Integrated Analysis of Metabolites and Biological Endpoints Bring New Insights into Sulfamethoxazole Stress Tolerance in Ryegrass
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
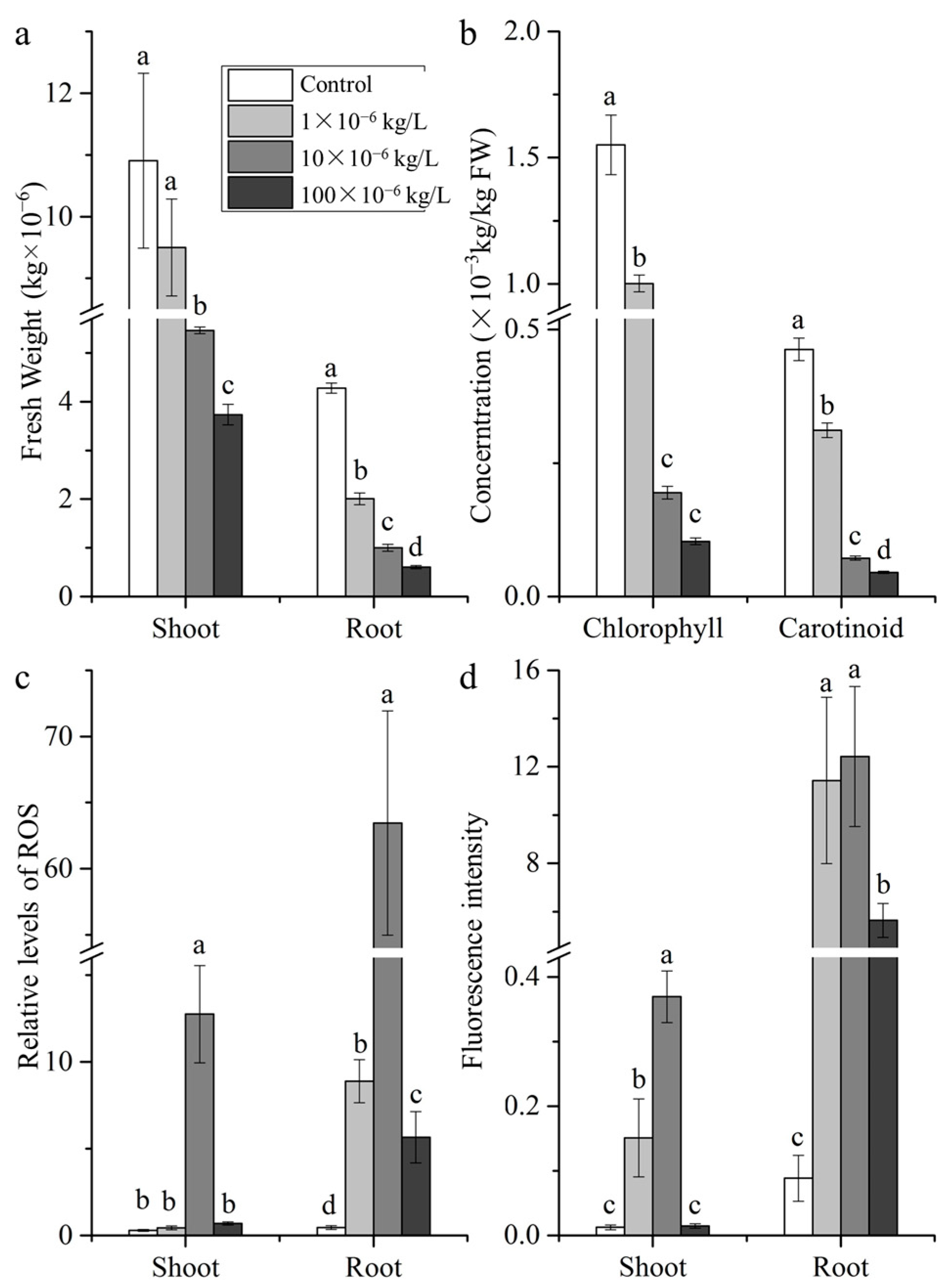
2.1. Morphological Characteristics
2.2. ROS and Cell Permeability
2.3. SOD, POD, and CAT Activities
2.4. Metabolite Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. ROS Levels and Cell Permeability
3.2. SOD, POD, and CAT Activity
3.3. Metabolites
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Halling-Sørensen, B.; Nors Nielsen, S.; Lanzky, P.F.; Ingerslev, F.; Holten Lützhøft, H.C.; Jørgensen, S.E. Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment—A review. Chemosphere 1998, 36, 357–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassouan, M.K.; Ballesteros, O.; Taoufiki, J.; Vílchez, J.L.; Cabrera-Aguilera, M.; Navalón, A. Multiresidue determination of quinolone antibacterials in eggs of laying hens by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 852, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetting, V.; Lee, K.A.; Tell, L.A. Pharmacokinetics of veterinary drugs in laying hens and residues in eggs: A review of the literature. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 521–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajda, A.; Posyniak, A. Doxycycline depletion and residues in eggs after oral administration to laying hens. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2015, 32, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmulak, T.; Tell, L.A.; Gehring, R.; Baynes, R.E.; Vickroy, T.W.; Riviere, J.E. Egg residue considerations during the treatment of backyard poultry. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2015, 247, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakordonets, L.; Tolstanova, G.; Yankovskiy, D.; Dyment, H.; Kramarev, S. Different regimes of multiprobiotic for prevention of immediate and delayed side effects of antibiotic therapy in children. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 2194–2201. [Google Scholar]
- Han, T.; Liang, Y.P.; Wu, Z.N.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.W.; Li, Q.F.; Chen, X.J.; Guo, W.L.; Jiang, L.N.; Pan, F.F.; et al. Effects of tetracycline on growth, oxidative stress response, and metabolite pattern of ryegrass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 380, 120885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Chu, L.M. Phytotoxicity of veterinary antibiotics to seed germination and root elongation of crops. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Qi, H.Z.; Zhou, Y.P. Metabonomics and the research of traditional Chinese Medicine. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 396–398, 1676–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño-Carrillo, C.V.; Sánchez, E.V.; Verduzco, C.V.; Herbert-Pucheta, J.E. Polyphenol-based nuclear magnetic resonance non-targeted metabolomics of temperature- and time-controlled blue and red maize sprouting. SN App. Sci. 2021, 3, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Lin, H.Q.; Zhou, B.S.; Yu, H.; Li, L.; Wang, C.X.; Li, X.Y.; Li, P.Y.; Liu, J.P.; et al. The effect of ginsenoside Rg5, isolated from black ginseng, on heart failure in zebrafish based on untargeted metabolomics. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 76, 104325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.J. Ecotoxicological mechanism of sulfamethoxazole on Chinese cabbage and rice seedlings. Zhejiang Gongshang Univ. 2023. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.W.; Lu, H.B.; Lu, S.Y.; Huang, Z.G. Impacts of sulfamethoxazole stress on vegetable growth and rhizosphere bacteria and the corresponding mitigation mechanism. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1303670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.T.; Li, J.; Zhou, S.S.; Li, K.; Niu, L.L.; Zhao, L.; Xu, D.M. Analysis of the effects of sulfamethoxazole on the secondary metabolites and antioxidants in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) and the underlying mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 165768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.F.; Cui, H.W.; Wang, C.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Duan, W.Y. Oxidative stress responses in two marine diatoms during sulfamethoxazole exposure and the toxicological evaluation using the IBRv2 index. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 2023, 276, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.X.; Song, Y.; Xu, W.Y.; Lu, N.N.; Chen, Y.; Jia, R.B.; Sun, S.H. Individual and combined toxicity of sulfamethoxazole and desethylatrazine to Chlorella vulgaris: Growth inhibition, photosynthetic activity and oxidative stress. Chem. Ecol. 2023, 39, 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.N.; Chen, C.; Li, G.D.; Liu, Q.Y.; Tian, L.L. Effects of Sulfamethoxazole (SMZ) on the Content of Chlorophylll (CHL) and Soluble Protein (SP), and the Superoxide Dismutases (SOD) Activity of Wheat, Triticum aestivum. Asian J. Ecotox. 2013, 8, 543–548, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.; Gao, Y.; Wu, H.; Hou, W.; Zhang, C.; Ma, H. Physiological effect of anatase TiO2 nanoparticles on Lemna minor. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 2147–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.M.; Ko, W.C.; Wu, J.S.; Wei, Y.H.; Wang, L.F.; Chang, E.E.; Lo, T.Y.; Cheng, H.H.; Chen, C.T. Mediating of caspase-independent apoptosis by cadmium through the mitochondria-ROS pathway in MRC-5 fibroblasts. J. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 91, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrander, L.; Cartier, L.; Bedard, K.; Banfi, B.; Lardy, B.; Plastre, O.; Sienkiewicz, A.; Fórró, L.; Schlegel, W.; Krause, K.H. NOX4 activity is determined by mRNA levels and reveals a unique pattern of ROS generation. Biochem. J. 2007, 406, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, S.; Ahmad, A.; Siddiqi, T.O.; Ahmad, P. Changes in growth, lipid peroxidation and some key antioxidant enzymes in chickpea genotypes under salt stress. Acta Physiol. Plant 2013, 35, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisany, W.; Sohrabi, Y.; Heidari, G.; Siosemardeh, A.; Ghassemi-Golezani, K. Changes in antioxidant enzymes activity and plant performance by salinity stress and zinc application in soybean (Glycine max L.). Plant Omics J. 2012, 5, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.D.; Tang, N.; Lin, D.B.; Deng, W.; Li, Z.G. Integration of multi-omics analyses highlights the secondary metabolism response of tomato fruit to low temperature storage. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Wang, B.S.; Wu, Z.N.; Dai, C.Y.; Zhao, J.J.; Mi, Z.R.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, C.; Miao, X.Y.; Zhou, J.G.; et al. Providing a view for toxicity mechanism of tetracycline by analysis of the connections between metabolites and biologic endpoints of wheat. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 212, 111998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Naqvi, F.N. Effect of water stress on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in local bread ryegrass hexaploids. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 8, 521–526. [Google Scholar]
- Zeeshan, M.; Iqbal, A.; Salam, A.; Hu, Y.X.; Khan, A.H.; Wang, X.; Miao, X.R.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhang, P.W. Zinc oxide nanoparticle-mediated root metabolic reprogramming for arsenic tolerance in Soybean. Plants 2024, 13, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Gao, Y.; Fang, Z. Integrating metabolism analysis with biologic endpoints provides view into nanotoxicological mechanisms of graphene oxide: From effect onset to cessation. Carbon 2016, 109, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Jia, J.; Han, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Shao, L.; Wang, X. Integrated Analysis of Metabolites and Biological Endpoints Bring New Insights into Sulfamethoxazole Stress Tolerance in Ryegrass. Plants 2025, 14, 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14040538
Yang Y, Jia J, Han T, Zhang H, Wang Y, Shao L, Wang X. Integrated Analysis of Metabolites and Biological Endpoints Bring New Insights into Sulfamethoxazole Stress Tolerance in Ryegrass. Plants. 2025; 14(4):538. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14040538
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yong, Jiangtao Jia, Tao Han, Heng Zhang, Yvjie Wang, Luying Shao, and Xinyi Wang. 2025. "Integrated Analysis of Metabolites and Biological Endpoints Bring New Insights into Sulfamethoxazole Stress Tolerance in Ryegrass" Plants 14, no. 4: 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14040538
APA StyleYang, Y., Jia, J., Han, T., Zhang, H., Wang, Y., Shao, L., & Wang, X. (2025). Integrated Analysis of Metabolites and Biological Endpoints Bring New Insights into Sulfamethoxazole Stress Tolerance in Ryegrass. Plants, 14(4), 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14040538





