochemistry underlying flower coloration, thereby enhancing researchers’ comprehension of flower color formation in ornamental plants [33,34]. Targeted metabolomics highlights the investigation of particular classes of metabolites with enhanced selectivity and precision [35]. Herein, UPLC-MS/MS was employed to profile the sepals of three H. macrophylla genotypes to discover flavonoid and anthocyanin substances that may explain the blue coloration in the ‘DB’ and ‘LB’ genotypes relative to the ‘GB’ genotype (Figure 2). These cultivars included 47 anthocyanin types, with blue sepals accumulating more than light blue or green ones. In the ‘LB’ and ‘DB’ sepals of H. macrophylla, the anthocyanin components are comparable, with the primary anthocyanin (delphinidin-3-O-glucoside) content being twice as high in the ‘DB’ compared to the ‘LB’. The elevated anthocyanin concentration in petals and sepals can intensify the coloration of flowers. For instance, anthocyanins are absent in the white flower mutants of Gentiana triflora, while they accumulate in significant quantities in G. triflora blue flowers, predominantly delphinidin [36,37]. A previous study of H. macrophylla ‘Endless Summer’ showed that carotenoids and flavonoids in blue sterile flowers decrease from bud to full bloom while anthocyanin increases to its peak [38,39]. Our investigation found that ‘DB’ had a similar effect, with anthocyanins at 1512 µg/g and reduced flavonoids. Likewise, in Gloriosa superba ‘Rothschildiana’ anthocyanin (cyanidin-3,5-O-diglucoside, cyanidin-3-O-glucoside, pelargonidin-3-O-glucoside, and pelargonidin-3,5-O-diglucoside) were the major content in the floral petals, resulting in intense petal color [40].
Like other species, anthocyanin was concentrated in the sepals of H. macrophylla. This study identified six pigment types that were exclusive to specific-colored samples, suggesting their significant significance in color formation. Twenty-five overlapping DAMs were identified across all cultivars, which may contribute to the variation in sepal hues (Figure 2B,C). Analysis showed significant variation in delphinidin-3-O-glucoside and delphinidin-3-O-sambubioside levels among ‘DB’, ‘LB,’ and ‘GB’ (Figure 2D). These results lend credence to the claims made by Yoshida et al. [7,15] and Zhang et al. [41] that the principal component of blue-violet flowers is delphinidin-3-O-glucoside. Delphinidin was mostly associated with the development of blue blooms. Several blue flowers, such as Cineraria, delphinium, Rhododendron, campanula, Petunia, Salvia miltiorrhiza, and Glycine soja, have been identified as containing delphinidin-3-O-glucoside, indicating that this compound may be responsible for the development of blue coloration in these flowers [42,43,44,45,46]. The study found delphinidin-3-O-glucoside in all colored flowers, especially in blue varieties, notably in ‘DB’ (Figure 2E,F). The ‘GB’ green flowers with a blue edge contained delphinidin-3-O-glucoside. This study identified four delphinidin derivatives: delphinin-3-O-glucoside, delphinidin-3-O-sambubioside, delphinidin-3,5-O-diglucoside, and delphinidin-3-O-rutinoside-7-O-glucoside, which are essential for the blue color formation in H. macrophylla. Malvidin derivatives are formed from delphinidin derivatives, modified into malvidin by the gene OMT.
The synthesis of anthocyanin, chlorophyll, and carotenoid metabolites is governed by multiple structural genes associated with these mechanisms. We identified 51 structural genes involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis, including CHS, F3′H, F3′5′H, DFR, ANS, BZ1, and 3AT (Figure 5). It is noteworthy that F3′5′H, DFR, ANS, BZ1, and 3AT genes exhibited a high level of expression in the cultivar ‘DB’, playing a key role in anthocyanins biosynthesis during the later stages [47]. In anthocyanin biosynthesis, DFR (dihydroflavonol 4-reductase), ANS (anthocyanidin synthase), and BZ1 (anthocyanidin 3-O-glucosyltransferase) are essential genes involved in the later stages of anthocyanin production. DFR catalyzes the conversion of dihydroflavonols to leucoanthocyanidins, while ANS facilitates the transformation of leucoanthocyanidins into anthocyanidins [18,44]. In this study, we identified 12 DFR genes among the DEGs. Notably, the expression of the DFR gene (cluster-46471.3) was significantly upregulated in the sepals of both ‘DB’ and ‘LB’ compared to ‘GB’, exhibiting 11.22-fold and 8.74-fold increases, respectively. A similar study was conducted on the Iris flower, where two DFR genes (IlDFR and IlaDFR) were cloned from I. laevigata (deep blue) and I. lactea (light blue), respectively. The data showed that DFR genes regulate delphinidin synthesis, essential for Iris flowers’ blue coloration [48]. A higher anthocyanin content was associated with higher expression levels of FvDFR30, FvDFR54, and FvDFR56 genes in strawberries, indicating that DFR genes may play a pivotal role in the synthesis of anthocyanins in strawberries [49].
The 3AT (3-O-acetyltransferase) gene plays a significant role in anthocyanin metabolism, particularly in the formation of flower color. The 3AT gene catalyzes the acetylation of anthocyanidin-3-glucosides, leading to the production of 3-O-acetylated anthocyanins, which contribute to the deepening of flower color [50]. In this study, one 3AT gene (cluster-38007.2) was related with 10 anthocyanins and expressed more in ‘DB’ than ‘LB’ or ‘GB’. Among them, pelargonidin-3,5-O-diglucoside exhibited a negative correlation in ‘DB’, ‘LB’, and ‘GB’. The remaining seven DAMs accumulated to a greater extent in ‘DB’ compared to ‘LB’ or ‘GB’. Additionally, cyanidin-3-O-5-O-(6-O-coumaroyl)-diglucoside and cyanidin-3,5-O-diglucoside were absent in ‘LB’. A prior study demonstrated the essential function of 3AT. The 3AT enzyme in Perilla frutescens can transfer p-coumaric and caffeic acids from their CoA esters to the 3-glucosyl moiety of delphinidin, cyanidin, and pelargonidin 3-glucosides. The research indicated that the 3AT enzyme results in a deep blue appearance of the flower hue due to acetylation [50]. In the anthocyanin-rich ‘Zijuan’ tea plant, 3AT was elevated along with other biosynthetic genes and TFs and was found to increase and alter anthocyanins [50]. These findings suggest that these genes may associated with sepal color variability in H. macrophylla.
Chlorophyll is a fundamental element in the floral coloration. This study identified structural genes associated with chlorophyll production. Thirteen of these genes expressed higher in the green mutant ‘GB’ than in the blue types ‘DB’ and ‘LB’. Numerous crucial genes were implicated in the extensively researched chlorophyll production pathway [51,52]. HemA catalyzes the conversion of glutamyl-tRNA to L-Glutamate 1-semialdehyde, serving as the primary enzyme in chlorophyll production and regulation during de-etiolation [53]. The protochlorophyllide reductase (POR), the enzyme facilitating the photoreduction of protochlorophyllide to chlorophyllide, is essential throughout the greening phase. In the ‘GB’ cultivar, the expression levels of HemA, HemE, HemF, CRD1, and PORA were elevated compared to ‘LB’ and ‘DB’, indicating a heightened rate of chlorophyll production and accumulation. Prior research on green chrysanthemum and carnation flowers found that pale green carnation petals had more chlorophyll than non-green carnation petals [54]. Similar observations were made regarding the transformation of lily petals from green to white, highlighting the link between the greening of hydrangea sepals and chlorophyll synthesis.
In addition to structural genes, TFs significantly contribute to anthocyanin biosynthesis, including MYB, bHLH, WD proteins, and WRKY proteins [55,56,57]. In Medicago truncatula, bHLH and WD40 proteins regulate the production of anthocyanins and proanthocyanidins [58]. Similarly, in Syringa oblata, SoNAC72-SoMYB44/SobHLH130 modulates floral pigmentation by directly interacting with the promoters of structural anthocyanin biosynthesis genes [59]. Prior research, including ours, displays that AN modulates the expression of CHS, DFR, and AAT1. Herein, we found several TFs linked to floral color, including MYB, ERF, bHLH, WRKY, and NAC. These transcription factors were expressed significantly and in higher quantities than others, especially in the ‘DB’ cultivar (Table 1). Our findings correspond with previous research indicating that transcription factors, including ERF, MYB, and bHLH, are pivotal in secondary metabolism, including floral pigmentation [57,60,61]. Particularly, in the comparison of ‘DB’ and ‘GB’, the quantity of upregulated TFs such as ERF, NAC, MYB, WRKY, and bHLH exceeded that of downregulated factors, indicating their essential function in the production of floral color.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
The experimental materials used in this study comprised three varieties of H. macrophylla. The first variety, designated as ‘Bo Da Lan’, exhibits a deep blue coloration (abbreviated as ‘DB’). The second cultivar, named ‘Qian Lan’, displays a light blue hue (referred to as ‘LB’). Additionally, a bud mutation strain is characterized by predominantly green sepals with a blue edge (abbreviated as ‘GB’). The ‘DB’ variety has emerged as a primary cultivation type of hydrangea, characterized by early flowering, larger inflorescence size, compact flowers, deeper coloration, and broad adaptability. The ‘LB’ variety exhibits smaller inflorescences and a lighter blue hue than ‘DB’, but demonstrates greater plant height. ‘GB’ is a bud mutation strain derived from ‘LB’. The primary distinction lies in the sepal color, with ‘GB’ exhibiting a predominantly green hue, uncommon within the hydrangea group. For every cultivar, three or four biological replicas were collected.
This study used plants cultivated in the greenhouse at the nursery of Kunming Yang Chinese Rose Gardening Co., Ltd. (Kunming, China). The corymbs were collected from early May to mid-August during the blossoming period. The plants experienced analogous natural conditions. To investigate the color formation of these three cultivars, combined transcriptomic and metabolomic techniques were employed to elucidate the changes in metabolites and the relationship between metabolites and gene expression associated with floral sepal color variation. All experiments were performed with three biological replicates.
4.2. Floral Sepal Color Measurement
During the peak blooming period, the sepal hues were documented using the Royal Horticultural Society Color Chart with a white background and consistent lighting settings. Additionally, a CS-210 precision colorimeter (Hangzhou Caipu Technology, Hangzhou, China) was employed to measure the color variables of the identical flower sepals. The characteristics of the CIEL*a*b* hue coordinate system (chromatic components, a* and b*; lightness, L*) were determined. The CIELAB nonlinear modification of the RGB color space makes the real distance between two colors equal to their Euclidean distance (for distances less than 10 units). When working with color image processing techniques, CIELAB often yields excellent outcomes [62]. Each cultivar was measured five times as a replica.
4.3. Total Chlorophyll Content Measurement
Fresh sepals from three cultivars were collected and thoroughly washed with distilled water to remove surface contaminants. A small quantity of the sepals (about 0.2 g) was placed in a mortar, pounded with a pestle, and then 10 mL of 95% ethanol was introduced to enhance the extraction process. The resulting mixture was centrifuged at 5000× g for 10 min to separate the soluble pigments from the insoluble plant debris. The supernatant containing the extracted chlorophyll was collected and used for further analysis. The chlorophyll content was determined using a spectrophotometric method. The absorbance of the extract solution was measured at wavelengths of 645 nm and 663 nm using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer. Total chlorophyll content was determined by combining the amount of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. To acquire a single average read, three separate corymb reads were utilized to acquire a single average read. The data was collected from five individual plants.
4.4. RNA Extraction and RNA-Seq
RNA extraction was performed using the TransZol Up kit (Yun Geng Biology, Kunming, China), followed by reverse transcription of RNA to cDNA using the HiScript III RT SuperMix for qPCR (including gDNA wiper). The qPCR was conducted with the ChamQ Universal SYBR qPCR Master Mix. Sequencing adapters were attached to double-stranded cDNAs, followed by amplification and purification. Metware Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China) sequenced the cDNA libraries using Illumina sequencing. The assay was performed in three biological replicates.
4.5. De Novo Assembly and Functional Annotation
Raw sequencing data were preprocessed using Trimmomatic v0.39 [63] to remove adapter sequences, low-quality bases (Q < 20), and reads shorter than 50 bp. Pure reads GC content was computed, and FastQC produced the Q20 and Q30 values to evaluate base quality. High-quality clean reads were obtained through this filtering process. These clean reads were then assembled into Unigenes using Trinity v2.13.2 [64]. The assembled Unigenes were annotated by aligning them against multiple databases, including Pfam, KEGG, Nr, Swiss-Prot, GO, KOG/COG, and Trembl. Transcription factor (TF) analysis was conducted using iTAK [65]. Gene expression levels were quantified using the FPKM score, and differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between samples were identified using DESeq2 [66]. DEGs were defined as those with a |log2Fold Change| ≥ 1 and a false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05. Functional and network enrichment analyses of DEGs were performed using the Eggnog-mapper [67] tool, with a p-value < 0.05 considered indicative of significant enrichment.
4.6. UPLC-MS/MS for Targeted Metabolite Analysis
4.6.1. Chemicals and Reagents
HPLC-grade methanol (MeOH) was acquired from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany), formic acid from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA), and hydrochloric acid from Xinyang Chemical Reagent (Changsha, China). MilliQ water (Millipore, Bradford, PA, USA) was utilized in all investigations, and standards were acquired from isoReag (Shanghai, China). Standard stock solutions were produced at 1 mg/mL concentration in 50% MeOH. All stock solutions were kept at −20 °C. Before analysis, the stock solutions were diluted with 50% MeOH to generate working solutions.
4.6.2. Sample Preparation and Extraction
The sample was freeze-dried, pulverized (30 Hz, 1.5 min), and preserved at −80 °C until required. Fifty milligrams of powder were weighed and extracted using 0.5 mL of a methanol/water/hydrochloric acid solution (500:500:1, V/V/V). The extract was vortexed for 5 min, subjected to ultrasonic for 5 min, and centrifuged at 12,000× g at 4 °C for 3 min. The residue was further extracted by repeating the abovementioned methods under identical conditions. The resulting supernatants were obtained and filtered using a 0.22 μm membrane filter (Anpel) before LC-MS/MS analysis.
4.6.3. UPLC Conditions
A UPLC-ESI-MS/MS system (UPLC: ExionLC™ AD, MS: Applied Biosystems 6500 Triple Quadrupole, https://sciex.com.cn/) was employed to analyze the samples. The analytical conditions were as follows: UPLC: column, water; ACQUITY BEH C18 (1.7 µm, 2.1 mm × 100 mm); solvent system, water (0.1% formic acid), methanol (0.1% formic acid); gradient program, 95:5 V/V at 0 min, 50:50 V/V at 6 min, 5:95 V/V at 12 min, hold for 2 min, and 95:5 V/V at 14 min; hold for 2 min; flow rate: 0.35 mL/min; temperature: 40 °C; injection volume: 2 μL.
4.6.4. ESI-MS/MS Conditions and Metabolites Quantification
Linear ion trap (LIT) and triple quadrupole scans were obtained using a triple quadrupole-linear ion trap mass spectrometer (QTRAP), specifically the QTRAP® 6500+ LC-MS/MS System. This system features an ESI Turbo Ion-Spray interface, operates in positive ion mode, and is managed by Analyst 1.6.3 software (Sciex). The parameters for the ESI source operation were outlined as follows: Ion source: ESI+; source temperature: 550 °C; ion spray voltage (IS): 5500 V; curtain gas (CUR) was set at 35 psi. Anthocyanins were examined utilizing timed multiple reaction monitoring (MRM). The collection of data was conducted using Analyst 1.6.3 software (Sciex). Multiquant 3.0.3 software (Sciex) was employed for the quantification of all metabolites. The parameters for the mass spectrometer, including declustering potentials (DP) and collision energies (CE) for specific MRM transitions, were optimized further for DP and CE. A designated group of MRM transitions has been recorded for all times based on the metabolites eluted during that time frame. To maximize the precision of both qualitative and quantitative analyses, chromatographic peaks of the analytes were adjusted in various samples according to the retention time and peak shape data of anthocyanin standards in Metware database (MWDB). The subsequent approach was employed to determine and quantify anthocyanins. The concentration value (ng/mL) of every sample was determined by replacing the integrated peak area with the standard curve equation. The absolute Log2FC (fold change) was used to determine whether metabolites were significantly regulated across the groups. The subsequent formula was employed to quantify the metabolite levels in the sample (µg/g): The concentration of metabolites in the sample (µg/g) is calculated using the formula: Levels = c × V/1,000,000/m, where c represents the concentration, V denotes the extraction solvent volume (µL), and m indicates the mass of the sample (g).
4.6.5. Identification of Differential Accumulation Metabolites
Differential accumulated metabolites (DAMs) were screened based on the criteria of a VIP value greater than 1, a Log2FC of at least 1, and a p-value less than 0.05.
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
The qRT-PCR assay was conducted on chosen DEGs linked with the anthocyanin and chlorophyll production pathways and key transcription factors. Total RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis were performed as previously described [68,69]. Primer pairs are listed in the Supplementary Table S4. Actin was used as an endogenous control. Gene expression levels were determined using the delta CT technique [70]. The experiment was performed in triplicate.
4.8. Statistical Analysis
To compare the mean values, a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed on the data using SPSS 16.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and by employing Duncan’s multiple range tests at a significance level of p < 0.05. The outcomes of hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) for samples and metabolites were displayed as heatmaps accompanied by dendrograms. HCA and K-means were performed using the built-in functions in R version 4.4.2.
5. Conclusions
This study examined the anthocyanin metabolites and their corresponding genes in three hydrangea cultivars: ‘DB’, ‘LB’, and ‘GB’. A total of 47 anthocyanin metabolites were identified, predominantly consisting of delphinidin, cyanidin, and pelargonidin derivatives, with an observed increase in total content in deep blue flowering shade (‘DB’). Deciphering the transcriptome has revealed critical DEGs linked to pathways involved in the translation of hormone signals and the production of anthocyanins and chlorophylls, the two primary pigments in flower sepals. This elucidated the molecular mechanisms behind anthocyanin accumulation and production in hydrangea flower sepal pigmentation, enhancing our understanding of the biochemical basis of flower sepal color in H. macrophylla.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/plants14050742/s1, Figure S1: Concentration of anthocyanin contents in hydrangea cultivars: Figure S2: Unigene and NR analysis; Figure S3: Comparative analysis of DEGs in different samples; Figure S4: Transcription factor classification pie chart; Table S1: Summary of quality sample of RNA-seq data; Table S2: Summary of transcript and unigenes distribution, number and length; Table S3: Summary of annotation results of transcriptome data; Table S4: List of primers used for qRT-PCR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z. (Yiwei Zhou) and F.A.; Formal analysis, Y.K., U.A., D.W., W.H., Y.Z. (Ying Zhou), Y.Q. and Y.Z. (Yiwei Zhou); Funding acquisition, Y.K.; Investigation, Y.Z. (Ying Zhou) and Y.Q.; Methodology, Y.K. and D.W.; Project administration, F.A.; Software, U.A., W.H., Y.Z. (Ying Zhou), Y.Z. (Yiwei Zhou) and F.A.; Validation, Y.Q.; Writing—original draft, Y.K., Y.Z. (Yiwei Zhou) and F.A.; Writing—review & editing, Y.K., Y.Z. (Yiwei Zhou) and F.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number W2433051, Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department Local Universities Joint Project (202101BA070001-166), the Talent Introduction Project of Kunming University, grant number XJ20220003, and Yunnan Provincial Natural Science Basic Research Fund General Program, Project No. 202501AT070058.
Data Availability Statement
The transcriptome raw data have been submitted to the SRA database of the NCBI (PRJNA1208947).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Cai, M.; Wang, K.; Luo, L.; Pan, H.-t.; Zhang, Q.-x.; Yang, Y.-y. Production of interspecific hybrids between Hydrangea macrophylla and Hydrangea arborescens via ovary culture. HortScience 2015, 50, 1765–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardos, J.H.; Robacker, C.D.; Dirr, M.A.; Rinehart, T.A. Production and verification of Hydrangea macrophylla × H. angustipetala hybrids. HortScience 2009, 44, 1534–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samain, M.-S.; Wanke, S.; Goetghebeur, P. Unraveling extensive paraphyly in the genus Hydrangea sl with implications for the systematics of tribe Hydrangeeae. Syst. Bot. 2010, 35, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaing, M.T.; Jung, H.-J.; Han, T.-H. Trend of hydrangea cultivar development. Trends Agric. Life Sci. 2016, 53, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reed, S.; Riedel, G.; Pooler, M. Verification and establishment of Hydrangea macrophylla ‘Kardinal’x H. paniculata ‘Brussels Lace’interspecific hybrids. J. Environ. Hortic. 2001, 19, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Kariuda, M.; Itoi, H. Blueing of sepal colour of Hydrangea macrophylla. Phytochemistry 1985, 24, 2251–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Ito, D.; Shinkai, Y.; Kondo, T. Change of color and components in sepals of chameleon hydrangea during maturation and senescence. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 3159–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.M.; Jones, K.D.; Rinehart, T.A. Production and characterization of intergeneric hybrids between Dichroa febrifuga and Hydrangea macrophylla. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2008, 133, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Aoki, D.; Fukushima, K.; Yoshida, K. Direct mapping of hydrangea blue-complex in sepal tissues of Hydrangea macrophylla. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Ito, D.; Miki, N.; Kondo, T. Single-cell analysis clarifies mosaic color development in purple hydrangea sepal. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 3549–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Tao, J. Recent advances on the development and regulation of flower color in ornamental plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.; Yu, C.; Han, Y.; Guo, X.; Luo, L.; Pan, H.; Zheng, T.; Wang, J.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, Q. Determination of flavonoids and carotenoids and their contributions to various colors of rose cultivars (Rosa spp.). Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lu, M.; Tang, D.; Shi, Y. Composition of carotenoids and flavonoids in narcissus cultivars and their relationship with flower color. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapir, Y.; Gallagher, M.K.; Senden, E. What maintains flower colour variation within populations? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2021, 36, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Toyama-Kato, Y.; Kameda, K.; Kondo, T. Sepal color variation of Hydrangea macrophylla and vacuolar pH measured with a proton-selective microelectrode. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003, 44, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Qi, H.; Yang, S.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Liu, C. Role of delphinidin-3-glucoside in the sepal blue color change among Hydrangea macrophylla cultivars. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 313, 111902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumoto, Y.; Fukuchi-Mizutani, M.; Fukui, Y.; Brugliera, F.; Holton, T.A.; Karan, M.; Nakamura, N.; Yonekura-Sakakibara, K.; Togami, J.; Pigeaire, A. Engineering of the rose flavonoid biosynthetic pathway successfully generated blue-hued flowers accumulating delphinidin. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007, 48, 1589–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.C.; Perkins, J.; Peakall, R. Anthocyanin and flavonol glycoside metabolic pathways underpin floral color mimicry and contrast in a sexually deceptive orchid. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 860997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Dong, X.; Xue, C.; Liu, Z.; Cao, F. Exploring the molecular mechanism of blue flower color formation in Hydrangea macrophylla cv. “Forever Summer”. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 585665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.D.; Wang, S.; Rausher, M.D. Functional evolution of an anthocyanin pathway enzyme during a flower color transition. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enaru, B.; Drețcanu, G.; Pop, T.D.; Stǎnilǎ, A.; Diaconeasa, Z. Anthocyanins: Factors affecting their stability and degradation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Puche, L.; Cumplido-Laso, G.; Amil-Ruiz, F.; Hoffmann, T.; Ring, L.; Rodríguez-Franco, A.; Caballero, J.L.; Schwab, W.; Muñoz-Blanco, J.; Blanco-Portales, R. MYB10 plays a major role in the regulation of flavonoid/phenylpropanoid metabolism during ripening of Fragaria × ananassa fruits. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.-L.; Wang, Y.-X.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.-W.; Cui, X.; Zhuang, J. Two MYB transcription factors (CsMYB2 and CsMYB26) are involved in flavonoid biosynthesis in tea plant [Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze]. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Gu, H.; Wang, L.; Shao, Y.; Li, R.; Li, W. Exogenous ethylene promotes peel color transformation by regulating the degradation of chlorophyll and synthesis of anthocyanin in postharvest mango fruit. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 911542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hörtensteiner, S. The pathway of chlorophyll degradation: Catabolites, enzymes and pathway regulation. In Plastid Development in Leaves During Growth and Senescence; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 363–392. [Google Scholar]
- Bashandy, H.; Pietiäinen, M.; Carvalho, E.; Lim, K.-J.; Elomaa, P.; Martens, S.; Teeri, T.H. Anthocyanin biosynthesis in gerbera cultivar ‘Estelle’and its acyanic sport ‘Ivory’. Planta 2015, 242, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonnet, J.-F. Colour effects of co-pigmentation of anthocyanins revisited—1. A colorimetric definition using the CIELAB scale. Food Chem. 1998, 63, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, R.; Francioso, A.; Mosca, L.; Silva, P. Anthocyanins: A comprehensive review of their chemical properties and health effects on cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. Molecules 2020, 25, 3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco-Obando, W.; Hirsch, G.N.; Wetzstein, H.Y. Genotypic variation in flower induction and development in Hydrangea macrophylla. HortScience 2005, 40, 1695–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, Y.; Hattori, T.; Mogami, K.; Fudano, T.; Uehara, M. Selection of hydrangea (Hydrangea spp.) cultivars with high potential for unseasonable flower bud production in Japan. Hortic. J. 2018, 87, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhu, G.; Xu, Y.; Tan, J.; Liu, J. Diversity, classification, and EST-SSR-based association analysis of caladium ornamental traits. Physiol. Plant. 2023, 175, e13841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yin, M.; Abbas, F.; Sun, Y.; Gao, T.; Yan, F.; Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Yue, Y.; Yu, R. Classification and Association Analysis of Gerbera (Gerbera hybrida) Flower Color Traits. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 779288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Fan, H.; Yao, F.; Cao, X.; Liu, M.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y. Transcriptomics and targeted metabolomics profilings for elucidation of pigmentation in Lonicera japonica flowers at different developmental stages. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 145, 111981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, Y.; Qi, Y.; Wei, H.; Lei, Y.; Huang, F.; Abbas, F. Integrated metabolome and transcriptome analysis provides insights on the floral scent formation in Hydrangea arborescens. Physiol. Plant. 2023, 175, e13914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Ma, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Chen, Q.; Deng, Y. Metabolite profiling of external and internal petals in three different colors of tea flowers (Camellia sinensis) using widely targeted metabolomics. Metabolites 2023, 13, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuka, T.; Nishihara, M.; Mishiba, K.; Hirano, H.; Yamamura, S. Two different transposable elements inserted in flavonoid 3′, 5′-hydroxylase gene contribute to pink flower coloration in Gentiana scabra. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2006, 275, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuka, T.; Nishihara, M.; Mishiba, K.; Yamamura, S. Temporal expression of flavonoid biosynthesis-related genes regulates flower pigmentation in gentian plants. Plant Sci. 2005, 168, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lyu, T.; Lyu, Y. The Molecular Biology Analysis for the growing and development of Hydrangea macrophylla ‘Endless Summer’ under different light and temperature conditions. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Dai, L.; Qi, X.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Gao, K.; Qiu, S.; Jin, Y.; Deng, Y. Metabolomics reveals a key role of salicylic acid in embryo abortion underlying interspecific hybridization between Hydrangea macrophylla and H. arborescens. Plant Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, P.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Chang, J.; Zhang, H.; Shao, H.; Zhou, Y. Integrated Metabolome and Transcriptome Analysis of Petal Anthocyanin Accumulation Mechanism in Gloriosa superba ‘Rothschildiana’ during Different Flower Development Stages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.S.; Gao, J.M.; Shu, Q.Y.; Li, C.H.; Yao, J.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, J.J. Determination of anthocyanins and exploration of relationship between their composition and petal coloration in crape myrtle (Lagerstroemia hybrid). J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2008, 50, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Zheng, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xue, Y.; Tang, Q.; Xu, H.; Chen, M. Characterization variation of the differential coloring substances in rapeseed petals with different colors using UPLC-HESI-MS/MS. Molecules 2023, 28, 5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, R.; Dubouzet, J.G.; Matsumura, H.; Yasuda, K.; Iwashina, T. A new allele of flower color gene W1 encoding flavonoid 3′5′-hydroxylase is responsible for light purple flowers in wild soybean Glycine soja. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Lai, L.; Wang, F.; Sun, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, Y. Characterisation of flower colouration in 30 Rhododendron species via anthocyanin and flavonol identification and quantitative traits. Plant Biol. 2018, 20, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, N.; Nakayama, T. Achievements and perspectives in biochemistry concerning anthocyanin modification for blue flower coloration. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Hu, K.; Dai, S. Flower color breeding by molecular design in ornamentals. Mol. Plant Breed. 2008, 6, 16–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sibout, R.; Le Bris, P.; Legée, F.; Cézard, L.; Renault, H.; Lapierre, C. Structural redesigning Arabidopsis lignins into alkali-soluble lignins through the expression of p-coumaroyl-CoA: Monolignol transferase PMT. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tian, F.; Yu, F.; Li, X.; Huang, D. Association analysis of transcriptome and targeted metabolites identifies key genes involved in Iris germanica anthocyanin biosynthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-Z.; Tian, X.-C.; Feng, Y.-Q.; Qiao, H.-L.; Wu, A.-Y.; Li, X.; Hou, Y.-J.; Ma, Z.-H. The genome-wide identification of the dihydroflavonol 4-reductase (DFR) gene family and its expression analysis in different fruit coloring stages of strawberry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Fukui, Y.; Ashikari, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kusumi, T. Purification and characterization of anthocyanin 3-aromatic acyltransferase from Perilla frutescens. Plant Sci. 1998, 137, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Yonekura-Sakakibara, K.; Nakabayashi, R.; Higashi, Y.; Yamazaki, M.; Tohge, T.; Fernie, A.R. The flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in Arabidopsis: Structural and genetic diversity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 72, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qi, X.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, W.; Guan, J.; Liu, Z.; Ren, J.; Feng, H.; Zhang, Y. Transcriptome and metabolome profiling to explore the causes of purple leaves formation in non-heading Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. chinensis Makino var. mutliceps Hort.). Foods 2022, 11, 1787. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Huang, J.-C.; Wu, C.-Y.; Yu, S.-Q.; Wang, Y.-T.; Ye, C.; Shi, T.-Q.; Huang, H. A comprehensive review on the recent advances for 5-aminolevulinic acid production by the engineered bacteria. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2024, 45, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmiya, A. Molecular mechanisms underlying the diverse array of petal colors in chrysanthemum flowers. Breed. Sci. 2018, 68, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan, A.C.; Hellens, R.P.; Laing, W.A. MYB transcription factors that colour our fruit. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Osbourn, A.; Ma, P. MYB transcription factors as regulators of phenylpropanoid metabolism in plants. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 689–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, M.-G.; Wang, T.-Y.; Huang, X.-M.; Hu, G.-B.; Zhou, B.-Y.; Wang, H.-C.; Abbas, F. ERF transcription factors govern anthocyanin biosynthesis in litchi pericarp by modulating the expression of anthocyanin biosynthesis genes. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 337, 113464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, B.; Zhang, G.; Chen, L.; Dong, Q.; Wen, J.; Mysore, K.S.; Zhao, J. Regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis by Medicago truncatulab HLH transcription factor MtTT8. New Phytol. 2016, 210, 905–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, B.; Leng, P.; Wu, J.; Hu, Z. SoNAC72-SoMYB44/SobHLH130 module contributes to flower color fading via regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis by directly binding to the SoUFGT1 promoter in lilac (Syringa oblata). Hortic. Res. 2024, uhae326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.-C.; Zhuo, M.-G.; Abbas, F.; Hu, G.-B.; Wang, H.-C.; Huang, X.-M. Transcription factor LcNAC002 coregulates chlorophyll degradation and anthocyanin biosynthesis in litchi. Plant Physiol. 2023, 192, 1913–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.-C.; Zhuo, M.-G.; Abbas, F.; Zeng, R.-F.; Hu, G.-B.; Wang, H.-C.; Huang, X.-M. ROS-and CBF-mediated pathways are involved in chlorophyll degradation and anthocyanin accumulation enhanced by cool temperatures in ripening litchi fruits. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 212, 112888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiao, C.; Sun, H.; Rosli, H.G.; Pombo, M.A.; Zhang, P.; Banf, M.; Dai, X.; Martin, G.B.; Giovannoni, J.J.; et al. Itak: A program for genome-wide prediction and classification of plant transcription factors, transcriptional regulators, and protein kinases. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from rna-seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for rna-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manju; Deepika; Rohil, H. Real Time Hand Gesture Recognition Using CIELab Colour Space Model. Int. J. Comput. Organ. Trends 2024, 5, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P.; Huerta-Cepas, J. eggNOG-mapper v2: Functional annotation, orthology assignments, and domain prediction at the metagenomic scale. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, F.; Guo, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Amanullah, S.; Wang, H.C.; Shen, J. Metabolome and transcriptome analysis of terpene synthase genes and their putative role in floral aroma production in Litchi chinensis. Physiol. Plant. 2022, 174, e13796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Y.; Abbas, F.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, R.; Fan, Y. Auxin-responsive R2R3-MYB transcription factors HcMYB1 and HcMYB2 activate volatile biosynthesis in Hedychium coronarium flowers. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 710826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
