Enhancement by Burkholderia contaminans ZCC Combined with Biochar on the Remediation of Arsenic-Contaminated Soil by Pteris vittata
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of B. contaminans ZCC and Biochar Co-Application on Soil pH
2.2. Effects of B. contaminans ZCC and Biochar Co-Application on the Growth of P. vittata
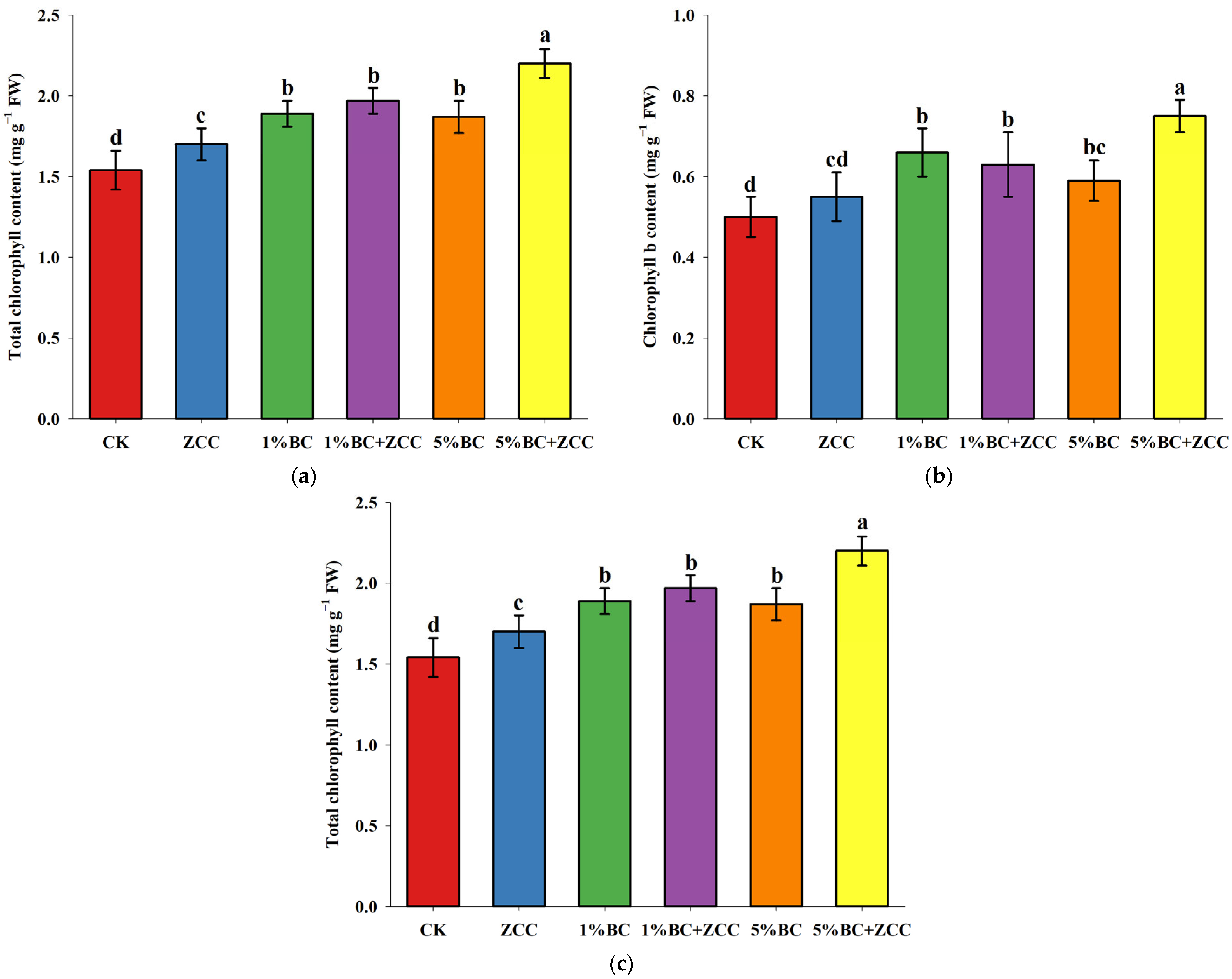
2.3. Effects of B. contaminans ZCC and Biochar Co-Application on Chlorophyll Content of P. vittata
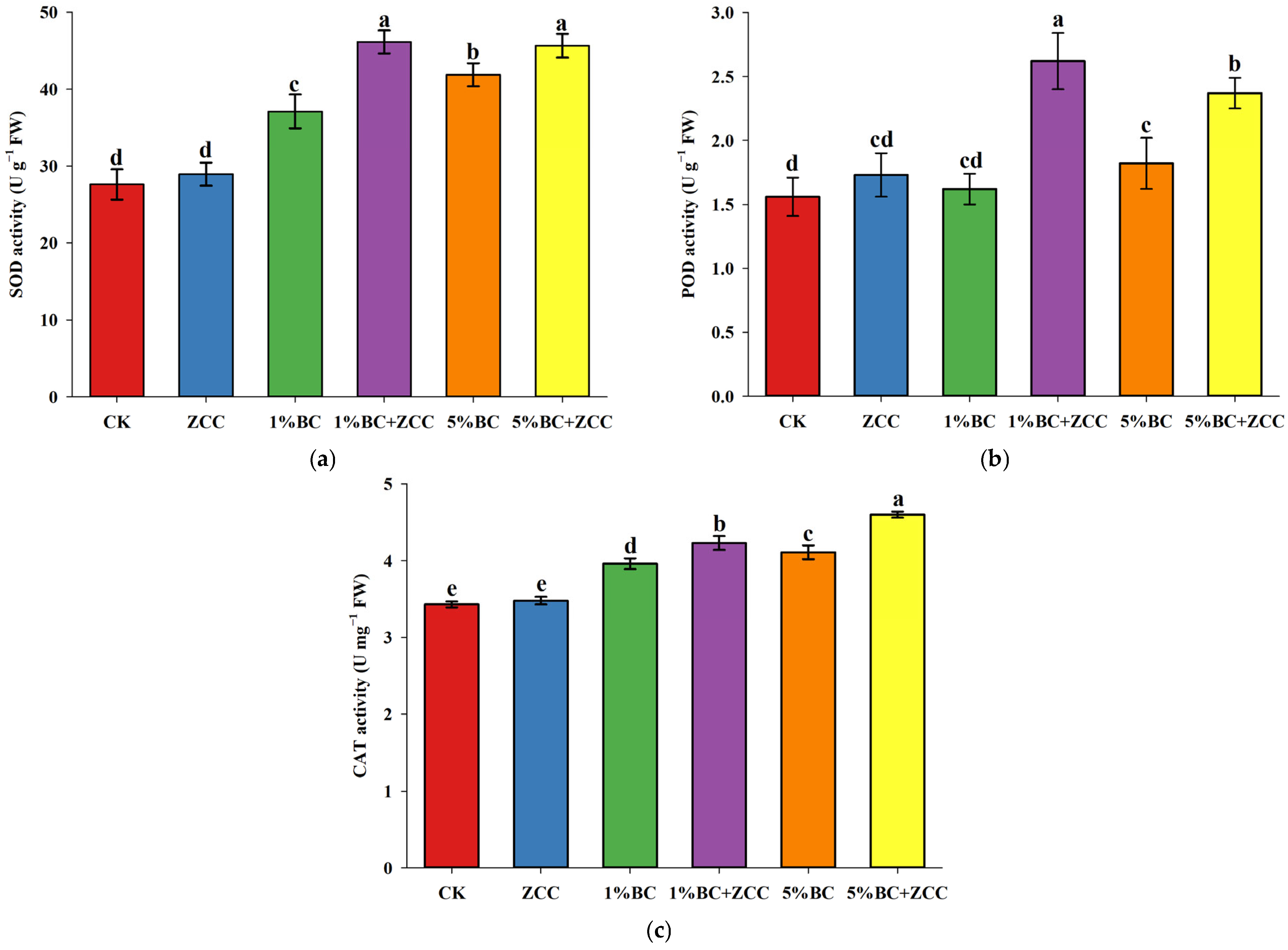
2.4. Effects of B. contaminans ZCC and Biochar Co-Application on Antioxidant Enzyme Activity in P. vittata Roots
2.5. Effects of B. contaminans ZCC and Biochar Co-Application on MDA and Proline Content in P. vittata Roots
2.6. Effects of B. contaminans ZCC and Biochar Co-Application on Arsenic Content in P. vittata Plant
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Soil and Plant Preparation
4.2. Bacterial Inoculum Preparation
4.3. Biochar Preparation
4.4. Greenhouse Pot Experiment with P. vittata
4.5. Soil pH Measurement
4.6. Plant Growth Analysis
4.7. Chlorophyll Content Determination
4.8. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity, MDA and Proline Content Assays
4.9. Arsenic Quantification in P. vittata Plant
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Lim, J.E.; Zhang, M.; Bolan, N.; Mohan, D.; Vithanage, M.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, N.; Cai, X.; Yuan, X.; Senadheera, S.; Cho, Y.; Ok, Y.S. A critical review of the interactions between rhizosphere and biochar during the remediation of metal(loid) contaminated soils. Biochar 2023, 5, 1481–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Gao, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; Dai, C.; Xu, W.; Feng, L.; Ma, M.; Zhu, Y.-G.; et al. Potential use of the Pteris vittata arsenic hyperaccumulation-regulation network for phytoremediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 368, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayiga, A.O.; Saha, U.K. Arsenic hyperaccumulating fern: Implications for remediation of arsenic contaminated soils. Geoderma 2016, 284, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Yang, R.; Xiang, X.Y.; Niu, L.L.; Yin, D.X. Enhancement of phytoextraction efficiency coupling Pteris vittata with low-dose biochar in arsenic-contaminated soil. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2023, 25, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilias, F.; Nikoli, T.; Kalderis, D.; Gasparatos, D. Towards a Soil Remediation Strategy Using Biochar: Effects on Soil Chemical Properties and Bioavailability of Potentially Toxic Elements. Toxics 2021, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compant, S.; Nowak, J.; Coenye, T.; Clément, C.; Barka, E.A. Diversity and occurrence of Burkholderia spp. in the natural environment. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 607–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.X.; Zhang, R.R.; Dai, J.X.; Lin, Z.T.; Li, Y.P.; Herzberg, M.; Zhang, J.L.; Al-Wathnani, H.; Zhang, C.K.; Feng, R.W.; et al. Potential of cadmium resistant Burkholderia contaminans strain ZCC in promoting growth of soy beans in the presence of cadmium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 211, 111914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, A.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, D.; Xu, J.; Rensing, C.; Zhang, L.; Xing, S.; Ni, W.; Yang, W. Biochar loaded with bacteria enhanced Cd/Zn phytoextraction by facilitating plant growth and shaping rhizospheric microbial community. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masscheleyn, P.H.; Delaune, R.D.; Patrick, W.H., Jr. Effect of redox potential and pH on arsenic speciation and solubility in a contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 1414–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szufa, S.; Unyay, H.; Piersa, P.; Kdzierska-Sar, A.; Romanowska-Duda, Z.; Likozar, B. Reduction of spruce phytotoxicity by superheated steam torrefaction and its use in stimulating the growth of ecological bio-products: Lemna minor L. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2025, 15, 17739–17760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, R.R.; Trugilho, P.F.; Silva, C.A.; Melo, I.C.N.D.; Melo, L.C.; Magriotis, Z.M.; Sánchez-Monedero, M.A.; Jorge, P.F. Properties of biochar derived from wood and high-nutrient biomasses with the aim of agronomic and environmental benefits. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojuederie, O.B.; Babalola, O.O. Microbial and Plant-Assisted Bioremediation of Heavy Metal Polluted Environments: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Rajkumar, M.; Zhang, C.; Freitas, H. Inoculation of Brassica oxyrrhina with plant growth promoting bacteria for the improvement of heavy metal phytoremediation under drought conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 320, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Vila, A.; Forján, R.; Guedes, R.S.; Covelo, E.F. Changes on the Phytoavailability of Nutrients in a Mine Soil Reclaimed with Compost and Biochar. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiello, C.A.; Chen, Y.; Gao, X.; Liu, S.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Bennett, M.R.; Rudgers, J.A.; Wagner, D.S.; Zygourakis, K.; Silberg, J.J. Biochar and Microbial Signaling: Production Conditions Determine Effects on Microbial Communication. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11496–11503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ullah, I.; Khan, A.; Park, G.-S.; Waqas, M.; Hong, S.-J.; Jung, B.; Kwak, Y.; Lee, I.-J.; Shin, J.-H. Improvement in phytoremediation potential of Solanum nigrum under cadmium contamination through endophytic-assisted Serratia sp. RSC-14 inoculation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 14032–14042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkin, A.J.; Kapoor, L.; Doss, C.G.P.; Hofmann, T.A.; Lawson, T.; Ramamoorthy, S. The role of photosynthesis related pigments in light harvesting, photoprotection and enhancement of photosynthetic yield in planta. Photosynth. Res. 2022, 152, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shomali, A.; Das, S.; Sarraf, M.; Johnson, R.; Janeeshma, E.; Kumar, V.; Aliniaeifard, S.; Puthur, J.T.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Modulation of plant photosynthetic processes during metal and metalloid stress, and strategies for manipulating photosynthesis-related traits. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 206, 108211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amalina, F.; Abd Razak, A.S.; Zularisam, A.W.; Aziz, M.A.A.; Krishnan, S.; Nasrullah, M. Comprehensive assessment of biochar integration in agricultural soil conditioning: Advantages, drawbacks, and future prospects. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2023, 132, 103508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Ren, X.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Lu, F.; Shi, J. Ecological effects of biochar in heavy metal-contaminated soils from multidimensional perspective: Using meta-analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 432, 132695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhao, S.; Wang, B. Combined application of biochar and PGPB on crop growth and heavy metals accumulation: A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 381, 126626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 909–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.W.; Ding, J.J.; Ali, B.; Nawaz, M.; Hassan, M.U.; Ali, A.; Rasheed, A.; Khan, M.N.; Ozdemir, F.A.; Iqbal, R. Putting biochar in action: A black gold for efficient mitigation of salinity stress in plants. Rev. Future directions. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 31237–31253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhangi-Abriz, S.; Torabian, S. Antioxidant enzyme and osmotic adjustment changes in bean seedlings as affected by biochar under salt stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 137, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Gao, J.; Liu, C.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, D. Key role of persistent free radicals in hydrogen peroxide activation by biochar: Implications to organic contaminant degradation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, D.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Ren, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tsang, D.C.; Crittenden, J.C. pH dependence of arsenic oxidation by rice-husk-derived biochar: Roles of redox-active moieties. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 9034–9044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; LeFevre, G.H.; Mattes, T.E. Black carbon impacts on Paraburkholderia xenovorans strain LB400 cell enrichment and activity: Implications toward lower-chlorinated polychlorinated biphenyls biodegradation potential. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 3895–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, B.; Zhu, L.; Xing, B. Effects and mechanisms of biochar-microbe interactions in soil improvement and pollution remediation: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar effects on soil biota—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liang, X.; Fu, R.; Li, M.; Chen, C. Effect of different biochar particle sizes together with bio-organic fertilizer on rhizosphere soil microecological environment on saline–alkali land. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 949190. [Google Scholar]
- Szabados, L.; Savouré, A. Proline: A multifunctional amino acid. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, S.; Hayat, Q.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wani, A.S.; Pichtel, J.; Ahmad, A. Role of proline under changing environments: A review. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Per, T.S.; Khan, N.A.; Reddy, P.S.; Masood, A.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Khan, M.I.R.; Anjum, N.A. Approaches in modulating proline metabolism in plants for salt and drought stress tolerance: Phytohormones, mineral nutrients and transgenics. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.A.; Bibi, S.; Chen, B. Preventative effect of crop straw-derived biochar on plant growth in an arsenic polluted acidic ultisol. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 151469. [Google Scholar]
- Alwutayd, K.M.; Alghanem, S.M.S.; Alshehri, D.; Saleem, M.H.; Hussain, S.; Ali, B.; Abeed, A.H.A. Advancing Arsenic Toxicity Mitigation in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) with Rice Straw Biochar and Silicon: A Study on Morpho-Physio-Biochemical Responses. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 2152–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.Q.; Komar, K.M.; Tu, C.; Zhang, W.; Cai, Y.; Kennelley, E.D. A fern that hyperaccumulates arsenic. Nature 2001, 409, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Rajkumar, M.; Zhang, C.; Freitas, H. Beneficial role of bacterial endophytes in heavy metal phytoremediation. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 174, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.X.; Chen, T.B.; Huang, Z.C.; Lei, M.; Liao, X.Y. Effect of arsenic on chloroplast ultrastructure and calcium distribution in arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata L. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 803–809. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.Y.; Chen, J.X.; Cao, Y.; Li, H.B.; Chen, Y.S.; Ma, L.Q. Pteris vittata coupled with phosphate rock effectively reduced As and Cd uptake by water spinach from contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.D.; El-Alawi, Y.; Penrose, D.M.; Glick, B.R.; Greenberg, B.M. Responses of three grass species to creosote during phytoremediation. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 130, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demiral, T.; Türkan, I. Comparative lipid peroxidation, antioxidant defense systems and proline content in roots of two rice cultivars differing in salt tolerance. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2005, 53, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.Y. Factors influencing arsenic accumulation by Pteris vittata: A comparative field study at two sites. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 141, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Treatment | pH |
|---|---|
| CK | 6.73 ± 0.23 c |
| ZCC | 6.98 ± 0.20 b |
| 1%BC | 7.08 ± 0.16 b |
| 1% BC + ZCC | 7.02 ± 0.16 b |
| 5% BC | 7.56 ± 0.09 a |
| 5% BC + ZCC | 7.50 ± 0.15 a |
| Treatment | Total Plant Fresh Weight (g) | Total Plant Dry Weight (g) | Height (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 12.94 ± 2.43 d | 1.94 ± 0.36 d | 19.25 ± 1.39 d |
| ZCC | 17.66 ± 1.70 c | 2.42 ± 0.51 c | 22.24 ± 1.38 c |
| 1% BC | 16.97 ± 0.54 c | 2.58 ± 0.38 c | 19.68 ± 0.85 d |
| 1% BC + ZCC | 29.54 ± 2.64 b | 4.32 ± 0.21 a | 27.11 ± 1.74 a |
| 5% BC | 28.50 ± 1.48 b | 3.79 ± 0.32 b | 25.11 ± 0.57 b |
| 5% BC + ZCC | 33.14 ± 3.16 a | 4.47 ± 0.38 a | 28.47 ± 1.19 a |
| Treatment | Content (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|
| CK | 15.83 ± 3.28 d |
| ZCC | 22.42 ± 4.85 c |
| 1% BC | 26.86 ± 5.80 c |
| 1% BC + ZCC | 38.48 ± 3.25 b |
| 5% BC | 37.02 ± 2.60 b |
| 5% BC + ZCC | 44.42 ± 6.14 a |
| Property | pH | OC (g kg−1) | TN (g kg−1) | TP (g kg−1) | TK (g kg−1) | AN (mg kg−1) | AP (mg kg−1) | AK (mg kg−1) | As (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 6.90 ± 0.20 | 5.29 ± 0.22 | 0.49 ± 0.02 | 0.42 ± 0.05 | 27.50 ± 3.10 | 34.00 ± 3.85 | 29.60 ± 3.28 | 46.00 ± 5.46 | 24.16 ± 2.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, D.; Alwathnani, H.; Rensing, C. Enhancement by Burkholderia contaminans ZCC Combined with Biochar on the Remediation of Arsenic-Contaminated Soil by Pteris vittata. Plants 2025, 14, 3169. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14203169
Yang X, Li Y, Zhou D, Alwathnani H, Rensing C. Enhancement by Burkholderia contaminans ZCC Combined with Biochar on the Remediation of Arsenic-Contaminated Soil by Pteris vittata. Plants. 2025; 14(20):3169. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14203169
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiaojun, Yuanping Li, Dan Zhou, Hend Alwathnani, and Christopher Rensing. 2025. "Enhancement by Burkholderia contaminans ZCC Combined with Biochar on the Remediation of Arsenic-Contaminated Soil by Pteris vittata" Plants 14, no. 20: 3169. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14203169
APA StyleYang, X., Li, Y., Zhou, D., Alwathnani, H., & Rensing, C. (2025). Enhancement by Burkholderia contaminans ZCC Combined with Biochar on the Remediation of Arsenic-Contaminated Soil by Pteris vittata. Plants, 14(20), 3169. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14203169






