The Effect of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria Bacillus thuringiensis LKT25 on Cadmium Accumulation and Physiological Responses in Solanum nigrum L.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
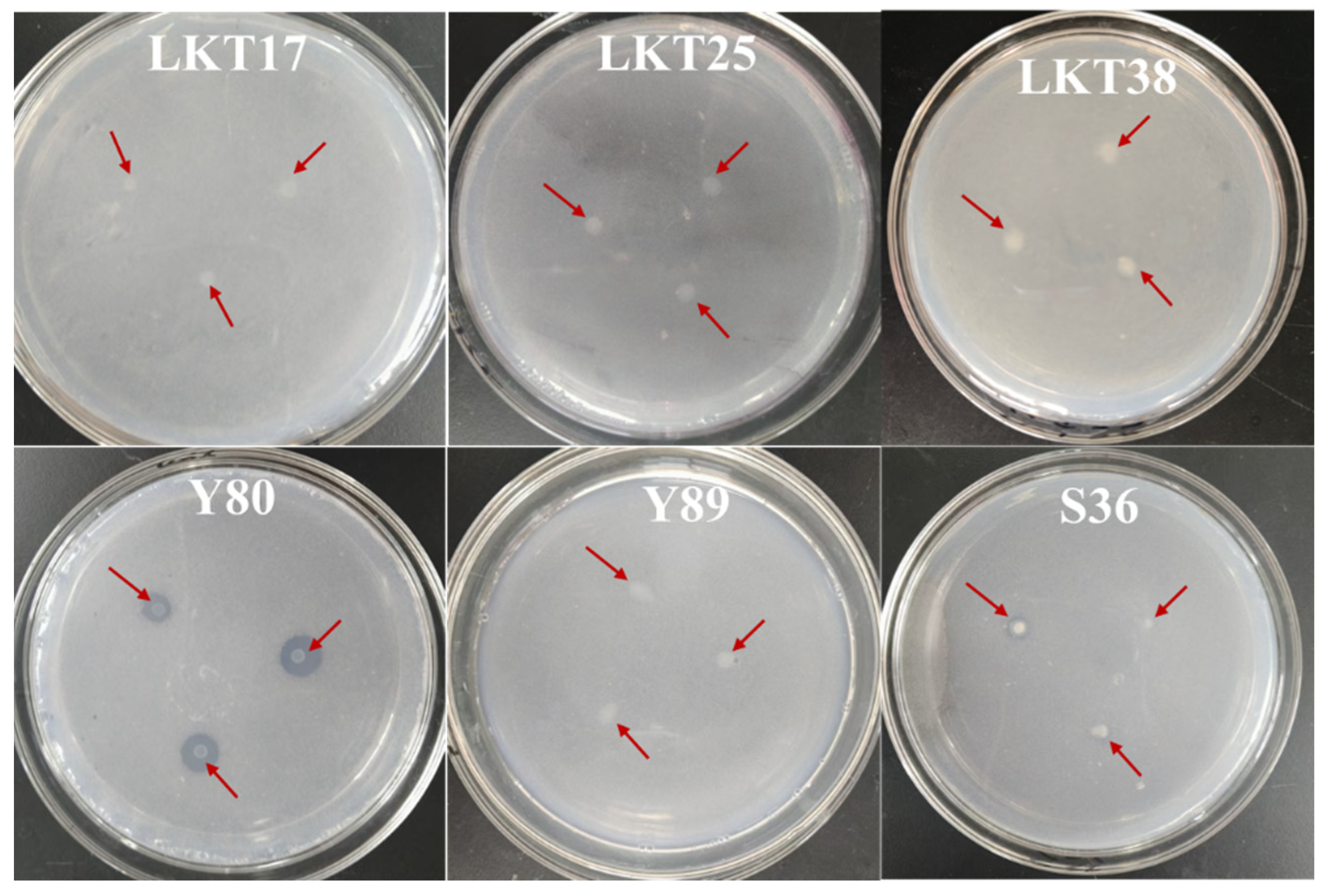
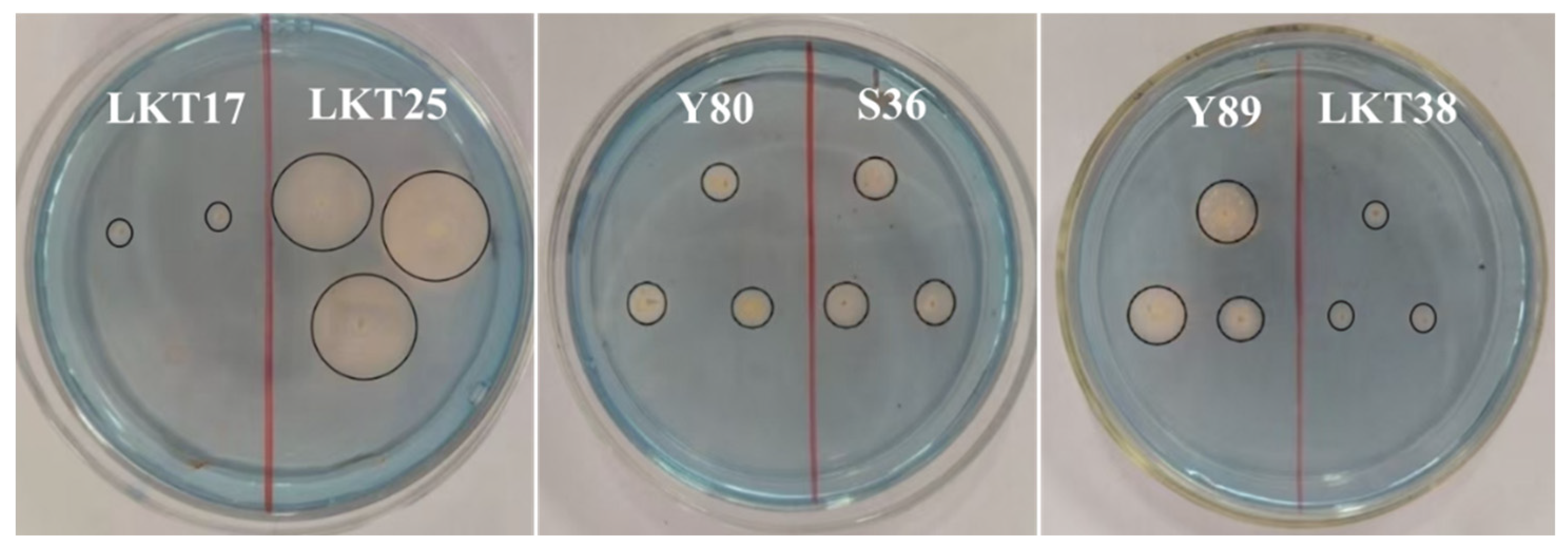
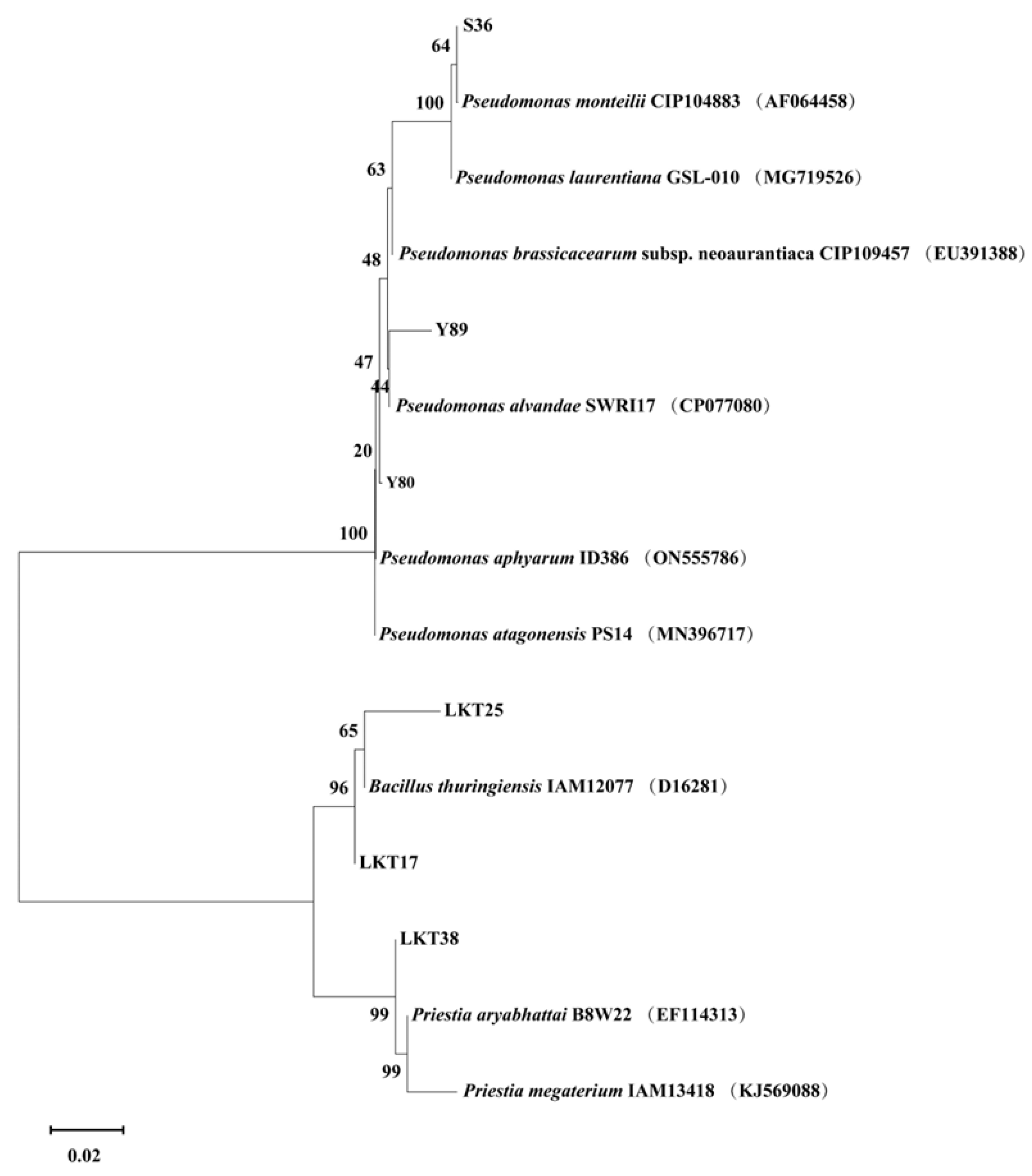
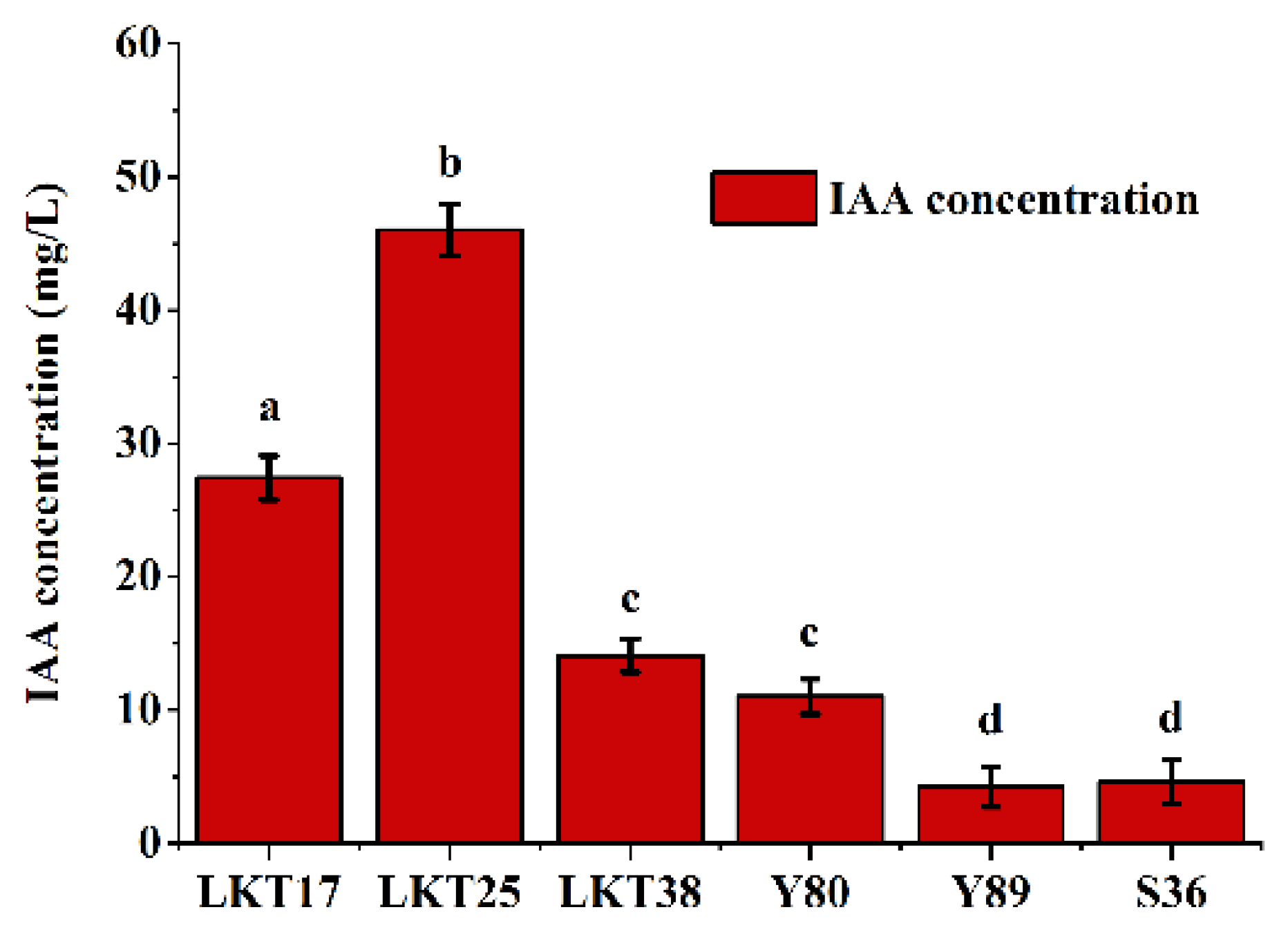
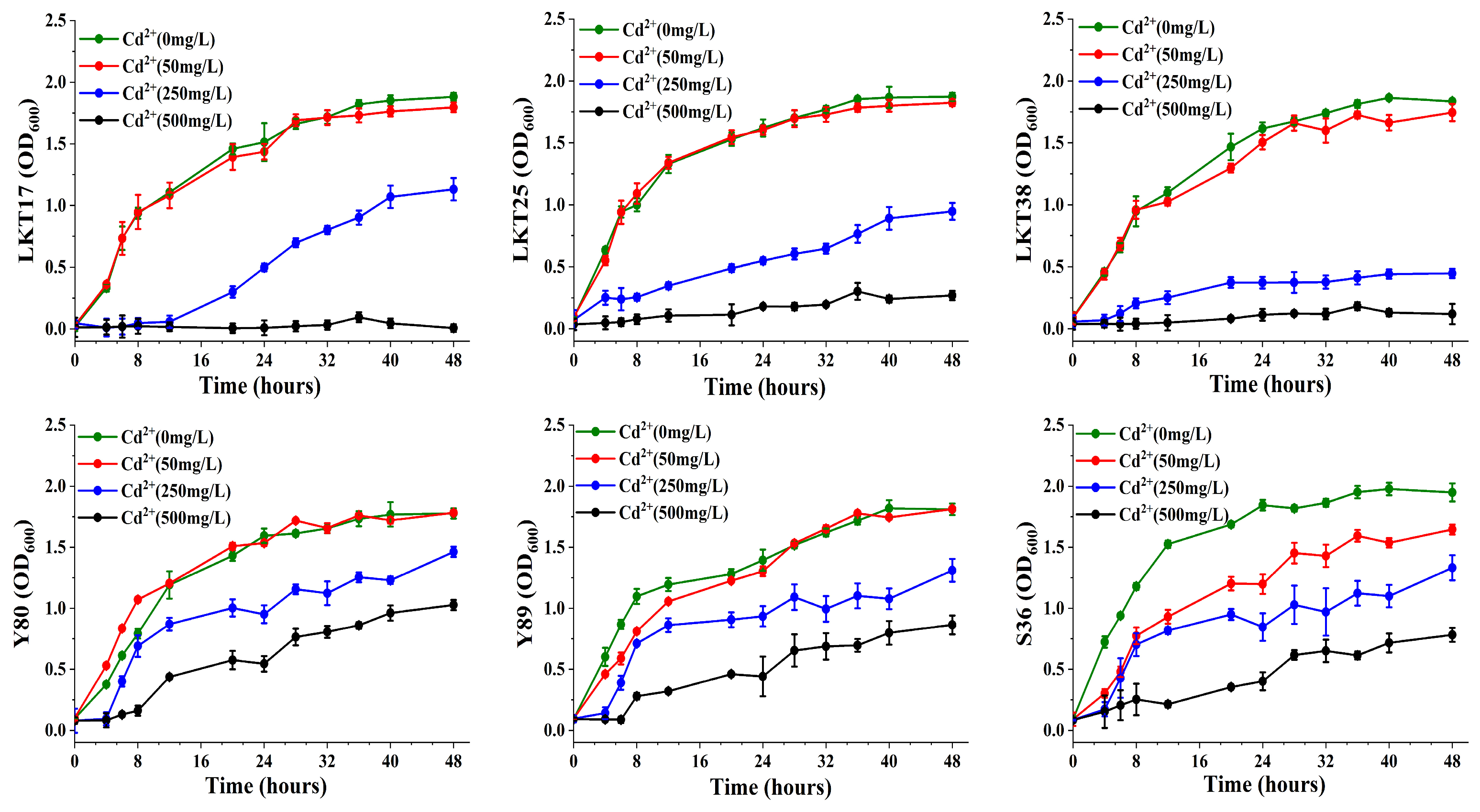
2.1. Molecular Identification and Cd Tolerance of Six Rhizosphere Bacterial Strains and Assessment of Their Plant Growth-Promoting Properties
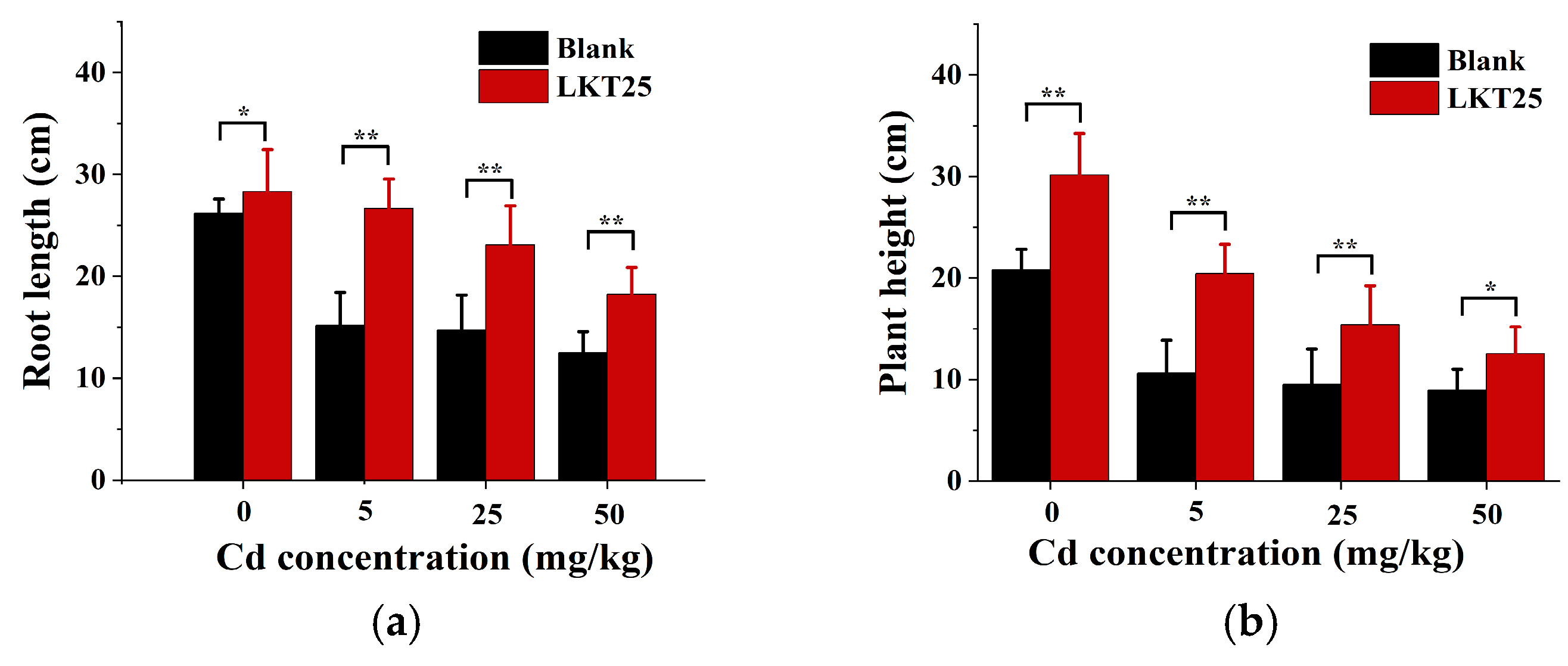
2.2. The Effect of LKT25 on the Growth and Development of S. nigrum Under Different Concentrations of Cd Stress
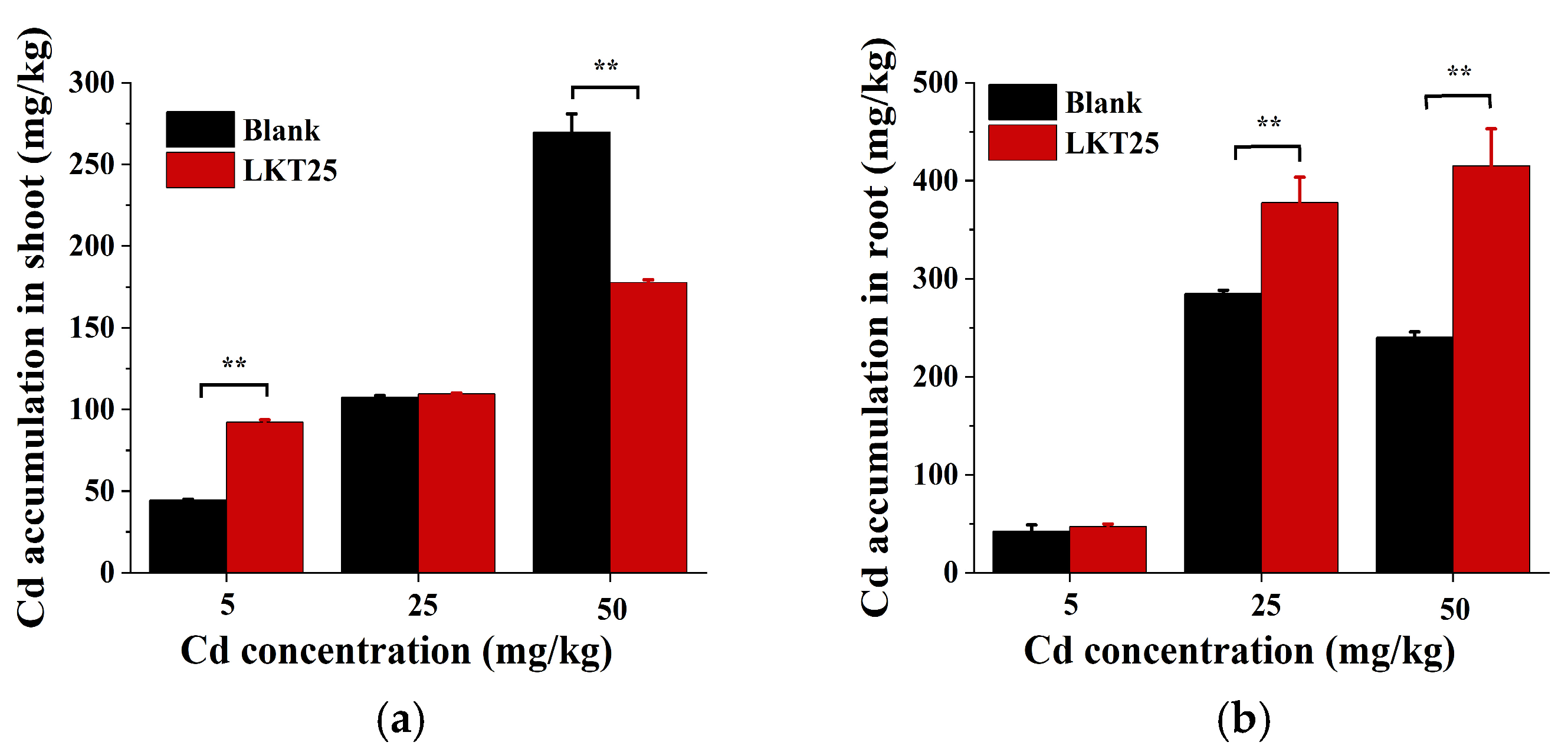
2.3. The Effect of LKT25 on Cd Accumulation of the S. nigrum
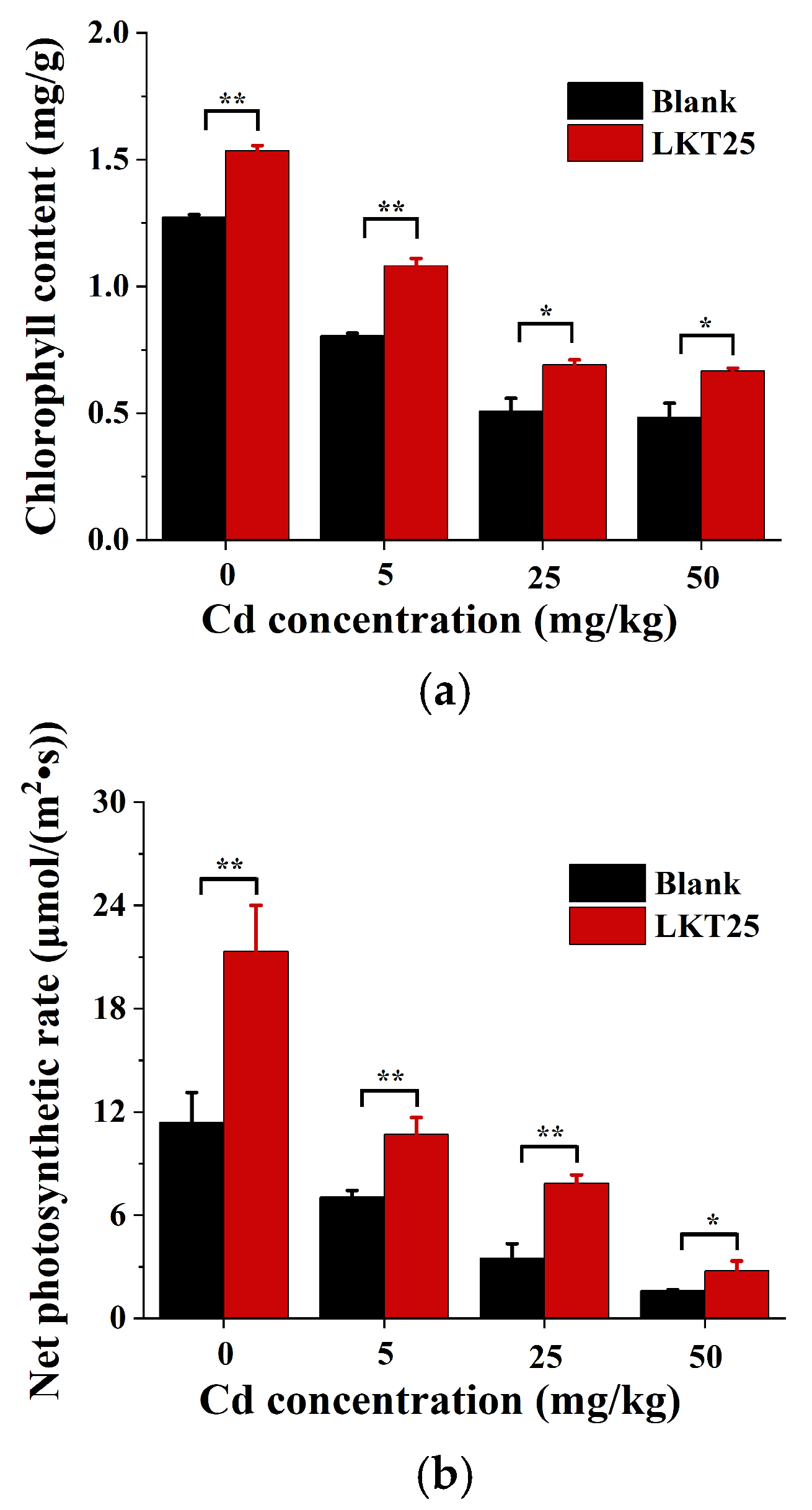
2.4. The Effect of LKT25 on Photosynthetic Parameters of the S. nigrum
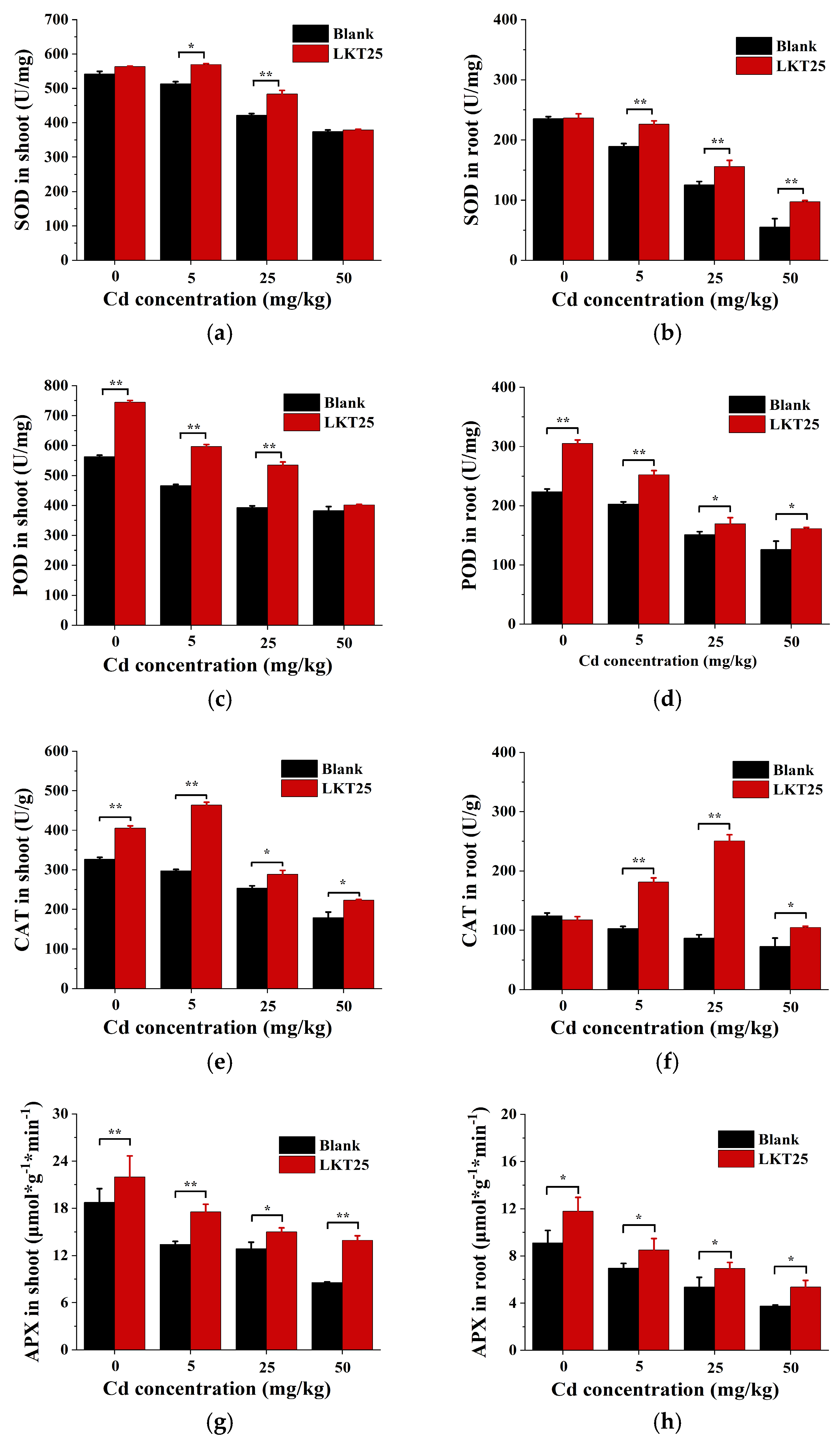
2.5. The Effect of LKT25 on the Antioxidant Enzyme Activity of S. nigrum
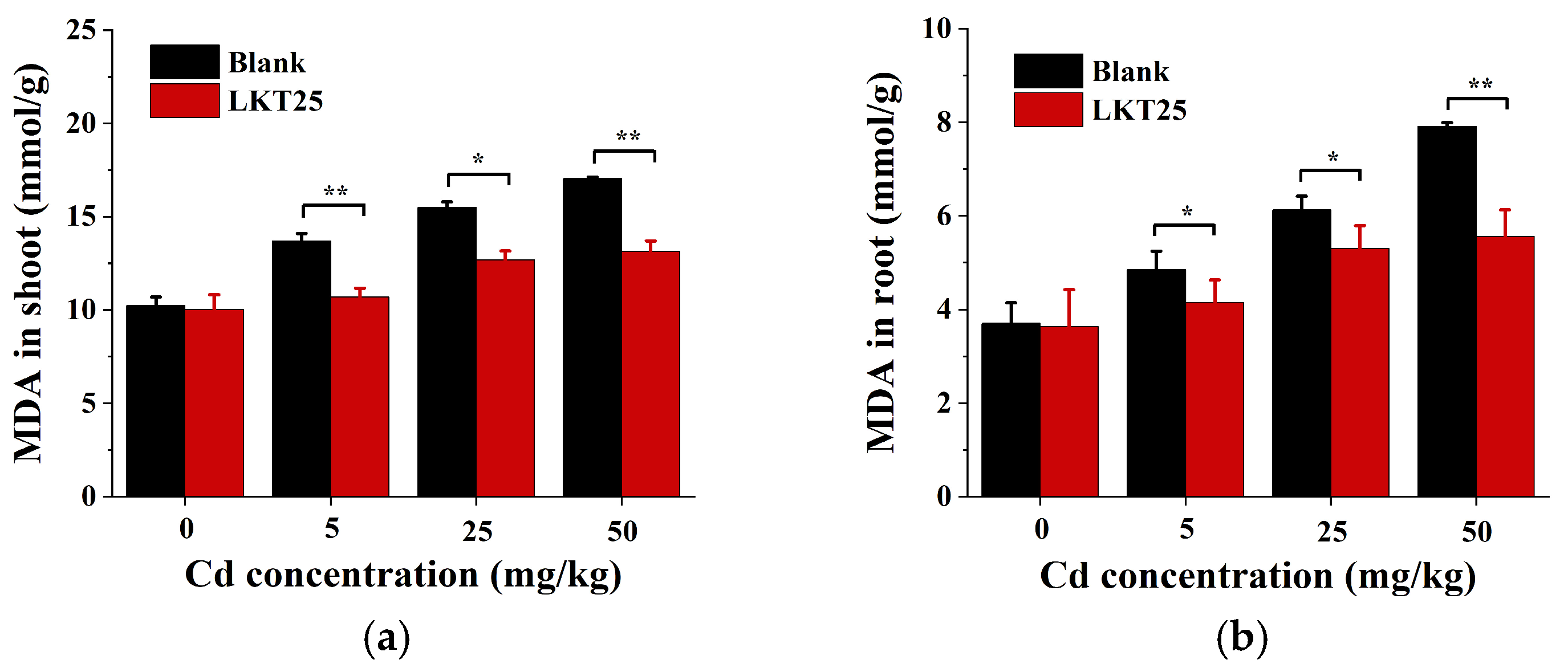
2.6. The Effects of LKT25 on Malondialdehyde (MDA) Levels in the Plant S. nigrum
3. Discussion
3.1. LKT25 Enhances the Growth and Photosynthetic Efficiency of S. nigrum
3.2. LKT25 Enhances the Antioxidant System of S. nigrum and Reduces Cd-Induced Oxidative Stress
3.3. LKT25 Regulates the Accumulation and Transport of Cd in S. nigrum
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation and Identification of PGPR from S. nigrum
4.2. Screening of Plant Growth-Promoting Traits
4.3. Growth Curve Analysis of Six Bacterial Strains Under Varying Cd Concentrations
4.4. Co-Culture of LKT25 with S. nigrum
4.4.1. Analysis of Physicochemical Parameters During the Co-Culture of LKT25 and S. nigrum Under Varying Soil Cd Concentrations
4.4.2. Determination of Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Different Tissues of S. nigrum
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Philippot, L.; Chenu, C.; Kappler, A.; Rillig, M.C.; Fierer, N. The interplay between microbial communities and soil properties. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, M.; Ma, Y. Mitigation of heavy metal stress in the soil through optimized interaction between plants and microbes. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.J.; Liu, X.C.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.Y.; Qiu, Y.Q.; Zhu, M.L.; Tan, W.S. Mechanism underlying the bioleaching process of LiCoO2 by sulfur-oxidizing and iron-oxidizing bacteria. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2019, 128, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.Y.; Jia, X.Y.; Wang, L.W.; McGrath, S.P.; Zhu, Y.G.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, F.J.; Bank, M.S.; O’Connor, D.; Nriagu, J. Global soil pollution by toxic metals threatens agriculture and human health. Science 2025, 388, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardhan, K.H.; Kumar, P.S.; Panda, R.C. A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: Current trends and future perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.S.; Tang, H.; Hu, Y.X.; Wang, X.H.; Ai, X.J.; Tang, L.; Matthew, C.; Cavanagh, J.; Qiu, J.P. Enrofloxacin at environmentally relevant concentrations enhances uptake and toxicity of cadmium in the earthworm Eisenia fetida in farm soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 308, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, Q.B.; Su, Q.Z.; Liu, G.Q.; Shen, Y.L.; Chen, F.J.; Lei, X.T.; Qing, S.M.; Wei, C.L.; Zhang, C.H.; Gao, J.S. Spatial distribution of and historical changes in heavy metals in the surface seawater and sediments of the Beibu Gulf, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moynihan, M.; Peterson, K.E.; Cantoral, A.; Song, P.X.K.; Jones, A.; Solano-González, M.; Meeker, J.; Basu, N.; Téllez-Rojo, M.M. Dietary predictors of urinary cadmium among pregnant women and children. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Teng, Y.G.; Lu, S.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, J.S. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Ji, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, W.; Li, H. Environmental contamination and health hazard of lead and cadmium around Chatian mercury mining deposit in western Hunan Province, China. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Khan, F.; Alqahtani, F.M.; Hashem, M.; Ahmad, F. Plant growth–promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) assisted bioremediation of Heavy Metal Toxicity. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 196, 2928–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M.S.; Chong, K.P. Formulation of biofertilizers from oil palm empty fruit bunches and plant growth-promoting microbes: A comprehensive and novel approach towards plant health. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2021, 33, 101647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.; Saez, J.M.; Costa, J.S.D.; Colin, V.L.; Fuents, M.S.; Cuozzo, S.A.; Benimeli, C.S.; Polti, M.A.; Amoroso, M.J. Actinobacteria: Current research and perspectives for bioremediation of pesticides and heavy metals. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrid, Y.; Cámara, C. The use of biological substrates for preconcentration and element speciation. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 33, pp. 41–79. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Li, Q.; Wu, M.; Lin, L.; Scholz, M. Review of remediation practices regarding cadmium-enriched farmland soil with particular reference to China. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 646–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Guo, G.; Ma, L.Q. A newly-discovered Cd-hyperaccumulator Solatium nigrum L. Sci. Bull. 2005, 50, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.K.; Wang, J. Cd bio-accumulative characteristics and physiological response of Solanum nigrum L. under different light intensities. J. Plant Nutr. 2012, 18, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.R.; Ullah, I.; Khan, A.L.; Hong, S.J.; Waqas, M.; Park, G.S.; Kwak, Y.; Choi, J.; Jung, B.K.; Park, M.; et al. Phytostabilization and physicochemical responses of Korean ecotype Solanum nigrum L. to cadmium contamination. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Habib, M.; Kakavand, S.N.; Zahid, Z.; Zahra, N.; Sharif, R.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Phytoremediation of cadmium: Physiological, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms. Biology 2020, 9, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennakoon, A.; Galahitigama, H.; Samarakoon, S.M.A.B.K.; Perera, I.J.J.U.N.; Thakshila, G.P.G.I.; Thiruketheeswaranathan, S.; Roshana, M.R.; Sandamal, S.; Sewwandi, G.P.G.S.M.; Bellanthudawa, B.K.A. Remediating contaminated environmental systems: The role of plants in cadmium removal. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2025, 27, 896–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, S.A.; Tanveer, M.; Hussain, S.; Bao, M.C.; Wang, L.C.; Khan, I.; Ullah, E.; Tung, S.A.; Samad, R.A.; Shahzad, B. Cadmium toxicity in Maize (Zea mays L.): Consequences on antioxidative systems, reactive oxygen species and cadmium accumulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 17022–17030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noctor, G.; Foyer, C.H. Ascorbate and glutathione: Keeping active oxygen under control. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1998, 49, 249–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad Hassan, M.; Ali Raza, M.; Ur Rehman, S.; Ansar, M.; Gitari, H.; Khan, I.; Wajid, M.; Ahmed, M.; Abbas Shah, G.; Peng, Y.; et al. Effect of cadmium toxicity on growth, oxidative damage, antioxidant defense system and cadmium accumulation in two sorghum cultivars. Plants 2020, 9, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, P.; Kim, K.; Krishnamoorthy, R.; Sundaram, S.; Sa, T. Endophytic bacteria improve nodule function and plant nitrogen in soybean on co-inoculation with Bradyrhizobium japonicum MN110. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 76, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Ishtiyaq, S.; Varun, M.; Favas, P.J.; Ogunkunle, C.O.; Paul, M.S. Bioremediation: Plants and microbes for restoration of heavy metal contaminated soils. In Bioenergy Crops; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 37–70. [Google Scholar]
- Jorquera, M.A.; Maruyama, F.; Ogram, A.V.; Navarrete, O.U.; Lagos, L.M.; Inostroza, N.G.; Acuña, J.J.; Rilling, J.I.; de La Luz Mora, M. Rhizobacterial community structures associated with native plants grown in Chilean extreme environments. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 72, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Ma, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Chu, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, P. Plant growth promoting endophyte promotes cadmium accumulation in Solanum nigrum L. by regulating plant homeostasis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 457, 131866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, G.E.H.; El-Ghareeb, D.; Already, R.; Assaeedi, A.S.A.; Organji, S.R.; Abulreesh, H.H.; Althubiani, A.S. Bioinsecticide Bacillus thuringiensis a comprehensive review. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2015, 25, 271–288. [Google Scholar]
- de Araújo, R.C.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Nadal, M.C.; de Souza Ribeiro, M.; Antônio, C.A.C.; Rodrigues, V.A.; de Souza, A.C.; Pasqual, M.; Dória, J. Acclimatization of Musa spp. seedlings using endophytic Bacillus spp. and Buttiauxella agrestis strains. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 248, 126750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, F.M.; Pereira, T.A.; Souza, P.S.; Guimarães, P.H.S.; Martins, A.D.; Schwana, R.F.; Pasqual, M.; D’oria, J. Beneficial effects of inoculation of growth-promoting bacteria in strawberry. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 223–225, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Salvatore, M.; Carafa, A.M.; Carratu, G. Assessment of heavy metals phytotoxicity using seed germination and root elongation tests: A comparison of two growth substrates. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1461–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.R.; Ullah, I.; Waqas, M.; Park, G.S.; Khan, A.L.; Hong, S.J.; Ullah, R.; Jung, B.K.; Park, C.E.; Ur-Rehman, S.; et al. Host plant growth promotion and cadmium detoxification in Solanum nigrum, mediated by endophytic fungi. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 136, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, B.R. Plant growth-promoting bacteria: Mechanisms and applications. Scientifica 2012, 2012, 963401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, R.D.; Ambrosini, A.; Passaglia, L.M. Plant growth-promoting bacteria as inoculants in agricultural soils. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2015, 38, 401–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansinenea, E. Bacillus spp.: As plant growth-promoting bacteria. In Secondary Metabolites of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizomicroorganisms; Singh, H., Keswani, C., Reddy, M., Sansinenea, E., García-Estrada, C., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 225–237. [Google Scholar]
- Tsavkelova, E.A.; Klimova, S.Y.; Cherdyntseva, T.A.; Netrusov, A.I. Microbial producers of plant growth stimulators and their practical use: A review. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2006, 42, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaepen, S.; Vanderleyden, J. Auxin and plant-microbe interactions. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a001438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.W.; You, Y.M.; Wang, J.C.; Chen, X.F.; Chu, S.H.; Wang, R.Y.; Zhang, X.; Yin, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, P. Two plant growth-promoting bacterial Bacillus strains possess different mechanisms in affecting cadmium uptake and detoxification of Solanum nigrum L. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.M.; Xu, M.J.; Wei, Q.P.; Tang, M.Y.; Guan, L.K.; Lou, L.Q.; Xu, X.M.; Hu, Z.B.; Chen, Y.H.; Shen, Z.G.; et al. Promotion of growth and phytoextraction of cadmium and lead in Solanum nigrum L. mediated by plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 111333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, B.; Hou, J.; Luo, Y.; Tang, C.; Franks, A.E. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria enhance the growth and Cd uptake of Sedum plumbizincicola in a Cd-contaminated soil. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Fu, Y.; Hu, S.; Leng, F.; Zhuang, Y.; Sun, W.; Wang, Y. Potential function of plant-growth-promoting endophytic Serratia fonticola CPSE11 from Codonopsis pilosula in phytoremediation of Cadmium ion (Cd2+). J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 380, 124994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.S.; Dietz, K.J. The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehab, A.E.D.; Ibrahim, A.H. The alleviative effects of salicylic acid on physiological indices and defense mechanisms of maize (Zea mays L. Giza 2) stressed with cadmium. Environ. Process. 2020, 7, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, K. Production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species in chloroplasts and their functions. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Serrano, M.; Romero-Puertas, M.C.; Zabalza, A.; Corpas, F.J.; Gomez, M.; Del, R.; Luis, A.; Sandalio, L.M. Cadmium effect on oxidative metabolism of pea (Pisum sativum L.) roots. Imaging of reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide accumulation in vivo. Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 1532–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Pourrut, B.; Dumat, C.; Nadeem, M.; Aslam, M.; Pinelli, E. Heavy-metal-induced reactive oxygen species: Phytotoxicity and physicochemical changes in plants. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 232, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Faraz, A.; Faizan, M.; Sami, F.; Siddiqui, H.; Hayat, S. Supplementation of Salicylic Acid and Citric Acid for Alleviation of Cadmium Toxicity to Brassica juncea. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 39, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fan, X.; Pu, G.; Song, F. Rhizophagus intraradices combined with Solanum nigrum for the remediation of soil highly contaminated with cadmium. Plant Soil 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Franklin, V.; Moreno-Riascos, S.; Ghneim-Herrera, T. Are endophytic bacteria an option for increasing heavy metal tolerance of plants? A meta-analysis of the effect size. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 8, 603668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cui, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Cui, Z. Combined toxicity and detoxification of lead, cadmium and arsenic in Solanum nigrum L. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.; Holmström, S.J.M. Siderophores in environmental research: Roles and applications. Microb. Biotechnol. 2014, 7, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Oliveira, R.S.; Freitas, H.; Zhang, C. Biochemical and molecular mechanisms of plant-microbe-metal interactions: Relevance for phytoremediation. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chang, W.; Fan, X.; Li, K.; Zhang, M.; Ping, Y.; He, X.; Song, F. Cocultivation with Solanum nigrum and inoculation with Rhizophagus intraradices can improve plant photosynthesis and antioxidant defense to alleviate cadmium toxicity to soybean. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 256, 114849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, H.B.; Nayak, L.; Das, S.; Adhya, T.K. Isolation of ACC deaminase producing PGPR from rice rhizosphere and evaluating their plant growth promoting activity under salt stress. Plant Soil 2013, 366, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etesami, H.; Maheshwari, D.K. Use of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs) with multiple plant growth promoting traits in stress agriculture: Action mechanisms and future prospects. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 156, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ma, L.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Pan, F.; Huang, L.; Yang, X.; Feng, Y. Inoculation of plant growth promoting bacteria from hyperaccumulator facilitated non-host root development and provided promising agents for elevated phytoremediation efficiency. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Luo, S.; Wu, Y.; Ye, J.; Wang, Q.; Xu, X.; Pan, F.; Khan, K.Y.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X. The effects of the endophytic bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens Sasm05 and IAA on the plant growth and cadmium uptake of Sedum alfredii Hance. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.W.; Wu, L.; Luo, N.; Mo, C.H.; Wong, M.H.; Li, H. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and the associated bacterial community influence the uptake of cadmium in rice. Geoderma 2019, 337, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, T.; Du, H.; Guo, P.; Wang, S.; Ma, M. Research progress in the joint remediation of plants–microbes–soil for heavy metal-contaminated soil in mining areas: A review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiodor, A.; Ajijah, N.; Dziewit, L.; Pranaw, K. Biopriming of seed with plant growth-promoting bacteria for improved germination and seedling growth. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1142966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwyn, B.; Neilands, J. Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 160, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timofeeva, A.M.; Galyamova, M.R.; Sedykh, S.E. Plant growth-promoting soil bacteria: Nitrogen fixation, phosphate solubilization, siderophore production, and other biological activities. Plants 2023, 12, 4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.A.; Weber, R.P. Colorimetric estimation of indoleacetic acid. Plant Physiol. 1951, 26, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworkin, M.; Foster, J.W. Experiments with some microorganisms which utilize ethane and hydrogen. J. Bacteriol. 1958, 75, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Chen, X.J.; Xu, M.Y.; Hai, R.; Zhou, A.F.; Tian, R.M.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Kempher, M.L.; Guo, J.; Sun, G.P.; et al. Adaptive evolution of Sphingobium hydrophobicum C1T in electronic waste contaminated river sediment. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Liu, T.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Lei, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S. Heavy metal bioaccumulation in rice from a high geological background area in Guizhou Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.P.; Wei, S.H.; Twardowska, I.; Zhang, Q. In search of the exclusion/low accumulation mechanisms: Cadmium uptake and accumulation from soil by cultivated (Solanum Melongena L.) and wild eggplants (Solanum torvum L.). J. Clean Prod. 2021, 323, 129141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.P.; Wei, S.H.; Twardowska, I.; Hou, N.; Zhang, Q. Cosmopolitan cadmium hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum: Exploring cadmium uptake, transport and physiological mechanisms of accumulation in different ecotypes as a way of enhancing its hyper accumulative capacity. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 320, 115878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.P.; Shan, C.J.; Zhao, H.; Li, J.C.; Jia, G.L.; Jiang, H.; Wu, S.Q.; Wang, Q. The difference in antioxidant capacity of four alfalfa cultivars in response to Zn. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 114, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Strain ID | ACC Deaminase | Siderophore Production | Nitrogenase |
|---|---|---|---|
| LKT25 | + | + | + |
| LKT17 | − | + | + |
| LKT38 | − | + | + |
| Y80 | − | + | + |
| Y89 | − | + | + |
| S36 | − | + | + |
| Treatment | Enrichment Coefficient | Transfer Coefficient | Cd Removal Rate (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoot | Root | Shoot | |||
| 5 mg/kg (Cd) | Blank | 8.87 ± 0.43 | 8.48 ± 0.31 | 1.05 ± 0.14 | 31.12 |
| LKT25 | 18.40 ± 1.4 ** | 9.44 ± 0.49 | 1.95 ± 0.26 * | 45.13 * | |
| 25 mg/kg (Cd) | Blank | 4.29 ± 0.15 | 11.40 ± 0.58 | 0.38 ± 0.03 | 15.32 |
| LKT25 | 4.38 ± 0.06 | 15.09 ± 0.14 * | 0.31 ± 0.02 | 22.95 * | |
| 50 mg/kg (Cd) | Blank | 5.39 ± 0.05 | 4.81 ± 0.23 | 1.12 ± 0.03 | 21.75 |
| LKT25 | 3.55 ± 0.05 * | 8.30 ± 0.35 ** | 0.42 ± 0.14 ** | 27.86 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, G.; Song, D.; Zhang, C.; Jia, X.; Ren, Y.; Wei, S.; Dai, H. The Effect of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria Bacillus thuringiensis LKT25 on Cadmium Accumulation and Physiological Responses in Solanum nigrum L. Plants 2025, 14, 2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182918
Kong G, Song D, Zhang C, Jia X, Ren Y, Wei S, Dai H. The Effect of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria Bacillus thuringiensis LKT25 on Cadmium Accumulation and Physiological Responses in Solanum nigrum L. Plants. 2025; 14(18):2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182918
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Guannan, Da Song, Chao Zhang, Xinyao Jia, Yingying Ren, Shuhe Wei, and Huiping Dai. 2025. "The Effect of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria Bacillus thuringiensis LKT25 on Cadmium Accumulation and Physiological Responses in Solanum nigrum L." Plants 14, no. 18: 2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182918
APA StyleKong, G., Song, D., Zhang, C., Jia, X., Ren, Y., Wei, S., & Dai, H. (2025). The Effect of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria Bacillus thuringiensis LKT25 on Cadmium Accumulation and Physiological Responses in Solanum nigrum L. Plants, 14(18), 2918. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182918







