Ecotoxicological Impacts of Heavy Metals on Medicinal Plant Quality and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Sources and Characteristics of Heavy Metal Pollution
1.2. Importance and Extensive Applications of Medicinal Plants
1.3. Overview and Roles of Rhizosphere Microorganisms
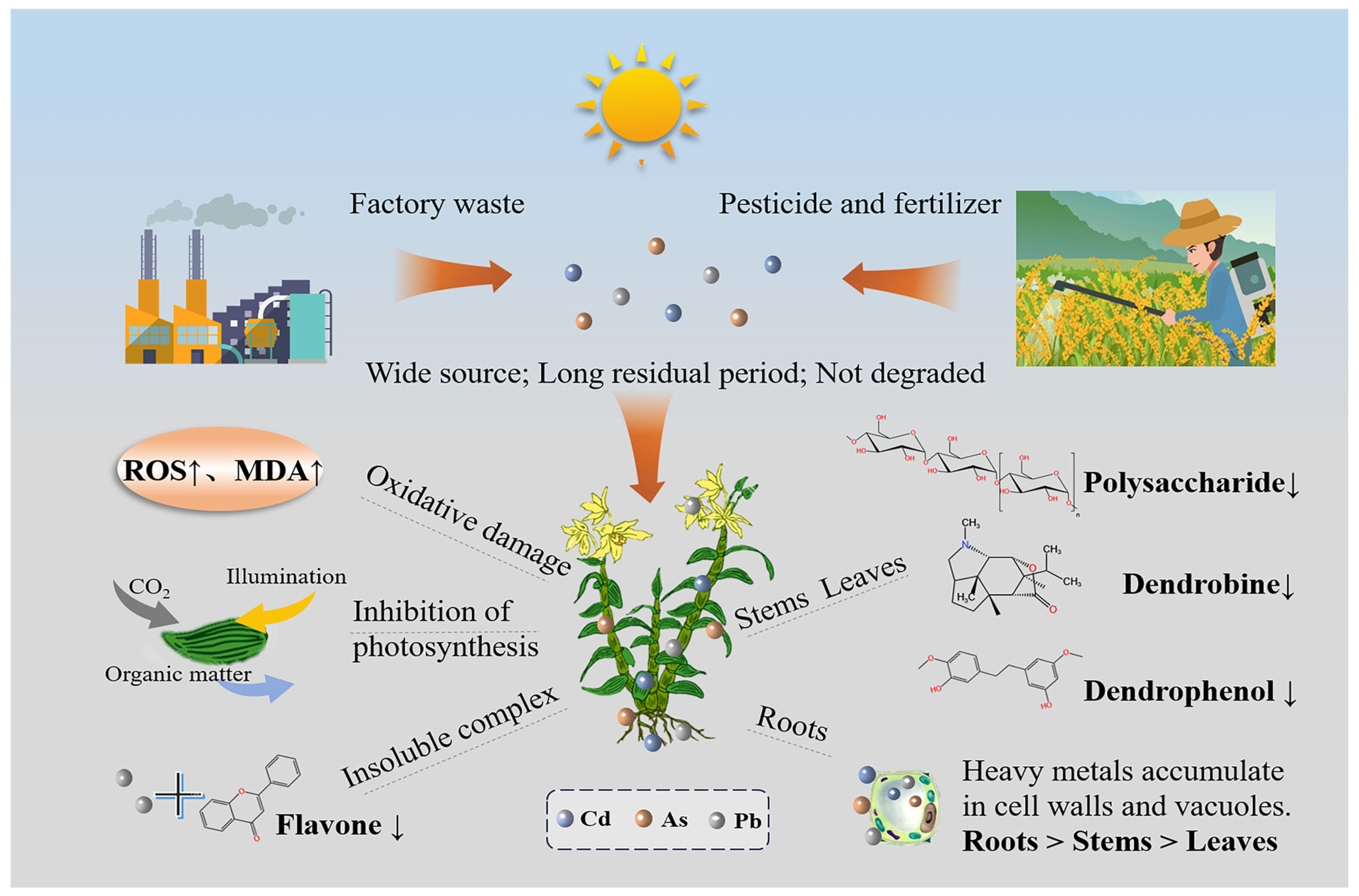
2. Comprehensive Effects of Heavy Metals on the Quality of Medicinal Plants
2.1. Effects of Heavy Metals on the Phenotypic Characteristics of Medicinal Plants
2.2. Mechanisms of Heavy Metal Effects on the Active Compounds in Medicinal Plants
2.2.1. Characteristics and Classification of Active Compounds in Medicinal Plants
2.2.2. Effects of Heavy Metals on the Synthesis and Accumulation of Active Compounds in Medicinal Plants
- (1)
- Cadmium (Cd):
- (2)
- Arsenic (As):
- (3)
- Lead (Pb):
2.3. Accumulation of Toxic and Hazardous Substances in Medicinal Plants Induced by Heavy Metals and Their Risk Assessment
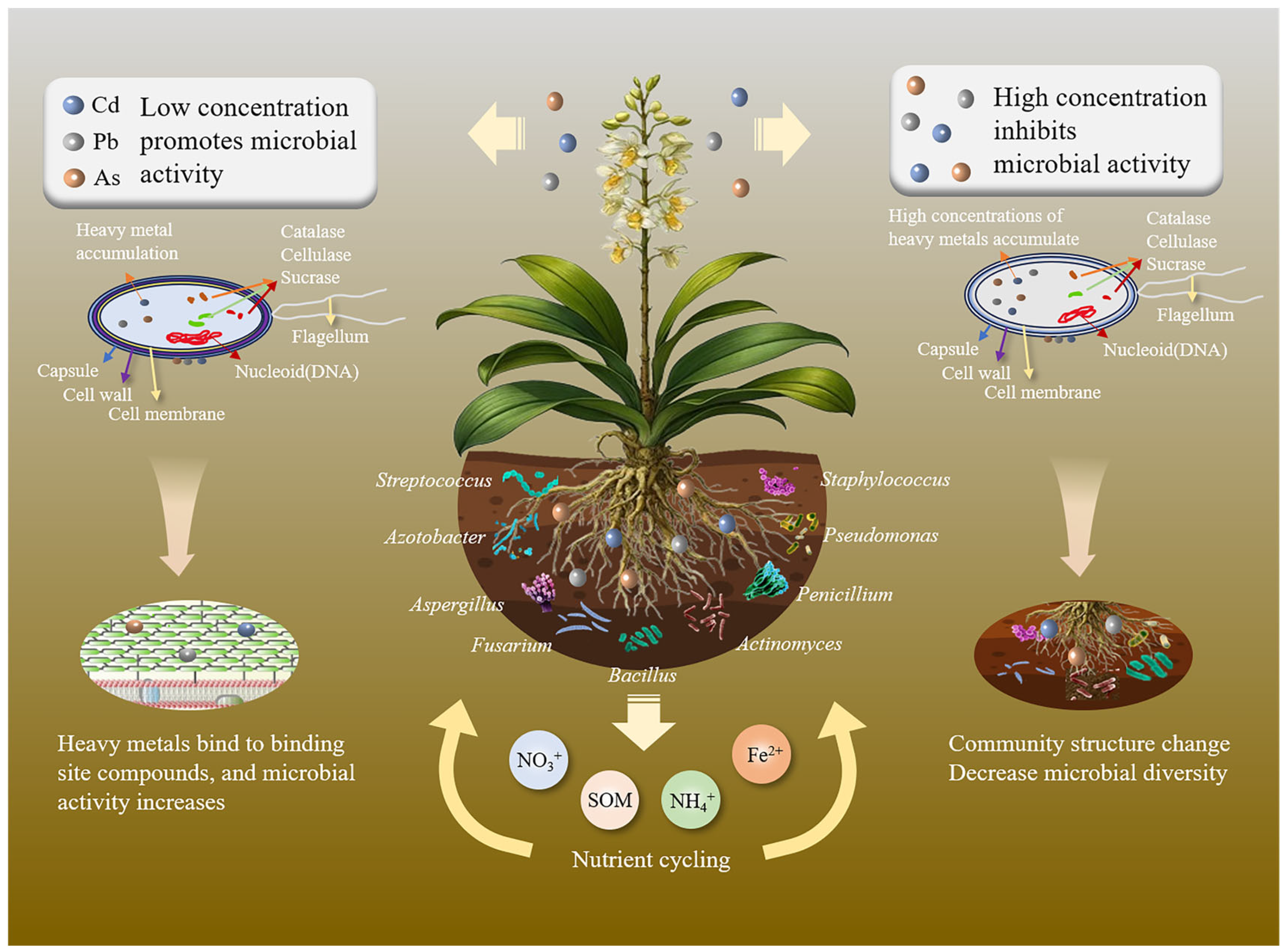
3. Mechanisms of Heavy Metal Effects on Rhizosphere Microorganisms in Medicinal Plants
3.1. Effects of Heavy Metals on Metabolic Activities of Rhizosphere Microorganisms
3.1.1. Mechanisms of Inhibition and Activation of Microbial Metabolic Pathways
3.1.2. Microbial Adaptation and Gene Expression Regulation Under Heavy Metal Stress
3.2. Effects of Heavy Metals on Rhizosphere Microbial Community Structure and Function
3.2.1. Changes in Rhizosphere Microbial Community Structure
3.2.2. Decreased Microbial Diversity and Its Ecological Consequences
3.2.3. Effects of Heavy Metals on Soil Nutrient Cycling Functions
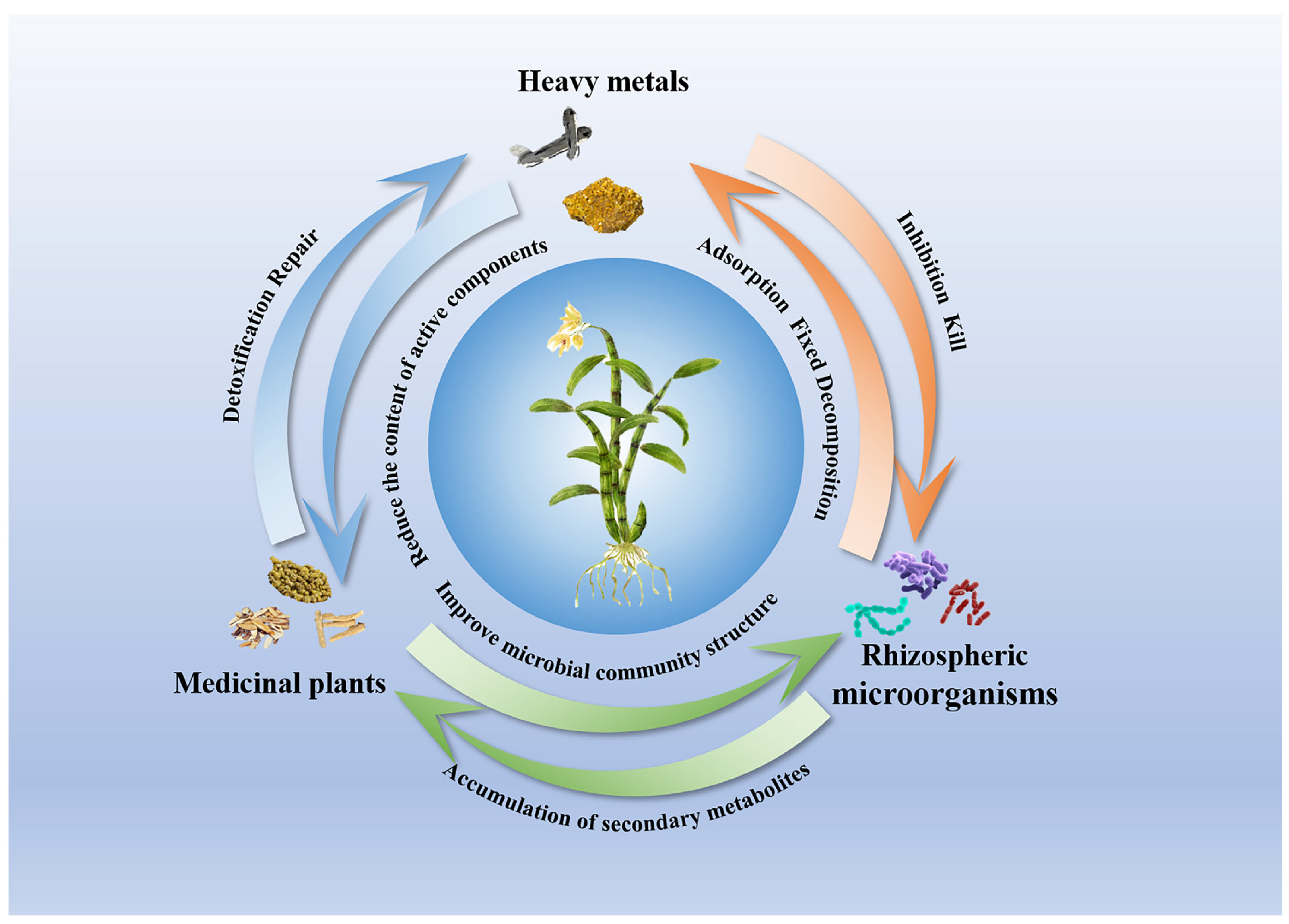
3.3. Linking Heavy Metal-Induced Rhizosphere Microbial Shifts to the Biosynthesis of Active Compounds in Medicinal Plants
4. Conclusions and Future Prospects
- (1)
- Enhanced monitoring and evaluation of heavy metal pollution are required
- (2)
- Comprehensive research on the effects of heavy metal pollution on medicinal plant quality should be undertaken
- (3)
- Rational planning and environmental management of medicinal plant cultivation areas require advancement
- (4)
- Greater research emphasis on the effects of heavy metal pollution on microbial ecological functions is necessary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hua, L.; Xia, Y.; Zou, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, H. Pollution source, hidden dangers and remediation technologies of heavy metal in soil. Environ. Ecol. 2024, 6, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Weng, L.; Ma, J.; Wu, X.; Li, Y. Review on the last ten years of research on source identification of heavy metal pollution in soils. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 2219–2238. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.; Jiang, T.; Liu, X.; Ma, X.; Yang, Z.; Hou, Q.; Xia, X.; Li, F. Research progress in current status of soil heavy metal pollution and analysis technology. Geol. China 2021, 48, 460–476. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Cui, K.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y. Occurrence, Bioavailability, and Environmental Risk of Heavy Metals and Metalloids in the Sediment and Drawdown Area of Fengshuba Drinking Water Reservoir. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2023, 33, 578–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, I.; Alkheraije, K.A. A review of important heavy metals toxicity with special emphasis on nephrotoxicity and its management in cattle. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1149720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janaszek, A.; Kowalik, R. Analysis of Heavy Metal Contaminants and Mobility in Sewage sludge-soil Mixtures for Sustainable Agricultural Practices. Water 2023, 15, 3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yue, H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Jia, Y.; Chang, S.; Wang, Z.; Tashi, T.; Li, W. Advances in the Study of Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fritillariae cirrhosae Bulbus and Its Main Components. Adv. Clin. Med. 2023, 13, 10212–10219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.-S.; Park, G.; Kim, Y.-U. Anti-Oxidative Bioactivities of Medicinal Herbs in the Treatment of Aging-Related Diseases. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, M.; Kong, F.; Yang, P.; Zhu, J.; Jia, J. Review of anti-tumor activity and mechanism of Chinese materia medica active ingredients. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2020, 51, 2587–2592. [Google Scholar]
- Lareen, A.; Burton, F.; Schäfer, P. Plant root-microbe communication in shaping root microbiomes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 90, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Zhu, M.; Pei, Y.; Ran, G.; Shi, Y.; Ding, J. Climate warming alters the soil microbial association network and role of keystone taxa in determining wheat quality in the field. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 326, 107817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, L.; Ma, Z. Enhanced Iron and Selenium Uptake in Plants by Volatile Emissions of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (BF06). Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Feng, F.; Cheng, J.; Ma, L.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, W.; et al. Rhizosphere Bacteria Help to Compensate for Pesticide-Induced Stress in Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 12542–12553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J. Mechanism of Soil Microbial Nutrient Utilization under Mulching in Hilly Region of Loess Plateau. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest AF University, Yangling, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Baloch, F.B.; Zeng, N.; Gong, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Baloch, S.B.; Ali, S.; Li, B. Rhizobacterial Volatile Organic Compounds: Implications for Agricultural Ecosystems’ Nutrient Cycling and Soil Health. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yizhu, L.; Imtiaz, M.; Ditta, A.; Rizwan, M.S.; Ashraf, M.; Mehmood, S.; Aziz, O.; Mubeen, F.; Ali, M.; Elahi, N.N.; et al. Response of growth, antioxidant enzymes and root exudates production towards As stress in Pteris vittata and in Astragalus sinicus colonized by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 27, 2340–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, X.; Guo, X.; Lei, Z.; Niu, J.; Liang, J.; Li, Z. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria promote growth and bioactive components accumulation of Astragalus mongholicus by regulating plant metabolism and rhizosphere microbiota. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wu, Y.-N.; Fan, Q.; Han, Q.-Q.; Paré, P.W.; Xu, R.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Wang, S.-M.; Zhang, J.-L. Improved Growth and Metabolite Accumulation in Codonopsis pilosula (Franch.) Nannf. by Inoculation of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens GB03. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8103–8108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ma, L.; Wei, R.; Ma, Y.; Ma, T.; Dang, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, S.; Ma, S.; Chen, G. Effect of Continuous Cropping on Growth and Lobetyolin Synthesis of the Medicinal Plant Codonopsis pilosula (Franch.) Nannf. Based on the Integrated Analysis of Plant-Metabolite-Soil Factors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 19604–19617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Tan, H.; Wang, M.; Jiang, T.; Wei, H.; Xu, W.; Jiang, Q.; Bao, H.; Ding, Y.; Wang, F.; et al. Research Progress of Soil Microorganisms in Response to Heavy Metals in Rice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8513–8522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkhi, I.; Benali, T.; Aanniz, T.; El Menyiy, N.; Guaouguaou, F.-E.; El Omari, N.; El-Shazly, M.; Zengin, G.; Bouyahya, A. Plant-Microbial Interaction: The Mechanism and the Application of Microbial Elicitor Induced Secondary Metabolites Biosynthesis in Medicinal Plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 167, 269–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Jia, M.; Chen, L.; Zheng, C.; Rahman, K.; Han, T.; Qin, L. The Regulatory Mechanism of Fungal Elicitor-Induced Secondary Metabolite Biosynthesis in Medical Plants. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 43, 238–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Gong, J.; Peng, W.; Luan, W.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Mei, X.; Yang, M.; Zhu, S. Alleviating Soil Acidification to Suppress Panax notoginseng Soil-Borne Disease by Modifying Soil Properties and the Microbiome. Plant Soil 2024, 502, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hou, D.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Fu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zheng, W.; Lu, L.; Tian, S. Distinct Rhizobacterial Functional Assemblies Assist Two Sedum alfredii Ecotypes to Adopt Different Survival Strategies under Lead Stress. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Ren, Y.; Bai, X.; Su, Y.; Han, J. Contributions of Beneficial Microorganisms in Soil Remediation and Quality Improvement of Medicinal Plants. Plants 2022, 11, 3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Li, G.; Tang, W.; Zhu, Q.; Li, X.; Du, C.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, L. Role of Sedum alfredii and Soil Microbes in the Remediation of Ultra-High Content Heavy Metals Contaminated Soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 339, 108090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cui, J.; Li, G.; Du, C.; Wen, K. Remediation Mechanism of High Concentrations of Multiple Heavy Metals in Contaminated Soil by Sedum Alfredii and Native Microorganisms. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 147, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S. Effects of Interaction between Claroideogolmus etuicatum and Bacillus aryabhattai on the Utilization of Organic Phosphorus in Camellia oleifera Abel. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Wei, Z.; Shao, Z.; Friman, V.-P.; Cao, K.; Yang, T.; Kramer, J.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Mei, X.; et al. Competition for Iron Drives Phytopathogen Control by Natural Rhizosphere Microbiomes. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabborova, D.; Mamarasulov, B.; Davranov, K.; Enakiev, Y.; Bisht, N.; Singh, S.; Stoyanov, S.; Garg, A.P. Diversity and Plant Growth Properties of Rhizospheric Bacteria Associated with Medicinal Plants. Indian J. Microbiol. 2024, 64, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, O.Y.A.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Kuramae, E.E. Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances: Ecological Function and Impact on Soil Aggregation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Parvez, S.S.; Goswami, A.; Banik, A. Exopolysaccharides from Agriculturally Important Microorganisms: Conferring Soil Nutrient Status and Plant Health. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 129954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Cui, H.; Fu, C.; Li, R.; Qi, F.; Liu, Z.; Yang, G.; Xiao, K.; Qiao, M. Unveiling the Crucial Role of Soil Microorganisms in Carbon Cycling: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 909, 168627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angon, P.B.; Islam, S.; Kc, S.; Das, A.; Anjum, N.; Poudel, A.; Suchi, S.A. Sources, Effects and Present Perspectives of Heavy Metals Contamination: Soil, Plants and Human Food Chain. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Ai, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, S. Responses of the Root Morphology and Photosynthetic Pigments of Ryegrass to Fertilizer Application under Combined Petroleum-Heavy Metal Stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 87874–87883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, M.; Nassar, D.; Shtaya, M. Heavy Metals Accumulation in Soil and Uptake by Barley (Hordeum vulgare) Irrigated with Contaminated Water. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, E.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Guo, J. Translocation of Heavy Metals from Soils into Floral Organs and Rewards of Cucurbita pepo: Implications for Plant Reproductive Fitness. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, H.; Zhao, M.; Li, Y.; Zhu, B. Progress of Immunomodulatory Effect and Clinical Application of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Pharm. Inf. 2020, 9, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Han, L.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Z.; Duan, X.; Song, X. Platycarya strobilacea Sieb. Et Zucc.: A Review of Its Traditional Uses, Botany, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Toxicology. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2022, 74, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Bai, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, W.; Shen, W.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Z. Structural Characterization and Immunostimulatory Activity of Heteropolysaccharides from Fuzhuan Brick Tea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speisky, H.; Shahidi, F.; Costa de Camargo, A.; Fuentes, J. Revisiting the Oxidation of Flavonoids: Loss, Conservation or Enhancement of Their Antioxidant Properties. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Sa, K.; Liang, J.; Sun, D.; Li, H.; Chen, L. Research Progress of Plant-Derived Natural Alkaloids in Central Nervous System Diseases. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 4885–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.E.; Lee, J.S. The Potential of Korean Bioactive Substances and Functional Foods for Immune Enhancement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Muema, F.W.; Kimutai, F.; Chen, G.; Guo, M. Phenolic Compounds from Carissa spinarum Are Characterized by Their Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Hepatoprotective Activities. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Four Part; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020; p. 0821.
- World Health Organization. Quality Control Methods for Medicinal Plant Materials; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. Guideline for Elemental Impurities Q3D(R2); European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/Q3D-R2_Guideline_Step4_2022_0308.pdf (accessed on 16 October 2025).
- United States Pharmacopeia. USP <232> Elemental Impurities—Limits & USP <233> Elemental Impurities—Procedures; United States Pharmacopeia: Rockville, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jańczak-Pieniążek, M.; Cichoński, J.; Michalik, P.; Chrzanowski, G. Effect of Heavy Metal Stress on Phenolic Compounds Accumulation in Winter Wheat Plants. Molecules 2022, 28, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S. Research on Cadmium Enrichment in Lonicera japonica Thunb. and Its Impact on Organic Acid Accumulation in Leaf. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, K.; Chen, K.; Liang, J.; Cui, L. Effects of Cadmium Stress on Seedlings Growth and Active Ingredients in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Plant Sci. J. 2013, 31, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Effects of Cadmium on Physiology and Quality Formation of Chrysanthemum indicum L. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Agric University, Nanjing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, S.; Liu, R.; Wang, X.; Yuan, J. Characteristics of Cadmium Enrichment of Jiangxi Daodi Medicinal Plant Plantago asiatica L. and its Transcriptome Analysis in Response to Cadmium Stress. Mol. Plant Breed. 2023, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kamali, S.; Iranbakhsh, A.; Ebadi, M.; Ardebili, Z.O.; Haghighat, S. Methyl jasmonate conferred Arsenic tolerance in Thymus kotschyanus by DNA hypomethylation, stimulating terpenoid metabolism, and upregulating two cytochrome P450 monooxygenases. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Mi, Y.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Yi, B.; He, L. Distribution of Arsenic in Root Tissue and Its Subcellular Characteristics of the Medicinal Plant Panax notoginseng. Chin. Bull. Bot. 2015, 50, 591–597. [Google Scholar]
- Nazir, F.; Jahan, B.; Iqbal, N.; Rajurkar, A.B.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Khan, M.I.R. Methyl Jasmonate Influences Ethylene Formation, Defense Systems, Nutrient Homeostasis and Carbohydrate Metabolism to Alleviate Arsenic-Induced Stress in Rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 202, 107990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhou, J.; Peng, C.; Qiao, J.; Xia, S.; Fan, Y.; Yao, L.; Qi, K.; Chen, D.; Guo, Z.; et al. Effects of Varied Forms of Arsenic Stress on Seedling Growth and Arsenic Distribution in Honeysuckle Plants. Processes 2023, 11, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Li, X.; Hua, J.; Xu, J. Effects of Pb pollution of soil and leaf surface on growth, Pb distribution and accumulation of wheat (Triticum aestivum). J. Plant Resour. Environ. 2010, 19, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, M.; Gao, L.; Ni, C.; Cao, W. Spectroscopy Characterization, Theoretical Study and Antioxidant Activities of the Flavonoids-Pb(II) Complexes. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1209, 127919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kısa, D.; Elmastaş, M.; Öztürk, L.; Kayır, Ö. Responses of the Phenolic Compounds of Zea Mays under Heavy Metal Stress. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2016, 59, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Huang, T. Effects of Lead, Copper, and Cadmium Stresses on growth and inherent quality of Prunalla vulgaris. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2010, 35, 263–267. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Liang, X.; Yang, F.; Cao, Q.; Li, G. Effects of Lead Stress on Net Photosynthetic Rate, SPAD Value and Ginsenoside Production in Ginseng (Panax ginseng). China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2014, 39, 3054–3059. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Lu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, P.; Hou, J.; Qian, J. Effects of Pb Stress on Nutrient Uptake and Secondary Metabolismin Submerged Macrophyte Vallisneria natans. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; He, J.; Pan, C.; Zhang, Z.; Dan, Y. Effect of Pb on Growth and Essential Oil Components of Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare L.) Plant. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 23, 326–331. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Xi, Y.; Gan, L.; Johnson, D.; Wu, Y.; Ren, D. Effects of Lead and Cadmium on Photosynthesis in Amaranthus spinosus and Assessment of Phytoremediation Potential. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2019, 21, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Hu, F. Analysis and Health Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Three Codonopsis radix Varieties in China. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 2475–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Chen, Z.; Yang, X.; Sheng, L.; Mao, H.; Zhu, S. Integrated Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Reveal Key Metabolic Pathway Responses in Pistia stratiotes under Cd Stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Feng, N.; Yan, Q.; Zhu, X. Carcinogenic risk assessment of three homologous Chinese medicinal materials based on arsenic exposure. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2018, 29, 2601–2603. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, T.; Jin, H.; Zhang, L.; Shi, S.; Shen, M.; Gao, F.; Ma, S. A Study to Carcinogenic Risk Assessment of Pb&As in Root and Rhizome Medicinal Meterials. Chin. Pharm. Aff. 2021, 35, 661–665. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Lu, N.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, D. Relationship between Heavy Metal Content in Polluted Soil and Soil Organic Matter and pH in Mining Areas. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 394, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, N.; Abdullahi, A.A.; Abdulkadir, A. Heavy Metals and Soil Microbes. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2016, 15, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, H.; Meli, P.; Butler, B.; Paolini, J.; Matus, F.; Merino, C.; Cornejo, P.; Kuzyakov, Y. Meta-Analysis of Heavy Metal Effects on Soil Enzyme Activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Li, Q.; Yan, H.; Luo, J.; Yang, M. Establishment of health risk assessment model for assessing medicinal and edible plants contaminated by heavy metals—Take Astragali Radix, Codonopsis radix and Laminariae Thallus as examples. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2019, 44, 5042–5050. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Qin, J.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, M. Residue analysis and health risk assessment of heavy metals in 24 Chinese medicinal materials in Xingqing District of Yinchuan City. Occup. Health 2023, 39, 33–38+42. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Yan, C.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Zeng, M.; Dong, Y.; Jiao, R. Heavy Metal Concentrations and Accumulation Characteristics of Dominant Woody Plants in Iron and Lead−Zinc Tailing Areas in Jiangxi, Southeast China. Forests 2023, 14, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, S.; Shen, Z.; Shi, H.; Long, G.; Deng, W.; Fan, W. Pollution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals in Panax notoginseng Planting Fields. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2022, 38, 645–653. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Chen, Z.; Yang, X.; Sheng, L.; Mao, H.; Zhu, S. Metagenomics reveal arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi altering functional gene expression of rhizosphere microbial community to enhance Iris tectorum’s resistance to Cr stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 895, 164970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Du, Y.; Yu, C.; Liu, W.; Zou, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, Y.; Tian, Z. The influences of heavy metals on soil microbial C, N, P cycling and heavy metal resistance under different fertilization regimes. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 370, 125915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquart, A.; Brayner, R.; El Hage Chahine, J.-M.; Ha-Duong, N.-T. Cd2+ and Pb2+ Complexation by Glutathione and the Phytochelatins. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 267, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ju, W.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Beiyuan, J.; Fan, Q.; Wei, S.; Li, S.; et al. Microbial Metabolic Limitation of Rhizosphere under Heavy Metal Stress: Evidence from Soil Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Yang, J.; Hu, B. Interaction between Arsenic Metabolism Genes and Arsenic Leads to a Lose-Lose Situation. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 312, 119971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Cai, K.; Cai, Y.; Huang, F. Research Advances on Biosorption and Detoxification Mechanisms of Heavy Metals by Bacteria. Biotechnol. Bull. 2016, 32, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chellaiah, E.R. Cadmium (heavy metals) bioremediation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A minireview. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, I.; Sohail, H.; Sun, J.; Nawaz, M.A.; Li, G.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Liu, J. Heavy Metal and Metalloid Toxicity in Horticultural Plants: Tolerance Mechanism and Remediation Strategies. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Molina, M.C.; Bautista, L.F.; Belda, I.; Carmona, M.; Díaz, E.; Durante-Rodríguez, G.; García-Salgado, S.; López-Asensio, J.; Martínez-Hidalgo, P.; Quijano, M.Á.; et al. Bioremediation of Soil Contaminated with Arsenic. In Microbes and Enzymes in Soil Health and Bioremediation; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 321–351. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; He, F.; Huang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, F.; Cong, X.; He, B.; Wang, Y. Dicranopteris dichotoma Rhizosphere-Derived Bacillus Sp. MQB12 Acts as an Enhancer of Plant Growth via Increasing Phosphorus Utilization, Hormone Synthesis, and Rhizosphere Microbial Abundance. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Deng, S.; Song, H.; Xu, J.; Cheng, Y. Bacterial metal ion efflux systems and metal homeostasis. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2024, 64, 672–686. [Google Scholar]
- Ardissone, S.; Redder, P.; Russo, G.; Frandi, A.; Fumeaux, C.; Patrignani, A.; Schlapbach, R.; Falquet, L.; Viollier, P.H. Cell Cycle Constraints and Environmental Control of Local DNA Hypomethylation in α-Proteobacteria. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, L.B.; Obayori, O.S.; Ilori, M.O.; Amund, O.O. Effects of Cadmium Perturbation on the Microbial Community Structure and Heavy Metal Resistome of a Tropical Agricultural Soil. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2020, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, K.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Wu, B. Responses of Soil N-Fixing Bacterial Communities to Redroot Pigweed (Amaranthus retroflexus L.) Invasion under Cu and Cd Heavy Metal Soil Pollution. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 267, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Singh, R.K.; Li, H.-B.; Guo, D.-J.; Sharma, A.; Verma, K.K.; Solanki, M.K.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Lakshmanan, P.; Yang, L.; et al. Nitrogen fixation and phytohormone stimulation of sugarcane plant through plant growth promoting diazotrophic Pseudomonas. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2023, 40, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González Henao, S.; Ghneim-Herrera, T. Heavy Metals in Soils and the Remediation Potential of Bacteria Associated with the Plant Microbiome. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 604216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.; Huang, X.; Su, X.; Bao, Y. Responses of Microbial Communities and Metabolic Profiles to the Rhizosphere of Tamarix ramosissima in Soils Contaminated by Multiple Heavy Metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusengemungu, L.; Gwanama, C.; Simuchimba, G.; Mubemba, B. Potential of Bioaugmentation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soils in the Zambian Copperbelt Using Autochthonous Filamentous Fungi. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1045671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Bani Mfarrej, M.F.; Rizwan, M.; Hussain, A.; Shahid, M.J.; Wang, X.; Nafees, M.; Waseem, M.; Alharby, H.F. Microbe-Citric Acid Assisted Phytoremediation of Chromium by Castor Bean (Ricinus communis L.). Chemosphere 2022, 296, 134065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Huo, Y.; Yang, D.; Yang, D. Influence of the plant growth promoting Rhizobium panacihumi on aluminum resistance in Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Ding, W. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria Alleviate Aluminum Toxicity and Ginger Bacterial Wilt in Acidic Continuous Cropping Soil. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1664–302X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Cao, P.; Wang, G.; Han, J. Microbial inoculant and garbage enzyme reduced cadmium (Cd) uptake in Salvia miltiorrhiza (Bge.) under Cd stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 192, 110311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Qiao, L.; Liu, X.-X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, Z.; Yu, C. Microbial Community Succession in Soils under Long-Term Heavy Metal Stress from Community Diversity-Structure to KEGG Function Pathways. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Ascher, J.; Ceccherini, M.T.; Landi, L.; Pietramellara, G.; Renella, G. Microbial diversity and soil functions. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 68, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borymski, S.; Cycoń, M.; Beckmann, M.; Mur, L.A.J.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Plant Species and Heavy Metals Affect Biodiversity of Microbial Communities Associated with Metal-Tolerant Plants in Metalliferous Soils. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyer, J.S.; Vinyard, B.; Maul, J.; Selmer, K.; Lupitskyy, R.; Rice, C.; Roberts, D.P. Combined Extraction Method for Metabolomic and PLFA Analysis of Soil. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2019, 135, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Tian, K.; Peng, X.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.; Tian, W. Cadmium/Zinc Stresses and Plant Cultivation Influenced Soil Microflora: A Pot Experiment Conducted in Field. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 277, 116384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconu, M.; Pavel, L.V.; Hlihor, R.-M.; Rosca, M.; Fertu, D.I.; Lenz, M.; Corvini, P.X.; Gavrilescu, M. Characterization of Heavy Metal Toxicity in Some Plants and Microorganisms—A Preliminary Approach for Environmental Bioremediation. New Biotechnol. 2020, 56, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Ren, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, L.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, A. Physicochemical Features, Metal Availability and Enzyme Activity in Heavy Metal-Polluted Soil Remediated by Biochar and Compost. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; You, X.; Tang, S.; Zhneg, T.; Cao, G.; He, L. Research progress on mechanisms of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to enhance resistance of medicinal plants in response to cadmium stress. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2025, 56, 1477–1488. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Wang, H.; Liang, C.; Zhang, Y. Advances on the enrichment of heavy metals in traditional Chinese medicine. Med. Res. Educ. 2022, 39, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Zuo, J.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Zu, M.; Liu, S.T. The Chinese Medicinal Plants Rhizosphere: Metabolites, Microorganisms, and Interaction. Rhizosphere 2022, 22, 100540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Key Mechanism | Regulatory Function | Specific Role | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Secondary Metabolite Synthesis and Plant Health Promotion | Root Exudate Regulation | Increased content of root exudates such as oxalic acid and acetic acid affects root morphology. | [16] |
| Secondary Metabolite Synthesis | Nitrogen-fixing bacteria may influence hormone signal transduction pathways. | [17] | |
| Stress Resistance in Medicinal Plants | Inoculation with Bacillus improves rhizosphere soil enzyme activity. | [18] | |
| Disease Resistance | Actinomycetes play a crucial role in decomposing cellulose, polyphenols, and lignin. | [19] | |
| Plant Hormone Regulation | Microorganisms influence plant growth by producing plant hormones or hormone analogs. | [20] | |
| Signal Communication | Microbial elicitors stimulate signaling pathways for the synthesis of secondary metabolites in medicinal plants. | [21,22] | |
| Disease Pressure Regulation | Microorganisms alter the rhizosphere environment to reduce the survival space of pathogens. | [23] | |
| Heavy Metal Detoxification and Environmental Remediation | Heavy Metal Detoxification | Microorganisms reduce heavy metal availability in soil through chelation or adsorption. | [24] |
| Biodegradation | Microorganisms metabolize recalcitrant organic macromolecules into water, carbon dioxide, and less toxic compounds. | [25] | |
| Bioaccumulation | Microorganisms immobilize environmental pollutants through bioaccumulation processes. | [26,27] | |
| Nutrient Acquisition and Transformation | Nutrient Absorption and Transformation | Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and soil bacteria mineralize organic phosphorus and produce siderophores. | [28,29] |
| Growth Promotion | Produces growth-promoting substances such as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). | [30] | |
| Soil Structure Improvement | Microbial extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) improve soil physical structure and increase aggregate stability. | [31] | |
| Water Management | Microbial extracellular polysaccharides help retain soil moisture. | [32] | |
| Organic Matter Degradation | Microorganisms promote the mineralization process of organic matter in soil. | [33] |
| Authority/Source | Cd | Pb | As | Scope | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (Vol. IV, 2020) | ≤1 mg·kg−1 | ≤5 mg·kg−1 | ≤2 mg·kg−1 | Raw herbal material | [45] |
| WHO (1998, Quality control methods for medicinal plant materials) | ≤0.3 mg·kg−1 | ≤10 mg·kg−1 | - | Dried plant materials | [46] |
| ICH Q3D (R2, 2022)—adopted by EMA & USP | 5 µg/day | 5 µg/day | 15 µg/day | Finished products, risk-based | [47] |
| USP <232>/<233> (aligned with ICH Q3D) | 5 µg/day | 5 µg/day | 15 µg/day | Finished drug products | [48] |
| Direction of Interaction | Specific Impact | References |
|---|---|---|
| Rhizosphere Organisms → Heavy Metals | The study showed two ecotypes recruited distinct rhizosphere microbiomes: The accumulator ecotype (AE) used diverse microbes (e.g., Flavobacterium) to promote growth and Pb uptake, while the non-accumulator ecotype (NAE) used specialized microbes (e.g., Pseudomonas) to reduce Pb stress and limit uptake. This was the first evidence that plants adapt to heavy metal stress through microbial ecological assembly. | [24] |
| Metagenomic analysis showed that arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) modified rhizosphere microbial gene expression in Iris tectorum’s., upregulating Cr detoxification and stress-response genes, thus enhancing plant resistance to chromium stress. This reveals microbial regulation of community function as a key mechanism of plant tolerance. | [77] | |
| Both Rhizobium panacihumi in Ginseng and Al stress-enriched bacteria (Bacillus, Pseudomonas) in Ginger enhanced Al tolerance by promoting growth, regulating metabolites and antioxidant genes, reducing ROS, and alleviating toxicity. | [96,97] | |
| Application of microbial inoculants (MI) and “garbage enzyme” (GE) reduced Cd in S. miltiorrhiza roots and altered rhizosphere microbes, increasing taxa like Brevundimonas, Microbacterium, Cupriavidus, and Aspergillus. The combined MIGE (MI+GE) treatment showed the strongest Cd reduction. | [98] | |
| Heavy Metals → Rhizosphere Organisms | Heavy metal stress constrains microbial metabolic capacity, alters soil ecoenzymatic stoichiometry, and causes pronounced C and P limitations in the rhizosphere. | [80] |
| Cadmium stress markedly alters soil microbial communities, enriching diverse heavy metals resistance and antioxidant genes that strengthen the resistome, while simultaneously causing the loss of certain species and functional genes involved in carbon and nitrogen cycling, thereby reducing ecological metabolic diversity. | [89] | |
| Cd and other heavy metals markedly diminish microbial diversity (e.g., Shannon index), alter relative abundance, and restructure community composition. Heavy metals act as strong environmental filters, enriching tolerant taxa (e.g., Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria) while suppressing sensitive groups (e.g., Acidobacteria), driving directional succession. | [93,99] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, H.; Wang, Y.; Bao, H.; Wang, F.; Jiang, Q.; He, X.; Li, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhu, C. Ecotoxicological Impacts of Heavy Metals on Medicinal Plant Quality and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities. Plants 2025, 14, 3214. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14203214
Bao H, Wang Y, Bao H, Wang F, Jiang Q, He X, Li H, Ding Y, Zhu C. Ecotoxicological Impacts of Heavy Metals on Medicinal Plant Quality and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities. Plants. 2025; 14(20):3214. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14203214
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Hexigeduleng, Yu Wang, Hainan Bao, Feijuan Wang, Qiong Jiang, Xiaoqi He, Hua Li, Yanfei Ding, and Cheng Zhu. 2025. "Ecotoxicological Impacts of Heavy Metals on Medicinal Plant Quality and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities" Plants 14, no. 20: 3214. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14203214
APA StyleBao, H., Wang, Y., Bao, H., Wang, F., Jiang, Q., He, X., Li, H., Ding, Y., & Zhu, C. (2025). Ecotoxicological Impacts of Heavy Metals on Medicinal Plant Quality and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities. Plants, 14(20), 3214. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14203214







