Endophytic Pseudomonas koreensis A1 of Bletilla striata as a Plant Growth Promoter and Biocontrol Agent Against Rice Sheath Blight
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
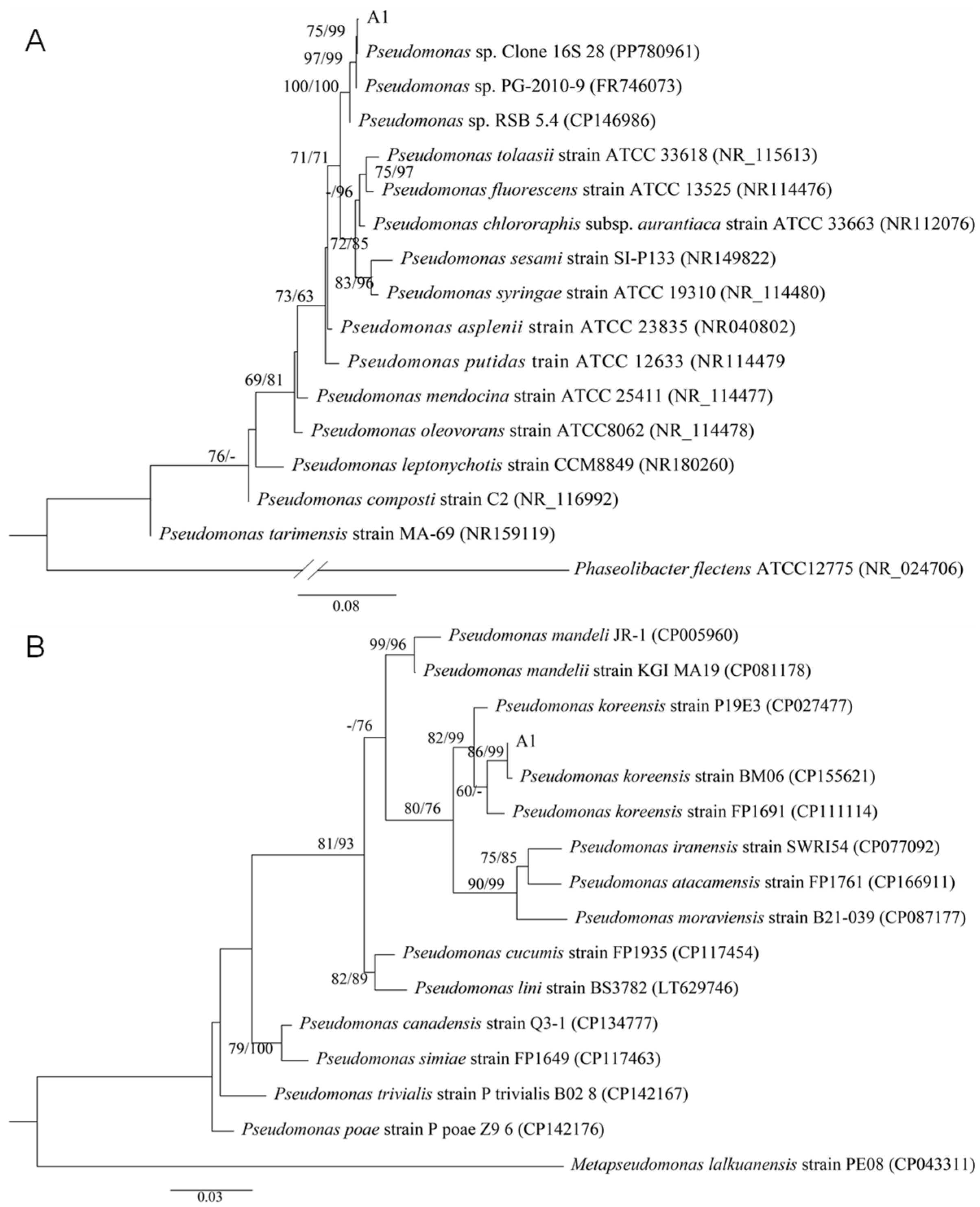
2.1. Isolation, Screening and Identification of Biocontrol strain A1
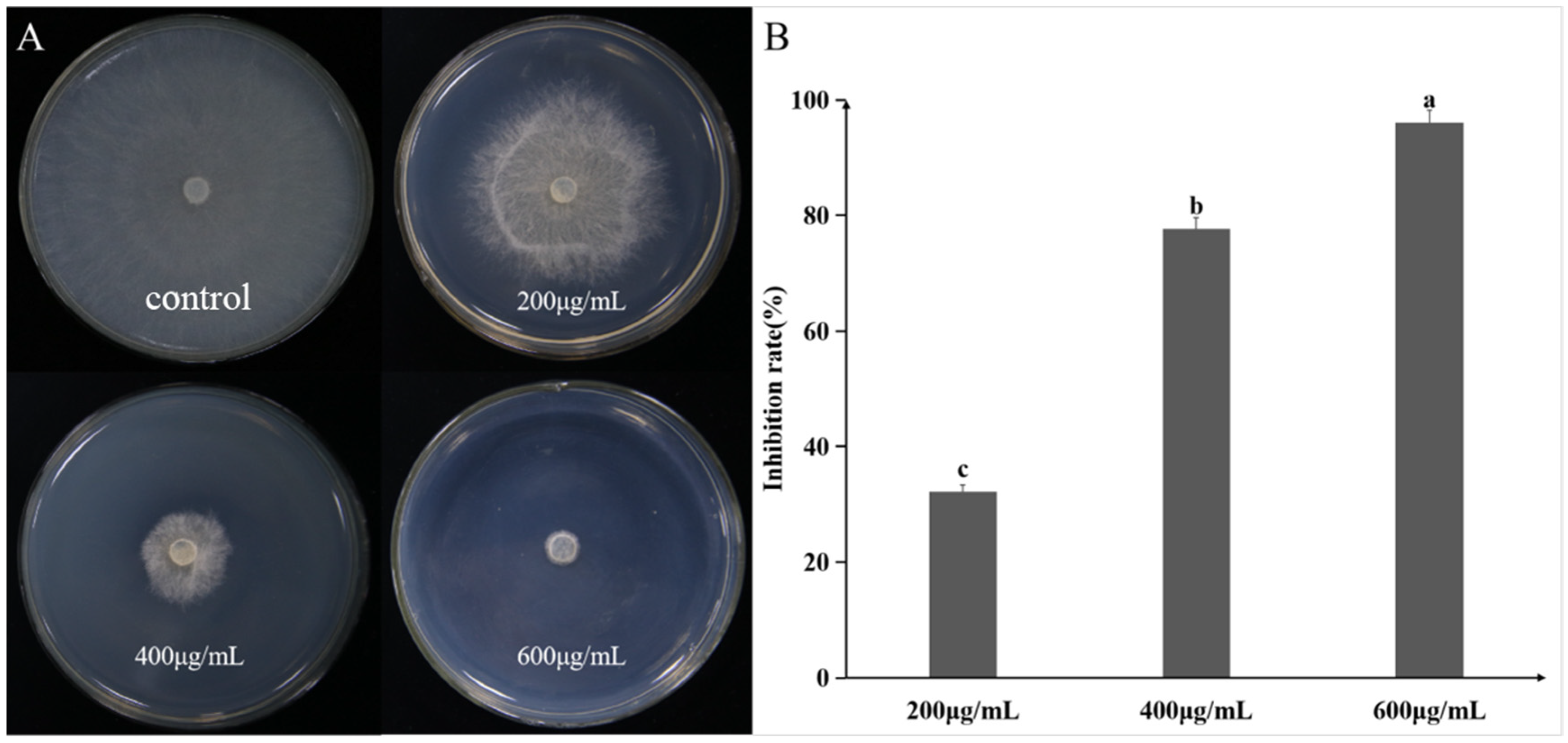
2.2. Antifungal Spectrum of Pseudomonas koreensis A1
2.3. Biocontrol Efficacy of P. koreensis A1 Against Rice Sheath Blight
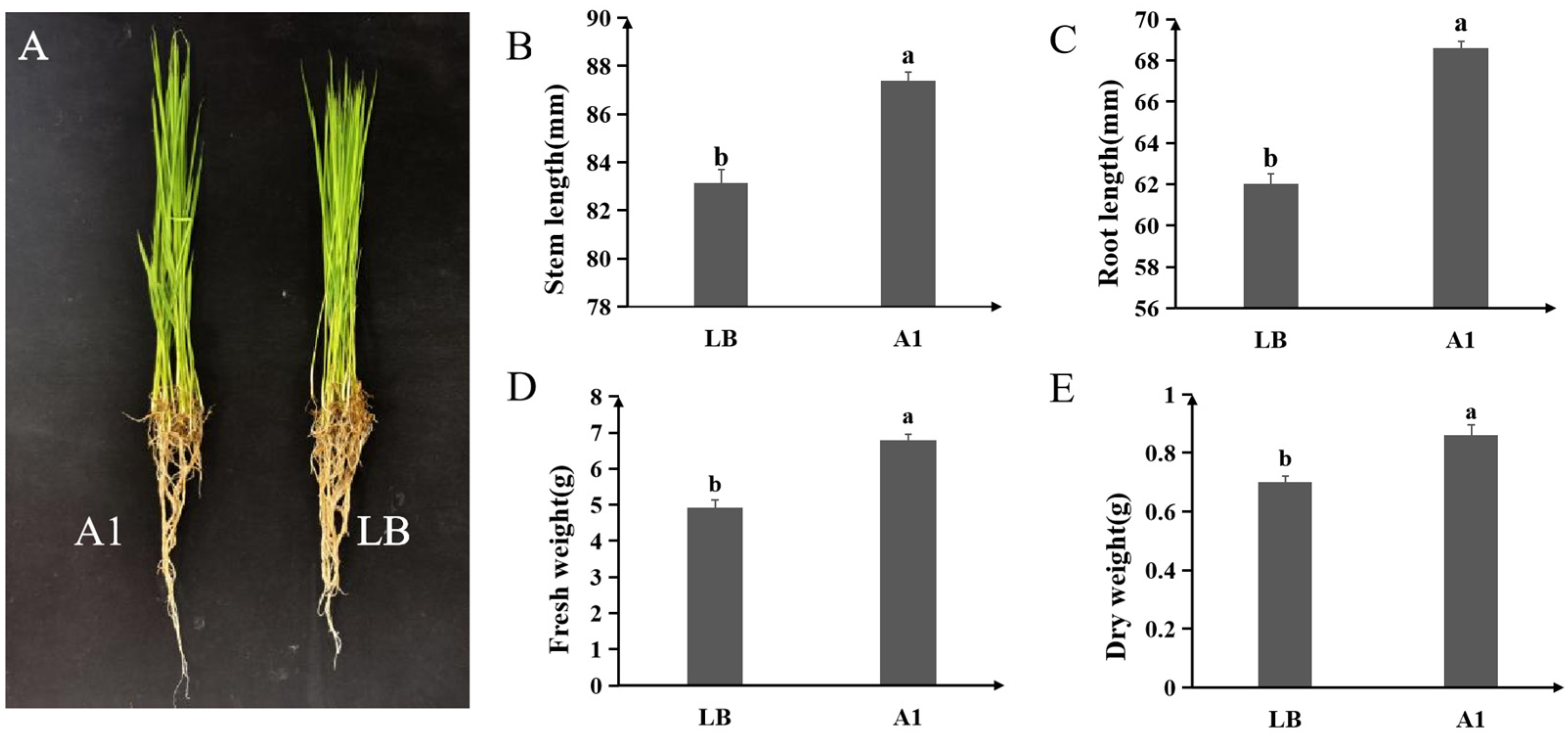
2.4. Strain A1 Promotes Rice Seedling Growth
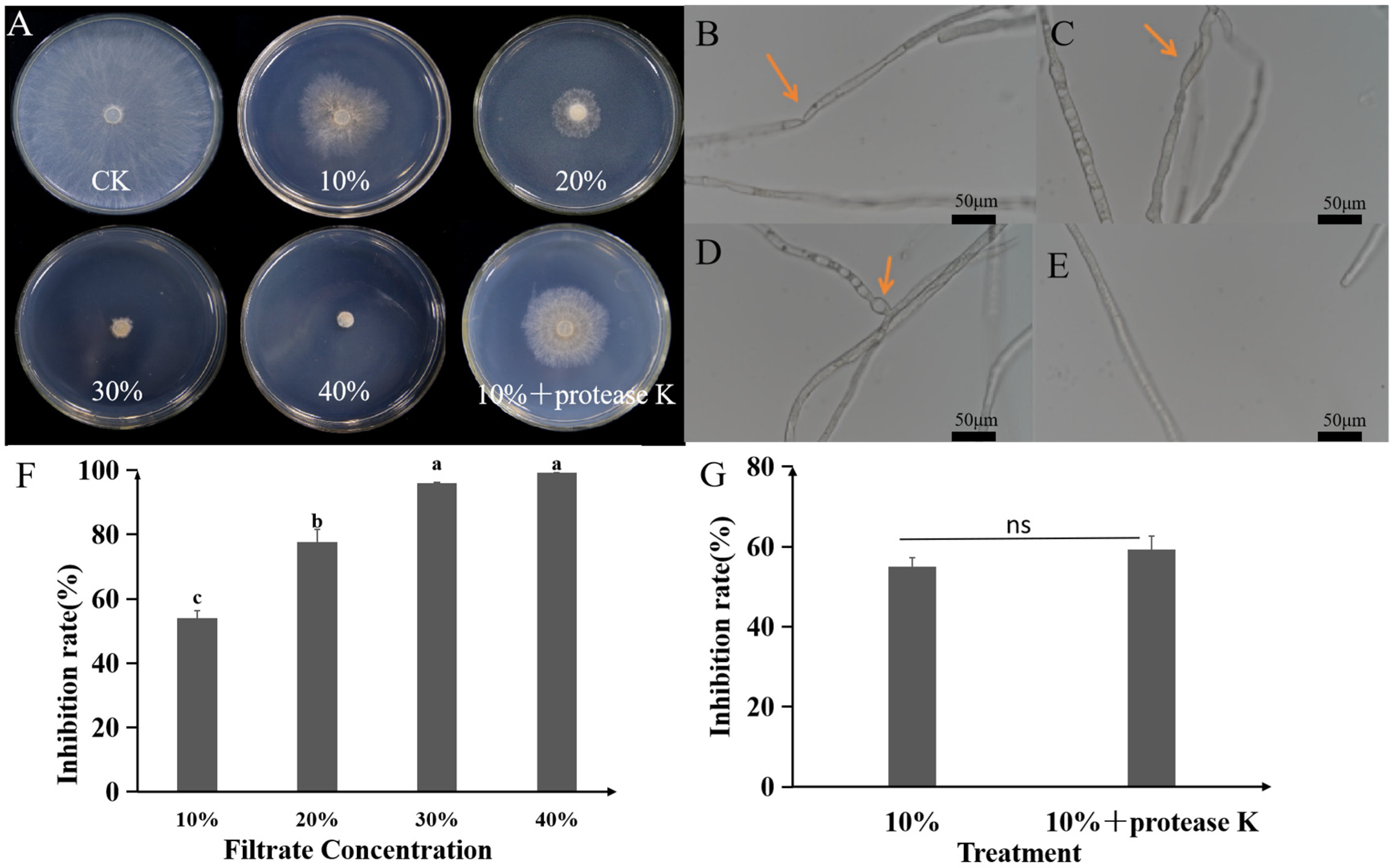
2.5. Antifungal Activity of Culture Filtrate and Crude Extract
2.6. LC-MS Analysis of the Antifungal Crude Extract
2.7. Plant Growth-Promoting and Biochemical Traits of P. koreensis A1
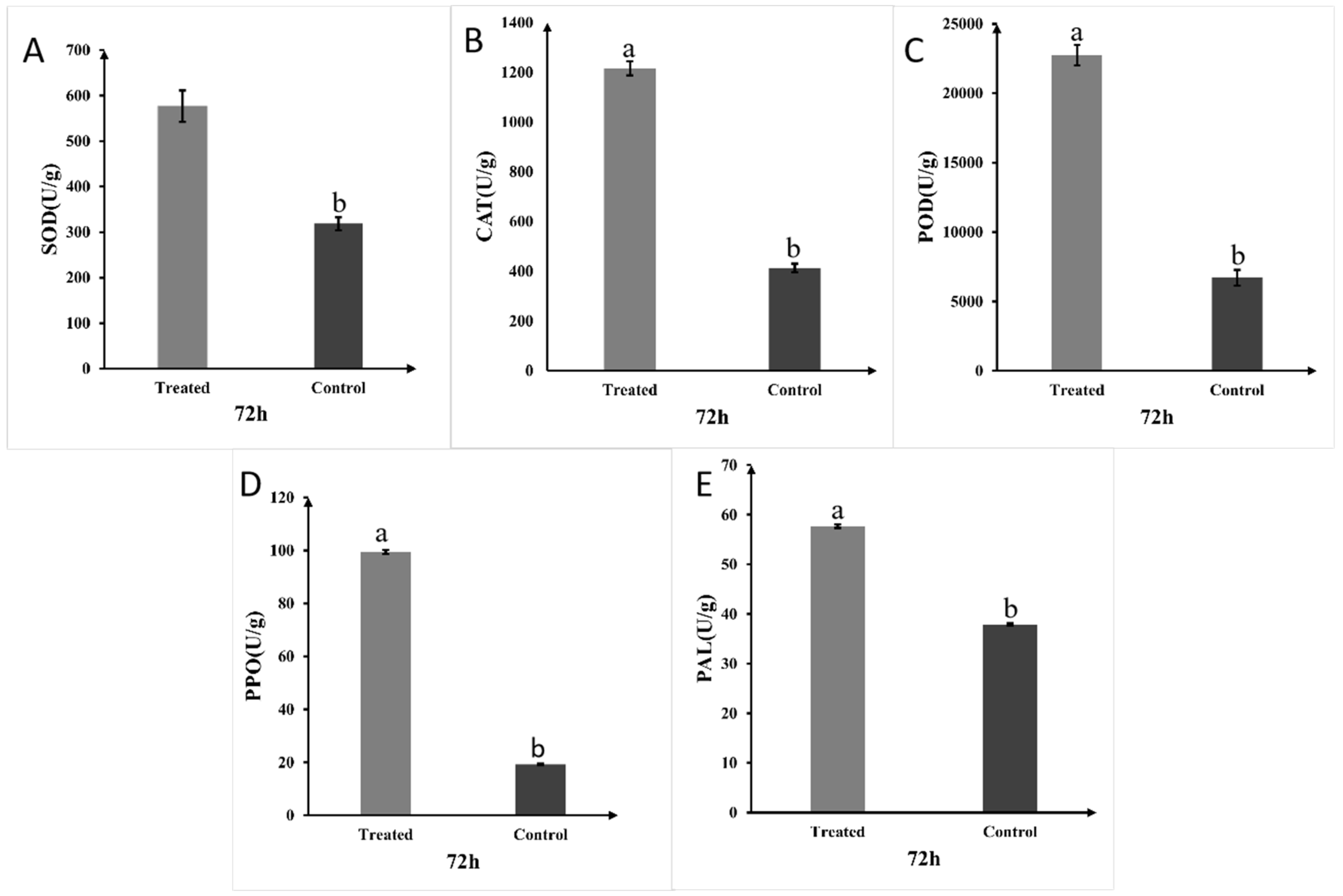
2.8. Strain A1 Primes Defense-Related Enzymes in Rice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation of Endophytic Bacteria from Bletilla striata Roots
4.2. Evaluation of Antifungal Activity Against Rhizoctonia solani
4.3. Molecular Identification of Strain A1
4.4. Assessment of Antifungal Spectrum
4.5. Antifungal Activity of Sterile Culture Filtrate
4.6. Detached Leaf Assay
4.7. Greenhouse Assessment of Biocontrol Efficacy
4.8. Field Trial for Control of Rice Sheath Blight
4.9. Antifungal Activity of Crude Extract
4.10. LC-MS Analysis of Antifungal Metabolites
4.11. Characterization of Plant Growth-Promoting Properties
4.11.1. Biosynthesis of Siderophores
4.11.2. Phosphorus Solubilization
4.11.3. Nitrogen Fixation
4.11.4. Extracellular Enzyme Activity
4.11.5. Indole-3-Acetic Acid (IAA) Production
4.12. Measurement of Defense-Related Enzyme Activities
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gross, B.L.; Zhao, Z. Archaeological and genetic insights into the origins of domesticated rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6190–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, C.; Zhou, M. Integrated biological and chemical control of rice sheath blight by Bacillus subtilis NJ-18 and jinggangmycin. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, B.; Eizenga, G.C. Rice sheath blight disease resistance identified in Oryza spp. accessions. Plant Dis. 2008, 92, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slaton, N.A.; Cartwright, R.D.; Meng, J.; Gbur, E.E.; Norman, R.J. Sheath blight severity and rice yield as affected by nitrogen fertilizer rate, application method, and fungicide. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Li, X.; Huo, H.; Cai, Y.; Cai, A. Bacillus velezensis Y6, a potential and efficient biocontrol agent in control of rice sheath blight caused by Rhizoctonia solani. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.K.; Karki, H.S.; Groth, D.E.; Jungkhun, N.; Ham, J.H. Biological control activities of rice-associated Bacillus sp. strains against sheath blight and bacterial panicle blight of rice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-J.; Galileya Medison, R.; Cao, S.; Wang, L.-Q.; Cheng, S.; Tan, L.-T.; Sun, Z.-X.; Zhou, Y. Isolation, identification, and biocontrol mechanisms of endophytic Burkholderia vietnamiensis C12 from Ficus tikoua Bur against Rhizoctonia solani. Biol. Control 2023, 178, 105132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alattas, H.; Glick, B.R.; Murphy, D.V.; Scott, C. Harnessing Pseudomonas spp. for sustainable plant crop protection. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1485197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, P.; Shanmugaiah, V.; Rajagopal, R.; Muthusamy, K.; Ramamoorthy, V. Pseudomonas fluorescens VSMKU3054 mediated induced systemic resistance in tomato against Ralstonia solanacearum. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2022, 119, 101836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhuo, T.; Hu, X.; Fan, X.; Zou, H. Identification of a Pseudomonas putida as biocontrol agent for tomato bacterial wilt disease. Biol. Control 2017, 114, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, T.; Guo, M.; Huang, L.; Yang, L.; Kan, J.; Zalán, Z.; Hegyi, F.; Takács, K.; et al. Antifungal mechanisms of volatile organic compounds produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens ZX as biological fumigants against Botrytis cinerea. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 267, 127253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.-H.; Nie, Q.-W.; Medison, R.G.; Zheng, T.-W.; Meng, X.-J.; Sun, Z.-X.; Zhou, Y. Evaluation of Pseudomonas koreensis B17-12 as a potential biological control agent against postharvest diseases of tomato. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2024, 132, 102311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eljounaidi, K.; Lee, S.K.; Bae, H. Bacterial endophytes as potential biocontrol agents of vascular wilt diseases—Review and future prospects. Biol. Control 2016, 103, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stierle, A.; Strobel, G.; Stierle, D. Taxol and taxane production by taxomyces andreanae, an endophytic fungus of pacific yew. Science 1993, 260, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, O.A.A.; Li, L.; Ma, J.B.; Hatab, S.; Xu, L.; Guo, J.W.; Rasulov, B.A.; Liu, Y.H.; Hedlund, B.P.; Li, W.J. Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of endophytic bacterial populations from chinese traditional medicinal plant licorice and characterization of the bioactive secondary metabolites produced by Bacillus atrophaeus against Verticillium dahliae. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Galileya Medison, R.; Zheng, T.-W.; Meng, X.-J.; Sun, Z.-X.; Zhou, Y. Biocontrol potential of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens YZU-SG146 from Fraxinus hupehensis against Verticillium wilt of cotton. Biol. Control 2023, 183, 105246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, X.; Fang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, L.; Guo, H.; Zheng, X. Bletilla striata: Medicinal uses, phytochemistry and pharmacological activities. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 195, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Pan, Y.; Chen, J. Chemical constituents, pharmacologic properties, and clinical applications of Bletilla striata. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chota, A.; George, B.P.; Abrahamse, H. Potential treatment of breast and lung cancer using Dicoma anomala, an african medicinal plant. Molecules 2020, 25, 4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, F.; Althagafi, H.A.; Jafri, I.; Oyouni, A.A.A.; Althaqafi, M.M.; Al-Hijab, L.Y.A.; Al-Hazmi, N.E.; Elagib, S.M.; Naguib, D.M. Phytochemical composition and bioactivities of some hydrophytes: Antioxidant, antiparasitic, antibacterial, and anticancer aroperties and mechanisms. Plants 2024, 13, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.S.; Jain, R.; Bhardwaj, P.; Thakur, A.; Kumari, M.; Bhushan, S.; Kumar, S. Plant probiotics—Endophytes pivotal to plant health. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 263, 127148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, H.; Rai, A.K.; Dahiya, D.; Chettri, R.; Nigam, P.S. Exploring endophytes for in vitro synthesis of bioactive compounds similar to metabolites produced in vivo by host plants. AIMS Microbiol. 2021, 7, 175–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafikova, G.F.; Korshunova, T.Y.; Minnebaev, L.F.; Chetverikov, S.P.; Loginov, O.N. A new bacterial strain, Pseudomonas koreensis IB-4, as a promising agent for plant pathogen biological control. Microbiology 2016, 85, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Ai, C.; Xin, L.; Zhou, G. The siderophore-producing bacterium, Bacillus subtilis CAS15, has a biocontrol effect on Fusarium wilt and promotes the growth of pepper. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2011, 47, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shi, H.; Heng, J.; Wang, D.; Bian, K. Antimicrobial, plant growth-promoting and genomic properties of the peanut endophyte Bacillus velezensis LDO2. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 218, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernava, T. How microbiome studies could further improve biological control. Biol. Control 2021, 160, 104669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorotkiewicz-Jach, A.; Markwitz, P.; Drulis-Kawa, Z. The In vitro anti-Pseudomonal activity of Cu2+, strawberry furanone, gentamicin, and lytic phages alone and in combination: Pros and cons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivkovic, I.; Gruic-Sovulj, I. Exploring mechanisms of mupirocin resistance and hyper-resistance. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2024, 52, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Librizzi, V.; Malacrinò, A.; Li Destri Nicosia, M.G.; Barger, N.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; Pangallo, S.; Agosteo, G.E.; Schena, L. Extracts from environmental strains of Pseudomonas spp. effectively control fungal plant diseases. Plants 2022, 11, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsmark, J.K.; Duke, S.O.; Cedergreeen, N. Potential ecological roles of artemisinin produced by Artemisia annua L. J. Chem. Ecol. 2014, 40, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Yue, C.; Zeng, X.; Chen, X. Artemisinin Targets Transcription Factor PDR1 and Impairs Candida glabrata Mitochondrial Function. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballeira, N.M.; O’Neill, R.; Parang, K. Racemic and optically active 2-methoxy-4-oxatetradecanoic acids: Novel synthetic fatty acids with selective antifungal properties. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2005, 136, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, Z.; Zainab, B.; Rashid, U.; Darwish, N.M.; Gatasheh, M.K.; Abbasi, A.M. In silico screening of synthetic and natural compounds to inhibit the binding capacity of heavy metal compounds against EGFR Protein of lung cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 2941962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzollini, A.; Boggia, L.; Boccard, J.; Sgorbini, B.; Lecoultre, N.; Allard, P.M.; Rubiolo, P.; Rudaz, S.; Gindro, K.; Bicchi, C.; et al. Dynamics of metabolite induction in fungal co-cultures by metabolomics at both volatile and non-volatile levels. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekharan, S.K.; Shemesh, M. The Bacillary postbiotics, including 2-undecanone, suppress the virulence of pathogenic microorganisms. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, X.; Fu, Y.; Zou, L.; Cai, H.; Zhou, Y.; Tu, M. Isolation, identification, and biocontrol mechanisms of endophytic Burkholderia arboris DHR18 from rubber tree against red root rot disease. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetan, K.K.; Varma, P.K.; Chandrasekhar, V.; Kumar, P.A.; Vasanthi, V. Plant, bacteria and fungi crosstalk: Direct and indirect biocontrol mechanisms of sugarcane rhizoplane Pseudomonas species against Fusarium wilt. Rhizosphere 2024, 31, 100952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macagnan, D.; Romeiro, R.d.S.; Pomella, A.W.V.; deSouza, J.T. Production of lytic enzymes and siderophores, and inhibition of germination of basidiospores of Moniliophthora (ex Crinipellis) perniciosa by phylloplane actinomycetes. Biol. Control 2008, 47, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shine, M.B.; Yang, J.W.; El-Habbak, M.; Nagyabhyru, P.; Fu, D.Q.; Navarre, D.; Ghabrial, S.; Kachroo, P.; Kachroo, A. Cooperative functioning between phenylalanine ammonia lyase and isochorismate synthase activities contributes to salicylic acid biosynthesis in soybean. New Phytol. 2016, 212, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, H.; Lieberei, R.; Strnad, M.; Novák, O.; Gruz, J.; Rensing, S.A.; von Schwartzenberg, K. Polyphenol oxidases in Physcomitrella: Functional PPO1 knockout modulates cytokinin-dependent development in the moss Physcomitrella patens. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 5121–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhi, P.; Chang, C. Priming seeds for the future: Plant immune memory and application in crop protection. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 961840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrath, U.; Beckers, G.J.; Langenbach, C.J.; Jaskiewicz, M.R. Priming for enhanced defense. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2015, 53, 97–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Fu, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Li, S.; Deng, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhu, J.; et al. Comparative transcriptome analyses of gene expression changes triggered by Rhizoctonia solani AG1 IA infection in resistant and susceptible rice varieties. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yan, S.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, S.; Su, J.; Cui, Z.; Huo, J.; Sun, Y.; et al. Defense-related enzyme activities and metabolomic analysis reveal differentially accumulated metabolites and response pathways for sheath blight resistance in rice. Plants 2024, 13, 3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spilker, T.; Baldwin, A.; Bumford, A.; Dowson, C.G.; Mahenthiralingam, E.; LiPuma, J.J. Expanded multilocus sequence typing for Burkholderia species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 2607–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liang, W.; Liu, M. Biocontrol potential of endophytic Bacillus velezensis strain QSE-21 against postharvest grey mould of fruit. Biol. Control 2021, 161, 104711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.M.; Sharma, S.; Pinnaka, A.K.; Kumari, A.; Korpole, S. Isolation and characterization of diverse antimicrobial lipopeptides produced by Citrobacter and Enterobacter. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.H.; Lim, Y.; Lee, S.E.; Yang, N.W.; Rhee, J.H. CAS agar diffusion assay for the measurement of siderophores in biological fluids. J. Microbiol. Methods 2001, 44, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nautiyal, C.S. An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 170, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaqat, F.; Eltem, R. Identification and characterization of endophytic bacteria isolated from in vitro cultures of peach and pear rootstocks. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-H.; Zhang, W.-W.; Zhuang, Y.-Q.; Xiao, T. Biocontrol activities of bacteria from cowdung against the rice sheath blight pathogen. J. Plant Dis. Protect. 2017, 124, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.-W.; Liu, L.; Nie, Q.-W.; Hsiang, T.; Sun, Z.-X.; Zhou, Y. Isolation, identification and biocontrol mechanisms of endophytic bacterium D61-A from Fraxinus hupehensis against Rhizoctonia solani. Biol. Control 2021, 158, 104621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chen, D.-D.; Peng, K.-S.; Cui, Z.-W.; Zhang, X.-J.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.-A. Identification and characterization of Bacillus subtilis from grass carp (Ctenopharynodon idellus) for use as probiotic additives in aquatic feed. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 52, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
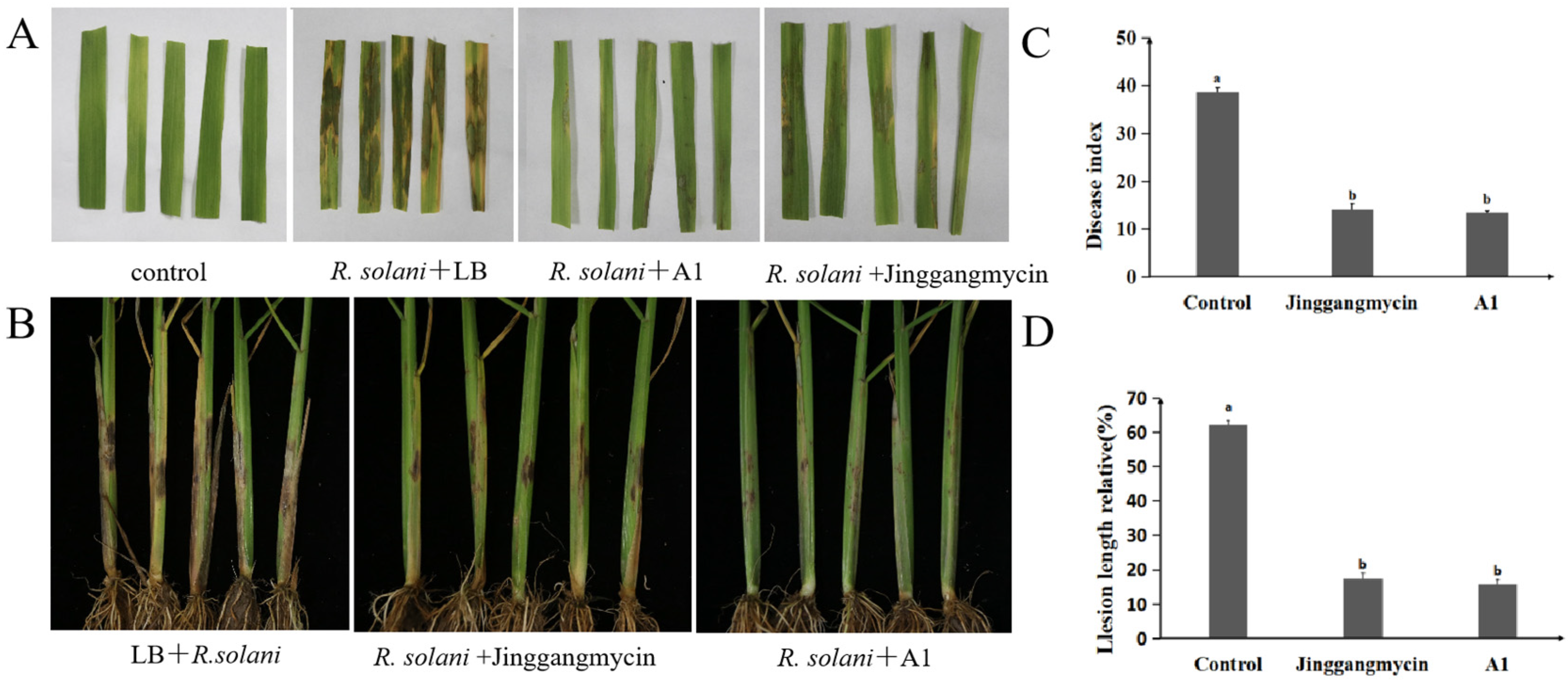




| Treatment | Disease Index | Control (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Control (LB) | 12.72 ± 0.95 a | - |
| Jinggangmycin | 3.58 ± 1.13 b | 69.63% |
| A1 (108 cfu/mL) | 2.94 ± 0.52 b | 72.53% |
| Material Type | Peak Time | Mass/Charge |
|---|---|---|
| Artemisinin | 6.035–6.071 | 281.1394 |
| Pseudomonic Acid | 7.278–7.314 | 499.2913 |
| Tetradecane | 7.314–7.349 | 197.2275 |
| 2-Undecanone | 7.830–7.866 | 169.1598 |
| 2-Nonanone | 8.046–8.082 | 141.1285 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, J.-W.; Qiu, Y.; Luo, J.-X.; Liu, J.-L.; Feng, H.-J.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, S. Endophytic Pseudomonas koreensis A1 of Bletilla striata as a Plant Growth Promoter and Biocontrol Agent Against Rice Sheath Blight. Plants 2025, 14, 3546. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14223546
Jiang J-W, Qiu Y, Luo J-X, Liu J-L, Feng H-J, Zhou Y, Cheng S. Endophytic Pseudomonas koreensis A1 of Bletilla striata as a Plant Growth Promoter and Biocontrol Agent Against Rice Sheath Blight. Plants. 2025; 14(22):3546. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14223546
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Jian-Wei, Yue Qiu, Jing-Xue Luo, Jia-Le Liu, Hua-Jian Feng, Yi Zhou, and Sheng Cheng. 2025. "Endophytic Pseudomonas koreensis A1 of Bletilla striata as a Plant Growth Promoter and Biocontrol Agent Against Rice Sheath Blight" Plants 14, no. 22: 3546. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14223546
APA StyleJiang, J.-W., Qiu, Y., Luo, J.-X., Liu, J.-L., Feng, H.-J., Zhou, Y., & Cheng, S. (2025). Endophytic Pseudomonas koreensis A1 of Bletilla striata as a Plant Growth Promoter and Biocontrol Agent Against Rice Sheath Blight. Plants, 14(22), 3546. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14223546






