Comparative Analysis of Rice Yield and Economic Performance Across Different Planting Patterns in Double-Cropping Rice Systems Under Global Warming
Abstract
1. Introduction
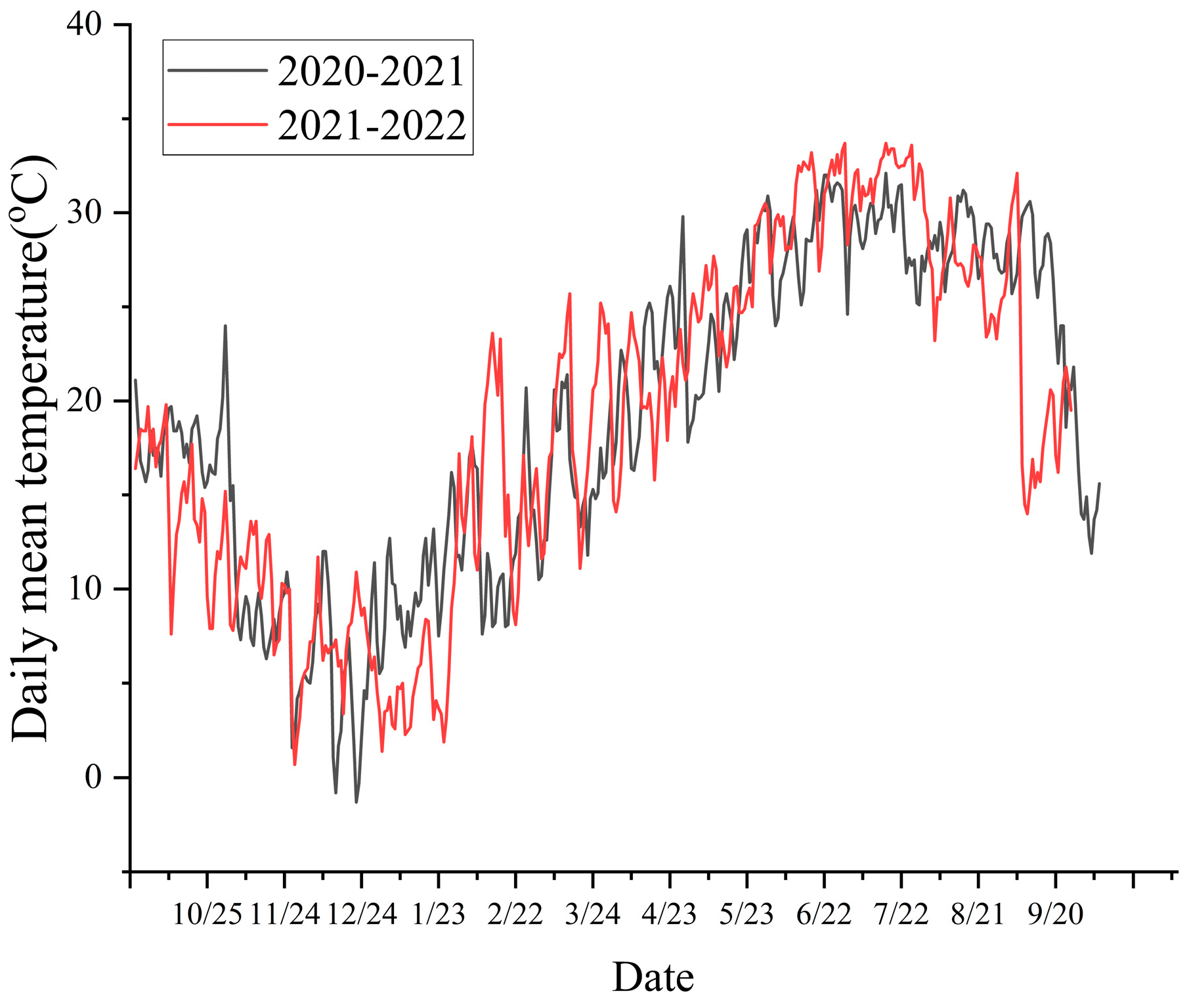
2. Results
2.1. The Effect of Different Planting Patterns on Rice Yield and Annual Grain Yield
2.1.1. Yield and Its Composition
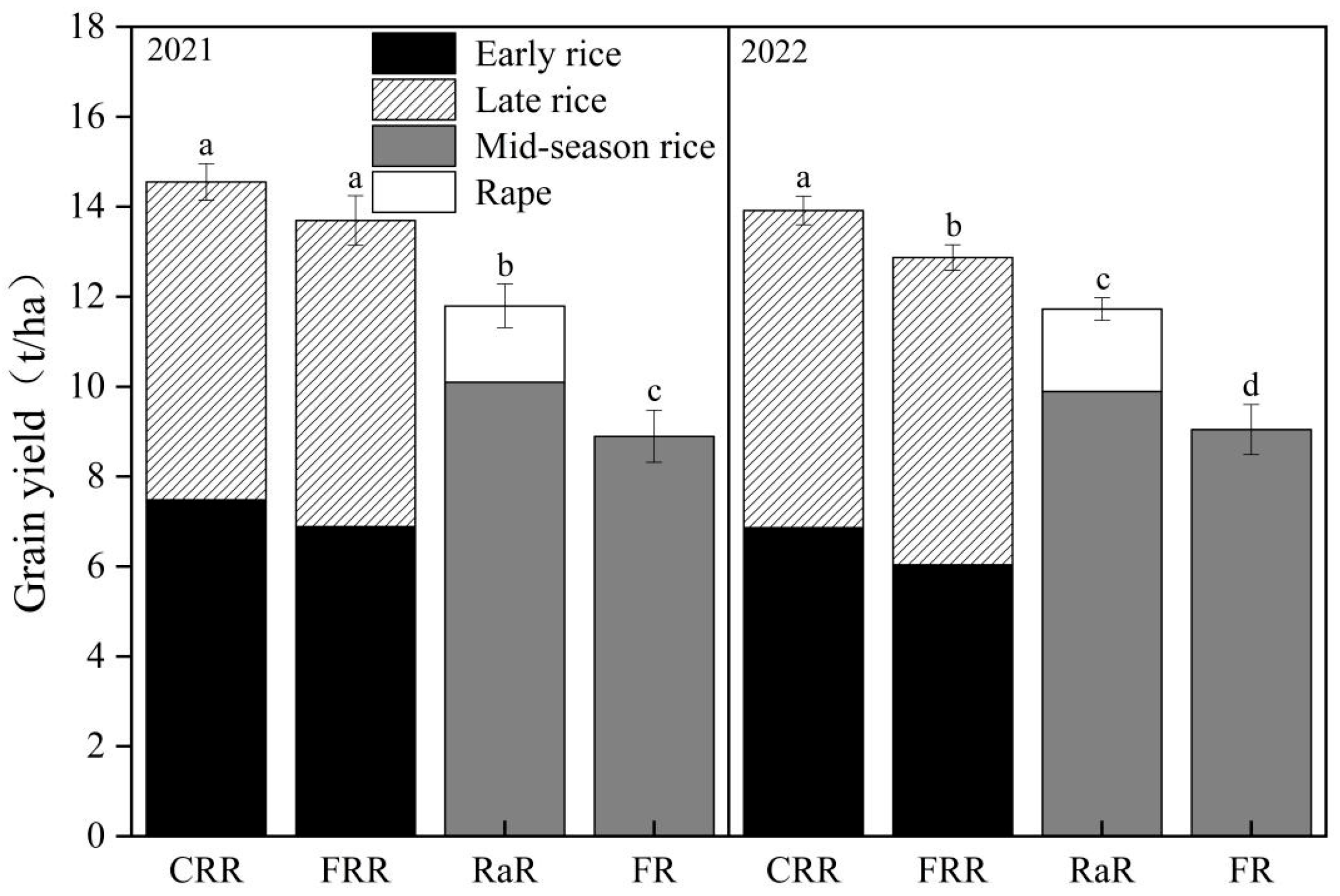
2.1.2. Annual Grain Yield
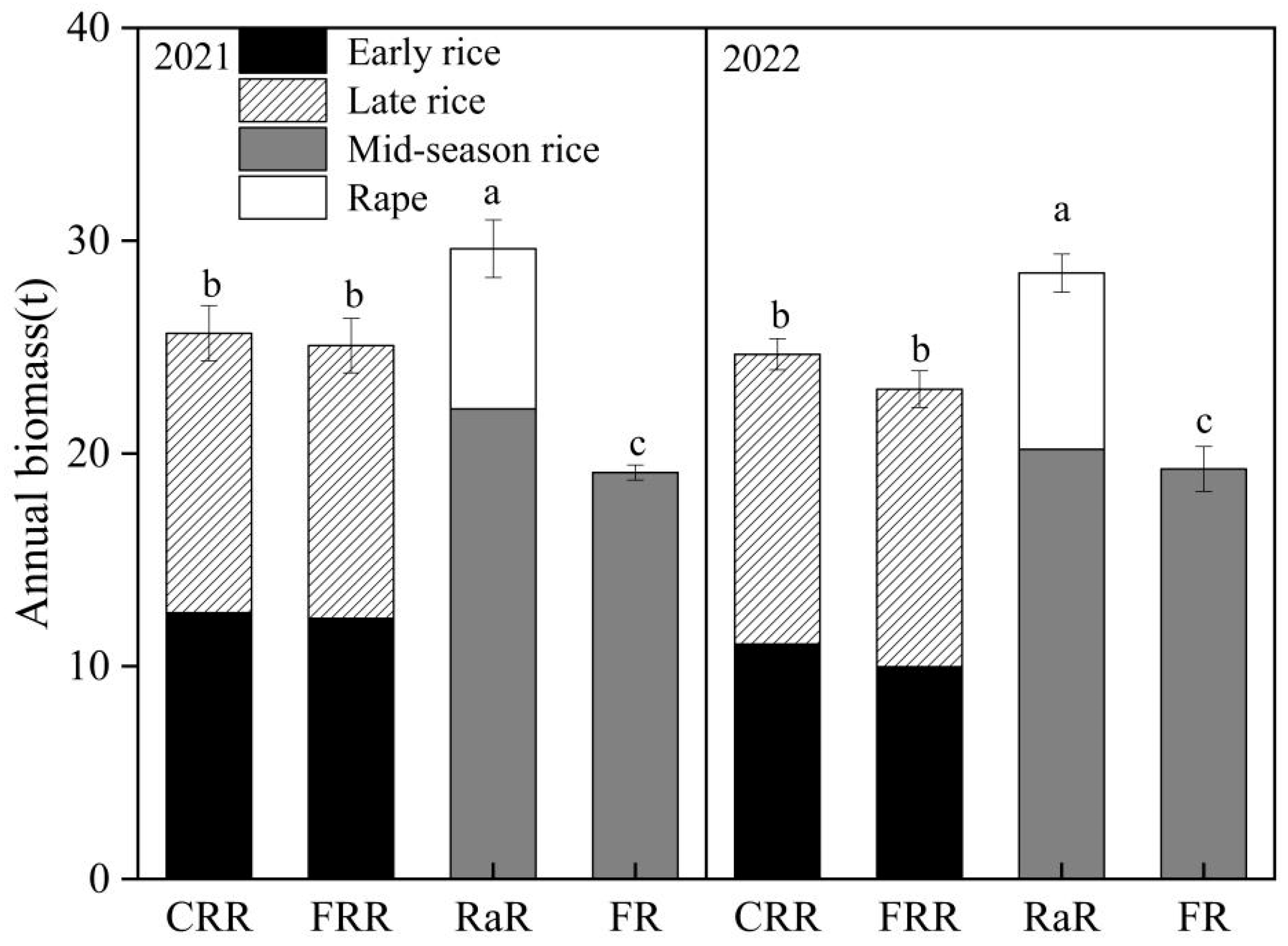
2.1.3. Annual Biomass
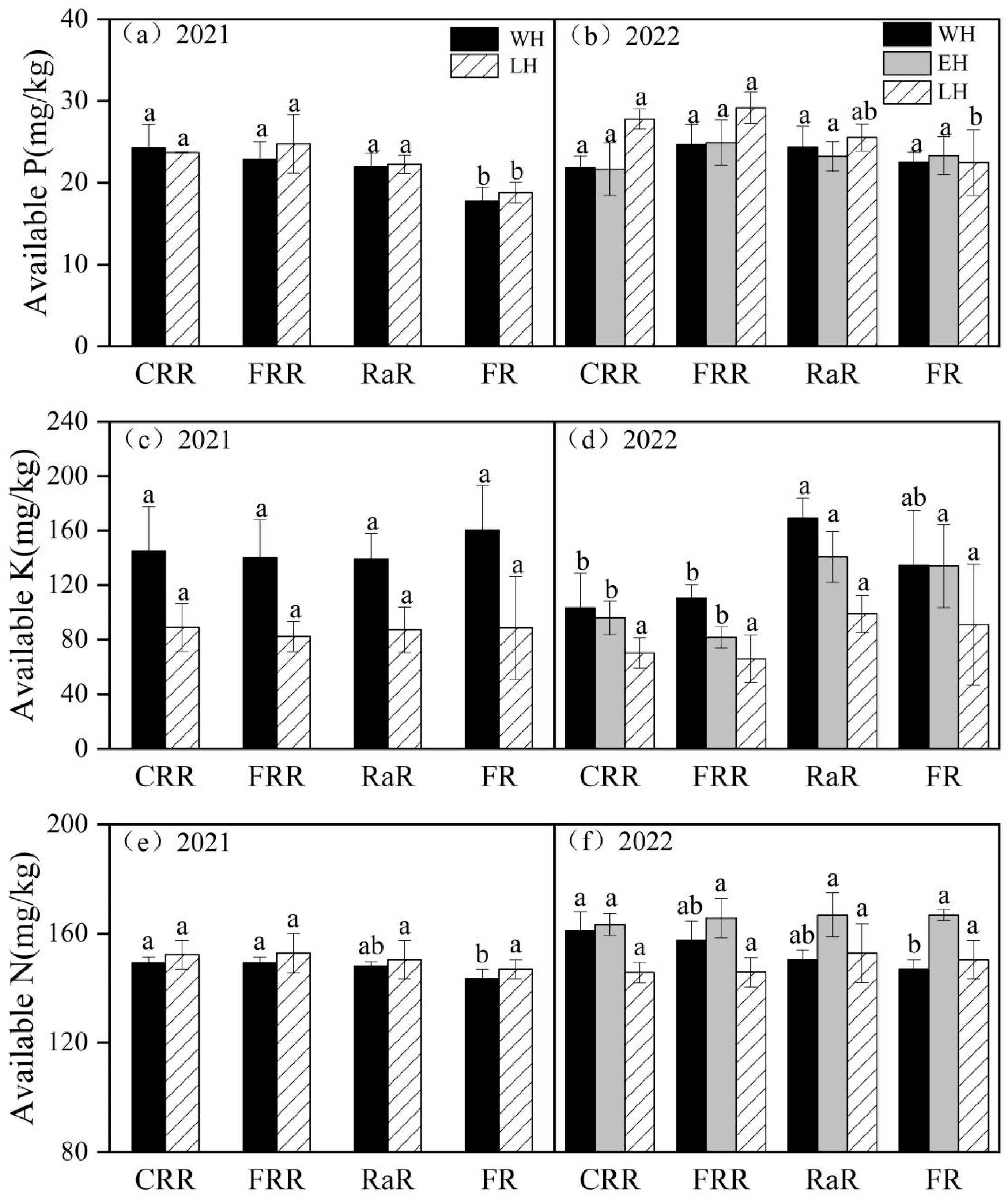
2.2. The Available Nutrient of Soil
2.3. The Effect of Different Planting Patterns on Economic Benefits
3. Discussion
3.1. The Analysis of Different Planting Patterns on Grain Yield and Yield Formation
3.2. The Analysis of Different Planting Patterns on Soil Quality
3.3. Economic Benefit of Different Planting Patterns
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Site Description
4.2. Experimental Materials and Design
4.3. Sampling and Analysis
4.3.1. Crop Yield
4.3.2. Dry Matter Production
4.3.3. The Available Nutrient of Soil
4.3.4. Agricultural Input Costs
4.4. Statistics and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RaR | rape–rice |
| FR | fallow–rice |
| CRR | Chinese milk vetch–early rice–late rice |
| FRR | fallow–early rice–late rice |
| CNY | Chinese Yuan |
References
- Guo, Y.; Wu, W.; Bryant, C. Quantifying Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Rice Yield Gaps in Double-Cropping Systems: A Case Study in Pearl River Delta, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Long, W.; Wang, H.; Long, P.; Xu, Y.; Fu, Z. Matter Production Characteristics and Nitrogen Use Efficiency under Different Nitrogen Application Patterns in Chinese Double-Cropping Rice Systems. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ikinci, A. Effects of Climate Change on Fruit Growing: Risks and Solutions for the Future. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Change 2025, 15, 268–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijan, F.; Masoud, R. Exploring the impact of the recent global warming on extreme weather events in Central Asia using the counterfactual climate data ATTRICI v1.1. Clim. Change 2024, 177, 80. [Google Scholar]
- Masud, M.; Juthee, S.; Hosenuzzaman, M.; Islam, M.; Haque, M.; Matin, M. Current understanding of heat shock protein-mediated responses to heat stress in rice. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2025, 237, 106192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, P.; Tang, H.; Wu, W.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Q.; Li, Z. Shifts in the extent and location of rice cropping areas match the climate change pattern in China during 1980–2010. Reg. Environ. Change 2015, 15, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, H.; Yamashita, H.; Wada, K.; Yonemaru, J. Real-time emulation of future global warming reveals realistic impacts on the phenological response and quality deterioration in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2316497121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, T.; Zhang, N.; Mo, D.; Liu, Z.; Yang, T.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Ding, Y.; Yu, J. Higher N2O emissions and lower rice yield within double-cropped rice systems of South China under warming. Field Crops Res. 2025, 322, 109709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, H.; Pan, X.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, G. Differential Impacts of Whole-Growth-Duration Warming on the Grain Yield and Quality Between Early and Late Rice (Oryza sativa) in a Double Rice Cropping System. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2025, 211, e70052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, T.; Xiong, R.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tang, F.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, S. Effect of climate warming on the grain quality of early rice in a double-cropped rice field: A 3-year measurement. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1133665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Qian, H.; Li, H.; Tang, J.; Yang, T.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ding, Y.; Yu, J. Effect of warming on rice yield and methane emissions in a Chinese tropical double-rice cropping system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 348, 108409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, W.; Zeng, Y.; Shi, Q.; Pan, X.; Huang, S.; Shang, Q.; Tan, X.; Li, M.; Hu, S.; Zeng, Y. Changes in safe production period and temperature-light resources of double-cropping rice in Jiangxi over the past 30 years. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2016, 30, 323–334, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ai, Z.; Guo, X.; Liu, W.; Ma, G.; Qing, X. Changes in safe production date of double-cropping rice in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Acta Agron. Sin. 2014, 40, 1320–1329, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, J. Responses of potential double cropping areas expansion and appropriate crop management practices to climate change in northern China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1441396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Hou, Q.; Wang, X.; Ni, W. Effects of different fertilizing models on growth of single crop rice and nitrogen and phosphorus runoff losses. J. Zhejiang Univ. Agric. Life Sci. 2020, 46, 225–233, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Zhou, G.; Cao, W. Effects of Milk Vetch (Astragalus sinicus) as Winter Green Manure on Rice Yield and Rate of Fertilizer Application in Rice Paddies in South China. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2020, 26, 2115–2126, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chang, D.; Wang, H.; Zhou, G.; Gao, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, C.; Cao, W. Yield and Nitrogen Uptake of Rice and Soil Nitrogen Supply Capacity under Fertilizer Reduction in a Rice-Rice-Chinese Milk Vetch Rotation System, Northern Jiangxi Province, China. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2023, 29, 1449–1460, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, C.; Lv, Y.; Gao, S.; Cao, W. Long-term green manuring enhances crop N uptake and reduces N losses in rice production system. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 220, 105369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Xu, C.; Zhang, L.; Xie, J.; Zhou, G.; Liu, J.; Hu, F.; Gao, S.; Cao, W. Application of milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) with reduced chemical fertilizer improves rice yield and nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium use efficiency in southern China. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 144, 126762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Yuan, B.; Jin, Z.; Man, J.; Peng, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Nie, L. Comparative study on annual yield, water consumption, irrigation water use efficiency and economic benefits of different rice-oilseed rape rotation systems in Central China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 247, 106741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Yang, X.; Zheng, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Sun, S.; Li, K.; Dong, C. Effects of climate change on the extension of the potential double cropping region and crop water requirements in Northern China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 268, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerioli, T.; Gentimis, T.; Linscombe, S.D.; Famoso, A.N. Effect of rice planting date and optimal planting window for Southwest Louisiana. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, A.; Cowan, N.J.; Drewer, J.; Tomer, R.; Kumar, V.; Sharma, S.; Paul, A.; Jain, N.; Kumar, S.; Jha, G.; et al. The impact of different fertiliser management options and cultivars on nitrogen use efficiency and yield for rice cropping in the Indo-Gangetic Plain: Two seasons of methane, nitrous oxide and ammonia emissions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 355, 108593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garinie, T.; Lelièvre, Y.; Nusillard, W.; Zito, S.; Thiéry, D.; Moreau, J. Current and future perspectives on Lobesia botrana pest oviposition behavior in the context of climate change and fungicide applications. Crop Prot. 2025, 193, 107198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukura, K.; Mizutani, N.; Tanaka, S.; Tanaka, Y. Evaluation of overwintering risk of tropical and subtropical insect pests in temperate regions. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Hu, M.; He, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, C.; et al. Responses of Yield and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Rice to Climate Resources under Different Crop Rotation Patterns and Planting Methods. Plants 2024, 13, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, K.; Nayak, A.; Patra, R.; Tripathi, R.; Swain, C.; Mishra, P.; Satapathy, M.; Eeswaran, R.; Garnaik, S. Multi-criteria assessment of climate smartness in rice-based cropping systems. Farm. Syst. 2025, 3, 100135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, W.; Xie, X.; Yin, C.; Hou, H.; Yan, W.; Wang, G. Net global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensity as affected by different water management strategies in Chinese double rice-cropping systems. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Huang, T. Differences in net global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensity between major rice-based cropping systems in China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Fang, S.; Cao, F.; Chen, J.; Shan, S.; Liu, Y.; Lei, T.; Tian, A.; Tao, Z.; Zou, Y. Early sowing increases grain yield of machine-transplanted late-season rice under single-seed sowing. Field Crops Res. 2020, 253, 107832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, Z. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Tao, Z.; Lei, T.; Cao, F.; Chen, J.; Yin, X.; Zou, Y.; Liang, T. Improving lodging resistance while maintaining high grain yield by promoting pre-heading growth in rice. Field Crops Res. 2021, 270, 108212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, J.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.; Shah, F.; Li, X. Effects of fertilization on crop production and nutrient-supplying capacity under rice-oilseed rape rotation system. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1270. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, D.; Ding, Y. The study of changing characteristics of the winter temperature and extreme cold events in China over the past six decades. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 2480–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wu, G. Differences in Temperature Variation Between Winter and Summer Across China in Recent Decades. Int. J. Climatol. 2025, 45, e8828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Ren, T.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liao, S.; Li, X.; Cong, R.; Lu, J. Rotation with oilseed rape as the winter crop enhances rice yield and improves soil indigenous nutrient supply. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 212, 105065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Park, K.; Jung, K.; Ali, M.; Lee, D.; Gutierrez, J.; Kim, P. Effect of Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) as a green manure on rice productivity and methane emission in paddy soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 138, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; He, Y.; Tu, S.; Xu, C.; Liu, G.; Wang, H.; Cao, W.; Liu, H. Chinese Milk Vetch Improves Plant Growth, Development and 15N Recovery in the Rice-Based Rotation System of South China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhao, Z.; Pan, X.; Huang, S.; Tan, X.; Wu, J.; Shi, Q. Integration of Growing Milk Vetch in Winter and Reducing Nitrogen Fertilizer Application Can Improve Rice Yield in Double-Rice Cropping System. Rice Sci. 2016, 23, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Tian, A.; Zhou, X.; Gao, W.; Li, Z.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Yin, X.; et al. Yield performance of machine-transplanted double-season rice grown following oilseed rape. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhai, P. Extraordinary hot extreme in summer 2022 over the Yangtze River basin modulated by the La Niña condition under global warming. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2024, 15, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Lin, X.; Song, L. Global warming and urbanization triggering the record -breaking heat event in summer 2023 over Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, China. Urban Clim. 2025, 59, 102271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Ahmed, S.; Alam, M.; Hossain, A. Adverse effects of heat shock in rice (Oryza sativa L.) and approaches to mitigate it for sustainable rice production under the changing climate: A comprehensive review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e41072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M. Impact of climate change on rice and adaptation strategies: A review. Adv. Resour. Res. 2024, 4, 252–262. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Huang, G.; Wang, C.; Lin, Q.; Xu, N. Effects of winter green manure cultivation on rice yield and soil fertility in paddy field. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2013, 21, 1209–1216, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noppol, A.; Sukanya, S.; Ryusuke, H. Impact of burning on soil organic carbon of maize-upland rice system in Mae Chaem Basin of Northern Thailand. Geoderma 2021, 392, 115002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Sun, Q.; Li, Q.; Ashraf, U.; Hu, X.; Li, L. Optimal Soil, Climate, and Management Factors for Maximizing Crop Yield and Soil Nutrients in a Rice-Oilseed Rotation System with Straw Return. Agriculture 2024, 14, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, H.; Jia, X.; Ma, J. Effects of water management and nitrogen application strategies on nutrient absorption, transfer, and distribution in rice. Acta Agron. Sin. 2011, 37, 2221–2232, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Xie, Q.; Zhou, Y.; He, F.; Yousaf, M.; Zhu, B.; Liu, Z. Long-term legume green manure residue incorporation is more beneficial to improving bacterial richness, soil quality and rice yield than mowing under double-rice cropping system in Dongting Lake Plain, China. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1603434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Dai, J.; Hu, W.; Yu, C.; Brooks, M.; Liao, X.; Qin, L. Effects of oilseed rape green manure on phosphorus availability of red soil and rice yield in rice-green manure rotation system. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1417504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Q.; Ren, T.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, W.; Lu, J. Comparison of phosphorus application on crop yield and soil phosphorus pool in rapeseed/wheat-rice rotations: An 8-year field experiment. Field Crops Res. 2025, 332, 110017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.; Lin, B.; Yi, K.; Xue, B.; Hua, S. Comprehensive illustration of the improvement of soil conditions and rice production through paddy-upland rotations for sustainable agricultural development. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 248, 106453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ren, T.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cong, R.; Li, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Lu, J. Soil organic nitrogen sequestrated more in oilseed rape-rice rotation than in wheat-rice rotation under different fertilizations. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 381, 109445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ge, T.; Wang, W.; Yuan, H.; Wegner, C.; Zhu, Z.; Whiteley, A.; Wu, J. Cropping systems modulate the rate and magnitude of soil microbial autotrophic CO2 fixation in soil. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Meng, G.; Jiang, W.; Liu, Y.; Athar, M.; Noor, S.; Muhammad, N.; Umair, H.; Huang, G. Effects of Winter Cropping on rice Yield, Economic Benefit, and Resource Utilization Efficiency on Different Cropping Systems of Paddy Field in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2023, 17, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, W.; Xie, W.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y. Cost-Benefit Analysis for Single and Double Rice Cropping Systems under the Background of Global Warming. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gao, D.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Cui, T.; Tong, Z.; Luo, X. Comparison of matter production and the light and temperature resources utilization efficiencies of the main cropping systems for paddy fields in the Dongting Lake region. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2022, 30, 1309–1317, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
| Year | Season | Treatment | Panicles (104/ha) | Spikelets per Panicle | Seed Setting Rate (%) | 1000-Grain Weight (g) | Yield (t/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | Early rice | CRR | 396 a | 101 a | 83.23 a | 24.80 a | 7.48 a |
| FRR | 404 a | 94 a | 81.89 a | 24.44 a | 6.89 a | ||
| Late rice | CRR | 284 a | 151 a | 92.44 a | 20.59 a | 7.08 a | |
| FRR | 286 a | 148 a | 88.75 a | 20.33 a | 6.81 a | ||
| Mid-season rice | RaR | 190 a | 286 a | 83.79 a | 26.16 a | 10.10 a | |
| FR | 171 a | 278 a | 84.17 a | 25.94 a | 8.90 b | ||
| 2022 | Early rice | CRR | 299 a | 106 a | 89.97 a | 25.40 a | 6.86 a |
| FRR | 301 a | 95 b | 89.62 a | 26.27 a | 6.04 b | ||
| Late rice | CRR | 364 a | 138 a | 73.10 a | 20.39 a | 7.05 a | |
| FRR | 358 a | 137 a | 70.77 a | 20.58 a | 6.83 a | ||
| Mid-season rice | RaR | 263 a | 233 a | 70.98 a | 26.05 a | 9.98 a | |
| FR | 251 a | 238 a | 67.51 a | 26.16 a | 9.05 b |
| Year | Treatment | Cost (Chinese Yuan) | Total Income (Chinese Yuan) | Net Income (Chinese Yuan) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seed | Fertilizer | Pesticide | Labor | Machinery | Total Cost | 1st Season + 2nd Season Total | ||||
| 2021 | Crops | Early rice | 450 | 2286 | 1289 | 4648 | 2699 | 11,372 | ||
| Late rice | 900 | 2482 | 1859 | 6297 | 2699 | 14,236 | ||||
| Chinese milk vetch | 1048 | 0 | 0 | 225 | 0 | 1273 | ||||
| rape | 360 | 1919 | 2279 | 1349 | 1949 | 7856 | ||||
| rice (hole direct seeding) | 4048 | 3340 | 2429 | 3598 | 2699 | 16,114 | ||||
| 2022 | rice (transplanting) | 3373 | 3536 | 2429 | 5997 | 2699 | 18,033 | |||
| 2021 | Planting patterns | CRR | 2397 | 4768 | 3148 | 10,945 | 5397 | 26,881 | 37,697 | 10,816 |
| FRR | 1350 | 4768 | 3148 | 11,169 | 5397 | 25,608 | 35,688 | 9980 | ||
| RaR | 4408 | 5259 | 4708 | 4948 | 4648 | 23,970 | 35,778 | 11,808 | ||
| FR | 4048 | 3340 | 2429 | 3598 | 2699 | 16,114 | 22,250 | 6136 | ||
| 2022 | CRR | 2397 | 4768 | 3148 | 10,945 | 5397 | 26,881 | 36,255 | 9374 | |
| FRR | 1350 | 4768 | 3148 | 11,169 | 5397 | 25,608 | 33,788 | 8180 | ||
| RaR | 3733 | 5455 | 4708 | 7346 | 4648 | 25,890 | 36,334 | 10,444 | ||
| FR | 3373 | 3536 | 2429 | 5997 | 2699 | 18,033 | 22,625 | 4592 | ||
| Crop | Sowing Date–Harvest Date | Transplanting Modes and Density | Fertilizer Amount | Fertilizer Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early rice | 24 March 2021–14 July 2021 | Artificial transplanting 25 cm × 14 cm | N: 120 kg/hm2 P2O5: 75 kg/hm2 K2O: 120 kg/hm2 | Nitrogen fertilizer was applied at the rate of basal fertilizer: tillering fertilizer: panicle fertilizer = 5:2:3, phosphorus fertilizer was both applied as basal fertilizer, and potassium fertilizer was applied at the rate of basal fertilizer: panicle fertilizer = 7:3 |
| 28 March 2022–17 July 2022 | ||||
| Late rice | 26 June 2021–14 October 2021 | Artificial transplanting 25 cm × 16 cm | N: 150 kg/hm2 P2O5: 75 kg/hm2 K2O: 120 kg/hm2 | |
| 1 July 2022–25 October 2022 | ||||
| Rape | 19 October 2020–29 April 2021 | Broadcast sowing 6 kg/hm2 | N: 120 kg/hm2 P2O5: 33.6 kg/hm2 K2O: 38.4 kg/hm2 | The special compound fertilizer was applied to rape as basal fertilizer |
| 13 October 2021–25 April 2022 | ||||
| Mid-season rice | 8 May 2021–29 September 2021 | Hole direct seeding 27 cm × 16 cm | N: 195 kg/hm2 P2O5: 90 kg/hm2 K2O: 180 kg/hm2 | Nitrogen fertilizer was applied at the rate of basal fertilizer: tillering fertilizer: panicle fertilizer = 4:2:4, phosphorus fertilizer was both applied as basal fertilizer, and potassium fertilizer was applied at the rate of basal fertilizer: panicle fertilizer = 6:4 |
| 10 May 2022–30 September 2022 | Artificial transplanting 30 cm × 16 cm | N: 225 kg/hm2 P2O5: 90 kg/hm2 K2O: 180 kg/hm2 |
| Crop | Seed Prices (CNY/kg) | Frequency of Medication | Man-Hour (h) | Selling Price (According to Local Market) (CNY/kg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herbicide | Pesticide | |||||
| early rice | 10 | 1 | 2 | 120 | 2.2 | |
| later rice | 20 | 1 | 2 | 120 | 3 | |
| mid-season rice | Direct broadcast | 90 | 1 | 3 | 90 | 2.5 |
| transplanting | 150 | |||||
| rape | 60 | 1 | 4 | 90 | 6.2 | |
| Chinese milk vetch | 30 | 15 | ||||
| Other cost item | Labor cost (CNY/h) | rape special fertilizer (CNY/kg) | Urea (CNY/kg) | potassium chloride (CNY/kg) | Calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer (CNY/kg) | |
| 15 | 4 | 3 | 4.4 | 1 | ||
| Tillage of rice (CNY/ha) | Rape ditching (CNY/ha) | Herbicide (CNY/ha) | Pesticides (CNY/ha) | Spraying pesticides by drone (CNY/ha) | ||
| 1500 | 750 | 150 | 450 | 120 | ||
| Transplanting (CNY/ha) | Hole direct seeding (CNY/ha) | Harvest of rice and rape (CNY/ha) | ||||
| Early rice | Late rice | Mid- season rice | Mid- season rice | |||
| 2850 | 4500 | 3750 | 2250 | 1500 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Q.; Wang, J.; Lv, W.; Chen, M.; Xiong, W.; Chen, L.; Zeng, Y. Comparative Analysis of Rice Yield and Economic Performance Across Different Planting Patterns in Double-Cropping Rice Systems Under Global Warming. Plants 2025, 14, 3593. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233593
Su Q, Wang J, Lv W, Chen M, Xiong W, Chen L, Zeng Y. Comparative Analysis of Rice Yield and Economic Performance Across Different Planting Patterns in Double-Cropping Rice Systems Under Global Warming. Plants. 2025; 14(23):3593. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233593
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Qianxing, Jinyao Wang, Weisheng Lv, Ming Chen, Wen Xiong, Le Chen, and Yongjun Zeng. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of Rice Yield and Economic Performance Across Different Planting Patterns in Double-Cropping Rice Systems Under Global Warming" Plants 14, no. 23: 3593. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233593
APA StyleSu, Q., Wang, J., Lv, W., Chen, M., Xiong, W., Chen, L., & Zeng, Y. (2025). Comparative Analysis of Rice Yield and Economic Performance Across Different Planting Patterns in Double-Cropping Rice Systems Under Global Warming. Plants, 14(23), 3593. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14233593





